Yamagata Castle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 is a flatland-style Japanese castle located in the center of the city of Yamagata, eastern
is a flatland-style Japanese castle located in the center of the city of Yamagata, eastern Yamagata Castle Ruins
was a strong supporter of the Ashikaga shogunate">DF 58 of 80/nowiki>">DF 58 of 80">("Shi ...
was a strong supporter of the Ashikaga shogunate and the Northern Court. Shiba Kaneyori later changed his surname to "Mogami", and the Mogami clan continued to rule for about 275 years. However, by the Sengoku period, the Mogami had lost much of heir power due to a succession of internal conflicts and short-lived leaders. The aggressive Date clan invaded Mogami territory and after a series of battles, reduced the Mogami to a subordinate position. However, the Date clan itself then fell victim to internal political conflicts. Taking advantage of the situation, Mogami Yoshimori regained his independence, and married his daughter to Date Terumune. Their son was  is a flatland-style Japanese castle located in the center of the city of Yamagata, eastern
is a flatland-style Japanese castle located in the center of the city of Yamagata, eastern Yamagata Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Yamagata Prefecture has a population of 1,079,950 (1 June 2019) and has a geographic area of 9,325 km² (3,600 sq mi). Yamagata Prefecture borders Akita Prefecture to the nor ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. Throughout the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
, Yamagata Castle was the headquarters for the ''daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominall ...
'' of Yamagata Domain. The castle was also known as . The castle grounds are protected as a National Historic Site by the Japanese governmentAgency for Cultural Affairs
The is a special body of the Japanese Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT). It was set up in 1968 to promote Japanese arts and culture.
The agency's budget for FY 2018 rose to ¥107.7 billion.
Overview
The ag ...
Overview
The Yamagata Basin is a long and narrow inland valley of theMogami River
The is a river in Yamagata Prefecture, Japan.
Description and history
It is 224 km long and has a watershed of 7,040 km2. It is regarded as one of the three most rapid rivers of Japan (along with the Fuji River and the Kuma River).
...
bounded by the Ōu Mountains to the east. It is an important communications center for the southeastern portion of the Tōhoku region
The , Northeast region, or consists of the northeastern portion of Honshu, the largest island of Japan. This traditional region consists of six prefectures (''ken''): Akita, Aomori, Fukushima, Iwate, Miyagi, and Yamagata.
Tōhoku reta ...
of Japan. connecting the Shōnai Plains and the Sea of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, i ...
to the west with the Yonezawa Basin to the south, and the Sendai Plains and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
across the Ōu Mountains. In addition to riverine traffic, the route of the Ushū Kaidō highway also passes through the area. Yamagata Castle is located at the southern end of the Yamagata Basin.
History
Early history
The first castle on this site dates to the middle of theMuromachi period
The is a division of Japanese history running from approximately 1336 to 1573. The period marks the governance of the Muromachi or Ashikaga shogunate (''Muromachi bakufu'' or ''Ashikaga bakufu''), which was officially established in 1338 by ...
, when Shiba Kaneyori established himself as lord of the surrounding area of Dewa Province and built a fortified residence on the site of what is now the inner bailey of Yamagata Castle. The Shiba clan
was a Japanese clan. Papinot, Jacques Edmond Joseph. (1906). ''Dictionnaire d’histoire et de géographie du Japon''; Papinot, (2003).html" ;"title="DF 58 of 80">("Shiba," ''Nobiliare du Japon'', p. 54 DF_58_of_80">("Shi_...
_was_a_strong_supporter_of_the_Ashikaga_shogunate.html" ;"title="DF 58 of 80/nowiki>">DF 58 of 80">("Shi ...Date Masamune
was a regional ruler of Japan's Azuchi–Momoyama period through early Edo period. Heir to a long line of powerful ''daimyō'' in the Tōhoku region, he went on to found the modern-day city of Sendai. An outstanding tactician, he was made ...
, and this relationship provided security for the Mogami clan.
Mogami Yoshimori's eldest son, Mogami Yoshiaki fought many battle against various cadet branches of his own clan as well as the local warlords of many strongholds across Dewa Province from his base at Yamagata, with the Date clan sometimes assisting, but more often hindering his efforts to unit the province. However, following an invasion by Uesugi Kagekatsu, who captured the Shōnai region, Yoshiaki was forced to submit to Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Cour ...
. Yoshiaki rebuilt Yamagata Castle in 1592, adding a second bailey and third bailey, and a number of two-story and three-story ''yagura'' watchtowers. The castle never had a '' tenshu''. He also laid out the '' jōkamachi'' for what later became the city of Yamagata. However, his relations with the Toyotomi were always strained, as the Toyotomi favored the Uesugi clan, and Mogami Yoshiaki's daughter Komahime was killed by Hideyoshi when he purged Toyotomi Hidetsugu and his household. At the time of the Sekigahara campaign
The Sekigahara Campaign was a series of battles in Japan fought between the Eastern Army aligned with Tokugawa Ieyasu and the Western Army loyal to Ishida Mitsunari, culminating in the decisive Battle of Sekigahara. The conflict was sparked ...
, Mogami Yoshiaki sided with Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fello ...
. The forces of the Uesugi clan under Naoe Kanetsugu invaded the Yonezawa basin. Despite being severely outnumbered, the Mogami were able to repulse the invasion. The Mogami were rewarded after the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
with an increase in territory to 570,000 ''koku
The is a Chinese-based Japanese unit of volume. 1 koku is equivalent to 10 or approximately , or about . It converts, in turn, to 100 shō and 1000 gō. One ''gō'' is the volume of the "rice cup", the plastic measuring cup that is supplied ...
'' with the recovery of the Shōnai region. This led to a further expansion of Yamagata Castle.
However, after the death of Yoshiaki in 1614, an internal conflict erupted between his major retainers, providing an excuse for attainder of the domain by the shogunate in 1622.
Later history
The Tokugawa shogunate broke up the Mogami domain into many smaller territories. In 1622, Yamagata Caste was awarded to Torii Tadamune, the son of Torii Mototada who had heroically died at the Battle of Fushimi Castle near Kyoto at the time of the Battle of Sekigahara. However, he was relocated toTakatō Castle
is a Japanese castle located in the city of Ina, southern Nagano Prefecture, Japan. At the end of the Edo period, Takatō Castle was home to a cadet branch of the Naitō clan, '' daimyō'' of Takatō Domain. The castle was also known as . Bui ...
in Echigo Province
was an old province in north-central Japan, on the shores of the Sea of Japan. It bordered on Uzen, Iwashiro, Kōzuke, Shinano, and Etchū Provinces. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005). "''Echigo''" in . It corresponds today to Niig ...
in 1636, and the castle and Yamagata Domain passed through a large number of ''daimyō'' clans, often for less than a single generation, and its revenues were severely reduced. With their reduced revenues, these ''daimyō'' could not afford to maintain this huge a castle and the by the middle of the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
, the main bailey was allowed to fall into ruins, the second bailey was used as the residence of the ''daimyō'' , and the western half of the third bailey was plowed up for farmland. The castle was in the hands of a cadet branch the Mizuno clan at the time of the Meiji restoration
The , referred to at the time as the , and also known as the Meiji Renovation, Revolution, Regeneration, Reform, or Renewal, was a political event that restored practical imperial rule to Japan in 1868 under Emperor Meiji. Although there were ...
.
With the abolition of the han system
The in the Empire of Japan and its replacement by a system of prefectures in 1871 was the culmination of the Meiji Restoration begun in 1868, the starting year of the Meiji period. Under the reform, all daimyos (, ''daimyō'', feudal lord ...
in 1871, Yamagata Domain became Yamagata Prefecture, and in 1872 the castle grounds were sold to the government, and were used as a base for the Imperial Japanese Army
The was the official ground-based armed force of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945. It was controlled by the Imperial Japanese Army General Staff Office and the Ministry of the Army, both of which were nominally subordinate to the Emper ...
’s IJA 32nd Infantry Regiment. Many sakura were planted around the castle grounds in 1906 to commemorate the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
. After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the site of the castle became Kajō Park, containing the Yamagata Prefectural Museum. The East Gate of the castle and the site of castle keep were restored in 1986, and the Higashi Otemon Gate of the second bailey was restored in 1991. In 2004 the stonework of the Inchimon Gate was restored, and a bridge leading to main bailey was reconstructed in 2006. Renovations and archaeological investigations are ongoing, and Yamagata City plans to restore as much of the castle as possible to its early Edo-period condition by the year 2033. The castle was listed as one of the 100 Fine Castles of Japan by the in 2006.
Structure
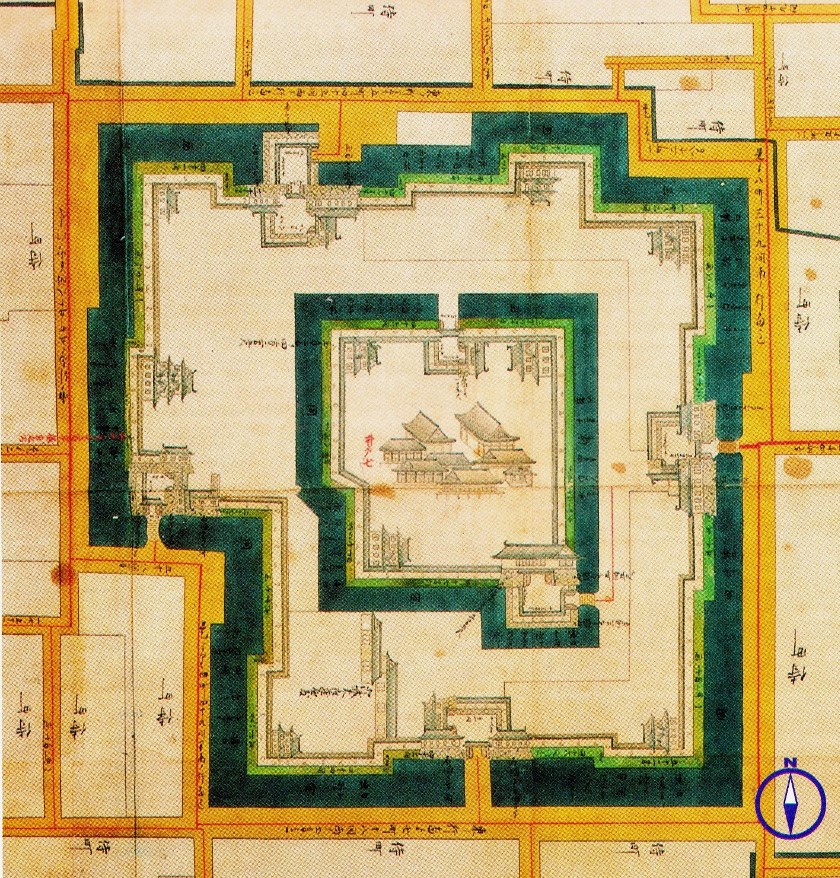
Yamagata Castle consists of three concentric square areas. The inner bailey is 200 meters square, was protected by clay walls and wet moats, and had gates at the southeast and north sides and a corner ''yagura''. Within the enclosure was the foundation for a ''tenshu'', which was never actually constructed. The second bailey measured 500 meters on each side, and completely surrounded the inner bailey. Its outer walls were indented in places to enable flanking fire against an attacking enemy. This enclosure had large ''Masugata''-gates on the south and east, and a smaller gate in the north. The third area was about 2 kilometer on each side, and enclosed the semi-fortified residences of important retainers. The size of original castle thus exceeded Aoba Castle inSendai
is the capital city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 designated cities. The city was founded in 1600 by the ''daimyō'' Date M ...
and Aizuwakamatsu Castle
, also known as Tsuruga Castle (鶴ヶ城 ''Tsuru-ga-jō'') is a concrete replica of a traditional Japanese castle in northern Japan, at the center of the city of Aizuwakamatsu, in Fukushima Prefecture.
Background
Aizu Wakamatsu Castle is locate ...
, making it by far the largest castle in the Tōhoku region. However, without a massive ''tenshu'' or stone walls, it was deceptively plain.
See also
* List of Historic Sites of Japan (Yamagata)Literature
* * * * * *External links
Yamagata Castle Jcastle Profile
Notes
{{Authority control Historic Sites of Japan Castles in Yamagata Prefecture History of Yamagata Prefecture Yamagata, Yamagata Dewa Province Mogami clan Mizuno clan