Weald on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
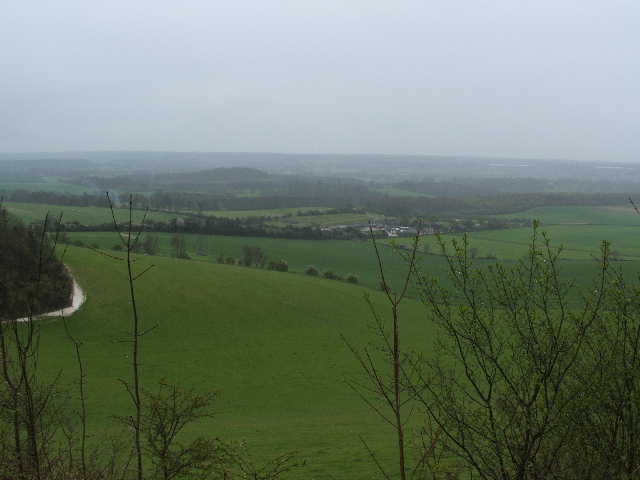 The Weald () is an area of
The Weald () is an area of
 The Weald is the eroded remains of a geological structure, an
The Weald is the eroded remains of a geological structure, an
 Prehistoric evidence suggests that, following the
Prehistoric evidence suggests that, following the
 The Weald begins north-east of
The Weald begins north-east of
South East England
South East England is one of the nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It consists of the counties of Buckinghamshire, East Sussex, Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Kent, Oxfordshire, Berkshi ...
between the parallel chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. C ...
escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s of the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and the South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the eas ...
. It crosses the counties of Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
, Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
, Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
and Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. It has three separate parts: the sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
"High Weald" in the centre; the clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
"Low Weald" periphery; and the Greensand Ridge
The Greensand Ridge, also known as the Wealden Greensand is an extensive, prominent, often wooded, mixed greensand/sandstone escarpment in south-east England. Forming part of the Weald, a former dense forest in Sussex, Surrey and Kent, it r ...
, which stretches around the north and west of the Weald and includes its highest points. The Weald once was covered with forest, and its name, Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
in origin, signifies "woodland". The term is still used today, as scattered farms and villages sometimes refer to the Weald in their names.
Etymology
The name "Weald" is derived from theOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
', meaning "forest" (cognate of German ''Wald'', but unrelated to English "wood", which has a different origin). This comes from a Germanic root of the same meaning, and ultimately from Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
. ''Weald'' is specifically a West Saxon
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
form; '' wold'' is the Anglian form of the word. The Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old Englis ...
form of the word is ''wēld'', and the modern spelling is a reintroduction of the Old English form attributed to its use by William Lambarde
William Lambarde (18 October 1536 – 19 August 1601) was an English antiquarian, writer on legal subjects, and politician. He is particularly remembered as the author of ''A Perambulation of Kent'' (1576), the first English county history; ''Ei ...
in his ''A Perambulation of Kent'' of 1576.
In early medieval Britain, the area had the name ''Andredes weald'', meaning "the forest of Andred", the latter derived from ''Anderida
Anderitum (also ''Anderida'' or ''Anderidos'') was a Saxon Shore fort in the Roman province of Britannia. The ruins adjoin the west end of the village of Pevensey in East Sussex, England. The fort was built in the 290s and was abandoned after it ...
'', the Roman name of present-day Pevensey
Pevensey ( ) is a village and civil parish in the Wealden district of East Sussex, England. The main village is located north-east of Eastbourne, one mile (1.6 km) inland from Pevensey Bay. The settlement of Pevensey Bay forms part ...
. The area is also referred to in early English texts as ''Andredesleage'', where the second element, ''leage,'' is another Old English word for "woodland", represented by the modern '.
The adjective for "Weald" is "wealden".
Geology
 The Weald is the eroded remains of a geological structure, an
The Weald is the eroded remains of a geological structure, an anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is t ...
, a dome of layered Lower Cretaceous
Lower may refer to:
* Lower (surname)
* Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
* Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
Nizhny (russian: Ни́жний; masculine), Nizhnyaya (; feminine), or Nizhneye (russian: Н� ...
rocks cut through by weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs '' in situ'' (on site, with little or no movement ...
to expose the layers as sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
ridges and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
valleys. The oldest rocks exposed at the centre of the anticline are correlated with the Purbeck Beds of the Upper Jurassic
The Late Jurassic is the third epoch of the Jurassic Period, and it spans the geologic time from 163.5 ± 1.0 to 145.0 ± 0.8 million years ago (Ma), which is preserved in Upper Jurassic strata.Owen 1987.
In European lithostratigraphy, the name ...
. Above these, the Cretaceous rocks, include the Wealden Group
The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group (a sequence of rock strata) in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of paralic to continental (freshwater) facies sedimenta ...
of alternating sands and claysthe Ashdown Sand Formation, Wadhurst Clay Formation
The Wadhurst Clay Formation is a geological unit which forms part of the Wealden Group and the middle part of the now unofficial Hastings Beds. These geological units make up the core of the geology of the High Weald in the English counties of West ...
, Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation
The Tunbridge Wells Sand Formation is a geological unit which forms part of the Wealden Group and the uppermost and youngest part of the unofficial Hastings Beds. These geological units make up the core of the geology of the Weald in the English c ...
(collectively known as the Hastings Beds
The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group (a sequence of rock strata) in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of paralic to continental (freshwater) facies sedimen ...
) and the Weald Clay
Weald Clay or the Weald Clay Formation is a Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock unit underlying areas of South East England, between the North and South Downs, in an area called the Weald Basin. It is the uppermost unit of the Wealden Group of ...
. The Wealden Group
The Wealden Group, occasionally also referred to as the Wealden Supergroup, is a group (a sequence of rock strata) in the lithostratigraphy of southern England. The Wealden group consists of paralic to continental (freshwater) facies sedimenta ...
is overlain by the Lower Greensand
The Lower Greensand Group is a geological unit present across large areas of Southern England. It was deposited during the Aptian and Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. It predominantly consists of sandstone and unconsolidated sand that were ...
and the Gault
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in Fo ...
Formation, consisting of the Gault
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in Fo ...
and the Upper Greensand
Greensand or green sand is a sand or sandstone which has a greenish color. This term is specifically applied to shallow marine sediment that contains noticeable quantities of rounded greenish grains. These grains are called ''glauconies'' and c ...
.
The rocks of the central part of the anticline include hard sandstones, and these form hills now called the ''High Weald''. The peripheral areas are mostly of softer sandstones and clays and form a gentler rolling landscape, the ''Low Weald''. The Weald–Artois Anticline
The Weald–Artois Anticline, or Wealden Anticline, is a large anticline, a geological structure running between the regions of the Weald in southern England and Artois in northern France. The fold formed during the Alpine orogeny, from the late ...
continues some further south-eastwards under the Straits of Dover
The Strait of Dover or Dover Strait (french: Pas de Calais - ''Strait of Calais''), is the strait at the narrowest part of the English Channel, marking the boundary between the Channel and the North Sea, separating Great Britain from continen ...
, and includes the Boulonnais of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
.
Many important fossils have been found in the sandstones and clays of the Weald, including, for example, ''Baryonyx
''Baryonyx'' () is a genus of theropod dinosaur which lived in the Barremian stage of the Early Cretaceous period, about 130–125 million years ago. The first skeleton was discovered in 1983 in the Smokejack Clay Pit, of Surrey, England, in s ...
''. The famous scientific hoax of Piltdown Man
The Piltdown Man was a paleoanthropological fraud in which bone fragments were presented as the fossilised remains of a previously unknown early human. Although there were doubts about its authenticity virtually from the beginning, the remains ...
was claimed to have come from a gravel pit at Piltdown
Piltdown is a series of hamlets in East Sussex, England. It is located south of Ashdown Forest. It is best known for the Piltdown Man hoax where amateur archaeologist Charles Dawson claimed to have discovered evidence of the " missing link" in ...
near Uckfield
Uckfield () is a town in the Wealden District of East Sussex in South East England. The town is on the River Uck, one of the tributaries of the River Ouse, on the southern edge of the Weald.
Etymology
'Uckfield', first recorded in writing as ...
. The first ''Iguanodon
''Iguanodon'' ( ; meaning ' iguana-tooth'), named in 1825, is a genus of iguanodontian dinosaur. While many species have been classified in the genus ''Iguanodon'', dating from the late Jurassic Period to the early Cretaceous Period of Asia, ...
'' was identified after Mary Mantell unearthed some fossilised teeth by a road in Sussex in 1822. Her husband, the geologist Gideon Mantell
Gideon Algernon Mantell MRCS FRS (3 February 1790 – 10 November 1852) was a British obstetrician, geologist and palaeontologist. His attempts to reconstruct the structure and life of ''Iguanodon'' began the scientific study of dinosaurs: in ...
, noticed they were similar to modern iguana teeth but many times larger; this important find led to the discovery of dinosaurs.
The area contains significant reserves of shale oil, totalling 4.4 billion barrels of oil
A barrel is one of several units of volume applied in various contexts; there are dry barrels, fluid barrels (such as the U.K. beer barrel and U.S. beer barrel), oil barrels, and so forth. For historical reasons the volumes of some barrel units ...
in the Wealden basin according to a 2014 study, which then Business and Energy Minister Michael Fallon
Sir Michael Cathel Fallon (born 14 May 1952) is a British politician who served as Secretary of State for Defence from 2014 to 2017. A member of the Conservative Party, he served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Sevenoaks from 1997 to 2019, ...
said "will bring jobs and business opportunities" and significantly help with UK energy self-sufficiency. Fracking
Fracking (also known as hydraulic fracturing, hydrofracturing, or hydrofracking) is a well stimulation technique involving the fracturing of bedrock formations by a pressurized liquid. The process involves the high-pressure injection of "frac ...
in the area would be required to achieve these objectives, which has been opposed by environmental groups.
History
 Prehistoric evidence suggests that, following the
Prehistoric evidence suggests that, following the Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
hunter-gatherers, the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
inhabitants had turned to farming, with the resultant clearance of the forest. With the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
came the first use of the Weald as an industrial area. Wealden sandstones contain ironstone
Ironstone is a sedimentary rock, either deposited directly as a ferruginous sediment or created by chemical replacement, that contains a substantial proportion of an iron ore compound from which iron (Fe) can be smelted commercially. Not to be con ...
, and with the additional presence of large amounts of timber for making charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, ...
for fuel, the area was the centre of the Wealden iron industry
The Wealden iron industry was located in the Weald of south-eastern England. It was formerly an important industry, producing a large proportion of the bar iron made in England in the 16th century and most British cannon until about 1770. Iron ...
from then, through the Roman times, until the last forge was closed in 1813. The index to the Ordnance Survey Map of Roman Britain lists 33 iron mines; and 67% of these are in the Weald.
The entire Weald was originally heavily forested. According to the 9th-century ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of A ...
'', the Weald measured or longer by in the Saxon era, stretching from Lympne
Lympne (), formerly also Lymne, is a village on the former shallow-gradient sea cliffs above the expansive agricultural plain of Romney Marsh in Kent. The settlement forms an L shape stretching from Port Lympne Zoo via Lympne Castle facing Lymp ...
, near Romney Marsh
Romney Marsh is a sparsely populated wetland area in the counties of Kent and East Sussex in the south-east of England. It covers about . The Marsh has been in use for centuries, though its inhabitants commonly suffered from malaria until ...
in Kent, to the Forest of Bere
The Forest of Bere is a mixed-use partially forested area in Hampshire immediately north of Fareham, Portsmouth and Roman Road, Havant and including a small part of the South Downs National Park.New Forest
The New Forest is one of the largest remaining tracts of unenclosed pasture land, heathland and forest in Southern England, covering southwest Hampshire and southeast Wiltshire. It was proclaimed a royal forest by William the Conqueror, fea ...
in Hampshire.'The Kent and Sussex Weald, Peter Brandon, published by Phillimore and Company, 2003 The area was sparsely inhabited and inhospitable, being used mainly as a resource by people living on its fringes, much as in other places in Britain such as Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite which forms the uplands dates from the Carboniferous P ...
, the Fens
The Fens, also known as the , in eastern England are a naturally marshy region supporting a rich ecology and numerous species. Most of the fens were drained centuries ago, resulting in a flat, dry, low-lying agricultural region supported by a ...
and the Forest of Arden
Arden is an area located mainly in Warwickshire, England, with parts in Staffordshire and Worcestershire, and is traditionally regarded as extending from the River Avon to the River Tame. It was once heavily wooded, giving rise to the name 'F ...
. The Weald was used for centuries, possibly since the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
, for transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower val ...
of animals along droveway
A drovers' road, drove ''roador droveway is a route for droving livestock on foot from one place to another, such as to market or between summer and winter pasture (see transhumance). Many drovers' roads were ancient routes of unknown age; ...
s in the summer months. Over the centuries, deforestation for the shipbuilding, charcoal, forest glass
Forest glass (''Waldglas'' in German) is late medieval glass produced in northwestern and central Europe from approximately 1000–1700 AD using wood ash and sand as the main raw materials and made in factories known as glasshouses in forest a ...
, and brickmaking industries has left the Low Weald with only remnants of that woodland cover.
While most of the Weald was used for transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower val ...
by communities at the edge of the Weald, several parts of the forest on the higher ridges in the interior seem to have been used for hunting by the kings of Sussex. The pattern of droveways which occurs across the rest of the Weald is absent from these areas. These areas include St Leonard's Forest
St Leonard's Forest is at the western end of the Wealden Forest Ridge which runs from Horsham to Tonbridge, and is part of the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It lies on the ridge to the south of the A264 between Horsham and Crawl ...
, Worth Forest, Ashdown Forest
Ashdown Forest is an ancient area of open heathland occupying the highest sandy ridge-top of the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is situated some south of London in the county of East Sussex, England. Rising to an elevation
...
and Dallington Forest
Dallington Forest is a biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) east of Heathfield in East Sussex. The SSSI is part of the larger Dallington Forest.
The Willingford Stream has cut through forest, creating a steep sided valley with ...
.
The forests of the Weald were often used as a place of refuge and sanctuary. The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' relates events during the Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
conquest of Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
when the native Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
(whom the Anglo-Saxons called ''Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
'') were driven from the coastal towns into the recesses of the forest for sanctuary,:
Until the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Ren ...
the forest was a notorious hiding place for bandit
Banditry is a type of organized crime committed by outlaws typically involving the threat or use of violence. A person who engages in banditry is known as a bandit and primarily commits crimes such as extortion, robbery, and murder, either as an ...
s, highwaymen
A highwayman was a robber who stole from travellers. This type of thief usually travelled and robbed by horse as compared to a footpad who travelled and robbed on foot; mounted highwaymen were widely considered to be socially superior to fo ...
and outlaw
An outlaw, in its original and legal meaning, is a person declared as outside the protection of the law. In pre-modern societies, all legal protection was withdrawn from the criminal, so that anyone was legally empowered to persecute or kill th ...
s.
Settlements on the Weald are widely scattered. Villages evolved from small settlements in the woods, typically apart; close enough to be an easy walk but not so close as to encourage unnecessary intrusion. Few of the settlements are mentioned in the Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
; however Goudhurst's church dates from the early 12th century or before and Wadhurst was big enough by the mid-13th century to be granted a royal charter permitting a market to be held. Before then, the Weald was used as summer grazing land, particularly for pannage
Pannage (also referred to as ''Eichelmast'' or ''Eckerich'' in Germany, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Austria, Slovenia and Croatia) is the practice of releasing livestock- pigs in a forest, so that they can feed on fallen acorns, be ...
by inhabitants of the surrounding areas. Many places within the Weald have retained names from this time, linking them to the original communities by the addition of the suffix "''-den''": for example, Tenterden
Tenterden is a town in the borough of Ashford in Kent, England. It stands on the edge of the remnant forest the Weald, overlooking the valley of the River Rother. It was a member of the Cinque Ports Confederation. Its riverside today is ...
was the area used by the people of Thanet. Permanent settlements in much of the Weald developed much later than in other parts of lowland Britain, although there were as many as one hundred furnaces and forges operating by the later 16th century, employing large numbers of people.
In the 12th century, the Weald still extended so far that citizens of London could hunt wild bull and the boar in Hampstead
Hampstead () is an area in London, which lies northwest of Charing Cross, and extends from the A5 road (Roman Watling Street) to Hampstead Heath, a large, hilly expanse of parkland. The area forms the northwest part of the London Borough o ...
.
In 1216 during the First Barons' War
The First Barons' War (1215–1217) was a civil war in the Kingdom of England in which a group of rebellious major landowners (commonly referred to as barons) led by Robert Fitzwalter waged war against King John of England. The conflict resulte ...
, a guerilla force of archers from the Weald, led by William of Cassingham
William of Cassingham (or Willikin of the Weald) (died 1257) was a country squire of Cassingham (now Kensham) in Kent at the time of the First Barons' War. During that conflict, he raised a guerrilla force of archers which opposed the otherwise ...
(nicknamed Willikin of the Weald), ambushed the French occupying army led by Prince Louis near Lewes
Lewes () is the county town of East Sussex, England. It is the police and judicial centre for all of Sussex and is home to Sussex Police, East Sussex Fire & Rescue Service, Lewes Crown Court and HMP Lewes. The civil parish is the centre of t ...
and drove them to the coast at Winchelsea
Winchelsea () is a small town in the non-metropolitan county of East Sussex, within the historic county of Sussex, England, located between the High Weald and the Romney Marsh, approximately south west of Rye and north east of Hastings. The ...
. The timely arrival of a French fleet allowed the French forces to narrowly escape starvation. William was later granted a pension from the crown and made warden of the Weald in reward for his services.
The inhabitants of the Weald remained largely independent and hostile to outsiders during the next decades. In 1264 during the Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the fu ...
, the royalist army of King Henry III of England
Henry III (1 October 1207 – 16 November 1272), also known as Henry of Winchester, was King of England, Lord of Ireland, and Duke of Aquitaine from 1216 until his death in 1272. The son of King John and Isabella of Angoulême, Henry ...
marched through the Weald in order to force the submission of the Cinque Ports
The Confederation of Cinque Ports () is a historic group of coastal towns in south-east England – predominantly in Kent and Sussex, with one outlier ( Brightlingsea) in Essex. The name is Old French, meaning "five harbours", and alludes to t ...
. Even though they were not aligned with the rebellious barons, the Weald's natives – mostly operating as archers – opposed the royalist advance, using guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run ta ...
. Even though they were unable to stop the army, their attacks inflicted substantial losses on the royalists. In retribution, King Henry ordered the execution of any Weald archers who were captured alive, for instance beheading 300 after a local shot his cook. The king also fined the Battle Abbey
Battle Abbey is a partially ruined Benedictine abbey in Battle, East Sussex, England. The abbey was built on the site of the Battle of Hastings and dedicated to St Martin of Tours. It is a Scheduled Monument.
The Grade I listed site is now ...
for the disloyalty of its tenants.
In the first edition of ''On The Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'', Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
used an estimate for the erosion of the chalk, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
and clay strata of the Weald in his theory of natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charl ...
. Charles Darwin was a follower of Lyell's theory of uniformitarianism
Uniformitarianism, also known as the Doctrine of Uniformity or the Uniformitarian Principle, is the assumption that the same natural laws and processes that operate in our present-day scientific observations have always operated in the universe in ...
and decided to expand upon Lyell's theory with a quantitative estimate to determine if there was enough time in the history of the Earth to uphold his principles of evolution. He assumed the rate of erosion was around one inch per century and calculated the age of the Weald at around 300 million years. Were that true, he reasoned, the Earth itself must be much older. In 1862, William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) published a paper "On the age of the sun's heat", in which – unaware of the process of solar fusion – he calculated the Sun had been burning for less than a million years, and put the outside limit of the age of the Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion, or core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating is based on evidence from radiometric age-dating of ...
at 200 million years. Based on these estimates he denounced Darwin's geological estimates as imprecise. Darwin saw Lord Kelvin's calculation as one of the most serious criticisms to his theory and removed his calculations on the Weald from the third edition of ''On the Origin of Species''.
Modern chronostratigraphy shows that the Weald Clays were laid down around 130 million years ago in the Early Cretaceous.
Geography
 The Weald begins north-east of
The Weald begins north-east of Petersfield
Petersfield is a market town and civil parish in the East Hampshire district of Hampshire, England. It is north of Portsmouth. The town has its own railway station on the Portsmouth Direct line, the mainline rail link connecting Portsmouth a ...
in Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
and extends across Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant ur ...
and Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
in the north, and Sussex in the south. The western parts in Hampshire and West Sussex, known as the Western Weald
The western Weald is an area of undulating countryside in Hampshire and West Sussex containing a mixture of woodland and heathland areas.
It lies to the south of the towns of Bordon, Haslemere and Rake and to the west of the town of Pulborough. ...
, are included in the South Downs National Park
The South Downs National Park is England's newest national park, designated on 31 March 2010. The park, covering an area of in southern England, stretches for from Winchester in the west to Eastbourne in the east through the counties of Hamp ...
. Other protected parts of the Weald are included in the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty and the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. In extent it covers about from west to east, and about from north to south, covering an area of some . The eastern end of the High Weald, the English Channel
The English Channel, "The Sleeve"; nrf, la Maunche, "The Sleeve" ( Cotentinais) or ( Jèrriais), ( Guernésiais), "The Channel"; br, Mor Breizh, "Sea of Brittany"; cy, Môr Udd, "Lord's Sea"; kw, Mor Bretannek, "British Sea"; nl, Het Ka ...
coast, is marked in the centre by the high sandstone cliffs from Hastings
Hastings () is a large seaside town and borough in East Sussex on the south coast of England,
east to the county town of Lewes and south east of London. The town gives its name to the Battle of Hastings, which took place to the north-west ...
to Pett Level
Pett is a village and civil parish in the Rother district of East Sussex, England. The village is located north-east of Hastings on the edge of Pett Level, the one-time marshes stretching along the coast of Rye Bay.
The road through the vill ...
; and by former sea cliffs now fronted by the Pevensey and Romney Marshes on either side.
Much of the ''High Weald'', the central part, is designated as the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. Its landscape is described as one of
Ashdown Forest
Ashdown Forest is an ancient area of open heathland occupying the highest sandy ridge-top of the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is situated some south of London in the county of East Sussex, England. Rising to an elevation
...
, an extensive area of heathland and woodland occupying the highest sandy ridge-top at the centre of the High Weald, is a former royal deer-hunting forest created by the Normans and said to be the largest remaining part of ''Andredesweald''.
There are centres of settlement, the largest of which are Horsham
Horsham is a market town on the upper reaches of the River Arun on the fringe of the Weald in West Sussex, England. The town is south south-west of London, north-west of Brighton and north-east of the county town of Chichester. Nearby to ...
, Burgess Hill
Burgess Hill is a town and civil parish in West Sussex, England, close to the border with East Sussex, on the edge of the South Downs National Park, south of London, north of Brighton and Hove, and northeast of the county town, Chichester. It h ...
, East Grinstead
East Grinstead is a town in West Sussex, England, near the East Sussex, Surrey, and Kent borders, south of London, northeast of Brighton, and northeast of the county town of Chichester. Situated in the extreme northeast of the county, the civ ...
, Haywards Heath
Haywards Heath is a town in West Sussex, England, south of London, north of Brighton, south of Gatwick Airport and northeast of the county town, Chichester. Nearby towns include Burgess Hill to the southwest, Horsham to the northwest, Cra ...
, Tonbridge
Tonbridge ( ) is a market town in Kent, England, on the River Medway, north of Royal Tunbridge Wells, south west of Maidstone and south east of London. In the administrative borough of Tonbridge and Malling, it had an estimated population ...
, Tunbridge Wells
Royal Tunbridge Wells is a town in Kent, England, southeast of central London. It lies close to the border with East Sussex on the northern edge of the High Weald, whose sandstone geology is exemplified by the rock formation High Rocks. T ...
, Crowborough
Crowborough is a town and civil parish in East Sussex, England, in the Weald at the edge of Ashdown Forest in the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, 7 miles (11 km) south-west of Royal Tunbridge Wells and 33 miles ( ...
; and the area along the coast from Hastings and Bexhill-on-Sea
Bexhill-on-Sea (often shortened to Bexhill) is a seaside town and civil parish situated in the county of East Sussex in South East England. An ancient town and part of the local government district of Rother, Bexhill is home to a number of ...
to Rye and Hythe
Hythe, from Anglo-Saxon ''hȳð'', may refer to a landing-place, port or haven, either as an element in a toponym, such as Rotherhithe in London, or to:
Places Australia
* Hythe, Tasmania
Canada
*Hythe, Alberta, a village in Canada
England
* ...
.
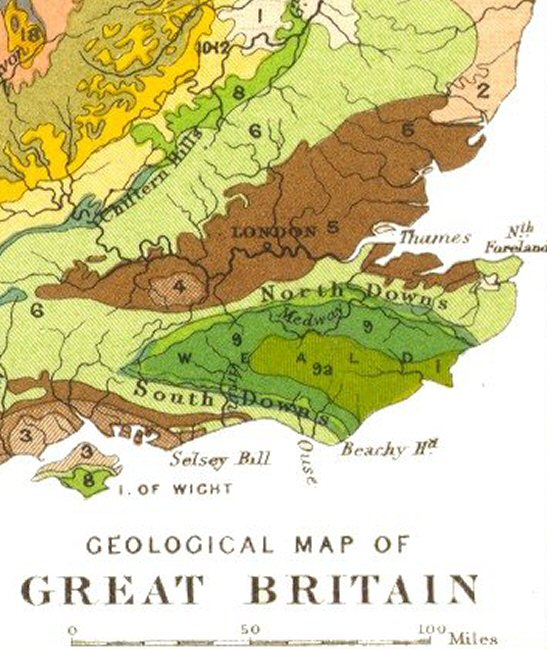
The geological map shows the High Weald in lime green (9a).
The ''Low Weald'', the periphery of the Weald, is shown as darker green on the map (9), and has an entirely different character. It is in effect the eroded outer edges of the High Weald, revealing a mixture of sandstone outcrops within the underlying clay. As a result, the landscape is of wide and low-lying clay vales with small woodlands ( “shaws”) and fields. There is a great deal of surface water: ponds and many meandering streams.
Some areas, such as the flat plain around Crawley
Crawley () is a large town and borough in West Sussex, England. It is south of London, north of Brighton and Hove, and north-east of the county town of Chichester. Crawley covers an area of and had a population of 106,597 at the time of ...
, have been utilised for urban use: here are Gatwick Airport
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after ...
and its related developments and the Horley
Horley is a town in the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey, England, south of the towns of Reigate and Redhill. The county border with West Sussex is to the south with Crawley and Gatwick Airport close to the town.
It has its own eco ...
-Crawley commuter settlements. Otherwise the Low Weald retains its historic settlement pattern, where the villages and small towns occupy harder outcrops of rocks. There are no large towns on the Low Weald, although Ashford Ashford may refer to:
Places
Australia
*Ashford, New South Wales
*Ashford, South Australia
*Electoral district of Ashford, South Australia
Ireland
*Ashford, County Wicklow
*Ashford Castle, County Galway
United Kingdom
*Ashford, Kent, a town
**B ...
, Sevenoaks
Sevenoaks is a town in Kent with a population of 29,506 situated south-east of London, England. Also classified as a civil parish, Sevenoaks is served by a commuter main line railway into London. Sevenoaks is from Charing Cross, the traditio ...
and Reigate
Reigate ( ) is a town in Surrey, England, around south of central London. The settlement is recorded in Domesday Book in 1086 as ''Cherchefelle'' and first appears with its modern name in the 1190s. The earliest archaeological evidence for huma ...
lie immediately on the northern edge. Settlements tend to be small and linear, because of its original wooded nature and heavy clay soils.
The Weald is drained by the many streams radiating from it, the majority being tributaries of the surrounding major rivers: particularly the Mole, Medway
Medway is a unitary authority district and conurbation in Kent, South East England. It had a population of 278,016 in 2019. The unitary authority was formed in 1998 when Rochester-upon-Medway amalgamated with the Borough of Gillingham to ...
, Stour, Rother, Cuckmere
The River Cuckmere rises near Heathfield in East Sussex, England on the southern slopes of the Weald. The name of the river probably comes from an Old English word meaning "fast-flowing", since it descends over 100 m (328 ft) in it ...
, Ouse
Ouse may refer to:
Places Rivers in England
* River Ouse, Yorkshire
* River Ouse, Sussex
* River Great Ouse, Northamptonshire and East Anglia
** River Little Ouse, a tributary of the River Great Ouse
Other places
* Ouse, Tasmania, a town in Aus ...
, Adur and Arun. Many of these streams provided the power for the watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in the production ...
s, blast furnaces
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being "forced" or supplied above atmospheric ...
and hammers of the iron industry and the cloth mills.
Transport infrastructure
The M25, M26 andM20 motorway
The M20 is a motorway in Kent, England. It follows on from the A20 at Swanley, meeting the M25, and continuing on to Folkestone, providing a link to the Channel Tunnel and the ports at Dover. It is long. Although not signposted in Eng ...
s all use the Vale of Holmesdale
Holmesdale, also known as the Vale of Holmesdale, is a valley in South-East England that falls between the hill ranges of the North Downs and the Greensand Ridge of the Weald, in the counties of Kent and Surrey. It stretches from Folkestone o ...
to the north, and therefore run along or near the northern edge of the Weald. The M23/A23 road
The A23 road is a major road in the United Kingdom between London and Brighton, East Sussex, England. It is managed by Transport for London for the section inside the Greater London boundary, Surrey County Council and West Sussex County Cou ...
to Brighton
Brighton () is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the City of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located south of London.
Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze A ...
, uses the western, narrower, part of the Weald where there are stream headwaters, crossing it from north to south. Other roads take similar routes, although they often have long hills and many bends: the more sedate, but busy A21 trunk road to Hastings is still beset with traffic delays, despite having had some new sections.
Five railways once crossed the Weald, now reduced to three. Building them provided the engineers with difficulties in crossing the terrain, with the hard sandstone adding to their problems. The Brighton Main Line
The Brighton Main Line (also known as the South Central Main Line) is a major railway line in the United Kingdom that links Brighton, on the south coast of England, with central London. In London the line has two branches, out of and station ...
followed the same route as its road predecessors: although it necessitated the long tunnel near Balcombe and the Ouse Valley Viaduct
The Ouse Valley Viaduct (or the Balcombe Viaduct) carries the London-Brighton Railway Line over the River Ouse in Sussex. It is located to the north of Haywards Heath and the south of Balcombe. Known for its ornate design, the structure has ...
. Tributaries of the River Ouse provided some assistance in the building of now-closed East Grinstead
East Grinstead is a town in West Sussex, England, near the East Sussex, Surrey, and Kent borders, south of London, northeast of Brighton, and northeast of the county town of Chichester. Situated in the extreme northeast of the county, the civ ...
-Lewes
Lewes () is the county town of East Sussex, England. It is the police and judicial centre for all of Sussex and is home to Sussex Police, East Sussex Fire & Rescue Service, Lewes Crown Court and HMP Lewes. The civil parish is the centre of t ...
and the Uckfield
Uckfield () is a town in the Wealden District of East Sussex in South East England. The town is on the River Uck, one of the tributaries of the River Ouse, on the southern edge of the Weald.
Etymology
'Uckfield', first recorded in writing as ...
-Lewes lines. The principal main-line railway to Hastings had to negotiate difficult terrain when it was first built, necessitating many sharp curves and tunnels; and similar problems had to be faced with the Ashford-Hastings line.
Several long-distance footpaths
A long-distance trail (or long-distance footpath, track, way, greenway (landscape), greenway) is a longer recreational trail mainly through rural areas used for hiking, backpacking (wilderness), backpacking, cycling, horse riding or cross-cou ...
criss-cross the Weald, and it is well-mapped recreationally, covered by routes from:
* The Ramblers' Association
The Ramblers is the trading name of the Ramblers Association, Great Britain's leading walking charity. The Ramblers is also a membership organisation with around 100,000 members and a network of volunteers who maintain and protect the path ...
s and most District Councils for walkers
* Sustrans
Sustrans is a United Kingdom-based walking, wheeling and cycling charity, and the custodian of the National Cycle Network.
Its flagship project is the National Cycle Network, which has created of signed cycle routes throughout the United K ...
and local county councils for cyclists
Cycling, also, when on a two-wheeled bicycle, called bicycling or biking, is the use of cycles for transport, recreation, exercise or sport. People engaged in cycling are referred to as "cyclists", "bicyclists", or "bikers". Apart from two ...
Farming
Neither the thin infertile sands of the High Weald or the wet sticky clays of the Low Weald are suited to intensive arable farming and thetopography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
of the area often increases the difficulties. There are limited areas of fertile greensand which can be used for intensive vegetable growing, as in the valley of the Western Rother. Historically the area of cereals grown has varied greatly with changes in prices, increasing during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
and during and since World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
About 60% of the High Weald farmed land is grassland, with about 20% being arable
The Weald has its own breed of cattle, called the Sussex
Sussex (), from the Old English (), is a historic county in South East England that was formerly an independent medieval Anglo-Saxon kingdom. It is bounded to the west by Hampshire, north by Surrey, northeast by Kent, south by the Englis ...
, although it has been as numerous in Kent and parts of Surrey. Bred from the strong hardy oxen, which continued to be used to plough the clay soils of the Low Weald longer than in most places, these red beef cattle were highly praised by Arthur Young in his book ''Agriculture of Sussex'' when visiting Sussex in the 1790s. William Cobbett commented on finding some of the finest cattle on some of the region's poorest subsistence farms on the High Weald. Pigs, which were kept by most households in the past, were able to be fattened in autumn on acorns in the extensive oak woods. In his novel ''Memoirs of a Fox-hunting Man'', the poet and novelist Siegfried Sassoon
Siegfried Loraine Sassoon (8 September 1886 – 1 September 1967) was an English war poet, writer, and soldier. Decorated for bravery on the Western Front, he became one of the leading poets of the First World War. His poetry both describ ...
refers to "the agricultural serenity of the Weald widespread in the delicate hazy sunshine".
Viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, r ...
has expanded quite rapidly across the Weald, where the climate and soil is well suited to the growing of grapes, with over 20 vineyards now in the Wealden district alone
Wildlife
The Weald has largely maintained its wooded character, with woodland still covering 23% of the overall area (one of the highest levels in England) and the proportion is considerably higher in some central parts. The sandstones of the Wealden rocks are usually acidic, often leading to the development of acidic habitats such asheathland
A heath () is a shrubland habitat found mainly on free-draining infertile, acidic soils and characterised by open, low-growing woody vegetation. Moorland is generally related to high-ground heaths with—especially in Great Britain—a coole ...
, the largest remaining areas of which are in Ashdown Forest
Ashdown Forest is an ancient area of open heathland occupying the highest sandy ridge-top of the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is situated some south of London in the county of East Sussex, England. Rising to an elevation
...
and near Thursley
Thursley is a village and civil parish in southwest Surrey, west of the A3 between Milford and Hindhead. An associated hamlet is Bowlhead Green. To the east is Brook. In the south of the parish rises the Greensand Ridge, in this section reach ...
.
Although common in France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
became extinct in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
by the 17th century, but wild breeding populations have recently returned in the Weald, following escapes from boar farms.
Culture
The Weald has been associated with many writers, particularly in the 19th and early 20th centuries. These includeVita Sackville-West
Victoria Mary, Lady Nicolson, Order of the Companions of Honour, CH (Birth name, née Sackville-West; 9 March 1892 – 2 June 1962), usually known as Vita Sackville-West, was an English author and garden designer.
Sackville-West was a su ...
(1892–1962), Sir Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for '' A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ...
(1859-1930) and Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)'' The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
(1865–1936). The setting for A.A. Milne's ''Winnie-the-Pooh
Winnie-the-Pooh, also called Pooh Bear and Pooh, is a fictional anthropomorphic teddy bear created by English author A. A. Milne and English illustrator E. H. Shepard.
The first collection of stories about the character was the book ''Win ...
'' stories was inspired by Ashdown Forest
Ashdown Forest is an ancient area of open heathland occupying the highest sandy ridge-top of the High Weald Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. It is situated some south of London in the county of East Sussex, England. Rising to an elevation
...
, near Milne's country home at Hartfield
Hartfield is a village and civil parish in the Wealden district of East Sussex, England. The parish also includes the settlements of Colemans Hatch, Hammerwood and Holtye, all lying on the northern edge of Ashdown Forest.
Geography
The main ...
. John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or m ...
(1620–1706), whose family estate was Wotton House
Wotton House, Wotton Underwood, Buckinghamshire, England, is a stately home built between 1704 and 1714, to a design very similar to that of the contemporary version of Buckingham House. The house is an example of English Baroque and a Grade I ...
on the River Tillingbourne
The River Tillingbourne (also known as the Tilling Bourne) runs along the south side of the North Downs and joins the River Wey at Guildford. Its source is a mile south of Tilling Springs to the north of Leith Hill at and it runs through Friday ...
near Dorking
Dorking () is a market town in Surrey in South East England, about south of London. It is in Mole Valley, Mole Valley District and the non-metropolitan district, council headquarters are to the east of the centre. The High Street runs roughl ...
, Surrey, was an essayist, diarist, and early author of botany, gardening and geography. The second half of E. M. Forster's ''A Room with a View
''A Room with a View'' is a 1908 novel by English writer E. M. Forster, about a young woman in the restrained culture of Edwardian era England. Set in Italy and England, the story is both a romance and a humorous critique of English society a ...
'' takes place at the protagonist's family home, "Windy Corner", in the Weald.
Sir Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from 1 ...
, British statesman and a prolific writer himself, did much of his writing at his country house, Chartwell
Chartwell is a country house near Westerham, Kent, in South East England. For over forty years it was the home of Winston Churchill. He bought the property in September 1922 and lived there until shortly before his death in January 1965. In th ...
, near Westerham, which has extensive views over the Weald. The view from the house was of crucial importance to Churchill; he once remarked, "I bought Chartwell for that view."
In the early 21st century, Tunbridge Wells Borough Council promoted "Seven Wonders of the Weald":
* Bayham Old Abbey
Bayham Old Abbey is an English Heritage property, located near Lamberhurst, Kent, England. Founded c. 1207 through a combination of the failing Premonstratensian monasteries of Otham and Brockley, Bayham functioned as an abbey until its dissolu ...
* Bedgebury Pinetum
Bedgebury National Pinetum at Bedgebury, Kent, in the United Kingdom, is a recreational and conservational arboretum managed by Forestry England that was established as the National Conifer Collection in 1925 and is now recognised as the most c ...
* Bewl Water
* Finchcocks
* Lamberhurst Vineyard
* Marle Place
* Scotney Castle
Scotney Castle is an English country house with formal garden
A formal garden is a garden with a clear structure, geometric shapes and in most cases a symmetrical layout. Its origin goes back to the gardens which are located in the desert are ...
Sport
The game ofcricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
may have originated prior to the 13th century in the Weald . The related game of stoolball is still popular in the Weald, it was originally played mainly by women's teams, but since the formation of the Sussex league at the beginning of the 20th century it has been played by both men and women.
Other English wealds and wolds
Several other areas in southern England have the name "Weald", includingNorth Weald
North Weald Bassett or simply North Weald is a village and civil parish in the Epping Forest district of Essex, England. The village is within the North Weald Ridges and Valleys landscape area.
A market is held every Saturday and Bank Holiday Mo ...
in Essex
Essex () is a Ceremonial counties of England, county in the East of England. One of the home counties, it borders Suffolk and Cambridgeshire to the north, the North Sea to the east, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent across the estuary of the Riv ...
, and Harrow Weald
Harrow Weald is a suburban district in Greater London, England. Located about north of Harrow, Harrow Weald is formed from a leafy 1930s suburban development along with ancient woodland of Harrow Weald Common. It forms part of the London Bor ...
in north-west London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
.
"Wold" is used as the name for various open rolling upland areas in the North of England, including the Yorkshire Wolds
The Yorkshire Wolds are low hills in the counties of the East Riding of Yorkshire and North Yorkshire in north-eastern England. The name also applies to the district in which the hills lie.
On the western edge, the Wolds rise to an escarpment wh ...
and the Lincolnshire Wolds, although these are, by contrast, chalk uplands.
The Cotswolds
The Cotswolds (, ) is a region in central-southwest England, along a range of rolling hills that rise from the meadows of the upper Thames to an escarpment above the Severn Valley and Evesham Vale.
The area is defined by the bedrock of J ...
are a major geographical feature of central England, forming a south-west to north-east line across the country.
See also
*Weald and Downland Open Air Museum
The Weald and Downland Living Museum (formerly known as the Weald and Downland Open Air Museum until January 2017) is an open-air museum in Singleton, West Sussex. The museum is a registered charity.
The museum covers , with over 50 historic bu ...
* Recreational walks in Kent
The following is a list of recreational walks in Kent, England.
Short walks
*Ashenbank Wood. Woodland Trust managed wood categorised as ancient woodland in Cobham, Gravesend with two waymarked routes, either part of the Darnley Trail with some ...
* History of Sussex
Sussex , from the Old English 'Sūþsēaxe' (' South Saxons'), is a historic county in South East England.
Evidence from a fossil of Boxgrove Man (''Homo heidelbergensis'') shows that Sussex has been inhabited for at least 500,000 years. It ...
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * *Further reading
* {{Coord, 51, N, 0.4, E, region:GB, display=title Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty in England Hills of East Sussex Hills of Kent Hills of Surrey Hills of West Sussex Wealden District Forests and woodlands of Kent Forests and woodlands of East Sussex Forests and woodlands of Surrey