Veil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the

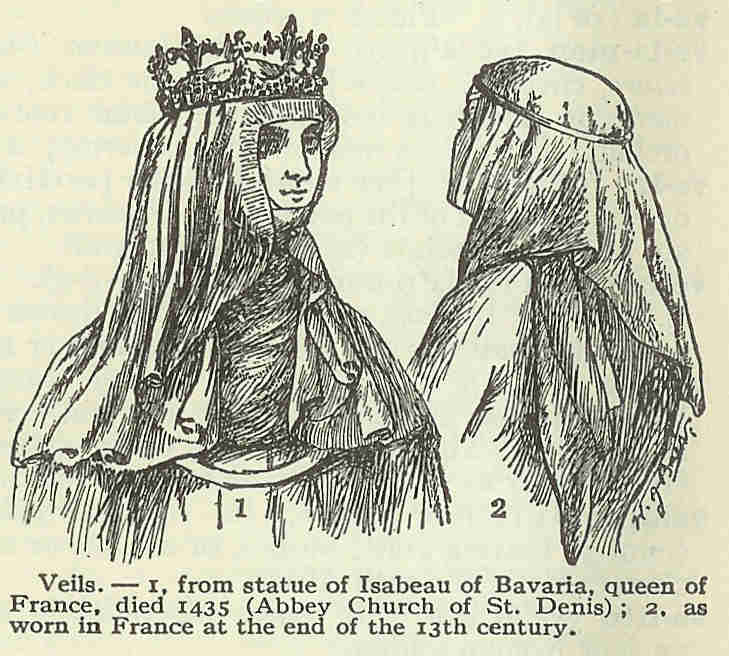 For many centuries, until around 1175,
For many centuries, until around 1175,
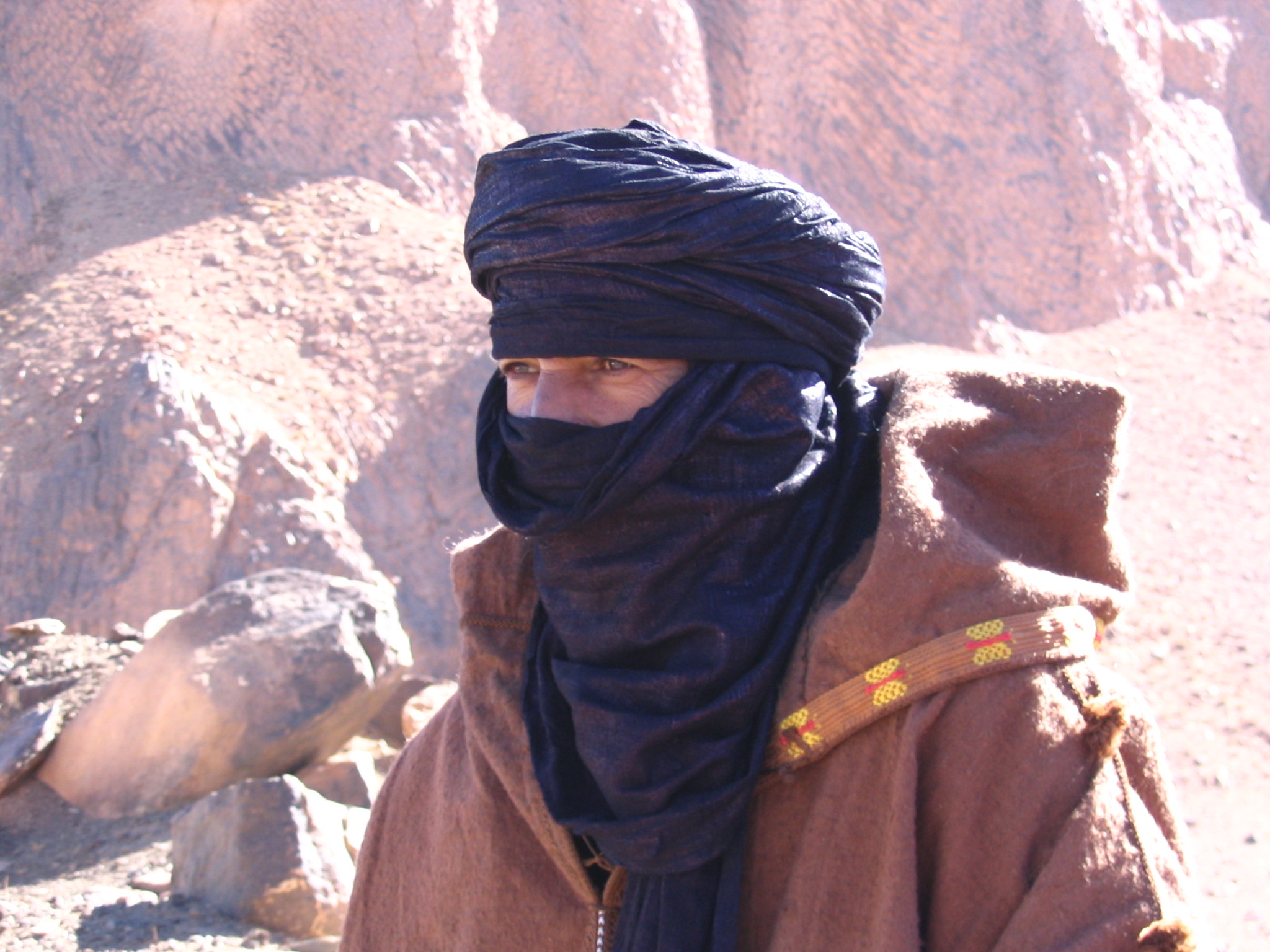 Among the Tuareg, Songhai, Hausa, and Fulani of
Among the Tuareg, Songhai, Hausa, and Fulani of  In some parts of
In some parts of
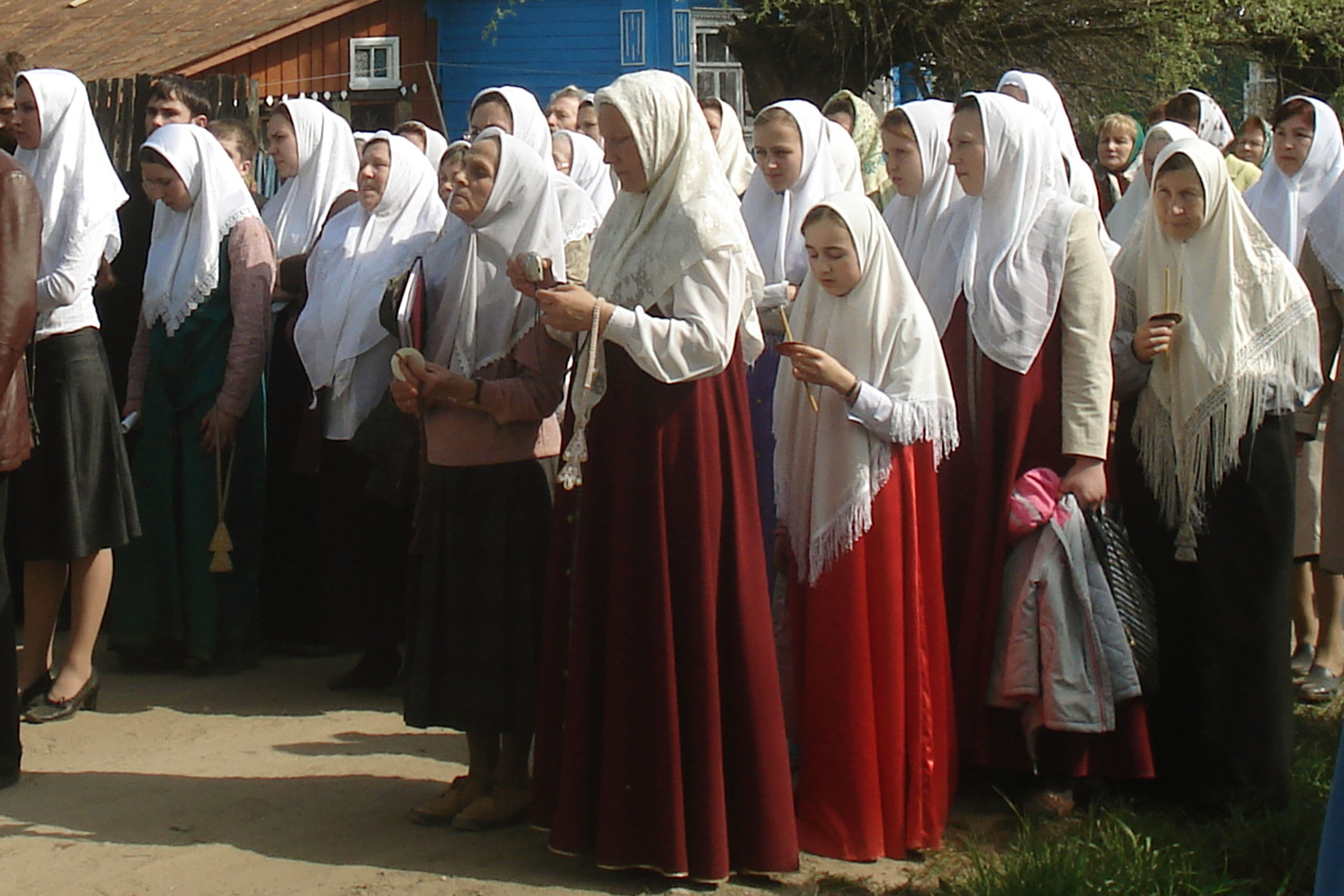


 Traditionally, in Christianity, women were enjoined to cover their heads, and men were instructed to remove their hat when praying or prophesying. Wearing a veil (also known as a headcovering) is seen as a sign of humility before God, as well as a reminder of the bridal relationship between Christ and the church. This practice is based on in the
Traditionally, in Christianity, women were enjoined to cover their heads, and men were instructed to remove their hat when praying or prophesying. Wearing a veil (also known as a headcovering) is seen as a sign of humility before God, as well as a reminder of the bridal relationship between Christ and the church. This practice is based on in the

 Among Christian churches which have a liturgical tradition, several different types of veils are used. These veils are often symbolically tied to the veils in the Tabernacle in the wilderness and in Solomon's Temple. The purpose of these veils was not so much to obscure as to shield the most sacred things from the eyes of sinful men. In Solomon's Temple the veil was placed between the "Inner Sanctuary" and the "
Among Christian churches which have a liturgical tradition, several different types of veils are used. These veils are often symbolically tied to the veils in the Tabernacle in the wilderness and in Solomon's Temple. The purpose of these veils was not so much to obscure as to shield the most sacred things from the eyes of sinful men. In Solomon's Temple the veil was placed between the "Inner Sanctuary" and the "
 The veil is one of the oldest parts of a bridal ensemble, dating as far back as Greek and Roman times, to hide a bride "from evil spirits who might want to thwart her happiness" or to frighten the spirits away. The veil also served to hide the bride's face from the groom prior to the wedding, as superstition says that it is bad luck for the groom to see the bride before the ceremony.
In the context of weddings in Western Christian culture, the veil has been used to symbolize
The veil is one of the oldest parts of a bridal ensemble, dating as far back as Greek and Roman times, to hide a bride "from evil spirits who might want to thwart her happiness" or to frighten the spirits away. The veil also served to hide the bride's face from the groom prior to the wedding, as superstition says that it is bad luck for the groom to see the bride before the ceremony.
In the context of weddings in Western Christian culture, the veil has been used to symbolize
 In
In
 In Christian theology, St. Paul's words concerning how marriage symbolizes the union of Christ and His Church underlie part of the tradition of veiling in the marriage ceremony. In historic Christian traditions, the veil is seen as "a visible sign that the woman is under the authority of a man" and that she is submitting herself to her husband's Christ-like leadership and loving care. As such, the practice of the wedding veil is part of the wider ordinance of the woman's headcovering in Christianity, rooted in .
The removing of the veil can be seen as a symbol of the temple veil that was torn when Christ died, giving believers direct access to God, and in the same way, the bride and the groom, once married, now have full access to one another.
In Christian theology, St. Paul's words concerning how marriage symbolizes the union of Christ and His Church underlie part of the tradition of veiling in the marriage ceremony. In historic Christian traditions, the veil is seen as "a visible sign that the woman is under the authority of a man" and that she is submitting herself to her husband's Christ-like leadership and loving care. As such, the practice of the wedding veil is part of the wider ordinance of the woman's headcovering in Christianity, rooted in .
The removing of the veil can be seen as a symbol of the temple veil that was torn when Christ died, giving believers direct access to God, and in the same way, the bride and the groom, once married, now have full access to one another.
The Veil: Women Writers on Its History, Lore, and Politics
'. University of California Press. .
Curtain
article from '' The Jewish Encyclopedia'' {{Authority control Catholic religious clothing Ceremonial clothing Christian clothing Eastern Christian vestments Eucharistic objects History of clothing Islamic female clothing Medieval European costume Modesty
 A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the
A veil is an article of clothing or hanging cloth that is intended to cover some part of the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
or face, or an object of some significance. Veiling has a long history in European, Asian, and African societies. The practice has been prominent in different forms in Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. The practice of veiling is especially associated with women and sacred objects, though in some cultures, it is men, rather than women, who are expected to wear a veil. Besides its enduring religious significance, veiling continues to play a role in some modern secular contexts, such as wedding customs.
History

Antiquity
Elite women in ancientMesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
and in the Macedonian and Persian empires wore the veil as a sign of respectability and high status. The earliest attested reference to veiling is found a Middle Assyrian law code dating from between 1400 and 1100 BC. Assyria had explicit sumptuary laws detailing which women must veil and which women must not, depending upon the woman's class, rank, and occupation in society. Female slaves and prostitutes were forbidden to veil and faced harsh penalties if they did so. The Middle Assyrian law code states:§ 40. A wife-of-a-man, or idows or ssyrianwomen who go out into the main thoroughfare hall not havetheir heads are ��A prostitute shall not veil herself, her head shall be bare. Whoever sees a veiled prostitute shall seize her, secure witnesses, and bring her to the palace entrance. They shall not take her jewelry; he who has seized her shall take her clothing; they shall strike her 50 blows with rods; they shall pour hot pitch over her head. And if a man should see a veiled prostitute and release her and not bring her to the palace entrance: they shall strike that man 50 blows with rods; the one who informs against him shall take his clothing; they shall pierce his ears, thread (them) on a cord, tie (it) at his back; he shall perform the king's service for one full month. Slave-women shall not veil themselves, and he who should see a veiled slave-woman shall seize her and bring her to the palace entrance: they shall cut off her ears; he who seizes her shall take her clothing.Veiling was thus not only a marker of aristocratic rank, but also served to "differentiate between 'respectable' women and those who were publicly available". The veiling of matrons was also customary in
ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
. Between 550 and 323 B.C.E respectable women in classical Greek society were expected to seclude themselves and wear clothing that concealed them from the eyes of strange men.Ahmed 1992, p. 26-28.
The Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the earliest attested form of the Greek language. It was spoken on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC). The language is preserved in inscriptions in Linear B, a script first atteste ...
term , ''a-pu-ko-wo-ko'', possibly meaning "headband makers" or "craftsmen of horse veil", and written in Linear B
Linear B is a syllabary, syllabic script that was used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest Attested language, attested form of the Greek language. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries, the earliest known examp ...
syllabic script, is also attested since ca. 1300 BC. In ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
the word for veil was (''kalyptra''; Ionic Greek
Ionic or Ionian Greek () was a subdialect of the Eastern or Attic–Ionic dialect group of Ancient Greek. The Ionic group traditionally comprises three dialectal varieties that were spoken in Euboea (West Ionic), the northern Cyclades (Centr ...
: , ''kalyptrē''; from the verb , ''kalyptō'', "I cover").
Classical Greek and Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
statues sometimes depict Greek women with both their head and face covered by a veil. Caroline Galt and Lloyd Llewellyn-Jones have both argued from such representations and literary references that it was commonplace for women (at least those of higher status) in ancient Greece to cover their hair and face in public. Roman women were expected to wear veils as a symbol of the husband's authority over his wife; a married woman who omitted the veil was seen as withdrawing herself from marriage. In 166 BC, consul Sulpicius Gallus divorced his wife because she had left the house unveiled, thus allowing all to see, as he said, what only he should see. Unmarried girls normally did not veil their heads, but matrons did so to show their modesty and chastity, their ''pudicitia''. Veils also protected women against the evil eye, it was thought.
A veil called ''flammeum'' was the most prominent feature of the costume worn by the bride at Roman weddings. The veil was a deep yellow color reminiscent of a candle flame. The ''flammeum'' also evoked the veil of the Flaminica Dialis, the Roman priestess who could not divorce her husband, the high priest of Jupiter, and thus was seen as a good omen for lifelong fidelity to one man. The Romans apparently thought of the bride as being "clouded over with a veil" and connected the verb ''nubere'' (to be married) with ''nubes'', the word for cloud.
Intermixing of populations resulted in a convergence of the cultural practices of Greek, Persian, and Mesopotamian empires and the Semitic-speaking peoples of the Middle East. With the spread of Christianity, the ordinance of headcovering by women became normative throughout Christendom because it was enjoined in the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
and by the Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical peri ...
. Veiling and seclusion of women appear to have established themselves among Jews and Christians, before spreading to urban Arabs of the upper classes and eventually among the urban masses. In the rural areas it was common to cover the hair, but not the face.
Later history
 For many centuries, until around 1175,
For many centuries, until around 1175, Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
and then Anglo-Norman women, with the exception of young unmarried girls, wore veils that entirely covered their hair, and often their necks up to their chins (see wimple). Only in the Tudor period (1485), when hoods became increasingly popular, did veils of this type become less common. This varied greatly from one country to another. In Italy, veils, including face veils, were worn in some regions until the 1970s. Women in southern Italy often covered their heads to show that they were modest, well-behaved and pious. They generally wore a '' cuffia'' (cap), then the '' fazzoletto'' (kerchief/head scarves) a long triangular or rectangular piece of cloth that could be tied in various ways, and sometimes covered the whole face except the eyes, sometimes ''bende (lit. swaddles, bandages)'' or a wimple underneath too.
For centuries, European women have worn sheer veils, but only under certain circumstances. Sometimes a veil of this type was draped over and pinned to the bonnet or hat of a woman in mourning, especially at the funeral and during the subsequent period of "high mourning". They would also have been used, as an alternative to a mask, as a simple method of hiding the identity of a woman who was traveling to meet a lover, or doing anything she did not want other people to find out about. More pragmatically, veils were also sometimes worn to protect the complexion from sun and wind damage (when untanned skin was fashionable), or to keep dust out of a woman's face, much as the keffiyeh (worn by men) is used today.
In Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
, and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
the concept of covering the head is or was associated with propriety and modesty. Most traditional depictions of the Virgin Mary
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is an important figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, various titles such as Perpetual virginity ...
, the mother of Christ, show her veiled. During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
most European married women covered their hair rather than their face, with a variety of styles of wimple, kerchiefs and headscarves. Veiling, covering the hair, was the normative practice of Christian women until at least the 19th century and still extant in certain regions, in accordance with Christian teaching delineated by Saint Paul in . While in the Western world this practice largely lapsed in the 1960s with the rise of the sexual revolution, traditional congregations, such as those of Conservative Anabaptist Christians, as well as certain Oriental Orthodox Christians and Eastern Orthodox Christians, continue observing the ordinance of headcovering. Other Christian women, including certain Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
, as well as certain conservative Reformed Christian women (such as those belonging to the Heritage Reformed Congregations or Free Presbyterian Church of North America), continue to wear a headcovering at least during prayer and worship. Lace face-veils are often worn by female relatives at funerals in some Catholic countries. In Orthodox Judaism
Orthodox Judaism is a collective term for the traditionalist branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Torah, Written and Oral Torah, Oral, as literally revelation, revealed by God in Ju ...
, married women cover their hair for reasons of modesty; many Orthodox Jewish women wear headscarves ( tichel) for this purpose.
Christian Byzantine literature expressed rigid norms pertaining to veiling of women, which have been influenced by Persian traditions, although there is evidence to suggest that they differed significantly from actual practice. Since Islam identified with the monotheistic religions practiced in the Byzantine and Sasanian empires, in the aftermath of the early Muslim conquests
The early Muslim conquests or early Islamic conquests (), also known as the Arab conquests, were initiated in the 7th century by Muhammad, the founder of Islam. He established the first Islamic state in Medina, Arabian Peninsula, Arabia that ...
veiling of women was adopted as an appropriate expression of Qur'anic ideals regarding modesty and piety. Veiling gradually spread to upper-class Arab women, and eventually, it became widespread among Muslim women in cities throughout the Middle East. Veiling of Arab Muslim women became especially pervasive under Ottoman rule as a mark of rank and exclusive lifestyle, and Istanbul of the 17th century witnessed differentiated dress styles that reflected geographical and occupational identities. Women in rural areas were much slower to adopt veiling because the garments interfered with their work in the fields. Since wearing a veil was impractical for working women, "a veiled woman silently announced that her husband was rich enough to keep her idle." By the 19th century, upper-class urban Muslim and Christian women in Egypt wore a garment which included a head cover and a ''burqa'' ( muslin cloth that covered the lower nose and the mouth). Up to the first half of the twentieth century, rural women in the Maghreb and Egypt put on a face veil when they visited urban areas, "as a sign of civilization". The practice of veiling gradually declined in much of the Muslim world during the 20th century before making a comeback in recent decades. The choice, or the forced option for women to veil remains controversial, whether a personal choice as an outward sign of religious devotion, or a forced one because of extremist groups that require a veil, under severe penalty, even death. The motives and reasons for wearing a hijab are wide and various, but ultimately depend on each individual person's situation and can not be said to come from any one distinct reason or motive. Although religion can be a common reason for choosing to veil, the practice also reflects political and personal conviction, so that it can serve as a medium through which personal choices can be revealed, in countries where veiling is indeed a choice, such as Turkey.
Veils for men
 Among the Tuareg, Songhai, Hausa, and Fulani of
Among the Tuareg, Songhai, Hausa, and Fulani of West Africa
West Africa, also known as Western Africa, is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Gha ...
, women do not traditionally wear the veil, while men do. Male veiling was also common among the Berber Sanhaja tribes. The North African male veil, which covers the mouth and sometimes part of the nose, is called '' litham'' in Arabic and '' tagelmust'' by the Tuareg. Tuareg boys start wearing the veil at the onset of puberty and veiling is regarded as a mark of manhood. It is considered improper for a man to appear unveiled in front of elders, especially those from his wife's family.
Ancient African rock engravings depicting human faces with eyes but no mouth or nose suggest that the origins of litham are pre-Islamic and even pre-historic. Wearing of the litham is not viewed as a religious requirement, although it was apparently believed to provide magical protection against evil forces. In practice, the litham has served as protection from the dust and extremes of temperature characterizing the desert environment. Its use by the Almoravids gave it a political significance during their conquests.
 In some parts of
In some parts of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, and Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
, men wear a ''sehra'' (headdress) on their wedding day. This is a male veil covering the whole face and neck. The sehra is made from either flowers or beads. The most common sehra is made from fresh marigolds. The groom wears this throughout the day concealing his face even during the wedding ceremony. In Northern India today, grooms can be seen arriving on a horse with the sehra wrapped around the head.
Veiling and religion
Biblical references
Biblical references include: * Hebrew: ''mitpachat'' (Ruth 3:15; marg., "sheet" or "apron;" R.V., "mantle"). In Isaiah 3:22, this word is plural, rendered "wimples;" R.V., "shawls", i. e., wraps. * ''Massekah'' (Isaiah 25:7; in Isaiah 28:20 rendered "covering"). The word denotes something spread out and covering or concealing something else (compare with 2 Corinthians 3:13–15, American Standard Version (1901)). * ''Masveh'' (Exodus 34:33, 35), the veil on the face of Moses. This verse should be read, "And when Moses had done speaking with them, he put a veil on his face", as in the Revised Version. When Moses spoke to them, he was without the veil; only when he ceased speaking, he put on the veil (compare with 2 Corinthians 3:13). * ''Parochet'' (Exodus 26:31–35), the veil of the tabernacle and the temple, which hung between the holy place and the most holy (2 Chronicles 3:14). In the temple, a partition wall separated these two places. In it were two folding doors, which are supposed to have been always open, the entrance being concealed by the veil which the high priest lifted when he entered into the sanctuary on the Day of Atonement. This veil was rent when Christ died on the cross (Matthew 27:51; Mark 15:38; Luke 23:45). * ''Tza'iph'' (Genesis 24:65).Rebecca
Rebecca () appears in the Hebrew Bible as the wife of Isaac and the mother of Jacob and Esau. According to biblical tradition, Rebecca's father was Bethuel the Aramean from Paddan Aram, also called Aram-Naharaim. Rebecca's brother was Laban (Bi ...
"took a veil and covered herself". (See also Genesis 38:14,19) Hebrew
Hebrew (; ''ʿÎbrit'') is a Northwest Semitic languages, Northwest Semitic language within the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. A regional dialect of the Canaanite languages, it was natively spoken by the Israelites and ...
women generally appeared in public with the face visible (Genesis 12:14; 24:16; 29:10; 1 Samuel 1:12).
* ''Radhidh'' (Song of Solomon 5:7, R.V. "mantle;" Isaiah 3:23). The word probably denotes some kind of cloak or wrapper.
* ''Masak'', the veil which hung before the entrance to the holy place (Exodus 26:36–37).
Note: , which the King James Version
The King James Version (KJV), also the King James Bible (KJB) and the Authorized Version (AV), is an Early Modern English Bible translations, Early Modern English translation of the Christianity, Christian Bible for the Church of England, wh ...
renders as: "And unto Sarah
Sarah (born Sarai) is a biblical matriarch, prophet, and major figure in Abrahamic religions. While different Abrahamic faiths portray her differently, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam all depict her character similarly, as that of a pious woma ...
he said, Behold, I have given thy brother a thousand pieces of silver: Behold, he is to thee a covering of the eyes, unto all that are with thee, and with all other: Thus, she was reproved" has been interpreted in one source as implied advice to Sarah to conform to a supposed custom of married women, and wear a complete veil, covering the eyes as well as the rest of the face, but the phrase is generally taken to refer not to Sarah's eyes, but to the eyes of others, and to be merely a metaphorical expression concerning vindication of Sarah ( NASB, RSV), silencing criticism ( GWT), allaying suspicions ( NJB), righting a wrong ( BBE, NLT), covering or recompensing the problem caused her ( NIV, New Life Version, NIRV, TNIV, JB), a sign of her innocence ( ESV, CEV, HCSB). The final phrase in the verse, which KJV takes to mean, "she was reproved", is taken by almost all other versions to mean instead, "she was vindicated", and the word "הוא", which KJV interprets as "he" (Abraham), is interpreted as "it" (the money). Thus, the general view is that this passage has nothing to do with material veils.

Judaism
After the destruction of the Temple inJerusalem
Jerusalem is a city in the Southern Levant, on a plateau in the Judaean Mountains between the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and the Dead Sea. It is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest cities in the world, and ...
, the synagogue
A synagogue, also called a shul or a temple, is a place of worship for Jews and Samaritans. It is a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels) where Jews attend religious services or special ceremonies such as wed ...
s that were established took the design of the Tabernacle as their plan. The Ark of the Law, which contains the scroll
A scroll (from the Old French ''escroe'' or ''escroue''), also known as a roll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing.
Structure
A scroll is usually partitioned into pages, which are sometimes separate sheets of papyru ...
s of the Torah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
, is covered with an embroidered curtain or veil called a '' parokhet''. (See also below regarding the traditional Jewish custom of veiling – and unveiling – the bride.)
Christianity
Veiling of women


 Traditionally, in Christianity, women were enjoined to cover their heads, and men were instructed to remove their hat when praying or prophesying. Wearing a veil (also known as a headcovering) is seen as a sign of humility before God, as well as a reminder of the bridal relationship between Christ and the church. This practice is based on in the
Traditionally, in Christianity, women were enjoined to cover their heads, and men were instructed to remove their hat when praying or prophesying. Wearing a veil (also known as a headcovering) is seen as a sign of humility before God, as well as a reminder of the bridal relationship between Christ and the church. This practice is based on in the Christian Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
, where St. Paul writes:
The early Church Fathers, including Tertullian of Carthage, Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens, also known as Clement of Alexandria (; – ), was a Christian theology, Christian theologian and philosopher who taught at the Catechetical School of Alexandria. Among his pupils were Origen and Alexander of Jerusalem. A ...
, Hippolytus of Rome
Hippolytus of Rome ( , ; Romanized: , – ) was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second–third centuries Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians. Suggested communitie ...
, John Chrysostom and Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced the development of Western philosop ...
attested in their writings that men should pray uncovered, and that women should wear a headcovering. John Chrysostom (407) delineated Saint Paul's teaching on the wearing of headcoverings by Christian women, continually:
Additionally, the Church Fathers taught that because the hair of a woman has sexual potency, it should only be for her husband to see and covered the rest of the time.
In Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
and North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, from the arrival of Christianity to those lands to the mid-20th century, women in most mainstream Christian denominations
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
wore head coverings (often in the form of a scarf, cap, veil or hat). These included many Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
, Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
, Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
, Methodist
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother ...
, Moravian, and Reformed (including Continental Reformed, Congregationalist and Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
traditions) Churches. In these denominations, the practice now continues in certain congregations and by individuals who have sought to follow the precedent set in Scripture and church history.
Christian veiling throughout the day is still practiced by those who wear plain dress, such as traditional Anabaptists including Mennonites
Mennonites are a group of Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian communities tracing their roots to the epoch of the Radical Reformation. The name ''Mennonites'' is derived from the cleric Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland, part of ...
( Old Order Mennonites and Conservative Mennonites
Conservative Mennonites include numerous Conservative Anabaptist groups that identify with the theologically conservative element among Mennonite Anabaptist Christian fellowships, but who are not Old Order groups or mainline denominations.
Co ...
), Hutterites, Schwarzenau Brethren ( Old Order Schwarzenau Brethren and Dunkard Brethren Church), River Brethren ( Old Order River Brethren and Calvary Holiness Church), Apostolic Christians, Amish
The Amish (, also or ; ; ), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptism, Anabaptist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, church fellowships with Swiss people, Swiss and Alsace, Alsatian origins. As they ...
(Old Order Amish, New Order Amish, Para-Amish and Beachy Amish), and Charity Christians, as well as Conservative Quakers.
Many Holiness Christians who practice the doctrine of outward holiness, also practice headcovering (such as the Calvary Holiness Church). The Plymouth Brethren and conservative Reformed and Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
churches, along with Traditionalist Catholics, practice headcovering when praying at home and while attending public liturgies. In many Oriental Orthodox Churches and certain Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
congregations, the custom of women's covering their heads continues in church (and when praying privately at home).
Veiling of nuns and consecrated virgins
A veil forms part of the headdress of some orders of nuns orreligious sister
A religious sister (abbreviated: Sr.) in the Catholic Church is a woman who has taken public vows in a religious institute dedicated to apostolic works, as distinguished from a nun who lives a cloistered monastic life dedicated to prayer and ...
s in Catholicism, Lutheranism and Anglicanism; this is why a woman who becomes a nun is said "to take the veil". In medieval times married women normally covered their hair outside the house, and a nun's veil is based on secular medieval styles, often reflecting the fashion of widows in their attire. In many institutes, a white veil is used as the "veil of probation" during novitiate.
A black veil is the traditional sign of a professed nun. Some monasteries or communities bestow the black veil at the first profession of vows, but usually it is bestowed with the profession of solemn vows. When the vows have been professed the white veil of a novice will be swapped for the black veil of the professed, and she is usually crowned with a wreath of flowers.
A veil of consecration, longer and fuller, is used by some orders whose nuns receive the consecration of virgins who are already in solemn vows or who are being consecrated as a virgin in the same ceremony. References to "consecrated nuns" in medieval literature refers to solemnly professed nuns who received the consecration of virgins from their bishops, usually some years after their final profession of vows. The reintroduced rite of the consecration of virgins for women living in the world provides, as the Roman Ritual.
Since the reintroduction of the rite of consecration of virgins for women living in the world in 1970, the newly consecrated virgin receives a veil as a sign of her consecration, as in ancient times.
The nuptial symbolism of the rite was displayed particularly in the bestowal of the veil on the virgin by the bishop, as can be found in the writings of Ambrose of Milan and in the oldest liturgical sources.
After the promulgation of Pope Paul VI's decree '' Perfectae caritatis'' on the adaption and renewal of religious life most monastic orders for nuns retained the veil. Regarding other institutes of religious sister
A religious sister (abbreviated: Sr.) in the Catholic Church is a woman who has taken public vows in a religious institute dedicated to apostolic works, as distinguished from a nun who lives a cloistered monastic life dedicated to prayer and ...
s who work as teachers, nurses or in other active apostolates, some wear the veil, while some others have abolished the use of the veil.
The fullest versions of the nun's veil cover the top of the head and flow down around and over the shoulders. In western Christianity, it does not wrap around the neck or face. In those orders that retain one, the starched white covering about the face, neck, and shoulders is known as a wimple and is a separate garment.
The Catholic Church has revived the ancient practice of women to be consecrated by their bishop as a consecrated virgin living in the world. These virgins are set aside as sacred persons who belong only to Christ and the service of the church. The veil is a bridal one, because the ''velatio virginum'' primarily signified the newly consecrated virgin as the Bride of Christ. In ancient times his veil was called the ''flammeum'' because it was supposed to remind the virgin of the indissoluble nuptial bond she was contracting with Christ. The wearing of the ''flammeum'' for the sacred virgin Bride of Christ arose from the bridal attire of the strictest pagan marriage which did not permit of divorce at the time. The flammeum was a visible reminder that divorce was not possible with Christ, their Divine spouse.
In Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
and in the Eastern Rites of the Catholic Church, a veil called an '' epanokamelavkion'' is used by both nuns and monks, in both cases covering completely the '' kamilavkion'', a cylindrical hat they both wear. In Slavic practice, when the veil is worn over the hat, the entire headdress is referred to as a '' klobuk''. Nuns wear an additional veil under the ''klobuk'', called an '' apostolnik'', which is drawn together to cover the neck and shoulders as well as the head, leaving the face itself open.
Some female members of Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
and Anglican
Anglicanism, also known as Episcopalianism in some countries, is a Western Christianity, Western Christian tradition which developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the ...
religious communities also wear a veil, differing according to the traditions of each community.
Veiling of objects

 Among Christian churches which have a liturgical tradition, several different types of veils are used. These veils are often symbolically tied to the veils in the Tabernacle in the wilderness and in Solomon's Temple. The purpose of these veils was not so much to obscure as to shield the most sacred things from the eyes of sinful men. In Solomon's Temple the veil was placed between the "Inner Sanctuary" and the "
Among Christian churches which have a liturgical tradition, several different types of veils are used. These veils are often symbolically tied to the veils in the Tabernacle in the wilderness and in Solomon's Temple. The purpose of these veils was not so much to obscure as to shield the most sacred things from the eyes of sinful men. In Solomon's Temple the veil was placed between the "Inner Sanctuary" and the "Holy of Holies
The Holy of Holies ( or ''Kodesh HaKodashim''; also ''hadDəḇīr'', 'the Sanctuary') is a term in the Hebrew Bible that refers to the inner sanctuary of the Tabernacle, where the Shekhinah (God in Judaism, God's presence) appeared. According ...
". According to the New Testament, this veil was torn when Jesus Christ
Jesus (AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ, Jesus of Nazareth, and many Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, other names and titles, was a 1st-century Jewish preacher and religious leader. He is the Jesus in Chris ...
died on the cross.
; Tabernacle veil
: Used to cover the church tabernacle
A tabernacle or a sacrament house is a fixed, locked box in which the Eucharist in the Catholic Church, Eucharist (consecrated communion hosts) is stored as part of the "reserved sacrament" rite (Christianity), rite. A container for the same p ...
, particularly in the Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
tradition but in some others as well, when the Eucharist
The Eucharist ( ; from , ), also called Holy Communion, the Blessed Sacrament or the Lord's Supper, is a Christianity, Christian Rite (Christianity), rite, considered a sacrament in most churches and an Ordinance (Christianity), ordinance in ...
is actually stored in it. The veil is used to remind worshipers that the (usually metal) tabernacle cabinet echoes the tabernacle tent of the Hebrew Scriptures, and it signals that the tabernacle is actually in use. It may be of any liturgical color, but is most often white (always appropriate for the Eucharist), cloth of gold or silver (which may substitute for any liturgical color aside from violet), or the liturgical color of the day (red, green or violet). It may be simple, unadorned linen or silk, or it may be fringed or otherwise decorated. It is often designed to match the vestment
Vestments are Liturgy, liturgical garments and articles associated primarily with the Christianity, Christian religion, especially by Eastern Christianity, Eastern Churches, Catholic Church, Catholics (of all rites), Lutherans, and Anglicans. ...
s of the celebrants.
; Ciborium veil
: The ciborium is a goblet-like metal vessel with a cover, used in the Roman Catholic Church and some others to hold the consecrated hosts of the Eucharist when, for instance, it is stored in the tabernacle or when communion is to be distributed. It may be veiled with a white cloth, usually silk. This veiling was formerly required but is now optional. In part, it signals that the ciborium actually contains the consecrated Eucharist at the moment.
; Chalice veil
: During Eucharistic celebrations, a veil is often used to cover the chalice and paten to keep dust and flying insects away from the bread and wine. Often made of rich material, the chalice veils have not only a practical purpose, but are also intended to show honor to vessels used for the sacrament
A sacrament is a Christian rite which is recognized as being particularly important and significant. There are various views on the existence, number and meaning of such rites. Many Christians consider the sacraments to be a visible symbol ...
.
: In the West, a single chalice veil is normally used. The veil will usually be the same material and color as the priest's vestments, though it may also be white. It covers the chalice and paten when not actually in use on the altar.
: In the East, three veils are used: one for the chalice, one for the diskos (paten), and a third one (the Aër) is used to cover both. The veils for the chalice and diskos are usually square with four lappets hanging down the sides, so that when the veil is laid out flat it will be shaped like a cross. The Aër is rectangular and usually larger than the chalice veil used in the West. The Aër also figures prominently in other liturgical respects.
; Humeral veil
: The humeral veil is used in both Roman Catholic and Anglican Churches during the liturgy of Exposition and Benediction of the Blessed Sacrament
Benediction of the Blessed Sacrament, also called Benediction with the Blessed Sacrament or the Rite of Eucharistic Exposition and Benediction, is a devotional ceremony, celebrated especially in the Roman Catholic Church, but also in some other C ...
, and on some other occasions when special respect is shown to the Eucharist. From the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for "shoulders," it is an oblong piece of cloth worn as a sort of shawl, used to symbolize a more profound awareness of the respect due to the Eucharist by shielding the celebrant's hands from actually contacting the vessel holding the Eucharist, either a monstrance or ciborium, or in some cases to shield the vessel itself from the eyes of participants. It is worn only by bishop
A bishop is an ordained member of the clergy who is entrusted with a position of Episcopal polity, authority and oversight in a religious institution. In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance and administration of di ...
s, priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
s or deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions.
Major Christian denominations, such as the Cathol ...
s.
; Vimpa
: A vimpa is a veil or shawl worn over the shoulders of servers who carry the miter and crosier in Roman Catholic liturgical functions when they are not being used by the bishop.
; Chancel veil
: In the early liturgies, there was often a veil that separated the sanctuary from the rest of the church (again, based upon the biblical description of the Tabernacle). In the Byzantine liturgy this veil developed into the iconostasis, but a veil or curtain is still used behind the Royal Doors (the main doors leading into the sanctuary), and is opened and closed at specific times during the liturgy. In the West, it developed into the Rood Veil, and later the Rood Screen, and finally the chancel
In church architecture, the chancel is the space around the altar, including the Choir (architecture), choir and the sanctuary (sometimes called the presbytery), at the liturgical east end of a traditional Christian church building. It may termi ...
rail, the low sanctuary railing in those churches that still have this. In some of the Eastern Churches (for instance, the Syrian liturgy) the use of a veil across the entire sanctuary has been retained.
; Lenten veiling
: Some churches veil their crosses during Passiontide with a fine semi-transparent mesh. The color of the veil may be black, red, purple, or white, depending upon the liturgical day and practice of the church. In traditional churches, there will sometimes be curtains placed to either side of the altar.
The Veil of Our Lady is a liturgical feast celebrating the protection afforded by the intercessions of the Virgin Mary.
Islam
A variety of headdresses worn by Muslim women and girls in accordance with '' hijab'' (the principle of dressing modestly) are sometimes referred to as veils. The principal aim of the Muslim veil is to cover the ''Awrah'' (parts of the body that are considered private). Many of these garments cover the hair, ears, and throat, but do not cover the face. Depending on geography and culture, the veil is referenced and worn in different ways. The '' khimar'' is a type of headscarf. The '' niqāb'' and '' burqa'' are two kinds of veils that cover most of the face except for a slit or hole for the eyes. InAlgeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, a larger veil called the '' haïk'' includes a triangular panel to cover the lower part of the face. In the Arabian Peninsula and parts of North Africa (specifically Saudi Arabia), the abaya is worn constructed like a loose robe covering everything but the face itself. In another location, such as Iran, the chador is worn as the semicircles of fabric are draped over the head like a shawl and held in place under the neck by hand. The two terms for veiling that are directly mentioned in the Quran is the jilbab and the khimar. In these references, the veiling is meant to promote modesty by covering the genitals and breasts of women.
The Afghan burqa covers the entire body, obscuring the face completely, except for a grille or netting over the eyes to allow the wearer to see. The '' boshiya'' is a veil that may be worn over a headscarf; it covers the entire face and is made of a sheer fabric so the wearer is able to see through it. It has been suggested that the practice of wearing a veil – uncommon among the Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
tribes prior to the rise of Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
– originated in the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived History of the Roman Empire, the events that caused the ...
, and then spread.
The Bedouin living in Southern Palestine and the Sinai peninsula also use face veils. The traditional veils in Palestine are short and decorated with coins. In northern Sinai, the veil sections are longer, and often contain embroidery, chains, pendants, beads, … The Bedouin-style mask is known as al-maghrun, al-baghrah, or al-niqab.
In the UAE, Qatar and Oman, a face mask known as the burghu is used, and in Bahrain, Qatar and Oman, the batulah is used.
In Central Asian sedentary Muslim areas (today Uzbekistan and Tajikistan) women wore veils which when worn the entire face was shrouded, called Paranja or faranji. The traditional veil in Central Asia worn before modern times was the faranji but it was banned by the Soviet Communists.Abdullaev 2010, p. 381.
In Pakistan, upper and middle-class women in towns wear burqas over their normal clothes in public. The burqa is the most visible dress in Pakistan. It is typically a tent-like garment worn over the ordinary clothes and is made of white cotton. Many upper-class women wear a two-piece burqa which is usually black in colour but sometimes navy blue or dark red. It consists of a long cloak and a separate headpiece with a drop-down face veil. Some educated urban women no longer wear the burqa. The burqa is also not worn by rural peasant women who work in the fields. In rural areas only elite women wear burqas.
Restrictions
The wearing of head and especially face coverings by Muslim women has raised political issues in the West; including inQuebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, and across Europe. Countries and territories that have banned or partially banned the veil include, among others:
*France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, where full-face veils (burqa and niqab) have been banned in public places since April 2011, with a 150-euro fine for breaching the ban. All religious veils have been banned in public schools.
*Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, also banned full face veils in public places, in July 2011.
*Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
has several towns and cities which have banned the full face veil, including Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
.
*Russia's Stavropol region has announced a ban on hijabs in government schools, which was challenged but upheld by the Russian Supreme Court.
Places where headscarves continue to be a contentious political issue include:
*United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, where the Home Office Minister Jeremy Browne called for a national debate about headscarves and their role in public environments in Britain.
*Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, where there is much discussion as to whether the province should allow people wearing a veil over their face to vote without removing it.
*Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, with a large Muslim population, the European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights (ECtHR), also known as the Strasbourg Court, is an international court of the Council of Europe which interprets the European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR). The court hears applications alleging that a co ...
has allowed countries to ban full-face veils, as it does not breach the European Convention on Human Rights
The European Convention on Human Rights (ECHR; formally the Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms) is a Supranational law, supranational convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Draf ...
.
Indian religions
InIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, from 1st century B.C. societies advocated the use of the veil for married Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
women which came to be known as Ghoonghat. Buddhists attempted to counter this growing practice around 3rd century CE. Rational opposition against veiling and seclusion from spirited ladies resulted in system not becoming popular for several centuries. Under the Medieval Islamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an Early modern period, early modern empire in South Asia. At its peak, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus River Basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to ...
, various aspects of veiling and seclusion of women was adopted, such as the concept of Purdah and Zenana, partly as an additional protection for women. Purdah became common in the 15th and 16th century, as both ''Vidyāpati'' and ''Chaitanya'' mention it.
Sikhism was highly critical of all forms of strict veiling, Guru Amar Das condemned it and rejected seclusion and veiling of women, which saw decline of veiling among some classes during late medieval period. This was stressed by Bhagat Kabir.
Bridal veils
 The veil is one of the oldest parts of a bridal ensemble, dating as far back as Greek and Roman times, to hide a bride "from evil spirits who might want to thwart her happiness" or to frighten the spirits away. The veil also served to hide the bride's face from the groom prior to the wedding, as superstition says that it is bad luck for the groom to see the bride before the ceremony.
In the context of weddings in Western Christian culture, the veil has been used to symbolize
The veil is one of the oldest parts of a bridal ensemble, dating as far back as Greek and Roman times, to hide a bride "from evil spirits who might want to thwart her happiness" or to frighten the spirits away. The veil also served to hide the bride's face from the groom prior to the wedding, as superstition says that it is bad luck for the groom to see the bride before the ceremony.
In the context of weddings in Western Christian culture, the veil has been used to symbolize modesty
Modesty, sometimes known as demureness, is a mode of dress and deportment which intends to avoid the encouraging of sexual attraction in others. The word ''modesty'' comes from the Latin word ''wikt:modestus, modestus'' which means 'keeping with ...
before God, obedience, and when the veil is white, chastity
Chastity, also known as purity, is a virtue related to temperance. Someone who is ''chaste'' refrains from sexual activity that is considered immoral or from any sexual activity, according to their state of life. In some contexts, for exampl ...
; the practice of the wedding veil is part of the larger practice of the woman's headcovering in Christianity, rooted in .Wenger, John C. and Elmer S. Yoder. "Prayer Veil." Global Anabaptist Mennonite Encyclopedia. 1989. By the 17th and 18th century, bridal veils were occasionally worn, but were generally out of fashion in Britain and North America, with brides choosing from many other options instead. However, the bridal veil returned to popularity after Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in January 1901. Her reign of 63 year ...
wore a veil in her wedding to Prince Albert in 1840. The bridal veil became a status symbol during the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the reign of Queen Victoria, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. Slightly different definitions are sometimes used. The era followed the ...
, and the weight, length, and quality of the veil indicated the bride's social status. Bridal veils worn over the face were not common until the second half of the 19th century.
The tradition of a veiled bride's face continues today wherein, a virgin bride, especially in Christian or Jewish culture, enters the marriage ritual with a veiled face and head, and remains fully veiled, both head and face, until the ceremony concludes. After the full conclusion of the wedding ceremony, either the bride's father lifts the veil, presenting the bride to the groom who then kisses her, or the new groom lifts her face veil in order to kiss her. Some see the lifting of the veil as symbolically consummating the marriage, representing another thin membrane (the hymen) that will be physically penetrated on the wedding night. In Orthodox Judaism, as well as among Christians in certain parts of the world such as Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, women will then wear a headcovering in public after being married (as well as while worshipping). In Scandinavia, the bridal veil is usually worn under a traditional crown and does not cover the bride's face; instead, the veil is attached to and hangs from the back.
A bridal veil is not normally worn during a civil marriage ceremony, nor when the bride is remarrying. In these cases, when it is worn, the veil is worn as a fashion accessory as part of the bridal attire, instead of for its symbolism.
Judaism
 In
In Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
, the tradition of the bride wearing a veil during the wedding ceremony dates back to biblical times. According to the Torah in , Isaac is brought Rebekah to marry by his father Abraham's servant, and Rebekah took her veil and covered herself when Isaac was approaching.
In a traditional Jewish wedding, just before the ceremony, the '' badeken'' takes place, at which the groom places the veil over the bride's face, and either he or the officiating rabbi gives her a blessing. The veil stays on her face until just before the end of the wedding ceremony – when they are legally married according to Jewish law – then the groom helps lift the veil off her face. The most often cited interpretation for the ''badeken'' is that, according to , when Jacob went to marry Rachel, his father-in-law Laban tricked him into marrying Leah, Rachel's older and homelier sister.
Many say that the veiling ceremony takes place to make sure that the groom is marrying the right bride. Some say that as the groom places the veil over his bride, he makes an implicit promise to clothe and protect her. Finally, by covering her face, the groom recognizes that he is marrying the bride for her inner beauty; while looks will fade with time, his love will be everlasting. In some ultra-orthodox communities, it is a custom for the bride to wear an opaque veil as she is escorted to the groom. This is said to show her complete willingness to enter into the marriage and her absolute trust that she is marrying the right man.
In ancient Judaism, the lifting of the veil took place just prior to the consummation of the marriage in sexual union. The uncovering or unveiling that takes place in the wedding ceremony is a symbol of what will take place in the marriage bed. Just as the two become one through their words spoken in wedding vows, so these words are a sign of the physical oneness that they will consummate later on. The lifting of the veil is a symbol and anticipation of this.
Christianity
 In Christian theology, St. Paul's words concerning how marriage symbolizes the union of Christ and His Church underlie part of the tradition of veiling in the marriage ceremony. In historic Christian traditions, the veil is seen as "a visible sign that the woman is under the authority of a man" and that she is submitting herself to her husband's Christ-like leadership and loving care. As such, the practice of the wedding veil is part of the wider ordinance of the woman's headcovering in Christianity, rooted in .
The removing of the veil can be seen as a symbol of the temple veil that was torn when Christ died, giving believers direct access to God, and in the same way, the bride and the groom, once married, now have full access to one another.
In Christian theology, St. Paul's words concerning how marriage symbolizes the union of Christ and His Church underlie part of the tradition of veiling in the marriage ceremony. In historic Christian traditions, the veil is seen as "a visible sign that the woman is under the authority of a man" and that she is submitting herself to her husband's Christ-like leadership and loving care. As such, the practice of the wedding veil is part of the wider ordinance of the woman's headcovering in Christianity, rooted in .
The removing of the veil can be seen as a symbol of the temple veil that was torn when Christ died, giving believers direct access to God, and in the same way, the bride and the groom, once married, now have full access to one another.
Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
In 2019 a letter bythe Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
President Russell M. Nelson and his counselors, Dallin H. Oaks and Henry B. Eyring, declared that "Veiling the faces of deceased, 'endowed' embers who have been through a temple ceremonywomen prior to burial is optional"; previously it had been required. The letter went on to say that such veiling, "may be done if the sister expressed such a desire while she was living. In cases where the wishes of the deceased sister on this matter are not known, her family should be consulted." That same year veiling of women during part of the temple endowment ceremony was also made optional where it had been required before.
Mourning veils
Veils remained a part of Western mourning dress customs into the early 20th century. The tradition of widow's veiling has its roots in the attire of a Christian nun, which symbolized modesty and chastity, and the mourning veil became a way to demonstrate sincerity and piety. The mourning veil was commonly seen as a means of shielding the mourner and hiding her grief, and, on the contrary, seen by some women as a means of publicly expressing their emotions. Widows in the Victorian era were expected to wear mourning veils for at least three months and up to two and a half years, depending on the custom. Mourning veils have also been sometimes perceived as expressions of elegance or even sex appeal. In a 19th-century American etiquette book one finds: "Black is becoming, and young widows, fair, plump, and smiling, with their roguish eyes sparkling under their black veils are very seducing".Interpretations
One view is that as a religious item, it is intended to honor a person, object or space. The actual sociocultural, psychological, and sociosexual functions of veils have not been studied extensively but most likely include the maintenance of social distance and the communication of social status and cultural identity.Brenner, S. (1996). Reconstructing Self and Society: Javanese Muslim Women and "The Veil". American Ethnologist, Vol. 23, No. 4, pp. 673–697 A veil also has symbolic interpretations, as something partially concealing, disguising, or obscuring.Tradition of veil use in China
China has a long tradition of wearing veils. Veils were used to cover the face and had been used since theHan dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC ...
, where they were called "facial clothes" or "facial hats"; they were used to protect its wearer's face from the wind and sand when they would ride horses or when they would travel on long trips. In the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed ...
, mili and weimao were used to cover the face when horse riding. In the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Fiv ...
, women would wear a veiled hat or veil when they left their houses, honggaitou on their wedding, a veil called 'white jade silk' during their mourning period.
See also
* Nuptial veil * PurdahReferences
Further reading
* Heath, Jennifer (ed.). (2008).The Veil: Women Writers on Its History, Lore, and Politics
'. University of California Press. .
External links
Curtain
article from '' The Jewish Encyclopedia'' {{Authority control Catholic religious clothing Ceremonial clothing Christian clothing Eastern Christian vestments Eucharistic objects History of clothing Islamic female clothing Medieval European costume Modesty