Wnt signaling pathway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of
signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
pathways which begin with proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsparacrine Paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over ...
) or same-cell communication (autocrine Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with p ...
). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans.
Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's elect ...
to a Frizzled family receptor
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part by the SPATS1 gene. The noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway regulates the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is co ...
that is responsible for the shape of the cell. The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway regulates calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
inside the cell.
Wnt signaling was first identified for its role in carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
, then for its function in embryonic development. The embryonic processes it controls include body axis patterning, cell fate specification, cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation r ...
and cell migration
Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. Tissue formation during embryonic development, wound healing and immune responses all require the orchestrated movement of cells in particular dir ...
. These processes are necessary for proper formation of important tissues including bone, heart and muscle. Its role in embryonic development was discovered when genetic mutations in Wnt pathway proteins produced abnormal fruit fly embryos
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male spe ...
. Later research found that the genes responsible for these abnormalities also influenced breast cancer development in mice. Wnt signaling also controls tissue regeneration
In biology, regeneration is the process of renewal, restoration, and tissue growth that makes genomes, cells, organisms, and ecosystems resilient to natural fluctuations or events that cause disturbance or damage. Every species is capable of ...
in adult bone marrow, skin and intestine.
This pathway's clinical importance was demonstrated by mutations that lead to various diseases, including breast
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and sec ...
and prostate cancer, glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality ...
, type II diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinatio ...
and others. In recent years, researchers reported first successful use of Wnt pathway inhibitors in mouse models of disease.
History and etymology
The discovery of Wnt signaling was influenced by research ononcogenic
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
(cancer-causing) retroviruses
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
. In 1982, Roel Nusse and Harold Varmus infected mice with mouse mammary tumor virus in order to mutate mouse genes to see which mutated genes could cause breast tumors. They identified a new mouse proto-oncogene that they named int1 (integration 1).
Int1 is highly conserved across multiple species, including humans and ''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
''. Its presence in '' D. melanogaster'' led researchers to discover in 1987 that the int1 gene in ''Drosophila'' was actually the already known and characterized ''Drosophila'' gene known as Wingless (Wg). Since previous research by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard and Eric Wieschaus (which won them the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
in Physiology or Medicine in 1995) had already established the function of Wg as a segment polarity gene involved in the formation of the body axis during embryonic development, researchers determined that the mammalian int1 discovered in mice is also involved in embryonic development.
Continued research led to the discovery of further int1-related genes; however, because those genes were not identified in the same manner as int1, the int gene nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally ag ...
was inadequate. Thus, the int/Wingless family became the Wnt family and int1 became Wnt1. The name Wnt is a portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of words
 Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted
Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted

 The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve β-catenin. Its role is to help regulate calcium release from the
The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve β-catenin. Its role is to help regulate calcium release from the
 Cell migration during embryonic development allows for the establishment of body axes, tissue formation, limb induction and several other processes. Wnt signaling helps mediate this process, particularly during convergent extension. Signaling from both the Wnt PCP pathway and canonical Wnt pathway is required for proper convergent extension during gastrulation. Convergent extension is further regulated by the Wnt/calcium pathway, which blocks convergent extension when activated. Wnt signaling also induces cell migration in later stages of development through the control of the migration behavior of neuroblasts, neural crest cells, myocytes, and tracheal cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in another key migration process known as the Epithelial–mesenchymal transition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This process allows epithelial cells to transform into mesenchymal cells so that they are no longer held in place at the laminin. It involves cadherin down-regulation so that cells can detach from laminin and migrate. Wnt signaling is an inducer of EMT, particularly in mammary development.
Cell migration during embryonic development allows for the establishment of body axes, tissue formation, limb induction and several other processes. Wnt signaling helps mediate this process, particularly during convergent extension. Signaling from both the Wnt PCP pathway and canonical Wnt pathway is required for proper convergent extension during gastrulation. Convergent extension is further regulated by the Wnt/calcium pathway, which blocks convergent extension when activated. Wnt signaling also induces cell migration in later stages of development through the control of the migration behavior of neuroblasts, neural crest cells, myocytes, and tracheal cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in another key migration process known as the Epithelial–mesenchymal transition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This process allows epithelial cells to transform into mesenchymal cells so that they are no longer held in place at the laminin. It involves cadherin down-regulation so that cells can detach from laminin and migrate. Wnt signaling is an inducer of EMT, particularly in mammary development.
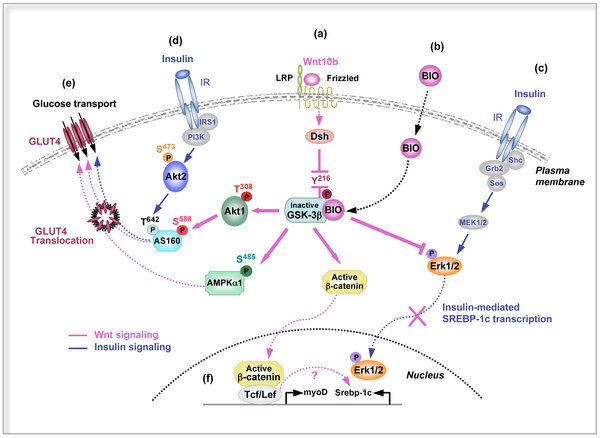 Insulin is a peptide hormone involved in glucose homeostasis within certain organisms. Specifically, it leads to upregulation of glucose transporters in the cell membrane in order to increase glucose uptake from the bloodstream. This process is partially mediated by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which can increase a cell's insulin sensitivity. In particular, Wnt10b is a Wnt protein that increases this sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells.
Insulin is a peptide hormone involved in glucose homeostasis within certain organisms. Specifically, it leads to upregulation of glucose transporters in the cell membrane in order to increase glucose uptake from the bloodstream. This process is partially mediated by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which can increase a cell's insulin sensitivity. In particular, Wnt10b is a Wnt protein that increases this sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells.
Proteins
 Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted
Wnt comprises a diverse family of secreted lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
-modified signaling glycoproteins that are 350–400 amino acids in length. The lipid modification of all Wnts is palmitoleoylation
Palmitoleoylation is type of protein lipidation where the monounsaturated fatty acid palmitoleic acid is covalently attached to serine or threonine residues of proteins. Palmitoleoylation appears to play a significant role in trafficking and ta ...
of a single totally conserved serine residue. Palmitoleoylation is necessary because it is required for Wnt to bind to its carrier protein Wntless (WLS) so it can be transported to the plasma membrane for secretion and it allows the Wnt protein to bind its receptor Frizzled Wnt proteins also undergo glycosylation
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate (or ' glycan'), i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor) in order to form a glycoconjugate. In biology (but not al ...
, which attaches a carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may o ...
in order to ensure proper secretion. In Wnt signaling, these proteins act as ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electr ...
to activate the different Wnt pathways via paracrine and autocrine routes.
These proteins are highly conserved across species. They can be found in mice, humans, ''Xenopus'', zebrafish, ''Drosophila'' and many others.
Mechanism

Foundation
Wnt signaling begins when a Wnt protein binds to the N-terminal extra-cellular cysteine-rich domain of a Frizzled (Fz) family receptor. These receptors span the plasma membrane seven times and constitute a distinct family of G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). However, to facilitate Wnt signaling, co-receptors may be required alongside the interaction between the Wnt protein and Fz receptor. Examples include lipoprotein receptor-related protein ( LRP)-5/6, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), andROR2
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2, also known as neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ROR2'' gene located on position 9 of the long arm of chromosome 9. This protein ...
. Upon activation of the receptor, a signal is sent to the phosphoprotein Dishevelled (Dsh), which is located in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
. This signal is transmitted via a direct interaction between Fz and Dsh. Dsh proteins are present in all organisms and they all share the following highly conserved protein domains: an amino-terminal DIX domain, a central PDZ domain, and a carboxy-terminal DEP domain
In molecular biology, the DEP domain (Dishevelled, Egl-10 and Pleckstrin domain) is a globular protein domain of about 80 amino acids that is found in over 50 proteins involved in G-protein signalling pathways. It was named after the three prote ...
. These different domains are important because after Dsh, the Wnt signal can branch off into multiple pathways and each pathway interacts with a different combination of the three domains.
Canonical and noncanonical pathways
The three best characterized Wnt signaling pathways are the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. As their names suggest, these pathways belong to one of two categories: canonical or noncanonical. The difference between the categories is that a canonical pathway involves the protein beta-catenin (β-catenin) while a noncanonical pathway operates independently of it.
Canonical pathway
The canonical Wnt pathway (or Wnt/β-catenin pathway) is the Wnt pathway that causes an accumulation ofβ-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
in the cytoplasm and its eventual translocation into the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
* Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucl ...
to act as a transcriptional coactivator of transcription factors that belong to the TCF/LEF family. Without Wnt, β-catenin would not accumulate in the cytoplasm since a destruction complex would normally degrade it. This destruction complex includes the following proteins: Axin, adenomatosis polyposis coli (APC), protein phosphatase 2A Protein phosphatase 2A may refer to:
* Protein phosphatase 2
Protein phosphatase 2 (PP2), also known as PP2A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPP2CA'' gene. The PP2A heterotrimeric protein phosphatase is ubiquitously expressed ...
(PP2A), glycogen synthase kinase 3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules onto serine and threonine amino acid residues. First discovered in 1980 as a regulatory kinase for its namesake, glycogen s ...
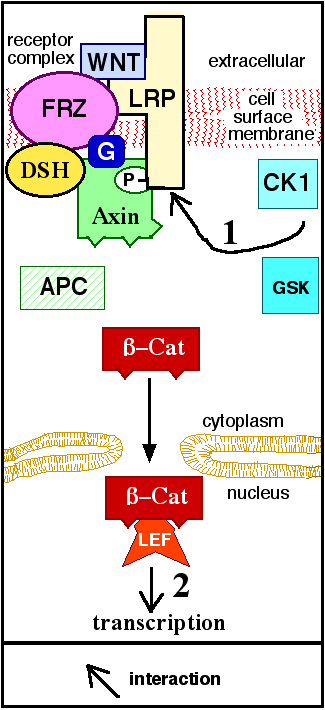
(GSK3) and casein kinase 1α (CK1α). It degrades β-catenin by targeting it for ubiquitination, which subsequently sends it to the proteasome to be digested. However, as soon as Wnt binds Fz and LRP5/ 6, the destruction complex function becomes disrupted. This is due to Wnt causing the translocation of the negative Wnt regulator, Axin, and the destruction complex to the plasma membrane. Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
by other proteins in the destruction complex subsequently binds Axin to the cytoplasmic tail of LRP5/6. Axin becomes de-phosphorylated and its stability and levels decrease. Dsh then becomes activated via phosphorylation and its DIX and PDZ domains inhibit the GSK3 activity of the destruction complex. This allows β-catenin to accumulate and localize to the nucleus and subsequently induce a cellular response via gene transduction alongside the TCF/LEF (T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancing factor) transcription factors. β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
recruits other transcriptional coactivators, such as BCL9
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL9'' gene.
Function
BCL9, together with its paralogue gene BCL9L (BCL9 like or BCL9.2), have been extensively studied for their role as transcriptional beta-cate ...
, Pygopus and Parafibromin/Hyrax. The complexity of the transcriptional complex assembled by β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
is beginning to emerge thanks to new high-throughput proteomics studies. However, a unified theory of how β‐catenin drives target gene expression is still missing, and tissue-specific players might assist β‐catenin to define its target genes. The extensivity of the β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
interacting proteins complicates our understanding: β-catenin may be directly phosphorylated at Ser552 by Akt, which causes its disassociation from cell-cell contacts and accumulation in cytosol, thereafter 14-3-3ζ interacts with β-catenin (pSer552) and enhances its nuclear translocation. BCL9
B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BCL9'' gene.
Function
BCL9, together with its paralogue gene BCL9L (BCL9 like or BCL9.2), have been extensively studied for their role as transcriptional beta-cate ...
and Pygopus have been reported, in fact, to possess several β-catenin
Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CTNNB1'' gene.
Beta-catenin is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell–cell adhesion and gene transcrip ...
-independent functions (therefore, likely, Wnt signaling-independent).

Noncanonical pathways
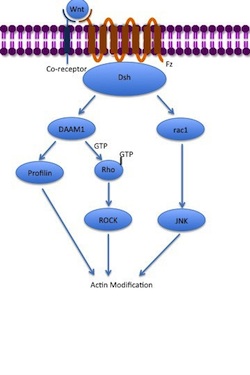
The noncanonical planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway does not involve β-catenin. It does not use LRP-5/6 as its co-receptor and is thought to use NRH1, Ryk, PTK7 orROR2
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2, also known as neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ROR2'' gene located on position 9 of the long arm of chromosome 9. This protein ...
. The PCP pathway is activated via the binding of Wnt to Fz and its co-receptor. The receptor then recruits Dsh, which uses its PDZ and DIX domains to form a complex with Dishevelled-associated activator of morphogenesis 1 ( DAAM1). Daam1 then activates the small G-protein Rho
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the sa ...
through a guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is ...
exchange factor. Rho activates Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), which is one of the major regulators of the cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is co ...
. Dsh also forms a complex with rac1 and mediates profilin
Profilin is an actin-binding protein involved in the dynamic turnover and reconstruction of the actin cytoskeleton. It is found in all eukaryotic organisms. Profilin is important for spatially and temporally controlled growth of actin microfilame ...
binding to actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
. Rac1 activates JNK and can also lead to actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many f ...
. Profilin
Profilin is an actin-binding protein involved in the dynamic turnover and reconstruction of the actin cytoskeleton. It is found in all eukaryotic organisms. Profilin is important for spatially and temporally controlled growth of actin microfilame ...
binding to actin can result in restructuring of the cytoskeleton and gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. ...
.
 The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve β-catenin. Its role is to help regulate calcium release from the
The noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway also does not involve β-catenin. Its role is to help regulate calcium release from the endoplasmic reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum ...
(ER) in order to control intracellular calcium levels. Like other Wnt pathways, upon ligand binding, the activated Fz receptor directly interacts with Dsh and activates specific Dsh-protein domains. The domains involved in Wnt/calcium signaling are the PDZ and DEP domains. However, unlike other Wnt pathways, the Fz receptor directly interfaces with a trimeric G-protein. This co-stimulation of Dsh and the G-protein can lead to the activation of either PLC or cGMP-specific PDE. If PLC is activated, the plasma membrane component PIP2 is cleaved into DAG and IP3. When IP3 binds its receptor on the ER, calcium is released. Increased concentrations of calcium and DAG can activate Cdc42 through PKC. Cdc42 is an important regulator of ventral patterning. Increased calcium also activates calcineurin and CaMKII. CaMKII induces activation of the transcription factor NFAT, which regulates cell adhesion, migration and tissue separation. Calcineurin activates TAK1 and NLK kinase, which can interfere with TCF/β-Catenin signaling in the canonical Wnt pathway. However, if PDE is activated, calcium release from the ER is inhibited. PDE mediates this through the inhibition of PKG, which subsequently causes the inhibition of calcium release.
Integrated Wnt Pathway
The binary distinction of canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling pathways has come under scrutiny and an integrated, convergent Wnt pathway has been proposed. Some evidence for this was found for one Wnt ligand (Wnt5A). Evidence for a convergent Wnt signaling pathway that shows integrated activation of Wnt/Ca2+ and Wnt/β-catenin signaling, for multiple Wnt ligands, was described in mammalian cell lines.Other pathways
Wnt signaling also regulates a number of other signaling pathways that have not been as extensively elucidated. One such pathway includes the interaction between Wnt and GSK3. During cell growth, Wnt can inhibit GSK3 in order to activate mTOR in the absence of β-catenin. However, Wnt can also serve as a negative regulator of mTOR via activation of the tumor suppressor TSC2, which is upregulated via Dsh and GSK3 interaction. During myogenesis, Wnt uses PA and CREB to activate MyoD and Myf5 genes. Wnt also acts in conjunction with Ryk and Src to allow for regulation of neuron repulsion duringaxonal guidance
Axon guidance (also called axon pathfinding) is a subfield of neural development concerning the process by which neurons send out axons to reach their correct targets. Axons often follow very precise paths in the nervous system, and how they mana ...
. Wnt regulates gastrulation
Gastrulation is the stage in the early embryonic development of most animals, during which the blastula (a single-layered hollow sphere of cells), or in mammals the blastocyst is reorganized into a multilayered structure known as the gastrula. ...
when CK1 serves as an inhibitor of Rap1-ATPase in order to modulate the cytoskeleton during gastrulation. Further regulation of gastrulation is achieved when Wnt uses ROR2 along with the CDC42 and JNK pathway to regulate the expression of PAPC. Dsh can also interact with aPKC, Pa3, Par6 and LGl in order to control cell polarity and microtubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
cytoskeleton development. While these pathways overlap with components associated with PCP and Wnt/Calcium signaling, they are considered distinct pathways because they produce different responses.
Regulation
In order to ensure proper functioning, Wnt signaling is constantly regulated at several points along its signaling pathways. For example, Wnt proteins arepalmitoylated
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (''S''-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (''O''-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically membrane prot ...
. The protein ''porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethiz ...
'' mediates this process, which means that it helps regulate when the Wnt ligand is secreted by determining when it is fully formed. Secretion is further controlled with proteins such as GPR177 (wntless) and evenness interrupted Evenness may refer to:
*Species evenness
*evenness of numbers, for which see parity (mathematics)
** evenness of zero, a special case of the above
See also
*Even (disambiguation)
Even may refer to:
General
* Even (given name), a Norwegian male p ...
and complexes such as the retromer complex.
Upon secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classic ...
, the ligand can be prevented from reaching its receptor through the binding of proteins such as the stabilizers Dally and glypican 3 (GPC3), which inhibit diffusion. In cancer cells, both the heparan sulfate chains and the core protein of GPC3 are involved in regulating Wnt binding and activation for cell proliferation. Wnt recognizes a heparan sulfate structure on GPC3, which contains IdoA2S and GlcNS6S, and the 3-O-sulfation in GlcNS6S3S enhances the binding of Wnt to the heparan sulfate glypican. A cysteine-rich domain at the N-lobe of GPC3 has been identified to form a Wnt-binding hydrophobic groove including phenylalanine-41 that interacts with Wnt. Blocking the Wnt binding domain using a nanobody called HN3 can inhibit Wnt activation.
At the Fz receptor, the binding of proteins other than Wnt can antagonize signaling. Specific antagonists include Dickkopf
Dickkopf (DKK) is a family of proteins consisting of five members as of 2020. The most well-studied is Dickkopf-related protein 1 (DKK1). DKK proteins inhibit the Wnt signaling pathway coreceptors LRP5 and LRP6. They bind with high affinity as ...
(Dkk), Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF-1), secreted Frizzled-related proteins (SFRP), Cerberus, Frzb, Wise, SOST Sost or SOST may refer to:
Places
* Sost, Afghanistan, a village in Badakhshan Province
*Sost, Pakistan
Sost or Sust ( ur, ) is a village in Gojal, Upper Hunza, Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan. It is the last town inside Pakistan on the Karak ...
, and Naked cuticle. These constitute inhibitors of Wnt signaling. However, other molecules also act as activators. Norrin
Norrin, also known as Norrie disease protein or X-linked exudative vitreoretinopathy 2 protein (EVR2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NDP'' gene. Mutations in the NDP gene are associated with the Norrie disease.
Function
Signa ...
and R-Spondin2 activate Wnt signaling in the absence of Wnt ligand.
Interactions between Wnt signaling pathways also regulate Wnt signaling. As previously mentioned, the Wnt/calcium pathway can inhibit TCF/β-catenin, preventing canonical Wnt pathway signaling. Prostaglandin E2 is an essential activator of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Interaction of PGE2 with its receptors E2/E4 stabilizes β-catenin through cAMP/PKA mediated phosphorylation. The synthesis of PGE2 is necessary for Wnt signaling mediated processes such as tissue regeneration and control of stem cell population in zebrafish and mouse. Intriguingly, the unstructured regions of several oversized Intrinsically disordered proteins play crucial roles in regulating Wnt signaling.
Induced cell responses
Embryonic development
Wnt signaling plays a critical role in embryonic development. It operates in bothvertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
and invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordat ...
, including humans, frogs, zebrafish, ''C. elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (r ...
'', ''Drosophila'' and others. It was first found in the segment polarity of Drosophila, where it helps to establish anterior and posterior polarities. It is implicated in other developmental processes. As its function in ''Drosophila'' suggests, it plays a key role in body axis formation, particularly the formation of the anteroposterior and dorsoventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
axes. It is involved in the induction of cell differentiation
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell alters from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular ...
to prompt formation of important organs such as lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either si ...
and ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
. Wnt further ensures the development of these tissues through proper regulation of cell proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation r ...
and migration. Wnt signaling functions can be divided into axis patterning, cell fate specification, cell proliferation and cell migration.
Axis patterning
In early embryo development, the formation of the primary body axes is a crucial step in establishing the organism's overall body plan. The axes include the anteroposterior axis, dorsoventral axis, and right-left axis. Wnt signaling is implicated in the formation of the anteroposterior and dorsoventral (DV) axes. Wnt signaling activity in anterior-posterior development can be seen in mammals, fish and frogs. In mammals, the primitive streak and other surrounding tissues produce the morphogenic compounds Wnts, BMPs,FGFs
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by macrophages; they are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in thei ...
, NODAL, Nodal and retinoic acid to establish the posterior region during late gastrula. These proteins form concentration gradients. Areas of highest concentration establish the posterior region while areas of lowest concentration indicate the anterior region. In fish and frogs, β-catenin produced by canonical Wnt signaling causes the formation of organizing centers, which, alongside BMPs, elicit posterior formation. Wnt involvement in DV axis formation can be seen in the activity of the formation of the Spemann organizer, which establishes the dorsal region. Canonical Wnt signaling β-catenin production induces the formation of this organizer via the activation of the genes twin and siamois. Similarly, in avian gastrulation, cells of the Koller's sickle express different mesodermal marker genes that allow for the differential movement of cells during the formation of the primitive streak. Wnt signaling activated by FGFs is responsible for this movement.
Wnt signaling is also involved in the axis formation of specific body parts and organ systems later in development. In vertebrates, sonic hedgehog (Shh) and Wnt morphogenetic signaling gradients establish the dorsoventral axis of the central nervous system during neural tube axial patterning. High Wnt signaling establishes the dorsal region while high Shh signaling indicates the ventral region. Wnt is involved in the DV formation of the central nervous system through its involvement in axon guidance. Wnt proteins guide the axons of the spinal cord in an anterior-posterior direction. Wnt is also involved in the formation of the limb DV axis. Specifically, Wnt7a helps produce the dorsal patterning of the developing limb.
In the embryonic differentiation waves model of development Wnt plays a critical role as part a signalling complex in competent cells ready to differentiate. Wnt reacts to the activity of the cytoskeleton, stabilizing the initial change created by a passing wave of contraction or expansion and simultaneously signals the nucleus through the use of its different signalling pathways as to which wave the individual cell has participated in. Wnt activity thereby amplifies mechanical signalling that occurs during development.
Cell fate specification
Cell fate specification or cell differentiation is a process where undifferentiated cells can become a more specialized cell type. Wnt signaling induces differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into mesoderm and endoderm progenitor cells. These progenitor cells further differentiate into cell types such as endothelial, cardiac and vascular smooth muscle lineages. Wnt signaling induces blood formation from stem cells. Specifically, Wnt3 leads to mesoderm committed cells with hematopoietic potential. Wnt1 antagonizes neural differentiation and is a major factor in self-renewal of neural stem cells. This allows for regeneration of nervous system cells, which is further evidence of a role in promoting neural stem cell proliferation. Wnt signaling is involved in germ cell determination, Gut (anatomy), gut tissue specification, hair follicle development, lung tissue development, trunk neural crest cell differentiation, nephron development, ovary development and Sex-determination system, sex determination. Wnt signaling also antagonizes heart formation, and Wnt inhibition was shown to be a critical inducer of heart tissue during development, and small molecule Wnt inhibitors are routinely used to produce cardiomyocytes from pluripotent stem cells.Cell proliferation
In order to have the mass differentiation of cells needed to form the specified cell tissues of different organisms, proliferation and growth of embryonic stem cells must take place. This process is mediated through canonical Wnt signaling, which increases nuclear and cytoplasmic β-catenin. Increased β-catenin can initiate transcriptional activation of proteins such as cyclin D1 and ''c-myc'', which control the G1 phase, G1 to S phase transition in the cell cycle. Entry into the S phase causes DNA replication and ultimately mitosis, which are responsible for cell proliferation. This proliferation increase is directly paired with cell differentiation because as the stem cells proliferate, they also differentiate. This allows for overall growth and development of specific tissue systems during embryonic development. This is apparent in systems such as the circulatory system where Wnt3a leads to proliferation and expansion of hematopoietic stem cells needed for red blood cell formation. The biochemistry of cancer stem cells is subtly different from that of other tumor cells. These so-called Wnt-addicted cells hijack and depend on constant stimulation of the Wnt pathway to promote their uncontrolled growth, survival and migration. In cancer, Wnt signaling can become independent of regular stimuli, through mutations in downstream oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes that become permanently activated even though the normal receptor has not received a signal. β-catenin binds to transcription factors such as the protein TCF4 and in combination the molecules activate the necessary genes. LF3 strongly inhibits this binding ''in vitro,'' in cell lines and reduced tumor growth in mouse models. It prevented replication and reduced their ability to migrate, all without affecting healthy cells. No cancer stem cells remained after treatment. The discovery was the product of "Drug design, rational drug design", involving AlphaScreens and ELISA technologies.Cell migration
 Cell migration during embryonic development allows for the establishment of body axes, tissue formation, limb induction and several other processes. Wnt signaling helps mediate this process, particularly during convergent extension. Signaling from both the Wnt PCP pathway and canonical Wnt pathway is required for proper convergent extension during gastrulation. Convergent extension is further regulated by the Wnt/calcium pathway, which blocks convergent extension when activated. Wnt signaling also induces cell migration in later stages of development through the control of the migration behavior of neuroblasts, neural crest cells, myocytes, and tracheal cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in another key migration process known as the Epithelial–mesenchymal transition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This process allows epithelial cells to transform into mesenchymal cells so that they are no longer held in place at the laminin. It involves cadherin down-regulation so that cells can detach from laminin and migrate. Wnt signaling is an inducer of EMT, particularly in mammary development.
Cell migration during embryonic development allows for the establishment of body axes, tissue formation, limb induction and several other processes. Wnt signaling helps mediate this process, particularly during convergent extension. Signaling from both the Wnt PCP pathway and canonical Wnt pathway is required for proper convergent extension during gastrulation. Convergent extension is further regulated by the Wnt/calcium pathway, which blocks convergent extension when activated. Wnt signaling also induces cell migration in later stages of development through the control of the migration behavior of neuroblasts, neural crest cells, myocytes, and tracheal cells.
Wnt signaling is involved in another key migration process known as the Epithelial–mesenchymal transition, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This process allows epithelial cells to transform into mesenchymal cells so that they are no longer held in place at the laminin. It involves cadherin down-regulation so that cells can detach from laminin and migrate. Wnt signaling is an inducer of EMT, particularly in mammary development.
Insulin sensitivity
 Insulin is a peptide hormone involved in glucose homeostasis within certain organisms. Specifically, it leads to upregulation of glucose transporters in the cell membrane in order to increase glucose uptake from the bloodstream. This process is partially mediated by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which can increase a cell's insulin sensitivity. In particular, Wnt10b is a Wnt protein that increases this sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells.
Insulin is a peptide hormone involved in glucose homeostasis within certain organisms. Specifically, it leads to upregulation of glucose transporters in the cell membrane in order to increase glucose uptake from the bloodstream. This process is partially mediated by activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which can increase a cell's insulin sensitivity. In particular, Wnt10b is a Wnt protein that increases this sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells.
Clinical implications
Cancer
Since its initial discovery, Wnt signaling has had an association with cancer. When Wnt1 was discovered, it was first identified as a proto-oncogene in a mouse model for breast cancer. The fact that Wnt1 is a Homology (biology), homolog of Wg shows that it is involved in embryonic development, which often calls for rapid cell division and migration. Misregulation of these processes can lead to tumor development via excess cell proliferation. Canonical Wnt pathway activity is involved in the development of Benign tumor, benign and Malignant tumor, malignant breast tumors. The role of Wnt pathway in tumor chemoresistance has been also well documented, as well as its role in the maintenance of a distinct subpopulation of cancer-initiating cells. Its presence is revealed by elevated levels of β-catenin in the nucleus and/or cytoplasm, which can be detected with immunohistochemical staining and Western blotting. Increased β-catenin expression is correlated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. This accumulation may be due to factors such as mutations in β-catenin, deficiencies in the β-catenin destruction complex, most frequently by mutations in structurally disordered regions of Adenomatous polyposis coli, APC, overexpression of Wnt ligands, loss of inhibitors and/or decreased activity of regulatory pathways (such as the Wnt/calcium pathway). Breast tumors can metastasize due to Wnt involvement in EMT. Research looking at metastasis of basal-like breast cancer to the lungs showed that repression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling can prevent EMT, which can inhibit metastasis. Wnt signaling has been implicated in the development of other cancers. Changes in CTNNB1 expression, which is the gene that encodes β-catenin, can be measured in breast, colorectal cancer, colorectal, melanoma, prostate cancer, prostate, lung cancer, lung, and other cancers. Increased expression of Wnt ligand-proteins such as Wnt1, Wnt2 and Wnt7A were observed in the development ofglioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality ...
, oesophageal cancer and ovarian cancer respectively. Other proteins that cause multiple cancer types in the absence of proper functioning include ROR1, ROR2, SFRP4, Wnt5A, WIF1 and those of the TCF/LEF family. Wnt signaling is further implicated in the pathogenesis of bone metastasis from breast and prostate cancer with studies suggesting discrete on and off states. Wnt is down-regulated during the dormancy stage by autocrine DKK1, Dkk1 to avoid immune surveillance, as well as during the dissemination stages by intracellular Dishevelled binding antagonist of beta catenin 1 (DACT1), Dact1. Meanwhile Wnt is activated during the early outgrowth phase by E-selectin.
The link between PGE2 and Wnt suggests that a chronic inflammation-related increase of PGE2 may lead to activation of the Wnt pathway in different tissues, resulting in carcinogenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnor ...
.
Type II diabetes
Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a common disease that causes reduced insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance in the periphery. It results in increased blood glucose levels, or hyperglycemia, which can be fatal if untreated. Since Wnt signaling is involved in insulin sensitivity, malfunctioning of its pathway could be involved. Overexpression of Wnt5b, for instance, may increase susceptibility due to its role in adipogenesis, since obesity and type II diabetes have high comorbidity. Wnt signaling is a strong activator of mitochondrial biogenesis. This leads to increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) known to cause DNA and cellular damage. This ROS-induced damage is significant because it can cause acute hepatic insulin resistance, or injury-induced insulin resistance. Mutations in Wnt signaling-associated transcription factors, such as TCF7L2, are linked to increased susceptibility.See also
*AXIN1 *GSK-3 *Management of hair loss *Wingless localisation element 3 (WLE3) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 1 (WISP1) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 2 (WISP2) *WNT1-inducible-signaling pathway protein 3 (WISP3)References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Wnt Signaling Pathway Signal transduction Genes Evolutionary developmental biology