Vascular disease on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Vascular disease is a class of diseases of the blood vessels – the
 *
*
 Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by endothelial cell dysfunction. Because of factors like pathogens, oxidized LDL particles and other inflammatory stimuli endothelial cells become active. The process causes thickening of the vessel wall, forming a plaque that consists of proliferating
Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by endothelial cell dysfunction. Because of factors like pathogens, oxidized LDL particles and other inflammatory stimuli endothelial cells become active. The process causes thickening of the vessel wall, forming a plaque that consists of proliferating
 Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or gangrene (tissue death) may occur.
More generally, treatments for vascular disease may include:
* Lowering cholesterol levels
* Lowering blood pressure
* Lowering blood glucose
* Changes in diet
* Increasing physical activity (as recommended by a healthcare provider)
* Weight loss
* Quitting smoking
* Stress reduction
Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or gangrene (tissue death) may occur.
More generally, treatments for vascular disease may include:
* Lowering cholesterol levels
* Lowering blood pressure
* Lowering blood glucose
* Changes in diet
* Increasing physical activity (as recommended by a healthcare provider)
* Weight loss
* Quitting smoking
* Stress reduction
arteries
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pu ...
and veins of the circulatory system of the body. Vascular disease is a subgroup of cardiovascular disease. Disorders in this vast network of blood vessels can cause a range of health problems that can sometimes become severe.
Types
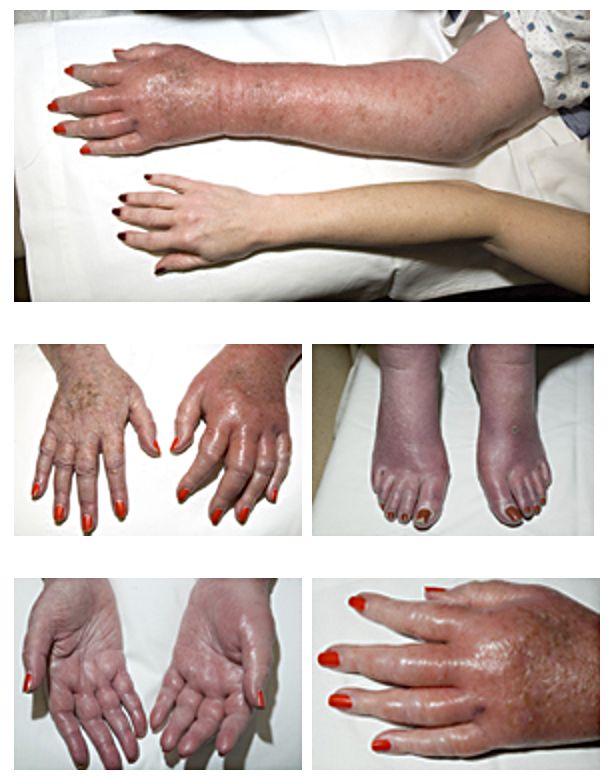
There are several types of vascular disease, and signs and symptoms can vary depending on the disease type. These types include: * Erythromelalgia - a rare peripheral vascular disease with syndromes that include burning pain, increased temperature, erythema and swelling that generally affect the hands and feet. *
* Peripheral artery disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease, and in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular dis ...
– occurs when atheromatous plaques build up in the arteries that supply blood to the arms and legs, causing the arteries to narrow or become blocked.
* Renal artery stenosis
Renal artery stenosis (RAS) is the narrowing of one or both of the renal arteries, most often caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. This narrowing of the renal artery can impede blood flow to the target kidney, resulting in renov ...
- the narrowing of renal arteries that carry blood to the kidneys from the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
.
* Buerger's disease
Thromboangiitis obliterans, also known as Buerger disease (English ; ) or Winiwarter-Buerger disease, is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet. It is strongly a ...
– inflammation and swelling in small blood vessels, causing the vessels to narrow or become blocked by blood clots.
* Raynaud's disease – a rare peripheral vascular disorder that causes constriction of the peripheral blood vessels in the fingers and toes when a person is cold or experiencing stress.
* Disseminated intravascular coagulation – a widespread activation of clotting in the smaller blood vessels.
* Cerebrovascular disease
Cerebrovascular disease includes a variety of medical conditions that affect the blood vessels of the brain and the cerebral circulation. Arteries supplying oxygen and nutrients to the brain are often damaged or deformed in these disorders. Th ...
– a group of vascular diseases that affect brain function.
Mechanism
 Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by endothelial cell dysfunction. Because of factors like pathogens, oxidized LDL particles and other inflammatory stimuli endothelial cells become active. The process causes thickening of the vessel wall, forming a plaque that consists of proliferating
Vascular disease is a pathological state of large and medium muscular arteries and is triggered by endothelial cell dysfunction. Because of factors like pathogens, oxidized LDL particles and other inflammatory stimuli endothelial cells become active. The process causes thickening of the vessel wall, forming a plaque that consists of proliferating smooth muscle cell
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit mus ...
s, macrophages and lymphocytes. The plaque results in restricted blood flow, decreasing the amount of oxygen and nutrients that reach certain organs. This plaque can also rupture, causing the formation of clots.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing vascular disease can be complex due to the variety of symptoms vascular diseases can cause. Reviewing a patient's family history and conducting a physical examination are important steps in making a diagnosis. Physical exams may differ depending on the type of vascular disease suspected. For example, in the case of aperipheral vascular disease
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is an abnormal narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain. When narrowing occurs in the heart, it is called coronary artery disease, and in the brain, it is called cerebrovascular dise ...
, a physical exam consists of checking blood flow
Hemodynamics or haemodynamics are the dynamics of blood flow. The circulatory system is controlled by homeostatic mechanisms of autoregulation, just as hydraulic circuits are controlled by control systems. The hemodynamic response continuously m ...
in a patient's legs.
Treatment
 Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or gangrene (tissue death) may occur.
More generally, treatments for vascular disease may include:
* Lowering cholesterol levels
* Lowering blood pressure
* Lowering blood glucose
* Changes in diet
* Increasing physical activity (as recommended by a healthcare provider)
* Weight loss
* Quitting smoking
* Stress reduction
Treatment varies based on the type of vascular disease being treated. In treating renal artery disease, a 2014 study indicates that balloon angioplasty can improve diastolic blood pressure and potentially reduce antihypertensive drug requirements. In the case of peripheral artery disease, treatment to prevent complications is important; without treatment, sores or gangrene (tissue death) may occur.
More generally, treatments for vascular disease may include:
* Lowering cholesterol levels
* Lowering blood pressure
* Lowering blood glucose
* Changes in diet
* Increasing physical activity (as recommended by a healthcare provider)
* Weight loss
* Quitting smoking
* Stress reduction
References
Further reading
*External links
{{Medicine Vascular diseases