Wellington on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wellington ( mi,


 Wellington was declared a city in 1840, and was chosen to be the capital city of New Zealand in 1865.
Wellington became the capital city in place of
Wellington was declared a city in 1840, and was chosen to be the capital city of New Zealand in 1865.
Wellington became the capital city in place of  Wellington is New Zealand's politics of New Zealand, political centre, housing the nation's major government institutions. The New Zealand Parliament relocated to the new capital city, having spent the first ten years of its existence in Auckland. A session of parliament officially met in the capital for the first time on 26 July 1865. At that time, the population of Wellington was just 4,900.
The Old Government Buildings, Wellington, Government Buildings were constructed at Lambton Quay in 1876. The site housed the original public sector organisations in New Zealand, government departments in New Zealand. The public service rapidly expanded beyond the capacity of the building, with the first department leaving shortly after it was opened; by 1975 only the Education Department remained, and by 1990 the building was empty. The capital city is also the location of the highest court, the Supreme Court of New Zealand, and the historic former High Court building (opened 1881) has been enlarged and restored for its use. The Governor-General's residence, Government House, Wellington, Government House (the current building completed in 1910) is situated in Newtown, opposite the Basin Reserve. Premier House (built in 1843 for Wellington's first mayor, George Hunter (mayor), George Hunter), the official residence of the Prime Minister of New Zealand, prime minister, is in Thorndon on Tinakori Road.
Over six months in 1939 and 1940 Wellington hosted the New Zealand Centennial Exhibition, celebrating a century since the signing of the
Wellington is New Zealand's politics of New Zealand, political centre, housing the nation's major government institutions. The New Zealand Parliament relocated to the new capital city, having spent the first ten years of its existence in Auckland. A session of parliament officially met in the capital for the first time on 26 July 1865. At that time, the population of Wellington was just 4,900.
The Old Government Buildings, Wellington, Government Buildings were constructed at Lambton Quay in 1876. The site housed the original public sector organisations in New Zealand, government departments in New Zealand. The public service rapidly expanded beyond the capacity of the building, with the first department leaving shortly after it was opened; by 1975 only the Education Department remained, and by 1990 the building was empty. The capital city is also the location of the highest court, the Supreme Court of New Zealand, and the historic former High Court building (opened 1881) has been enlarged and restored for its use. The Governor-General's residence, Government House, Wellington, Government House (the current building completed in 1910) is situated in Newtown, opposite the Basin Reserve. Premier House (built in 1843 for Wellington's first mayor, George Hunter (mayor), George Hunter), the official residence of the Prime Minister of New Zealand, prime minister, is in Thorndon on Tinakori Road.
Over six months in 1939 and 1940 Wellington hosted the New Zealand Centennial Exhibition, celebrating a century since the signing of the
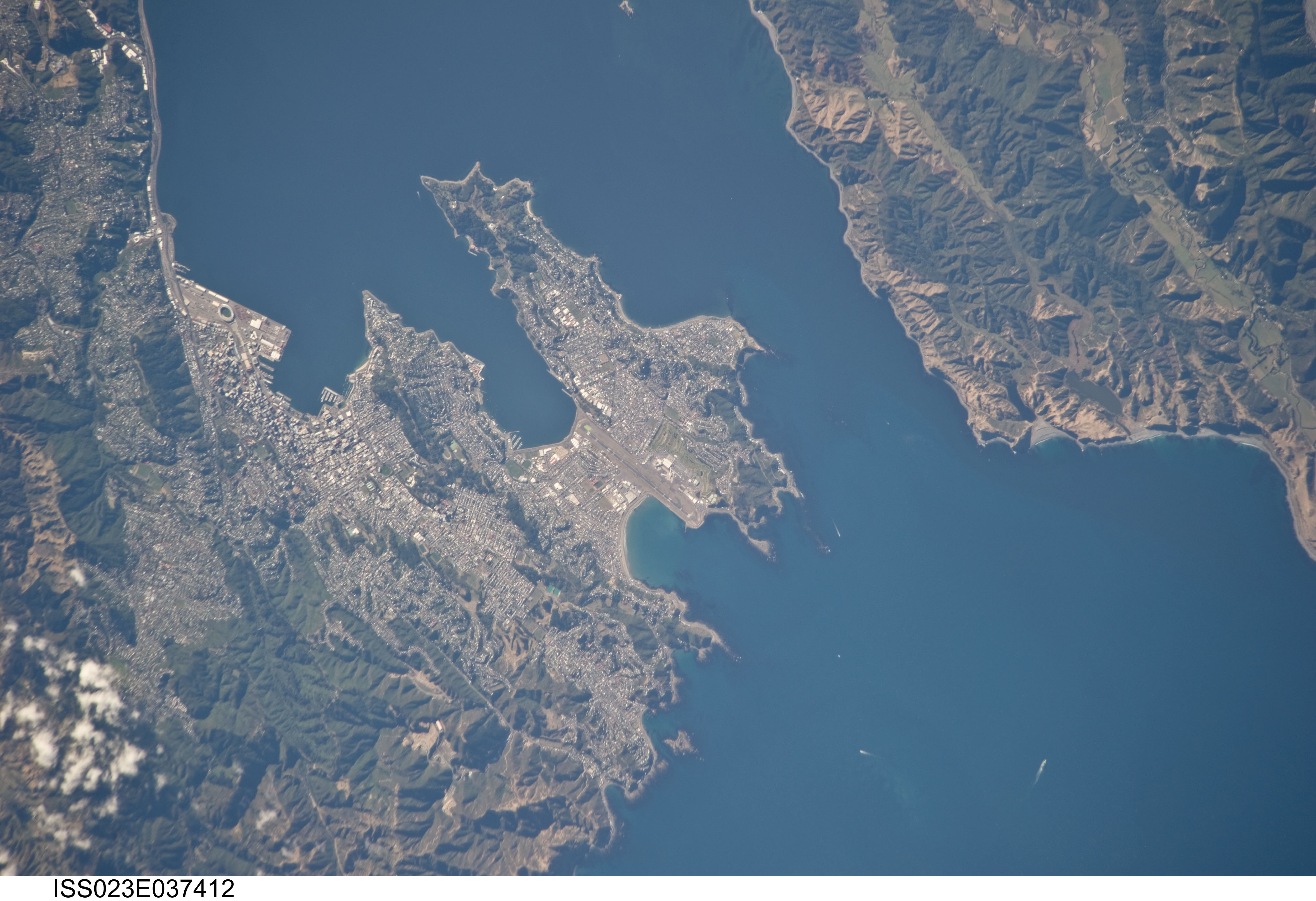

 Wellington is at the south-western tip of the North Island on
Wellington is at the south-western tip of the North Island on  Wellington's scenic natural harbour and green hillsides adorned with tiered suburbs of colonial villas are popular with tourists. The central business district (CBD) is close to Lambton Harbour, an arm of Wellington Harbour, which lies along an active Fault (geology), geological fault, clearly evident on its straight western shore. The land to the west of this rises abruptly, meaning that many suburbs sit high above the centre of the city. There is a network of bush walks and reserves maintained by the Wellington City, Wellington City Council and local volunteers. These include Otari-Wilton's Bush, dedicated to the protection and propagation of native plants. The Wellington region has of regional parks and forests. In the east is the Miramar Peninsula, connected to the rest of the city by a low-lying isthmus at
Wellington's scenic natural harbour and green hillsides adorned with tiered suburbs of colonial villas are popular with tourists. The central business district (CBD) is close to Lambton Harbour, an arm of Wellington Harbour, which lies along an active Fault (geology), geological fault, clearly evident on its straight western shore. The land to the west of this rises abruptly, meaning that many suburbs sit high above the centre of the city. There is a network of bush walks and reserves maintained by the Wellington City, Wellington City Council and local volunteers. These include Otari-Wilton's Bush, dedicated to the protection and propagation of native plants. The Wellington region has of regional parks and forests. In the east is the Miramar Peninsula, connected to the rest of the city by a low-lying isthmus at
 At the 2018 Census, 33.4% of Wellington's population was born overseas, compared with 27.1% nationally. The most common overseas birthplace is England, place of origin of 6.2% of the urban area's population. The next most-common countries of origin were India (3.1%), mainland China (2.6%), Australia (2.0%), the Philippines (1.7%), the United States (1.5%) South Africa (1.2%).
At the 2018 Census, 33.4% of Wellington's population was born overseas, compared with 27.1% nationally. The most common overseas birthplace is England, place of origin of 6.2% of the urban area's population. The next most-common countries of origin were India (3.1%), mainland China (2.6%), Australia (2.0%), the Philippines (1.7%), the United States (1.5%) South Africa (1.2%).
 Wellington showcases a variety of architectural styles from the past 150 years – 19th-century wooden cottages, such as the Italianate Katherine Mansfield Birthplace in Thorndon; streamlined Art Deco structures such as the old Wellington Free Ambulance headquarters, the Central Fire Station, Fountain Court Apartments, the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery, and the former Post and Telegraph Building; and the curves and vibrant colours of post-modern architecture in the CBD.
The oldest building is the 1858 Nairn Street Cottage in Mount Cook, Wellington, Mount Cook. The tallest building is the Majestic Centre on Willis Street at 116 metres high, the second tallest being the structural expressionist Aon Centre (Wellington) at 103 metres. Futuna Chapel in Karori is an iconic building designed by Māori architect John Scott and is architecturally considered one of the most significant New Zealand buildings of the 20th century.
Wellington showcases a variety of architectural styles from the past 150 years – 19th-century wooden cottages, such as the Italianate Katherine Mansfield Birthplace in Thorndon; streamlined Art Deco structures such as the old Wellington Free Ambulance headquarters, the Central Fire Station, Fountain Court Apartments, the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery, and the former Post and Telegraph Building; and the curves and vibrant colours of post-modern architecture in the CBD.
The oldest building is the 1858 Nairn Street Cottage in Mount Cook, Wellington, Mount Cook. The tallest building is the Majestic Centre on Willis Street at 116 metres high, the second tallest being the structural expressionist Aon Centre (Wellington) at 103 metres. Futuna Chapel in Karori is an iconic building designed by Māori architect John Scott and is architecturally considered one of the most significant New Zealand buildings of the 20th century.
 Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's is an example of 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture adapted to colonial conditions and materials, as is St Mary of the Angels, Wellington, St Mary of the Angels. Sacred Heart Cathedral, Wellington, Sacred Heart Cathedral is a Palladian architecture, Palladian Revival Basilica with the Portico of a Roman Temple, Roman or Greek temple. The Museum of Wellington City & Sea in the Wellington Harbour Board Head Office and Bond Store, Bond Store is in the Second French Empire style, and the Wellington Harbour Board Wharf Office Building is in a late English Classical style. There are several restored theatre buildings: the St. James Theatre, Wellington, St James Theatre, the Opera House, Wellington, Opera House and the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre.
Civic Square, Wellington, Te Ngākau Civic Square is surrounded by the Wellington Town Hall, Town Hall and council offices, the Michael Fowler Centre, the Wellington Central Library, the City-to-Sea bridge, Wellington, City-to-Sea Bridge, and the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery.
As it is the capital city, there are many notable government buildings. The Executive Wing of New Zealand Parliament Buildings, on the corner of Lambton Quay and Molesworth Street, was constructed between 1969 and 1981 and is commonly referred to as Beehive (New Zealand), the Beehive. Across the road is the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere, part of the Government Buildings (Wellington, NZ), old Government Buildings which now houses part of Victoria University of Wellington's Law Faculty.
A modernist building housing the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa lies on the waterfront, on Cable Street. It is strengthened using base isolation – essentially seating the entire building on supports made from lead, steel and rubber that slow down the effect of an earthquake.
Other notable buildings include Wellington Town Hall, Wellington railway station, Dominion Museum (now Massey University), Aon Centre (Wellington), Wellington Regional Stadium, and Wellington Airport at
Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's is an example of 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture adapted to colonial conditions and materials, as is St Mary of the Angels, Wellington, St Mary of the Angels. Sacred Heart Cathedral, Wellington, Sacred Heart Cathedral is a Palladian architecture, Palladian Revival Basilica with the Portico of a Roman Temple, Roman or Greek temple. The Museum of Wellington City & Sea in the Wellington Harbour Board Head Office and Bond Store, Bond Store is in the Second French Empire style, and the Wellington Harbour Board Wharf Office Building is in a late English Classical style. There are several restored theatre buildings: the St. James Theatre, Wellington, St James Theatre, the Opera House, Wellington, Opera House and the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre.
Civic Square, Wellington, Te Ngākau Civic Square is surrounded by the Wellington Town Hall, Town Hall and council offices, the Michael Fowler Centre, the Wellington Central Library, the City-to-Sea bridge, Wellington, City-to-Sea Bridge, and the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery.
As it is the capital city, there are many notable government buildings. The Executive Wing of New Zealand Parliament Buildings, on the corner of Lambton Quay and Molesworth Street, was constructed between 1969 and 1981 and is commonly referred to as Beehive (New Zealand), the Beehive. Across the road is the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere, part of the Government Buildings (Wellington, NZ), old Government Buildings which now houses part of Victoria University of Wellington's Law Faculty.
A modernist building housing the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa lies on the waterfront, on Cable Street. It is strengthened using base isolation – essentially seating the entire building on supports made from lead, steel and rubber that slow down the effect of an earthquake.
Other notable buildings include Wellington Town Hall, Wellington railway station, Dominion Museum (now Massey University), Aon Centre (Wellington), Wellington Regional Stadium, and Wellington Airport at  Wellington contains many iconic sculptures and structures, such as the Bucket Fountain in Cuba Street and ''Invisible City'' by Anton Parsons on Lambton Quay. Kinetic sculptures have been commissioned, such as the Zephyrometer. This 26-metre orange spike built for movement by artist Phil Price has been described as "tall, soaring and elegantly simple", which "reflects the swaying of the yacht masts in the Evans Bay Marina behind it" and "moves like the needle on the dial of a nautical instrument, measuring the speed of the sea or wind or vessel."
Wellington has many different architectural styles, such as classic Painted ladies, Painted Ladies in Mount Victoria, Newtown and Oriental Bay, Wooden Art Deco houses spread throughout (especially further north in the Hutt Valley), the classic masonry buildings in Cuba Street, State housing, state houses particularly in the Hutt and Wellington's southern suburbs, Railways Department's Housing Scheme, railway houses in Ngaio, New Zealand, Ngaio and other railway-side suburbs, large modern buildings in the city centre (such as the distinctive skyscraper called the Majestic Centre) and grand Victorian buildings common in the inner city as well.
Wellington contains many iconic sculptures and structures, such as the Bucket Fountain in Cuba Street and ''Invisible City'' by Anton Parsons on Lambton Quay. Kinetic sculptures have been commissioned, such as the Zephyrometer. This 26-metre orange spike built for movement by artist Phil Price has been described as "tall, soaring and elegantly simple", which "reflects the swaying of the yacht masts in the Evans Bay Marina behind it" and "moves like the needle on the dial of a nautical instrument, measuring the speed of the sea or wind or vessel."
Wellington has many different architectural styles, such as classic Painted ladies, Painted Ladies in Mount Victoria, Newtown and Oriental Bay, Wooden Art Deco houses spread throughout (especially further north in the Hutt Valley), the classic masonry buildings in Cuba Street, State housing, state houses particularly in the Hutt and Wellington's southern suburbs, Railways Department's Housing Scheme, railway houses in Ngaio, New Zealand, Ngaio and other railway-side suburbs, large modern buildings in the city centre (such as the distinctive skyscraper called the Majestic Centre) and grand Victorian buildings common in the inner city as well.

 A Wellington City Council survey conducted in March 2009 found the typical central city apartment dweller was a New Zealand native aged 24 to 35 with a professional job in the downtown area, with household income higher than surrounding areas. Three-quarters (73%) walked to work or university, 13% travelled by car, 6% by bus, 2% bicycled (although 31% own bicycles), and did not travel very far since 73% worked or studied in the central city. The large majority (88%) did not have children in their apartments; 39% were couples without children; 32% were single-person households; 15% were groups of people flatting together. Most (56%) owned their apartment; 42% rented. The report continued: "The four most important reasons for living in an apartment were given as lifestyle and city living (23%), close to work (20%), close to shops and cafes (11%) and low maintenance (11%) ... City noise and noise from neighbours were the main turnoffs for apartment dwellers (27%), followed by a lack of outdoor space (17%), living close to neighbours (9%) and apartment size and a lack of storage space (8%)."
Households are primarily one-family, making up 66.9% of households, followed by single-person households (24.7%); there were fewer multiperson households and even fewer households containing two or more families. These counts are from the 2013 census for the Wellington region (which includes the surrounding area in addition to the four cities).
A Wellington City Council survey conducted in March 2009 found the typical central city apartment dweller was a New Zealand native aged 24 to 35 with a professional job in the downtown area, with household income higher than surrounding areas. Three-quarters (73%) walked to work or university, 13% travelled by car, 6% by bus, 2% bicycled (although 31% own bicycles), and did not travel very far since 73% worked or studied in the central city. The large majority (88%) did not have children in their apartments; 39% were couples without children; 32% were single-person households; 15% were groups of people flatting together. Most (56%) owned their apartment; 42% rented. The report continued: "The four most important reasons for living in an apartment were given as lifestyle and city living (23%), close to work (20%), close to shops and cafes (11%) and low maintenance (11%) ... City noise and noise from neighbours were the main turnoffs for apartment dwellers (27%), followed by a lack of outdoor space (17%), living close to neighbours (9%) and apartment size and a lack of storage space (8%)."
Households are primarily one-family, making up 66.9% of households, followed by single-person households (24.7%); there were fewer multiperson households and even fewer households containing two or more families. These counts are from the 2013 census for the Wellington region (which includes the surrounding area in addition to the four cities).
 Wellington Harbour ranks as one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The port handles approximately 10.5 million tonnes of cargo on an annual basis, importing petroleum products, motor vehicles, minerals and exporting meats, wood products, dairy products, wool, and fruit. Many cruise ships also use the port.
The Government sector has long been a mainstay of the economy, which has typically risen and fallen with it. Traditionally, its central location meant it was the location of many head offices of various sectors – particularly finance, technology and heavy industry – many of which have since relocated to Auckland following economic deregulation and privatisation.
In recent years, tourism, arts and culture, film, and information and communications technology, ICT have played a bigger role in the economy. Wellington's median income is well above the average in New Zealand, and the highest of all New Zealand cities. It has a much higher proportion of people with tertiary qualifications than the national average. Major companies with their headquarters in Wellington include:
* Wellington Harbour, Centreport
* Chorus Limited, Chorus Networks
* Contact Energy
* The Co-operative Bank (New Zealand), The Cooperative Bank
* Datacom Group
* Infratil
* Kiwibank
* Meridian Energy
* NZ Post
* NZX
* Todd Corporation
* Trade Me
* Weta Digital
*
Wellington Harbour ranks as one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The port handles approximately 10.5 million tonnes of cargo on an annual basis, importing petroleum products, motor vehicles, minerals and exporting meats, wood products, dairy products, wool, and fruit. Many cruise ships also use the port.
The Government sector has long been a mainstay of the economy, which has typically risen and fallen with it. Traditionally, its central location meant it was the location of many head offices of various sectors – particularly finance, technology and heavy industry – many of which have since relocated to Auckland following economic deregulation and privatisation.
In recent years, tourism, arts and culture, film, and information and communications technology, ICT have played a bigger role in the economy. Wellington's median income is well above the average in New Zealand, and the highest of all New Zealand cities. It has a much higher proportion of people with tertiary qualifications than the national average. Major companies with their headquarters in Wellington include:
* Wellington Harbour, Centreport
* Chorus Limited, Chorus Networks
* Contact Energy
* The Co-operative Bank (New Zealand), The Cooperative Bank
* Datacom Group
* Infratil
* Kiwibank
* Meridian Energy
* NZ Post
* NZX
* Todd Corporation
* Trade Me
* Weta Digital
*
 Tourism is a major contributor to the city's economy, injecting approximately NZ$1.3 billion into the region annually and accounting for 9% of total FTE employment. The city is consistently named as New Zealanders' favourite destination in the quarterly FlyBuys Colmar Brunton Mood of the Traveller survey and it was ranked fourth in Lonely Planet Best in Travel 2011's Top 10 Cities to Visit in 2011. New Zealanders make up the largest visitor market, with 3.6 million visits each year; New Zealand visitors spend on average NZ$2.4 million a day. There are approximately 540,000 international visitors each year, who spend 3.7 million nights and NZ$436 million. The largest international visitor market is Australia, with over 210,000 visitors spending approximately NZ$334 million annually.
Tourism is a major contributor to the city's economy, injecting approximately NZ$1.3 billion into the region annually and accounting for 9% of total FTE employment. The city is consistently named as New Zealanders' favourite destination in the quarterly FlyBuys Colmar Brunton Mood of the Traveller survey and it was ranked fourth in Lonely Planet Best in Travel 2011's Top 10 Cities to Visit in 2011. New Zealanders make up the largest visitor market, with 3.6 million visits each year; New Zealand visitors spend on average NZ$2.4 million a day. There are approximately 540,000 international visitors each year, who spend 3.7 million nights and NZ$436 million. The largest international visitor market is Australia, with over 210,000 visitors spending approximately NZ$334 million annually.
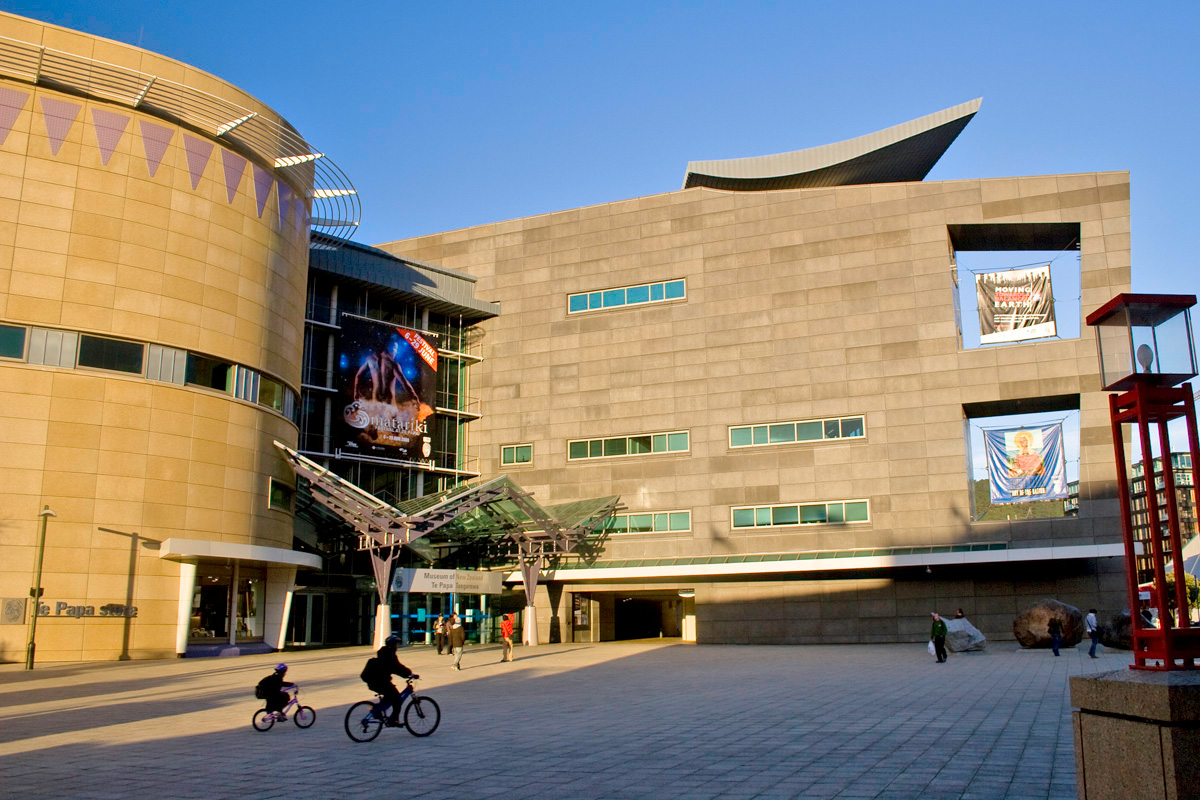 It has been argued that the construction of the Te Papa museum helped transform Wellington into a tourist destination. Wellington is marketed as the 'coolest little capital in the world' by Positively Wellington Tourism, an award-winning regional tourism organisation set up as a council controlled organisation by Wellington City Council in 1997. The organisation's council funding comes through the Downtown Levy commercial rate. In the decade to 2010, the city saw growth of over 60% in commercial guest nights. It has been promoted through a variety of campaigns and taglines, starting with the iconic Absolutely Positively Wellington advertisements. The long-term domestic marketing strategy was a finalist in the 2011 CAANZ Media Awards.
It has been argued that the construction of the Te Papa museum helped transform Wellington into a tourist destination. Wellington is marketed as the 'coolest little capital in the world' by Positively Wellington Tourism, an award-winning regional tourism organisation set up as a council controlled organisation by Wellington City Council in 1997. The organisation's council funding comes through the Downtown Levy commercial rate. In the decade to 2010, the city saw growth of over 60% in commercial guest nights. It has been promoted through a variety of campaigns and taglines, starting with the iconic Absolutely Positively Wellington advertisements. The long-term domestic marketing strategy was a finalist in the 2011 CAANZ Media Awards.
 Popular tourist attractions include Museum of Wellington City & Sea, Wellington Museum, Wellington Zoo, Zealandia (wildlife sanctuary), Zealandia and Wellington Cable Car. Cruise ship, Cruise tourism is experiencing a major boom in line with nationwide development. The 2010/11 season saw 125,000 passengers and crew visit on 60 liners. There were 80 vessels booked for visits in the 2011/12 season – estimated to inject more than NZ$31 million into the economy and representing a 74% increase in the space of two years.
Wellington is a popular conference tourism destination due to its compact nature, cultural attractions, award-winning restaurants and access to government agencies. In the year ending March 2011, there were 6,495 conference events involving nearly 800,000 delegate days; this injected approximately NZ$100 million into the economy.
Popular tourist attractions include Museum of Wellington City & Sea, Wellington Museum, Wellington Zoo, Zealandia (wildlife sanctuary), Zealandia and Wellington Cable Car. Cruise ship, Cruise tourism is experiencing a major boom in line with nationwide development. The 2010/11 season saw 125,000 passengers and crew visit on 60 liners. There were 80 vessels booked for visits in the 2011/12 season – estimated to inject more than NZ$31 million into the economy and representing a 74% increase in the space of two years.
Wellington is a popular conference tourism destination due to its compact nature, cultural attractions, award-winning restaurants and access to government agencies. In the year ending March 2011, there were 6,495 conference events involving nearly 800,000 delegate days; this injected approximately NZ$100 million into the economy.
 Wellington's culture has been befamed across the world since the 1990s for being notably "cool", incongruous and influential given the city's relatively small size (near half a million). It has been traditionally acclaimed as New Zealand's "cultural and creative capital". The city is known for its coffee scene, with now-globally common foods and drinks such as the flat white perfected here. Wellington has a strong coffee culture – the city has more cafés per capita than New York City – and was pioneered by Italians, Italian and Greek language, Greek immigrants to areas such as Mount Victoria, Wellington, Mount Victoria, Island Bay, New Zealand, Island Bay and Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar. Nascent influence is derived from Ethiopians, Ethiopian migrants. Wellington's cultural vibrance and diversity is well-known across the world. It is New Zealand's second most ethnically diverse city, bested only by Auckland, and boasts a "melting pot" culture of significant minorities such as Malaysian New Zealanders, Malaysian, Italian New Zealanders, Italian, Dutch New Zealanders, Dutch, Korean New Zealanders, Korean, Chinese New Zealanders, Chinese, Greek New Zealanders, Greek, Indian New Zealanders, Indian, Samoan New Zealanders, Samoan and indigenous Taranaki Whānui ki te Upoko o te Ika, Taranaki Whānui communities as a result. In particular, Wellington is noted for is contributions to art, cuisine and international filmmaking (with Avatar (2009 film), Avatar and The Lord of the Rings (film series), The Lord of the Rings being largely produced in the city) among many other factors listed below. The World of Wearable Art, World of Wearable Arts (WOW) is an annual event that brings lots of visitors to Wellington every year.
Wellington's culture has been befamed across the world since the 1990s for being notably "cool", incongruous and influential given the city's relatively small size (near half a million). It has been traditionally acclaimed as New Zealand's "cultural and creative capital". The city is known for its coffee scene, with now-globally common foods and drinks such as the flat white perfected here. Wellington has a strong coffee culture – the city has more cafés per capita than New York City – and was pioneered by Italians, Italian and Greek language, Greek immigrants to areas such as Mount Victoria, Wellington, Mount Victoria, Island Bay, New Zealand, Island Bay and Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar. Nascent influence is derived from Ethiopians, Ethiopian migrants. Wellington's cultural vibrance and diversity is well-known across the world. It is New Zealand's second most ethnically diverse city, bested only by Auckland, and boasts a "melting pot" culture of significant minorities such as Malaysian New Zealanders, Malaysian, Italian New Zealanders, Italian, Dutch New Zealanders, Dutch, Korean New Zealanders, Korean, Chinese New Zealanders, Chinese, Greek New Zealanders, Greek, Indian New Zealanders, Indian, Samoan New Zealanders, Samoan and indigenous Taranaki Whānui ki te Upoko o te Ika, Taranaki Whānui communities as a result. In particular, Wellington is noted for is contributions to art, cuisine and international filmmaking (with Avatar (2009 film), Avatar and The Lord of the Rings (film series), The Lord of the Rings being largely produced in the city) among many other factors listed below. The World of Wearable Art, World of Wearable Arts (WOW) is an annual event that brings lots of visitors to Wellington every year.
 Wellington is home to many cultural institutions, including Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa, Te Papa (the Museum of New Zealand), the National Library of New Zealand, Archives New Zealand, Wellington Museum (formerly the Wellington Museum of City and Sea), the Katherine Mansfield House and Garden (formerly Katherine Mansfield Birthplace), Colonial Cottage, the Wellington Cable Car Museum, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, Reserve Bank Museum, Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's, the New Zealand National War Memorial, National War Memorial Ngā Taonga Sound & Vision, Ngā Taonga Sound and Vision and the City Gallery Wellington, Wellington City Gallery.
Wellington is home to many cultural institutions, including Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa, Te Papa (the Museum of New Zealand), the National Library of New Zealand, Archives New Zealand, Wellington Museum (formerly the Wellington Museum of City and Sea), the Katherine Mansfield House and Garden (formerly Katherine Mansfield Birthplace), Colonial Cottage, the Wellington Cable Car Museum, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, Reserve Bank Museum, Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's, the New Zealand National War Memorial, National War Memorial Ngā Taonga Sound & Vision, Ngā Taonga Sound and Vision and the City Gallery Wellington, Wellington City Gallery.
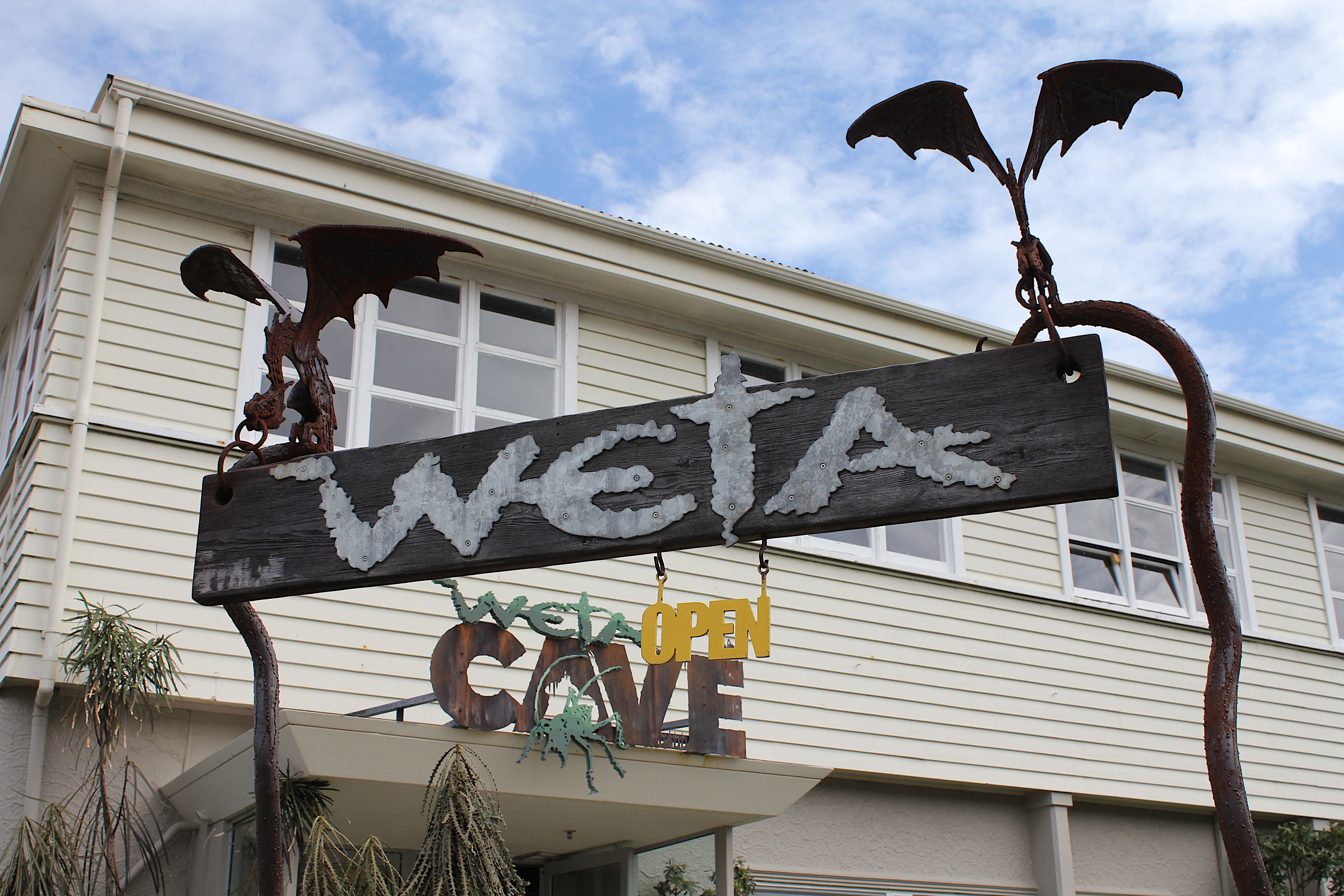 Filmmakers Peter Jackson, Sir Peter Jackson, Richard Taylor (filmmaker), Sir Richard Taylor and a growing team of creative professionals have turned the eastern suburb of Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar into a film-making, post-production and special effects infrastructure centre, giving rise to the moniker 'Wellywood'. Jackson's companies include Weta Workshop, Weta Digital, Camperdown Studios, post-production house Park Road Post, and Stone Street Studios near Wellington Airport. Films shot partly or wholly in Wellington include the The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''Lord of The Rings'' trilogy, ''King Kong (2005 film), King Kong'' and ''Avatar (2009 film), Avatar''. Jackson described Wellington: "Well, it's windy. But it's actually a lovely place, where you're pretty much surrounded by water and the bay. The city itself is quite small, but the surrounding areas are very reminiscent of the hills up in northern California, like Marin County, California, Marin County near San Francisco and the Bay Area climate and some of the architecture. Kind of a cross between that and Hawaii."
Sometime Wellington directors Jane Campion and Geoff Murphy have reached the world's screens with their independent spirit. Emerging Kiwi filmmakers, like Robert Sarkies, Taika Waititi, Costa Botes and Jennifer Bush-Daumec, are extending the Wellington-based lineage and cinematic scope. There are agencies to assist film-makers with tasks such as securing permits and scouting locations.
Wellington has a large number of independent cinemas, including the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre, Penthouse, the Roxy and Light House, which participate in film festivals throughout the year. Wellington has one of the country's highest turn-outs for the annual New Zealand International Film Festivals, New Zealand International Film Festival. There are a number of other film festivals hosted in Wellington such as Doc Edge (documentary), the Japanese Film Festival and Show Me Shorts (short films).
Filmmakers Peter Jackson, Sir Peter Jackson, Richard Taylor (filmmaker), Sir Richard Taylor and a growing team of creative professionals have turned the eastern suburb of Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar into a film-making, post-production and special effects infrastructure centre, giving rise to the moniker 'Wellywood'. Jackson's companies include Weta Workshop, Weta Digital, Camperdown Studios, post-production house Park Road Post, and Stone Street Studios near Wellington Airport. Films shot partly or wholly in Wellington include the The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''Lord of The Rings'' trilogy, ''King Kong (2005 film), King Kong'' and ''Avatar (2009 film), Avatar''. Jackson described Wellington: "Well, it's windy. But it's actually a lovely place, where you're pretty much surrounded by water and the bay. The city itself is quite small, but the surrounding areas are very reminiscent of the hills up in northern California, like Marin County, California, Marin County near San Francisco and the Bay Area climate and some of the architecture. Kind of a cross between that and Hawaii."
Sometime Wellington directors Jane Campion and Geoff Murphy have reached the world's screens with their independent spirit. Emerging Kiwi filmmakers, like Robert Sarkies, Taika Waititi, Costa Botes and Jennifer Bush-Daumec, are extending the Wellington-based lineage and cinematic scope. There are agencies to assist film-makers with tasks such as securing permits and scouting locations.
Wellington has a large number of independent cinemas, including the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre, Penthouse, the Roxy and Light House, which participate in film festivals throughout the year. Wellington has one of the country's highest turn-outs for the annual New Zealand International Film Festivals, New Zealand International Film Festival. There are a number of other film festivals hosted in Wellington such as Doc Edge (documentary), the Japanese Film Festival and Show Me Shorts (short films).
File:St James Theatre.jpg, St. James Theatre, Wellington, St. James Theatre on Courtenay Place, Wellington, Courtenay Place, the main street of Wellington's entertainment district
File:Te Auaha.tif, Te Auaha, venue and performing arts school, Wellington
File:Te Whaea.tif, Te Whaea, venue and home to the New Zealand School of Dance and Toi Whakaari: NZ Drama School
File:BATS Theatre foyer 03 (cropped).jpg, BATS Theatre foyer
File:Circa Theatre.jpg, Circa Theatre
File:The Opera House, Wellington, interior.jpg, The Opera House (interior)
File:Hannah Playhouse.jpg, The Hannah Playhouse
File:Wellington NZ7 3363.jpg
File:Wellington NZ7 3367.jpg
 Wellington is characterised by small dining establishments, and its coffee culture, café culture is internationally recognised, being known for its large number of coffeehouses. There are a few iconic cafes that started the obsession with coffee that Wellington has. One of these is the Deluxe Expresso Bar that opened in 1988. Wellington Restaurants offer cuisines including from Europe, Asia and Polynesia; for dishes that have a distinctly cuisine of New Zealand, New Zealand style, there are lamb, pork and cervena (venison), salmon, crayfish (lobster), Bluff oysters, pāua (abalone), mussels, scallops, Paphies australis, pipis and tuatua (both New Zealand shellfish); kumara (sweet potato); kiwifruit and tamarillo; and Pavlova (food), pavlova, the national dessert.
Wellington is characterised by small dining establishments, and its coffee culture, café culture is internationally recognised, being known for its large number of coffeehouses. There are a few iconic cafes that started the obsession with coffee that Wellington has. One of these is the Deluxe Expresso Bar that opened in 1988. Wellington Restaurants offer cuisines including from Europe, Asia and Polynesia; for dishes that have a distinctly cuisine of New Zealand, New Zealand style, there are lamb, pork and cervena (venison), salmon, crayfish (lobster), Bluff oysters, pāua (abalone), mussels, scallops, Paphies australis, pipis and tuatua (both New Zealand shellfish); kumara (sweet potato); kiwifruit and tamarillo; and Pavlova (food), pavlova, the national dessert.
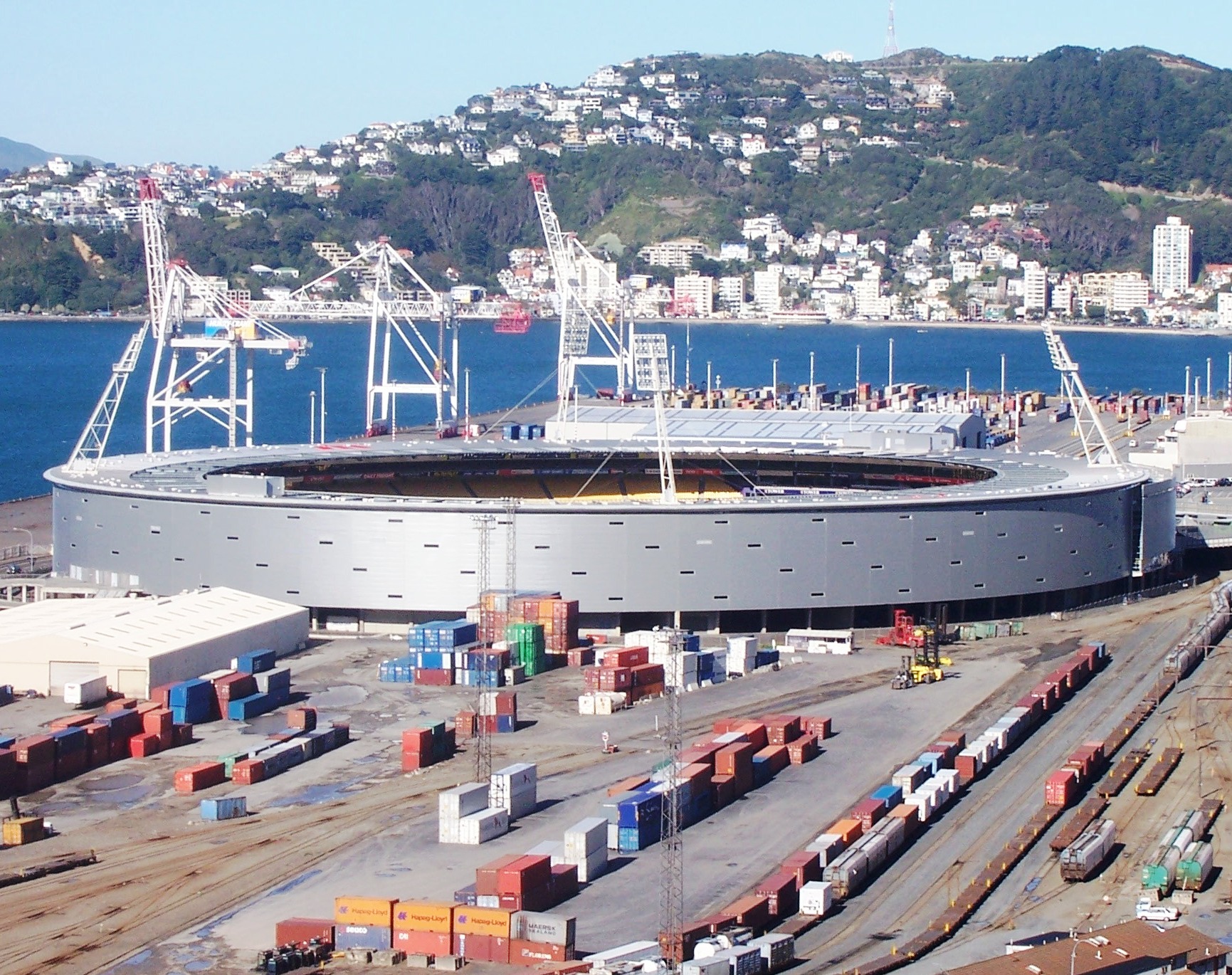 Wellington is the home to:
* Hurricanes (rugby union), Hurricanes – Super Rugby team based in Wellington
* Wellington Rugby Football Union, Wellington Lions – ITM Cup rugby team
* Wellington Phoenix FC – Association football, football (soccer) club playing in the Australasian A-League, the only fully professional football club in New Zealand
* Team Wellington – in the semi-professional New Zealand Football Championship
* Central Pulse – netball team representing the Lower North Island in the ANZ Championship, primarily based in Wellington
* Wellington Firebirds and Wellington Blaze – men's and women's cricket teams
* Wellington Saints – basketball team in the National Basketball League (New Zealand), National Basketball League
Sporting events include:
* six pool games and two quarter-final games at the 2011 Rugby World Cup
* the Wellington Sevens – a round of the IRB Sevens World Series held at the Wellington Regional Stadium over several days every February.
* the 2011 Tae Kwon Do World Champs
* The 2014 World Field Target Championships
* the World Fell running, Mountain Running Championships in 2005
* the Wellington 500 Street racing, street race for touring car racing, touring cars, between 1985 and 1996
Wellington is the home to:
* Hurricanes (rugby union), Hurricanes – Super Rugby team based in Wellington
* Wellington Rugby Football Union, Wellington Lions – ITM Cup rugby team
* Wellington Phoenix FC – Association football, football (soccer) club playing in the Australasian A-League, the only fully professional football club in New Zealand
* Team Wellington – in the semi-professional New Zealand Football Championship
* Central Pulse – netball team representing the Lower North Island in the ANZ Championship, primarily based in Wellington
* Wellington Firebirds and Wellington Blaze – men's and women's cricket teams
* Wellington Saints – basketball team in the National Basketball League (New Zealand), National Basketball League
Sporting events include:
* six pool games and two quarter-final games at the 2011 Rugby World Cup
* the Wellington Sevens – a round of the IRB Sevens World Series held at the Wellington Regional Stadium over several days every February.
* the 2011 Tae Kwon Do World Champs
* The 2014 World Field Target Championships
* the World Fell running, Mountain Running Championships in 2005
* the Wellington 500 Street racing, street race for touring car racing, touring cars, between 1985 and 1996
 Wellington city is administered by the Territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authority of Wellington City Council. The present mayor of the Wellington City Council is Tory Whanau, who was 2022 Wellington City mayoral election, elected in 2022.
Wellington is also part of the wider
Wellington city is administered by the Territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authority of Wellington City Council. The present mayor of the Wellington City Council is Tory Whanau, who was 2022 Wellington City mayoral election, elected in 2022.
Wellington is also part of the wider
 Victoria University of Wellington has four campuses and works with a three-trimester system (beginning March, July, and November). It enrolled 21,380 students in 2008; of these, 16,609 were full-time students. Of all students, 56% were female and 44% male. While the student body was primarily New Zealanders of European descent, 1,713 were Maori, 1,024 were Pacific students, 2,765 were international students. 5,751 degrees, diplomas and certificates were awarded. The university has 1,930 full-time employees.
Massey University has a Wellington campus known as the "creative campus" and offers courses in communication and business, engineering and technology, health and well-being, and creative arts. Its school of design was established in 1886 and has research centres for studying public health, sleep, Maori health, small & medium enterprises, disasters, and tertiary teaching excellence. It combined with Victoria University to create the New Zealand School of Music.
The University of Otago has a Wellington branch with its Wellington School of Medicine and Health.
Whitireia New Zealand has large campuses in Porirua, Wellington and Kapiti; the Wellington Institute of Technology and New Zealand's National Drama school, Toi Whakaari. The Wellington area has numerous primary and secondary schools.
Victoria University of Wellington has four campuses and works with a three-trimester system (beginning March, July, and November). It enrolled 21,380 students in 2008; of these, 16,609 were full-time students. Of all students, 56% were female and 44% male. While the student body was primarily New Zealanders of European descent, 1,713 were Maori, 1,024 were Pacific students, 2,765 were international students. 5,751 degrees, diplomas and certificates were awarded. The university has 1,930 full-time employees.
Massey University has a Wellington campus known as the "creative campus" and offers courses in communication and business, engineering and technology, health and well-being, and creative arts. Its school of design was established in 1886 and has research centres for studying public health, sleep, Maori health, small & medium enterprises, disasters, and tertiary teaching excellence. It combined with Victoria University to create the New Zealand School of Music.
The University of Otago has a Wellington branch with its Wellington School of Medicine and Health.
Whitireia New Zealand has large campuses in Porirua, Wellington and Kapiti; the Wellington Institute of Technology and New Zealand's National Drama school, Toi Whakaari. The Wellington area has numerous primary and secondary schools.
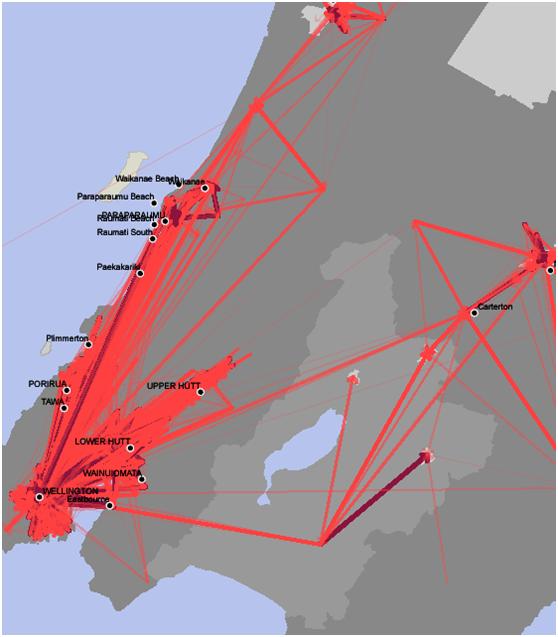 Wellington is served by State Highway 1 (New Zealand), State Highway 1 in the west and State Highway 2 (New Zealand), State Highway 2 in the east, meeting at the Ngauranga Interchange north of the city centre, where SH 1 runs through the city to the airport. There are two other state highways in the wider region: State Highway 58 (New Zealand), State Highway 58 which provides a direct connection between the Hutt Valley and Porirua, and State Highway 59 (New Zealand), State Highway 59 which follows a coastal route between Linden and Mackays Crossing and was previously part of SH 1. Road access into the capital is constrained by the mountainous terrain – between Wellington and the Kapiti Coast, SH 1 passes through the steep and narrow Wainui Saddle, nearby SH 59 travels along the Centennial Highway, a narrow section of road between the Paekākāriki Escarpment and the Tasman Sea, and between Wellington and Wairarapa SH 2 transverses the Rimutaka Ranges on a similar narrow winding road. Wellington has two motorways: the Johnsonville–Porirua Motorway (largely part of SH 1, with the northernmost section part of SH 59) and the Wellington Urban Motorway (entirely part of SH 1), which in combination with a small non-motorway section in the Ngauranga Gorge connect Porirua with Wellington city. A third motorway in the wider region, the Transmission Gully Motorway forming part of the SH 1 route and officially opened on 30 March 2022, leaves the Johnsonville-Porirua Motorway at the boundary between Wellington and Porirua and provides the main route between Wellington and the wider North Island.
Bus transport in Wellington is supplied by several different operators under the banner of Metlink. Buses serve almost every part of Wellington city, with most of them running along the "Golden Mile" from Wellington railway station to Courtenay Place, Wellington, Courtenay Place. Until October 2017 there were nine trolleybus routes, all other buses running on Diesel fuel, diesel. The Trolleybuses in Wellington, trolleybus network was the last public system of its kind in the southern hemisphere.
Wellington lies at the southern end of the North Island Main Trunk railway (NIMT) and the Wairarapa Line, converging on Wellington railway station at the northern end of central Wellington. One long-distance service leaves from Wellington: the Capital Connection, for commuters from Palmerston North. The Northern Explorer to Auckland was discontinued in December 2021.
Four Railway electrification system, electrified suburban rail, suburban lines radiate from Wellington railway station to the outer suburbs to the north of Wellington – the Johnsonville Line through the hillside suburbs north of central Wellington; the Kapiti Line along the NIMT to Waikanae on the Kapiti Coast via Porirua and Paraparaumu; the Melling Line to Lower Hutt via Petone; and the Hutt Valley Line along the Wairarapa Line via Waterloo and Taitā, New Zealand, Taitā to Upper Hutt. A diesel-hauled carriage service, the Wairarapa Connection, connects several times daily to Masterton in the Wairarapa via the Rimutaka Tunnel. Combined, these five services carry 11.64 million passengers per year.
Wellington is served by State Highway 1 (New Zealand), State Highway 1 in the west and State Highway 2 (New Zealand), State Highway 2 in the east, meeting at the Ngauranga Interchange north of the city centre, where SH 1 runs through the city to the airport. There are two other state highways in the wider region: State Highway 58 (New Zealand), State Highway 58 which provides a direct connection between the Hutt Valley and Porirua, and State Highway 59 (New Zealand), State Highway 59 which follows a coastal route between Linden and Mackays Crossing and was previously part of SH 1. Road access into the capital is constrained by the mountainous terrain – between Wellington and the Kapiti Coast, SH 1 passes through the steep and narrow Wainui Saddle, nearby SH 59 travels along the Centennial Highway, a narrow section of road between the Paekākāriki Escarpment and the Tasman Sea, and between Wellington and Wairarapa SH 2 transverses the Rimutaka Ranges on a similar narrow winding road. Wellington has two motorways: the Johnsonville–Porirua Motorway (largely part of SH 1, with the northernmost section part of SH 59) and the Wellington Urban Motorway (entirely part of SH 1), which in combination with a small non-motorway section in the Ngauranga Gorge connect Porirua with Wellington city. A third motorway in the wider region, the Transmission Gully Motorway forming part of the SH 1 route and officially opened on 30 March 2022, leaves the Johnsonville-Porirua Motorway at the boundary between Wellington and Porirua and provides the main route between Wellington and the wider North Island.
Bus transport in Wellington is supplied by several different operators under the banner of Metlink. Buses serve almost every part of Wellington city, with most of them running along the "Golden Mile" from Wellington railway station to Courtenay Place, Wellington, Courtenay Place. Until October 2017 there were nine trolleybus routes, all other buses running on Diesel fuel, diesel. The Trolleybuses in Wellington, trolleybus network was the last public system of its kind in the southern hemisphere.
Wellington lies at the southern end of the North Island Main Trunk railway (NIMT) and the Wairarapa Line, converging on Wellington railway station at the northern end of central Wellington. One long-distance service leaves from Wellington: the Capital Connection, for commuters from Palmerston North. The Northern Explorer to Auckland was discontinued in December 2021.
Four Railway electrification system, electrified suburban rail, suburban lines radiate from Wellington railway station to the outer suburbs to the north of Wellington – the Johnsonville Line through the hillside suburbs north of central Wellington; the Kapiti Line along the NIMT to Waikanae on the Kapiti Coast via Porirua and Paraparaumu; the Melling Line to Lower Hutt via Petone; and the Hutt Valley Line along the Wairarapa Line via Waterloo and Taitā, New Zealand, Taitā to Upper Hutt. A diesel-hauled carriage service, the Wairarapa Connection, connects several times daily to Masterton in the Wairarapa via the Rimutaka Tunnel. Combined, these five services carry 11.64 million passengers per year.
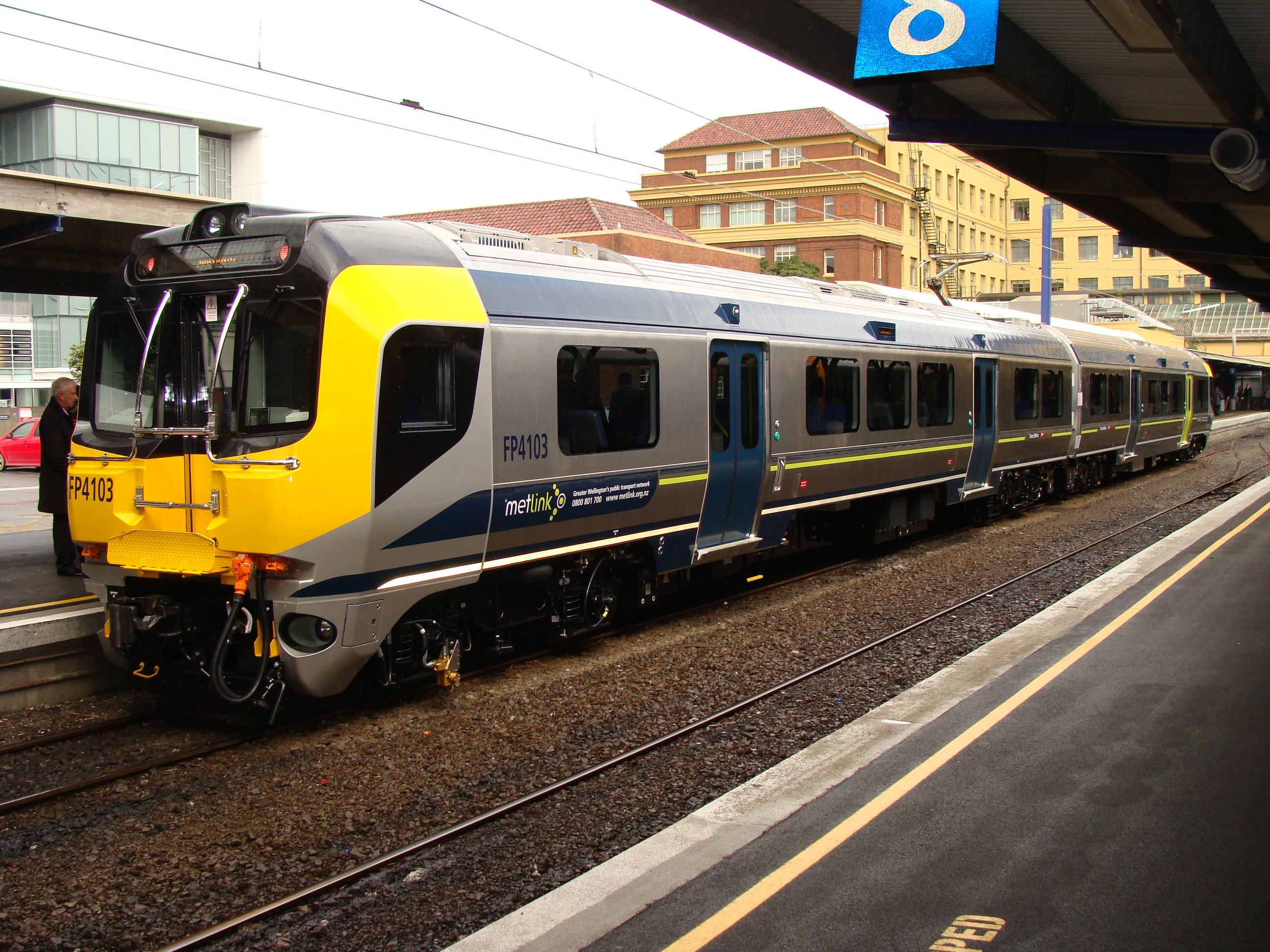 Wellington is the North Island port for
Wellington is the North Island port for

 The urban areas of the four local authorities have a combined population of residents as of .
The four cities comprising the Wellington metropolitan area have a total population of with the urban area containing % of that population. The remaining areas are largely mountainous and sparsely farmed or parkland and are outside the urban area boundary. More than most cities, life is dominated by its central business district (CBD). Approximately 62,000 people work in the CBD, only 4,000 fewer than work in Auckland's CBD, despite that city having four times the population.
The Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki combined urban area in the Kapiti Coast district is sometimes included in the Wellington metro area due to its exurban nature and strong transport links with Wellington. If included as part of Wellington metro, Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki would add to the population (as of ).
Featherston, New Zealand, Featherston and Greytown, New Zealand, Greytown in the Wairarapa are rarely considered part of the Wellington metropolitan area, being physically separated from the rest of the metropolitan area by the Remutaka Range. However, both have significant proportions of their employed population working in Wellington city and the Hutt Valley (36.1% and 17.1% in 2006 respectively) and are considered part of the Wellington functional urban area by Statistics New Zealand.
The four urban areas combined had a usual resident population of 401,850 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 26,307 people (7.0%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, and an increase of 42,726 people (11.9%) since the 2006 New Zealand census, 2006 census. There were 196,911 males and 204,936 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.961 males per female. Of the total population, 74,892 people (18.6%) were aged up to 15 years, 93,966 (23.4%) were 15 to 29, 185,052 (46.1%) were 30 to 64, and 47,952 (11.9%) were 65 or older.
The urban areas of the four local authorities have a combined population of residents as of .
The four cities comprising the Wellington metropolitan area have a total population of with the urban area containing % of that population. The remaining areas are largely mountainous and sparsely farmed or parkland and are outside the urban area boundary. More than most cities, life is dominated by its central business district (CBD). Approximately 62,000 people work in the CBD, only 4,000 fewer than work in Auckland's CBD, despite that city having four times the population.
The Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki combined urban area in the Kapiti Coast district is sometimes included in the Wellington metro area due to its exurban nature and strong transport links with Wellington. If included as part of Wellington metro, Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki would add to the population (as of ).
Featherston, New Zealand, Featherston and Greytown, New Zealand, Greytown in the Wairarapa are rarely considered part of the Wellington metropolitan area, being physically separated from the rest of the metropolitan area by the Remutaka Range. However, both have significant proportions of their employed population working in Wellington city and the Hutt Valley (36.1% and 17.1% in 2006 respectively) and are considered part of the Wellington functional urban area by Statistics New Zealand.
The four urban areas combined had a usual resident population of 401,850 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 26,307 people (7.0%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, and an increase of 42,726 people (11.9%) since the 2006 New Zealand census, 2006 census. There were 196,911 males and 204,936 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.961 males per female. Of the total population, 74,892 people (18.6%) were aged up to 15 years, 93,966 (23.4%) were 15 to 29, 185,052 (46.1%) were 30 to 64, and 47,952 (11.9%) were 65 or older.
"Wellington City Annual Economic Profile 2013"
, by Infometrics for Grow Wellington Ltd.
Greater Wellington Regional Council
Official NZ Tourism website for Wellington
Wellington City Council
Wellington
in Te Ara the Encyclopedia of New Zealand
Notes on a New Zealand City: Wellington
{{Authority control Wellington, Capitals in Oceania Former provincial capitals of New Zealand Populated coastal places in New Zealand Populated places established in 1840 Populated places in the Wellington Region Port cities in New Zealand
Te Whanganui-a-Tara
Te Whanganui-a-Tara is the Māori name for Wellington Harbour. The term is also used to refer to the city of Wellington which lies on the shores of the harbour. ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'' translates as "the great harbour of Tara", named for Tara, a s ...
or ) is the capital city of New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metro area, and is the administrative centre of the Wellington Region
Greater Wellington, also known as the Wellington Region (Māori: ''Te Upoko o te Ika''), is a non-unitary region of New Zealand that occupies the southernmost part of the North Island. The region covers an area of , and has a population of
T ...
. It is the world's southernmost capital of a sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
. Wellington features a temperate maritime climate, and is the world's windiest city by average wind speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer.
Wind speed ...
.
Legends recount that Kupe
Kupe ( ~1180-1320) was a legendary Polynesian explorer, navigator and great rangatira of Hawaiki, who is said to have been the first human to discover New Zealand. Whether Kupe existed historically is likely but difficult to confirm. He is g ...
discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century, with initial settlement by Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
iwi
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori roughly means "people" or "nation", and is often translated as "tribe", or "a confederation of tribes". The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, ...
such as Rangitāne and Muaūpoko
Muaūpoko is a Māori iwi on the Kapiti Coast of New Zealand.
Muaūpoko are descended from the ancestor Tara, whose name has been given to many New Zealand landmarks, most notably Te Whanganui-a-Tara (Wellington). His people were known as Ng� ...
. The disruptions of the Musket Wars
The Musket Wars were a series of as many as 3,000 battles and raids fought throughout New Zealand (including the Chatham Islands) among Māori between 1807 and 1837, after Māori first obtained muskets and then engaged in an intertribal arms rac ...
led to them being overwhelmed by northern iwi such as Te Āti Awa
Te Āti Awa is a Māori iwi with traditional bases in the Taranaki and Wellington regions of New Zealand. Approximately 17,000 people registered their affiliation to Te Āti Awa in 2001, with around 10,000 in Taranaki, 2,000 in Wellington and aro ...
by the early 19th century.
Wellington's current form was originally designed by Captain William Mein Smith
William Mein Smith (also known as Kapene Mete; 1798 – 3 January 1869) was a key figure in the settlement of Wellington, New Zealand. As the Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company at Port Nicholson from 1840 to 1843, he ...
, the first Surveyor General for Edward Wakefield's New Zealand Company
The New Zealand Company, chartered in the United Kingdom, was a company that existed in the first half of the 19th century on a business model focused on the systematic colonisation of New Zealand. The company was formed to carry out the principl ...
, in 1840. The Wellington urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
, which only includes urbanised areas within Wellington City, has a population of as of . The wider Wellington metropolitan area, including the cities of Lower Hutt, Porirua and Upper Hutt
Upper Hutt ( mi, Te Awa Kairangi ki Uta) is a city in the Wellington Region of New Zealand and one of the four cities that constitute the Wellington metropolitan area.
Geography
The Upper Hutt city centre lies approximately 26 km north-e ...
, has a population of as of . The city has served as New Zealand's capital since 1865, a status that is not defined in legislation, but established by convention; the New Zealand Government and Parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
, the Supreme Court and most of the public service are based in the city.
Wellington's economy is primarily service-based, with an emphasis on finance, business services, government, and the film industry. It is the centre of New Zealand's film and special effects industries, and increasingly a hub for information technology and innovation, with two public research universities. Wellington is one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The city is chiefly served by Wellington International Airport
Wellington International Airport (formerly known as Rongotai Airport) is an international airport located in the suburb of Rongotai in Wellington. It lies 3 NM or 5.5 km south-east from the city centre. It is a hub for Air New Zealand an ...
in Rongotai
Rongotai is a suburb of Wellington, New Zealand, located southeast of the city centre. It is on the Rongotai isthmus, between the Miramar Peninsula and the suburbs of Kilbirnie and Lyall Bay. It is known mostly for being the location of the We ...
, the country's second-busiest airport. Wellington's transport network includes train and bus lines which reach as far as the Kapiti Coast and the Wairarapa, and ferries connect the city to the South Island.
Often referred to as New Zealand's cultural capital, the culture of Wellington is a diverse and often youth-driven one which has wielded influence across Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern and Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of and a population of around 44.5 million ...
. One of the world's most liveable cities
City quality of life indices are lists of cities that are ranked according to a defined measure of living conditions. In addition to considering the provision of clean water, clean air, adequate food and shelter, many indexes also measure more ...
, the 2021 Global Livability Ranking tied Wellington with Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and List of cities in Japan, largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, ...
as fourth in the world. From 2017 to 2018, Deutsche Bank
Deutsche Bank AG (), sometimes referred to simply as Deutsche, is a German multinational investment bank and financial services company headquartered in Frankfurt, Germany, and dual-listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange and the New York Sto ...
ranked it first in the world for both livability and non-pollution. Cultural precincts such as Cuba Street and Newtown are renowned for creative innovation, " op shops", historic character, and food. Wellington is a leading financial centre in the Asia-Pacific region, being ranked 35th in the world by the Global Financial Centres Index
The Global Financial Centres Index (GFCI) is a ranking of the competitiveness of financial centres based on over 29,000 financial centre assessments from an online questionnaire together with over 100 indices from organisations such as the World ...
for 2021. The global city has grown from a bustling Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
settlement, to a colonial outpost, and from there to an Australasia
Australasia is a region that comprises Australia, New Zealand and some neighbouring islands in the Pacific Ocean. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologi ...
n capital that has experienced a "remarkable creative resurgence".
Toponymy
Wellington takes its name from Arthur Wellesley, the firstDuke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish people, Anglo-Irish soldier and Tories (British political party), Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of Uni ...
and victor of the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
(1815): his title comes from the town of Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by metr ...
in the English county of Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
. It was named in November 1840 by the original settlers of the New Zealand Company
The New Zealand Company, chartered in the United Kingdom, was a company that existed in the first half of the 19th century on a business model focused on the systematic colonisation of New Zealand. The company was formed to carry out the principl ...
on the suggestion of the directors of the same, in recognition of the Duke's strong support for the company's principles of colonisation and his "strenuous and successful defence against its enemies of the measure for colonising South Australia". One of the founders of the settlement, Edward Jerningham Wakefield
Edward Jerningham Wakefield (25 June 1820 – 3 March 1879), known as Jerningham Wakefield, was the only son of Edward Gibbon Wakefield. As such, he was closely associated with his father's interest in colonisation. He worked for the New Zealand ...
, reported that the settlers "took up the views of the directors with great cordiality and the new name was at once adopted".Wakefield, Edward Jerningham (1845). ''Adventure in New Zealand'', Vol. 1, pub. John Murray.
In the Māori language, Wellington has three names. refers to Wellington Harbour and means "the great harbour of Tara". Another is , commonly held to be a phonetic Māori transliteration of "Port Nick", short for "Port Nicholson
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
". An alternative possible etymology for comes from a shortening of the phrase , meaning "the journey into the night", referring to the exodus of Te Āti Awa
Te Āti Awa is a Māori iwi with traditional bases in the Taranaki and Wellington regions of New Zealand. Approximately 17,000 people registered their affiliation to Te Āti Awa in 2001, with around 10,000 in Taranaki, 2,000 in Wellington and aro ...
after they were displaced from the Wellington area by the first Europeans. The city's central marae
A ' (in New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan), ' (in Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term a ...
, the community supporting it and its group have the pseudo-tribal name of Ngāti Pōneke. is another, meaning 'The Head of the Fish of Māui' (often shortened to ''Te Upoko-o-te-Ika''), a traditional name for the southernmost part of the North Island, deriving from the legend of the fishing up of the island by the demi-god Māui. The legendary Maori explorer Kupe
Kupe ( ~1180-1320) was a legendary Polynesian explorer, navigator and great rangatira of Hawaiki, who is said to have been the first human to discover New Zealand. Whether Kupe existed historically is likely but difficult to confirm. He is g ...
, a chief from Hawaiki
In Polynesian mythology, (also rendered as in Cook Islands Māori, in Samoan, in Tahitian, in Hawaiian) is the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in many Māori stories. ...
(the homeland of Polynesian explorers, of unconfirmed geographical location, not to be confused with Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
), was said to have stayed in the harbour prior to 1000 CE. Here, it is said he had a notable impact on the area, with local mythology stating he named the two islands in the harbour after his daughters, Matiu (Somes Island), and Mākaro (Ward Island). However, the primary settlement of Wellington is said to have been executed by Tara, the son of Whatonga, a chief from the Māhia Peninsula
Māhia Peninsula (Maori: or ) is located on the east coast of New Zealand's North Island, in the Hawke's Bay region, between the towns of Wairoa and Gisborne.
Rocket Lab has set up its Launch Complex 1 close to Ahuriri Point at the south ...
, who told his son to travel south, to find more fertile lands to settle.
In New Zealand Sign Language
New Zealand Sign Language or NZSL ( mi, te reo Turi) is the main language of the deaf community in New Zealand. It became an official language of New Zealand in April 2006 under the New Zealand Sign Language Act 2006. The purpose of the act was ...
, the name is signed by raising the index, middle and ring fingers of one hand, palm forward, to form a "W", and shaking it slightly from side to side twice.
The city's location close to the mouth of the narrow Cook Strait leaves it vulnerable to strong gales, leading to the nickname
A nickname is a substitute for the proper name of a familiar person, place or thing. Commonly used to express affection, a form of endearment, and sometimes amusement, it can also be used to express defamation of character. As a concept, it is ...
of "Windy Wellington".
History

Māori settlement
Legends recount thatKupe
Kupe ( ~1180-1320) was a legendary Polynesian explorer, navigator and great rangatira of Hawaiki, who is said to have been the first human to discover New Zealand. Whether Kupe existed historically is likely but difficult to confirm. He is g ...
discovered and explored the region in about the 10th century. Before European colonisation, the area in which the city of Wellington would eventually be founded was seasonally inhabited by indigenous Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
. The earliest date with hard evidence for human activity in New Zealand is about 1280.
Wellington and its environs have been occupied by various Māori groups from the 12th century. The legendary Polynesian explorer Kupe
Kupe ( ~1180-1320) was a legendary Polynesian explorer, navigator and great rangatira of Hawaiki, who is said to have been the first human to discover New Zealand. Whether Kupe existed historically is likely but difficult to confirm. He is g ...
, a chief from Hawaiki
In Polynesian mythology, (also rendered as in Cook Islands Māori, in Samoan, in Tahitian, in Hawaiian) is the original home of the Polynesians, before dispersal across Polynesia. It also features as the underworld in many Māori stories. ...
(the homeland of Polynesian explorers, of unconfirmed geographical location, not to be confused with Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
), was said to have stayed in the harbour from . A later Māori explorer, Whatonga, named the harbour ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara
Te Whanganui-a-Tara is the Māori name for Wellington Harbour. The term is also used to refer to the city of Wellington which lies on the shores of the harbour. ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'' translates as "the great harbour of Tara", named for Tara, a s ...
'' after his son Tara. Before the 1820s, most of the inhabitants of the Wellington region were Whatonga's descendants.
At about 1820, the people living there were Ngāti Ira and other groups who traced their descent from the explorer Whatonga, including Rangitāne and Muaūpoko
Muaūpoko is a Māori iwi on the Kapiti Coast of New Zealand.
Muaūpoko are descended from the ancestor Tara, whose name has been given to many New Zealand landmarks, most notably Te Whanganui-a-Tara (Wellington). His people were known as Ng� ...
. However, these groups were eventually forced out of ''Te Whanganui-a-Tara'' by a series of migrations other iwi
Iwi () are the largest social units in New Zealand Māori society. In Māori roughly means "people" or "nation", and is often translated as "tribe", or "a confederation of tribes". The word is both singular and plural in the Māori language, ...
(Māori tribes) from the north. The migrating groups were Ngāti Toa
Ngāti Toa, Ngāti Toarangatira or Ngāti Toa Rangatira, is a Māori '' iwi'' (tribe) based in the southern North Island and in the northern South Island of New Zealand. Its '' rohe'' (tribal area) extends from Whanganui in the north, Palmerston ...
, which came from Kāwhia, Ngāti Rangatahi, from near Taumarunui
Taumarunui is a small town in the King Country of the central North Island of New Zealand. It is on an alluvial plain set within rugged terrain on the upper reaches of the Whanganui River, 65 km south of Te Kuiti and 55 km west of T ...
, and Te Atiawa, Ngāti Tama
Ngāti Tama is a historic Māori iwi of present-day New Zealand which whakapapas back to Tama Ariki, the chief navigator on the Tokomaru waka. The iwi of Ngati Tama is located in north Taranaki around Poutama. The Mōhakatino river marks the ...
, Ngāti Mutunga
Ngāti Mutunga is a Māori iwi (tribe) of New Zealand, whose original tribal lands were in north Taranaki. They migrated from Taranaki, first to Wellington (with Ngāti Toa and other Taranaki Hāpu), and then to the Chatham Islands (along wit ...
, Taranaki and Ngāti Ruanui
Ngāti Ruanui is a Māori iwi traditionally based in the Taranaki region of New Zealand. In the 2006 census, 7,035 people claimed affiliation to the iwi. However, most members now live outside the traditional areas of the iwi.
History Early his ...
from Taranaki
Taranaki is a region in the west of New Zealand's North Island. It is named after its main geographical feature, the stratovolcano of Mount Taranaki, also known as Mount Egmont.
The main centre is the city of New Plymouth. The New Plymouth D ...
. Ngāti Mutunga later moved on to the Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands ( ) (Moriori: ''Rēkohu'', 'Misty Sun'; mi, Wharekauri) are an archipelago in the Pacific Ocean about east of New Zealand's South Island. They are administered as part of New Zealand. The archipelago consists of about te ...
. The Waitangi Tribunal
The Waitangi Tribunal (Māori: ''Te Rōpū Whakamana i te Tiriti o Waitangi'') is a New Zealand permanent commission of inquiry established under the Treaty of Waitangi Act 1975. It is charged with investigating and making recommendations on cla ...
has found that at the time of the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the History of New Zealand, history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in ...
in 1840, Te Atiawa, Taranaki, Ngāti Ruanui, Ngāti Tama, and Ngāti Toa held mana whenua interests in the area, through conquest and occupation.
Early European settlement
Steps towards Pākehā (European) settlement in the area began in 1839, when ColonelWilliam Wakefield
William Hayward Wakefield (1801 – 19 September 1848) was an English colonel, the leader of the first colonising expedition to New Zealand and one of the founders of Wellington. As a leader, he attracted much controversy.
Early life
William W ...
arrived to purchase land for the New Zealand Company
The New Zealand Company, chartered in the United Kingdom, was a company that existed in the first half of the 19th century on a business model focused on the systematic colonisation of New Zealand. The company was formed to carry out the principl ...
to sell to prospective British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
settlers. Prior to this time, the Māori inhabitants had had contact with Pākehā whalers and traders.
European settlement began with the arrival of an advance party of the New Zealand Company on the ship ''Tory
A Tory () is a person who holds a political philosophy known as Toryism, based on a British version of traditionalism and conservatism, which upholds the supremacy of social order as it has evolved in the English culture throughout history. The ...
'' on 20 September 1839, followed by 150 settlers on the ''Aurora
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
'' on 22 January 1840. Thus the Wellington settlement preceded the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the History of New Zealand, history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in ...
(on 6 February 1840). The 1840 settlers constructed their first homes at Petone
Petone (Māori: ''Pito-one''), a large suburb of Lower Hutt, Wellington, stands at the southern end of the Hutt Valley, on the northern shore of Wellington Harbour. The Māori name means "end of the sand beach".
Europeans first settled in P ...
(which they called Britannia for a time) on the flat area at the mouth of the Hutt River. Within months that area proved swampy and flood-prone, and most of the newcomers transplanted their settlement across Wellington Harbour to Thorndon in the present-day site of Wellington city.
National capital
 Wellington was declared a city in 1840, and was chosen to be the capital city of New Zealand in 1865.
Wellington became the capital city in place of
Wellington was declared a city in 1840, and was chosen to be the capital city of New Zealand in 1865.
Wellington became the capital city in place of Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The most populous urban area in the country and the fifth largest city in Oceania, Auckland has an urban population of about ...
, which William Hobson
Captain William Hobson (26 September 1792 – 10 September 1842) was a British Royal Navy officer who served as the first Governor of New Zealand. He was a co-author of the Treaty of Waitangi.
Hobson was dispatched from London in July 1 ...
had made the capital in 1841
Events
January–March
* January 20 – Charles Elliot of the United Kingdom, and Qishan of the Qing dynasty, agree to the Convention of Chuenpi.
* January 26 – Britain occupies Hong Kong. Later in the year, the first census of the i ...
. The New Zealand Parliament
The New Zealand Parliament ( mi, Pāremata Aotearoa) is the unicameral legislature of New Zealand, consisting of the King of New Zealand (King-in-Parliament) and the New Zealand House of Representatives. The King is usually represented by hi ...
had first met in Wellington on 7 July 1862, on a temporary basis; in November 1863, the Prime Minister of New Zealand
The prime minister of New Zealand ( mi, Te pirimia o Aotearoa) is the head of government of New Zealand. The prime minister, Jacinda Ardern, leader of the New Zealand Labour Party, took office on 26 October 2017.
The prime minister (inform ...
, Alfred Domett
Alfred Domett (20 May 18112 November 1887) was the fourth premier of New Zealand, a close friend of the poet Robert Browning and author of the epic poem ''Ranolf and Amohia, a South Sea Day Dream''. Born in England, he emigrated to New Zealan ...
, placed a resolution before Parliament in Auckland that "... it has become necessary that the seat of government ... should be transferred to some suitable locality in Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
egion
Aigio, also written as ''Aeghion, Aegion, Aegio, Egio'' ( el, Αίγιο, Aígio, ; la, Aegium), is a town and a former municipality in Achaea, West Greece, on the Peloponnese. Since the 2011 local government reform, it is part of the municipalit ...
" There had been some concerns that the more populous South Island (where the goldfields were located) would choose to form a separate colony in the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
. Several commissioners (delegates) invited from Australia, chosen for their neutral status, declared that the city was a suitable location because of its central location in New Zealand and its good harbour; it was believed that the whole Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
fleet could fit into the harbour. Wellington's status as capital is a result of Constitutional convention (political custom), constitutional convention rather than statute.
Treaty of Waitangi
The Treaty of Waitangi ( mi, Te Tiriti o Waitangi) is a document of central importance to the History of New Zealand, history, to the political constitution of the state, and to the national mythos of New Zealand. It has played a major role in ...
. Held on 55 acres of land at Rongotai it featured three exhibition courts, grand Art Deco-style edifices and a hugely popular three-acre amusement park. Wellington attracted more than 2.5 million visitors at a time when New Zealand's population was 1.6 million.
Geography
 Wellington is at the south-western tip of the North Island on
Wellington is at the south-western tip of the North Island on Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
, separating the North and South Islands. On a clear day the snowcapped Kaikoura Ranges are visible to the south across the strait. To the north stretch the golden beaches of the Kapiti Coast. On the east the Remutaka Range divides Wellington from the broad plains of the Wairarapa, a list of wine-producing regions, wine region of national notability.
With a latitude of 41° 17' South, Wellington is the List of southernmost items, southernmost capital city in the world. Wellington ties with Canberra, Australia, as the extreme points of Earth#Remoteness, most remote capital city, apart from each other.
Wellington is more densely populated than most other cities in New Zealand due to the restricted amount of land that is available between its harbour and the surrounding hills. It has very few open areas in which to expand, and this has brought about the development of the suburban towns. Because of its location in the Roaring Forties and its exposure to the winds blowing through Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
, Wellington is the world's windiest city, with an average wind speed of .
 Wellington's scenic natural harbour and green hillsides adorned with tiered suburbs of colonial villas are popular with tourists. The central business district (CBD) is close to Lambton Harbour, an arm of Wellington Harbour, which lies along an active Fault (geology), geological fault, clearly evident on its straight western shore. The land to the west of this rises abruptly, meaning that many suburbs sit high above the centre of the city. There is a network of bush walks and reserves maintained by the Wellington City, Wellington City Council and local volunteers. These include Otari-Wilton's Bush, dedicated to the protection and propagation of native plants. The Wellington region has of regional parks and forests. In the east is the Miramar Peninsula, connected to the rest of the city by a low-lying isthmus at
Wellington's scenic natural harbour and green hillsides adorned with tiered suburbs of colonial villas are popular with tourists. The central business district (CBD) is close to Lambton Harbour, an arm of Wellington Harbour, which lies along an active Fault (geology), geological fault, clearly evident on its straight western shore. The land to the west of this rises abruptly, meaning that many suburbs sit high above the centre of the city. There is a network of bush walks and reserves maintained by the Wellington City, Wellington City Council and local volunteers. These include Otari-Wilton's Bush, dedicated to the protection and propagation of native plants. The Wellington region has of regional parks and forests. In the east is the Miramar Peninsula, connected to the rest of the city by a low-lying isthmus at Rongotai
Rongotai is a suburb of Wellington, New Zealand, located southeast of the city centre. It is on the Rongotai isthmus, between the Miramar Peninsula and the suburbs of Kilbirnie and Lyall Bay. It is known mostly for being the location of the We ...
, the site of Wellington International Airport
Wellington International Airport (formerly known as Rongotai Airport) is an international airport located in the suburb of Rongotai in Wellington. It lies 3 NM or 5.5 km south-east from the city centre. It is a hub for Air New Zealand an ...
. Industry has developed mainly in the Hutt Valley, where there are food-processing plants, engineering industries, vehicle assembly and oil refineries.
The narrow entrance to the harbour is to the east of the Miramar Peninsula, and contains the dangerous shallows of Barrett Reef, where many ships have been wrecked (notably the inter-island ferry in Timeline of New Zealand history#1960s, 1968). The harbour has three islands: Matiu/Somes Island, Makaro/Ward Island and Mokopuna Island. Only Matiu/Somes Island is large enough for habitation. It has been used as a quarantine station for people and animals, and was an internment, internment camp during World War I and World War II. It is a conservation island, providing refuge for endangered species, much like Kapiti Island farther up the coast. There is access during daylight hours by the Dominion Post Ferry.
Wellington is primarily surrounded by water, but some of the nearby locations are listed below.
Geology
Wellington suffered serious damage in a series of 1848 Marlborough earthquake, earthquakes in Timeline of New Zealand history#1840s, 1848 and from another earthquake in Timeline of New Zealand history#1850s, 1855. The 1855 Wairarapa earthquake occurred on the Wairarapa Fault to the north and east of Wellington. It was probably the most powerful earthquake in recorded New Zealand history, with an estimated magnitude of at least 8.2 on the Moment magnitude scale. It caused vertical movements of two to three metres over a large area, including raising land out of the harbour and turning it into a tidal swamp. Much of this land was subsequently Reclamation of Wellington Harbour, reclaimed and is now part of the central business district. For this reason, the street named Lambton Quay is 100 to 200 metres (325 to 650 ft) from the harbour – plaques set into the footpath mark the shoreline in Timeline of New Zealand history#1840s, 1840, indicating the extent of reclamation. The 1942 Wairarapa earthquakes caused considerable damage in Wellington. The area has high seismic activity even by New Zealand standards, with a major fault, the Wellington Fault, running through the centre of the city and several others nearby. Several hundred minor faults lines have been identified within the urban area. Inhabitants, particularly in high-rise buildings, typically notice several earthquakes every year. For many years after the 1855 earthquake, the majority of buildings were made entirely from wood. The 1996-restored Government Buildings (Wellington, New Zealand), Government Buildings near Parliament is the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere. While masonry and structural steel have subsequently been used in building construction, especially for office buildings, timber framing remains the primary structural component of almost all residential construction. Residents place their confidence in good building code, building regulations, which became more stringent in the 20th century. Since the Canterbury earthquakes of 2010 Canterbury earthquake, 2010 and 2011 Christchurch earthquake, 2011, earthquake readiness has become even more of an issue, with buildings declared by Wellington City Council to be earthquake-prone, and the costs of meeting new standards. Every five years a year-long slow quake occurs beneath Wellington, stretching from Kapiti to the Marlborough Sounds. It was first measured in 2003, and reappeared in 2008 and 2013. It releases as much energy as a magnitude 7 quake, but as it happens slowly there is no damage. During July and August 2013 there were many earthquakes, mostly in Cook Strait near Seddon. The sequence started at 5:09 pm on Sunday 21 July 2013 when the magnitude 6.5 2013 Seddon earthquake, Seddon earthquake hit the city, but no tsunami report was confirmed nor any major damage. At 2:31 pm on Friday 16 August 2013 the 2013 Lake Grassmere earthquake, Lake Grassmere earthquake struck, this time magnitude 6.6, but again no major damage occurred, though many buildings were evacuated. On Monday 20 January 2014 at 3:52 pm 2014 Eketahuna earthquake, a rolling 6.2 magnitude earthquake struck the lower North Island 15 km east of Eketahuna and was felt in Wellington, but little damage was reported initially, except at Wellington Airport where one of the two giant eagle sculptures commemorating The Hobbit became detached from the ceiling. At two minutes after midnight on Monday 14 November 2016, the 7.8 magnitude 2016 Kaikoura earthquake, Kaikoura earthquake, which was centred between Culverden and Kaikoura in the South Island, caused the Wellington CBD, Victoria University of Wellington, and the Public transport in the Wellington Region#Trains, Wellington suburban rail network to be largely closed for the day to allow inspections. The earthquake damaged a considerable number of buildings, with 65% of the damage being in Wellington. Subsequently, a number of recent buildings were demolished rather than being rebuilt, often a decision made by the insurer. Two of the buildings demolished were about eleven years old – the seven-storey NZDF headquarters and Statistics House at Centreport on the waterfront. The docks were closed for several weeks after the earthquake.Relief
Steep landforms shape and constrain much of Wellington city. Notable hills in and around Wellington include: * Mount Victoria, Wellington, Mount Victoria – 196 m. Mt Vic is a popular walk for tourists and Wellingtonians alike, as from the summit one can see most of Wellington. There are numerous mountain bike and walking tracks on the hill. * Mount Albert – 178 m * Mount Cook, Wellington, Mount Cook * Mount Alfred (west of Evans Bay) – 122 m * Mount Kaukau – 445 m. Site of Wellington's main television transmitter. * Mount Crawford * Brooklyn Hill – 299 m * Wrights Hill Fortress, Wrights Hill * Mākara Peak – summit (412m) is within the 250ha Makara Peak Mountain Bike Park that includes 45km of trails * Te Ahumairangi Hill, Te Ahumairangi (Tinakori) HillClimate
Averaging 2,055 hours of sunshine per year, the climate of Wellington is temperate Oceanic climate, marine, (Köppen climate classification, Köppen: ''Cfb''), generally moderate all year round with warm summers and mild winters, and rarely sees temperatures above or below . The hottest recorded temperature in the city is , while is the coldest. The city is notorious for its southerly blasts in winter, which may make the temperature feel much colder. It is generally very windy all year round with high rainfall; average annual rainfall is , June and July being the wettest months. Frosts are quite common in the hill suburbs and the Hutt Valley between May and September. Snow is very rare at low altitudes, although snow fell on the city and many other parts of the Wellington region during separate 2011 New Zealand snowstorms, events on 25 July 2011 and 15 August 2011. Snow at higher altitudes is more common, with light flurries recorded in higher suburbs every few years. On 29 January 2019, the suburb of Kelburn reached , the highest temperature since records began in 1927.Demographics
Wellington City covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. This comprises people in the Wellington urban area and people in the surrounding rural areas. Wellington City had a population of 202,737 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 11,781 people (6.2%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, and an increase of 23,271 people (13.0%) since the 2006 New Zealand census, 2006 census. There were 74,841 households. There were 98,823 males and 103,911 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.95 males per female. The median age was 34.1 years (compared with 37.4 years nationally), with 32,856 people (16.2%) aged under 15 years, 54,999 (27.1%) aged 15 to 29, 93,669 (46.2%) aged 30 to 64, and 21,213 (10.5%) aged 65 or older. Of those at least 15 years old, 74,922 (44.1%) people had a bachelor or higher degree, and 12,690 (7.5%) people had no formal qualifications. The median income was $41,800, compared with $31,800 nationally. 48,633 people (28.6%) earned over $70,000 compared to 17.2% nationally. The employment status of those at least 15 was that 96,453 (56.8%) people were employed full-time, 24,738 (14.6%) were part-time, and 7,719 (4.5%) were unemployed.Quality of living
Wellington ranks 12th in the world for quality of living, according to a 2014 study by consulting company Mercer; of cities in the Asia–Pacific region, Wellington ranked third behind Auckland and Sydney (). In 2009, Wellington was ranked as a highly affordable city in terms of cost of living, coming in at 139th most expensive city out of 143 cities in the Mercer worldwide Cost of Living Survey. Between 2009 and 2020 the cost of living in Wellington increased, and it is now ranked 123rd most expensive city out of a total of 209 cities.Culture and identity
In addition to governmental institutions, Wellington accommodates several of the nation's largest and oldest cultural institutions, such as the Archives New Zealand, National Archives, the National Library of New Zealand, National Library, New Zealand's national museum, Te Papa and numerous theatres. It plays host to many artistic and cultural organisations, including the New Zealand Symphony Orchestra and Royal New Zealand Ballet. Its architectural attractions include the Old Government Buildings, Wellington, Old Government Buildings – one of the largest wooden buildings in the world – as well as the iconic Beehive (New Zealand), Beehive, the executive wing of New Zealand Parliament Buildings, Parliament Buildings as well as internationally renowned Futuna Chapel. The city's art scene includes many art galleries, including the national art collection at Toi Art at Te Papa. Wellington also has many events such as CubaDupa, the Newtown, New Zealand#Newtown Festival, Newtown Festival, Diwali Festival of Lights and Gardens Magic at the Botanical Gardens. At the 2018 census, ethnicities were 74.1% European/Pākehā, 8.6% Māori, 5.1% Pacific peoples, 18.3% Asian, and 4.5% other ethnicities. People may identify with more than one ethnicity. English is the most spoken language (96.0%) followed by French (3.2%), Te Reo Maori (2.2%), Mandarin (2.0%) and German (2.0%). Percentages add up to more than 100% as people may select more than one language. Although some people objected to giving their religion, 53.2% had no religion, 31.4% were Christian, 3.7% were Hindu, 1.6% were Muslim, 1.7% were Buddhist and 3.3% had other religions. At the 2018 Census, 33.4% of Wellington's population was born overseas, compared with 27.1% nationally. The most common overseas birthplace is England, place of origin of 6.2% of the urban area's population. The next most-common countries of origin were India (3.1%), mainland China (2.6%), Australia (2.0%), the Philippines (1.7%), the United States (1.5%) South Africa (1.2%).
At the 2018 Census, 33.4% of Wellington's population was born overseas, compared with 27.1% nationally. The most common overseas birthplace is England, place of origin of 6.2% of the urban area's population. The next most-common countries of origin were India (3.1%), mainland China (2.6%), Australia (2.0%), the Philippines (1.7%), the United States (1.5%) South Africa (1.2%).
Architecture
 Wellington showcases a variety of architectural styles from the past 150 years – 19th-century wooden cottages, such as the Italianate Katherine Mansfield Birthplace in Thorndon; streamlined Art Deco structures such as the old Wellington Free Ambulance headquarters, the Central Fire Station, Fountain Court Apartments, the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery, and the former Post and Telegraph Building; and the curves and vibrant colours of post-modern architecture in the CBD.
The oldest building is the 1858 Nairn Street Cottage in Mount Cook, Wellington, Mount Cook. The tallest building is the Majestic Centre on Willis Street at 116 metres high, the second tallest being the structural expressionist Aon Centre (Wellington) at 103 metres. Futuna Chapel in Karori is an iconic building designed by Māori architect John Scott and is architecturally considered one of the most significant New Zealand buildings of the 20th century.
Wellington showcases a variety of architectural styles from the past 150 years – 19th-century wooden cottages, such as the Italianate Katherine Mansfield Birthplace in Thorndon; streamlined Art Deco structures such as the old Wellington Free Ambulance headquarters, the Central Fire Station, Fountain Court Apartments, the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery, and the former Post and Telegraph Building; and the curves and vibrant colours of post-modern architecture in the CBD.
The oldest building is the 1858 Nairn Street Cottage in Mount Cook, Wellington, Mount Cook. The tallest building is the Majestic Centre on Willis Street at 116 metres high, the second tallest being the structural expressionist Aon Centre (Wellington) at 103 metres. Futuna Chapel in Karori is an iconic building designed by Māori architect John Scott and is architecturally considered one of the most significant New Zealand buildings of the 20th century.
 Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's is an example of 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture adapted to colonial conditions and materials, as is St Mary of the Angels, Wellington, St Mary of the Angels. Sacred Heart Cathedral, Wellington, Sacred Heart Cathedral is a Palladian architecture, Palladian Revival Basilica with the Portico of a Roman Temple, Roman or Greek temple. The Museum of Wellington City & Sea in the Wellington Harbour Board Head Office and Bond Store, Bond Store is in the Second French Empire style, and the Wellington Harbour Board Wharf Office Building is in a late English Classical style. There are several restored theatre buildings: the St. James Theatre, Wellington, St James Theatre, the Opera House, Wellington, Opera House and the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre.
Civic Square, Wellington, Te Ngākau Civic Square is surrounded by the Wellington Town Hall, Town Hall and council offices, the Michael Fowler Centre, the Wellington Central Library, the City-to-Sea bridge, Wellington, City-to-Sea Bridge, and the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery.
As it is the capital city, there are many notable government buildings. The Executive Wing of New Zealand Parliament Buildings, on the corner of Lambton Quay and Molesworth Street, was constructed between 1969 and 1981 and is commonly referred to as Beehive (New Zealand), the Beehive. Across the road is the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere, part of the Government Buildings (Wellington, NZ), old Government Buildings which now houses part of Victoria University of Wellington's Law Faculty.
A modernist building housing the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa lies on the waterfront, on Cable Street. It is strengthened using base isolation – essentially seating the entire building on supports made from lead, steel and rubber that slow down the effect of an earthquake.
Other notable buildings include Wellington Town Hall, Wellington railway station, Dominion Museum (now Massey University), Aon Centre (Wellington), Wellington Regional Stadium, and Wellington Airport at
Old St Paul's, Wellington, Old St Paul's is an example of 19th-century Gothic Revival architecture adapted to colonial conditions and materials, as is St Mary of the Angels, Wellington, St Mary of the Angels. Sacred Heart Cathedral, Wellington, Sacred Heart Cathedral is a Palladian architecture, Palladian Revival Basilica with the Portico of a Roman Temple, Roman or Greek temple. The Museum of Wellington City & Sea in the Wellington Harbour Board Head Office and Bond Store, Bond Store is in the Second French Empire style, and the Wellington Harbour Board Wharf Office Building is in a late English Classical style. There are several restored theatre buildings: the St. James Theatre, Wellington, St James Theatre, the Opera House, Wellington, Opera House and the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre.
Civic Square, Wellington, Te Ngākau Civic Square is surrounded by the Wellington Town Hall, Town Hall and council offices, the Michael Fowler Centre, the Wellington Central Library, the City-to-Sea bridge, Wellington, City-to-Sea Bridge, and the City Gallery Wellington, City Gallery.
As it is the capital city, there are many notable government buildings. The Executive Wing of New Zealand Parliament Buildings, on the corner of Lambton Quay and Molesworth Street, was constructed between 1969 and 1981 and is commonly referred to as Beehive (New Zealand), the Beehive. Across the road is the largest wooden building in the Southern Hemisphere, part of the Government Buildings (Wellington, NZ), old Government Buildings which now houses part of Victoria University of Wellington's Law Faculty.
A modernist building housing the Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa lies on the waterfront, on Cable Street. It is strengthened using base isolation – essentially seating the entire building on supports made from lead, steel and rubber that slow down the effect of an earthquake.
Other notable buildings include Wellington Town Hall, Wellington railway station, Dominion Museum (now Massey University), Aon Centre (Wellington), Wellington Regional Stadium, and Wellington Airport at Rongotai
Rongotai is a suburb of Wellington, New Zealand, located southeast of the city centre. It is on the Rongotai isthmus, between the Miramar Peninsula and the suburbs of Kilbirnie and Lyall Bay. It is known mostly for being the location of the We ...
. Leading architects include Frederick Thatcher, Frederick de Jersey Clere, W. Gray Young, William Alington (architect), Bill Alington, Ian Athfield, Roger Walker (architect), Roger Walker. Wellington contains many iconic sculptures and structures, such as the Bucket Fountain in Cuba Street and ''Invisible City'' by Anton Parsons on Lambton Quay. Kinetic sculptures have been commissioned, such as the Zephyrometer. This 26-metre orange spike built for movement by artist Phil Price has been described as "tall, soaring and elegantly simple", which "reflects the swaying of the yacht masts in the Evans Bay Marina behind it" and "moves like the needle on the dial of a nautical instrument, measuring the speed of the sea or wind or vessel."
Wellington has many different architectural styles, such as classic Painted ladies, Painted Ladies in Mount Victoria, Newtown and Oriental Bay, Wooden Art Deco houses spread throughout (especially further north in the Hutt Valley), the classic masonry buildings in Cuba Street, State housing, state houses particularly in the Hutt and Wellington's southern suburbs, Railways Department's Housing Scheme, railway houses in Ngaio, New Zealand, Ngaio and other railway-side suburbs, large modern buildings in the city centre (such as the distinctive skyscraper called the Majestic Centre) and grand Victorian buildings common in the inner city as well.
Wellington contains many iconic sculptures and structures, such as the Bucket Fountain in Cuba Street and ''Invisible City'' by Anton Parsons on Lambton Quay. Kinetic sculptures have been commissioned, such as the Zephyrometer. This 26-metre orange spike built for movement by artist Phil Price has been described as "tall, soaring and elegantly simple", which "reflects the swaying of the yacht masts in the Evans Bay Marina behind it" and "moves like the needle on the dial of a nautical instrument, measuring the speed of the sea or wind or vessel."
Wellington has many different architectural styles, such as classic Painted ladies, Painted Ladies in Mount Victoria, Newtown and Oriental Bay, Wooden Art Deco houses spread throughout (especially further north in the Hutt Valley), the classic masonry buildings in Cuba Street, State housing, state houses particularly in the Hutt and Wellington's southern suburbs, Railways Department's Housing Scheme, railway houses in Ngaio, New Zealand, Ngaio and other railway-side suburbs, large modern buildings in the city centre (such as the distinctive skyscraper called the Majestic Centre) and grand Victorian buildings common in the inner city as well.
Housing and real estate

House prices
Historic
Wellington experienced a real estate boom in the early 2000s and the effects of the international property bust at the start of 2007. In 2005, the market was described as "robust". By 2008, property values had declined by about 9.3% over a 12-month period, according to one estimate. More expensive properties declined more steeply, sometimes by as much as 20%. "From 2004 to early 2007, rental yields were eroded and positive cash flow property investments disappeared as house values climbed faster than rents. Then that trend reversed and yields slowly began improving," according to two ''The New Zealand Herald'' reporters writing in May 2009. In the middle of 2009 house prices had dropped, interest rates were low, and buy-to-let property investment was again looking attractive, particularly in the Lambton precinct, according to these two reporters.Current
Since 2009, house prices in Wellington have increased significantly. In May 2021, the Real Estate Institute of New Zealand (REINZ) reported the median house price was $1,057,000 in Wellington City, $930,000 in Porirua, $873,500 in Lower Hutt and $828,000 in Upper Hutt, compared to a national median house price of $820,000. The substantial increase in house prices has made it difficult for first home buyers to purchase a home in the city and is also credited with pushing up the house prices in neighbouring cities like Porirua. Housing costs have been identified making it difficult for some professions, like nurses, to afford to live in Wellington. The median rent in Wellington has also increased significantly in recent years to $600 per week, higher even than Auckland.Housing quality
Despite the high cost of housing in the capital, the quality of housing in Wellington has been criticised as being poor. 18.4% of houses in Wellington City are sometimes or always mouldy and 24% are sometimes or always damp. Both of these are higher than the New Zealand average.Demographics
 A Wellington City Council survey conducted in March 2009 found the typical central city apartment dweller was a New Zealand native aged 24 to 35 with a professional job in the downtown area, with household income higher than surrounding areas. Three-quarters (73%) walked to work or university, 13% travelled by car, 6% by bus, 2% bicycled (although 31% own bicycles), and did not travel very far since 73% worked or studied in the central city. The large majority (88%) did not have children in their apartments; 39% were couples without children; 32% were single-person households; 15% were groups of people flatting together. Most (56%) owned their apartment; 42% rented. The report continued: "The four most important reasons for living in an apartment were given as lifestyle and city living (23%), close to work (20%), close to shops and cafes (11%) and low maintenance (11%) ... City noise and noise from neighbours were the main turnoffs for apartment dwellers (27%), followed by a lack of outdoor space (17%), living close to neighbours (9%) and apartment size and a lack of storage space (8%)."
Households are primarily one-family, making up 66.9% of households, followed by single-person households (24.7%); there were fewer multiperson households and even fewer households containing two or more families. These counts are from the 2013 census for the Wellington region (which includes the surrounding area in addition to the four cities).
A Wellington City Council survey conducted in March 2009 found the typical central city apartment dweller was a New Zealand native aged 24 to 35 with a professional job in the downtown area, with household income higher than surrounding areas. Three-quarters (73%) walked to work or university, 13% travelled by car, 6% by bus, 2% bicycled (although 31% own bicycles), and did not travel very far since 73% worked or studied in the central city. The large majority (88%) did not have children in their apartments; 39% were couples without children; 32% were single-person households; 15% were groups of people flatting together. Most (56%) owned their apartment; 42% rented. The report continued: "The four most important reasons for living in an apartment were given as lifestyle and city living (23%), close to work (20%), close to shops and cafes (11%) and low maintenance (11%) ... City noise and noise from neighbours were the main turnoffs for apartment dwellers (27%), followed by a lack of outdoor space (17%), living close to neighbours (9%) and apartment size and a lack of storage space (8%)."
Households are primarily one-family, making up 66.9% of households, followed by single-person households (24.7%); there were fewer multiperson households and even fewer households containing two or more families. These counts are from the 2013 census for the Wellington region (which includes the surrounding area in addition to the four cities).
Economy
 Wellington Harbour ranks as one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The port handles approximately 10.5 million tonnes of cargo on an annual basis, importing petroleum products, motor vehicles, minerals and exporting meats, wood products, dairy products, wool, and fruit. Many cruise ships also use the port.
The Government sector has long been a mainstay of the economy, which has typically risen and fallen with it. Traditionally, its central location meant it was the location of many head offices of various sectors – particularly finance, technology and heavy industry – many of which have since relocated to Auckland following economic deregulation and privatisation.
In recent years, tourism, arts and culture, film, and information and communications technology, ICT have played a bigger role in the economy. Wellington's median income is well above the average in New Zealand, and the highest of all New Zealand cities. It has a much higher proportion of people with tertiary qualifications than the national average. Major companies with their headquarters in Wellington include:
* Wellington Harbour, Centreport
* Chorus Limited, Chorus Networks
* Contact Energy
* The Co-operative Bank (New Zealand), The Cooperative Bank
* Datacom Group
* Infratil
* Kiwibank
* Meridian Energy
* NZ Post
* NZX
* Todd Corporation
* Trade Me
* Weta Digital
*
Wellington Harbour ranks as one of New Zealand's chief seaports and serves both domestic and international shipping. The port handles approximately 10.5 million tonnes of cargo on an annual basis, importing petroleum products, motor vehicles, minerals and exporting meats, wood products, dairy products, wool, and fruit. Many cruise ships also use the port.
The Government sector has long been a mainstay of the economy, which has typically risen and fallen with it. Traditionally, its central location meant it was the location of many head offices of various sectors – particularly finance, technology and heavy industry – many of which have since relocated to Auckland following economic deregulation and privatisation.
In recent years, tourism, arts and culture, film, and information and communications technology, ICT have played a bigger role in the economy. Wellington's median income is well above the average in New Zealand, and the highest of all New Zealand cities. It has a much higher proportion of people with tertiary qualifications than the national average. Major companies with their headquarters in Wellington include:
* Wellington Harbour, Centreport
* Chorus Limited, Chorus Networks
* Contact Energy
* The Co-operative Bank (New Zealand), The Cooperative Bank
* Datacom Group
* Infratil
* Kiwibank
* Meridian Energy
* NZ Post
* NZX
* Todd Corporation
* Trade Me
* Weta Digital
* Wellington International Airport
Wellington International Airport (formerly known as Rongotai Airport) is an international airport located in the suburb of Rongotai in Wellington. It lies 3 NM or 5.5 km south-east from the city centre. It is a hub for Air New Zealand an ...
* Xero (software), Xero
* Z Energy
At the 2013 census, the largest employment industries for Wellington residents were professional, scientific and technical services (25,836 people), public administration and safety (24,336 people), health care and social assistance (17,446 people), education and training (16,550 people) and retail trade (16,203 people). In addition, Wellington is an important centre of the New Zealand film and theatre industry, and second to Auckland in terms of numbers of screen industry businesses.
Tourism
 It has been argued that the construction of the Te Papa museum helped transform Wellington into a tourist destination. Wellington is marketed as the 'coolest little capital in the world' by Positively Wellington Tourism, an award-winning regional tourism organisation set up as a council controlled organisation by Wellington City Council in 1997. The organisation's council funding comes through the Downtown Levy commercial rate. In the decade to 2010, the city saw growth of over 60% in commercial guest nights. It has been promoted through a variety of campaigns and taglines, starting with the iconic Absolutely Positively Wellington advertisements. The long-term domestic marketing strategy was a finalist in the 2011 CAANZ Media Awards.
It has been argued that the construction of the Te Papa museum helped transform Wellington into a tourist destination. Wellington is marketed as the 'coolest little capital in the world' by Positively Wellington Tourism, an award-winning regional tourism organisation set up as a council controlled organisation by Wellington City Council in 1997. The organisation's council funding comes through the Downtown Levy commercial rate. In the decade to 2010, the city saw growth of over 60% in commercial guest nights. It has been promoted through a variety of campaigns and taglines, starting with the iconic Absolutely Positively Wellington advertisements. The long-term domestic marketing strategy was a finalist in the 2011 CAANZ Media Awards.
Arts and culture
Culture
 Wellington's culture has been befamed across the world since the 1990s for being notably "cool", incongruous and influential given the city's relatively small size (near half a million). It has been traditionally acclaimed as New Zealand's "cultural and creative capital". The city is known for its coffee scene, with now-globally common foods and drinks such as the flat white perfected here. Wellington has a strong coffee culture – the city has more cafés per capita than New York City – and was pioneered by Italians, Italian and Greek language, Greek immigrants to areas such as Mount Victoria, Wellington, Mount Victoria, Island Bay, New Zealand, Island Bay and Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar. Nascent influence is derived from Ethiopians, Ethiopian migrants. Wellington's cultural vibrance and diversity is well-known across the world. It is New Zealand's second most ethnically diverse city, bested only by Auckland, and boasts a "melting pot" culture of significant minorities such as Malaysian New Zealanders, Malaysian, Italian New Zealanders, Italian, Dutch New Zealanders, Dutch, Korean New Zealanders, Korean, Chinese New Zealanders, Chinese, Greek New Zealanders, Greek, Indian New Zealanders, Indian, Samoan New Zealanders, Samoan and indigenous Taranaki Whānui ki te Upoko o te Ika, Taranaki Whānui communities as a result. In particular, Wellington is noted for is contributions to art, cuisine and international filmmaking (with Avatar (2009 film), Avatar and The Lord of the Rings (film series), The Lord of the Rings being largely produced in the city) among many other factors listed below. The World of Wearable Art, World of Wearable Arts (WOW) is an annual event that brings lots of visitors to Wellington every year.
Wellington's culture has been befamed across the world since the 1990s for being notably "cool", incongruous and influential given the city's relatively small size (near half a million). It has been traditionally acclaimed as New Zealand's "cultural and creative capital". The city is known for its coffee scene, with now-globally common foods and drinks such as the flat white perfected here. Wellington has a strong coffee culture – the city has more cafés per capita than New York City – and was pioneered by Italians, Italian and Greek language, Greek immigrants to areas such as Mount Victoria, Wellington, Mount Victoria, Island Bay, New Zealand, Island Bay and Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar. Nascent influence is derived from Ethiopians, Ethiopian migrants. Wellington's cultural vibrance and diversity is well-known across the world. It is New Zealand's second most ethnically diverse city, bested only by Auckland, and boasts a "melting pot" culture of significant minorities such as Malaysian New Zealanders, Malaysian, Italian New Zealanders, Italian, Dutch New Zealanders, Dutch, Korean New Zealanders, Korean, Chinese New Zealanders, Chinese, Greek New Zealanders, Greek, Indian New Zealanders, Indian, Samoan New Zealanders, Samoan and indigenous Taranaki Whānui ki te Upoko o te Ika, Taranaki Whānui communities as a result. In particular, Wellington is noted for is contributions to art, cuisine and international filmmaking (with Avatar (2009 film), Avatar and The Lord of the Rings (film series), The Lord of the Rings being largely produced in the city) among many other factors listed below. The World of Wearable Art, World of Wearable Arts (WOW) is an annual event that brings lots of visitors to Wellington every year.
Museums and cultural institutions
Festivals
Wellington is home to many high-profile events and cultural celebrations, including the biennial New Zealand Festival of the Arts, biennial Wellington Jazz Festival, biennial Capital E National Arts Festival for Children and major events such as Brancott Estate World of Wearable Art, TEDxWellington, Cuba Street Carnival, Visa Wellington on a Plate, New Zealand Fringe Festival, New Zealand International Comedy Festival, New Zealand Affordable Art Show, Out In The Square and Homegrown Music Festival (New Zealand), Homegrown Music Festival. The annual children's Artsplash Festival brings together hundreds of students from across the region. The week-long festival includes music and dance performances and the presentation of visual arts.Film
 Filmmakers Peter Jackson, Sir Peter Jackson, Richard Taylor (filmmaker), Sir Richard Taylor and a growing team of creative professionals have turned the eastern suburb of Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar into a film-making, post-production and special effects infrastructure centre, giving rise to the moniker 'Wellywood'. Jackson's companies include Weta Workshop, Weta Digital, Camperdown Studios, post-production house Park Road Post, and Stone Street Studios near Wellington Airport. Films shot partly or wholly in Wellington include the The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''Lord of The Rings'' trilogy, ''King Kong (2005 film), King Kong'' and ''Avatar (2009 film), Avatar''. Jackson described Wellington: "Well, it's windy. But it's actually a lovely place, where you're pretty much surrounded by water and the bay. The city itself is quite small, but the surrounding areas are very reminiscent of the hills up in northern California, like Marin County, California, Marin County near San Francisco and the Bay Area climate and some of the architecture. Kind of a cross between that and Hawaii."
Sometime Wellington directors Jane Campion and Geoff Murphy have reached the world's screens with their independent spirit. Emerging Kiwi filmmakers, like Robert Sarkies, Taika Waititi, Costa Botes and Jennifer Bush-Daumec, are extending the Wellington-based lineage and cinematic scope. There are agencies to assist film-makers with tasks such as securing permits and scouting locations.
Wellington has a large number of independent cinemas, including the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre, Penthouse, the Roxy and Light House, which participate in film festivals throughout the year. Wellington has one of the country's highest turn-outs for the annual New Zealand International Film Festivals, New Zealand International Film Festival. There are a number of other film festivals hosted in Wellington such as Doc Edge (documentary), the Japanese Film Festival and Show Me Shorts (short films).
Filmmakers Peter Jackson, Sir Peter Jackson, Richard Taylor (filmmaker), Sir Richard Taylor and a growing team of creative professionals have turned the eastern suburb of Miramar, New Zealand, Miramar into a film-making, post-production and special effects infrastructure centre, giving rise to the moniker 'Wellywood'. Jackson's companies include Weta Workshop, Weta Digital, Camperdown Studios, post-production house Park Road Post, and Stone Street Studios near Wellington Airport. Films shot partly or wholly in Wellington include the The Lord of the Rings (film series), ''Lord of The Rings'' trilogy, ''King Kong (2005 film), King Kong'' and ''Avatar (2009 film), Avatar''. Jackson described Wellington: "Well, it's windy. But it's actually a lovely place, where you're pretty much surrounded by water and the bay. The city itself is quite small, but the surrounding areas are very reminiscent of the hills up in northern California, like Marin County, California, Marin County near San Francisco and the Bay Area climate and some of the architecture. Kind of a cross between that and Hawaii."
Sometime Wellington directors Jane Campion and Geoff Murphy have reached the world's screens with their independent spirit. Emerging Kiwi filmmakers, like Robert Sarkies, Taika Waititi, Costa Botes and Jennifer Bush-Daumec, are extending the Wellington-based lineage and cinematic scope. There are agencies to assist film-makers with tasks such as securing permits and scouting locations.
Wellington has a large number of independent cinemas, including the Embassy Theatre, Wellington, Embassy Theatre, Penthouse, the Roxy and Light House, which participate in film festivals throughout the year. Wellington has one of the country's highest turn-outs for the annual New Zealand International Film Festivals, New Zealand International Film Festival. There are a number of other film festivals hosted in Wellington such as Doc Edge (documentary), the Japanese Film Festival and Show Me Shorts (short films).
Music
The music scene has produced bands such as The Warratahs, The Mockers, The Phoenix Foundation, Shihad, Beastwars (band), Beastwars, Fly My Pretties, Rhian Sheehan, Birchville Cat Motel, Black Boned Angel, Fat Freddy's Drop, The Black Seeds, Fur Patrol, Flight of the Conchords, Connan Mockasin, Rhombus (band), Rhombus and Module (musician), Module, Weta (band), Weta, Demoniac. The New Zealand School of Music was established in 2005 through a merger of the conservatory and theory programmes at Massey University and Victoria University of Wellington. New Zealand Symphony Orchestra, Nevine String Quartet and Chamber music New Zealand are based in Wellington. The city is also home to the Rodger Fox, Rodger Fox Big Band.Theatre and dance
Wellington is home to BATS Theatre, Circa Theatre, the national kaupapa Māori theatre company Taki Rua, the National Theatre for Children at Capital E, the Royal New Zealand Ballet, and contemporary dance company Footnote Dance, Footnote. Venues include St. James Theatre (Wellington), St James' Theatre on Courtenay Place, Opera House, Wellington, The Opera House on Manners Street and the Hannah Playhouse. Te Whaea National Dance & Drama Centre, houses New Zealand's university-level schools, Toi Whakaari: New Zealand Drama School & the New Zealand School of Dance, these are separate entities that share the building's facilities. The theatre's and studio's are which also are available for hire and used for public presentation and rehearsals by many groups. Whitireia New Zealand, Te Auaha the Whitireia Performing Arts Centre is downtown off Cuba Street.Comedy
Many of New Zealand's prominent comedians have either come from Wellington or got their start there, such as Ginette McDonald ("Lyn of Tawa"), Raybon Kan, Dai Henwood, Ben Hurley, Steve Wrigley, Guy Williams, the Flight of the Conchords and the satirist John Clarke (satirist), John Clarke ("Fred Dagg"). Wellington is home to groups that perform improvised theatre and improvisational comedy, including Wellington Improvisation Troupe (WIT), The Improvisors and youth group Joe Improv. The comedy group Breaking the 5th Wall operated out of Wellington and regularly did shows around the city, performing a mix of sketch comedy and semi-improvised theatre. In 2012 the group disbanded when some of its members moved to Australia. Wellington hosts shows in the annual New Zealand International Comedy Festival.Visual arts
From 1936 to 1992 Wellington was home to the National Art Gallery of New Zealand, when it was amalgamated into Museum of New Zealand Te Papa Tongarewa. Wellington is home to the New Zealand Academy of Fine Arts and the Arts Foundation of New Zealand. The city's arts centre, Wellington Arts Centre, Toi Pōneke, is a nexus of creative projects, collaborations, and multi-disciplinary production. Arts Programmes and Services Manager Eric Vaughn Holowacz and a small team based in the Abel Smith Street facility have produced ambitious initiatives such as Opening Notes, Drive by Art, and public art projects. The city is home to experimental arts publication ''White Fungus (magazine), White Fungus''. The Learning Connexion provides art classes. Other visual art galleries include the City Gallery.Cuisine
Sport
 Wellington is the home to:
* Hurricanes (rugby union), Hurricanes – Super Rugby team based in Wellington
* Wellington Rugby Football Union, Wellington Lions – ITM Cup rugby team
* Wellington Phoenix FC – Association football, football (soccer) club playing in the Australasian A-League, the only fully professional football club in New Zealand
* Team Wellington – in the semi-professional New Zealand Football Championship
* Central Pulse – netball team representing the Lower North Island in the ANZ Championship, primarily based in Wellington
* Wellington Firebirds and Wellington Blaze – men's and women's cricket teams
* Wellington Saints – basketball team in the National Basketball League (New Zealand), National Basketball League
Sporting events include:
* six pool games and two quarter-final games at the 2011 Rugby World Cup
* the Wellington Sevens – a round of the IRB Sevens World Series held at the Wellington Regional Stadium over several days every February.
* the 2011 Tae Kwon Do World Champs
* The 2014 World Field Target Championships
* the World Fell running, Mountain Running Championships in 2005
* the Wellington 500 Street racing, street race for touring car racing, touring cars, between 1985 and 1996
Wellington is the home to:
* Hurricanes (rugby union), Hurricanes – Super Rugby team based in Wellington
* Wellington Rugby Football Union, Wellington Lions – ITM Cup rugby team
* Wellington Phoenix FC – Association football, football (soccer) club playing in the Australasian A-League, the only fully professional football club in New Zealand
* Team Wellington – in the semi-professional New Zealand Football Championship
* Central Pulse – netball team representing the Lower North Island in the ANZ Championship, primarily based in Wellington
* Wellington Firebirds and Wellington Blaze – men's and women's cricket teams
* Wellington Saints – basketball team in the National Basketball League (New Zealand), National Basketball League
Sporting events include:
* six pool games and two quarter-final games at the 2011 Rugby World Cup
* the Wellington Sevens – a round of the IRB Sevens World Series held at the Wellington Regional Stadium over several days every February.
* the 2011 Tae Kwon Do World Champs
* The 2014 World Field Target Championships
* the World Fell running, Mountain Running Championships in 2005
* the Wellington 500 Street racing, street race for touring car racing, touring cars, between 1985 and 1996
Government
Local
Wellington Region
Greater Wellington, also known as the Wellington Region (Māori: ''Te Upoko o te Ika''), is a non-unitary region of New Zealand that occupies the southernmost part of the North Island. The region covers an area of , and has a population of
T ...
, administered by the Wellington Regional Council, Greater Wellington Region Council. The local authorities are responsible for a wide variety of public services, which include management and maintenance of local roads, and land-use planning.
Community boards
The Wellington City Council has created two local Community boards in New Zealand, community boards under the provisions of Part 4 of the Local Government Act 2002 for certain parts of the city: *The Tawa Community Board representing the northern suburbs of Tawa, New Zealand, Tawa, Grenada North and Takapu Valley, Takapū Valley; and *The Mākara/Ōhāriu Community Board representing the rural suburbs of Ohariu, New Zealand, Ohariu, Mākara and Mākara Beach.National
Wellington is covered by four general electorates: Mana (New Zealand electorate), Mana, Ōhāriu, Rongotai (New Zealand electorate), Rongotai, and Wellington Central (New Zealand electorate), Wellington Central. It is also covered by two Māori electorates: Te Tai Hauāuru, and Te Tai Tonga. Each electorate returns one member to the New Zealand House of Representatives. All electorates are held by the governing New Zealand Labour Party, Labour Party. In addition, there are a number of Wellington-based list MPs, who are elected via party lists. Due to Wellington being the capital city of New Zealand, its residents are more likely to participate in politics compared to other cities in New Zealand.Education
Wellington offers a variety of college and university programs for tertiary education in New Zealand, tertiary students: Victoria University of Wellington has four campuses and works with a three-trimester system (beginning March, July, and November). It enrolled 21,380 students in 2008; of these, 16,609 were full-time students. Of all students, 56% were female and 44% male. While the student body was primarily New Zealanders of European descent, 1,713 were Maori, 1,024 were Pacific students, 2,765 were international students. 5,751 degrees, diplomas and certificates were awarded. The university has 1,930 full-time employees.
Massey University has a Wellington campus known as the "creative campus" and offers courses in communication and business, engineering and technology, health and well-being, and creative arts. Its school of design was established in 1886 and has research centres for studying public health, sleep, Maori health, small & medium enterprises, disasters, and tertiary teaching excellence. It combined with Victoria University to create the New Zealand School of Music.
The University of Otago has a Wellington branch with its Wellington School of Medicine and Health.
Whitireia New Zealand has large campuses in Porirua, Wellington and Kapiti; the Wellington Institute of Technology and New Zealand's National Drama school, Toi Whakaari. The Wellington area has numerous primary and secondary schools.
Victoria University of Wellington has four campuses and works with a three-trimester system (beginning March, July, and November). It enrolled 21,380 students in 2008; of these, 16,609 were full-time students. Of all students, 56% were female and 44% male. While the student body was primarily New Zealanders of European descent, 1,713 were Maori, 1,024 were Pacific students, 2,765 were international students. 5,751 degrees, diplomas and certificates were awarded. The university has 1,930 full-time employees.
Massey University has a Wellington campus known as the "creative campus" and offers courses in communication and business, engineering and technology, health and well-being, and creative arts. Its school of design was established in 1886 and has research centres for studying public health, sleep, Maori health, small & medium enterprises, disasters, and tertiary teaching excellence. It combined with Victoria University to create the New Zealand School of Music.
The University of Otago has a Wellington branch with its Wellington School of Medicine and Health.
Whitireia New Zealand has large campuses in Porirua, Wellington and Kapiti; the Wellington Institute of Technology and New Zealand's National Drama school, Toi Whakaari. The Wellington area has numerous primary and secondary schools.
Transport
 Wellington is served by State Highway 1 (New Zealand), State Highway 1 in the west and State Highway 2 (New Zealand), State Highway 2 in the east, meeting at the Ngauranga Interchange north of the city centre, where SH 1 runs through the city to the airport. There are two other state highways in the wider region: State Highway 58 (New Zealand), State Highway 58 which provides a direct connection between the Hutt Valley and Porirua, and State Highway 59 (New Zealand), State Highway 59 which follows a coastal route between Linden and Mackays Crossing and was previously part of SH 1. Road access into the capital is constrained by the mountainous terrain – between Wellington and the Kapiti Coast, SH 1 passes through the steep and narrow Wainui Saddle, nearby SH 59 travels along the Centennial Highway, a narrow section of road between the Paekākāriki Escarpment and the Tasman Sea, and between Wellington and Wairarapa SH 2 transverses the Rimutaka Ranges on a similar narrow winding road. Wellington has two motorways: the Johnsonville–Porirua Motorway (largely part of SH 1, with the northernmost section part of SH 59) and the Wellington Urban Motorway (entirely part of SH 1), which in combination with a small non-motorway section in the Ngauranga Gorge connect Porirua with Wellington city. A third motorway in the wider region, the Transmission Gully Motorway forming part of the SH 1 route and officially opened on 30 March 2022, leaves the Johnsonville-Porirua Motorway at the boundary between Wellington and Porirua and provides the main route between Wellington and the wider North Island.
Bus transport in Wellington is supplied by several different operators under the banner of Metlink. Buses serve almost every part of Wellington city, with most of them running along the "Golden Mile" from Wellington railway station to Courtenay Place, Wellington, Courtenay Place. Until October 2017 there were nine trolleybus routes, all other buses running on Diesel fuel, diesel. The Trolleybuses in Wellington, trolleybus network was the last public system of its kind in the southern hemisphere.
Wellington lies at the southern end of the North Island Main Trunk railway (NIMT) and the Wairarapa Line, converging on Wellington railway station at the northern end of central Wellington. One long-distance service leaves from Wellington: the Capital Connection, for commuters from Palmerston North. The Northern Explorer to Auckland was discontinued in December 2021.
Four Railway electrification system, electrified suburban rail, suburban lines radiate from Wellington railway station to the outer suburbs to the north of Wellington – the Johnsonville Line through the hillside suburbs north of central Wellington; the Kapiti Line along the NIMT to Waikanae on the Kapiti Coast via Porirua and Paraparaumu; the Melling Line to Lower Hutt via Petone; and the Hutt Valley Line along the Wairarapa Line via Waterloo and Taitā, New Zealand, Taitā to Upper Hutt. A diesel-hauled carriage service, the Wairarapa Connection, connects several times daily to Masterton in the Wairarapa via the Rimutaka Tunnel. Combined, these five services carry 11.64 million passengers per year.
Wellington is served by State Highway 1 (New Zealand), State Highway 1 in the west and State Highway 2 (New Zealand), State Highway 2 in the east, meeting at the Ngauranga Interchange north of the city centre, where SH 1 runs through the city to the airport. There are two other state highways in the wider region: State Highway 58 (New Zealand), State Highway 58 which provides a direct connection between the Hutt Valley and Porirua, and State Highway 59 (New Zealand), State Highway 59 which follows a coastal route between Linden and Mackays Crossing and was previously part of SH 1. Road access into the capital is constrained by the mountainous terrain – between Wellington and the Kapiti Coast, SH 1 passes through the steep and narrow Wainui Saddle, nearby SH 59 travels along the Centennial Highway, a narrow section of road between the Paekākāriki Escarpment and the Tasman Sea, and between Wellington and Wairarapa SH 2 transverses the Rimutaka Ranges on a similar narrow winding road. Wellington has two motorways: the Johnsonville–Porirua Motorway (largely part of SH 1, with the northernmost section part of SH 59) and the Wellington Urban Motorway (entirely part of SH 1), which in combination with a small non-motorway section in the Ngauranga Gorge connect Porirua with Wellington city. A third motorway in the wider region, the Transmission Gully Motorway forming part of the SH 1 route and officially opened on 30 March 2022, leaves the Johnsonville-Porirua Motorway at the boundary between Wellington and Porirua and provides the main route between Wellington and the wider North Island.
Bus transport in Wellington is supplied by several different operators under the banner of Metlink. Buses serve almost every part of Wellington city, with most of them running along the "Golden Mile" from Wellington railway station to Courtenay Place, Wellington, Courtenay Place. Until October 2017 there were nine trolleybus routes, all other buses running on Diesel fuel, diesel. The Trolleybuses in Wellington, trolleybus network was the last public system of its kind in the southern hemisphere.
Wellington lies at the southern end of the North Island Main Trunk railway (NIMT) and the Wairarapa Line, converging on Wellington railway station at the northern end of central Wellington. One long-distance service leaves from Wellington: the Capital Connection, for commuters from Palmerston North. The Northern Explorer to Auckland was discontinued in December 2021.
Four Railway electrification system, electrified suburban rail, suburban lines radiate from Wellington railway station to the outer suburbs to the north of Wellington – the Johnsonville Line through the hillside suburbs north of central Wellington; the Kapiti Line along the NIMT to Waikanae on the Kapiti Coast via Porirua and Paraparaumu; the Melling Line to Lower Hutt via Petone; and the Hutt Valley Line along the Wairarapa Line via Waterloo and Taitā, New Zealand, Taitā to Upper Hutt. A diesel-hauled carriage service, the Wairarapa Connection, connects several times daily to Masterton in the Wairarapa via the Rimutaka Tunnel. Combined, these five services carry 11.64 million passengers per year.
Cook Strait
Cook Strait ( mi, Te Moana-o-Raukawa) separates the North and South Islands of New Zealand. The strait connects the Tasman Sea on the northwest with the South Pacific Ocean on the southeast. It is wide at its narrowest point,McLintock, A ...
ferries to Picton, New Zealand, Picton in the South Island, provided by state-owned Interislander and private Strait Shipping, Bluebridge. Local ferries connect Wellington city centre with Eastbourne and Seatoun.
Wellington International Airport
Wellington International Airport (formerly known as Rongotai Airport) is an international airport located in the suburb of Rongotai in Wellington. It lies 3 NM or 5.5 km south-east from the city centre. It is a hub for Air New Zealand an ...
is south-east of the city centre. It is serviced by flights from across New Zealand, Australia, Singapore (via Melbourne), and Fiji. Flights to other international destinations require a transfer at another airport, as aircraft range is limited by Wellington's short () runway, which has become an issue in recent years in regards to the Wellington region's economic performance.
Infrastructure
Electric power
Wellington's first public electricity supply was established in 1904, alongside the introduction of electric trams, and was originally supplied at 105 volts 80 hertz. The conversion to the now-standard 230/400 volts 50 hertz began in 1925, the same year the city was connected to the Mangahao Power Station, Mangahao hydroelectric scheme. Between 1924 and 1968, the city's supply was supplemented by a coal-fired power station at Evans Bay. Today, Wellington city is supplied from four Transpower New Zealand Limited, Transpower substations: Takapu Road, Kaiwharawhara, Wilton, and Central Park (Mount Cook). Wellington Electricity owns and operates the local distribution network. The city is home to two large wind farms, Project West Wind, West Wind and Mill Creek Wind Farm, Mill Creek, which combined contribute up to 213 MW of electricity to the city and the national grid. While Wellington experiences regular strong winds, and only 63% of Wellington Electricity's network is underground, the city has a very reliable power supply. In the year to March 2018, Wellington Electricity disclosed the average customer spent just 55 minutes without power due to unplanned outages.Natural gas
Wellington was one of the original nine towns and cities in New Zealand to be supplied with natural gas when the Kapuni, Kapuni gas field entered production in 1970, and a high-pressure pipeline from the field in Taranaki to the city was completed. The high-pressure transmission pipelines supplying Wellington are now owned and operated by First Gas, with Powerco owning and operating the medium- and low-pressure distribution pipelines within the urban area.The three waters
The "three waters" – drinking water, stormwater, and wastewater services for the Wellington metropolitan area are provided by five councils: Wellington City, Hutt, Upper Hutt and Porirua city councils, and the Wellington Region, Greater Wellington Regional Council. However, the water assets of these councils are managed by an infrastructure asset management company, Wellington Water. Wellington's first piped water supply came from a spring in 1867. Wellington Region, Greater Wellington Regional Council now supplies Lower Hutt, Porirua, Upper Hutt and Wellington with up to 220 million litres a day. The water comes from Wainuiomata River (since 1884), Hutt River (1914), Ōrongorongo River (1926) and the Lower Hutt aquifer. There are four wastewater treatment stations serving the Wellington metropolitan area, located at: * Moa Point (serving Wellington city) * Seaview (serving Lower Hutt and Upper Hutt) * Karori (serving the suburb) * Porirua (serving northern Wellington suburbs, Tawa and Porirua city) The Wellington metropolitan area faces challenges with ageing infrastructure for the three waters, and there have been some significant failures, particularly in wastewater systems. The water supply is vulnerable to severe disruption during a major earthquake, although a wide range of projects are planned to improve resilience of the water supply and allow a limited water supply post-earthquake. In May 2021, the Wellington City Council approved a 10 year plan that included expenditure of $2.7billion on water pipe maintenance and upgrades in Wellington city, and an additional $147 to $208 million for plant upgrades at the Moa Point wastewater treatment plant.Media
Radio
Wellington is List of radio stations in Wellington, served by 26 full-power radio stations: 17 on FM, four on AM, and five on both FM and AM.Television
Television broadcasts began in Wellington on 1 July 1961 with the launch of channel WNTV1, becoming the third New Zealand city (after Auckland and Christchurch) to receive regular television broadcasts. WNTV1's main studios were in Waring Taylor Street in central Wellington and broadcast from a transmitter atop Mount Victoria. In 1967, the Mount Victoria transmitter was replaced with a more powerful transmitter at Mount Kaukau. In November 1969, WNTV1 was networked with its counterpart stations in Auckland, Christchurch and Dunedin to form NZBC TV. In 1975, the NZBC was broken up with Wellington and Dunedin studios taking over NZBC TV as TVNZ 1, Television One while Auckland and Christchurch studios launched TVNZ 2, Television Two. At the same time, the Wellington studios moved to the new purpose-built Avalon, New Zealand, Avalon Television Centre in Lower Hutt. In 1980, Televisions One and Two merged under a single company, TVNZ, Television New Zealand (TVNZ). The majority of television production moved to Auckland over the 1980s, culminating in the opening of TVNZ's new Auckland television centre in 1989. Today, digital terrestrial television (Freeview (New Zealand), Freeview) is available in the city, transmitting from Mount Kaukau plus three infill transmitters at Baxters Knob, Fitzherbert, and Haywards.Twin cities
Wellington is twinned with the following cities: * Sydney, Australia (1983) * Xiamen, China (1987) * Sakai, Japan (1994) * Beijing, China (2006) * Canberra, Australia (2016) It also has historical ties with Chania, Greece; Harrogate, England; and Çanakkale, Turkey.Wellington metropolitan area
The wider metropolitan area for Wellington encompasses areas administered by four local government in New Zealand, local authorities: Wellington City Council, Wellington City itself, on the peninsula between Cook Strait and Wellington Harbour; Porirua, Porirua City on Porirua Harbour to the north, notable for its largeMāori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the C ...
and Pasifika New Zealanders, Pasifika communities; and Lower Hutt, Lower Hutt City and Upper Hutt, Upper Hutt City, largely suburban areas to the northeast, together known as the Hutt Valley. Depending on the source, the Wellington metro area may include Waikanae, Paraparaumu and Paekākāriki on the Kapiti Coast, and/or Featherston, New Zealand, Featherston and Greytown, New Zealand, Greytown in the Wairarapa.

 The urban areas of the four local authorities have a combined population of residents as of .
The four cities comprising the Wellington metropolitan area have a total population of with the urban area containing % of that population. The remaining areas are largely mountainous and sparsely farmed or parkland and are outside the urban area boundary. More than most cities, life is dominated by its central business district (CBD). Approximately 62,000 people work in the CBD, only 4,000 fewer than work in Auckland's CBD, despite that city having four times the population.
The Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki combined urban area in the Kapiti Coast district is sometimes included in the Wellington metro area due to its exurban nature and strong transport links with Wellington. If included as part of Wellington metro, Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki would add to the population (as of ).
Featherston, New Zealand, Featherston and Greytown, New Zealand, Greytown in the Wairarapa are rarely considered part of the Wellington metropolitan area, being physically separated from the rest of the metropolitan area by the Remutaka Range. However, both have significant proportions of their employed population working in Wellington city and the Hutt Valley (36.1% and 17.1% in 2006 respectively) and are considered part of the Wellington functional urban area by Statistics New Zealand.
The four urban areas combined had a usual resident population of 401,850 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 26,307 people (7.0%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, and an increase of 42,726 people (11.9%) since the 2006 New Zealand census, 2006 census. There were 196,911 males and 204,936 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.961 males per female. Of the total population, 74,892 people (18.6%) were aged up to 15 years, 93,966 (23.4%) were 15 to 29, 185,052 (46.1%) were 30 to 64, and 47,952 (11.9%) were 65 or older.
The urban areas of the four local authorities have a combined population of residents as of .
The four cities comprising the Wellington metropolitan area have a total population of with the urban area containing % of that population. The remaining areas are largely mountainous and sparsely farmed or parkland and are outside the urban area boundary. More than most cities, life is dominated by its central business district (CBD). Approximately 62,000 people work in the CBD, only 4,000 fewer than work in Auckland's CBD, despite that city having four times the population.
The Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki combined urban area in the Kapiti Coast district is sometimes included in the Wellington metro area due to its exurban nature and strong transport links with Wellington. If included as part of Wellington metro, Waikanae-Paraparaumu-Paekākāriki would add to the population (as of ).
Featherston, New Zealand, Featherston and Greytown, New Zealand, Greytown in the Wairarapa are rarely considered part of the Wellington metropolitan area, being physically separated from the rest of the metropolitan area by the Remutaka Range. However, both have significant proportions of their employed population working in Wellington city and the Hutt Valley (36.1% and 17.1% in 2006 respectively) and are considered part of the Wellington functional urban area by Statistics New Zealand.
The four urban areas combined had a usual resident population of 401,850 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 26,307 people (7.0%) since the 2013 New Zealand census, 2013 census, and an increase of 42,726 people (11.9%) since the 2006 New Zealand census, 2006 census. There were 196,911 males and 204,936 females, giving a sex ratio of 0.961 males per female. Of the total population, 74,892 people (18.6%) were aged up to 15 years, 93,966 (23.4%) were 15 to 29, 185,052 (46.1%) were 30 to 64, and 47,952 (11.9%) were 65 or older.
See also
* List of people from WellingtonNotes
References
Further reading
;Published in the 19th century * * ;Published in the 20th century * * *"Wellington City Annual Economic Profile 2013"
, by Infometrics for Grow Wellington Ltd.
External links
Greater Wellington Regional Council
Official NZ Tourism website for Wellington
Wellington City Council
Wellington
in Te Ara the Encyclopedia of New Zealand
Notes on a New Zealand City: Wellington
{{Authority control Wellington, Capitals in Oceania Former provincial capitals of New Zealand Populated coastal places in New Zealand Populated places established in 1840 Populated places in the Wellington Region Port cities in New Zealand