Recent additions on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Holocene ( ) is the current
 The climate throughout the Holocene has shown significant variability despite ice core records from Greenland suggesting a more stable climate following the preceding ice age. Marine chemical fluxes during the Holocene were lower than during the Younger Dryas, but were still considerable enough to imply notable changes in the climate. The Greenland ice core records indicate that climate changes became more regional and had a larger effect on the mid-to-low latitudes and mid-to-high latitudes after ~5600 B.P. During the transition from the last glacial to the Holocene, the
The climate throughout the Holocene has shown significant variability despite ice core records from Greenland suggesting a more stable climate following the preceding ice age. Marine chemical fluxes during the Holocene were lower than during the Younger Dryas, but were still considerable enough to imply notable changes in the climate. The Greenland ice core records indicate that climate changes became more regional and had a larger effect on the mid-to-low latitudes and mid-to-high latitudes after ~5600 B.P. During the transition from the last glacial to the Holocene, the
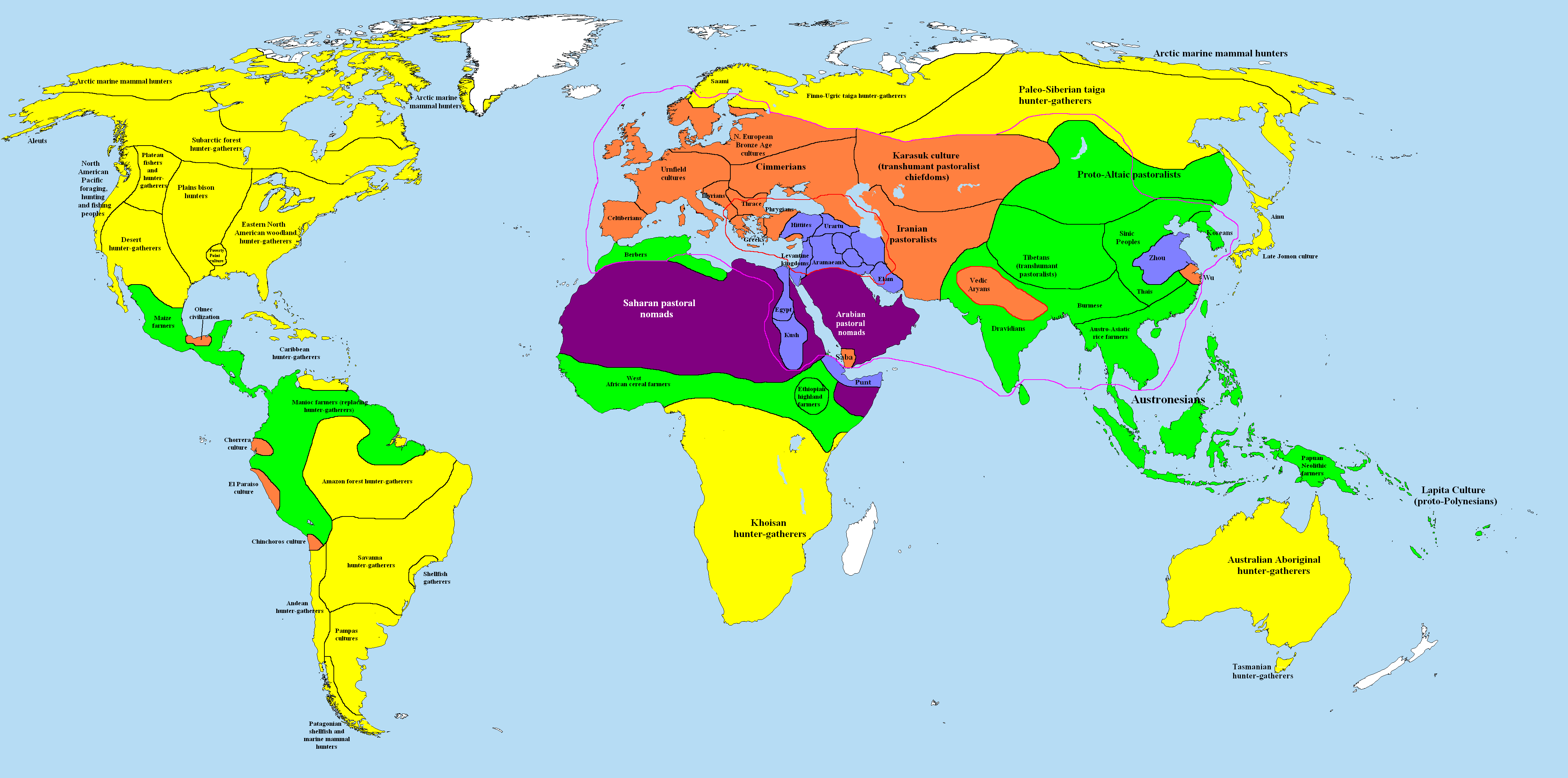 The beginning of the Holocene corresponds with the beginning of the
The beginning of the Holocene corresponds with the beginning of the
The Holocene epoch explained by the BBC
{{Authority control Geological epochs Quaternary geochronology Interglacials Historical eras
geological epoch
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
. It began approximately 11,650 cal Cal or CAL may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Cal'' (novel), a 1983 novel by Bernard MacLaverty
* "Cal" (short story), a science fiction short story by Isaac Asimov
* ''Cal'' (1984 film), an Irish drama starring John Lynch and Helen Mir ...
years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC
The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolution
A technological revolution is a period in which one or more technologies is replaced by another novel technology in a short amount of time. It is an era of accelerated technological progress characterized by new innovations whose rapid applic ...
s, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global significance for the future evolution of living species, including approximately synchronous lithospheric evidence, or more recently hydrospheric and atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
evidence of the human impact. In July 2018, the International Union of Geological Sciences
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) is an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the field of geology.
About
The IUGS was founded in 1961 and is a Scientific Union member of the Inte ...
split the Holocene Epoch into three distinct ages Ages may refer to:
*Advanced glycation end-products, known as AGEs
*Ages, Kentucky, census-designated place, United States
* ''Ages'' (album) by German electronic musician Edgar Froese
*The geologic time scale, a system of chronological measuremen ...
based on the climate, Greenlandian (11,700 years ago to 8,200 years ago), Northgrippian (8,200 years ago to 4,200 years ago) and Meghalayan (4,200 years ago to the present), as proposed by International Commission on Stratigraphy. The oldest age, the Greenlandian was characterized by a warming following the preceding ice age. The Northgrippian Age is known for vast cooling due to a disruption in ocean circulations that was caused by the melting of glaciers. The most recent age of the Holocene is the present Meghalayan, which began with extreme drought that lasted around 200 years.
Etymology
The word is formed from two Ancient Greek words. ''Holos'' () is the Greek word for "whole". "Cene" comes from the Greek word ''kainos'' (), meaning "new". The concept is that this epoch is "entirely new". The suffix '-cene' is used for all the seven epochs of theCenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
Era.
Overview
It is accepted by the International Commission on Stratigraphy that the Holocene started approximately 11,650cal Cal or CAL may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Cal'' (novel), a 1983 novel by Bernard MacLaverty
* "Cal" (short story), a science fiction short story by Isaac Asimov
* ''Cal'' (1984 film), an Irish drama starring John Lynch and Helen Mir ...
years BP (9,700 BCE). The Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy (SQS) observes the terms ‘recent’ to be an incorrect way of referring to the Holocene, and the term ‘modern’ may be used instead to describe current processes. It also observes the term ‘Flandrian’ may be used as a synonym for Holocene, although it is becoming outdated. The International Commission on Stratigraphy, however, considers the Holocene an epoch following the Pleistocene and specifically the last glacial period. Local names for the last glacial period include the Wisconsinan
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cor ...
in North America, the Weichselian in Europe, the Devensian in Britain, the Llanquihue in Chile and the Otiran in New Zealand.
The Holocene can be subdivided into five time intervals, or chronozone
A chronozone or chron is a unit in chronostratigraphy, defined by events such as
geomagnetic reversals (magnetozones), or based on the presence of specific fossils (biozone or biochronozone).
According to the International Commission on Stratig ...
s, based on climatic fluctuations:
* Preboreal
The Preboreal is an informal stage of the Holocene epoch. It is preceded by the Tarantian and succeeded by the Boreal. It lasted from 10,300 to 9,000 BP in radiocarbon years or 8350BC to 7050BC in Gregorian calendar years (8th millennium BC). I ...
(10 ka–9 ka BP),
* Boreal
Boreal may refer to:
Climatology and geography
*Boreal (age), the first climatic phase of the Blytt-Sernander sequence of northern Europe, during the Holocene epoch
*Boreal climate, a climate characterized by long winters and short, cool to mild ...
(9 ka–8 ka BP),
* Atlantic (8 ka–5 ka BP),
* Subboreal
The Subboreal is a climatic period, immediately before the present one, of the Holocene. It lasted from 3710 to 450 BCE.
Etymology
The composite scientific term ''Subboreal'', meaning "below the Boreal," is derived from the Latin ''sub'' (bel ...
(5 ka–2.5 ka BP) and
* Subatlantic
The Subatlantic is the current climatic age of the Holocene epoch. It started about 2,500 years BP and is still ongoing. Its average temperatures are slightly lower than during the preceding Subboreal and Atlantic. During its course, the tempe ...
(2.5 ka BP–present).
: ''Note: " ka BP" means "kilo-annum Before Present", i.e. 1,000 years before 1950 (non-calibrated C14 dates)''
Geologists working in different regions are studying sea levels, peat bogs and ice core
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ic ...
samples by a variety of methods, with a view toward further verifying and refining the Blytt–Sernander sequence. This is a classification of climatic periods initially defined by plant remains in peat mosses. Though the method was once thought to be of little interest, based on 14C dating of peats that was inconsistent with the claimed chronozones, investigators have found a general correspondence across Eurasia and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. The scheme was defined for Northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
, but the climate changes
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
were claimed to occur more widely. The periods of the scheme include a few of the final pre-Holocene oscillations of the last glacial period and then classify climates of more recent prehistory.
Paleontologists have not defined any faunal stages for the Holocene. If subdivision is necessary, periods of human technological development, such as the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
, Neolithic, and Bronze Age, are usually used. However, the time periods referenced by these terms vary with the emergence of those technologies in different parts of the world.
According to some scholars, a third division, the Anthropocene, has now begun. This term is used to denote the present time interval in which many geologically significant conditions and processes have been profoundly altered by human activities.
The 'Anthropocene' (a term coined by Paul J. Crutzen
Paul Jozef Crutzen (; 3 December 1933 – 28 January 2021) was a Dutch meteorologist and atmospheric chemist. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1995 for his work on atmospheric chemistry and specifically for his efforts in studying ...
and Eugene Stoermer in 2000) is not a formally defined geological unit. The Subcommission on Quaternary Stratigraphy of the International Commission on Stratigraphy has a working group to determine whether it should be.
In May 2019, members of the working group voted in favour of recognizing the Anthropocene as formal chrono-stratigraphic unit, with stratigraphic signals around the mid-twentieth century CE as its base. The exact criteria have still to be decided upon, after which the recommendation also has to be approved by the working group's parent bodies (ultimately the International Union of Geological Sciences).
Geology
The Holocene is a geologic epoch that follows directly after the Pleistocene. Continental motions due to plate tectonics are less than a kilometre over a span of only 10,000 years. However, ice melt caused world sea levels to rise about in the early part of the Holocene and another 30 m in the later part of the Holocene. In addition, many areas above about 40 degrees north latitude had been depressed by the weight of the Pleistocene glaciers and rose as much as due to post-glacial rebound over the late Pleistocene and Holocene, and are still rising today. The sea-level rise and temporaryland depression
In geology, a depression is a landform sunken or depressed below the surrounding area. Depressions form by various mechanisms.
Types
Erosion-related:
* Blowout: a depression created by wind erosion typically in either a partially vegetated ...
allowed temporary marine incursions into areas that are now far from the sea. For example, marine fossils from the Holocene epoch have been found in locations such as Vermont and Michigan. Other than higher-latitude temporary marine incursions associated with glacial depression, Holocene fossils are found primarily in lakebed, floodplain, and cave deposits. Holocene marine deposits along low-latitude coastlines are rare because the rise in sea levels during the period exceeds any likely tectonic uplift of non-glacial origin.
Post-glacial rebound in the Scandinavia region resulted in a shrinking Baltic Sea. The region continues to rise, still causing weak earthquakes across Northern Europe. An equivalent event in North America was the rebound of Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
, as it shrank from its larger, immediate post-glacial Tyrrell Sea
The Tyrrell Sea, named after Canada, Canadian geologist Joseph Tyrrell, is another name for prehistoric Hudson Bay, namely as it existed during the retreat of the Laurentide Ice Sheet.
Roughly 8,000 years before present, BP, the Laurentide Ice She ...
phase, to its present boundaries.
Climate
 The climate throughout the Holocene has shown significant variability despite ice core records from Greenland suggesting a more stable climate following the preceding ice age. Marine chemical fluxes during the Holocene were lower than during the Younger Dryas, but were still considerable enough to imply notable changes in the climate. The Greenland ice core records indicate that climate changes became more regional and had a larger effect on the mid-to-low latitudes and mid-to-high latitudes after ~5600 B.P. During the transition from the last glacial to the Holocene, the
The climate throughout the Holocene has shown significant variability despite ice core records from Greenland suggesting a more stable climate following the preceding ice age. Marine chemical fluxes during the Holocene were lower than during the Younger Dryas, but were still considerable enough to imply notable changes in the climate. The Greenland ice core records indicate that climate changes became more regional and had a larger effect on the mid-to-low latitudes and mid-to-high latitudes after ~5600 B.P. During the transition from the last glacial to the Holocene, the Huelmo–Mascardi Cold Reversal
The Huelmo–Mascardi Cold Reversal (HMCR) is a cooling event in South America between 11,400 and 10,200 14C years BP. This cooling began about 550 years before the Younger Dryas cooling in the Northern Hemisphere, and both periods ended at abo ...
in the Southern Hemisphere began before the Younger Dryas, and the maximum warmth flowed south to north from 11,000 to 7,000 years ago. It appears that this was influenced by the residual glacial ice remaining in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
until the later date.
The Holocene climatic optimum
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period that occurred in the interval roughly 9,000 to 5,000 years ago BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimu ...
(HCO) was a period of warming throughout the globe. It has been suggested that the warming was not uniform across the world. Ice core measurements imply that the sea surface temperature (SST) gradient east of New Zealand, across the subtropical front (STF), was around 2 degrees Celsius. This temperature gradient is significantly less than modern times, which is around 6 degrees Celsius. A study utilizing five SST proxies from 37°S to 60°S latitude confirmed that the strong temperature gradient was confined to the area immediately south of the STF, and is correlated with reduced westerly winds near New Zealand. From the 10th-14th century, the climate was similar to that of modern times during a period known as the Medieval climate optimum, or the Medieval warm period (MWP). It was found that the warming that is taking place in current years is both more frequent and more spatially homogeneous than what was experienced during the MWP. A warming of +1 degree Celsius occurs 5-40 times more frequently in modern years than during the MWP. The major forcing during the MWP was due to greater solar activity, which led to heterogeneity compared to the greenhouse gas forcing of modern years that leads to more homogeneous warming. This was followed by the Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age (LIA) was a period of regional cooling, particularly pronounced in the North Atlantic region. It was not a true ice age of global extent. The term was introduced into scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939. Ma ...
, from the 13th or 14th century to the mid-19th century.
The temporal and spatial extent of climate change during the Holocene is an area of considerable uncertainty, with radiative forcing
Radiative forcing (or climate forcing) is the change in energy flux in the atmosphere caused by natural or anthropogenic factors of climate change as measured by watts / metre2. It is a scientific concept used to quantify and compare the external ...
recently proposed to be the origin of cycles identified in the North Atlantic region. Climate cyclicity through the Holocene (Bond events
Bond events are North Atlantic ice rafting events that are tentatively linked to climate fluctuations in the Holocene. Eight such events have been identified. Bond events were previously believed to exhibit a roughly cycle, but the primary perio ...
) has been observed in or near marine settings and is strongly controlled by glacial input to the North Atlantic. Periodicities of ≈2500, ≈1500, and ≈1000 years are generally observed in the North Atlantic. At the same time spectral analyses of the continental record, which is remote from oceanic influence, reveal persistent periodicities of 1,000 and 500 years that may correspond to solar activity variations during the Holocene Epoch. A 1,500-year cycle corresponding to the North Atlantic oceanic circulation may have had widespread global distribution in the Late Holocene.
Ecological developments
Animal and plant life have not evolved much during the relatively short Holocene, but there have been major shifts in the richness and abundance of plants and animals. A number of large animals including mammoths and mastodons, saber-toothed cats like '' Smilodon'' and '' Homotherium'', and giant sloths went extinct in the late Pleistocene and early Holocene. The extinction of some megafauna in America could be attributed to the Clovis people; this culture was known for " Clovis points" which were fashioned on spears for hunting animals. Shrubs, herbs, and mosses had also changed in relative abundance from the Pleistocene to Holocene, identified by permafrost core samples. Throughout the world, ecosystems in cooler climates that were previously regional have been isolated in higher altitude ecological "islands". The '' 8.2-ka event'', an abrupt cold spell recorded as a negative excursion in the record lasting 400 years, is the most prominent climatic event occurring in the Holocene Epoch, and may have marked a resurgence of ice cover. It has been suggested that this event was caused by the final drainage of Lake Agassiz, which had been confined by the glaciers, disrupting the thermohaline circulation of the Atlantic. This disruption was the result of an ice dam overHudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
collapsing sending cold lake Agassiz water into the North Atlantic ocean. Furthermore, studies show that the melting of Lake Agassiz led to sea-level rise which flooded the North American coastal landscape. The basal peat plant was then used to determine the resulting local sea-level rise of 0.20-0.56m in the Mississippi Delta
The Mississippi Delta, also known as the Yazoo–Mississippi Delta, or simply the Delta, is the distinctive northwest section of the U.S. state of Mississippi (and portions of Arkansas and Louisiana) that lies between the Mississippi and Yazoo ...
. Subsequent research, however, suggested that the discharge was probably superimposed upon a longer episode of cooler climate lasting up to 600 years and observed that the extent of the area affected was unclear.
Human developments
 The beginning of the Holocene corresponds with the beginning of the
The beginning of the Holocene corresponds with the beginning of the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
age in most of Europe. In regions such as the Middle East and Anatolia, the term Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are someti ...
is preferred in place of Mesolithic, as they refer to approximately the same time period. Cultures in this period include Hamburgian
The Hamburg culture or Hamburgian (15,500-13,100 BP) was a Late Upper Paleolithic culture of reindeer hunters in northwestern Europe during the last part of the Weichsel Glaciation beginning during the Bölling interstadial. Sites are found close ...
, Federmesser
''Federmesser'' group is an archaeological umbrella term
including the late Upper Paleolithic to Mesolithic cultures of the Northern European Plain, dating to between 14,000 and 12,800 years ago (the late Magdalenian). It is closely related t ...
, and the Natufian culture
The Natufian culture () is a Late Epipaleolithic archaeological culture of the Levant, dating to around 15,000 to 11,500 years ago. The culture was unusual in that it supported a sedentary or semi-sedentary population even before the introduction ...
, during which the oldest inhabited places still existing on Earth were first settled, such as Tell es-Sultan (Jericho) in the Middle East. There is also evolving archeological evidence of proto-religion at locations such as Göbekli Tepe, as long ago as the 9th millennium BCE
The 9th millennium BC spanned the years 9000 BC to 8001 BC (11 to 10 thousand years ago). In chronological terms, it is the first full millennium of the current Holocene epoch that is generally reckoned to have begun by 9700 BC (11.7 thousand ...
.
The preceding period of the Late Pleistocene had already brought advancements such as the bow and arrow, creating more efficient forms of hunting and replacing spear throwers. In Holocene, however, the domestication of plants and animals allowed human civilization to develop villages and towns in centralized locations. Archaeological data shows that between 10,000 to 7,000 BP rapid domestication of plants and animals took place in tropical and subtropical parts of Asia, Africa, and Central America. The development of farming allowed human civilization to transition away from hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
nomadic cultures, which did not establish permanent settlements, to a more sustainable sedentary lifestyle. This form of lifestyle change allowed human civilization to develop towns and villages in centralized locations, which gave rise to the world known today. It is believed that the domestication of plants and animals began in the early part of the Holocene in the tropical areas of the planet. Because these areas had warm, moist temperatures, the climate was perfect for effective farming. Culture development and human population change, specifically in South America, has also been linked to spikes in hydroclimate resulting in climate variability in the mid-Holocene (8.2 - 4.2 k cal BP). Climate change on seasonality and available moisture also allowed for favorable agricultural conditions which promoted human development for Maya and Tiwanaku regions.
Extinction event
TheHolocene extinction
The Holocene extinction, or Anthropocene extinction, is the ongoing extinction event during the Holocene epoch. The extinctions span numerous families of bacteria, fungi, plants, and animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, f ...
, otherwise referred to as the ''sixth mass extinction'' or ''Anthropocene extinction'', is an ongoing extinction event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp change in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. I ...
of species during the present Holocene epoch (with the more recent time sometimes called Anthropocene) as a result of human activity. The included extinctions
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
span numerous families of bacteria, fungi, plants and animals, including mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, birds, reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, fish and invertebrates. With widespread degradation of highly biodiverse habitats such as coral reefs and rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfores ...
s, as well as other areas, the vast majority of these extinctions are thought to be undocumented, as the species are undiscovered at the time of their extinction, or no one has yet discovered their extinction. The current rate of extinction of species is estimated at 100 to 1,000 times higher than natural background extinction rates.
Gallery
See also
*4.2-kiloyear event
The 4.2-kiloyear (thousand years) BP aridification event (long-term drought) was one of the most severe climatic events of the Holocene epoch. It defines the beginning of the current Meghalayan age in the Holocene epoch.
Starting around 2200&n ...
* 8.2-kiloyear event
In climatology, the so-called "8.2-kiloyear event" was a Abrupt climate change, sudden decrease in global temperatures that occurred approximately 8,200 years before the present (Before Present, BP), that is, 6,251 Common Era, BC. It defines the ...
* 10th millennium BC
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC (c. 12 ka to c. 11 ka). It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic ( Northern Europe and Western Europe) and Epip ...
* Blytt–Sernander system
The Blytt–Sernander classification, or sequence, is a series of north European climatic periods or phases based on the study of Denmark, Danish peat bogs by Axel Blytt (1876) and Rutger Sernander (1908). The classification was incorporated into a ...
* Holocene calendar
* African humid period
* Older Peron
* Outburst flood
* Piora Oscillation
The Piora Oscillation was an abrupt cold and wet period in the climate history of the Holocene Epoch; it is roughly dated to c. 3900-3000 BC. Some researchers associate the Piora Oscillation with the end of the Atlantic climate regime, and the st ...
* Quaternary extinction event
References
Further reading
* * *External links
The Holocene epoch explained by the BBC
{{Authority control Geological epochs Quaternary geochronology Interglacials Historical eras