Yggdrasil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Yggdrasil (from
Yggdrasil (from
 The generally accepted meaning of Old Norse ' is "Odin's horse", meaning "
The generally accepted meaning of Old Norse ' is "Odin's horse", meaning "
 In the second stanza of the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''
In the second stanza of the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''
 In stanza 138 of the poem ''
In stanza 138 of the poem ''

 Yggdrasil is mentioned in two books in the ''
Yggdrasil is mentioned in two books in the ''
 Connections have been proposed between the wood
Connections have been proposed between the wood
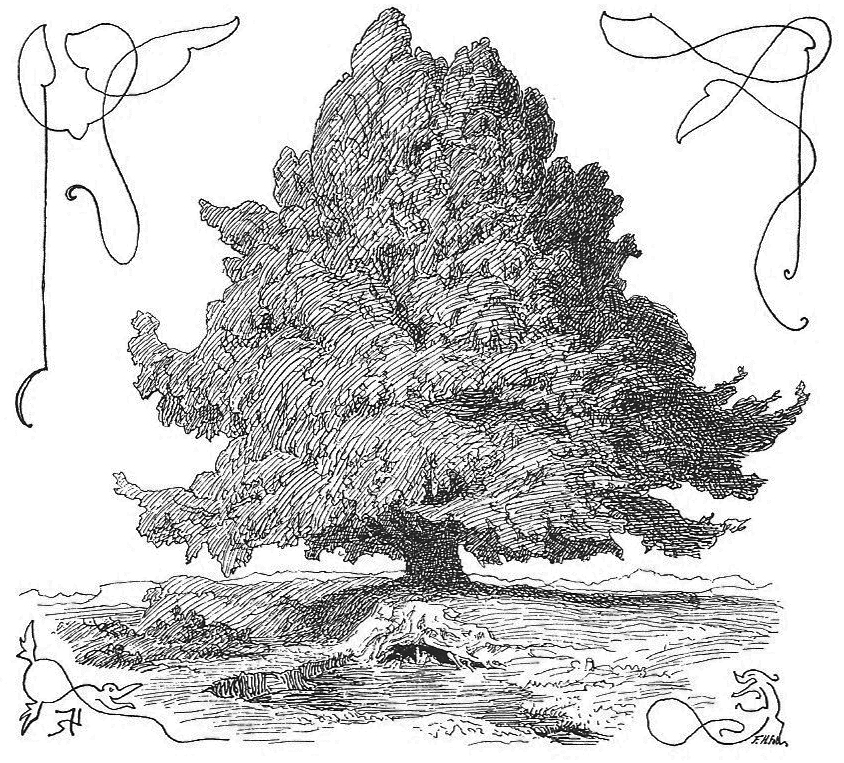
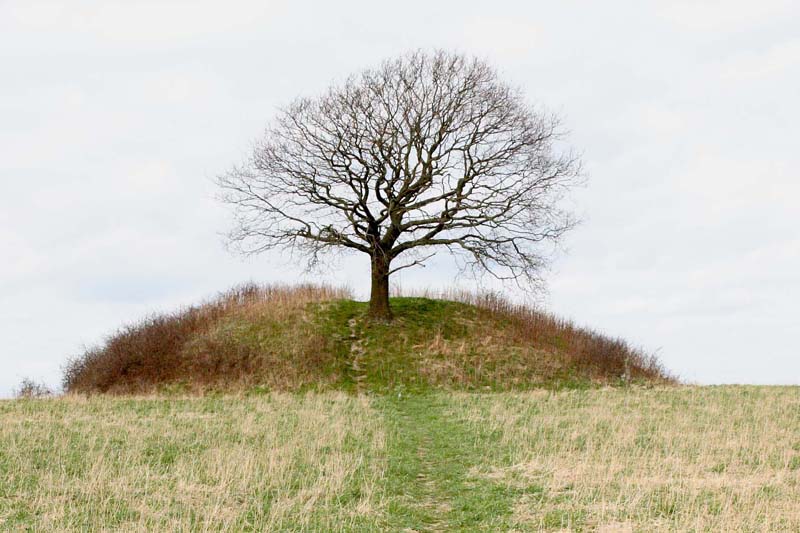 Continuing as late as the 19th century, warden trees were venerated in areas of Germany and Scandinavia, considered to be guardians and bringers of luck, and offerings were sometimes made to them. A massive
Continuing as late as the 19th century, warden trees were venerated in areas of Germany and Scandinavia, considered to be guardians and bringers of luck, and offerings were sometimes made to them. A massive
 Yggdrasil (from
Yggdrasil (from Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
), in Norse cosmology
Norse cosmology is the study of the cosmos (cosmology) as perceived by the ancient North Germanic peoples. The topic encompasses concepts from Norse mythology, such as notions of time and space, cosmogony, personifications, anthropogeny, and es ...
, is an immense and central sacred tree
A sacred tree is a tree which is considered to be sacred, or worthy of spiritual respect or reverence. Such trees appear throughout world history in various cultures including the ancient Greek, Hindu mythology, Celtic and Germanic mythologies. T ...
. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic med ...
'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' ( is, Snorra Edda) or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often assumed to have been ...
'' compiled in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson
Snorri Sturluson ( ; ; 1179 – 22 September 1241) was an Icelandic historian, poet, and politician. He was elected twice as lawspeaker of the Icelandic parliament, the Althing. He is commonly thought to have authored or compiled portions of th ...
. In both sources, Yggdrasil is an immense ash tree
''Fraxinus'' (), commonly called ash, is a genus of flowering plants in the olive and lilac family, Oleaceae. It contains 45–65 species of usually medium to large trees, mostly deciduous, though a number of subtropical species are evergr ...
that is central to the cosmos and considered very holy. The gods
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater ...
go to Yggdrasil daily to assemble at their traditional governing assemblies, called things. The branches of Yggdrasil extend far into the heavens, and the tree is supported by three roots that extend far away into other locations; one to the well Urðarbrunnr
Urðarbrunnr (Old Norse "Well of Urðr"; either referring to a Germanic concept of fate—''urðr''—or the norn named UrðrSimek (2007:342).) is a well in Norse mythology. Urðarbrunnr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th ...
in the heavens, one to the spring Hvergelmir
In Norse mythology, Hvergelmir (Old Norse: ; "bubbling boiling spring"Orchard (1997:93)) is a major spring. Hvergelmir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', writte ...
, and another to the well Mímisbrunnr
In Norse mythology, Mímisbrunnr (Old Norse " Mímir's well"Simek (2007:216).) is a well associated with the being Mímir, located beneath the world tree Yggdrasil. Mímisbrunnr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century fr ...
. Creatures live within Yggdrasil, including the dragon Níðhöggr
In Norse mythology, Níðhöggr (''Malice Striker'', in Old Norse traditionally also spelled Níðhǫggr , often anglicized NidhoggWhile the suffix of the name, ''-höggr'', clearly means "striker" the prefix is not as clear. In particular, the ...
, an unnamed eagle, and the stags Dáinn, Dvalinn, Duneyrr and Duraþrór
In Norse mythology, four stags or harts (male red deer) eat among the branches of the World Tree Yggdrasill. According to the Poetic Edda, the stags crane their necks upward to chomp at the branches. The morning dew gathers in their horns and form ...
.
Scholars generally consider ''Hoddmímis holt
In Norse mythology, Hoddmímis holt (Old Norse "Hoard-Mímir's"Simek (2007:154). holt) is a location where Líf and Lífþrasir are foretold to survive the long winters of Fimbulvetr. Hoddmímis holt is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled i ...
'', ''Mímameiðr
In Norse mythology, Mímameiðr ( Old Norse " Mimi's tree"Simek (2007:216)) is a tree whose branches stretch over every land, is unharmed by fire or metal, bears fruit that assists pregnant women, and upon whose highest bough roosts the cock Ví� ...
'', and ''Læraðr
Læraðr is a tree in Norse mythology, often identified with Yggdrasill. It stands at the top of the Valhöll. Two animals, the goat Heiðrún and the Hart (deer), hart Eikþyrnir, graze its foliage.
Etymology
The meaning of Læraðr / Léraðr is ...
'' to be other names for the tree. The tree is an example of sacred trees and groves in Germanic paganism and mythology
Trees hold a particular role in Germanic paganism and Germanic mythology, both as individuals ( sacred trees) and in groups (sacred groves). The central role of trees in Germanic religion is noted in the earliest written reports about the Germanic ...
, and scholars in the field of Germanic philology
Germanic philology is the philological study of the Germanic languages, particularly from a comparative or historical perspective.
The beginnings of research into the Germanic languages began in the 16th century, with the discovery of literary tex ...
have long discussed its implications.
Etymology
 The generally accepted meaning of Old Norse ' is "Odin's horse", meaning "
The generally accepted meaning of Old Norse ' is "Odin's horse", meaning "gallows
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks ...
". This interpretation comes about because ' means "horse" and ' is one of Odin's many names. The ''Poetic Edda'' poem ' describes how Odin sacrificed himself by hanging from a tree, making this tree Odin's gallows. This tree may have been Yggdrasil. Gallows can be called "the horse of the hanged" and therefore Odin's gallows may have developed into the expression "Odin's horse", which then became the name of the tree.
Nevertheless, scholarly opinions regarding the precise meaning of the name ' vary, particularly on the issue of whether ' is the name of the tree itself or if only the full term ' (where Old Norse ' means "ash tree") refers specifically to the tree. According to this interpretation, ' would mean the world tree
The world tree is a motif present in several religions and mythologies, particularly Indo-European religions, Siberian religions, and Native American religions. The world tree is represented as a colossal tree which supports the heavens, thereb ...
upon which "the horse din's horseof the highest god din
DIN or Din or din may refer to:
People and language
* Din (name), people with the name
* Dīn, an Arabic word with three general senses: judgment, custom, and religion from which the name originates
* Dinka language (ISO 639 code: din), spoken by ...
is bound". Both of these etymologies rely on a presumed but unattested ''*Yggsdrasill''.
A third interpretation, presented by F. Detter, is that the name ' refers to the word ' ("terror"), yet not in reference to the Odinic name, and so ' would then mean "tree of terror, gallows". F. R. Schröder has proposed a fourth etymology according to which ' means "yew pillar", deriving ' from ''*igwja'' (meaning " yew-tree"), and ' from ''*dher-'' (meaning "support").
Attestations
''Poetic Edda''
In the ''Poetic Edda'', the tree is mentioned in the three poems ''Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world and ...
'', ''Hávamál
''Hávamál'' ( ; Old Norse: ,Unnormalised spelling in the :Title: Final stanza: ../ref> classical pron. , Modern Icelandic pron. , ‘Words of he High One��) is presented as a single poem in the Icelandic , a collection of Old Norse poems f ...
'' and ''Grímnismál
''Grímnismál'' (Old Norse: ; 'The Lay of Grímnir') is one of the mythological poems of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the Codex Regius manuscript and the AM 748 I 4to fragment. It is spoken through the voice of ''Grímnir'', one of ...
''.
''Völuspá''
 In the second stanza of the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''
In the second stanza of the ''Poetic Edda'' poem ''Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world and ...
'', the völva
In Germanic paganism, a seeress is a woman said to have the ability to foretell future events and perform sorcery. They are also referred to with many other names meaning "prophetess", "staff bearer", "wise woman" and "sorceress", and they are ...
(a shamanic seeress) reciting the poem to the god Odin says that she remembers far back to "early times", being raised by jötnar, recalls nine worlds and nine ''ídiðiur'' (rendered in a variety of ways by translators—Dronke, for example, provides "nine wood-ogresses"), and when Yggdrasil was a seed ("glorious tree of good measure, under the ground"). In stanza 19, the völva says:
In stanza 20, the völva says that from the lake under the tree come three "maidens deep in knowledge" named Urðr
Urðr ( Old Norse "fate"Orchard (1997:169).) is one of the Norns in Norse mythology. Along with Verðandi (possibly "happening" or "present"Orchard (1997:174).) and Skuld (possibly "debt" or "future"Orchard (1997:151).), Urðr makes up a trio o ...
, Verðandi
In Norse mythology, Verðandi (Old Norse, meaning possibly "happening" or "present"Orchard (1997:174).), sometimes anglicized as Verdandi or Verthandi, is one of the norns. Along with Urðr (Old Norse "fate"Orchard (1997:169).) and Skuld (possib ...
, and Skuld. The maidens "incised the slip of wood", "laid down laws" and "chose lives" for the children of mankind and the destinies (') of men. In stanza 27, the völva details that she is aware that "Heimdallr
In Norse mythology, Heimdall (from Old Norse Heimdallr) is a god who keeps watch for invaders and the onset of Ragnarök from his dwelling Himinbjörg, where the burning rainbow bridge Bifröst meets the sky. He is attested as possessing for ...
's hearing is couched beneath the bright-nurtured holy tree." In stanza 45, Yggdrasil receives a final mention in the poem. The völva describes, as a part of the onset of Ragnarök, that Heimdallr blows Gjallarhorn, that Odin speaks with Mímir
Mímir or Mim is a figure in Norse mythology, renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, who is beheaded during the Æsir–Vanir War. Afterward, the god Odin carries around Mímir's head and it recites secret knowledge and counsel to him.
Mímir ...
's head, and then:
''Hávamál''
Hávamál
''Hávamál'' ( ; Old Norse: ,Unnormalised spelling in the :Title: Final stanza: ../ref> classical pron. , Modern Icelandic pron. , ‘Words of he High One��) is presented as a single poem in the Icelandic , a collection of Old Norse poems f ...
'', Odin describes how he once sacrificed himself to himself by hanging on a tree. The stanza reads:
In the stanza that follows, Odin describes how he had no food nor drink there, that he peered downward, and that "I took up the runes, screaming I took them, then I fell back from there." While Yggdrasil is not mentioned by name in the poem and other trees exist in Norse mythology, the tree is near universally accepted as Yggdrasil, and if the tree is Yggdrasil, then the name ''Yggdrasil'' directly relates to this story.
''Grímnismál''
In the poem ''Grímnismál
''Grímnismál'' (Old Norse: ; 'The Lay of Grímnir') is one of the mythological poems of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the Codex Regius manuscript and the AM 748 I 4to fragment. It is spoken through the voice of ''Grímnir'', one of ...
'', Odin (disguised as '' Grímnir'') provides the young Agnar with cosmological lore. Yggdrasil is first mentioned in the poem in stanza 29, where Odin says that, because the " bridge of the Æsir burns" and the "sacred waters
Sacred waters are sacred natural sites characterized by tangible topographical land formations such as rivers, lakes, springs, reservoirs, and oceans, as opposed to holy water which is water elevated with the sacramental blessing of a cleric ...
boil," Thor must wade through the rivers Körmt and Örmt
In Norse mythology, Körmt and Örmt are two rivers which Thor wades through every day when he goes to judgment by Yggdrasill. The source for this is a strophe in ''Grímnismál'' which is also quoted in the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', ...
and two rivers named Kerlaugar
In Norse mythology, the Kerlaugar (plural form of Old Norse ''kerlaug'' "kettle-bath",Orchard (1997:100).) i.e. "bath-tub", are two rivers through which the god Thor wades. The Kerlaugar are attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th c ...
to go "sit as judge at the ash of Yggdrasill". In the stanza that follows, a list of names of horses are given that the Æsir ride to "sit as judges" at Yggdrasil.
In stanza 31, Odin says that the ash Yggdrasil has three roots that grow in three directions. He details that beneath the first lives Hel, under the second live frost jötnar, and beneath the third lives mankind. Stanza 32 details that a squirrel named Ratatoskr
In Norse mythology, Ratatoskr (Old Norse, generally considered to mean "drill-tooth"Orchard (1997:129), Simek (2007:261), and Byock (2005:173). or "bore-tooth"Lindow (2001:259).) is a squirrel who runs up and down the world tree Yggdrasil to carry ...
must run across Yggdrasil and bring "the eagle's word" from above to Níðhöggr below. Stanza 33 describes that four hart
Hart often refers to:
* Hart (deer)
Hart may also refer to:
Organizations
* Hart Racing Engines, a former Formula One engine manufacturer
* Hart Skis, US ski manufacturer
* Hart Stores, a Canadian chain of department stores
* Hart's Reptile Wo ...
s named Dáinn, Dvalinn, Duneyrr and Duraþrór consume "the highest boughs" of Yggdrasil.
In stanza 34, Odin says that more serpents lie beneath Yggdrasil "than any fool can imagine" and lists them as Góinn and Móinn (possibly meaning Old Norse "land animal"), which he describes as sons of Grafvitnir (Old Norse, possibly "ditch wolf"), Grábakr (Old Norse "Greyback"), Grafvölluðr (Old Norse, possibly "the one digging under the plain" or possibly amended as "the one ruling in the ditch"), Ófnir (Old Norse "the winding one, the twisting one"), and Sváfnir (Old Norse, possibly "the one who puts to sleep = death"), who Odin adds that he thinks will forever gnaw on the tree's branches.
In stanza 35, Odin says that Yggdrasil "suffers agony more than men know", as a hart bites it from above, it decays on its sides, and Níðhöggr bites it from beneath. In stanza 44, Odin provides a list of things that are what he refers to as the "noblest" of their kind. Within the list, Odin mentions Yggdrasil first, and states that it is the "noblest of trees".
''Prose Edda''

 Yggdrasil is mentioned in two books in the ''
Yggdrasil is mentioned in two books in the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' ( is, Snorra Edda) or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often assumed to have been ...
''; ''Gylfaginning
''Gylfaginning'' (Old Norse: 'The Beguiling of Gylfi' or 'The Deluding of Gylfi'; c. 20,000 words; 13th century Old Norse pronunciation ) is the first part of the 13th century ''Prose Edda'' after the Prologue. The ''Gylfaginning'' deals with t ...
'' and ''Skáldskaparmál
''Skáldskaparmál'' (Old Norse: 'The Language of Poetry'; c. 50,000 words; ; ) is the second part of the ''Prose Edda''.
The section consists of a dialogue between Ægir, the divine personification of the sea, and Bragi, the god of poetry, ...
''. In ''Gylfaginning'', Yggdrasil is introduced in chapter 15. In chapter 15, Gangleri (described as king Gylfi
In Norse mythology, Gylfi (Old Norse: ), ''Gylfe'', ''Gylvi'', or ''Gylve'' was the earliest recorded king in Scandinavia. He often uses the name Gangleri when appearing in disguise. The traditions on Gylfi deal with how he was tricked by the god ...
in disguise) asks where is the chief or holiest place of the gods. High
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift t ...
replies "It is the ash Yggdrasil. There the gods must hold their courts each day". Gangleri asks what there is to tell about Yggdrasil. Just-As-High says that Yggdrasil is the biggest and best of all trees, that its branches extend out over all of the world and reach out over the sky. Three of the roots of the tree support it, and these three roots also extend extremely far: one "is among the Æsir
The Æsir (Old Norse: ) are the gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. They include Odin, Frigg, Höðr, Thor, and Baldr. The second Norse pantheon is the Vanir. In Norse mythology, the two pantheons wage war against each other, ...
, the second among the frost jötnar, and the third over Niflheim. The root over Niflheim is gnawed at by the wyrm Níðhöggr
In Norse mythology, Níðhöggr (''Malice Striker'', in Old Norse traditionally also spelled Níðhǫggr , often anglicized NidhoggWhile the suffix of the name, ''-höggr'', clearly means "striker" the prefix is not as clear. In particular, the ...
, and beneath this root is the spring Hvergelmir
In Norse mythology, Hvergelmir (Old Norse: ; "bubbling boiling spring"Orchard (1997:93)) is a major spring. Hvergelmir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', writte ...
. Beneath the root that reaches the frost jötnar is the well Mímisbrunnr
In Norse mythology, Mímisbrunnr (Old Norse " Mímir's well"Simek (2007:216).) is a well associated with the being Mímir, located beneath the world tree Yggdrasil. Mímisbrunnr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century fr ...
, "which has wisdom and intelligence contained in it, and the master of the well is called Mimir". Just-As-High provides details regarding Mímisbrunnr and then describes that the third root of the well "extends to heaven" and that beneath the root is the "very holy" well Urðarbrunnr
Urðarbrunnr (Old Norse "Well of Urðr"; either referring to a Germanic concept of fate—''urðr''—or the norn named UrðrSimek (2007:342).) is a well in Norse mythology. Urðarbrunnr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th ...
. At Urðarbrunnr the gods hold their court, and every day the Æsir ride to Urðarbrunnr up over the bridge Bifröst
In Norse mythology, Bifröst (), also called Bilröst, is a burning rainbow bridge that reaches between Midgard (Earth) and Asgard, the realm of the gods. The bridge is attested as ''Bilröst'' in the '' Poetic Edda''; compiled in the 13th cen ...
. Later in the chapter, a stanza from ''Grímnismál'' mentioning Yggdrasil is quoted in support.
In chapter 16, Gangleri asks "what other particularly notable things are there to tell about the ash?" High says there is quite a lot to tell about. High continues that an eagle sits on the branches of Yggdrasil and that it has much knowledge. Between the eyes of the eagle sits a hawk called Veðrfölnir. A squirrel called Ratatoskr
In Norse mythology, Ratatoskr (Old Norse, generally considered to mean "drill-tooth"Orchard (1997:129), Simek (2007:261), and Byock (2005:173). or "bore-tooth"Lindow (2001:259).) is a squirrel who runs up and down the world tree Yggdrasil to carry ...
scurries up and down the ash Yggdrasil carrying "malicious messages" between the eagle and Níðhöggr. Four stags named Dáinn, Dvalinn, Duneyrr, and Duraþrór run between the branches of Yggdrasil and consume its foliage. In the spring Hvergelmir are so many snakes along with Níðhöggr "that no tongue can enumerate them". Two stanzas from ''Grímnismál'' are then cited in support. High continues that the norns that live by the holy well Urðarbrunnr each day take water from the well and mud from around it and pour it over Yggdrasil so that the branches of the ash do not rot away or decay. High provides more information about Urðarbrunnr, cites a stanza from ''Völuspá'' in support, and adds that dew falls from Yggdrasil to the earth, explaining that "this is what people call honeydew, and from it bees feed".
In chapter 41, the stanza from ''Grímnismál'' is quoted that mentions that Yggdrasil is the foremost of trees. In chapter 54, as part of the events of Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (; non, wikt:ragnarǫk, Ragnarǫk) is a series of events, including a great battle, foretelling the death of numerous great figures (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdallr, and Loki), natural disast ...
, High describes that Odin will ride to the well Mímisbrunnr and consult Mímir on behalf of himself and his people. After this, "the ash Yggdrasil will shake and nothing will be unafraid in heaven or on earth", and then the Æsir and Einherjar
In Norse mythology, the einherjar (singular einheri) literally "army of one", "those who fight alone"Simek, Rudolf. 1993. Dictionary of Northern Mythology. Translated by Angela Hall. p. 71Orchard (1997:36) and Lindow (2001:104).) are those who h ...
will don their war gear and advance to the field of Vígríðr
In Norse mythology, Vígríðr or Óskópnir is a large field foretold to host a battle between the forces of the gods and the forces of Surtr as part of the events of Ragnarök. The field is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th ...
. Further into the chapter, the stanza in ''Völuspá'' that details this sequence is cited.
In the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Skáldskaparmál
''Skáldskaparmál'' (Old Norse: 'The Language of Poetry'; c. 50,000 words; ; ) is the second part of the ''Prose Edda''.
The section consists of a dialogue between Ægir, the divine personification of the sea, and Bragi, the god of poetry, ...
'', Yggdrasil receives a single mention, though not by name. In chapter 64, names for king
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen regnant, queen, which title is also given to the queen consort, consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contempora ...
s and duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are r ...
s are given. "Illustrious one" is provided as an example, appearing in a Christianity-influenced work by the skald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditional ...
Hallvarðr Háreksblesi Hallvarðr Háreksblesi was one of the skalds of Canute the Great. Nothing is known about his life or family but eight fragments of his poetry on Canute have been preserved. While Hallvarðr's poetry resembles that of Canute's other poets in many re ...
: "There is not under the pole of the earth ggdrasilan illustrious one closer to the lord of monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedic ...
s odthan you."
Theories
Shamanic origins
Hilda Ellis Davidson
Hilda Roderick Ellis Davidson (born Hilda Roderick Ellis; 1 October 1914 – 12 January 2006) was an English folklorist. She was a scholar at the University of Cambridge and The Folklore Society, and specialized in the study of Celtic and G ...
comments that the existence of nine worlds around Yggdrasil is mentioned more than once in Old Norse sources, but the identity of the worlds is never stated outright, though it can be deduced from various sources. Davidson comments that "no doubt the identity of the nine varied from time to time as the emphasis changed or new imagery arrived". Davidson says that it is unclear where the nine worlds are located in relation to the tree; they could either exist one above the other or perhaps be grouped around the tree, but there are references to worlds existing beneath the tree, while the gods are pictured as in the sky, a rainbow bridge (Bifröst
In Norse mythology, Bifröst (), also called Bilröst, is a burning rainbow bridge that reaches between Midgard (Earth) and Asgard, the realm of the gods. The bridge is attested as ''Bilröst'' in the '' Poetic Edda''; compiled in the 13th cen ...
) connecting the tree with other worlds. Davidson opines that "those who have tried to produce a convincing diagram of the Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and S ...
n cosmos from what we are told in the sources have only added to the confusion".
Davidson notes parallels between Yggdrasil and shamanic
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a spirit world through altered states of consciousness, such as trance. The goal of this is usually to direct spirits or spiri ...
lore in northern Eurasia:
The conception of the tree rising through a number of worlds is found in northern Eurasia and forms part of the shamanic lore shared by many peoples of this region. This seems to be a very ancient conception, perhaps based on theDavidson says that the notion of an eagle atop a tree and the world serpent coiled around the roots of the tree has parallels in other cosmologies fromPole Star A pole star or polar star is a star, preferably bright, nearly aligned with the axis of a rotating astronomical body. Currently, Earth's pole stars are Polaris (Alpha Ursae Minoris), a bright magnitude-2 star aligned approximately with its ..., the centre of the heavens, and the image of the central tree in Scandinavia may have been influenced by it.... AmongSiberia Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...n shamans, a central tree may be used as a ladder to ascend the heavens.
Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. She goes on to say that Norse cosmology may have been influenced by these Asiatic cosmologies from a northern location. Davidson adds, on the other hand, that it is attested that the Germanic people
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
s worshiped their deities in open forest clearings and that a sky god
The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.
The daytime sky deities are typically distinct from the nighttime ones. Stith Thompson's '' Moti ...
was particularly connected with the oak tree, and therefore "a central tree was a natural symbol for them also".
Mímameiðr, Hoddmímis holt, and Ragnarök
Hoddmímis holt
In Norse mythology, Hoddmímis holt (Old Norse "Hoard-Mímir's"Simek (2007:154). holt) is a location where Líf and Lífþrasir are foretold to survive the long winters of Fimbulvetr. Hoddmímis holt is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled i ...
(Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
"Hoard-Mímir
Mímir or Mim is a figure in Norse mythology, renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, who is beheaded during the Æsir–Vanir War. Afterward, the god Odin carries around Mímir's head and it recites secret knowledge and counsel to him.
Mímir ...
's" holt
Holt or holte may refer to:
Natural world
*Holt (den), an otter den
* Holt, an area of woodland
Places Australia
* Holt, Australian Capital Territory
* Division of Holt, an electoral district in the Australian House of Representatives in Vic ...
) and the tree Mímameiðr
In Norse mythology, Mímameiðr ( Old Norse " Mimi's tree"Simek (2007:216)) is a tree whose branches stretch over every land, is unharmed by fire or metal, bears fruit that assists pregnant women, and upon whose highest bough roosts the cock Ví� ...
("Mímir's tree"), generally thought to refer to the world tree Yggdrasil, and the spring Mímisbrunnr
In Norse mythology, Mímisbrunnr (Old Norse " Mímir's well"Simek (2007:216).) is a well associated with the being Mímir, located beneath the world tree Yggdrasil. Mímisbrunnr is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century fr ...
. John Lindow concurs that ''Mímameiðr'' may be another name for Yggdrasil and that if the Hoard-Mímir of the name ''Hoddmímis holt'' is the same figure as Mímir
Mímir or Mim is a figure in Norse mythology, renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, who is beheaded during the Æsir–Vanir War. Afterward, the god Odin carries around Mímir's head and it recites secret knowledge and counsel to him.
Mímir ...
(associated with the spring named after him, Mímisbrunnr), then the Mímir's holt—Yggdrasil—and Mímir's spring may be within the same proximity.
Carolyne Larrington notes that it is nowhere expressly stated what will happen to Yggdrasil during the events of Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (; non, wikt:ragnarǫk, Ragnarǫk) is a series of events, including a great battle, foretelling the death of numerous great figures (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdallr, and Loki), natural disast ...
. Larrington points to a connection between the primordial figure of Mímir
Mímir or Mim is a figure in Norse mythology, renowned for his knowledge and wisdom, who is beheaded during the Æsir–Vanir War. Afterward, the god Odin carries around Mímir's head and it recites secret knowledge and counsel to him.
Mímir ...
and Yggdrasil in the poem ''Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world and ...
'', and theorizes that "it is possible that Hoddmimir is another name for Mimir, and that the two survivors hide in Yggdrasill."
Rudolf Simek
Rudolf Simek (born 21 February 1954) is an Austrian philologist and religious studies scholar who is Professor and Chair of Ancient German and Nordic Studies at the University of Bonn. Simek specializes in Germanic studies, and is the author o ...
theorizes that the survival of Líf and Lífþrasir
In Norse mythology, Líf (identical with the Old Norse noun meaning "life, the life of the body")Cleasby & Vigfusson s.v. ''líf''. and Lífþrasir (Old Norse masculine name from ''líf'' and ''þrasir'' and defined by ''Lexicon Poëticum'' as ' ...
through Ragnarök by hiding in Hoddmímis holt is "a case of reduplication of the anthropogeny, understandable from the cyclic nature of the Eddic eschatology". Simek says that Hoddmímis holt "should not be understood literally as a wood or even a forest in which the two keep themselves hidden, but rather as an alternative name for the world-tree Yggdrasill. Thus, the creation of mankind from tree trunks (Askr, Embla) is repeated after the Ragnarǫk as well." Simek says that in Germanic regions, the concept of mankind originating from trees is ancient. Simek additionally points out legendary parallels in a Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
n legend of a shepherd
A shepherd or sheepherder is a person who tends, herds, feeds, or guards flocks of sheep. ''Shepherd'' derives from Old English ''sceaphierde (''sceap'' 'sheep' + ''hierde'' ' herder'). ''Shepherding is one of the world's oldest occupations, ...
who lives inside a tree, whose descendants repopulate the land after life there has been wiped out by plague (citing a retelling by F. R. Schröder). In addition, Simek points to an Old Norse parallel in the figure of Örvar-Oddr
Örvar-Oddr ( non, Ǫrvar-Oddr , "Arrow-Odd" or "Arrow's Point") is a legendary hero about whom an anonymous Icelander wrote a ''fornaldarsaga'' in the latter part of the 13th century. ''Örvar-Odds saga'', the Saga of Örvar-Odd, became very popul ...
, "who is rejuvenated after living as a tree-man (''Ǫrvar-Odds saga'' 24–27)".
Warden trees, Irminsul, and sacred trees
 Continuing as late as the 19th century, warden trees were venerated in areas of Germany and Scandinavia, considered to be guardians and bringers of luck, and offerings were sometimes made to them. A massive
Continuing as late as the 19th century, warden trees were venerated in areas of Germany and Scandinavia, considered to be guardians and bringers of luck, and offerings were sometimes made to them. A massive birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' cont ...
tree standing atop a burial mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
and located beside a farm in western Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
is recorded as having had ale poured over its roots during festivals. The tree was felled in 1874.
Davidson comments that "the position of the tree in the centre as a source of luck and protection for gods and men is confirmed" by these rituals to Warden Trees. Davidson notes that the gods are described as meeting beneath Yggdrasil to hold their things, and the related Irminsul
An Irminsul (Old Saxon 'great pillar') was a sacred, pillar-like object attested as playing an important role in the Germanic paganism of the Saxons. Medieval sources describe how an Irminsul was destroyed by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars. ...
, which may have been a pillar, was also symbolic of the center of the world. Davidson details that it would be difficult to ascertain whether a tree or pillar came first, and that this likely depends on if the holy location was in a thickly wooded area or not. Davidson notes that there is no mention of a sacred tree
A sacred tree is a tree which is considered to be sacred, or worthy of spiritual respect or reverence. Such trees appear throughout world history in various cultures including the ancient Greek, Hindu mythology, Celtic and Germanic mythologies. T ...
at Þingvellir
Þingvellir (, anglicised as ThingvellirThe spelling ''Pingvellir'' is sometimes seen, although the letter "p" is unrelated to the letter "þ" (thorn), which is pronounced as "th".) was the site of the Alþing, the annual parliament of Iceland ...
in Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
yet that Adam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle ''Gest ...
describes a huge tree standing next to the Temple at Uppsala in Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, which Adam describes as remaining green throughout summer and winter, and that no one knew what type of tree it was. Davidson comments that while it is uncertain that Adam's informant actually witnessed that tree is unknown, but that the existence of sacred trees in pre-Christian Germanic Europe is further evidenced by records of their destruction by early Christian missionaries, such as Thor's Oak
Donar's Oak (also Thor's Oak or, via ''interpretatio romana'', Jove's Oak) was a sacred tree of the Germanic pagans located in an unclear location around what is now the region of Hesse, Germany. According to the 8th century ''Vita Bonifatii auc ...
by Saint Boniface
Boniface, OSB ( la, Bonifatius; 675 – 5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of the Frankish Empire during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations o ...
.
Ken Dowden comments that behind Irminsul, Thor's Oak in Geismar, and the sacred tree at Uppsala
Uppsala (, or all ending in , ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the county seat of Uppsala County and the fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Located north of the ca ...
"looms a mythic prototype, an Yggdrasil, the world-ash of the Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Norse people) were a North Germanic ethnolinguistic group of the Early Middle Ages, during which they spoke the Old Norse language. The language belongs to the North Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages and is the ...
".
Modern influence
Thomas Carlyle
Thomas Carlyle (4 December 17955 February 1881) was a Scottish essayist, historian and philosopher. A leading writer of the Victorian era, he exerted a profound influence on 19th-century art, literature and philosophy.
Born in Ecclefechan, ...
adopted "Igdrasil" as a favorite symbol; it features in both '' On Heroes, Hero-Worship, & the Heroic in History'' (1841) and ''Past and Present'' (1843).
Modern works of art depicting Yggdrasil include ''Die Nornen'' (painting, 1888) by K. Ehrenberg; ''Yggdrasil'' (fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plast ...
, 1933) by Axel Revold, located in the University of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top universit ...
library auditorium in Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
; ''Hjortene beiter i løvet på Yggdrasil asken'' (wood relief carving
In wood carving relief carving is a type in which figures or patterns are carved in a flat panel of wood; the same term is also used for carving in stone, ivory carving and various other materials. The figures project only slightly from the bac ...
, 1938) on the Oslo City Hall
Oslo City Hall ( no, Oslo rådhus) is a municipal building in Oslo, the capital of Norway. It houses the city council, the city's administration and various other municipal organisations. The building as it stands today was constructed between ...
by Dagfin Werenskiold; and the bronze relief on the doors of the Swedish Museum of National Antiquities
The Swedish History Museum ( sv, Historiska museet or Statens historiska museum) is a museum located in Stockholm, Sweden, that covers Swedish archaeology and cultural history from the Mesolithic period to present day. Founded in 1866, it operates ...
(around 1950) by B. Marklund in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
, Sweden.
Poems mentioning Yggdrasil include ''Vårdträdet'' by Viktor Rydberg
Abraham Viktor Rydberg (; 18 December 182821 September 1895) was a Swedish writer and a member of the Swedish Academy, 1877–1895. "Primarily a classical idealist", Viktor Rydberg has been described as "Sweden's last Romantic" and by 1859 was ...
and ''Yggdrasill'' by J. Linke.
In ''Overlord
An overlord in the English feudal system was a lord of a manor who had subinfeudated a particular manor, estate or fee, to a tenant. The tenant thenceforth owed to the overlord one of a variety of services, usually military service or ser ...
'', a Japanese light novel series written by Kugane Maruyama, ''Yggdrasil'' is the name of a popular DMMORPG, where the protagonist got trapped after its shutdown.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * *External links
{{Authority control Locations in Norse mythology Trees in Germanic paganism Trees in Germanic mythology Trees in mythology