Western Catalan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Catalan language, Catalan dialects feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, Morphology (linguistics), morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibility between its dialects is very high, estimates ranging from 90% to 95%.Central Catalan has 90% to 95% inherent intelligibility for speakers of Valencian (1989 R. Hall, Jr.), cited o
The Catalan language, Catalan dialects feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, Morphology (linguistics), morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibility between its dialects is very high, estimates ranging from 90% to 95%.Central Catalan has 90% to 95% inherent intelligibility for speakers of Valencian (1989 R. Hall, Jr.), cited o
Ethnologue
The only exception is the isolated idiosyncratic Algherese dialect, Alguerese dialect.
For , , (Valencian); , , (North-Western). In verbs, the 1st person present indicative ending is , or in all conjugations.
For example, (Central), (Balearic), (Northern), ('I speak'). In verbs, the inchoative desinences are /, , , . In verbs, the inchoative desinences are , , , . In nouns and adjectives, maintenance of of medieval plurals in proparoxytone words.
E.g., 'men', 'youth'. In nouns and adjectives, loss of of medieval plurals in proparoxytone words.
E.g., 'men', 'youth'.
''El català continental distingeix els fonemes vocàlics accentuats è oberta de mots com "mel", i é tancada de mots com "vent"''
Diccionari català-valencià-balear. may refer to: *Northern Catalan, Northern–Eastern Catalan, Central Catalan, Central–Eastern Catalan and Northwestern Catalan, all spoken in mainland Catalonia, as opposed to Insular Catalan (mainly Balearic Catalan)
 The Catalan language, Catalan dialects feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, Morphology (linguistics), morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibility between its dialects is very high, estimates ranging from 90% to 95%.Central Catalan has 90% to 95% inherent intelligibility for speakers of Valencian (1989 R. Hall, Jr.), cited o
The Catalan language, Catalan dialects feature a relative uniformity, especially when compared to other Romance languages; both in terms of vocabulary, semantics, syntax, Morphology (linguistics), morphology, and phonology. Mutual intelligibility between its dialects is very high, estimates ranging from 90% to 95%.Central Catalan has 90% to 95% inherent intelligibility for speakers of Valencian (1989 R. Hall, Jr.), cited oEthnologue
The only exception is the isolated idiosyncratic Algherese dialect, Alguerese dialect.
Overview
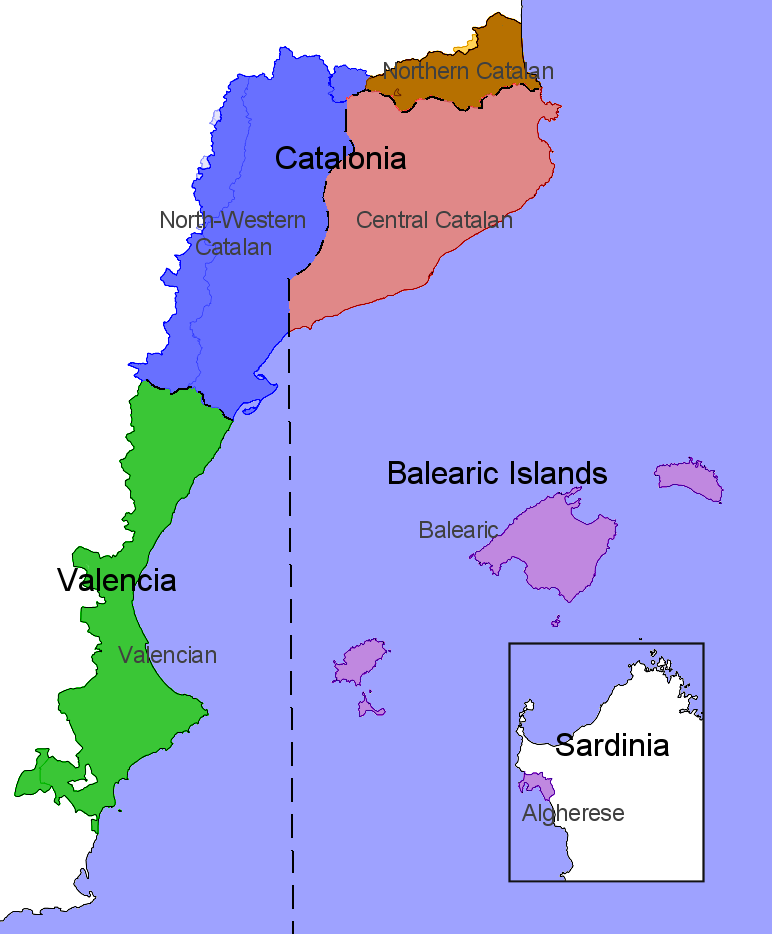
In 1861, linguist Manuel Milà i Fontanals split Catalan into two main dialects: Western and Eastern. The most obvious phonetic difference lies in the treatment of unstressed a and e, which have merged to in Eastern dialects, but remain distinct as and in Western dialects. There are a few other differences in pronunciation, verbal morphology, and vocabulary. Western Catalan comprises the two dialects of Northwestern Catalan and Valencian language, Valencian; the Eastern block comprises three to four dialects (depending on their classification): Central Catalan, Central, Northern Catalan, Roussillonese (Northern Catalan), and Insular (Balearic dialect, Balearic and Algherese dialect, Alguerese). Each dialect can be further subdivided into several subdialects. There are two spoken standards for the language based on the Eastern and Western dialects respectively: * In Catalonia, the Institut d'Estudis Catalans (IEC) regulates the spoken standard based on Central Catalan, which has the highest number of speakers and is spoken in the densely populated regions of the Barcelona Province (Spain), Barcelona province, the eastern half of the province of Tarragona, and most of the province of Girona. * In the Valencian Community, the Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua adapts the Pompeu Fabra, Fabran guidelines to the Valencian variety, and regulates an alternative spoken standard based on the Southern Valencian subdialect. Despite having fewer speakers than the Central Valencian subdialect,Xarxa Cruscat de l'Institut d'Estudis Catalans Southern Valencian has been less influenced by Spanish. It is spoken in the South and North of the province of Valencia, Valencia and province of Alicante, Alicante provinces respectively, in cities such as Gandia, Alcoi and Xàtiva. Valencians are only surpassed in number of Catalan-speakers by Catalans themselves, representing approximately a third of the whole Catalan-speaking population. Therefore, in the context of Valencian language controversy, linguistic conflict, recognition and respect towards the dual standard, as well as the dual Catalan–Valencian denomination, pacifies the tense central–periphery relations between Catalonia and the Valencian community.Pronunciation
Vowels
Catalan has inherited the typical vowel system of Vulgar Latin, with seven stressed phonemes: , a common feature in Western Romance languages, Western Romance, except Spanish, Asturian language, Asturian, and Aragonese language, Aragonese. Balearic dialect, Balearic has also instances of stressed . Dialects differ in the different degrees of vowel reduction, and the incidence of the pair . In Eastern Catalan (except Majorcan), unstressed vowels reduce to three: ; ; remains distinct. There are a few instances of unreduced , in some words. Algherese dialect, Alguerese has lowered to , similar to Eastern dialects spoken in the Barcelona metropolitan area (however, in the latter dialects the vowels are distinct as vs. ). In Majorcan, unstressed vowels reduce to four: follow the Eastern Catalan reduction pattern; however reduce to , with remaining distinct, as in Western Catalan. In Western Catalan, unstressed vowels reduce to five: ; ; remain distinct. This reduction pattern, inherited from Proto-Romance, is also found in Italian and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Some Western dialects present further reduction or vowel harmony in some cases. Central, Western, and Balearic differ in the lexical incidence of stressed and . Usually, words with in central Catalan correspond to in Balearic and in Western Catalan. Words with in Balearic almost always have in central and western Catalan as well. As a result, Western Catalan has a much higher incidence of .Morphology
In verbs, the 1st person present indicative ending is ( in verbs of the 2nd and 3rd conjugation), or .For , , (Valencian); , , (North-Western). In verbs, the 1st person present indicative ending is , or in all conjugations.
For example, (Central), (Balearic), (Northern), ('I speak'). In verbs, the inchoative desinences are /, , , . In verbs, the inchoative desinences are , , , . In nouns and adjectives, maintenance of of medieval plurals in proparoxytone words.
E.g., 'men', 'youth'. In nouns and adjectives, loss of of medieval plurals in proparoxytone words.
E.g., 'men', 'youth'.
Vocabulary
Despite its relative lexical unity, the two dialectal blocks of Catalan (Eastern and Western) show some differences in word choices. Any lexical divergence within any of the two groups can be explained as an archaism. Also, usually Central Catalan acts as an innovative element.Insular Catalan
Insular Catalan may refer to: *the Balearic Catalan, Balearic subdialects, mainly spoken on the islands of Ibiza, Majorca and Minorca. *Algherese dialect, Algherese, the Catalan variety spoken in the Sardinian city of Alghero.Continental Catalan
Continental CatalanDiccionari català-valencià-balear. may refer to: *Northern Catalan, Northern–Eastern Catalan, Central Catalan, Central–Eastern Catalan and Northwestern Catalan, all spoken in mainland Catalonia, as opposed to Insular Catalan (mainly Balearic Catalan)
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * {{Language varieties Catalan dialects, Catalan language