Web literacy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Web literacy comprises the skills and competencies needed for reading, writing and participating on the web.Mozilla Web Literacy Map v1.1.0
/ref> It has been described as "both content and activity" – i.e., web users should not just learn about the web but also about how to make their own website.Davidson, C.N. & Surman, M
"Why Web Literacy Should Be Part of Every Education"
Fast Company. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
7 Pillars of Information Literacy Core Model
Retrieved 12 February 2015.
 The
The
"Why Mozilla cares about Web Literacy"
Retrieved 2 February 2015. Web literacy is described as "the skills and competencies needed for reading, writing and participating on the web". Work on what was originally entitled a Web Literacy 'Standard' began in early 2013. Version 1.0 was launched at the Mozilla Festival later that year.
BoingBoing. Retrieved 12 February 2015. Going forward, 'standard' was seen to be problematic and against the ethos of what the Mozilla community was trying to achieve.The Web Literacy Standard is dead (long live the Web Literacy Map!)
Doug Belshaw's blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. ''Literacy Version 1.1'' of th
Web Literacy Map
was released in early 2014Why the Web Literacy Map will remain at v1.1 until MozFest
Mozilla Webmaker blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. and underpins the Mozilla Foundation'
Webmaker resources section
where learners and mentors can find activities that help teach related areas. Although the Web Literacy Map is a list of strands, skills and competencies, it is most commonly represented as a competency grid. The Mozilla community finalised the version 1.5 of the Web Literacy Map at the end of March 2015.Building version 1.5 of Mozilla’s Web Literacy Map
Mozilla Webmaker blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. This involves small changes to the competencies layer and a comprehensive review of the skills they contain.Help us redefine the skills underpinning three Web Literacy Map competencies!
Literaci.es. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
/ref> It has been described as "both content and activity" – i.e., web users should not just learn about the web but also about how to make their own website.Davidson, C.N. & Surman, M
"Why Web Literacy Should Be Part of Every Education"
Fast Company. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
History of the concept
In the latter part of the 1990s, literacy researchers started to explore the differences between printed text and the network-enabled devices with screens. This research was largely focused on two areas: the credibility of information that can be found on theWorld Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet.
Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web ...
Detweiler, M. C., Hess, S. M., & Peck, A. C. (1996, October). Acquiring User-Centered Design Skills by Designing and Evaluating World Wide Web Pages. In ''Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting'' (Vol. 40, No. 8, pp. 459-462). SAGE Publications and the difference that hypertext makes to 'reading' and 'writing'.Snyder, I., & Joyce, M. (Eds.). (1998). ''Page to screen: Taking literacy into the electronic era.'' Psychology Press. These skills were included in definitions of information literacy and included in a SCONUL
SCONUL (Society of College, National and University Libraries) is the membership organisation for all academic and national libraries in the UK and Ireland.
History
SCONUL was founded in 1950 as the Standing Conference of National and University ...
position paper in 1999.SCONUL Advisory Committee on Information Literacy (1999) Information skills in higher education:
a SCONUL position paper. Prepared by the Information Skills Task Force, on behalf of SCONUL. This paper became the '7 Pillars of Information Literacy', which was last updated in 2011.SCONUL. (2011)7 Pillars of Information Literacy Core Model
Retrieved 12 February 2015.
Web Literacy Map
 The
The Mozilla Foundation
The Mozilla Foundation (stylized as moz://a) is an American non-profit organization that exists to support and collectively lead the open source Mozilla project. Founded in July 2003, the organization sets the policies that govern development, ...
is a non-profit organization that promotes openness, innovation and participation on the Internet. It has created a Web Literacy Map in consultation with a community of stakeholders from formal and informal education, as well as industry.Belshaw, D.A.J. & Smith, K.L"Why Mozilla cares about Web Literacy"
Retrieved 2 February 2015. Web literacy is described as "the skills and competencies needed for reading, writing and participating on the web". Work on what was originally entitled a Web Literacy 'Standard' began in early 2013. Version 1.0 was launched at the Mozilla Festival later that year.
BoingBoing. Retrieved 12 February 2015. Going forward, 'standard' was seen to be problematic and against the ethos of what the Mozilla community was trying to achieve.The Web Literacy Standard is dead (long live the Web Literacy Map!)
Doug Belshaw's blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. ''Literacy Version 1.1'' of th
Web Literacy Map
was released in early 2014Why the Web Literacy Map will remain at v1.1 until MozFest
Mozilla Webmaker blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. and underpins the Mozilla Foundation'
Webmaker resources section
where learners and mentors can find activities that help teach related areas. Although the Web Literacy Map is a list of strands, skills and competencies, it is most commonly represented as a competency grid. The Mozilla community finalised the version 1.5 of the Web Literacy Map at the end of March 2015.Building version 1.5 of Mozilla’s Web Literacy Map
Mozilla Webmaker blog. Retrieved 12 February 2015. This involves small changes to the competencies layer and a comprehensive review of the skills they contain.Help us redefine the skills underpinning three Web Literacy Map competencies!
Literaci.es. Retrieved 12 February 2015.
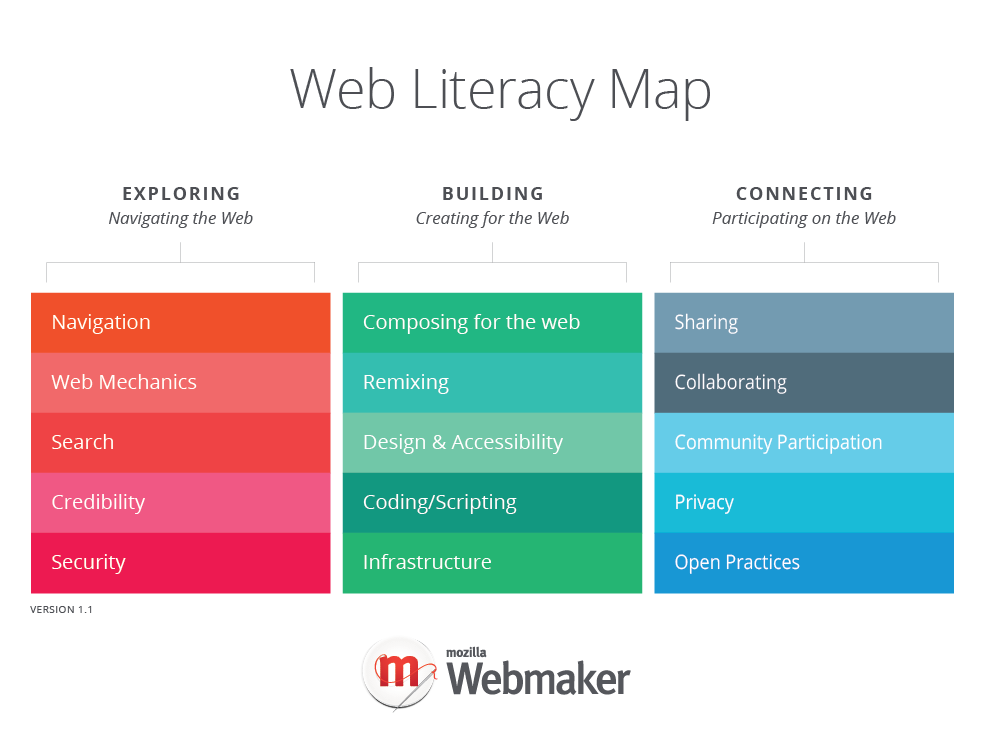
Exploring
''(Navigating the Web)'' * Navigation ''(Using software tools to browse the web)'' * Web Mechanics ''(Understanding the web ecosystem)'' * Search ''(Locating information, people and resources via the web)'' * Credibility ''(Critically evaluating information found on the web)'' * Security ''(Keeping systems, identities, and content safe)''Building
''(Creating for the Web)'' * Composing for the Web ''(Creating and curating content)'' * Remixing ''(Modifying existing web resources to create something new)'' * Design & Accessibility ''(Creating universally effective communications through web resources)'' * Coding/Scripting ''(Creating interactive experiences on the web)'' * Infrastructure ''(Understanding the Internet stack)''Connecting
''(Participating on the Web)'' * Sharing ''(Creating web resources with others)'' * Collaborating ''(Providing access to web resources)'' * Community Participation ''(Getting involved in web communities and understanding their practices)'' * Privacy ''(Examining the consequences of sharing data online)'' * Open Practices ''(Helping to keep the web democratic and universally accessible)''See also
* Cyber self-defense *Computer literacy
Computer literacy is defined as the knowledge and ability to use computers and related technology efficiently, with skill levels ranging from elementary use to computer programming and advanced problem solving. Computer literacy can also refer ...
* Digital literacy
* Information literacy
References
{{reflist Literacy Computing and society World Wide Web