Vicsek fractal on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
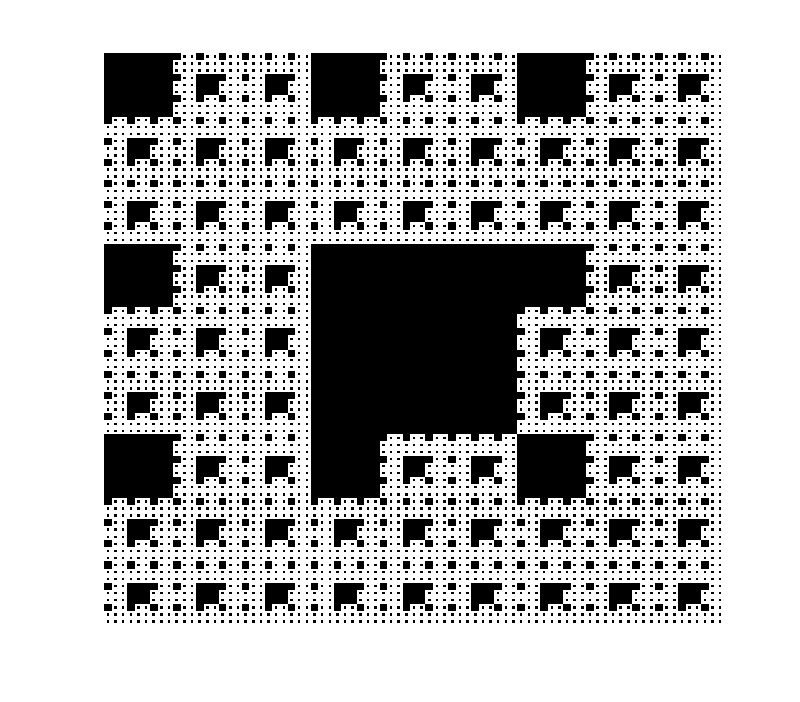
In mathematics the Vicsek fractal, also known as Vicsek snowflake or box fractal, is a fractal arising from a construction similar to that of the Sierpiński carpet, proposed by Tamás Vicsek. It has applications including as compact fractal antenna, antennas, particularly in cellular phones.

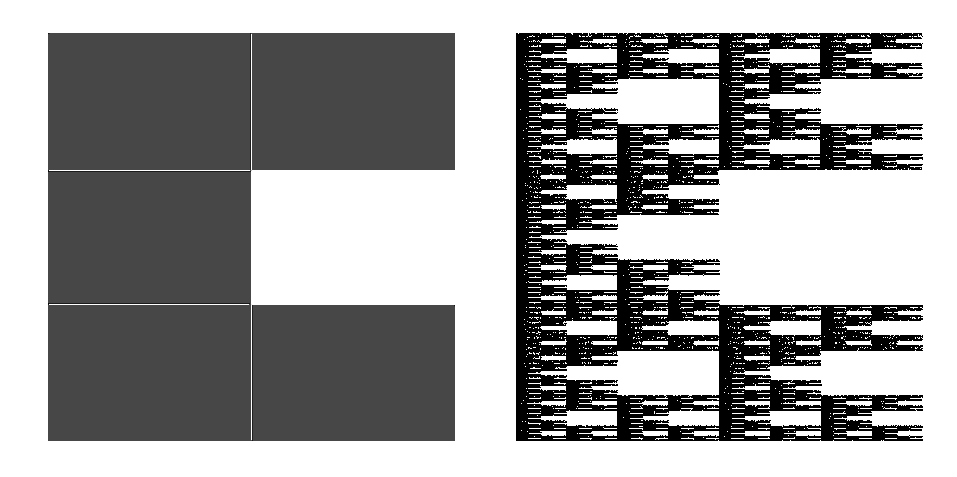 ''Box fractal'' also refers to various iterated fractals created by a square tiling, square or rectangular grid with various boxes removed or absent and, at each iteration, those present and/or those absent have the previous image scaled down and drawn within them. The Sierpinski triangle may be approximated by a box fractal with one corner removed. The Sierpinski carpet is a box fractal with the middle square removed.
''Box fractal'' also refers to various iterated fractals created by a square tiling, square or rectangular grid with various boxes removed or absent and, at each iteration, those present and/or those absent have the previous image scaled down and drawn within them. The Sierpinski triangle may be approximated by a box fractal with one corner removed. The Sierpinski carpet is a box fractal with the middle square removed.
File:Box fractal2.png, Self-similarities I — removing corner squares.
File:Box fractal3.png, Self-similarities II — keeping corner squares.4






 ''Box fractal'' also refers to various iterated fractals created by a square tiling, square or rectangular grid with various boxes removed or absent and, at each iteration, those present and/or those absent have the previous image scaled down and drawn within them. The Sierpinski triangle may be approximated by a box fractal with one corner removed. The Sierpinski carpet is a box fractal with the middle square removed.
''Box fractal'' also refers to various iterated fractals created by a square tiling, square or rectangular grid with various boxes removed or absent and, at each iteration, those present and/or those absent have the previous image scaled down and drawn within them. The Sierpinski triangle may be approximated by a box fractal with one corner removed. The Sierpinski carpet is a box fractal with the middle square removed.
Construction
The basic square is decomposed into nine smaller squares in the 3-by-3 grid. The four squares at the corners and the middle square are left, the other squares being removed. The process is repeated recursively for each of the five remaining subsquares. The Vicsek fractal is the set obtained at the limit of this procedure. The Hausdorff dimension of this fractal is ≈ 1.46497. An alternative construction (shown below in the left image) is to remove the four corner squares and leave the middle square and the squares above, below, left and right of it. The two constructions produce identical limiting curves, but one is rotated by 45 degrees with respect to the other.
Properties
The Vicsek fractal has the surprising property that it has zero area yet an infinite perimeter, due to its non-integer dimension. At each iteration, four squares are removed for every five retained, meaning that at iteration ''n'' the area is (assuming an initial square of side length 1). When ''n'' approached infinity, the area approaches zero. The perimeter however is , because each side is divided into three parts and the center one is replaced with three sides, yielding an increase of three to five. The perimeter approaches infinity as ''n'' increases. The boundary of the Vicsek fractal is the Koch snowflake#Variants of the Koch curve, Type 1 quadratic Koch curve.Analogues in higher dimensions
There is a three-dimensional analogue of the Vicsek fractal. It is constructed by subdividing each cube into 27 smaller ones, and removing all but the "center cross", the central cube and the six cubes touching the center of each face. Its Hausdorff dimension is ≈ 1.7712. Similarly to the two-dimensional Vicsek fractal, this figure has zero volume. Each iteration retains 7 cubes for every 27, resulting in a volume of at iteration ''n'', which approaches zero as ''n'' approaches infinity. There exist an infinite number of Cross section (geometry), cross sections which yield the two-dimensional Vicsek fractal.See also
* Box-counting dimension * Cross crosslet * List of fractals by Hausdorff dimension * Sierpinski carpet * Sierpinski triangle * n-flake, ''n''-flakeReferences
External links
* {{Fractals Fractals L-systems Eponymous geometric shapes