Wave action (continuum mechanics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In continuum mechanics, wave action refers to a conservable measure of the
In continuum mechanics, wave action refers to a conservable measure of the
 In continuum mechanics, wave action refers to a conservable measure of the
In continuum mechanics, wave action refers to a conservable measure of the wave
In physics, mathematics, and related fields, a wave is a propagating dynamic disturbance (change from equilibrium) of one or more quantities. Waves can be periodic, in which case those quantities oscillate repeatedly about an equilibrium (re ...
part of a motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and m ...
. For small-amplitude
The amplitude of a periodic variable is a measure of its change in a single period (such as time or spatial period). The amplitude of a non-periodic signal is its magnitude compared with a reference value. There are various definitions of am ...
and slowly varying waves, the wave action density is:
:
where is the intrinsic wave energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
and is the intrinsic frequency of the slowly modulated waves – intrinsic here implying: as observed in a frame of reference moving with the mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value (magnitude and sign) of a given data set.
For a data set, the '' ari ...
velocity of the motion.
The action
Action may refer to:
* Action (narrative), a literary mode
* Action fiction, a type of genre fiction
* Action game, a genre of video game
Film
* Action film, a genre of film
* ''Action'' (1921 film), a film by John Ford
* ''Action'' (1980 fil ...
of a wave was introduced by in the study of the (pseudo) energy and momentum of waves in plasmas. derived the conservation of wave action – identified as an adiabatic invariant
A property of a physical system, such as the entropy of a gas, that stays approximately constant when changes occur slowly is called an adiabatic invariant. By this it is meant that if a system is varied between two end points, as the time for the ...
– from an averaged Lagrangian
In continuum mechanics, Whitham's averaged Lagrangian method – or in short Whitham's method – is used to study the Lagrangian dynamics of Slowly varying envelope approximation, slowly-varying wave trains in an inhomogeneous (moving) transmissi ...
description of slowly varying nonlinear
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many othe ...
wave trains in inhomogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
media
Media may refer to:
Communication
* Media (communication), tools used to deliver information or data
** Advertising media, various media, content, buying and placement for advertising
** Broadcast media, communications delivered over mass e ...
:
:
where is the wave-action density flux and is the divergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of t ...
of . The description of waves in inhomogeneous and moving media was further elaborated by for the case of small-amplitude waves; they also called the quantity ''wave action'' (by which name it has been referred to subsequently). For small-amplitude waves the conservation of wave action becomes:
: using and
where is the group velocity and the mean velocity of the inhomogeneous moving medium. While the ''total energy'' (the sum of the energies of the mean motion and of the wave motion) is conserved for a non-dissipative system, the energy of the wave motion is not conserved, since in general there can be an exchange of energy with the mean motion. However, wave action is a quantity which is conserved for the wave-part of the motion.
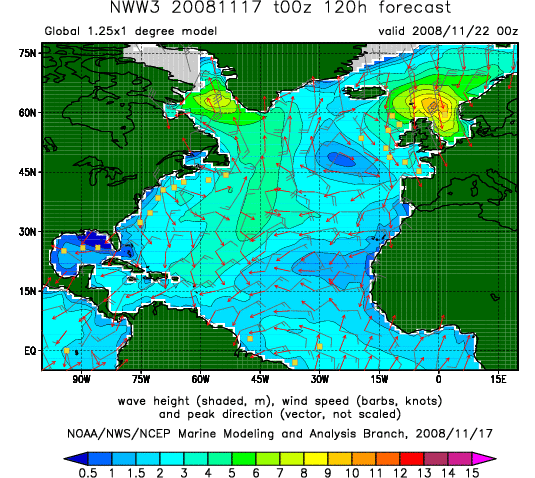
The equation for the conservation of wave action is for instance used extensively in wind wave model
In fluid dynamics, wind wave modeling describes the effort to depict the sea state and predict the evolution of the energy of wind waves using numerical techniques. These simulations consider atmospheric wind forcing, nonlinear wave interactio ...
s to forecast sea state
In oceanography, sea state is the general condition of the free surface on a large body of water—with respect to wind waves and swell—at a certain location and moment. A sea state is characterized by statistics, including the wave height, ...
s as needed by mariners, the offshore industry and for coastal defense. Also in and acoustics the concept of wave action is used.
The derivation of an exact wave-action equation for more general wave motion – not limited to slowly modulated waves, small-amplitude waves or (non-dissipative) conservative system In mathematics, a conservative system is a dynamical system which stands in contrast to a dissipative system. Roughly speaking, such systems have no friction or other mechanism to dissipate the dynamics, and thus, their phase space does not shrink o ...
s – was provided and analysed by using the framework of the generalised Lagrangian mean for the separation of wave and mean motion.
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * {{physical oceanography Continuum mechanics Waves