Zürich German on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Zürich German (
Zürich German (
online
* Weber, Albert: ''Zürichdeutsche Grammatik. Ein Wegweiser zur guten Mundart''. With the participation of

 Zürich German (
Zürich German (German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
: ''Zürichdeutsch'', natively ''Züritüütsch'' ) is the High Alemannic
High Alemannic is a dialect of Alemannic German spoken in the westernmost Austrian state of Vorarlberg and in Switzerland and Liechtenstein.
Language area
The High Alemannic dialects are spoken in Liechtenstein and in most of German-speaking S ...
dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety of a language that is ...
spoken in the Canton of Zürich
The canton of Zürich (german: Kanton Zürich ; rm, Chantun Turitg; french: Canton de Zurich; it, Canton Zurigo) is a Swiss canton in the northeastern part of the country. With a population of (as of ), it is the most populous canton in the ...
, Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
.
Its area covers most of the canton, with the exception of the parts north of the Thur and the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, source ...
, which belong to the areal of the northeastern (Schaffhausen and Thurgau) Swiss dialects.
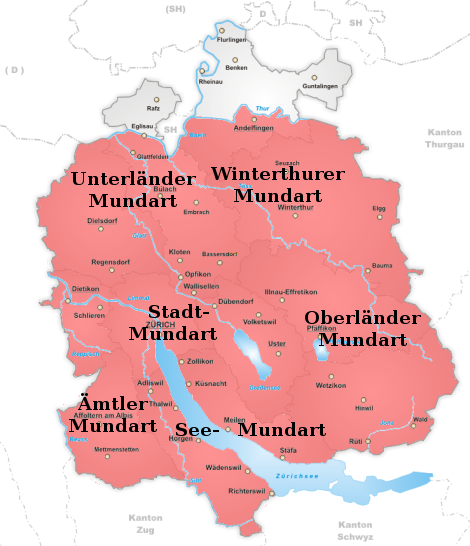
Zürich German was traditionally divided into six sub-dialects, now increasingly homogenised owing to larger commuting distances:
*The dialect of the town of Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Z ...
(''Stadt-Mundart'')
*The dialect spoken around Lake Zürich
__NOTOC__
Lake Zurich ( Swiss German/ Alemannic: ''Zürisee''; German: ''Zürichsee''; rm, Lai da Turitg) is a lake in Switzerland, extending southeast of the city of Zürich. Depending on the context, Lake Zurich or ''Zürichsee'' can be used ...
(''See-Mundart'')
*The dialect of the Knonauer Amt west of the Albis
The Albis is a chain of hills in the Canton of Zürich, Switzerland, stretching for some 19 km from Sihlbrugg in the south to Waldegg near Zürich in the north. The chain forms, among others, the border between the Affoltern and Horgen di ...
(''Ämtler Mundart'')
*The dialect of the area of Winterthur
, neighboring_municipalities = Brütten, Dinhard, Elsau, Hettlingen, Illnau-Effretikon, Kyburg, Lindau, Neftenbach, Oberembrach, Pfungen, Rickenbach, Schlatt, Seuzach, Wiesendangen, Zell
, twintowns = Hall in Tirol (Austria ...
*The dialect of the Zürcher Oberland
The Zürcher Oberland ("Zurich highlands") in Switzerland, is the hilly south-eastern part of the canton of Zurich, bordering on the Toggenburg, including the districts of Uster, Hinwil, Pfäffikon as well as the Töss Valley as far as the dis ...
around Lake Pfäffikon
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
and the upper Tösstal valley
*The dialect of the Zürcher Unterland
The ''Zürcher Unterland'' ("Zurich lowlands") comprises the northwestern part of the canton of Zurich, including the districts of Bülach and Dielsdorf.
Geographically, it is located in the Swiss plateau, between the Limmat valley, the city of ...
around Bülach
, neighboring_municipalities= Bachenbülach, Eglisau, Embrach, Glattfelden, Hochfelden, Höri, Rorbas, Winkel
, twintowns = Santeramo in Colle (Italy)
Bülach () is an historic town and a municipality in Switzerland in the cant ...
and Dielsdorf
Like all Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
dialects, it is essentially a spoken language
A spoken language is a language produced by articulate sounds or (depending on one's definition) manual gestures, as opposed to a written language. An oral language or vocal language is a language produced with the vocal tract in contrast with a si ...
, whereas the written language
A written language is the representation of a spoken or gestural language by means of a writing system. Written language is an invention in that it must be taught to children, who will pick up spoken language or sign language by exposure eve ...
is standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
. Likewise, there is no official orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
of the Zürich dialect. When it is written, it rarely follows the guidelines published by Eugen Dieth
Eugen Dieth (18 November 1893, in Neukirch an der Thur – 24 May 1956, in Zollikon) was a Swiss linguist, phonetician and dialectologist. He is well known for his work in English and German phonetics, and for co-initiating the Survey of English D ...
in his book ''Schwyzertütschi Dialäktschrift''. Furthermore, Dieth's spelling uses a lot of diacritical marks
A diacritic (also diacritical mark, diacritical point, diacritical sign, or accent) is a glyph added to a letter or to a basic glyph. The term derives from the Ancient Greek (, "distinguishing"), from (, "to distinguish"). The word ''diacriti ...
not found on a normal keyboard
Keyboard may refer to:
Text input
* Keyboard, part of a typewriter
* Computer keyboard
** Keyboard layout, the software control of computer keyboards and their mapping
** Keyboard technology, computer keyboard hardware and firmware
Music
* Mu ...
. Young people often use Swiss German for personal messages, such as when texting
Text messaging, or texting, is the act of composing and sending electronic messages, typically consisting of alphabetic and numeric characters, between two or more users of mobile devices, desktops/laptops, or another type of compatible comput ...
with their mobile phones
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while ...
. As they do not have a standard way of writing they tend to blend Standard German spelling with Swiss German phrasing.
The Zürich dialect is generally perceived as fast spoken, less melodic than, for example, the Bernese. Characteristic of the city dialect is that it most easily adopts external influences; in particular, the second generation Italians (secondi) have had a crucial influence, as has the English language through the media. The wave of Turkish and ex-Yugoslavian immigration of the 1990s is leaving its imprint on the dialect of the city in particular.
Further reading
* (proposed orthography) * Salzmann, Martin: ''Resumptive Prolepsis: A study in indirect A'-dependencies''. Utrecht: LOT, 2006 (=LOT Dissertation Series 136). ''Chapter 4: Resumptives in Zurich German relative clauses''online
* Weber, Albert: ''Zürichdeutsche Grammatik. Ein Wegweiser zur guten Mundart''. With the participation of
Eugen Dieth
Eugen Dieth (18 November 1893, in Neukirch an der Thur – 24 May 1956, in Zollikon) was a Swiss linguist, phonetician and dialectologist. He is well known for his work in English and German phonetics, and for co-initiating the Survey of English D ...
. Zürich (=und Wörterbücher des Schweizerdeutschen in allgemeinverständlicher Darstellung. Bd. I).
* Weber, Albert and Bächtold, Jacques M.. ''Zürichdeutsches Wörterbuch''. Zürich (=Grammatiken und Wörterbücher des Schweizerdeutschen in allgemeinverständlicher Darstellung. Bd. III).
*
*
*
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zürich German Canton of Zürich Culture of Zürich Swiss German language German dialects