Y Gogledd on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the
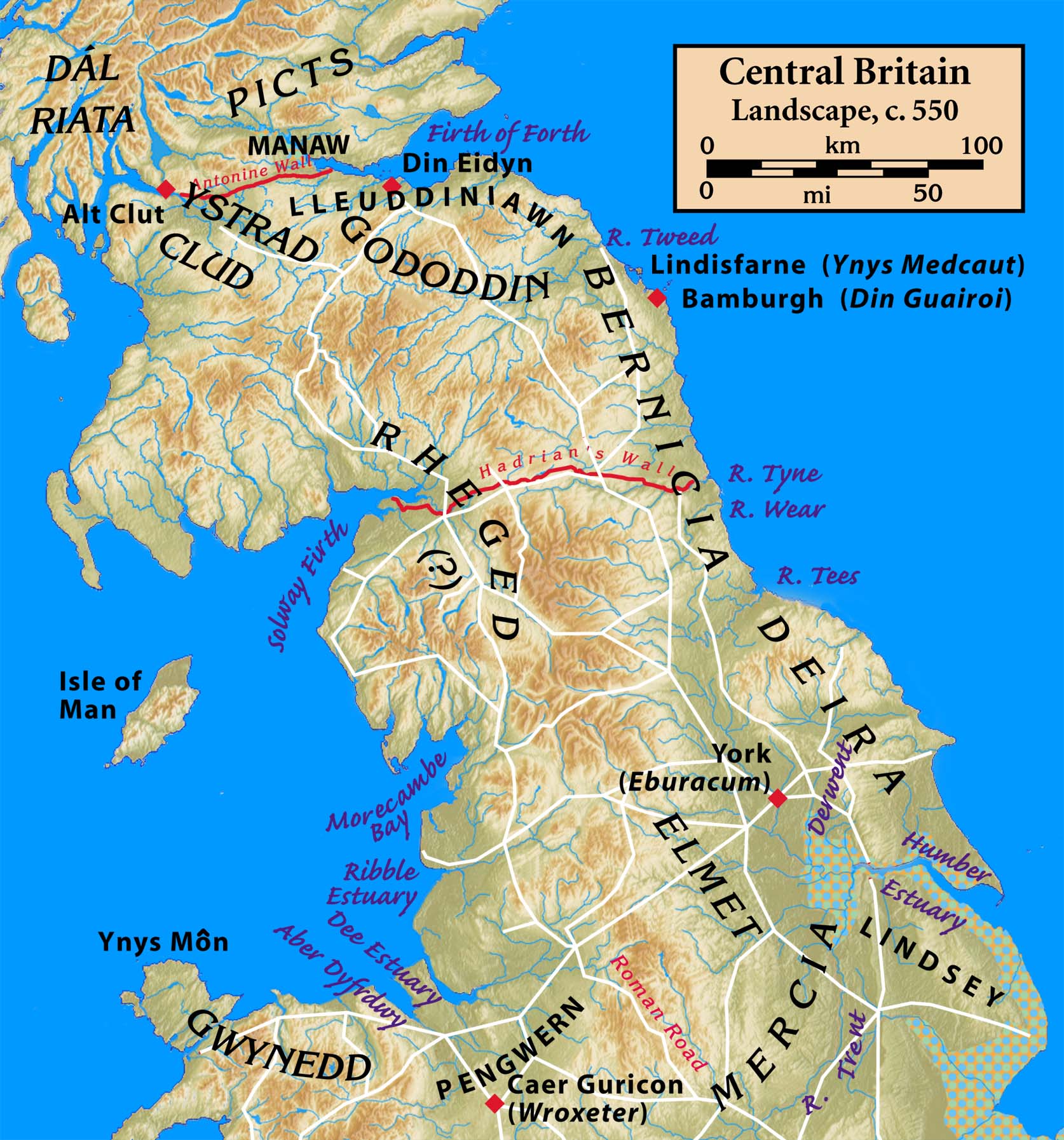
 The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the
The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the
"What's in a name? Britons, Angles, ethnicity and material culture from the fourth to seventh centuries."
''Heroic Age'' 4 (Winter 2001). {{Barbarian kingdoms Celtic Britons Medieval England 1st millennium in Scotland Sub-Roman Britain Anglo-Saxon England Medieval Wales Northern England History of Cumbria History of Dumfries and Galloway History of Northumberland History of the Scottish Borders History of Yorkshire Barbarian kingdoms Regions of England Regions of Scotland Historical regions in the United Kingdom Scottish Lowlands
 Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the
Yr Hen Ogledd (), in English the Old North, is the historical region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing soc ...
which is now Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Kingdom of Jorvik, and the ...
and the southern Scottish Lowlands that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. ...
known as Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the souther ...
which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry ('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word ''combrogi.'' The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of North Britain
North Britain is a term which has been occasionally used, particularly in the 17th and 18th centuries, for either the northern part of Great Britain or Scotland, which occupies the northernmost third of the island. "North Britains" could also re ...
inhabited by the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from e ...
, Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
, and Scoti
''Scoti'' or ''Scotti'' is a Latin name for the Gaels,Duffy, Seán. ''Medieval Ireland: An Encyclopedia''. Routledge, 2005. p.698 first attested in the late 3rd century. At first it referred to all Gaels, whether in Ireland or Great Britain, but l ...
.
The major kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd were Elmet
Elmet ( cy, Elfed), sometimes Elmed or Elmete, was an independent Brittonic kingdom between about the 5th century and early 7th century, in what later became the smaller area of the West Riding of Yorkshire then West Yorkshire, South Yorkshir ...
, Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
, Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and b ...
, and the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
. Smaller kingdoms included Aeron and Calchfynydd. Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in Britain's sub-Roman and early medieval periods, approximately the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Cas ...
, Lleuddiniawn, and Manaw Gododdin
Manaw Gododdin was the narrow coastal region on the south side of the Firth of Forth, part of the Brythonic-speaking Kingdom of Gododdin in the post-Roman Era. It is notable as the homeland of Cunedda prior to his conquest of North Wales, and ...
were evidently parts of Gododdin. The Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the '' vertex'' of the angle.
Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles a ...
kingdoms of Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/Cumbric: ''Deywr'' or ''Deifr''; ang, Derenrice or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic *''daru' ...
and Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
both had Brittonic-derived names, suggesting they may have been Brittonic kingdoms in origin. All the kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd except Strathclyde were conquered by Anglo-Saxons and Picts by about 800; Strathclyde was incorporated into the rising Middle Irish
Middle Irish, sometimes called Middle Gaelic ( ga, An Mheán-Ghaeilge, gd, Meadhan-Ghàidhlig), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of late Old Engl ...
-speaking Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
in the 11th century.
The memory of the Hen Ogledd remained strong in Wales. Welsh tradition included genealogies of the ''Gwŷr y Gogledd'', or Men of the North, and several important Welsh dynasties traced their lineage to them. A number of important early Welsh texts were attributed to the Men of the North, such as Taliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts ...
, Aneirin
Aneirin , Aneurin or Neirin was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd, probably that of Gododdin at Edinburgh, in modern Scotland. From the 17th c ...
, Myrddin Wyllt
Myrddin Wyllt (—"Myrddin the Wild", kw, Marzhin Gwyls, br, Merzhin Gueld) is a figure in medieval Welsh legend. In Middle Welsh poetry he is accounted a chief bard, the speaker of several poems in The Black Book of Carmarthen and The Red B ...
, and the Cynfeirdd
Medieval Welsh literature is the literature written in the Welsh language during the Middle Ages. This includes material starting from the 5th century AD, when Welsh was in the process of becoming distinct from Common Brittonic, and continuing t ...
poets. Heroes of the north such as Urien
Urien (; ), often referred to as Urien Rheged or Uriens, was a late 6th-century king of Rheged, an early British kingdom of the Hen Ogledd (today's northern England and southern Scotland) of the House of Rheged. His power and his victories, ...
, Owain mab Urien
Owain mab Urien (Middle Welsh Owein) (died c. 595) was the son of Urien, king of Rheged c. 590, and fought with his father against the Angles of Bernicia. The historical figure of Owain became incorporated into the Arthurian cycle of legends wh ...
, and Coel Hen
Coel (Old Welsh: ''Coil''), also called ''Coel Hen'' (Coel the Old) and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman ...
and his descendants feature in Welsh poetry and the Welsh Triads
The Welsh Triads ( cy, Trioedd Ynys Prydein, "Triads of the Island of Britain") are a group of related texts in medieval manuscripts which preserve fragments of Welsh folklore, mythology and traditional history in groups of three. The triad is a ...
.
Background
Almost nothing is reliably known of Central Britain before c. 550. There had never been a period of long-term, effectiveRoman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
control north of the Tyne– Solway line, and south of that line effective Roman control ended long before the traditionally given date of departure of the Roman military
The military of ancient Rome, according to Titus Livius, one of the more illustrious historians of Rome over the centuries, was a key element in the rise of Rome over "above seven hundred years" from a small settlement in Latium to the capital o ...
from Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
in 407. It was noted in the writings of Ammianus Marcellinus
Ammianus Marcellinus (occasionally anglicised as Ammian) (born , died 400) was a Roman soldier and historian who wrote the penultimate major historical account surviving from antiquity (preceding Procopius). His work, known as the ''Res Gestae ...
and others that there was ever-decreasing Roman control from about AD 100 onward, and in the years after 360 there was widespread disorder and the large-scale permanent abandonment of territory by the Romans.
By 550, the region was controlled by native Brittonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
-speaking peoples except for the eastern coastal areas, which were controlled by the Anglian peoples of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
and Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/Cumbric: ''Deywr'' or ''Deifr''; ang, Derenrice or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic *''daru' ...
. To the north were the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from e ...
(now also accepted as Brittonic speakers prior to Gaelicisation) with the Gaelic kingdom of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
to the northwest. All of these peoples would play a role in the history of the Old North.
Historical context
From a historical perspective, wars were frequently internecine, and Britons were aggressors as well as defenders, as was also true of theAngles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Picts, and Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langu ...
. However, those Welsh stories of the Hen Ogledd that tell of Britons fighting Anglians have a counterpart, told from the opposite side. The story of the demise of the kingdoms of the Old North is the story of the rise of the Kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
from two coastal kingdoms to become the premier power in Britain north of the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between t ...
and south of the Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde is the mouth of the River Clyde. It is located on the west coast of Scotland and constitutes the deepest coastal waters in the British Isles (it is 164 metres deep at its deepest). The firth is sheltered from the Atlantic ...
and the Firth of Forth.

 The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the
The interests of kingdoms of this era were not restricted to their immediate vicinity. Alliances were not made only within the same ethnic groups, nor were enmities restricted to nearby different ethnic groups. An alliance of Britons fought against another alliance of Britons at the Battle of Arfderydd
The Battle of Arfderydd (also known as Arderydd) was fought, according to the Annales Cambriae, in 573. The opposing armies are variously given in a number of Old Welsh sources, perhaps suggesting a number of allied armies were involved. The main ...
. Áedán mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (pronounced in Old Irish; ga, Aodhán mac Gabhráin, lang), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and par ...
of Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
appears in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' ( en, The Descent of the Men of the North) is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and norther ...
'', a genealogy among the pedigrees of the Men of the North. The ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'' states that Oswiu
Oswiu, also known as Oswy or Oswig ( ang, Ōswīg; c. 612 – 15 February 670), was King of Bernicia from 642 and of Northumbria from 654 until his death. He is notable for his role at the Synod of Whitby in 664, which ultimately brought the chu ...
, king of Northumbria, married a Briton who may have had some Pictish ancestry. A marriage between the Northumbrian and Pictish royal families would produce the Pictish king Talorgan I. Áedán mac Gabráin fought as an ally of the Britons against the Northumbrians. Cadwallon ap Cadfan
Cadwallon ap Cadfan (died 634A difference in the interpretation of Bede's dates has led to the question of whether Cadwallon was killed in 634 or the year earlier, 633. Cadwallon died in the year after the Battle of Hatfield Chase, which Bede rep ...
of the Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Based in northwest Wales, th ...
allied with Penda of Mercia
Penda (died 15 November 655)Manuscript A of the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' gives the year as 655. Bede also gives the year as 655 and specifies a date, 15 November. R. L. Poole (''Studies in Chronology and History'', 1934) put forward the theor ...
to defeat Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin ( ang, Ēadwine; c. 586 – 12 October 632/633), also known as Eadwine or Æduinus, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from about 616 until his death. He converted to Christi ...
.
Conquest and defeat did not necessarily mean the extirpation of one culture and its replacement by another. The Brittonic region of northwestern England was absorbed by Anglian Northumbria in the 7th century, yet it would re-emerge 300 years later as South Cumbria, joined with North Cumbria (Strathclyde) into a single state.
Societal context
The organisation of the Men of the North wastribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
, based on kinship groups of extended families, owing allegiance to a dominant "royal" family, sometimes indirectly through client relationships, and receiving protection in return. For Celtic peoples, this organisation was still in effect hundreds of years later, as shown in the Irish Brehon law
Early Irish law, historically referred to as (English: Freeman-ism) or (English: Law of Freemen), also called Brehon law, comprised the statutes which governed everyday life in Early Medieval Ireland. They were partially eclipsed by the Norma ...
, the Welsh Laws of Hywel Dda
''Cyfraith Hywel'' (; ''Laws of Hywel''), also known as Welsh law ( la, Leges Walliæ), was the system of law practised in medieval Wales before its final conquest by England. Subsequently, the Welsh law's criminal codes were superseded by t ...
, and the Scottish Laws of the Brets and Scots. The Anglo-Saxon law
Anglo-Saxon law (Old English ''ǣ'', later ''lagu'' "law"; dōm "decree, judgment") is a body of written rules and customs that were in place during the Anglo-Saxon period in England, before the Norman conquest. This body of law, along with early ...
had culturally different origins, but with many similarities to Celtic law
A number of law codes have in the past been in use in the various Celtic nations since the Middle Ages.
While these vary considerably in details, there are certain points of similarity.
The Brehon Laws governed everyday life and politics in Ire ...
. Like Celtic law, it was based on cultural tradition, without any perceivable debt to the Roman occupation of Britain."Anglo-Saxon law" is a modern neologism
A neologism Greek νέο- ''néo''(="new") and λόγος /''lógos'' meaning "speech, utterance"] is a relatively recent or isolated term, word, or phrase that may be in the process of entering common use, but that has not been fully accepted int ...
for the Saxon Law of Wessex, the Anglian Law of Mercia, and the Danelaw
The Danelaw (, also known as the Danelagh; ang, Dena lagu; da, Danelagen) was the part of England in which the laws of the Danes held sway and dominated those of the Anglo-Saxons. The Danelaw contrasts with the West Saxon law and the Mercian ...
, all of which were sufficiently similar to merit inclusion within this umbrella term. The laws of Anglian Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
were supplanted by the Danelaw, but were certainly similar to these. The origins of English law have been much studied. For example, the 12th century '' Tractatus de legibus et consuetudinibus regni Angliae'' (''Treatise on the laws and customs of the Kingdom of England'') is the book of authority on English common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipres ...
, and scholars have held that it owes a debt to Norman law Norman law (, , ) refers to the customary law of the Duchy of Normandy which developed between the 10th and 13th centuries and which survives today in the legal systems of Jersey and the other Channel Islands. It grew out of a mingling of Frankish ...
and to Germanic law
Germanic law is a scholarly term used to described a series of commonalities between the various law codes (the ''Leges Barbarorum'', 'laws of the barbarians', also called Leges) of the early Germanic peoples. These were compared with statements ...
, and not to Roman law
Roman law is the legal system of ancient Rome, including the legal developments spanning over a thousand years of jurisprudence, from the Twelve Tables (c. 449 BC), to the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'' (AD 529) ordered by Eastern Roman emperor Ju ...
.
A primary ''royal court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be appl ...
'' ( cy, llys) would be maintained as a "capital", but it was not the bureaucratic administrative centre of modern society, nor the settlement or '' civitas'' of Roman rule. As the ruler and protector of his kingdom, the king would maintain multiple courts throughout his territory, travelling among them to exercise his authority and to address the needs of his people, such as in the dispensing of justice. This ancient method of dispensing justice survived as a part of royal procedure until the reforms of Henry II (reigned 1154–1189) modernised the administration of law.
Language
Modern scholarship uses the term "Cumbric" for the Brittonic language spoken in the Hen Ogledd. It appears to have been very closely related to Old Welsh, with some local variances, and more distantly related to Cornish, Breton and the pre-Gaelic form ofPictish
Pictish is the extinct Brittonic language spoken by the Picts, the people of eastern and northern Scotland from Late Antiquity to the Early Middle Ages. Virtually no direct attestations of Pictish remain, short of a limited number of geographica ...
. There are no surviving texts written in the dialect; evidence for it comes from placenames, proper names in a few early inscription
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the w ...
s and later non-Cumbric sources, two terms in the ''Leges inter Brettos et Scottos
The Leges inter Brettos et Scottos or Laws of the Brets and Scots was a legal codification under David I of Scotland (reigned 1124 – 1153). Only a small fragment of the original document survives, describing the penalties for several offences ...
'', and the corpus of poetry by the ''cynfeirdd
Medieval Welsh literature is the literature written in the Welsh language during the Middle Ages. This includes material starting from the 5th century AD, when Welsh was in the process of becoming distinct from Common Brittonic, and continuing t ...
'', the "early poets", nearly all of which deals with the north.Koch 2006, p. 516.
The ''cynfeirdd'' poetry is the largest source of information, and it is generally accepted that some part of the corpus was first composed in the Hen Ogledd. However, it survives entirely in later manuscripts created in Wales where the oral tradition continued on, and it is unknown how faithful they are to the originals. Still, the texts do contain discernible variances that distinguish the speech from the Welsh dialects. In particular, these texts contain a number of archaisms – features that appear to have once been common in all Brittonic varieties, but which later vanished from Welsh and the Southwestern Brittonic languages
The Southwestern Brittonic languages ( kw, Brythonek Dyghowbarthgorlewin, br, Predeneg Kreisteizkornôg) are the Brittonic Celtic languages spoken in what is now South West England and Brittany since the Early Middle Ages. During the period of ...
. In general, however, the differences appear to be slight, and the distinction between Cumbric and Old Welsh is largely geographical rather than linguistic.Koch 2006, p. 517.
Cumbric gradually disappeared as the area was conquered by the Anglo-Saxons, and later the Scots and Norse, though it survived in the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
, centred at Alt Clut in what is now Dumbarton
Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990.
Dumbarton was the ca ...
in Scotland. Kenneth H. Jackson
Prof Kenneth Hurlstone Jackson CBE FRSE FSA DLitt (1 November 1909 – 20 February 1991) was an English linguistics, linguist and a translator who specialised in the Celtic languages. He demonstrated how the text of the Ulster Cycle of tales, wr ...
suggested that it re-emerged in Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
in the 10th century, as Strathclyde established hegemony over that area. It is unknown when Cumbric finally became extinct, but the series of counting systems of Brittonic origin recorded in Northern England since the 18th century have been proposed as evidence of a survival of elements of Cumbric; though the view has been largely rejected on linguistic grounds, with evidence pointing to the fact that it was imported to England after the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
era.
Welsh tradition
One of the traditional stories relating to the genealogies of Welsh dynasties derived fromCunedda
Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda ''Wledig'' ( 5th century), was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of western Europe.
Name
The name ''Cunedda'' (spelled ''Cuned ...
and his sons as "Men of the North". Cunedda himself is held to be the progenitor of the royal dynasty of the Kingdom of Gwynedd, one of the largest and most powerful of the medieval Welsh kingdoms, and an ongoing connection to the Hen Ogledd. Cunedda genealogy shows him as a descendant of one of Magnus Maximus
Magnus Maximus (; cy, Macsen Wledig ; died 8 August 388) was Roman emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 383 to 388. He usurped the throne from emperor Gratian in 383 through negotiation with emperor Theodosius I.
He was made emperor in B ...
' generals, Paternus, who Maximus appointed as commander at Alt Clut. The Welsh and the Men of the North saw themselves as one people and the Welsh name for themselves, ''Cymry'', derives from this ancient relationship although this is debatable as while Gwynedd seemed to have good relationships with them along with Caredigion but it is unknown how the other Welsh Kingdoms saw them as they weren’t unified themselves, especially the southern Kingdoms like Dyfed and the Ystrad Tywi who had heavy Irish presence at the time. 'Cymry' was a term that referred to both the Welsh and the Men of the North but was sometimes applied to others as well such as the Picts and the Irish. It is derived from the Brittonic word c''ombrogoi'', which meant "fellow-countrymen", and it is worth noting in passing that its Breton counterpart ''kenvroiz'' still has this original meaning "compatriots". The word began to be used as an endonym by the Men of the North during the early 7th century (and possibly earlier), and was used throughout the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
to describe both the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
. Before this, and for some centuries after, the traditional as well as the more literary term was ''Brythoniaid'', recalling the still older time when all on the island remained a unity. ''Cymry'' survives today in the native name for Wales (''Cymru'', land of the ''Cymry''), and in the English county name Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
, both meaning "homeland", "mother country".
Many of the traditional sources of information about the Hen Ogledd survive in Welsh tradition, and bards such as Aneirin
Aneirin , Aneurin or Neirin was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd, probably that of Gododdin at Edinburgh, in modern Scotland. From the 17th c ...
(the reputed author of ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia a ...
'') are thought to have been court poets in the Hen Ogledd.
Nature of the sources
A listing of passages from the literary and historical sources, particularly relevant to the Hen Ogledd, can be found in SirEdward Anwyl
Sir Edward Anwyl (5 August 1866 – 8 August 1914) was a Welsh academic, specializing in the Celtic languages.
Anwyl was born in Chester, England, and educated at the King's School, Chester. He went on to study at Oriel College, Oxford, and ...
's article ''Wales and the Britons of the North''. A somewhat dated introduction to the study of old Welsh poetry can be found in his 1904 article ''Prolegomena to the Study of Old Welsh Poetry''.
Literary sources
* The bardic poetry attributed toTaliesin
Taliesin ( , ; 6th century AD) was an early Brittonic poet of Sub-Roman Britain whose work has possibly survived in a Middle Welsh manuscript, the '' Book of Taliesin''. Taliesin was a renowned bard who is believed to have sung at the courts ...
, Aneirin
Aneirin , Aneurin or Neirin was an early Medieval Brythonic war poet. He is believed to have been a bard or court poet in one of the Cumbric kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd, probably that of Gododdin at Edinburgh, in modern Scotland. From the 17th c ...
, and Llywarch Hen.
* The genealogical tracts of the Harleian genealogies
__NOTOC__
The Harleian genealogies are a collection of Old Welsh genealogies preserved in British Library, Harley MS 3859. Part of the Harleian Library, the manuscript, which also contains the ''Annales Cambriae'' (Recension A) and a version of ...
, the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' ( en, The Descent of the Men of the North) is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and norther ...
'', and the genealogies of Jesus College MS 20.
* The '' Triads of the Island of Britain'' (note that most of the triads published in the notorious third volume of '' The Myvyrian Archaiology of Wales'' are known to be the forgeries of Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10 March 1747 – 18 December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclop ...
, and are not considered valid sources of historical information). The standard scholarly edition is ''Trioedd Ynys Prydein'' by Rachel Bromwich
Rachel Bromwich (30 July 1915 – 15 December 2010) born Rachel Sheldon Amos, was a British scholar. Her focus was on medieval Welsh literature, and she taught Celtic Languages and Literature in the Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse and Celtic a ...
.
* The other elegies
An elegy is a poem of serious reflection, and in English literature usually a lament for the dead. However, according to ''The Oxford Handbook of the Elegy'', "for all of its pervasiveness ... the 'elegy' remains remarkably ill defined: sometime ...
( cy, marwnadau) and songs of praise ( cy, canu mawl), as well as certain mythological stories, that have been preserved.
Stories praising a patron and the construction of flattering genealogies are neither unbiased nor reliable sources of historically accurate information. However, while they may exaggerate and make apocryphal assertions, they do not falsify or change the historical facts that were known to the bards' listeners, as that would bring ridicule and disrepute to both the bards and their patrons. In addition, the existence of stories of defeat and tragedy
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy ...
, as well as stories of victory, lends additional credibility to their value as sources of history. Within that context, the stories contain useful information, much of it incidental, about an era of British history where very little is reliably known.
Historical sources
* The ''Historia Brittonum
''The History of the Britons'' ( la, Historia Brittonum) is a purported history of the indigenous British ( Brittonic) people that was written around 828 and survives in numerous recensions that date from after the 11th century. The ''Historia B ...
'' attributed to Nennius
* The ''Annales Cambriae
The (Latin for ''Annals of Wales'') is the title given to a complex of Latin chronicles compiled or derived from diverse sources at St David's in Dyfed, Wales. The earliest is a 12th-century presumed copy of a mid-10th-century original; later ed ...
''
* The '' Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''
* The ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People
The ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' ( la, Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum), written by Bede in about AD 731, is a history of the Christian Churches in England, and of England generally; its main focus is on the conflict b ...
'' by Bede
* The ''Annals of Tigernach
The ''Annals of Tigernach'' (abbr. AT, ga, Annála Tiarnaigh) are chronicles probably originating in Clonmacnoise, Ireland. The language is a mixture of Latin and Old and Middle Irish.
Many of the pre-historic entries come from the 12th-centur ...
''
These sources are not without deficiencies. Both the authors and their later transcribers sometimes displayed a partisanship that promoted their own interests, portraying their own agendas in a positive light, always on the side of justice and moral rectitude. Facts in opposition to those agendas are sometimes omitted, and apocryphal entries are sometimes added.
While Bede was a Northumbrian partisan and spoke with prejudice against the native Britons, his ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' is highly regarded for its effort towards an accurate telling of history, and for its use of reliable sources. When passing along "traditional" information that lacks a historical foundation, Bede takes care to note it as such.
The ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae
''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'' ( la, On the Ruin and Conquest of Britain, sometimes just ''On the Ruin of Britain'') is a work written in Latin by the 6th-century AD British cleric St Gildas. It is a sermon in three parts condemning ...
'' by Gildas
Gildas ( Breton: ''Gweltaz''; c. 450/500 – c. 570) — also known as Gildas the Wise or ''Gildas Sapiens'' — was a 6th-century British monk best known for his scathing religious polemic ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', which recount ...
(c. 516–570) is occasionally relevant in that it mentions early people and places also mentioned in the literary and historical sources. The work was intended to preach Christianity to Gildas' contemporaries and was not meant to be a history. It is one of the few contemporary accounts of his era to have survived.Place names
Brittonic place names in Scotland south of the Forth and Clyde, and in Cumberland and neighbouring counties, indicate areas of Hen Ogledd inhabited by Britons in the early Middle Ages. Isolated locations of later British presence are also indicated by place names ofOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th c ...
and Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
origin. In Yorkshire, the names of Walden
''Walden'' (; first published in 1854 as ''Walden; or, Life in the Woods'') is a book by American transcendentalist writer Henry David Thoreau. The text is a reflection upon the author's simple living in natural surroundings. The work is part ...
, Walton Walton may refer to:
People
* Walton (given name)
* Walton (surname)
* Susana, Lady Walton (1926–2010), Argentine writer
Places
Canada
* Walton, Nova Scotia, a community
** Walton River (Nova Scotia)
*Walton, Ontario, a hamlet
United Kingdo ...
and Walburn, from Old English ''walas'' "Britons or Welshmen", indicate Britons encountered by the Anglo-Saxons, and the name of Birkby, from Old Norse ''Breta'' "Britons", indicates a place where the Vikings met Britons.
Dubious and fraudulent sources
The ''Historia Regum Britanniae
''Historia regum Britanniae'' (''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called ''De gestis Britonum'' (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a pseudohistorical account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. I ...
'' of Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth ( la, Galfridus Monemutensis, Galfridus Arturus, cy, Gruffudd ap Arthur, Sieffre o Fynwy; 1095 – 1155) was a British cleric from Monmouth, Wales and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography ...
is disparaged as pseudohistory
Pseudohistory is a form of pseudoscholarship that attempts to distort or misrepresent the historical record, often by employing methods resembling those used in scholarly historical research. The related term cryptohistory is applied to pseudohi ...
, though it looms large as a source for the largely fictional chivalric romance
As a literary genre, the chivalric romance is a type of prose and verse narrative that was popular in the noble courts of High Medieval and Early Modern Europe. They were fantastic stories about marvel-filled adventures, often of a chivalri ...
stories known collectively as the Matter of Britain
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It was one of the three great Wester ...
. The lack of historical value attributed to the ''Historia'' lies only partly in the fact that it contains so many fictions and falsifications of history; the fact that historical accuracy clearly was not a consideration in its creation makes any references to actual people and places no more than a literary convenience.
The ''Iolo Manuscripts'' are a collection of manuscripts presented in the early 19th century by Edward Williams, who is better known as Iolo Morganwg
Edward Williams, better known by his bardic name Iolo Morganwg (; 10 March 1747 – 18 December 1826), was a Welsh antiquarian, poet and collector.Jones, Mary (2004)"Edward Williams/Iolo Morganwg/Iolo Morgannwg" From ''Jones' Celtic Encyclop ...
. Containing various tales, anecdotal material and elaborate genealogies that connect virtually everyone of note with everyone else of note (and with many connections to Arthur
Arthur is a common male given name of Brythonic origin. Its popularity derives from it being the name of the legendary hero King Arthur. The etymology is disputed. It may derive from the Celtic ''Artos'' meaning “Bear”. Another theory, more wi ...
and Iolo's native region of Morgannwg
Morgannwg was a medieval Welsh kingdom formed via the merger of the kingdoms of the Kingdom of Glywysing and the Kingdom of Gwent.
Formation of Morgannwg
First under King Morgan the Generous (fl. ) until the end of the reign of his descendant ...
), they were at first accepted as genuine, but have since been shown to be an assortment of forged or doctored manuscripts, transcriptions, and fantasies, mainly invented by Iolo himself. A list of works tainted by their reliance on the material presented by Iolo (sometimes without attribution) would be quite long.
Kingdoms and regions
Major kingdoms
Places in the Old North that are mentioned as kingdoms in the literary and historical sources include: *Alt Clut
Dumbarton Castle ( gd, Dùn Breatainn, ; ) has the longest recorded history of any stronghold in Scotland. It sits on a volcanic plug of basalt known as Dumbarton Rock which is high and overlooks the Scottish town of Dumbarton.
History
Dumba ...
or Ystrad Clud – a kingdom centred at what is now Dumbarton
Dumbarton (; also sco, Dumbairton; ) is a town in West Dunbartonshire, Scotland, on the north bank of the River Clyde where the River Leven flows into the Clyde estuary. In 2006, it had an estimated population of 19,990.
Dumbarton was the ca ...
in Scotland. Later known as the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to as ...
, it was one of the best attested of the northern British kingdoms. It was also the last surviving, as it operated as an independent realm into the 11th century before it was finally absorbed by the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland (; , ) was a sovereign state in northwest Europe traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a l ...
.
* Elmet
Elmet ( cy, Elfed), sometimes Elmed or Elmete, was an independent Brittonic kingdom between about the 5th century and early 7th century, in what later became the smaller area of the West Riding of Yorkshire then West Yorkshire, South Yorkshir ...
– centred in western Yorkshire
Yorkshire ( ; abbreviated Yorks), formally known as the County of York, is a historic county in northern England and by far the largest in the United Kingdom. Because of its large area in comparison with other English counties, functions have ...
in northern England. It was located south of the other northern British kingdoms, and well east of present-day Wales, but managed to survive into the early 7th century.
* Gododdin
The Gododdin () were a Brittonic people of north-eastern Britannia, the area known as the Hen Ogledd or Old North (modern south-east Scotland and north-east England), in the sub-Roman period. Descendants of the Votadini, they are best known ...
– a kingdom in what is now southeastern Scotland and northeastern England, the area previously noted as the territory of the Votadini. They are the subjects of the poem ''Y Gododdin
''Y Gododdin'' () is a medieval Welsh poem consisting of a series of elegies to the men of the Brittonic kingdom of Gododdin and its allies who, according to the conventional interpretation, died fighting the Angles of Deira and Bernicia a ...
'', which memorialises a disastrous raid by an army raised by the Gododdin on the Angles of Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
.Koch 2006, pp. 823–826.
* Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic and b ...
– a major kingdom that evidently included parts of present-day Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in North West England, bordering Scotland. The county and Cumbria County Council, its local government, came into existence in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972. C ...
, though its full extent is unknown. It may have covered a vast area at one point, as it is very closely associated with its king Urien
Urien (; ), often referred to as Urien Rheged or Uriens, was a late 6th-century king of Rheged, an early British kingdom of the Hen Ogledd (today's northern England and southern Scotland) of the House of Rheged. His power and his victories, ...
, whose name is tied to places all over northwestern Britain.
Minor kingdoms and other regions
Several regions are mentioned in the sources, assumed to be notable regions within one of the kingdoms if not separate kingdoms themselves: * Aeron – a minor kingdom mentioned in sources such as ''Y Gododdin'', its location is uncertain, but several scholars have suggested that it was in the Ayrshire region of southwest Scotland. It is frequently associated withUrien Rheged
Urien (; ), often referred to as Urien Rheged or Uriens, was a late 6th-century king of Rheged, an early British kingdom of the Hen Ogledd (today's northern England and southern Scotland) of the House of Rheged. His power and his victories, ...
, and may have been part of his realm.
* Calchfynydd ("Chalkmountain") – almost nothing is known about this area, though it was likely somewhere in the Hen Ogledd, as an evident ruler, Cadrawd Calchfynydd
Calchfynydd (Welsh ''calch'' "lime" + ''mynydd'' "mountain") was an obscure Britonnic kingdom or sub-kingdom of sub-Roman Britain. Its exact location is unknown and virtually nothing certain is known about it.
The name survives in the epithet of ...
, is listed in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' ( en, The Descent of the Men of the North) is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and norther ...
''. William Forbes Skene
William Forbes Skene WS FRSE FSA(Scot) DCL LLD (7 June 1809 – 29 August 1892), was a Scottish lawyer, historian and antiquary.
He co-founded the Scottish legal firm Skene Edwards which was prominent throughout the 20th century but disappeare ...
suggested an identification with Kelso (formerly Calchow) in the Scottish Borders.
* Eidyn
Eidyn was the region around modern Edinburgh in Britain's sub-Roman and early medieval periods, approximately the 5th–7th centuries. It centred on the stronghold of Din Eidyn, thought to have been at Castle Rock, now the site of Edinburgh Cas ...
– this was the area around the modern city of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
, then known as Din Eidyn (Fort of Eidyn). It was closely associated with the Gododdin kingdom.Koch 2006, pp. 623–625. Kenneth H. Jackson
Prof Kenneth Hurlstone Jackson CBE FRSE FSA DLitt (1 November 1909 – 20 February 1991) was an English linguistics, linguist and a translator who specialised in the Celtic languages. He demonstrated how the text of the Ulster Cycle of tales, wr ...
argued strongly that ''Eidyn'' referred exclusively to Edinburgh, but other scholars have taken it as a designation for the wider area.Williams 1972, p. 64. The name may survive today in toponyms such as Edinburgh, Dunedin
Dunedin ( ; mi, Ōtepoti) is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand (after Christchurch), and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from , the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. Th ...
, and Carriden (from ''Caer Eidyn''), located fifteen miles to the west.Dumville, p. 297. Din Eidyn was besieged by the Angles in 638 and was under their control for most of the next three centuries.
* Manaw Gododdin
Manaw Gododdin was the narrow coastal region on the south side of the Firth of Forth, part of the Brythonic-speaking Kingdom of Gododdin in the post-Roman Era. It is notable as the homeland of Cunedda prior to his conquest of North Wales, and ...
– the coastal area south of the Firth of Forth, and part of the territory of the Gododdin. The name survives in Slamannan Moor and the village of Slamannan
Slamannan ( gd, Sliabh Mhanainn) is a village in the south of the Falkirk council area in Central Scotland. It is south-west of Falkirk, east of Cumbernauld and north-east of Airdrie.
Slamannan is located at the cross of the B803 and B8022 ...
, in Stirlingshire
Stirlingshire or the County of Stirling, gd, Siorrachd Sruighlea) is a historic county and registration countyRegisters of Scotland. Publications, leaflets, Land Register Counties. of Scotland. Its county town is Stirling.
It borders Perth ...
. This is derived from ''Sliabh Manann'', the 'Moor of Manann'. It also appears in the name of Dalmeny
Dalmeny ( gd, Dùn Mheinidh, IPA: �t̪uːnˈvenɪʝ is a village and civil parish in Scotland. It is located on the south side of the Firth of Forth, southeast of South Queensferry and west of Edinburgh city centre. It lies within the tradit ...
, some 5 miles northwest of Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of t ...
, and formerly known as Dumanyn, assumed to be derived from ''Dun Manann''. The name also survives north of the Forth in Pictish Manaw as the name of the burgh of Clackmannan
Clackmannan ( ; gd, Clach Mhanainn, perhaps meaning "Stone of Manau"), is a small town and civil parish set in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. Situated within the Forth Valley, Clackmannan is south-east of Alloa and south of Tillicoultry. ...
and the eponymous county of Clackmannanshire
Clackmannanshire (; sco, Clackmannanshire; gd, Siorrachd Chlach Mhannainn) is a historic county, council area, registration county and Lieutenancy area in Scotland, bordering the council areas of Stirling, Fife, and Perth & Kinross and the ...
,, ''Celtic Britain'', The Picts and the Scots. derived from ''Clach Manann'', the 'stone of Manann', referring to a monument stone located there.
* Novant
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
– a kingdom mentioned in ''Y Gododdin'', presumably related to the Iron Age Novantae
The Novantae were a people of the late 2nd century who lived in what is now Galloway and Carrick, in southwesternmost Scotland. They are mentioned briefly in Ptolemy's ''Geography'' (written c. 150), and there is no other historical record of th ...
tribe of southwestern Scotland.
* ''Regio Dunutinga'' – a minor kingdom or region in North Yorkshire
North Yorkshire is the largest ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county (lieutenancy area) in England, covering an area of . Around 40% of the county is covered by National parks of the United Kingdom, national parks, including most of ...
mentioned in the ''Life of Wilfrid
The ''Vita Sancti Wilfrithi'' or ''Life of St Wilfrid'' (spelled "Wilfrid" in the modern era) is an early 8th-century hagiographic text recounting the life of the Northumbrian bishop, Wilfrid. Although a hagiography, it has few miracles, while ...
''. It was evidently named for a ruler named Dunaut, perhaps the Dunaut ap Pabo known from the genealogies. Its name may survive in the modern town of Dent
Dent may refer to:
People
* Dent (surname)
* Dent May (active 2007), American musician
* Dent Mowrey (1888–1960), American composer, musician and music teacher
* Dent Oliver (1918–1973), international speedway rider
Places France
* Dent d' ...
, Cumbria.
Kingdoms that were not part of the Old North but are part of its history include:
* Dál Riata
Dál Riata or Dál Riada (also Dalriada) () was a Gaelic kingdom that encompassed the western seaboard of Scotland and north-eastern Ireland, on each side of the North Channel. At its height in the 6th and 7th centuries, it covered what is n ...
– Though this was a Gaelic kingdom, the family of Áedán mac Gabráin
Áedán mac Gabráin (pronounced in Old Irish; ga, Aodhán mac Gabhráin, lang), also written as Aedan, was a king of Dál Riata from 574 until c. 609 AD. The kingdom of Dál Riata was situated in modern Argyll and Bute, Scotland, and par ...
of Dál Riata appears in the ''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd
''Bonedd Gwŷr y Gogledd'' ( en, The Descent of the Men of the North) is a brief Middle Welsh tract which claims to give the pedigrees of twenty 6th century rulers of the Hen Ogledd, the Brittonic-speaking parts of southern Scotland and norther ...
''
* Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
and its predecessor states, Bernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
and Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/Cumbric: ''Deywr'' or ''Deifr''; ang, Derenrice or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic *''daru' ...
* Pictish kingdom
Possible kingdoms
The following names appear in historical and literary sources, but it is unknown whether or not they refer to British kingdoms and regions of the ''Hen Ogledd''. * Bryneich – this is the British name for the Anglo-Saxon kingdom ofBernicia
Bernicia ( ang, Bernice, Bryneich, Beornice; la, Bernicia) was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England.
The Anglian territory of Bernicia was ap ...
. There was probably a British kingdom in this area before the Anglian kingdom, it this is uncertain.
* Deifr
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/Cumbric: ''Deywr'' or ''Deifr''; ang, Derenrice or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic *''daru' ...
or Dewr – this was the British name for Anglo-Saxon Deira
Deira ( ; Old Welsh/Cumbric: ''Deywr'' or ''Deifr''; ang, Derenrice or ) was an area of Post-Roman Britain, and a later Anglian kingdom.
Etymology
The name of the kingdom is of Brythonic origin, and is derived from the Proto-Celtic *''daru' ...
, a region between the River Tees and the Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal rivers Ouse and Trent. From there to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between t ...
. The name is of British origin, as with Bryneich, it is unknown if it represented an earlier British kingdom.Koch 2006, pp. 584–585.
See also
*Wales in the Early Middle Ages
Wales in the early Middle Ages covers the time between the Roman departure from Wales c. 383 until the end of the 10th century. In that time there was a gradual consolidation of power into increasingly hierarchical kingdoms. The end of the early ...
* Scotland in the Early Middle Ages
* History of Anglo-Saxon England
* England in the Middle Ages
* Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
* Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum
, conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia
, common_name=Mercia
, status=Kingdom
, status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879) Client state of Wessex ()
, life_span=527–918
, era= Heptarchy
, event_start=
, date_start=
, ...
* Kingdom of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Based in northwest Wales, th ...
* Historical basis for King Arthur
The historicity of King Arthur has been debated both by academics and popular writers. While there have been many suggestions that Arthur was a real historical person, current consensus among academic historians holds him to be a mythological or ...
* Cumbric language
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the souther ...
* King Cole
Coel (Old Welsh: ''Coil''), also called ''Coel Hen'' (Coel the Old) and King Cole, is a figure prominent in Welsh literature and legend since the Middle Ages. Early Welsh tradition knew of a Coel Hen, a 4th-century leader in Roman or Sub-Roman ...
Notes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Alcock, Leslie. ''Kings and Warriors, Craftsmen and Priests in Northern Britain, AD 550–850''. Edinburgh, 2003. * Alcock, Leslie. "Gwyr y Gogledd. An archaeological appraisal." ''Archaeologia Cambrensis
''Archaeologia Cambrensis'' is a Welsh archaeological and historical scholarly journal published annually by the Cambrian Archaeological Association. It contains historical essays, excavation reports, and book reviews, as well as society not ...
'' 132 (1984 for 1983). pp. 1–18.
* Cessford, Craig. "Northern England and the Gododdin poem." ''Northern History'' 33 (1997). pp. 218–22.
* Clarkson, Tim. ''The Men of the North: the Britons of Southern Scotland.'' Edinburgh: John Donald, Birlinn Ltd, 2010.
* Clarkson, Tim. ''Strathclyde and the Anglo-Saxons in the Viking Age.'' Edinburgh: John Donald, Birlinn Ltd, 2014.
* Dark, Kenneth R. ''Civitas to Kingdom. British political continuity, 300–800.'' London: Leicester UP, 1994.
* Dumville, David N. "Early Welsh Poetry: Problems of Historicity." In ''Early Welsh Poetry: Studies in the Book of Aneirin'', ed. Brynley F. Roberts. Aberystwyth, 1988. 1–16.
* Dumville, David N. "The origins of Northumbria: Some aspects of the British background." In ''The Origins of Anglo-Saxon Kingdoms'', ed. S. Bassett. Leicester: Leicester University Press, 1989. pp. 213–22.
* Higham, N.J. "Britons in Northern England: Through a Thick Glass Darkly." ''Northern History'' 38 (2001). pp. 5–25.
* Macquarrie, A. "The Kings of Strathclyde, c.400–1018." In ''Medieval Scotland: Government, Lordship and Community'', ed. A. Grant and K.J. Stringer. Edinburgh: Edinburgh UP, 1993. pp. 1–19.
* Miller, Molly. "Historicity and the pedigrees of north countrymen." '' Bulletin of the Board of Celtic Studies'' 26 (1975). pp. 255–80.
* Woolf, Alex. "Cædualla Rex Brettonum and the Passing of the Old North." ''Northern History'' 41.1 (2004): 1–20.
External links
* Matthews, Keith J"What's in a name? Britons, Angles, ethnicity and material culture from the fourth to seventh centuries."
''Heroic Age'' 4 (Winter 2001). {{Barbarian kingdoms Celtic Britons Medieval England 1st millennium in Scotland Sub-Roman Britain Anglo-Saxon England Medieval Wales Northern England History of Cumbria History of Dumfries and Galloway History of Northumberland History of the Scottish Borders History of Yorkshire Barbarian kingdoms Regions of England Regions of Scotland Historical regions in the United Kingdom Scottish Lowlands