Vágar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vágar ( da, Vågø) is one of the 18 islands in the archipelago of the
 * Tindhólmur
* Gáshólmur
*
* Tindhólmur
* Gáshólmur
*
Stamps.fo
(public domain by
Personal website
with 78 aerial photos of Vágar {{DEFAULTSORT:Vagar Islands of the Faroe Islands Important Bird Areas of the Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
and the most westerly of the ''large islands''. With a size of , it ranks number three, behind Streymoy and Eysturoy
Eysturoy (pronounced estroimeaning 'East Island') is a region and the second-largest of the Faroe Islands, both in size and population.
Description
Eysturoy is separated by a narrow sound from the main island of Streymoy. Eysturoy is extremely ...
. Vágar region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics ( physical geography), human impact characteristics ( human geography), and the interaction of humanity an ...
also comprises the island of Mykines.
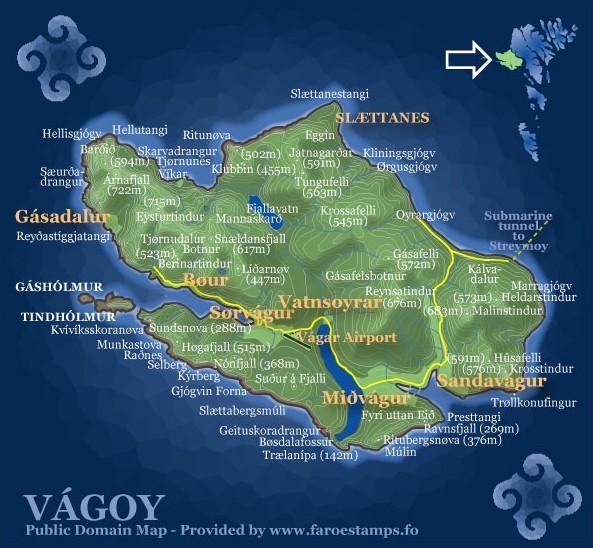
The Vágar island shape is very distinctive, since on maps it resembles a dog's head. The fjord Sørvágsfjørður
Sørvágsfjørður is a fjord on the west side of the island of Vágar, Vágoy in the Faroe Islands which is approximately long.
At the end of the fjord lies the village of Sørvágur. On the northside of the fjord lies the small village of B� ...
is the mouth and the lake Fjallavatn is the eye.
History
Vágar is the first port of call for most foreigners travelling to theFaroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
, as it is home to the islands’ only airport, Vágar Airport. An airfield was built there during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
by the British, who occupied the Faroe Islands with the islanders' consent. After the war it lay unused for about 20 years, but was then put back into service and expanded/modernised as required. It handles about 290,000 passengers a year (2016). Such large numbers by Faroese standards put a considerable strain on transport facilities, with the result that a road tunnel ( Vágatunnilin) measuring in length and running under the sea now connects Vágar with the two largest islands in the Faroes and thus the capital Tórshavn
Tórshavn (; lit. "Thor's harbour"), usually locally referred to as simply ''Havn'', is the capital and largest city of the Faroe Islands. It is located in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the ...
.
Tourism
The country's two largest lakes - Sørvágsvatn and Fjallavatn - are to be found there, and the tourist association organises excursions throughout the summer.Villages
Vágar has three large villages:Miðvágur
Miðvágur ( da, Midvåg), is a village in the Faroe Islands on Vágar. It has been a municipality until 1 January 2009 when it fused with Sandavágur into Vága kommuna.
Located on the south coast of the island of Vágar, Miðvágur is the ...
, Sandavágur
Sandavágur ( da, Sandevåg) is a city on the south coast of the Faroese island of Vágar.
The name ''Sandavágur'' means ''sandy bay'' and refers to the sandy beach which used to be much larger than present. From one point in Sandavágur you ca ...
and Sørvágur :''There is also a town called Vágur on Suðuroy.''
Sørvágur ( da, Sørvåg) is a village on the island of Vágar in the Faroe Islands.
It is located at the landward end of Sørvágsfjørður. Sørvágur is the largest village in Sørvágur ...
and three small ones: Gásadalur, Bøur and Vatnsoyrar. Earlier there were two more villages: Slættanes, which was abandoned in 1965 and Víkar, which was abandoned in 1910.
The largest is Miðvágur
Miðvágur ( da, Midvåg), is a village in the Faroe Islands on Vágar. It has been a municipality until 1 January 2009 when it fused with Sandavágur into Vága kommuna.
Located on the south coast of the island of Vágar, Miðvágur is the ...
, which has 1,130 inhabitants (01-2020). It is in the middle of the island and so has naturally become a centre, with a doctor's surgery, co-op and vicarage. It is also a historic village and was home to Beinta Broberg, a clergyman's wife who was dubbed “Wicked Beinta”. The story of her life was told in the famous novel '' Barbara'' by Jørgen-Frantz Jacobsen
Jørgen-Frantz Jacobsen (November 29, 1900 – March 24, 1938) was a Faroese writer. He has a distinct place in Scandinavian literature, as he is the only Faroese writer to achieve international best-seller status. This status derives ...
, which was filmed in 1997 by Niels Malmros. The farmhouse Kálvalíð to the north is the oldest house in the village and possibly in the Faroe Islands too. It is now the village museum.
To the east of Miðvágur lies Sandavágur, which has a population of 958 (01-2020). It too is a historic village. It was home to the law speaker of the Faroe Islands until 1816, when the office was abolished and the islands became a Danish administrative district. The clergyman V. U. Hammershaimb, who was born in Sandavágur in 1819 and became the father of the Faroese written language, was the son of the last law speaker.
The Sandavágur stone with a runic inscription dating back to around 1200 was found there in 1917 and can now be seen in the Sandavágur church.
The third large village is Sørvágur :''There is also a town called Vágur on Suðuroy.''
Sørvágur ( da, Sørvåg) is a village on the island of Vágar in the Faroe Islands.
It is located at the landward end of Sørvágsfjørður. Sørvágur is the largest village in Sørvágur ...
, which is on the western side of the island near the airport and has 1,136 inhabitants (01-2020). During World War II, when the airfield was being built in 1942–1944, 5,000 British soldiers lived in Sørvágur, but now few traces remain of their camp to the south of the village. Tindhólmur, Gáshólmur and the two “drangar” (freestanding cliffs) belong to the village. The view out to them is among the most beautiful in the Faroe Islands.
Vágar has two other old villages: Bøur, which lies west of Sørvágur and has 74 inhabitants (01-2020), and Gásadalur, which lies further west on the Mykinesfjørður strait and has 16 inhabitants (01-2020). Many people have moved away from this village, but it now has a road link in the form of a Gásadalstunnilin through the mountain and it is hoped that the village will start to grow again.
A new village, Vatnsoyrar, which has 44 inhabitants (01-2020), appeared on Vágar in 1921. It was founded by three men, each of whom was given a plot of land to farm and set up home there with his family. The village is in the upland pasture
Upland pasture (rough grazing and/or semi-natural rough grazing) is a type of semi-natural grassland located in uplands of rolling foothills or upon higher slopes, greater than 350 meters (1148.29 feet) and less than 600 meters (1968.50 feet) from ...
s belonging to Miðvágur and so forms part of Miðvágur District. When the British occupied the Faroe Islands and built the airfield on Vágar, Vatnsoyrar was their headquarters. The local population was evacuated, but was able to return home when the war ended.
At the northernmost point of the island, in the upland pastures belonging to Sandavágur, lay the village of Slættanes, which was founded in 1835. It grew for a time and at its largest was home to around 70 people. It also had a school, which can be seen on a stamp. The last residents left in 1964.
Another new village, Víkar, was founded in the upland pastures belonging to Gásadalur on the north side of the island in 1833. The area was good for farming, but the settlement was very isolated, and getting to the next village was a difficult business. The last few inhabitants moved away in 1910.
The beaches at Bøur, Miðvágur
Miðvágur ( da, Midvåg), is a village in the Faroe Islands on Vágar. It has been a municipality until 1 January 2009 when it fused with Sandavágur into Vága kommuna.
Located on the south coast of the island of Vágar, Miðvágur is the ...
and Sandavágur
Sandavágur ( da, Sandevåg) is a city on the south coast of the Faroese island of Vágar.
The name ''Sandavágur'' means ''sandy bay'' and refers to the sandy beach which used to be much larger than present. From one point in Sandavágur you ca ...
are recognised as official ''grind'' beaches.
Geography
Climate
Important Bird Area
The north-west, west and south-west coasts of the island have been identified as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International because of their significance as breeding sites forseabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same enviro ...
s, especially northern fulmar
The northern fulmar (''Fulmarus glacialis''), fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is a highly abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hem ...
s (100,000 pairs), European storm petrel
The European storm petrel, British storm petrel, or just storm petrel (''Hydrobates pelagicus'') is a seabird in the northern storm petrel family, Hydrobatidae. The small, square-tailed bird is entirely black except for a broad, white rump and ...
s (5000 pairs), European shag
The European shag or common shag (''Gulosus aristotelis'') is a species of cormorant. It is the only member of the monotypic genus ''Gulosus''. It breeds around the rocky coasts of western and southern Europe, southwest Asia and north Africa, mai ...
s (500 pairs), great skuas (20 pairs), black-legged kittiwakes (8400 pairs), Atlantic puffins (40,000 pairs), common guillemot
The common murre or common guillemot (''Uria aalge'') is a large auk. It has a circumpolar distribution, occurring in low-Arctic and boreal waters in the North Atlantic and North Pacific. It spends most of its time at sea, only coming to land to ...
s (2700 individuals) and black guillemots (400 pairs).BirdLife International. (2012). Important Bird Areas factsheet: Vágar. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org on 2012-02-24.
Mountains
There are 41 mountains on Vágar, the major ones are:Major lakes
Major waterfalls
* Bøsdalafossur * Múlafossur * ReipsáfossurIslets and rocks in the sea
 * Tindhólmur
* Gáshólmur
*
* Tindhólmur
* Gáshólmur
* Skerhólmur
 Skerhólmur is a small islet in the middle of Sørvágsfjørður o ...
Skerhólmur is a small islet in the middle of Sørvágsfjørður o ...
* Trøllkonufingur
* Dunnesdrangar
* Filpusardrangur
* Drangarnir - Lítli Drangur, Stóri Drangur
 Skerhólmur is a small islet in the middle of Sørvágsfjørður o ...
Skerhólmur is a small islet in the middle of Sørvágsfjørður o ...References
External links
Stamps.fo
(public domain by
Postverk Føroya
Posta is the postal service of the Faroe Islands and was founded on 1 April 1976 under the Home Rule of the Faroe Islands. On 16 December 2005, it became a public joint stock company under the name P/F Postverk Føroya (retroactive from 1 Januar ...
)
Personal website
with 78 aerial photos of Vágar {{DEFAULTSORT:Vagar Islands of the Faroe Islands Important Bird Areas of the Faroe Islands