Willem Barentsz on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Willem Barentsz (; – 20 June 1597), anglicized as William Barents or Barentz, was a
 On 5 June 1594, Barentsz left the island of
On 5 June 1594, Barentsz left the island of

 In 1596, disappointed by the failure of previous expeditions, the States-General announced they would no longer
In 1596, disappointed by the failure of previous expeditions, the States-General announced they would no longer  The ships once again found themselves at Bear Island on 1 July, which led to a disagreement between Barentsz and Van Heemskerk on one side and Rijp on the other. They agreed to part ways, with Barentsz continuing northeast, while Rijp headed due north in an attempt to cross directly over the north pole to reach China. Barentsz reached Novaya Zemlya on 17 July. Anxious to avoid becoming entrapped in the surrounding ice, he intended to head for the Vaigatch Strait, but their ship became stuck within the many icebergs and floes. Stranded, the 16-man crew was forced to spend the winter on a barren bluff. After a failed attempt to melt the
The ships once again found themselves at Bear Island on 1 July, which led to a disagreement between Barentsz and Van Heemskerk on one side and Rijp on the other. They agreed to part ways, with Barentsz continuing northeast, while Rijp headed due north in an attempt to cross directly over the north pole to reach China. Barentsz reached Novaya Zemlya on 17 July. Anxious to avoid becoming entrapped in the surrounding ice, he intended to head for the Vaigatch Strait, but their ship became stuck within the many icebergs and floes. Stranded, the 16-man crew was forced to spend the winter on a barren bluff. After a failed attempt to melt the  Dealing with extreme cold, the crew realised that their socks would burn before their feet could even feel the warmth of a fire – and took to sleeping with warmed stones and cannonballs. They used the merchant fabrics aboard the ship to make additional blankets and clothing. The ship bore salted beef, butter, cheese, bread,
Dealing with extreme cold, the crew realised that their socks would burn before their feet could even feel the warmth of a fire – and took to sleeping with warmed stones and cannonballs. They used the merchant fabrics aboard the ship to make additional blankets and clothing. The ship bore salted beef, butter, cheese, bread,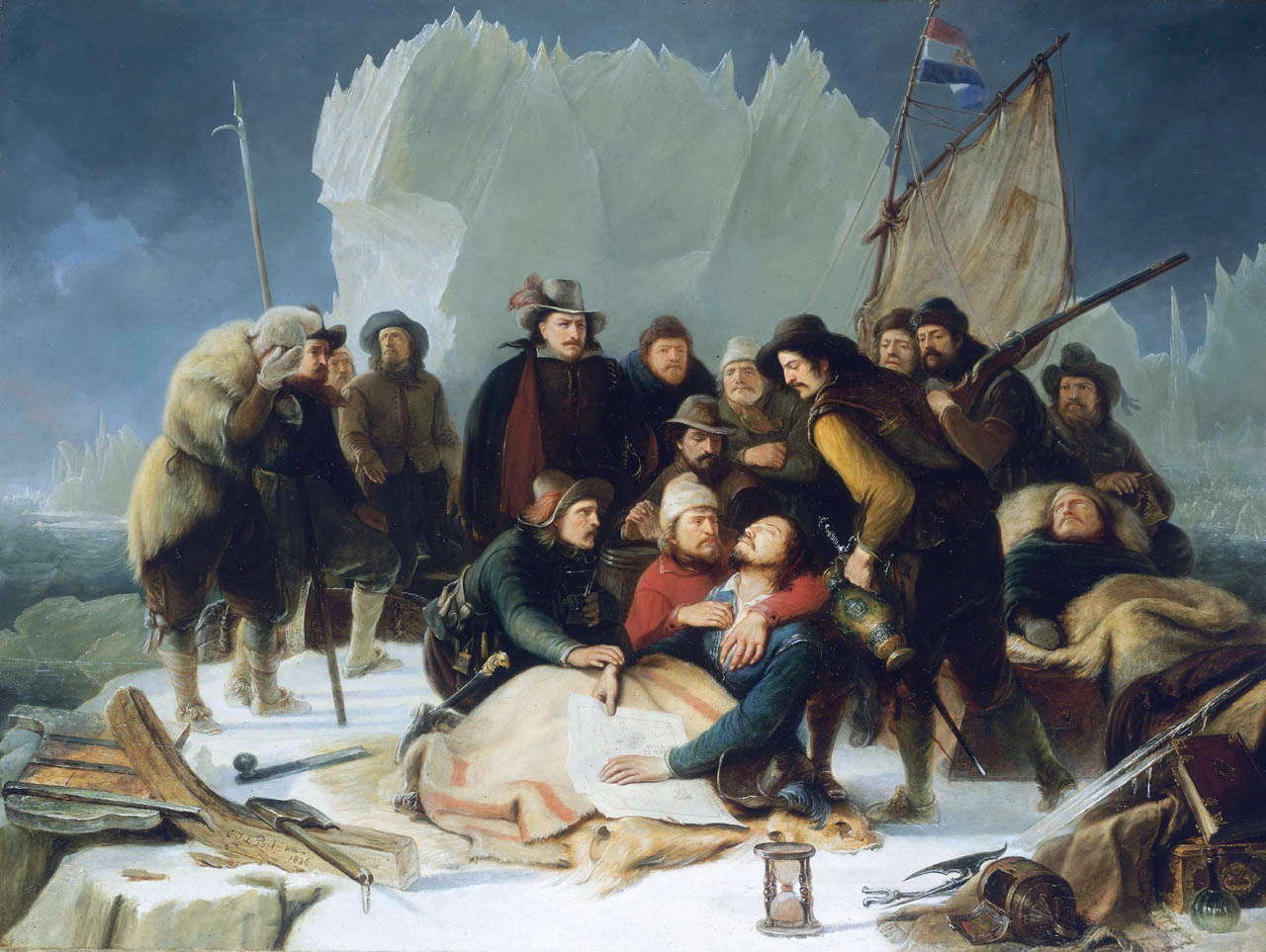  Proving somewhat successful at hunting, the group caught
Proving somewhat successful at hunting, the group caught
The Dutch at the North pole and the Dutch in Maine
3 March 1857. The young cabin boy had died during the winter months in the shelter.
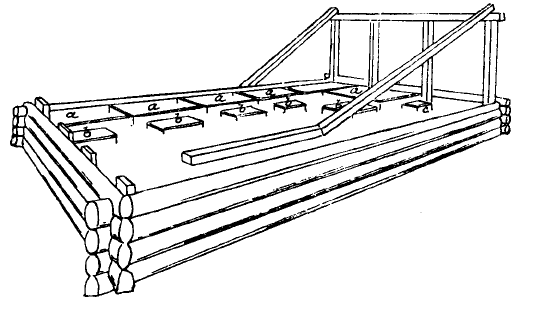 The wooden lodge where Barentsz' crew sheltered was found undisturbed by Norwegian seal hunter Elling Carlsen in 1871. Making a sketch of the lodge's construction, Carlsen recorded finding two copper cooking pots, a barrel, a tool chest, clock, crowbar, flute, clothing, two empty chests, a cooking tripod and a number of pictures. Captain Gunderson landed at the site on 17 August 1875 and collected a grappling iron, two maps and a handwritten translation of Pet and Jackman's voyages. The following year, Charles L.W. Gardiner also visited the site on 29 July where he collected 112 more objects, including the message by Barentsz and Heemskerck describing their settlement to future visitors. All of these objects eventually ended up in the
The wooden lodge where Barentsz' crew sheltered was found undisturbed by Norwegian seal hunter Elling Carlsen in 1871. Making a sketch of the lodge's construction, Carlsen recorded finding two copper cooking pots, a barrel, a tool chest, clock, crowbar, flute, clothing, two empty chests, a cooking tripod and a number of pictures. Captain Gunderson landed at the site on 17 August 1875 and collected a grappling iron, two maps and a handwritten translation of Pet and Jackman's voyages. The following year, Charles L.W. Gardiner also visited the site on 29 July where he collected 112 more objects, including the message by Barentsz and Heemskerck describing their settlement to future visitors. All of these objects eventually ended up in the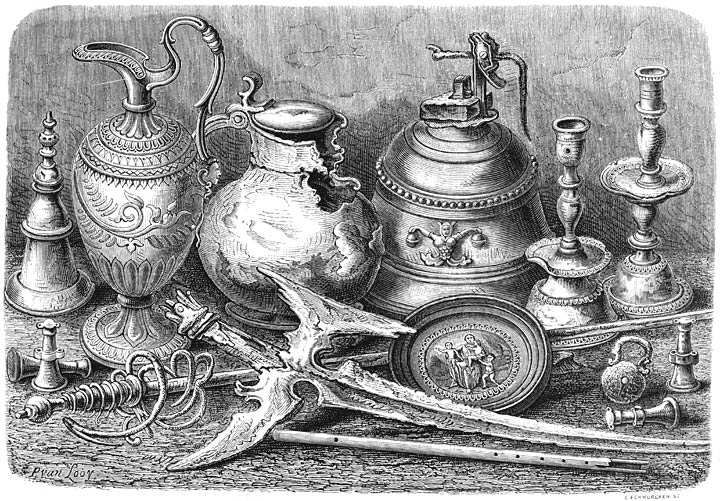  The amateur archaeologist Miloradovich's 1933 finds are held in the Arctic and Antarctic Museum in St. Petersburg. Dmitriy Kravchenko visited the site in 1977, 1979 and 1980 – and sent divers into the sea hoping to find the wreck of the large ship. He returned with a number of objects, which went to the Arkhangelsk Regional Museum of Local Lore (Russia). Another small collection exists at the Polar Museum in
The amateur archaeologist Miloradovich's 1933 finds are held in the Arctic and Antarctic Museum in St. Petersburg. Dmitriy Kravchenko visited the site in 1977, 1979 and 1980 – and sent divers into the sea hoping to find the wreck of the large ship. He returned with a number of objects, which went to the Arkhangelsk Regional Museum of Local Lore (Russia). Another small collection exists at the Polar Museum in
 Two of Barentsz' crewmembers later published their journals,
Two of Barentsz' crewmembers later published their journals, Website of the ''Stichting Expeditieschip Willem Barentsz''
/ref>
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
navigator
A navigator is the person on board a ship or aircraft responsible for its navigation.Grierson, MikeAviation History—Demise of the Flight Navigator FrancoFlyers.org website, October 14, 2008. Retrieved August 31, 2014. The navigator's prima ...
, cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an ...
, and Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
explorer
Exploration refers to the historical practice of discovering remote lands. It is studied by geographers and historians.
Two major eras of exploration occurred in human history: one of convergence, and one of divergence. The first, covering most ...
.
Barentsz went on three expeditions to the far north in search for a Northeast passage
The Northeast Passage (abbreviated as NEP) is the Arctic shipping routes, shipping route between the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific Oceans, along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Russia. The western route through the islands o ...
. He reached as far as Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
and the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipel ...
in his first two voyages, but was turned back on both occasions by ice. During a third expedition, the crew discovered Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Nor ...
and Bear Island, but subsequently became stranded on Novaya Zemlya for almost a year. Barentsz died on the return voyage in 1597.
The Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian terr ...
, among many other places, is named after him.
Life and career
Willem Barentsz was born around 1550 in the village Formerum on the islandTerschelling
Terschelling (; fry, Skylge; Terschelling dialect: ''Schylge'') is a municipality and an island in the northern Netherlands, one of the West Frisian Islands. It is situated between the islands of Vlieland and Ameland.
Wadden Islanders are k ...
in the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (F ...
, present-day Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
. ''Barentsz'' was not his surname
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community.
Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name ...
but rather his patronymic name, short for ''Barentszoon'' " Barent's son".
A cartographer by trade, Barentsz sailed to Spain and the Mediterranean to complete an atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geogra ...
of the Mediterranean region
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and wa ...
, which he co-published with Petrus Plancius
Petrus Plancius (; 1552 – 15 May 1622) was a Dutch-Flemish astronomer, cartographer and clergyman. He was born as Pieter Platevoet in Dranouter, now in Heuvelland, West Flanders. He studied theology in Germany and England. At the age of 24 he ...
.
His career as an explorer was spent searching for a Northeast passage
The Northeast Passage (abbreviated as NEP) is the Arctic shipping routes, shipping route between the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific Oceans, along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Russia. The western route through the islands o ...
in order to trade with China. He reasoned clear, open water north of Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
must exist since the sun shone 24 hours a day melting Arctic sea ice, indeed he thought the further north one went the less ice there would be.
First voyage
 On 5 June 1594, Barentsz left the island of
On 5 June 1594, Barentsz left the island of Texel
Texel (; Texels dialect: ) is a municipality and an island with a population of 13,643 in North Holland, Netherlands. It is the largest and most populated island of the West Frisian Islands in the Wadden Sea. The island is situated north of Den ...
aboard the small ship ''Mercury'', as part of a group of three ships sent out in separate directions to try to enter the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipel ...
, with the hopes of finding the Northeast passage above Siberia. Between 23 and 29 June, Barentsz stayed at Kildin Island
Kildin (also Kilduin; russian: Кильдин, North Sami: Gieldasuolu) is a small Russian island in the Barents Sea, off the Russian shore and about 120 km from Norway. Administratively, Kildin belongs to the Murmansk Oblast of the Russia ...
.
On 9 July, the crew encountered a polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear spec ...
for the first time. After shooting and wounding it with a musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded long gun that appeared as a smoothbore weapon in the early 16th century, at first as a heavier variant of the arquebus, capable of penetrating plate armour. By the mid-16th century, this type of musket gradually di ...
when it tried to climb aboard the ship, the seamen decided to capture it with the hope of bringing it back to Holland. Once leashed and brought aboard the ship however, the bear rampaged and had to be killed. This occurred in Bear Creek, Williams Island.
Upon discovering the Orange Islands, the crew came across a herd of approximately 200 walrus
The walrus (''Odobenus rosmarus'') is a large flippered marine mammal with a discontinuous distribution about the North Pole in the Arctic Ocean and subarctic seas of the Northern Hemisphere. The walrus is the only living species in the fami ...
es and tried to kill them with hatchets and pikes. Finding the task more difficult than they imagined, cold steel shattering against the tough hides of the animals, they left with only a few ivory tusks.
Barentsz reached the west coast of Novaya Zemlya
Novaya Zemlya (, also , ; rus, Но́вая Земля́, p=ˈnovəjə zʲɪmˈlʲa, ) is an archipelago in northern Russia. It is situated in the Arctic Ocean, in the extreme northeast of Europe, with Cape Flissingsky, on the northern island, ...
, and followed it northward before being forced to turn back in the face of large icebergs. Although they did not reach their ultimate goal, the trip was considered a success.
Jan Huyghen van Linschoten
Jan Huygen van Linschoten (1563 – 8 February 1611) was a Dutch merchant, trader and historian.
He travelled extensively along the East Indies regions under Portuguese influence and served as the archbishop's secretary in Goa between 1583 ...
was a member of this expedition and the second.
Second voyage
The following year, Prince Maurice of Orange was filled with "the most exaggerated hopes" on hearing of Barentsz' previous voyage, and named him chief pilot and conductor of a new expedition, which was accompanied by six ships loaded with merchant wares that the Dutch hoped to trade with China. Setting out on 2 June 1595, the voyage went between the Siberian coast andVaygach Island
Vaygach Island (russian: Вайга́ч, ''Vajgač''; Nenets: Вай Хабць, romanized: ''Vai Habcj’'') an island in the Arctic Sea between the Pechora Sea and the Kara Sea.
Vaygach Island is separated from the Yugorsky Peninsula in the ...
. On 30 August, the party came across approximately 20 Samoyed "wild men" with whom they were able to speak, due to a crewmember speaking their language. 4 September saw a small crew sent to States Island to search for a type of crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ...
that had been noticed earlier. The party was attacked by a polar bear, and two sailors were killed.
Eventually, the expedition turned back upon discovering that unexpected weather had left the Kara Sea
The Kara Sea (russian: Ка́рское мо́ре, ''Karskoye more'') is a marginal sea, separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and from the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya archipel ...
frozen. This expedition was largely considered to be a failure.
Third voyage

 In 1596, disappointed by the failure of previous expeditions, the States-General announced they would no longer
In 1596, disappointed by the failure of previous expeditions, the States-General announced they would no longer subsidize
A subsidy or government incentive is a form of financial aid or support extended to an economic sector (business, or individual) generally with the aim of promoting economic and social policy. Although commonly extended from the government, the ter ...
similar voyages – but instead offered a high reward for anybody who ''successfully'' navigated the Northeast Passage. The Town Council of Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
purchased and outfitted two small ships, captained by Jan Rijp and Jacob van Heemskerk, to search for the elusive channel under the command of Barentsz. They set off on 10 May or 15 May, and on 9 June discovered Bear Island.De Veer, Gerrit. "''The Three Voyages of William Barentsz to the Arctic Regions''" (English trans. 1609).
They discovered Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Nor ...
on 17 June, sighting its northwest coast. On 20 June they saw the entrance of a large bay, later called Raudfjorden
Raudfjorden (English: Red fjord) is a 20 km long and 5 km wide fjord on the northwestern coast of Spitsbergen. It has two southern branches, Klinckowströmfjorden and Ayerfjorden, split by the peninsula Buchananhalvøya. The fjord is s ...
. On 21 June they anchored between Cloven Cliff and Vogelsang, where they "set up a post with the arms of the Dutch upon it." On 25 June they entered Magdalenefjorden
Magdalenefjorden is an 8 km long and up to 5 km wide fjord between Reuschhalvøya and Hoelhalvøya, Albert I Land, on the west coast of Spitsbergen, the largest island in the Svalbard archipelago. It is large enough to accommodate ev ...
, which they named ''Tusk Bay'', in light of the walrus tusks they found there. The following day, 26 June, they sailed into the northern entrance of Forlandsundet, but were forced to turn back because of a shoal, which led them to call the fjord ''Keerwyck'' ("inlet where one is forced to turn back"). On 28 June they rounded the northern point of Prins Karls Forland
Prins Karls Forland or Forlandet, occasionally anglicized as Prince Charles Foreland, is an island off the west coast of Oscar II Land on Spitsbergen in the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard, Norway. The entire island and the surrounding sea area c ...
, which they named ''Vogelhoek'', on account of the large number of birds they saw there. They sailed south, passing Isfjorden and Bellsund
Bellsund is a long sound on the west coast of Spitsbergen, part of the Svalbard archipelago of Norway. It is separated from Van Mijenfjorden by the islands of Akseløya and Mariaholmen. Bellsund is located south of Nordenskiöld Land and north ...
, which were labelled on Barentsz's chart as ''Grooten Inwyck'' and ''Inwyck''.
 The ships once again found themselves at Bear Island on 1 July, which led to a disagreement between Barentsz and Van Heemskerk on one side and Rijp on the other. They agreed to part ways, with Barentsz continuing northeast, while Rijp headed due north in an attempt to cross directly over the north pole to reach China. Barentsz reached Novaya Zemlya on 17 July. Anxious to avoid becoming entrapped in the surrounding ice, he intended to head for the Vaigatch Strait, but their ship became stuck within the many icebergs and floes. Stranded, the 16-man crew was forced to spend the winter on a barren bluff. After a failed attempt to melt the
The ships once again found themselves at Bear Island on 1 July, which led to a disagreement between Barentsz and Van Heemskerk on one side and Rijp on the other. They agreed to part ways, with Barentsz continuing northeast, while Rijp headed due north in an attempt to cross directly over the north pole to reach China. Barentsz reached Novaya Zemlya on 17 July. Anxious to avoid becoming entrapped in the surrounding ice, he intended to head for the Vaigatch Strait, but their ship became stuck within the many icebergs and floes. Stranded, the 16-man crew was forced to spend the winter on a barren bluff. After a failed attempt to melt the permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
, the crew used driftwood and lumber from the ship to build a 7.8×5.5-metre lodge they called ''Het Behouden Huys'' (The Saved House).
 Dealing with extreme cold, the crew realised that their socks would burn before their feet could even feel the warmth of a fire – and took to sleeping with warmed stones and cannonballs. They used the merchant fabrics aboard the ship to make additional blankets and clothing. The ship bore salted beef, butter, cheese, bread,
Dealing with extreme cold, the crew realised that their socks would burn before their feet could even feel the warmth of a fire – and took to sleeping with warmed stones and cannonballs. They used the merchant fabrics aboard the ship to make additional blankets and clothing. The ship bore salted beef, butter, cheese, bread, barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, peas, beans, groats
Groats (or in some cases, "berries") are the hulled kernels of various cereal grains, such as oat, wheat, rye, and barley. Groats are whole grains that include the cereal germ and fiber-rich bran portion of the grain, as well as the endosp ...
, flour, oil, vinegar, mustard, salt, beer, wine, brandy, hardtack
Hardtack (or hard tack) is a simple type of dense biscuit or cracker made from flour, water, and sometimes salt. Hardtack is inexpensive and long-lasting. It is used for sustenance in the absence of perishable foods, commonly during long sea voy ...
, smoked bacon, ham and fish. Much of the beer froze, bursting the cask
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, u ...
s. By 8 November Gerrit de Veer
Gerrit de Veer (–) was a Dutch officer on Willem Barentsz' second and third voyages of 1595 and 1596 respectively, in search of the Northeast passage.
De Veer kept a diary of the voyages and in 1597, was the first person to observe and record ...
, the ship's carpenter who kept a diary, reported a shortage of beer and bread, with wine being rationed four days later.
In January 1597, the crew became the first to witness and record the atmospheric anomaly now coined the Novaya Zemlya effect
The Novaya Zemlya effect is a polar mirage caused by high refraction of sunlight between atmospheric thermal layers. The effect gives the impression that the sun is rising earlier than it actually should, and depending on the meteorological situ ...
, due to this sighting.
 Proving somewhat successful at hunting, the group caught
Proving somewhat successful at hunting, the group caught Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in ...
es in primitive traps. The raw flesh of the Arctic fox contains small amounts of vitamin C, which, unknown to the sailors, reduced the effects of scurvy. The crew were continually attacked by polar bears that infested the area where they camped. The bears turned the stranded and now empty ship into a wintertime abode. Primitive guns usually did not kill the bears on first or even second shot (unless well aimed at the heart) and were difficult to aim, while the cold and brittle metal weapons often shattered or bent.
By June, the ice had still not loosened its grip on the ship, and the remaining desperate scurvy
Scurvy is a deficiency disease, disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, anemia, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, ch ...
-ridden survivors took two open boats. Barentsz died at sea soon after on 20 June 1597. It is not known whether Barentsz was buried on the northern island of Novaya Zemlya, or at sea. It took seven more weeks for the boats to reach the Kola Peninsula
The Kola Peninsula (russian: Кольский полуостров, Kolsky poluostrov; sjd, Куэлнэгк нёа̄ррк) is a peninsula in the extreme northwest of Russia, and one of the largest peninsulas of Europe. Constituting the bulk ...
, where they were rescued by a Dutch merchant vessel commanded by former fellow explorer Jan Rijp who by that time had returned to the Netherlands and was on a second voyage, assuming the Barentsz crew to be lost, and found it by accident. By that time, only 12 crewmen remained. They did not reach Amsterdam until 1 November.Goorich, Frank Boott. "Man Upon the Sea", 1858. Sources differ on whether two men died on the ice floe and three in the boats, or three on the ice floe and two in the boats.De Peyster, John WattsThe Dutch at the North pole and the Dutch in Maine
3 March 1857. The young cabin boy had died during the winter months in the shelter.
Excavation and findings
Rijksmuseum Amsterdam
The Rijksmuseum () is the national museum of the Netherlands dedicated to Dutch arts and history and is located in Amsterdam. The museum is located at the Museum Square in the borough of Amsterdam South, close to the Van Gogh Museum, the Ste ...
, after some had initially been held in The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
.
 The amateur archaeologist Miloradovich's 1933 finds are held in the Arctic and Antarctic Museum in St. Petersburg. Dmitriy Kravchenko visited the site in 1977, 1979 and 1980 – and sent divers into the sea hoping to find the wreck of the large ship. He returned with a number of objects, which went to the Arkhangelsk Regional Museum of Local Lore (Russia). Another small collection exists at the Polar Museum in
The amateur archaeologist Miloradovich's 1933 finds are held in the Arctic and Antarctic Museum in St. Petersburg. Dmitriy Kravchenko visited the site in 1977, 1979 and 1980 – and sent divers into the sea hoping to find the wreck of the large ship. He returned with a number of objects, which went to the Arkhangelsk Regional Museum of Local Lore (Russia). Another small collection exists at the Polar Museum in Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies in Northern Norway. The municipality is the ...
(Norway).
In 1992, an expedition of three scientists, a journalist and two photographers commissioned by the ''Arctic Centre'' at the University of Groningen
The University of Groningen (abbreviated as UG; nl, Rijksuniversiteit Groningen, abbreviated as RUG) is a public research university of more than 30,000 students in the city of Groningen in the Netherlands. Founded in 1614, the university is th ...
, coupled with two scientists, a cook and a doctor sent by the '' Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute'' in St. Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, returned to the site, and erected a commemorative marker at the site of the cabin.
The location of Barentsz' wintering on the ice floes has become a tourist destination for icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller ...
cruiseships operating from Murmansk.
Legacy
 Two of Barentsz' crewmembers later published their journals,
Two of Barentsz' crewmembers later published their journals, Jan Huyghen van Linschoten
Jan Huygen van Linschoten (1563 – 8 February 1611) was a Dutch merchant, trader and historian.
He travelled extensively along the East Indies regions under Portuguese influence and served as the archbishop's secretary in Goa between 1583 ...
who had accompanied him on the first two voyages, and Gerrit de Veer who had acted as the ship's carpenter on the last two voyages.
In 1853, the former ''Murmean Sea'' was renamed Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian terr ...
in his honour. Barentsburg
Barentsburg (russian: Баренцбург) is the second-largest settlement in Svalbard, Norway, with about 455 inhabitants (). A coal mining town, the settlement is almost entirely made up of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians.
History
Rijpsburg, ...
, the second largest settlement on Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group rang ...
, Barentsøya
Barentsøya, sometimes anglicized as Barents Island, is an island in the Svalbard archipelago of Norway, lying between Edgeøya and Spitsbergen. Barents Island has no permanent human inhabitants. Named for the Dutch explorer Willem Barents (who ac ...
(Barents Island) and the Barents Region
The Barents Region is a name given, by advocates of establishing international cooperation after the fall of the Soviet Union, to the land along the coast of the Barents Sea, from Nordland in Norway to the Kola Peninsula in Russia and beyond al ...
were also named after Barentsz.
In the late 19th century, the Maritime Institute Willem Barentsz was opened on Terschelling.
In 1878, the Netherlands christened the ''Willem Barentsz'' Arctic exploration ship.
In 1931, Nijgh & Van Ditmar published a play written by Albert Helman
Lodewijk 'Lou' Lichtveld (7 November 1903 – 10 July 1996) was a Surinamese politician, playwright, poet and resistance fighter who wrote under the pseudonym "Albert Helman".
He gained notability in 1923 when he published the poetry collect ...
about Barentsz' third voyage, although it was never performed.
In 1946, the whaling ship ''Pan Gothia'' was re-christened the ''Willem Barentsz''. In 1953, the second ''Willem Barentsz'' whaling ship was produced.
A protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
in the molecular structure of the fruit fly was named ''Barentsz'', in honour of the explorer.
Dutch filmmaker Reinout Oerlemans
Reinout Oerlemans (; born 10 June 1971) is a Dutch soap opera actor, film director, television presenter and television producer. He is the founder of the TV production company Eyeworks.
In 1989, while studying law at the University of Amster ...
released a film called '' Nova Zembla'' in November 2011. It is the first Dutch 3D feature film.
In 2011, a team of volunteers started building a replica of Barentsz' ship in the Dutch town of Harlingen. The plan was to have the ship ready by 2018, when the Tall Ships' Races
The Tall Ships Races are races for sail training "tall ships" (sailing ships). The races are designed to encourage international friendship and training for young people in the art of sailing. The races are held annually in European waters and c ...
was scheduled to visit Harlingen./ref>
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Barentsz, Willem 16th-century Dutch explorers 16th-century Dutch cartographers 16th-century Dutch people 1550s births 1597 deaths Barents Sea Deaths from scurvy Dutch polar explorers Explorers of Svalbard Explorers of the Arctic People from Terschelling People of the Dutch Republic Early modern Netherlandish cartography