Wagria on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
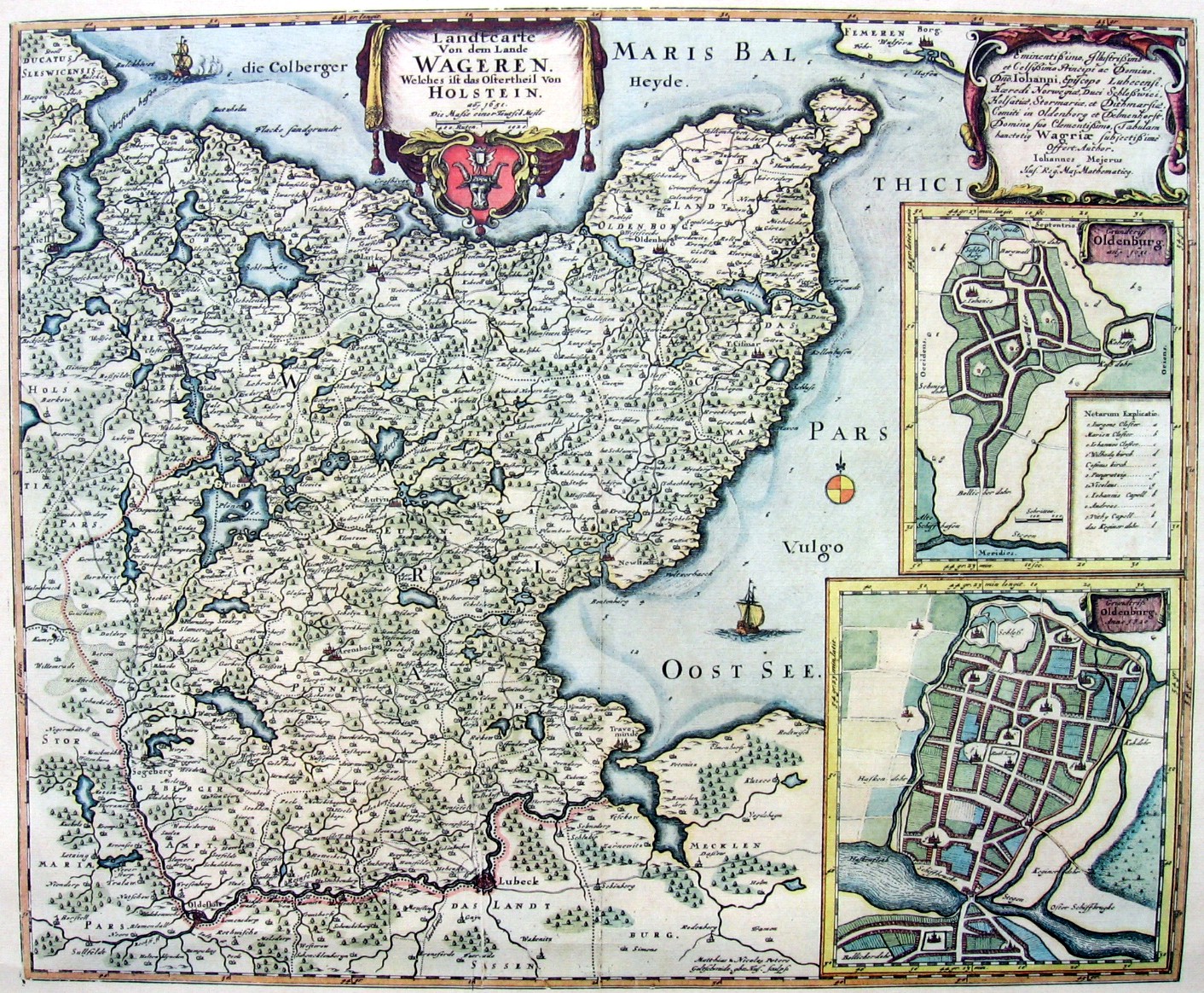 WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (german: Wagrien, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of
WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (german: Wagrien, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of
 In the
In the

 WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (german: Wagrien, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of
WagriaArnold, Benjamin (1991). ''Princes and territories in medieval Germany'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge and New York, p. 156. . (german: Wagrien, ''Waierland'' or ''Wagerland'') is the northeastern part of Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein (; da, Slesvig-Holsten; nds, Sleswig-Holsteen; frr, Slaswik-Holstiinj) is the northernmost of the 16 states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Sc ...
, corresponding roughly to the districts of Plön
Plön (; Holsatian: ''Plöön'') is the district seat of the Plön district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, and has about 8,700 inhabitants. It lies right on the shores of Schleswig-Holstein's biggest lake, the Great Plön Lake, as well as o ...
and Ostholstein. The word "Wagria" is derived derived from the Slavic Lechites
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Dist ...
tribe of Wagri
The Wagri, Wagiri, or Wagrians were a tribe of Polabian Slavs inhabiting Wagria, or eastern Holstein in northern Germany, from the ninth to twelfth centuries. They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrite confederacy.
In the Slavic uprisings of 9 ...
, which meant "those who live by the bays".
Geography
 In the
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, and as still shown on early modern maps, Wagria was bordered on the north and east by the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ...
from the Kiel Fjord
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland pe ...
to Lübeck Bay
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the st ...
, and inland by the rivers Schwentine
The Schwentine is a river in the North German state of Schleswig-Holstein. It is approximately long and rises on the hill of Bungsberg, the highest point in the state, near the village of Kasseedorf in Ostholstein. It then runs from its source to ...
and Trave
The Trave () is a river in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is approximately long, running from its source near the village of Gießelrade in Ostholstein to Travemünde, where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It passes through Bad Segeberg, Bad Old ...
. Today, Wagria generally refers just to the Oldenburg Peninsula (''Oldenburgische Halbinsel'') in Ostholstein.
The highest elevation in the peninsula is the Bungsberg at 168 metres.
History
The Lechitic (Slavic) root of the name, ''Wagria'', meant not only the so-called, present-day Wagrian peninsula, but the entire region between the Kiel Fjord, the middle reaches of the Trave, and the lower course of the river; a region with this name emerged at least as early as the 8th century. Wagria Castle occupied a central location in Oldenburg in Holstein (then called ''Starigard'', or "Old Castle"); its ramparts still exist. Important settlements in Wagria were Oldenburg, Old-Lübeck
Lübeck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of Lübeck (german: Hansestadt Lübeck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, Lübeck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
(Liubice Liubice, also known by the German name Alt-Lübeck ("Old Lübeck"), was a medieval West Slavic settlement near the site of modern Lübeck, Germany. Liubice was located at the confluence of the Schwartau with the Trave across from Teerhof Island, a ...
), and Plön
Plön (; Holsatian: ''Plöön'') is the district seat of the Plön district in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, and has about 8,700 inhabitants. It lies right on the shores of Schleswig-Holstein's biggest lake, the Great Plön Lake, as well as o ...
( Plune).
In 1143, according to the vivid account by contemporary chronicler, Helmold of Bosau, Count Adolf II of Schauenburg and Holstein introduced German settlers, not only from his own territories of Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
and Stormarn, but also from Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
and Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
, in order to develop the land of Wagria into a highly-profitable region as part of the German eastward expansion in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended around AD 150 ...
:
:''"Then a countless number of people from different tribes left, took their families and possessions with them and went with Count Adolf in Wagria to take possession of their promised land. Initially, those from Holsten were given the most sheltered area west of Segeberg, on the River Trave, on the Schwentine flood plain and everything from the Schwale to the Grimmelsberg and Lake Ploen. The country around Dargun was settled by the Westphalians, the Eutin area by the Dutch and Suesel by the Frisians. The Plön area remained uninhabited however. He allowed Oldenburg, Lütjenburg and other coastal areas be colonised by the Slavs, who had to pay taxes to him."''
The local Slavs were thus also involved in this expansion or development.

References
Sources
* Witt, Hermann (1982). ''1000 Jahre Wagrien von Luitschaburg bis Lütjenburg''. Sönksen Verlag, Plön. {{Authority control Regions of Schleswig-Holstein Plön (district) Ostholstein Obotrites Holstein Peninsulas of the Baltic Sea