Vickers Vimy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Vickers Vimy was a British
 The Vickers F.B.27 Vimy is an equal-span twin-engine four-bay biplane, with balanced ailerons on both upper and lower wings. The engine
The Vickers F.B.27 Vimy is an equal-span twin-engine four-bay biplane, with balanced ailerons on both upper and lower wings. The engine
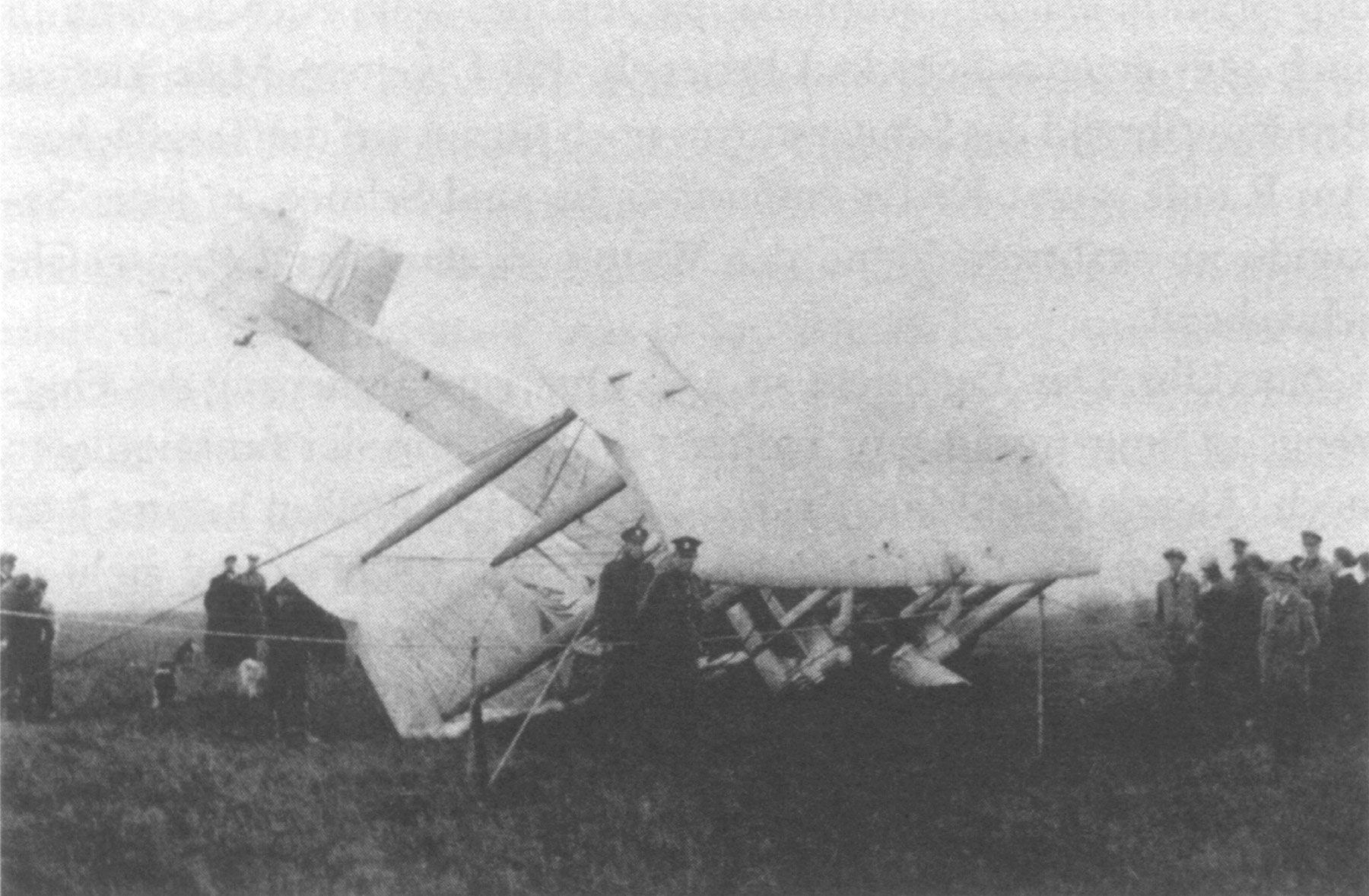 On 12 June 1918, according to ''
On 12 June 1918, according to ''
''Discover Collections: State Library of NSW.'' Retrieved: 4 December 2012. Vickers Vimy Reserve in Northgate, a suburb of Adelaide, is named in honour of the place the plane landed on its return to South Australia in 1920. In 1920


 The Vimy Commercial was a civilian version with a larger-diameter fuselage (largely of
The Vimy Commercial was a civilian version with a larger-diameter fuselage (largely of
''sinaman.com.'' Retrieved: 15 March 2008. During the war these bombers were initially highly successful due to the low-level bombing tactics used, with the air force chief-of-staff of the Zhili clique, General
 ;
*
;
*
 ;Australia
*Vimy IV ''G-EAOU'' at
;Australia
*Vimy IV ''G-EAOU'' at 
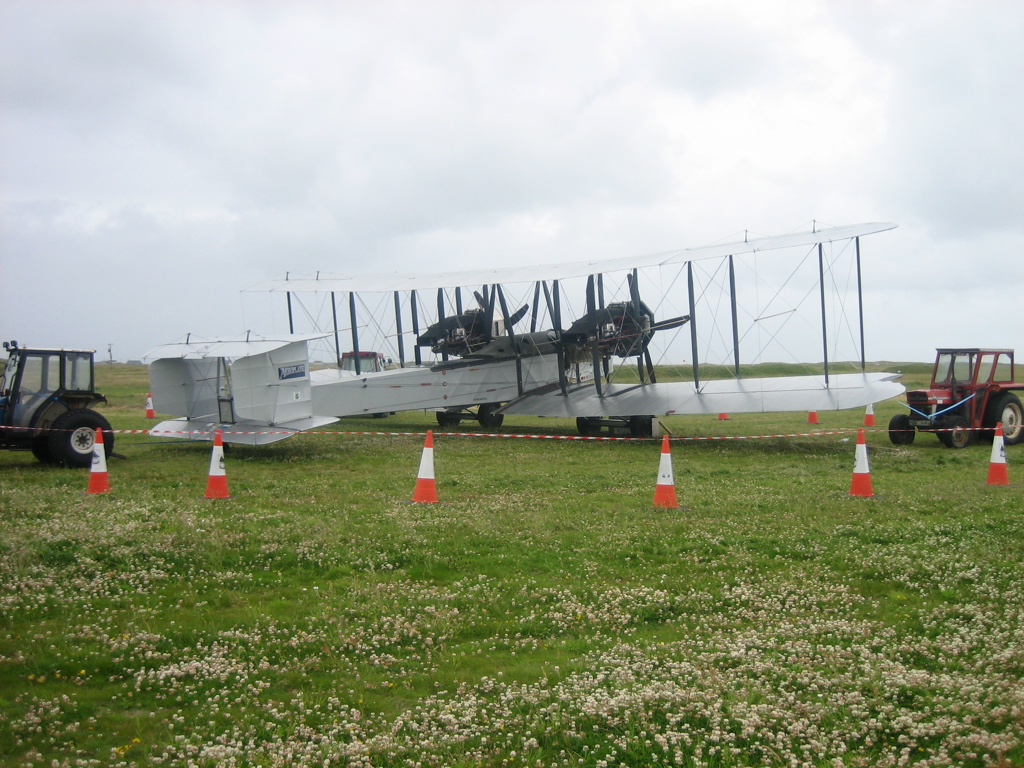 A replica transatlantic Vimy cockpit section was built by Vickers for the London Science Museum in the early 1920s, and three full-size replicas have also been built. The first was a taxiable replica commissioned by
A replica transatlantic Vimy cockpit section was built by Vickers for the London Science Museum in the early 1920s, and three full-size replicas have also been built. The first was a taxiable replica commissioned by

The Vickers Vimy-Commercial at Hendon, 1919
RAF Museum
Alcock and Brown's Vimy at the Science Museum London - archived article
Vickers Vimy online collection – State Library of NSW
Alcock and Brown's Vimy in the collection of the Science Museum London
National Geographic record of the 2005 re-enactment on the Atlantic flight
The Brooklands Vickers Vimy Replica Video List
{{Authority control 1910s British bomber aircraft
heavy bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range ( takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the larg ...
aircraft developed and manufactured by Vickers Limited
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entir ...
. Developed during the latter stages of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
to equip the Royal Flying Corps
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colors =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries =
, decorations ...
(RFC), the Vimy was designed by Reginald Kirshaw "Rex" Pierson, Vickers' chief designer.
Only a handful of Vickers Vimy aircraft had entered service by the time the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
came into effect, so the type did not serve in active combat operations during the war, but the Vimy became the core of the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(RAF)'s heavy bomber
Heavy bombers are bomber aircraft capable of delivering the largest payload of air-to-ground weaponry (usually bombs) and longest range ( takeoff to landing) of their era. Archetypal heavy bombers have therefore usually been among the larg ...
force throughout the 1920s. The Vimy achieved success as both a military and a civil aircraft, the latter using the ''Vimy Commercial'' variant. A dedicated transport derivative of the Vimy, the Vickers Vernon, became the first troop-transport aircraft operated by the RAF.
During the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
the Vimy set several records for long-distance flights, the most celebrated and significant of these being the first non-stop crossing of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, performed by John Alcock and Arthur Brown in June 1919. Other record-breaking flights were made from the United Kingdom to destinations such as South Africa and Australia. The Vimy continued to be operated until the 1930s in both military and civil capacities.
Design and development
Background
Throughout theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
both the Allied Powers and the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in W ...
made increasingly sophisticated use of new technologies in their attempts to break through the effective stalemate of trench warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising Trench#Military engineering, military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artille ...
. One key advance made during the conflict was in the use of fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air flying machine, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using wings that generate lift caused by the aircraft's forward airspeed and the shape of the wings. Fixed-wing aircraft are dist ...
, which were at that time rapidly advancing in capability and ability, for combat purposes. On 23 July 1917, in response to a bombing raid by German bombers on London, the Air Board, having determined that existing projects were not ambitious enough, decided to cancel all orders for experimental heavy bombers then underway. A week later, following protests from the Controller of the Technical Department, the Air Board placed an order for 100 Handley Page O/100 bombers, which was accompanied by orders for prototype heavy bombers being placed with both Handley Page
Handley Page Limited was a British aerospace manufacturer. Founded by Frederick Handley Page (later Sir Frederick) in 1909, it was the United Kingdom's first publicly traded aircraft manufacturing company. It went into voluntary liquidatio ...
and Vickers Limited
Vickers Limited was a British engineering conglomerate. The business began in Sheffield in 1828 as a steel foundry and became known for its church bells, going on to make shafts and propellers for ships, armour plate and then artillery. Entir ...
.
On 16 August 1917 Vickers was issued with a contract for three prototype aircraft and Rex Pierson
Reginald Kirshaw "Rex" Pierson CBE (9 February 1891 – 10 January 1948) was an English aircraft designer and chief designer at Vickers Limited later Vickers-Armstrongs Aircraft Ltd. He was responsible for the Vickers Vimy, a heavy bomber designe ...
, chief designer of Vickers' aviation division, started designing a large twin-engine biplane bomber, to be powered by either a pair of RAF 4d or 200 hp (150 kW) Hispano Suiza engines. Pierson discussed the proposed aircraft with Major J. C. Buchanan of the Air Board to establish the rough configuration of the aircraft, which was expected to meet the requirement for a night bomber which could attack targets within the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
.
Design
 The Vickers F.B.27 Vimy is an equal-span twin-engine four-bay biplane, with balanced ailerons on both upper and lower wings. The engine
The Vickers F.B.27 Vimy is an equal-span twin-engine four-bay biplane, with balanced ailerons on both upper and lower wings. The engine nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a "streamlined body, sized according to what it contains", such as an engine, fuel, or equipment on an aircraft. When attached by a pylon entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attache ...
s were positioned mid-gap and contained the fuel tanks. It has a biplane empennage
The empennage ( or ), also known as the tail or tail assembly, is a structure at the rear of an aircraft that provides stability during flight, in a way similar to the feathers on an arrow.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third e ...
with elevators on both upper and lower surfaces and twin rudders. The main undercarriage consists of two pairs of wheels, each pair carried on a pair of tubular steel V-struts. There is a tail-skid and an additional skid mounted below the nose of the fuselage to prevent nose-overs.
The aircraft was designed to accommodate a three-man crew and a payload of 12 bombs. In addition to the pilot's cockpit, which was positioned just ahead of the wings, there were two positions for gunners, one behind the wings and the other in the nose, each with a pair of Scarff ring
The Scarff ring was a type of machine gun mounting developed during the First World War by Warrant Officer (Gunner) F. W. Scarff of the Admiralty Air Department for use on two-seater aircraft. The mount incorporated bungee cord suspension in elev ...
-mounted Lewis guns; the rear cockpit mounting was commonly not fitted during the interwar period. Provision for a maximum of four spare drums of ammunition were present in the nose position, while up to six drums could be carried in the rear position.
The majority of the Vimy's payload of 250 lb bombs were stowed vertically inside the fuselage between the spars of the lower centre section; a typical load consisted of 12 bombs. In some variants further bombs could be stowed externally for a total of 18 bombs, if the particular engine used provided enough power. For anti-surface warfare
Anti-surface warfare (ASuW or ASUW) is the branch of naval warfare concerned with the suppression of surface combatants. More generally, it is any weapons, sensors, or operations intended to attack or limit the effectiveness of an adversary's ...
in the maritime environment, the Vimy could also be armed with a pair of torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, ...
es. To improve bombing accuracy, the Vimy was equipped with the High Altitude Drift Mk.1a bombsight. Standard equipment also included two Michelin
Michelin (; ; full name: ) is a French multinational tyre manufacturing company based in Clermont-Ferrand in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes ''région'' of France. It is the second largest tyre manufacturer in the world behind Bridgestone and larg ...
-built Mk.1 flare carriers.
The Vimy was powered by a range of different engines. Owing to engine supply difficulties, the prototype Vimys were tested with a number of different engine types, including Sunbeam Maori
The Sunbeam Afridi was an aero-engine produced by Sunbeam during the First World War.
Design and development
Conceived to replace the Crusader/Zulu on the production lines, Louis Coatalen designed a companion engine for the V-12 Cossack, givi ...
s, Salmson 9Zm
The Salmson water-cooled aero-engines, produced in France by Société des Moteurs Salmson from 1908 until 1920, were a series of pioneering aero-engines: unusually combining water-cooling with the radial arrangement of their cylinders.
Histor ...
water-cooled radials, and Fiat A.12bis engines, before production orders were placed for aircraft powered by the 230 hp (170 kW) BHP Puma, 400 hp (300 kW) Fiat, 400 hp (300 kW) Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American water-cooled 45° V-12 aircraft engine displacing and making designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It saw wide use in aero applications, and, once marinized, in marine use both ...
and the 300 hp (270 kW) Rolls-Royce Eagle VIII
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of ot ...
engines, with a total of 776 ordered before the end of the First World War. Of these, only aircraft powered by the Eagle engine, known as the Vimy IV, were delivered to the RAF. Due to the number of engine types used there are multiple conflicting official reports on the production numbers of each sub-variant of the Vimy.
Design and production of the prototypes was extremely rapid; the detailed design phase of what had become internally designated as the Vickers F.B.27 and the manufacture of the three prototypes was completed within four months.
Prototypes
By the time the first prototype had been completed the RAF 4D was not sufficiently developed, so it was fitted with the alternative Hispano Suiza engine. On 30 November 1917 the first prototype, flown by Captain Gordon Bell, made itsmaiden flight
The maiden flight, also known as first flight, of an aircraft is the first occasion on which it leaves the ground under its own power. The same term is also used for the first launch of rockets.
The maiden flight of a new aircraft type is alw ...
from Royal Flying Corps Station Joyce Green, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
. In January 1918 the first prototype was dispatched to RAF Martlesham Heath
Royal Air Force Martlesham Heath or more simply RAF Martlesham Heath is a former Royal Air Force station located southwest of Woodbridge, Suffolk, England. It was active between 1917 and 1963, and played an important role in the development o ...
, Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
, for the official trials of the type. Reportedly, the F.B.27 quickly made a positive impression: it was able to take off with a greater payload than the Handley Page O/400 despite having about half the effective engine power. The engines proved to be unreliable during these trials, leading to the aircraft's return to Joyce Green on 12 April 1918.
The first prototype was extensively modified, receiving new Salmson water-cooled aero-engines in place of the Hispano Suizas; other changes included the adoption of an alternative exhaust stack configuration, a 3-degree dihedral on the mainplanes, and a modified tail unit. Following these modifications, the prototype was used for several years, surviving the war and being allocated a civil registration. In August 1919 the prototype was flown from Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfields ...
to Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban ar ...
in the Netherlands as part of Vicker's exhibit at the Eerste Luchtverkeer Tentoonstelling Amsterdam.
During early 1918 the second prototype was completed. Unlike the first, it had plain elevators and aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around ...
s which had an inverse taper; the tops of the wings and tailplanes also differed. The defensive armament was increased, giving the rear gunner two separate guns; these changes would be standardised on production aircraft. The second prototype was powered by a pair of Sunbeam Maori
The Sunbeam Afridi was an aero-engine produced by Sunbeam during the First World War.
Design and development
Conceived to replace the Crusader/Zulu on the production lines, Louis Coatalen designed a companion engine for the V-12 Cossack, givi ...
engines, which were found to have an unreliable cooling system during initial testing at Joyce Green. On 26 April 1918 the aircraft was dispatched to RAF Martlesham Heath for official tests, but testing was interrupted by its loss in a crash following an engine failure.
During the first half of the 1918 the third prototype was also completed. It was powered by a pair of 400 hp (300 kW) Fiat A.12 engines, and had a redesigned nose section and nacelle
A nacelle ( ) is a "streamlined body, sized according to what it contains", such as an engine, fuel, or equipment on an aircraft. When attached by a pylon entirely outside the airframe, it is sometimes called a pod, in which case it is attache ...
s which were similar to production aircraft. On 15 August 1918 the third prototype was sent to RAF Martlesham Heath for performance tests; testing was delayed by the need to replace a cracked propeller. On 11 September 1918 it was lost when its payload of bombs detonated owing to a hard landing, the result of a pilot-induced stall.
It was decided to construct a fourth prototype to test the Rolls-Royce Eagle VIII
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of ot ...
engine. On 11 October 1918 this was flown from Joyce Green to Martlesham Heath to conduct official trials. Aside from being powered by the Eagle engine, it was identical to the earlier prototypes except for having a greatly increased fuel capacity and reshaped and enlarged rudders. By the time the fourth prototype commenced flying trials, mass production of the Vimy had already begun.
Production
Since the performance of the first prototype was satisfactory it was decided to start production before the evaluation of either of the other prototypes. On 26 March 1918 the first production contract, for 150 aircraft, was issued; these were built at Vickers' works inCrayford
Crayford is a town and electoral ward in South East London, England, within the London Borough of Bexley. It lies east of Bexleyheath and north west of Dartford. Crayford was in the historic county of Kent until 1965. The settlement de ...
in the Bexley. Production of the type by additional manufacturers was envisaged early on; in May 1918 follow-up contracts were issued to Clayton & Shuttleworth, Morgan & Co, and the Royal Aircraft Establishment
The Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) was a British research establishment, known by several different names during its history, that eventually came under the aegis of the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD), before finally losing its identity in me ...
(RAE), in addition to a separate production line at Vickers' Weybridge
Weybridge () is a town in the Borough of Elmbridge in Surrey, England, around southwest of central London. The settlement is recorded as ''Waigebrugge'' and ''Weibrugge'' in the 7th century and the name derives from a crossing point of the ...
complex. At one point over 1,000 aircraft had been ordered under wartime contracts. The type had received the official name of ''Vimy'', after the Battle of Vimy Ridge.
By the end of 1918 a total of 13 aircraft had been completed by Vickers; 7 at Crayford and 6 at Weybridge. Production continued after the signing of the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
, which led to Vickers ultimately completing 112 aircraft under wartime contracts. The majority, if not all, of Vimys ordered from Morgan & Co were completed, while Westland Aircraft manufactured 25 of the 75 units that they were contracted for. The numbers produced by the RAE are obscured by changes in serial number allocation and the apparent adoption of a piecemeal approach to manufacturing, which came into effect shortly after the end of the war; in February 1920, the RAE completed their final Vimy.
Production aircraft used several different types of engines, leading to various mark numbers being applied to the Vimy to distinguish between the emerging subtypes. The use of different engines was often because of availability; relatively few engines from Rolls-Royce Limited
Rolls-Royce was a British luxury car and later an aero-engine manufacturing business established in 1904 in Manchester by the partnership of Charles Rolls and Henry Royce. Building on Royce's good reputation established with his cranes, they ...
were used in the Vimy during 1918 owing to low output levels from that manufacturer, while other manufacturers also struggled to keep up with engine demand that year. At one point, there was considerable enthusiasm for powering the Vimy with American Liberty L-12
The Liberty L-12 is an American water-cooled 45° V-12 aircraft engine displacing and making designed for a high power-to-weight ratio and ease of mass production. It saw wide use in aero applications, and, once marinized, in marine use both ...
engines, because of their plentiful supply at the time, but all orders for the Liberty-equipped Vimy were terminated in January 1919 and no examples were ever completed. The BHP Puma was also intended for use on the Vimy, but it was cancelled without any aircraft being fitted with the engine.
Use of the Vimy extended beyond its original use as a bomber. A model with greater internal space was developed, known as the ''Vimy Commercial'' within the civil market. It saw service with the RAF; known as the Vickers Vernon, it became the first dedicated troop transport to be operated by the service. The Vimy was also used as an air ambulance
Air medical services is a comprehensive term covering the use of air transportation, aeroplane or helicopter, to move patients to and from healthcare facilities and accident scenes. Personnel provide comprehensive prehospital and emergency and cri ...
for transporting wounded troops to medical facilities, while some examples were configured to perform record-breaking long-distance flights. From 1923 to 1925 limited production batches of the Vimy were manufactured by Vickers. Between 1923 and 1931, at least another 43 early production aircraft were reconditioned to extend their service lives; at least one Vimy was reconditioned four times.
By October 1918 only three aircraft had been delivered to the Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(RAF), one of which had been deployed to France for use by the Independent Air Force
The Independent Air Force (IAF), also known as the Independent Force or the Independent Bombing Force and later known as the Inter-Allied Independent Air Force, was a First World War strategic bombing force which was part of Britain's Royal Air ...
. It had been envisioned that the Vimy would be able to conduct long-range bombing missions into Germany, having the ability to reach Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
from bases in France, but the Armistice of 11 November 1918
The Armistice of 11 November 1918 was the armistice signed at Le Francport near Compiègne that ended fighting on land, sea, and air in World War I between the Entente and their last remaining opponent, Germany. Previous armistices ...
brought an end to the conflict before the Vimy could be used on any offensive operations. After the war, the RAF rapidly contracted in size, which slowed the introduction of the Vimy. The Vimy only reached full service status in July 1919 when it entered service with 58 Squadron in Egypt, replacing the older Handley Page 0/400.
Operational history
RAF service
 On 12 June 1918, according to ''
On 12 June 1918, according to ''Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's olde ...
'', the Air Board were to initially deploy the first production Vimy units as maritime patrol aircraft
A maritime patrol aircraft (MPA), also known as a patrol aircraft, maritime reconnaissance aircraft, or by the older American term patrol bomber, is a fixed-wing aircraft designed to operate for long durations over water in maritime patrol ro ...
, equipped for anti-submarine warfare, and once this requirement had been satisfied, subsequent aircraft would be allocated to performing night bombing missions from bases in France. This had been due to a recently introduced policy under which the number of land-based aircraft allocated to anti-submarine patrols was to be vastly expanded, from 66 landplanes in November 1917 to a projected force of 726 landplanes, in which the newly available Vimy would be a key aircraft due to its long-range capabilities. During August 1918, the application of floats to the Vimy was studied, but it is not known if any aircraft were ever so fitted.
Throughout the 1920s, the Vimy formed the main heavy bomber force of the RAF; for some years, it was the only twin-engine bomber to be stationed at bases in Britain. On 1 April 1924, No. 9 Squadron and No. 58 Squadron, equipped with the Vimy, stood up, tripling the home-based heavy bomber force. On 1 July 1923, a newly formed Night Flying Flight, based at RAF Biggin Hill, equipped with the Vimy, was formed; during the general strike of 1926, this unit performed aerial deliveries of the British Gazette newspaper throughout the country. Between 1921 and 1926, the type formed the backbone of the airmail service between Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metr ...
and Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
. The Vimy served as a front line bomber in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and in the United Kingdom from 1919 until 1925, by which point it had been replaced by the newer Vickers Virginia.
Despite the emergence of the Virginia, which numerous Vimy squadrons were soon re-equipped with, the Vimy continued to equip a Special Reserve bomber squadron, 502 Squadron, stationed at Aldergrove in Northern Ireland
Northern Ireland ( ga, Tuaisceart Éireann ; sco, label=Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots, Norlin Airlann) is a part of the United Kingdom, situated in the north-east of the island of Ireland, that is #Descriptions, variously described as ...
until 1929. The Vimy continued to be used in secondary roles, such as its use as a training aircraft; many were re-engined with Bristol Jupiter
The Bristol Jupiter was a British nine-cylinder single-row piston radial engine built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. Originally designed late in World War I and known as the Cosmos Jupiter, a lengthy series of upgrades and developments turn ...
or Armstrong Siddeley Jaguar radial engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating type internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized star when viewed from the front, and is ...
s. The final Vimys, used as target aircraft for searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely luminosity, bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a part ...
crews, remained in use until 1938.
Long-distance flights
The most significant of the Vimy's many pioneering flights was the first non-stop crossing of theAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, made by Alcock and Brown in June 1919. An example was specially constructed for the attempt, with additional fuel tanks to extend its range and a revised undercarriage. Only one such aircraft was built; it is preserved and displayed in the London Science Museum.
In 1919, the Australian government offered £10,000 for the first All-Australian crew to fly an aeroplane from England to Australia. Keith Macpherson Smith, Ross Macpherson Smith and mechanics Jim Bennett and Wally Shiers completed the journey from Hounslow Heath Aerodrome to Darwin via Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
and Batavia on 10 December 1919. Their aircraft G-EAOU is preserved in a purpose-built, climate-controlled museum in the grounds of the airport in Smith's home town Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The dem ...
, Australia; "The trip from Darwin to Sydney took almost twice as long as the flight to Australia.""Vickers Vimy."''Discover Collections: State Library of NSW.'' Retrieved: 4 December 2012. Vickers Vimy Reserve in Northgate, a suburb of Adelaide, is named in honour of the place the plane landed on its return to South Australia in 1920. In 1920
Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colon ...
Pierre van Ryneveld
General Sir Hesperus Andrias van Ryneveld, (2 May 1891 – 2 December 1972), known as Sir Pierre van Ryneveld, was a South African military commander. He was the founding commander of the South African Air Force.
Military career
Van Ryneveld ...
and Major Quintin Brand
Air Vice-Marshal Sir Christopher Joseph Quintin Brand, (25 May 1893 – 7 March 1968) was a South African officer of the Royal Air Force.
Early life
Brand was born in Beaconsfield (now part of Kimberley, Northern Cape) in South Africa to a CID ...
attempted the first England to South Africa flight. They left Brooklands
Brooklands was a motor racing circuit and aerodrome built near Weybridge in Surrey, England, United Kingdom. It opened in 1907 and was the world's first purpose-built 'banked' motor racing circuit as well as one of Britain's first airfields ...
on 4 February 1920 in Vimy G-UABA, named ''Silver Queen''. They landed safely at Heliopolis, but as they continued the flight to Wadi Halfa they were forced to land due to engine overheating with still to go. A second Vimy was lent to the pair by the RAF at Heliopolis, and named ''Silver Queen II''. This second aircraft reached Bulawayo in Southern Rhodesia
Southern Rhodesia was a landlocked self-governing colony, self-governing British Crown colony in southern Africa, established in 1923 and consisting of British South Africa Company (BSAC) territories lying south of the Zambezi River. The reg ...
, where it was badly damaged when it failed to take off. Van Ryneveld and Brand then used a South African Air Force Airco DH.9
The Airco DH.9 (from de Havilland 9) – also known after 1920 as the de Havilland DH.9 – was a British single-engined biplane bomber developed and deployed during the First World War.
The DH.9 was a development of Airco's earlier successful ...
to continue the journey to Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. The South African government awarded them £5,000 each.
Vimy Commercial


 The Vimy Commercial was a civilian version with a larger-diameter fuselage (largely of
The Vimy Commercial was a civilian version with a larger-diameter fuselage (largely of spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfam ...
plywood), which was developed at and first flew from the Joyce Green airfield in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
on 13 April 1919. Initially, it bore the interim civil registration ''K-107'', later being re-registered as ''G-EAAV''.
The prototype entered the 1920 race to Cape Town; it left Brooklands on 24 January 1920 but crashed at Tabora
Tabora is the capital of Tanzania's Tabora Region and is classified as a municipality by the Tanzanian government. It is also the administrative seat of Tabora Urban District. According to the 2012 census, the district had a population of 226,999 ...
, Tanganyika
Tanganyika may refer to:
Places
* Tanganyika Territory (1916–1961), a former British territory which preceded the sovereign state
* Tanganyika (1961–1964), a sovereign state, comprising the mainland part of present-day Tanzania
* Tanzania Main ...
on 27 February.
In 1919, the Chinese Government placed a large order for aircraft with Vickers, including 100 Vimy Commercials, which was cut to 40 Vimy Commercials when the final contract was signed in 1920. A Chinese order for 100 is particularly noteworthy; forty of the forty-three built were delivered to China, but most remained in their crates unused, and only seven were put into civilian use.
Five Napier Lion
The Napier Lion is a 12-cylinder, petrol-fueled 'broad arrow' W12 configuration aircraft engine built by D. Napier & Son from 1917 until the 1930s. A number of advanced features made it the most powerful engine of its day and kept it in produ ...
-powered air ambulance versions of the Vimy Commercial were built for the RAF as the Vimy Ambulance. Fifty-five more bomber-transport versions of the Vimy Commercial were built for the RAF as the Vickers Vernon.
Role in the Second Zhili–Fengtian War
After the First Zhili–Fengtian War, 20 aircraft were secretly converted into bombers under the order of the Zhili clique warlord Cao Kun, and later participated in the Second Zhili–Fengtian War."我國最早航運機隊主力 -商用維美運輸機"(Vickers Vimy Commercial in Chinese language)''sinaman.com.'' Retrieved: 15 March 2008. During the war these bombers were initially highly successful due to the low-level bombing tactics used, with the air force chief-of-staff of the Zhili clique, General
Zhao Buli Zhao may refer to:
* Zhao (surname) (赵), a Chinese surname
** commonly spelled Chao in Taiwan or up until the early 20th century in other regions
** Chiu, from the Cantonese pronunciation
** Cho (Korean surname), represent the Hanja 趙 (Chinese ...
(趙步壢) personally flying many of the missions. However, on 17 September, returning from a successful bombing mission outside Shanhai Pass
Shanhai Pass or Shanhaiguan () is one of the major passes in the Great Wall of China, being the easternmost stronghold along the Ming Great Wall, and commands the narrowest choke point in the Liaoxi Corridor. It is located in Shanhaiguan ...
, General Zhao's aircraft was hit by ground fire from the Fengtian clique in the region of Nine Gates (Jiumenkou, 九門口) and had to make a forced landing. Zhao made a successful escape back to his base, but the bombers subsequently flew at much higher altitude to avoid ground fire, which greatly reduced their bombing accuracy and effectiveness.
After numerous battles between Chinese warlords
A warlord is a person who exercises military, economic, and political control over a region in a country without a strong national government; largely because of coercive control over the armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of h ...
, all of the aircraft fell into the hands of the Fengtian clique, forming its ''First Heavy Bomber Group''. These were in the process of being phased out at the time of the Mukden Incident
The Mukden Incident, or Manchurian Incident, known in Chinese as the 9.18 Incident (九・一八), was a false flag event staged by Japanese military personnel as a pretext for the 1931 Japanese invasion of Manchuria.
On September 18, 1931, ...
and therefore were subsequently captured by the Japanese, who soon disposed of them.
Variants
;F.B.27 Vimy: Prototypes; four built, powered by twoHispano-Suiza 8
The Hispano-Suiza 8 was a water-cooled V8 SOHC aero engine introduced by Hispano-Suiza in 1914, and was the most commonly used liquid-cooled engine in the aircraft of the Entente Powers during the First World War. The original Hispano-Suiza ...
piston engines..
;F.B.27A Vimy II: Twin-engine heavy bomber aircraft for the RAF, powered by two Rolls-Royce Eagle VIII
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of ot ...
piston engines.
;Vimy Ambulance: Air ambulance version for the RAF.
;Vimy Commercial: Civilian transport version, powered by two Rolls-Royce Eagle VIII
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of ot ...
and later Rolls-Royce Eagle IX
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of ...
piston engines.
;A.N.F. 'Express Les Mureaux': Vimy Commercial No.42 re-engined with 2x Lorraine 12Da
The Lorraine 12D, also referred to as Lorraine-Dietrich 12D, was a series of water-cooled V12 engines produced by the French company Lorraine-Dietrich. The first variant began production in 1917, and the engines were used to power bombers for the ...
V-12 engines.
Operators
Military operators
 ;
*
;
* Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) an ...
(Vimy, Vimy Ambulance & Vernon).
** No. 7 Squadron RAF
** No. 9 Squadron RAF
** No. 24 Squadron RAF
** No. 45 Squadron RAF
** No. 58 Squadron RAF
Number 58 Squadron was a squadron of the Royal Air Force.
History First World War
No. 58 Squadron was first formed at Cramlington, Northumberland, on 8 June 1916 as a squadron of the Royal Flying Corps from a nucleus split off from the Home ...
** No. 70 Squadron RAF
** No. 99 Squadron RAF
** No. 100 Squadron RAF
** No. 216 Squadron RAF
Number 216 Squadron is a squadron of the Royal Air Force based at RAF Waddington, Lincolnshire, since reforming on 1 April 2020 and is tasked with testing future drone swarm technology. It had previously operated Lockheed TriStar K1, KC1 and C ...
** No. 500 Squadron RAF
(Translation: "Whither the fates may call")
, colors=
, colors_label=
, march=
, mascot=
, equipment=
, equipment_label=
, battles=
, anniversaries=
, decorations=
, battle_honours= Channel and North Sea, 1939–41 Dunkirk Biscay ports, 1941 Atla ...
** No. 502 Squadron RAF
No. 502 (Ulster) Squadron was a Royal Auxiliary Air Force squadron that saw service in World War II. It was reformed in September 2013, and is the oldest of all the reserve squadrons, being formed in 1925.
History
Formation and early years
...
Civil operators
; *The Government ofChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
(Vimy Commercial).
;
*''Grands Express Aériens
The Compagnie des ''Grands Express Aériens'' was a pioneering French airline established 20 March 1919 and operating until merged with Compagnie des Messageries Aériennes to form Air Union on 1 January 1923.
Headquartered at 3, Rue d'Anjou, P ...
'' (Vimy Commercial).
;
* One aircraft.
;
*The Government of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(Vimy).
;
* Imperial Airways (Vimy Commercial).
*Instone Air Line
Instone Air Line was an early British airline from 1919 to 1924. Along with other private airlines of the time, it was absorbed into Imperial Airways.
This airline is not to be confused with Instone Air Line (1981) of Stansted, which operated ...
(Vimy Commercial).
On display
 ;Australia
*Vimy IV ''G-EAOU'' at
;Australia
*Vimy IV ''G-EAOU'' at Adelaide Airport
Adelaide Airport , also known as Adelaide International Airport, is the principal airport of Adelaide, South Australia and the fifth-busiest airport in Australia, servicing 8.5 million passengers in the financial year ending 30 June 201 ...
;United Kingdom
*Vimy IV – Alcock & Brown's transatlantic aircraft at the Science Museum London.

Replicas
 A replica transatlantic Vimy cockpit section was built by Vickers for the London Science Museum in the early 1920s, and three full-size replicas have also been built. The first was a taxiable replica commissioned by
A replica transatlantic Vimy cockpit section was built by Vickers for the London Science Museum in the early 1920s, and three full-size replicas have also been built. The first was a taxiable replica commissioned by British Lion Films
British Lion Films is a film production and distribution company active under several forms since 1919. Originally known as British Lion Film Corporation Ltd, it entered receivership on 1 June 1954. From 29 January 1955 to 1976, the company was kn ...
from Shawcraft Models Ltd of Iver Heath, Bucks; the planned film about Alcock & Brown's transatlantic flight was never made, but the model was completed and paid for. Its fate remains a mystery''Aeroplane'' magazine, May 2010 although it appeared on static display at the Battle of Britain air display at RAF Biggin Hill in 1955 and may have been subsequently stored dismantled in East London until at least the late 1980s. The engine nacelles appear in the mine scene from the film ' Daleks' Invasion Earth 2150 A.D.', so it may not have been in good condition by then.
In 1969 an airworthy Vimy replica (registered G-AWAU) was built by the Vintage Aircraft Flying Association at Brooklands; this was first flown by D. G. 'Dizzy' Addicott and Peter Hoar. It was badly damaged by fire and was displayed until February 2014 at the RAF Museum, Hendon, London). It is currently stored dismantled at the RAF Museum storage facility in Stafford
Stafford () is a market town and the county town of Staffordshire, in the West Midlands region of England. It lies about north of Wolverhampton, south of Stoke-on-Trent and northwest of Birmingham. The town had a population of 70,145 in th ...
.
A second flyable Vimy replica, NX71MY, was built in 1994 by an Australian-American team led by Lang Kidby and Peter McMillan, and this aircraft successfully recreated the three great pioneering Vimy flights: England to Australia flown by Lang Kidby and Peter McMillan (in 1994), England to South Africa flown by Mark Rebholz and John LaNoue (1999) and in 2005, Alcock and Brown's 1919 Atlantic crossing was recreated by Steve Fossett and Mark Rebholz. The aircraft was donated to Brooklands Museum
Brooklands Museum is a motoring and aviation museum occupying part of the former Brooklands motor-racing track in Weybridge, Surrey, England.
Formally opened in 1991, the museum is operated by the independent Brooklands Museum Trust Ltd, a pri ...
in 2006 and was kept airworthy in order to commemorate the 90th anniversaries of the Transatlantic and Australian flights, then retired in late 2009. Its final flight was made by John Dodd, Clive Edwards and Peter McMillan from Dunsfold to Brooklands on 15 November 2009 and four days later, in 18 hours, the aircraft was dismantled, transported the short distance to the museum and reassembled inside the main hangar by a dedicated volunteer team. Two days later a special Brooklands Vimy Exhibition was officially opened by Peter McMillan, and this unique aircraft is now on public display there.
Specifications
See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * Lynch, Brendan. ''Yesterday We Were in America - Alcock and Brown - First to fly the Atlantic non-stop''. Yeovil, England: Haynes Publishing, 2009 * * *Sims, Charles. "Talkback". '' Air Enthusiast''. No. 13, August–November 1980. p. 79. * * * Winchester, Jim, ed. "Vickers Vimy." ''Biplanes, Triplanes and Seaplanes (Aviation Factfile)''. London: Grange Books plc, 2004. .External links
The Vickers Vimy-Commercial at Hendon, 1919
RAF Museum
Alcock and Brown's Vimy at the Science Museum London - archived article
Vickers Vimy online collection – State Library of NSW
Alcock and Brown's Vimy in the collection of the Science Museum London
National Geographic record of the 2005 re-enactment on the Atlantic flight
The Brooklands Vickers Vimy Replica Video List
{{Authority control 1910s British bomber aircraft
Vimy
Vimy ( or ; ; Dutch: ''Wimi'') is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. Located east of Vimy is the Canadian National Vimy Memorial dedicated to the Battle of Vimy Ridge and the Canadian soldiers wh ...
Military aircraft of World War I
Aircraft first flown in 1917
Biplanes