Via Francigena on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Via Francigena () is an ancient road and pilgrimage route running from the
The Via Francigena () is an ancient road and pilgrimage route running from the
 In the
In the  At the end of the 10th century
At the end of the 10th century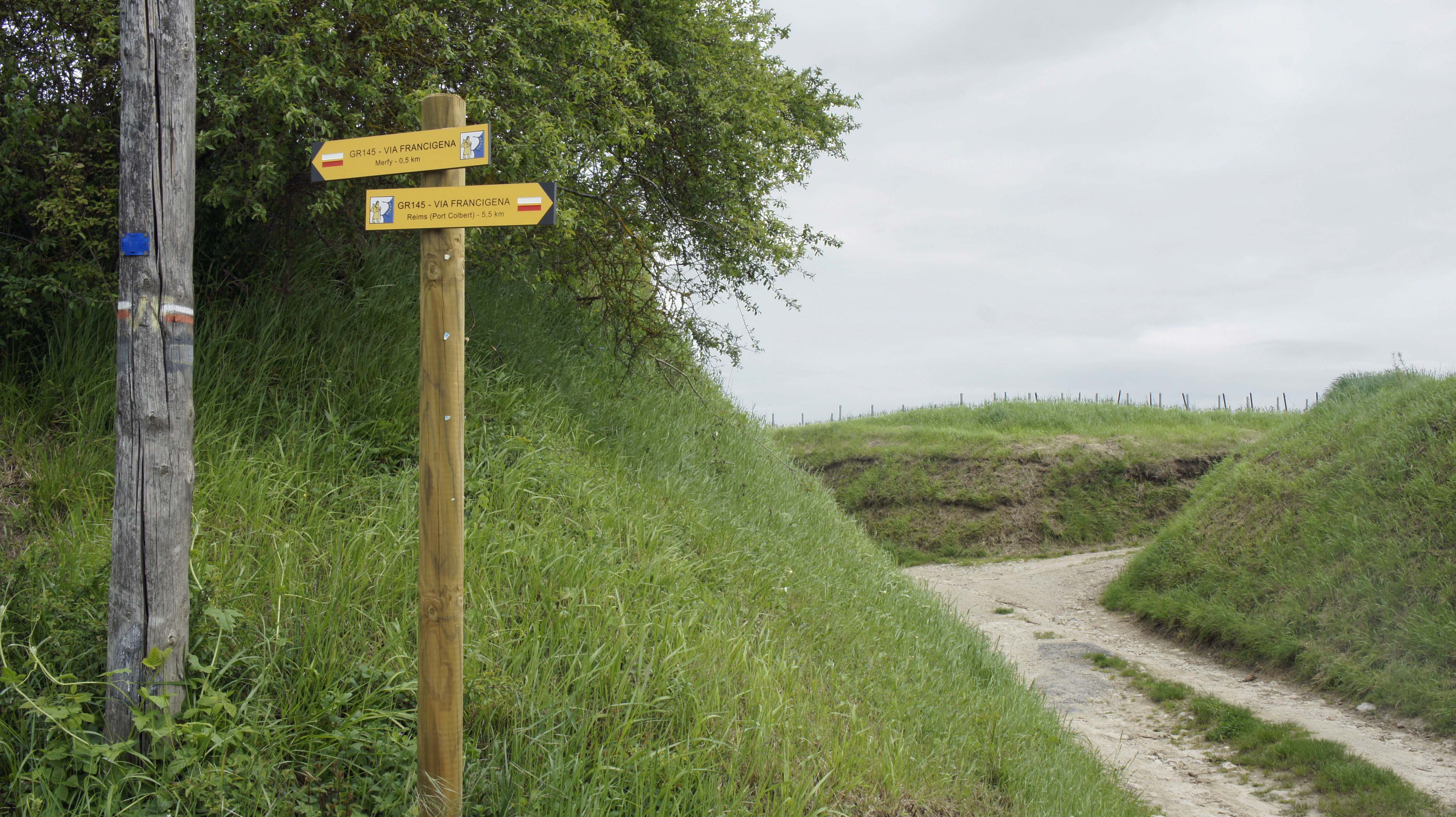  The Welsh king Rhodri Mawr in 880 and his grandson
The Welsh king Rhodri Mawr in 880 and his grandson 
 From Rome the path followed for a long stretch the
From Rome the path followed for a long stretch the
 Due to the scarcity of dedicated pilgrims' accommodation along the Via Francigena, pilgrims often camp out rather than staying in hotels or ''
Due to the scarcity of dedicated pilgrims' accommodation along the Via Francigena, pilgrims often camp out rather than staying in hotels or ''
 In England, the Via Francigena starts at the southern portico of Canterbury’s cathedral where the milestone zero of the route is located. The route passes through part of the county of
In England, the Via Francigena starts at the southern portico of Canterbury’s cathedral where the milestone zero of the route is located. The route passes through part of the county of
File:Canterbury Cathedral - Portal Nave Cross-spire.jpeg,
Kerschbaum & Gattinger, Via Francigena – DVD- Documentary of a modern pilgrimage to Rome
, Verlag EUROVIA, Vienna 2005 *Trezzini, La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma ''La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma'' (Association Via Francigena) 2000 * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. San Pellegrino sulle Via Francigene. Ed. Gangemi Cod. * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Topofrancigena da Canterbury a Roma (2004–2007) Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Guide-Vademecum da Canterbury a Roma. Ed.2002–03 * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Dormifrancigena da Canterbury a Roma.2006 + 2007 Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena
Via Francigena on URCamino
Canterbury City Council local info on the route through the UK
BBC News– Epic run from Canterbury to Rome follows pilgrimage
*
The GR145 Via Francigena in the Champagne-Ardenne region of France
Italian Ministry of Cultural and Heritage
Multiple language site of the official route in Italy including roadbooks, GPS and maps
La Via Francigena website for Italy ''(in Italian & English)''
The Via Francigena in Southern Italy, from Rome to Apulia ''(English version)''
Asociación de la vía Francígena en España
Association Internationale Via Francigena
Active since 1997 promoting cultural and tourist awareness of the Via Francigena to Roma
Confraternity of Pilgrims to Rome
United Kingdom pilgrim association providing information on the Via Francigena
European Association of Vie Francigene
Information on the route through Italy *
Dutch Association
Dutch Association of pilgrims walking or cycling to Rome
*
EUROVIA
Austrian pilgrim Association supporting pilgrims to Rome (German/English/Italian)
Camminando sulla Via Francigena. The Italian Community of pilgrims 3.0 ''(choose your language)''
La Francigena in Garfagnana
Route between Aulla and Lucca through the Garfagnana in Italy ''(in Italian)''
Via Francigena di San Francesco
Route from Roma to Rieti. *
Via Francigena Appia Pedemontana
Route from Roma to Formia {{Authority control Christian pilgrimages European Cultural Routes Hiking trails in Europe Hiking trails in Italy Hiking trails in Switzerland Italian words and phrases Medieval roads and tracks Pilgrimage routes
cathedral city
Cathedral city is a city status in the United Kingdom.
Cathedral city may also refer to:
* Cathedral City, California, a city in Southern California, United States
* Cathedral City Cheddar, a brand of Cheddar cheese
* Cathedral City High Scho ...
of Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of t ...
in England, through France and Switzerland, to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
and then to Apulia
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
, Italy, where there were ports of embarkation for the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
. It was known in Italy as the "''Via Francigena''" ("the road that comes from France") or the "''Via Romea Francigena''" ("the road to Rome that comes from France"). In medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
times it was an important road and pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
route for those wishing to visit the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
and the tombs of the apostle
An apostle (), in its literal sense, is an emissary, from Ancient Greek ἀπόστολος (''apóstolos''), literally "one who is sent off", from the verb ἀποστέλλειν (''apostéllein''), "to send off". The purpose of such sending ...
s Peter and Paul.
History of the pilgrimage to Rome
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, Via Francigena was the major pilgrimage route to Rome from the north. The route was first documented as the "Lombard Way", and was first called the ''Iter Francorum'' (the "Frankish Route") in the ''Itinerarium sancti Willibaldi'' of 725, a record of the travels of Willibald
Willibald (; c. 700 – c.787) was an 8th-century bishop of Eichstätt in Bavaria.
Information about his life is largely drawn from the Hodoeporicon (itinerary) of Willibald, a text written in the 8th century by Huneberc, an Anglo-Saxon nun fr ...
, bishop of Eichstätt in Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
. It was ''Via Francigena-Francisca'' in Italy and Burgundy, the ''Chemin des Anglois'' in the Frankish Kingdom (after the evangelisation of England in 607) and also the ''Chemin Romieu'', the road to Rome. The name ''Via Francigena'' is first mentioned in the ''Actum Clusio'', a parchment of 876 in the Abbey of San Salvatore at Monte Amiata (Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
).
 At the end of the 10th century
At the end of the 10th century Sigeric the Serious
Sigeric (died 28 October 994) was the Archbishop of Canterbury from 990 to 994. Educated at Glastonbury Abbey, he became a monk there before becoming an abbot and then Bishop of Ramsbury before his elevation to the archbishopric. An account of ...
, the Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Just ...
, used the Via Francigena to and from Rome in order to receive his ''pallium
The pallium (derived from the Roman ''pallium'' or ''palla'', a woolen cloak; : ''pallia'') is an ecclesiastical vestment in the Catholic Church, originally peculiar to the pope, but for many centuries bestowed by the Holy See upon metropol ...
''; he recorded his route and his stops on the return journey, but nothing in the document suggests that the route was then new, nor if he made the journey by foot or on horseback.
Later itineraries to Rome include the Leiðarvísir og borgarskipan of the Icelandic traveller Nikolás Bergsson (in 1154) and the one from Philip Augustus
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), byname Philip Augustus (french: Philippe Auguste), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks, but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French m ...
of France (in 1191). Two somewhat differing maps of the route appear in manuscripts of Matthew Paris
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris ( la, Matthæus Parisiensis, lit=Matthew the Parisian; c. 1200 – 1259), was an English Benedictine monk, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscripts and cartographer, based at St Albans Abbey ...
, ''Historia Anglorum'', from the 13th century.
Hywel Dda
Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell (died 949/950) was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubart ...
in 945 are both known to have visited Rome towards the end of their lives, but it is not known whether they went by land or by sea via the Straits of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaism, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to ...
. The Benedictine William of St-Thierry used the roads towards Rome on several occasions at the end of the 11th century. The return journey by sea was likely to be easier, thanks to the prevailing south-westerly winds, but tacking down to the Mediterranean would have made a very long journey indeed.
The Via Francigena was not a single road, like a Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
, paved with stone blocks and provided at intervals with a change of horses for official travellers. Rather, it comprised several possible routes that changed over the centuries as trade and pilgrimage waxed and waned. Depending on the time of year, the political situation, and the relative popularity of the shrines of the saints situated along the route, travellers may have used any of three or four crossings of the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
and the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
. The Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
financed the maintenance and security of the section of road through their territories as a trading route to the north from Rome, avoiding enemy-held cities such as Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
. Unlike Roman roads the Via Francigena did not connect cities, but relied more on abbey
An abbey is a type of monastery used by members of a religious order under the governance of an abbot or abbess. Abbeys provide a complex of buildings and land for religious activities, work, and housing of Christian monks and nuns.
The c ...
s.

Sigeric's itinerary
In around 990, ArchbishopSigeric
Sigeric (? – 22 August 415) was a Visigoth king for seven days in 415 AD.
Biography
His predecessor, Ataulf, had been mortally wounded in his stables at the palace of Barcelona by an assassin. The assassin was probably a loyal servant of Saru ...
journeyed from Canterbury to Rome and back, but only documented his itinerary on the return journey,Ortenberg "Anglo-Saxon Church and the Papacy" ''English Church and the Papacy in the Middle Ages'' p. 49 taken in 80 stages averaging about a day, for a total of some .
Modern pilgrims from England would follow Sigeric's route in the reverse order, and so would journey from Canterbury to the English coast before crossing the Channel to ''Sumeran'' (now called Sombres), landing at the village of Wissant
Wissant (; from nl, Witzand, lang, “white sand”) is a seaside commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France.
Geography
Wissant is a fishing port and farming village located approximately north of Boulogn ...
. The route continues through Guînes
Guînes (; vls, Giezene, lang; pcd, Guinne) is a commune in the northern French department of Pas-de-Calais. Historically it was spelt ''Guisnes''.
On 7 January 1785, Jean-Pierre Blanchard, a French pioneer in hydrogen-balloon flight, comple ...
(Sigeric's Gisne), Thérouanne
Thérouanne (; vls, Terenburg; Dutch ''Terwaan'') is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Hauts-de-France region of France. It is located west of Aire-sur-la-Lys and south of Saint-Omer, on the D 157 and D 341 road junction. Loca ...
(Teranburh), Bruay (Bruaei), and Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais department, which forms part of the region of Hauts-de-France; before the reorganization of 2014 it was in Nord-Pas-de-Calais. The historic centre of ...
(Atherats), before continuing on to Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded b ...
, Châlons-sur-Marne, Bar-sur-Aube, Langres
Langres () is a commune in northeastern France. It is a subprefecture of the department of Haute-Marne, in the region of Grand Est.
History
As the capital of the Romanized Gallic tribe known as the Lingones, it was called Andematunnum, th ...
, Champlitte
Champlitte is a commune in the Haute-Saône department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France. The inhabitants of Champlitte are known in French as the Chanitois.
History
During the Roman Era, Champlitte was close to two ma ...
, Besançon
Besançon (, , , ; archaic german: Bisanz; la, Vesontio) is the prefecture of the department of Doubs in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. The city is located in Eastern France, close to the Jura Mountains and the border with Switzer ...
, Pontarlier
Pontarlier ( ; Latin: ''Ariolica'') is a commune and one of the two sub-prefectures of the Doubs department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in eastern France near the Swiss border.
History
Pontarlier occupies the ancient Roman station o ...
, Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
and Saint-Maurice. From Saint-Maurice, the route traverses the Great St. Bernard Pass to Aosta
Aosta (, , ; french: Aoste , formerly ; frp, Aoûta , ''Veulla'' or ''Ouhta'' ; lat, Augusta Praetoria Salassorum; wae, Augschtal; pms, Osta) is the principal city of Aosta Valley, a bilingual region in the Italian Alps, north-northwest o ...
and then to Ivrea, Vercelli
Vercelli (; pms, Vërsèj ), is a city and ''comune'' of 46,552 inhabitants (January 1, 2017) in the Province of Vercelli, Piedmont, northern Italy. One of the oldest urban sites in northern Italy, it was founded, according to most historians, ...
, Pavia
Pavia (, , , ; la, Ticinum; Medieval Latin: ) is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy in northern Italy, south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It has a population of c. 73,086. The city was the ...
, Fidenza
Fidenza ( Parmigiano: ; locally ) is a town and ''comune ''in the province of Parma, Emilia-Romagna region, Italy. It has around 27,000 inhabitants. The town was renamed Fidenza in 1927, recalling its Roman name of ''Fidentia''; before, it was cal ...
, Pontremoli
Pontremoli (; local egl, Pontrémal; la, Apua) is a small city, ''comune'' former Latin Catholic bishopric in the province of Massa and Carrara, Tuscany region, central Italy.
Literally translated, Pontremoli means "Trembling Bridge" (from ''pon ...
, Filattiera
Filattiera is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Massa and Carrara in the Italian region Tuscany, located about northwest of Florence and about northwest of Massa.
Main sights
*Church of ''San Giorgio'' (12th century). It contains ...
, Aulla
Aulla is a ''comune'' in the province of Massa and Carrara, Tuscany, central Italy. It is located in the valley of the River Magra.
Geology
In 1977, the Italian geologist Augusto Azzaroli discovered a series of mammal rests with a correlated f ...
, Luni, Lucca
Lucca ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the Serchio River, in a fertile plain near the Ligurian Sea. The city has a population of about 89,000, while its province has a population of 383,957.
Lucca is known as one ...
, San Gimignano
San Gimignano () is a small walled medieval hill town in the province of Siena, Tuscany, north-central Italy. Known as the Town of Fine Towers, San Gimignano is famous for its medieval architecture, unique in the preservation of about a dozen of ...
, Poggibonsi
Poggibonsi is a town in the province of Siena, Tuscany, central Italy. It is located on the river Elsa and is the main centre of the Valdelsa Valley.
History
The area around Poggibonsi was already settled in the Neolithic age, although the fir ...
, Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centur ...
, San Quirico d'Orcia
San Quirico d'Orcia is a ''comune'' (municipality) of about 2,500 inhabitants in the Province of Siena in the Italian region Tuscany, located about southeast of Florence and about southeast of Siena inside the Valdorcia landscape. It is named i ...
, Bolsena, Viterbo
Viterbo (; Viterbese: ; lat-med, Viterbium) is a city and ''comune'' in the Lazio region of central Italy, the capital of the province of Viterbo.
It conquered and absorbed the neighboring town of Ferento (see Ferentium) in its early history ...
, Sutri, and finally Rome.
The final stretch towards the Apulian ports
 From Rome the path followed for a long stretch the
From Rome the path followed for a long stretch the Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: ''Via Appia'') is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, ...
or the parallel Via Latina
The Via Latina (Latin for "Latin Road") was a Roman road of Italy, running southeast from Rome for about 200 kilometers.
Route
It led from the Porta Latina in the Aurelian walls of Rome to the pass of Mount Algidus; it was important in the ear ...
up to Benevento
Benevento (, , ; la, Beneventum) is a city and '' comune'' of Campania, Italy, capital of the province of Benevento, northeast of Naples. It is situated on a hill above sea level at the confluence of the Calore Irpino (or Beneventano) and the ...
. From that town Via Traiana
Via Appia ''(white)'' and Via Traiana ''(red)''
The Via Traiana was an ancient Roman road. It was built by the emperor Trajan as an extension of the Via Appia from Beneventum, reaching Brundisium (Brindisi) by a shorter route (i.e. via Canusi ...
was taken up the Campanian Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
and Daunian Mountains
Daunian Mountains (in Italian Monti della Daunia or Monti Dauni, or also improperly Subappennino Dauno) are a mountain range in southern Italy, constituting the eastern appendix of the Campanian Apennines. They occupy the western fringe of Capit ...
, where stood, a fortress held by the Knights of Jerusalem in order to guarantee the safety of pilgrims along the mountain stretch. The road therefore reached Troia, in the high plain of Tavoliere delle Puglie
300px, The Tavoliere seen from the Gargano promontory.
The Tavoliere delle Puglie (; ) is a plain in northern Apulia, southern Italy, occupying nearly a half of the Capitanata traditional region. It covers a surface of c. 3,000 km², once c ...
(where Via Francigena is attested since 1024), and then continued towards Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Ital ...
, Brindisi
Brindisi ( , ) ; la, Brundisium; grc, Βρεντέσιον, translit=Brentésion; cms, Brunda), group=pron is a city in the region of Apulia in southern Italy, the capital of the province of Brindisi, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea.
Histo ...
and Otranto
Otranto (, , ; scn, label=Salentino, Oṭṛàntu; el, label= Griko, Δερεντό, Derentò; grc, Ὑδροῦς, translit=Hudroûs; la, Hydruntum) is a coastal town, port and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce (Apulia, Italy), in a ferti ...
, the main ports of embarkation for the Holy Land
The Holy Land; Arabic: or is an area roughly located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Eastern Bank of the Jordan River, traditionally synonymous both with the biblical Land of Israel and with the region of Palestine. The term "Holy ...
.
Today
Today some pilgrims still follow in Sigeric's ancient footsteps and travel on foot, on horseback or by bicycle on the ''Via Francigena'', although there are far fewer pilgrims on this route than on the Way of St. James pilgrims' route toSantiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela is the capital of the autonomous community of Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city has its origin in the shrine of Saint James the Great, now the Cathedral of Santiago de Compostela, as the destination of the Way of S ...
in Spain. Roughly 1,200 pilgrims were estimated to have walked the Via Francigena in 2012. One reason for this is a lack of infrastructure and suitable support facilities. Affordable pilgrims' accommodation and other facilities can be hard to come by for those traveling along the route. In 2011, James Saward-Anderson and Maxwell Hannah ran the entire route for Water Aid. They completed the route unassisted in 58 days.
Accommodation
pensions
A pension (, from Latin ''pensiō'', "payment") is a fund into which a sum of money is added during an employee's employment years and from which payments are drawn to support the person's retirement from work in the form of periodic payments ...
''. However increasingly in Italy, some monasteries and religious houses offer dedicated pilgrim's accommodation. These are called ''spedali'' and — like the ''refugios'' found on the Way of St. James in France and Spain — they offer cheap and simple dormitory-style accommodation. ''Spedali'' accept pilgrims who bear a valid ''credenziale'' (pilgrim's passport), usually for one night only. Some places offer meals as well.
As of 2016, the old guest houses dedicated to pilgrims were not reconditioned by tourist operators, due to the lack of economic return.
The state and path of the route
Only a few decades ago, interest in the Via Francigena was limited to scholars. This began to change in recent years when many who, after travelling the Way of St. James in Spain, wanted to make the pilgrimage to Rome on foot as well. In Italy, this gave birth to a network of lovers of the Via Francigena, who with paint and brush, began to mark its trails and paths. These people were joined by religious and local government agencies who also tried to recover the original route. Where possible today's route follows the ancient one but sometimes it deviates from the historical path in favour of paths and roads with low traffic. The potential for the tourist trade in Italy has been recognised but this has also led some to gain unfair economic advantage by diverting the path so that it passes next to their business, thus increasing footfall. In England, the Via Francigena starts at the southern portico of Canterbury’s cathedral where the milestone zero of the route is located. The route passes through part of the county of
In England, the Via Francigena starts at the southern portico of Canterbury’s cathedral where the milestone zero of the route is located. The route passes through part of the county of Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
, from Canterbury to the ferries at Dover.
In France, the Via Francigena (given the Grande Randonnée
The GR footpaths are a network of long-distance walking trails in Europe, mostly in France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Spain. They go by the following names: french: link=no, sentier de grande randonnée, vls, link=no, Groteroutepad, nl, L ...
designation 'GR145') goes through the '' régions Hauts-de-France
Hauts-de-France (; pcd, Heuts-d'Franche; , also ''Upper France'') is the northernmost region of France, created by the territorial reform of French regions in 2014, from a merger of Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy. Its prefecture is Lille. The ...
, Grand-Est and Bourgogne-Franche-Comté
Bourgogne-Franche-Comté (; , sometimes abbreviated BFC; Arpitan: ''Borgogne-Franche-Comtât'') is a region in Eastern France created by the 2014 territorial reform of French regions, from a merger of Burgundy and Franche-Comté. The new region ...
before reaching the Swiss border.
In Switzerland the Via Francigena (with the route designation '70') goes through the cantons of Vaud
Vaud ( ; french: (Canton de) Vaud, ; german: (Kanton) Waadt, or ), more formally the canton of Vaud, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of ten districts and its capital city is Lausanne. Its coat of arms ...
and Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
.
In Italy the Via Francigena goes through the ''Regione
The regions of Italy ( it, regioni d'Italia) are the first-level administrative divisions of the Italian Republic, constituting its second NUTS administrative level. There are twenty regions, five of which have higher autonomy than the rest. ...
'' of Valle d'Aosta, Piedmont
it, Piemontese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
, Emilia-Romagna
egl, Emigliàn (man) egl, Emiglièna (woman) rgn, Rumagnòl (man) rgn, Rumagnòla (woman) it, Emiliano (man) it, Emiliana (woman) or it, Romagnolo (man) it, Romagnola (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title ...
, Tuscany
it, Toscano (man) it, Toscana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Citizenship
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 = Italian
, demogra ...
, and finally about halfway through Lazio
it, Laziale
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
to Rome.
Walkers could choose to walk along the EuroVelo EV5 cycling route which bears the name the 'Via Francigena'. However, this EuroVelo route varies substantially from Sigeric's route and the one given by the Via Francigena Association.
In 1994 the Via Francigena was designated a Cultural Route, and in 2004 a Major Cultural Route.
In November 2009 the Italian government launched a project to recover the Italian leg of it. The object of the plan is to recover the entire route (disjointed parts of which are already signposted) "''not only in spiritual and religious terms but also in terms of the environment, architecture, culture, history, wine and cuisine and sport.''" The initiative was promoted by the Region of Tuscany, which hosts of the Via, and which presented a plan detailing the low environmental impact infrastructures to be created. The plan will be shared with other local authorities located along the route as an encouragement to carry out similar recovery work. Tuscany has also announced cooperation with the ''Opera Romana Pellegrinaggi'' (ORP), the Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
’s organisation for encouraging pilgrimages.
The final stretch, from Rome to the Apulia
it, Pugliese
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographic ...
n ports of embarcation for Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, has been renamed ''Via Francigena nel Sud'' (in Italian "Via Francigena in the South (Italy)") or else ''Vie Francigene del Sud'' ("The Francigena Ways to the South").
Gallery
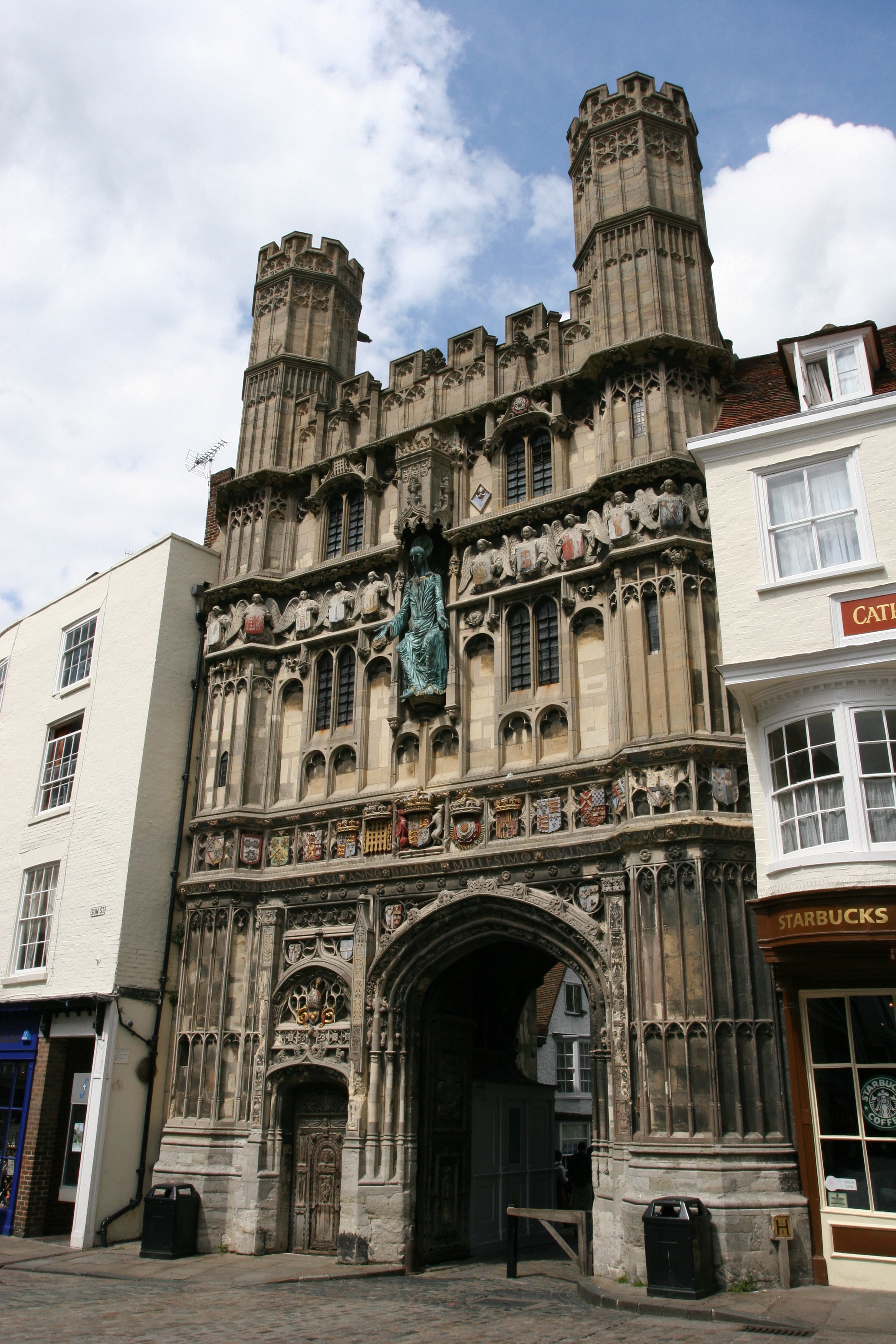
Canterbury Cathedral
Canterbury Cathedral in Canterbury, Kent, is one of the oldest and most famous Christian structures in England. It forms part of a World Heritage Site. It is the cathedral of the Archbishop of Canterbury, currently Justin Welby, leader of the ...
, the starting point of the Via Francigena.
File:Via Francigena 5644.JPG, Crossroads of the Via Francigena (designated in France as the ''Grande Randonnée
The GR footpaths are a network of long-distance walking trails in Europe, mostly in France, Belgium, the Netherlands and Spain. They go by the following names: french: link=no, sentier de grande randonnée, vls, link=no, Groteroutepad, nl, L ...
'' route GR145) and the GR654 in the ''département'' of Marne, northern France.
File:Lac du Great St Bernard Pass, 2010 August.JPG, The Great St. Bernard Pass in high summer.
File:Colonna guado po sigerico.JPG, Column built by the Compagnia di Sigerico at Soprarivo, Calendasco
Calendasco ( Piacentino: ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Piacenza in the Italian region Emilia-Romagna, located about northwest of Bologna and about northwest of Piacenza
Piacenza (; egl, label= Piacentino, Piaṡëin ...
. An identical one stands in the village of Corte Sant'Andrea, Lombardy.
File:Aulla-IMG 0485.JPG, Sigeric's station no. XXX in Aulla
Aulla is a ''comune'' in the province of Massa and Carrara, Tuscany, central Italy. It is located in the valley of the River Magra.
Geology
In 1977, the Italian geologist Augusto Azzaroli discovered a series of mammal rests with a correlated f ...
, Tuscany.
File:Passo-della-Cisa-2012.JPG, The Cisa Pass between Tuscany & Emilia-Romagna.
File:Veduta Antica di Rocca a Tentennano 1.jpg, Mediaeval Italian manuscript depicting the Castle of Tentennano on the Via Francigena.
File:Vatican City at Large.jpg, St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican City in Rome holds one of the destinations of the pilgrimage, the tomb of St. Peter the Apostle.
File:Via Francigena - Ariano Irpino, località Sprinia.jpeg, Via Francigena along Southern Apennines, near Ariano Irpino
Ariano Irpino (formerly Ariano di Puglia or simply Ariano) is an Italian city and municipality in the province of Avellino, in the Campania region. With a population of 22,535 (2017), it is the second-largest settlement of the Irpinia district an ...
, on the final route connecting Rome and the Apulian ports of embarkation for the Holy Land.
File:Settimo Vittone Via Francigena.JPG, A steep section of the Via Francigena in Settimo Vittone
Settimo Vittone ( pms, Ël Seto Viton) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Turin, Piedmont, northern Italy. It is located about north of Turin, in the Canavese
Canavese ( French: ''Canavais''; Piedmontese: ''Canavèis'') ...
, Piedmont.
See also
* Way of St. James * Valdorcia * Ponte della Maddalena – a river crossing en route. *Order of the Holy Sepulchre
The Equestrian Order of the Holy Sepulchre of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Equestris Sancti Sepulcri Hierosolymitani, links=yes, OESSH), also called Order of the Holy Sepulchre or Knights of the Holy Sepulchre, is a Catholic order of knighthood under ...
– The Order of the Holy Sepulchre was one such order of Pilgrimage providing Hospices on the Vía. (The road to Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
lay through Rome, as it still does for the intrepid.)
* EV5 Via Romea Francigena, a long-distance cycling route also running from London to Rome.
*CoEur devotional path
CoEur is a Christian devotional and hiking route in Italy and Switzerland. Its Italian subtitle, ''Nel cuore dei cammini d'Europa'', translates as "In the heart of Europe's paths".
History of the route
The path CoEUR was created in the late 1990 ...
References
Sources
Kerschbaum & Gattinger, Via Francigena – DVD- Documentary of a modern pilgrimage to Rome
, Verlag EUROVIA, Vienna 2005 *Trezzini, La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma ''La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma'' (Association Via Francigena) 2000 * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. San Pellegrino sulle Via Francigene. Ed. Gangemi Cod. * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Topofrancigena da Canterbury a Roma (2004–2007) Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Guide-Vademecum da Canterbury a Roma. Ed.2002–03 * Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Dormifrancigena da Canterbury a Roma.2006 + 2007 Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena
External links
Via Francigena on URCamino
Canterbury City Council local info on the route through the UK
BBC News– Epic run from Canterbury to Rome follows pilgrimage
*
The GR145 Via Francigena in the Champagne-Ardenne region of France
Italian Ministry of Cultural and Heritage
Multiple language site of the official route in Italy including roadbooks, GPS and maps
La Via Francigena website for Italy ''(in Italian & English)''
The Via Francigena in Southern Italy, from Rome to Apulia ''(English version)''
Via Francigena associations
*Asociación de la vía Francígena en España
Association Internationale Via Francigena
Active since 1997 promoting cultural and tourist awareness of the Via Francigena to Roma
Confraternity of Pilgrims to Rome
United Kingdom pilgrim association providing information on the Via Francigena
European Association of Vie Francigene
Information on the route through Italy *
Dutch Association
Dutch Association of pilgrims walking or cycling to Rome
*
EUROVIA
Austrian pilgrim Association supporting pilgrims to Rome (German/English/Italian)
Camminando sulla Via Francigena. The Italian Community of pilgrims 3.0 ''(choose your language)''
Related routes
*La Francigena in Garfagnana
Route between Aulla and Lucca through the Garfagnana in Italy ''(in Italian)''
Via Francigena di San Francesco
Route from Roma to Rieti. *
Via Francigena Appia Pedemontana
Route from Roma to Formia {{Authority control Christian pilgrimages European Cultural Routes Hiking trails in Europe Hiking trails in Italy Hiking trails in Switzerland Italian words and phrases Medieval roads and tracks Pilgrimage routes