WSR-74 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
WSR-74
It also has a dish diameter of 8 feet, and a maximum range of 579 km (313 nm) as it was used only for reflectivities (see Doppler dilemma).
 The WSR-57 network was very spread out, with 66 radars to cover the entire country. There was little to no overlap in case one of these vacuum-tube radars went down for maintenance. The WSR-74 was introduced as a "gap filler", as well as an updated radar that, among other things, was transistor-based.Roger C. Whiton, et al. "History of Operational Use of Weather Radar by U.S. Weather Services. Part I: The Pre-NEXRAD Era." Weather and Forecasting: Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 219–243. 19 Feb. 1998. American Meteorological Society. 5 Apr. 200
The WSR-57 network was very spread out, with 66 radars to cover the entire country. There was little to no overlap in case one of these vacuum-tube radars went down for maintenance. The WSR-74 was introduced as a "gap filler", as well as an updated radar that, among other things, was transistor-based.Roger C. Whiton, et al. "History of Operational Use of Weather Radar by U.S. Weather Services. Part I: The Pre-NEXRAD Era." Weather and Forecasting: Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 219–243. 19 Feb. 1998. American Meteorological Society. 5 Apr. 200
In the early 1970s, Enterprise Electronics Corporation (EEC), based out of Enterprise, Alabama won the contract to design, manufacture, test, and deliver the entire WSR-74 radar network (both C and S-Band versions). WSR-74C radars were generally local-use radars that didn't operate unless severe weather was expected, while WSR-74S radars were generally used to replace WSR-57 radars in the national weather surveillance network. When a network radar went down, a nearby local radar might have to supply updates like a network radar. NWS Lubbock received the first WSR-74C in August 1973 following widespread attention from the Lubbock F5 tornado of 1970. 128 of the WSR-57 and WSR-74 model radars were spread across the country as the National Weather Service's radar network until the 1990s. They were gradually replaced by the WSR-88D model (Weather Surveillance Radar - 1988, Doppler), constituting the
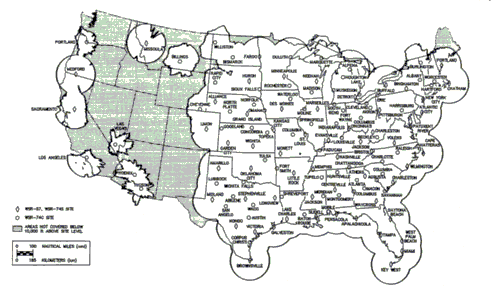 WSR-74 sites include the following two categories:
WSR-74 sites include the following two categories:Stormtrack.org Forum 10344
/ref>
radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, we ...
s were Weather Surveillance Radars designed in 1974 for the National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
. They were added to the existing network of the WSR-57 model to improve forecasts and severe weather warnings. Some have been sold to other countries like Australia, Greece, and Pakistan.
Radar properties
There are two types in the WSR-74 series, which are almost identical except for operating frequency. The WSR-74C (used for local warnings) operates in the C band, and the WSR-74S (used in the national network) operates in the S band (like the WSR-57 and the current WSR-88D). S band frequencies are better suited because they are not attenuated significantly in heavy rain while the C Band is strongly attenuated, and has a generally shorter maximum effective range. The WSR-74C uses a wavelength of 5.4 cm.Paul Sirvatka. "WSR - Weather Surveillance Radar." Radar. College of DuPage. 4 Apr. 200It also has a dish diameter of 8 feet, and a maximum range of 579 km (313 nm) as it was used only for reflectivities (see Doppler dilemma).
History
 The WSR-57 network was very spread out, with 66 radars to cover the entire country. There was little to no overlap in case one of these vacuum-tube radars went down for maintenance. The WSR-74 was introduced as a "gap filler", as well as an updated radar that, among other things, was transistor-based.Roger C. Whiton, et al. "History of Operational Use of Weather Radar by U.S. Weather Services. Part I: The Pre-NEXRAD Era." Weather and Forecasting: Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 219–243. 19 Feb. 1998. American Meteorological Society. 5 Apr. 200
The WSR-57 network was very spread out, with 66 radars to cover the entire country. There was little to no overlap in case one of these vacuum-tube radars went down for maintenance. The WSR-74 was introduced as a "gap filler", as well as an updated radar that, among other things, was transistor-based.Roger C. Whiton, et al. "History of Operational Use of Weather Radar by U.S. Weather Services. Part I: The Pre-NEXRAD Era." Weather and Forecasting: Vol. 13, No. 2, pp. 219–243. 19 Feb. 1998. American Meteorological Society. 5 Apr. 200In the early 1970s, Enterprise Electronics Corporation (EEC), based out of Enterprise, Alabama won the contract to design, manufacture, test, and deliver the entire WSR-74 radar network (both C and S-Band versions). WSR-74C radars were generally local-use radars that didn't operate unless severe weather was expected, while WSR-74S radars were generally used to replace WSR-57 radars in the national weather surveillance network. When a network radar went down, a nearby local radar might have to supply updates like a network radar. NWS Lubbock received the first WSR-74C in August 1973 following widespread attention from the Lubbock F5 tornado of 1970. 128 of the WSR-57 and WSR-74 model radars were spread across the country as the National Weather Service's radar network until the 1990s. They were gradually replaced by the WSR-88D model (Weather Surveillance Radar - 1988, Doppler), constituting the
NEXRAD
NEXRAD or Nexrad (Next-Generation Radar) is a network of 160 high-resolution S-band Doppler weather radars operated by the National Weather Service (NWS), an agency of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the United S ...
network. The WSR-74 had served the NWS for two decades.
The last WSR-74C used by the NWS was located in Williston, ND, before being decommissioned at the end of 2012.
No WSR-74S's are in the NWS inventory today, having been replaced by the WSR-88D, but some of these radars are in commercial use.
Radar sites in the US
 WSR-74 sites include the following two categories:
WSR-74 sites include the following two categories:/ref>
See also
{{US wx radarReferences