West Francia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
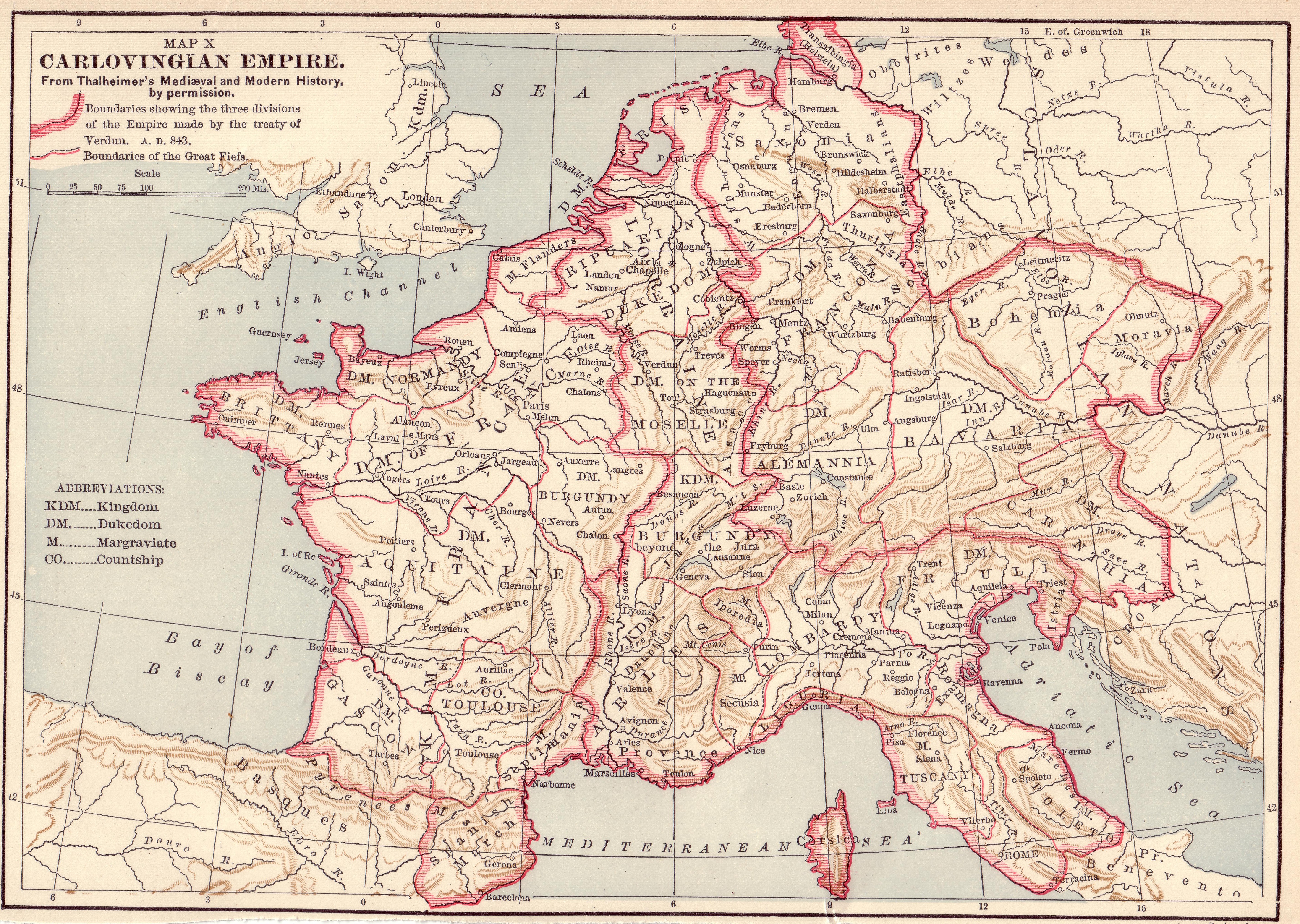 In August 843, after three years of civil war following the death of Louis the Pious on 20 June 840, the
In August 843, after three years of civil war following the death of Louis the Pious on 20 June 840, the
medieval history
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the Post-classical, post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with t ...
, West Francia (Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functione ...
: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
established by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqui ...
. It is considered the first polity in French history
The first written records for the history of France appeared in the Iron Age. What is now France made up the bulk of the region known to the Romans as Gaul. The first writings on indigenous populations mainly start in the first century BC. Greek ...
.
West Francia extended further north and south than modern metropolitan France
Metropolitan France (french: France métropolitaine or ''la Métropole''), also known as European France (french: Territoire européen de la France) is the area of France which is geographically in Europe. This collective name for the European ...
, but it did not extend as far east. It did not include such future French holdings as Lorraine
Lorraine , also , , ; Lorrain: ''Louréne''; Lorraine Franconian: ''Lottringe''; german: Lothringen ; lb, Loutrengen; nl, Lotharingen is a cultural and historical region in Northeastern France, now located in the administrative region of Gra ...
, the County
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
and Kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and ...
(the duchy was already a part of West Francia), Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
and Provence
Provence (, , , , ; oc, Provença or ''Prouvènço'' , ) is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which extends from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the Italian border to the east; it is bor ...
in the east and southeast for example. It also did not include the Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
peninsula in the west. In addition, by the 10th century the authority of the West Frankish monarchs was greatly reduced. This was contrasted by the evergrowing power of their vassals over their large and usually territorially contiguous fiefs.
The power vacuum left by a weak royal authority meant wars between fiefs were rampant, and so were conflicts between the vassals and the Frankish monarchs themselves. The period was also marked by endless Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raids on the kingdom and clashes between the West Franks and the Norsemen. This eventually led to the establishment of the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
, which was granted to the Norseman Rollo
Rollo ( nrf, Rou, ''Rolloun''; non, Hrólfr; french: Rollon; died between 928 and 933) was a Viking who became the first ruler of Normandy, today a region in northern France. He emerged as the outstanding warrior among the Norsemen who had se ...
and his men following their unsuccessful siege at Chartres in 911 in exchange for an oath of fealty to King Charles the Simple
Charles III (17 September 879 – 7 October 929), called the Simple or the Straightforward (from the Latin ''Carolus Simplex''), was the king of West Francia from 898 until 922 and the king of Lotharingia from 911 until 919–923. He was a mem ...
. The fiefdom
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of f ...
of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
was first a county then a duchy, and like other great fiefs of West Francia became largely autonomous, with magnates even more powerful than their monarch.
In Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
and Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the nort ...
the authority of the West Frankish king was barely felt. West Frankish kings were elected by the secular and ecclesiastic magnates, and for the half-century between 888 and 936 candidates from the Carolingian and Robertian houses were alternately chosen as monarchs.Lewis 1965, 179–180. By this time the power of king became weaker and more nominal, as the regional dukes and nobles became more powerful in their semi-independent regions. The Robertians, after becoming counts of Paris and dukes of France, became kings themselves and established the Capetian dynasty after 987, which is, although arbitrary, generally defined as the gradual transition towards the Kingdom of France.
Formation and borders
 In August 843, after three years of civil war following the death of Louis the Pious on 20 June 840, the
In August 843, after three years of civil war following the death of Louis the Pious on 20 June 840, the Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
was signed by his three sons and heirs. The youngest, Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a ...
, received western Francia. The contemporary West Frankish ''Annales Bertiniani
''Annales Bertiniani'' (''Annals of Saint Bertin'') are late Carolingian, Frankish annals that were found in the Abbey of Saint Bertin, Saint-Omer, France, after which they are named. Their account is taken to cover the period 830-82, thus contin ...
'' describes Charles arriving at Verdun, "where the distribution of portions" took place. After describing the portions of his brothers, Lothair the Emperor (Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Franc ...
) and Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
( East Francia), he notes that "the rest as far as Spain they ceded to Charles". The ''Annales Fuldenses
The ''Annales Fuldenses'' or ''Annals of Fulda'' are East Frankish chronicles that cover independently the period from the last years of Louis the Pious (died 840) to shortly after the end of effective Carolingian rule in East Francia with the a ...
'' of East Francia describe Charles as holding the western part after the kingdom was "divided in three".
Since the death of King Pippin I of Aquitaine in December 838, his son had been recognised by the Aquitainian nobility as King Pippin II of Aquitaine, although the succession had not been recognised by the emperor. Charles the Bald was at war with Pippin II from the start of his reign in 840, and the Treaty of Verdun ignored the claimant and assigned Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janu ...
to Charles. Accordingly, in June 845, after several military defeats, Charles signed the Treaty of Benoît-sur-Loire and recognised his nephew's rule. This agreement lasted until 25 March 848, when the Aquitainian barons recognised Charles as their king. Thereafter Charles's armies had the upper hand, and by 849 had secured most of Aquitaine. In May, Charles had himself crowned "King of the Franks and Aquitainians" in Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and Wenilo of Sens officiated at the coronation, which included the first instance of royal unction in West Francia. The idea of anointing Charles may be owed to Archbishop Hincmar of Reims, who composed no less than four ''ordines'' describing appropriate liturgies for a royal consecration. By the time of the Synod of Quierzy (858), Hincmar was claiming that Charles was anointed to the entire West Frankish kingdom. With the Treaty of Mersen in 870 the western part of
The Cambridge Illustrated History of France
/ref> Odo's brother Robert I ruled between 922 and 923 and was followed by Rudolph from 923 until 936.

 Outside the old Frankish territories and in the south local nobles were semi-independent after 887 as duchies were created: Burgundy,
Outside the old Frankish territories and in the south local nobles were semi-independent after 887 as duchies were created: Burgundy,
/ref> Norsemen began settling in
"The Coinages of Pippin I and II of Aquitaine"
''Revue numismatique'', 6th series, 31 (1989), 194–222. *Geoffrey Koziol. "Charles the Simple, Robert of Neustria, and the ''vexilla'' of Saint-Denis". ''Early Medieval Europe'' 14:4 (2006), 355–90. * Archibald R. Lewis
''The Development of Southern French and Catalan Society, 718–1050''
Austin: University of Texas Press, 1965. *Simon MacLean. ''Kingship and Politics in the Late Ninth Century: Charles the Fat and the end of the Carolingian Empire''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. * Janet L. Nelson. "Kingship, Law and Liturgy in the Political Thought of Hincmar of Rheims". ''English Historical Review'' 92 (1977), 241–79. Reprinted in ''Politics and Ritual in Early Medieval Europe'' (London: Hambledon, 1986), 133–72. *Alfred Richard. ''Histoire des Comtes de Poitou''
vol. 1
Paris: Alphonse Picard, 1903. *Julia M. H. Smith. ''Province and Empire: Brittany and the Carolingians''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992. {{Authority control Former monarchies of Europe 843 establishments 987 disestablishments States and territories established in the 840s States and territories disestablished in the 980s West Franks Establishments in the Carolingian Empire 9th century in France 10th century in France Former countries
(US) and Wenilo of Sens officiated at the coronation, which included the first instance of royal unction in West Francia. The idea of anointing Charles may be owed to Archbishop Hincmar of Reims, who composed no less than four ''ordines'' describing appropriate liturgies for a royal consecration. By the time of the Synod of Quierzy (858), Hincmar was claiming that Charles was anointed to the entire West Frankish kingdom. With the Treaty of Mersen in 870 the western part of
Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable ...
was added to West Francia. In 875 Charles the Bald was crowned Emperor of Rome.
The last record in the ''Annales Bertiniani'' dates to 882, and so the only contemporary narrative source for the next eighteen years in West Francia is the ''Annales Vedastini {{italic title
The ''Annales Vedastini'' or ''Annals of St-Vaast'' are a series of annals written in the early tenth century at the Abbey of St. Vaast in Arras. They are an important source for the ninth century. The years from 874 to 900 are covere ...
''. The next set of original annals from the West Frankish kingdom are those of Flodoard, who began his account with the year 919.
Reign of Charles the Fat
After the death of Charles's grandson,Carloman II
Carloman II ( 866 – 6 December 884) was the King of West Francia from 879 until his death. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, he and his elder brother, Louis III, divided the kingdom between themselves and ruled jointly until the latter's d ...
, on 12 December 884, the West Frankish nobles elected his uncle, Charles the Fat
Charles III (839 – 13 January 888), also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 888. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandso ...
, already king in East Francia and Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
, as their king. He was probably crowned "King in Gaul" (''rex in Gallia'') on 20 May 885 at Grand
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and c ...
. His reign was the only time after the death of Louis the Pious that all of Francia would be re-united under one ruler. In his capacity as king of West Francia, he seems to have granted the royal title and perhaps regalia to the semi-independent ruler of Brittany, Alan I. His handling of the Viking siege of Paris in 885–86 greatly reduced his prestige. In November 887 his nephew, Arnulf of Carinthia revolted and assumed the title as King of the East Franks. Charles retired and soon died on 13 January 888.
In Aquitaine, Duke Ranulf II may have had himself recognised as king, but he only lived another two years. Although Aquitaine did not become a separate kingdom, it was largely outside the control of the West Frankish kings.
Odo, Count of Paris
Odo (french: Eudes; c. 857 – 1 January 898) was the elected King of West Francia from 888 to 898. He was the first king from the Robertian dynasty. Before assuming the kingship, Odo was the count of Paris. His reign marked the definitive separa ...
was then elected by nobles as the new king of West Francia, and was crowned the next month. At this point, West Francia was composed of Neustria
Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks.
Neustria included the land between the Loire and the Silva Carbonaria, approximately the north of present-day France, with Paris, Orléans, Tours, Soissons as its main cities. It late ...
in the west and in the east by Francia proper, the region between the Meuse
The Meuse ( , , , ; wa, Moûze ) or Maas ( , ; li, Maos or ) is a major European river, rising in France and flowing through Belgium and the Netherlands before draining into the North Sea from the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta. It has a t ...
and the Seine.
Rise of Robertians
After the 860s, Lotharingian noble Robert the Strong became increasingly powerful as count of Anjou, Touraine and Maine. Robert's brother Hugh, abbot of Saint-Denis, was given control over Austrasia by Charles the Bald. Robert's son Odo was elected king in 888./ref> Odo's brother Robert I ruled between 922 and 923 and was followed by Rudolph from 923 until 936.
Hugh the Great
Hugh the Great (16 June 956) was the duke of the Franks and count of Paris.
Biography
Hugh was the son of King Robert I of France and Béatrice of Vermandois.Detlev Schwennicke, '' Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der E ...
, son of Robert I, was elevated to the title "duke of the Franks" by king Louis IV. In 987 his son Hugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; french: Hugues Capet ; c. 939 – 14 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, ...
was elected king and the Capetian dynasty began. At this point they controlled very little beyond the Île-de-France
The Île-de-France (, ; literally "Isle of France") is the most populous of the eighteen regions of France. Centred on the capital Paris, it is located in the north-central part of the country and often called the ''Région parisienne'' (; en, Pa ...
.
Rise of dukes
 Outside the old Frankish territories and in the south local nobles were semi-independent after 887 as duchies were created: Burgundy,
Outside the old Frankish territories and in the south local nobles were semi-independent after 887 as duchies were created: Burgundy, Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janu ...
, Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
, Gascony, Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, ...
and the County of Flanders
The County of Flanders was a historic territory in the Low Countries.
From 862 onwards, the counts of Flanders were among the original twelve peers of the Kingdom of France. For centuries, their estates around the cities of Ghent, Bruges and Yp ...
.
The power of the kings continued to decline, together with their inability to resist the Vikings and to oppose the rise of regional nobles who were no longer appointed by the king but became hereditary local dukes. In 877 Boso of Provence, brother-in-law of Charles the Bald, crowned himself as the king of Burgundy and Provence. His son Louis the Blind
Louis the Blind ( 880 – 5 June 928) was the king of Provence from 11 January 887, King of Italy from 12 October 900, and briefly Holy Roman Emperor, as Louis III, between 901 and 905. His father was a Bosonid and his mother was a Carolingia ...
was king of Provence from 890 and Emperor between 901 and 905. Rudolph II of Burgundy
Rudolph II (c. 11 July 880 – 11 July 937), a member of the Elder House of Welf, was King of Burgundy from 912 until his death. He initially succeeded in Upper Burgundy and also ruled as King of Italy from 922 to 926. In 933 Rudolph acquired t ...
established the Kingdom of Burgundy
Kingdom of Burgundy was a name given to various states located in Western Europe during the Middle Ages. The historical Burgundy correlates with the border area of France, Italy and Switzerland and includes the major modern cities of Geneva and ...
in 933.
Charles the Simple
After the death of East Francia's last Carolingian king Louis the Child,Lotharingia
Lotharingia ( la, regnum Lotharii regnum Lothariense Lotharingia; french: Lotharingie; german: Reich des Lothar Lotharingien Mittelreich; nl, Lotharingen) was a short-lived medieval successor kingdom of the Carolingian Empire. As a more durable ...
switched allegiance to the king of West Francia, Charles the Simple. After 911 the Duchy of Swabia extended westwards and added lands of Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
. Baldwin II of Flanders
Baldwin II ( 865 – 10 September 918) was the second margrave (or count) of Flanders, ruling from 879 to 918. He was nicknamed the Bald (''Calvus'') after his maternal grandfather, Emperor Charles the Bald.
Rule
Baldwin II was born around 86 ...
became increasingly powerful after the Odo's death in 898, gaining Boulogne and Ternois
The river Ternoise (; nl, Ternaas) is one of the small chalk streams that flow from the plateau of the southern Boulonnais and Picardy, via the Canche, into the English Channel. The basin of the Ternoise extends to and lies in the southern en ...
from Charles. The territory over which the king exercised actual control shrank considerably, and was reduced to lands between Normandy and river Loire. The royal court usually stayed in Rheims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
or Laon
Laon () is a city in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
History
Early history
The holy district of Laon, which rises a hundred metres above the otherwise flat Picardy plain, has always held strategic importance. ...
.The New Cambridge Medieval History: Volume 3, c.900–c.1024/ref> Norsemen began settling in
Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, and from 919 Magyars invaded repeatedly. In the absence of strong royal power, invaders were engaged and defeated by local nobles, like Richard of Burgundy and Robert of Neustria, who defeated Viking leader Rollo
Rollo ( nrf, Rou, ''Rolloun''; non, Hrólfr; french: Rollon; died between 928 and 933) was a Viking who became the first ruler of Normandy, today a region in northern France. He emerged as the outstanding warrior among the Norsemen who had se ...
in 911 at Chartres. The Norman threat was eventually ended, with the last Danegeld
Danegeld (; "Danish tax", literally "Dane yield" or tribute) was a tax raised to pay tribute or protection money to the Viking raiders to save a land from being ravaged. It was called the ''geld'' or ''gafol'' in eleventh-century sources. It ...
paid in 924 and 926. Both nobles became increasingly opposed to Charles, and in 922 deposed him and elected Robert I as the new king. After Robert's death in 923 nobles elected Rudolf as king, and kept Charles imprisoned until his death in 929. After the rule of king Charles the Simple, local dukes began issuing their own currency.
Rudolf
King Rudolf was supported by his brother Hugh the Black and son of Robert I,Hugh the Great
Hugh the Great (16 June 956) was the duke of the Franks and count of Paris.
Biography
Hugh was the son of King Robert I of France and Béatrice of Vermandois.Detlev Schwennicke, '' Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der E ...
. Dukes of Normandy refused to recognise Rudolf until 933. The King also had to move with his army against the southern nobles to receive their homage and loyalty, however, the count of Barcelona managed to avoid this completely.
After 925 Rudolf was involved in a war against the rebellious Herbert II, Count of Vermandois
Herbert II (died 23 February 943), Count of Vermandois, Count of Meaux, and Count of Soissons. He was the first to exercise power over the territory that became the province of Champagne.
Life
Herbert was the son of Herbert I of Vermandois. He w ...
, who received support from kings Henry the Fowler and Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
of East Francia. His rebellion continued until his death in 943.
Louis IV
King Louis IV and Duke Hugh the Great were married to sisters of East Frankish kingOtto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
who after the deaths of their husbands managed Carolingian and Robertine rule together with their brother Bruno the Great
Bruno the Great (german: Brun(o) von Sachsen, "Bruno of Saxony"; la, Bruno Magnus; May 925 – 11 October 965 AD) was Archbishop of Cologne''Religious Drama and Ecclesiastical Reform in the Tenth Century'', James H. Forse, ''Early Theatre'', V ...
, archbishop of Cologne, as regent.
After further victories by Herbert II, Louis was rescued only with the help of the large nobles and Otto I. In 942 Louis gave up Lotharingia to Otto I.
Succession conflict in Normandy led to a new war in which Louis was betrayed by Hugh the Great and captured by Danish prince Harald who eventually released him to the custody of Hugh, who freed the king only after receiving town of Laon
Laon () is a city in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France.
History
Early history
The holy district of Laon, which rises a hundred metres above the otherwise flat Picardy plain, has always held strategic importance. ...
as a compensation.
The last Carolingians: Lothair and Louis V
The 13-year oldLothair of France
Lothair (french: Lothaire; la, Lothārius; 941 – 2 March 986), sometimes called Lothair II,After the emperor Lothair I. IIICounting Lothair II of Lotharingia, who ruled over modern Lorraine and Belgium. or IV,Counting Lothair II of Ita ...
inherited all the lands of his father in 954. By this time they were so small that the Carolingian practice of dividing lands among the sons was not followed and his brother Charles received nothing. In 966 Lothair married Emma, stepdaughter of his maternal uncle Otto I. Despite this, in August 978 Lothair attacked the old imperial capital Aachen. Otto II
Otto II (955 – 7 December 983), called the Red (''der Rote''), was Holy Roman Emperor from 973 until his death in 983. A member of the Ottonian dynasty, Otto II was the youngest and sole surviving son of Otto the Great and Adelaide of Ita ...
retaliated by attacking Paris, but was defeated by the combined forces of king Lothar and nobles and peace was signed in 980, ending the brief Franco-German war.
Lothar managed to increase his power, but this was reversed with the coming of age of Hugh Capet
Hugh Capet (; french: Hugues Capet ; c. 939 – 14 October 996) was the King of the Franks from 987 to 996. He is the founder and first king from the House of Capet. The son of the powerful duke Hugh the Great and his wife Hedwige of Saxony, ...
, who began forming new alliances of nobles and eventually was elected as king in 987 after Lothair and his son and successor Louis V of France
Louis V ( – 22 May 987), also known as Louis the Do-Nothing (french: Louis le Fainéant), was a king of West Francia from 979 (co-reigning first with his father Lothair until 986) to his early death in 987. During his reign, the nobility essent ...
had both died prematurely, traditionally marking the end of the French branch of Carolingian dynasty as well as the end of West Francia as a kingdom. Hugh Capet would be the first ruler of a new royal house, the House of Capet
The House of Capet (french: Maison capétienne) or the Direct Capetians (''Capétiens directs''), also called the House of France (''la maison de France''), or simply the Capets, ruled the Kingdom of France from 987 to 1328. It was the most ...
, who would rule France through the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
.
List of kings
*Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a ...
(843–877)
*Louis the Stammerer
Louis II, known as Louis the Stammerer (french: Louis le Bègue; 1 November 846 – 10 April 879), was the king of Aquitaine and later the king of West Francia. He was the eldest son of Emperor Charles the Bald and Ermentrude of Orléans. Louis ...
(877–879)
* Louis III of France (879–882)
*Carloman II
Carloman II ( 866 – 6 December 884) was the King of West Francia from 879 until his death. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, he and his elder brother, Louis III, divided the kingdom between themselves and ruled jointly until the latter's d ...
(882–884)
*Charles the Fat
Charles III (839 – 13 January 888), also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 888. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandso ...
(885–888)
*Odo of France
Odo (french: Eudes; c. 857 – 1 January 898) was the elected King of West Francia from 888 to 898. He was the first king from the Robertian dynasty. Before assuming the kingship, Odo was the count of Paris. His reign marked the definitive sepa ...
(888–898)
*Charles the Simple
Charles III (17 September 879 – 7 October 929), called the Simple or the Straightforward (from the Latin ''Carolus Simplex''), was the king of West Francia from 898 until 922 and the king of Lotharingia from 911 until 919–923. He was a mem ...
(898–922)
*Robert I of France
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
(922–923)
*Rudolph of France
Rudolph (french: Rodolphe), sometimes called Ralph (; c. 890 – 14/15 January 936), was the king of France from 923 until his death in 936. He was elected to succeed his father-in-law, Robert I, and spent much of his reign defending his realm fr ...
(923–936)
*Louis IV of France
Louis IV (September 920 / September 921 – 10 September 954), called ''d'Outremer'' or ''Transmarinus'' (both meaning "from overseas"), reigned as King of West Francia from 936 to 954. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, he was the only son of ...
(936–954)
*Lothair of France
Lothair (french: Lothaire; la, Lothārius; 941 – 2 March 986), sometimes called Lothair II,After the emperor Lothair I. IIICounting Lothair II of Lotharingia, who ruled over modern Lorraine and Belgium. or IV,Counting Lothair II of Ita ...
(954–986)
*Louis V of France
Louis V ( – 22 May 987), also known as Louis the Do-Nothing (french: Louis le Fainéant), was a king of West Francia from 979 (co-reigning first with his father Lothair until 986) to his early death in 987. During his reign, the nobility essent ...
(986–987)
Notes
References
* Jim Bradbury. ''The Capetians: Kings of France, 987–1328''. London: Hambledon Continuum, 2007. *Simon Coupland"The Coinages of Pippin I and II of Aquitaine"
''Revue numismatique'', 6th series, 31 (1989), 194–222. *Geoffrey Koziol. "Charles the Simple, Robert of Neustria, and the ''vexilla'' of Saint-Denis". ''Early Medieval Europe'' 14:4 (2006), 355–90. * Archibald R. Lewis
''The Development of Southern French and Catalan Society, 718–1050''
Austin: University of Texas Press, 1965. *Simon MacLean. ''Kingship and Politics in the Late Ninth Century: Charles the Fat and the end of the Carolingian Empire''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. * Janet L. Nelson. "Kingship, Law and Liturgy in the Political Thought of Hincmar of Rheims". ''English Historical Review'' 92 (1977), 241–79. Reprinted in ''Politics and Ritual in Early Medieval Europe'' (London: Hambledon, 1986), 133–72. *Alfred Richard. ''Histoire des Comtes de Poitou''
vol. 1
Paris: Alphonse Picard, 1903. *Julia M. H. Smith. ''Province and Empire: Brittany and the Carolingians''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992. {{Authority control Former monarchies of Europe 843 establishments 987 disestablishments States and territories established in the 840s States and territories disestablished in the 980s West Franks Establishments in the Carolingian Empire 9th century in France 10th century in France Former countries