Valtellina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



 Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the
 During the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, the Valtellina belonged to the
During the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries, the Valtellina belonged to the
(PDF; 3.95 MB) This included the arresting under false pretenses and torturing to death of the (catholic) arch-priest
accessed 16 January 2012 and 600 people were killed on that night and in the following four days. The attack drove nearly all the Protestants out of the valley, prevented further Protestant incursions and took the Valtellina out of the
"Ernesto Genoni: Australia’s pioneer of biodynamic agriculture"
Journal of Organics, 1(1):57-81.


 In Valtellina, wines are produced mainly from ''Chiavennasca'' (the local name of
In Valtellina, wines are produced mainly from ''Chiavennasca'' (the local name of
File:Berninabahn zwischen Lagalb und Ospizio Bernina im Winter.jpg, Bernina Line of the Rhaetian Railway
File:Tirano-Rhaetischer Bahnhof.jpg, Tirano - Bernina Line train station
File:Parco Grosio La Rupe Magna.jpg, Rock Engraving Park-Grosio; Rupe Magna
File:Parco Grosio Rupe Magna 5.jpg, Rock Engraving Park-Grosio; Rupe Magna
An extensive history of the Valtellina area
Tourist information
{{Authority control Valleys of the Alps Valleys of Lombardy Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy Wine regions of Italy Wine regions of Switzerland



 Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy
(man), (woman) lmo, lumbard, links=no (man), (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, ...
region of northern Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, bordering Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. Today it is known for its ski center
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area – a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In North ...
, hot spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a spring produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circ ...
spas, bresaola
Bresaola ( , , , ) is air-dried, salted beef (but it can also be made of horse, venison and pork) that has been aged two or three months until it becomes hard and turns a dark red, almost purple color. It is made from top (inside) round, and ...
, cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During productio ...
s (in particular Bitto, named after the river Bitto) and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
s. In past centuries it was a key alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
pass between northern Italy and Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
and control of the Valtellina was much sought after, particularly during the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
as it was an important part of the Spanish Road
The Spanish Road ( Spanish: ''Camino Español'', German: ''Spanische Straße'') was a military road and trade route in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, linking the Duchy of Milan, the Franche-Comté and the Spanish Netherlands, ...
.
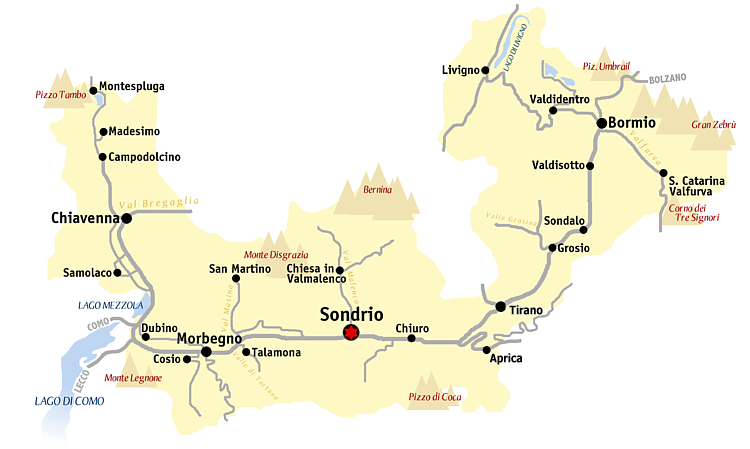
Geography
The most importantcomune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
of the valley is Sondrio
Sondrio (; lmo, Sùndri; rm, Sunder; archaic german: Sünders or ; la, Sundrium) is an Italian city and ''comune'' and Provincial Capital located in the heart of the Valtellina. , Sondrio counts approximately 21,876 inhabitants (2015) and it is ...
; the others major centers are Aprica
Aprica ( lmo, Abriga) is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Sondrio, Lombardy, northern Italy. It is located on the eponymous pass, the most favourable one connecting Valtellina to Val Camonica.
Its main source of income is tourism, us ...
, Morbegno, Tirano, Bormio
Bormio ( lmo, Bormi, rm, italic=yes, , german: Worms im Veltlintal) is a town and ''comune'' with a population of about 4,100 located in the Province of Sondrio, Lombardy region of the Alps in northern Italy.
The centre of the upper Valtellina ...
and Livigno
Livigno (; local lmo, Livígn ; german: Luwin) is a town, ''comune'' and a special-administered territory in the province of Sondrio, in the region of Lombardy, Italy, located in the Italian Alps, near the Swiss border.
History
Livigno's firs ...
. Although Livigno is on the northern side of the alpine watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
, it is considered part of Valtellina as it falls within the province of Sondrio
The Province of Sondrio ( it, provincia di Sondrio) is in the Lombardy region of northern Italy. Its provincial capital is the city of Sondrio. As of 2017, it has a population of 181,403.
History
The Province was established in 1815, within ...
.
History
Antiquity and the middle ages
The region was conquered in 16 BC by theRomans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
. By the 5th century it was Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
with around ten pieve
In the Middle Ages, a pieve (, ; la, plebe, link=no; plural ''pievi'') was a rural church with a baptistery, upon which other churches without baptisteries depended.
The Italian word ''pieve'' is descended from Latin ''plebs'' which, after t ...
(rural churches with a baptistery
In Christian architecture the baptistery or baptistry (Old French ''baptisterie''; Latin ''baptisterium''; Greek , 'bathing-place, baptistery', from , baptízein, 'to baptize') is the separate centrally planned structure surrounding the baptism ...
) under the Diocese of Como
The Diocese of Como ( la, Dioecesis Comensis) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical jurisdiction or diocese of the Catholic Church in northern Italy. It was established in the Fourth Century. It is a suffragan diocese in the ecclesiastical province of ...
. The Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
gained control over the area after 720, but about fifty years later Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
gave the valley to Saint Denis Monastery near Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
. Later the valley returned to the Bishop of Como.
Early modern period
Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
(the "Grey Leagues"), which was then a mutual-defense region independent of Switzerland but is now the easternmost Swiss Canton
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Co ...
of Graubünden. Graubünden is an area in which German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Romansh, Lombard and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
are all spoken, and hence during 16th century rule by Graubünden, the region became known variously as ''Veltlin'', ''Westtirol'' (West Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
), and the ''Welsche Vogteien'' ("Romanic Bailiwicks").
During the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
, the Valtellina was a theater of intense military and diplomatic struggle among France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, the Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
powers and the local authorities which culminated in the Valtellina war of 1620–1626. Control over the routes through the Valtellina to the passes between Lombardy and the Danube watershed was at stake as it formed part of the so-called Spanish Road
The Spanish Road ( Spanish: ''Camino Español'', German: ''Spanische Straße'') was a military road and trade route in the late sixteenth and early seventeenth centuries, linking the Duchy of Milan, the Franche-Comté and the Spanish Netherlands, ...
. The anti-Habsburg forces in the Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
put together a court named 'clerical overseers' that between 1618 and 1620 handed down a number of convictions (often ''in absentia
is Latin for absence. , a legal term, is Latin for "in the absence" or "while absent".
may also refer to:
* Award in absentia
* Declared death in absentia, or simply, death in absentia, legally declared death without a body
* Election in ab ...
'') against Catholics in the Leagues and Valtellina.Graubünden's religious history(PDF; 3.95 MB) This included the arresting under false pretenses and torturing to death of the (catholic) arch-priest
Nicolò Rusca
Nicolò Rusca (20 April 1563 – 24 July 1618) was an Italian priest who served in the Diocese of Como. Rusca was arrested under false pretenses and was killed through the use of torture in 1618. He was recognized by the Roman Catholic Church as ...
of Sondrio
Sondrio (; lmo, Sùndri; rm, Sunder; archaic german: Sünders or ; la, Sundrium) is an Italian city and ''comune'' and Provincial Capital located in the heart of the Valtellina. , Sondrio counts approximately 21,876 inhabitants (2015) and it is ...
.This and similar harsh judgments of the anti-Habsburg Thusis court led to a conspiracy to drive the Protestants out of the valley. The leader of the conspiracy, Giacomo Robustelli of the Planta family, had ties to Madrid, Rome and Paris. On the evening of 18/19 July 1620, a force of Valtellina rebels supported by Austrian and Italian troops marched into Tirano and began killing Protestants. When they finished in Tirano, they marched to Teglio
Teglio (''Téi'' in Valtellinese dialect) is a '' comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Sondrio in the Italian region Lombardy, located about northeast of Milan and about east of Sondrio
Sondrio (; lmo, Sùndri; rm, Sunder; archaic ...
, Sondrio
Sondrio (; lmo, Sùndri; rm, Sunder; archaic german: Sünders or ; la, Sundrium) is an Italian city and ''comune'' and Provincial Capital located in the heart of the Valtellina. , Sondrio counts approximately 21,876 inhabitants (2015) and it is ...
and further down the valley killing every Protestant that they found. Between 500Swiss Historyaccessed 16 January 2012 and 600 people were killed on that night and in the following four days. The attack drove nearly all the Protestants out of the valley, prevented further Protestant incursions and took the Valtellina out of the
Three Leagues
The Three Leagues, sometimes referred to as Raetia, was the alliance of 1471 of the League of God's House, the League of the Ten Jurisdictions, and the Grey League, leading eventually to the formation of the Swiss canton of Graubünden (Grison ...
. The killings in Valtellina were part of the conflicts in Graubünden known as the '' Bündner Wirren'' or Confusion of the Leagues.
In February 1623 France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, Savoy
Savoy (; frp, Savouè ; french: Savoie ) is a cultural-historical region in the Western Alps.
Situated on the cultural boundary between Occitania and Piedmont, the area extends from Lake Geneva in the north to the Dauphiné in the south.
Sa ...
, and Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
signed the Treaty of Paris in which all three signatories agreed to re-establish the territory of Valtellina by attempting to remove Spanish forces stationed there.
18th and 19th centuries
In 1797 the growing power of theFirst French Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
created the Cisalpine republic
The Cisalpine Republic ( it, Repubblica Cisalpina) was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organiz ...
in Northern Italy. On 10 October 1797, the French supported a revolt in the Valtellina against the Graubünden (''Grisons'' in French and English), and it joined the Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic ( it, Repubblica Cisalpina) was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organiz ...
.
After the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
in 1815 the Valtellina became part of the Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia
The Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia ( la, links=no, Regnum Langobardiae et Venetiae), commonly called the "Lombardo-Venetian Kingdom" ( it, links=no, Regno Lombardo-Veneto, german: links=no, Königreich Lombardo-Venetien), was a constituent land ...
, which was a constituent land of the Austrian Empire. In 1859 it came, together with Lombardy, to the Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
, and finally in 1861 it became part of the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
.
At the end of the 19th century there was substantial migration out of the Valtellina for reasons of the prevailing economically depressed conditions of the region and for young men to avoid conscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to Ancient history, antiquity and it continues in some countries to th ...
.Paull, John (2014"Ernesto Genoni: Australia’s pioneer of biodynamic agriculture"
Journal of Organics, 1(1):57-81.
Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, especially Western Australia
Western Australia (commonly abbreviated as WA) is a state of Australia occupying the western percent of the land area of Australia excluding external territories. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to t ...
, was a popular destination for such migrants.
Industrially, the area is famous as the home of the world's first mainline electrified railway
A railway electrification system supplies electric power to railway trains and trams without an on-board prime mover or local fuel supply.
Electric railways use either electric locomotives (hauling passengers or freight in separate cars), ele ...
. The electrification of the Ferrovia della Valtellina
The Ferrovia della Valtellina (Valtellina railway) is a railway line in Italy that runs from Lecco to Valtellina and Valchiavenna. It was opened in 1894 and electrified on the three-phase system in 1902. It is now electrified at 3 kV direct cur ...
took place in 1902, using three-phase
Three-phase electric power (abbreviated 3φ) is a common type of alternating current used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or four including an optional neutral ...
power at 3,600 V, with a maximum speed of 70 km/h. The system was designed by the brilliant Hungarian engineer Kálmán Kandó who was employed by main contractors the Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population o ...
-based Ganz
The Ganz Works or Ganz ( or , ''Ganz companies'', formerly ''Ganz and Partner Iron Mill and Machine Factory'') was a group of companies operating between 1845 and 1949 in Budapest, Hungary. It was named after Ábrahám Ganz, the founder and t ...
company.
Mussolini and the Valtellina Redoubt
During the last months ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
and other diehard fascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
leaders of the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
(RSI) proposed making a "last stand" against the advancing Allied armies in the Valtellina. The Fascist Party secretary Alessandro Pavolini
Alessandro Pavolini (27 September 1903 – 28 April 1945) was an Italian politician, journalist, and essayist, notable for his involvement in the Fascist government, during World War II, and also for his cruelty against the opponents of fascis ...
was the main proponent of the idea, which he first raised with Mussolini in September 1944. He pointed out that the valley was ringed with fortifications dating from World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, and had its own electricity generating capacity (hydroelectric). In the last months of 1944 Mussolini's government began moving munitions and food stores to the area. By January 1945, however, no firm decision to make a stand in the Valtellina had been taken. The Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
, represented by Ambassador Rudolf Rahn
Rudolf Rahn (16 March 1900 – 7 January 1975) was a German diplomat who served the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany. As a member of the Party, and as Plenipotentiary to the Italian Social Republic in the closing stages of the Second World War, h ...
, were opposed to the idea. In March, with the Allies advancing into the Po valley, Mussolini's Cabinet again discussed the idea. The RSI's military commander, Marshal Rodolfo Graziani
Rodolfo Graziani, 1st Marquis of Neghelli (; 11 August 1882 – 11 January 1955), was a prominent Italian military officer in the Kingdom of Italy's '' Regio Esercito'' ("Royal Army"), primarily noted for his campaigns in Africa before and durin ...
, who believed the war was already lost, opposed the plan. This ensured that no serious military preparations were made.
In early April Pavolini again raised the plan, which he called "the Epic of the 50,000," claiming that 50,000 Blackshirt
The Voluntary Militia for National Security ( it, Milizia Volontaria per la Sicurezza Nazionale, MVSN), commonly called the Blackshirts ( it, Camicie Nere, CCNN, singular: ) or (singular: ), was originally the paramilitary wing of the Nation ...
s would follow Mussolini if he made a stand in the Valtellina. The Germans, who by this time were negotiating with the Allies to surrender their armies in Italy, remained adamantly opposed. Filippo Anfuso
Filippo Anfuso (1 January 1901 – 13 December 1963) was an Italian writer, diplomat and Fascist politician.
Biography
Anfuso was born in Catania. His writing career started with a volume of short stories and poetry he published in 1917. Anfuso ...
, the RSI's under-secretary for foreign affairs, pointed out that valley was already mostly in the hands of the partisans. By mid April, the Valtellina plan was no longer a realistic possibility. Although Mussolini continued to fantasise about dying a heroic death there, the plan had no serious support. When Mussolini left Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
on 25 April, heading north, it was assumed he was going to the Valtellina, but his intentions were never made clear. He told some people he would go to Bolzano
Bolzano ( or ; german: Bozen, (formerly ); bar, Bozn; lld, Balsan or ) is the capital city of the province of South Tyrol in northern Italy. With a population of 108,245, Bolzano is also by far the largest city in South Tyrol and the third ...
, in the province of Bolzano, to join up with German forces. In any event, Mussolini's capture on 27 April by the partisans at Dongo, barely short of the Valtellina, ended any possibility of a fascist last stand.
Culture and language
The local dialect used to be a mix of Romansch andLombard language
Lombard (native name: ,Classical Milanese orthography, and . , Ticinese orthography. Modern Western orthography. or , Eastern unified orthography. depending on the orthography; pronunciation: ) is a language, belonging to the Gallo-Italic famil ...
. These days, however, only Italian and the Valtellinese variety of Lombard are spoken.

Folklore
''L'è foeu el sginer'' & ''l'è foeu l'ors de la tana''
On January 31st there was the tradition of ''l'è foeu el sginer'' ("January's out"), a custom very similar to that celebrated on February 2 known as ''l'è foeu l'ors de la tana'' ("the bear is out from its den"). Both celebrated the end of winter and the imminent arrival of spring. The two customs involved walking around the town and inviting people to leave their house under any pretext, like throwing a large piece of wood or a pot down the stairs. When people ran outside to check what had happened, they were greeted with the shout ''l'è foeu el sginer!'' or ''l'è foeu l'ors de la tana!''''Intraverser l’ann''
''Intraverser l'èn'' or ''intraverser l'ann'' (literally "to put the year across") also celebratedNew Year's Eve
In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve, also known as Old Year's Day or Saint Sylvester's Day in many countries, is the evening or the entire day of the last day of the year, on 31 December. The last day of the year is commonly referred to ...
: during the night young people used to build barricade
Barricade (from the French ''barrique'' - 'barrel') is any object or structure that creates a barrier or obstacle to control, block passage or force the flow of traffic in the desired direction. Adopted as a military term, a barricade denot ...
s of gates, door
A door is a hinged or otherwise movable barrier that allows ingress (entry) into and egress (exit) from an enclosure. The created opening in the wall is a ''doorway'' or ''portal''. A door's essential and primary purpose is to provide security b ...
s, benches, agricultural tools, logs, stairs, sledges, and carts in the main square
In Euclidean geometry, a square is a regular quadrilateral, which means that it has four equal sides and four equal angles (90- degree angles, π/2 radian angles, or right angles). It can also be defined as a rectangle with two equal-length a ...
or in front of the church, to prevent the old year from leaving. The next morning, the owners of the stolen objects had to go and recover them, dismantling the barricade and metaphorically opening up the way to the new year.
The ''gabinat''
On January 6th, the custom of the ''gabinat'' is still celebrated today, especially in Tirano, in the Upper Valley, and in the nearby Poschiavo Valley (Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
) Traditionally, children would suddenly enter other people's homes shouting ''gabinat!'' and in exchange, they would receive a handful of cooked chestnuts, some sweets or dried fruit. The adults competed to precede the other in exclaiming ''gabinat'' when they met. Whoever lost had to pay a pledge; often, the prize at stake was established in advance and the gabinat thus became the object of bets. In order to win, various strategies were adopted: stalking, disguises, fake illnesses ... Nowadays, it's only the childrean who do the ''gabinat'', and they usually show up to relatives, friends, and local shopkeepers.
The custom of the ''gabinat'' most likely comes from Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
, where Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
, New Year's Eve
In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve, also known as Old Year's Day or Saint Sylvester's Day in many countries, is the evening or the entire day of the last day of the year, on 31 December. The last day of the year is commonly referred to ...
and Epiphany were indicated with the name Geb-nacht (''Gaben'' means "gifts" and ''Nacht'' means "night", therefore "night of gifts"): on the eve of these holidays, the poor young people sang in front of the doors of the wealthiest in the hope to receive a gift.
''Andà a ciamà l'erba'' (Let's go call the grass)
On the first of March, throughout Valtellina and Valchiavenna, people used to go to ''ciamà l'erba'' ("call the grass"). The children walked in the meadows making noise withcowbell
A cowbell (or cow bell) is a bell worn around the neck of free-roaming livestock so herders can keep track of an animal via the sound of the bell when the animal is grazing out of view in hilly landscapes or vast plains. Although they are t ...
s to call the grass and awaken it from the winter slumber. This custom also served to propitiate a bountiful harvest.
The ''Carneval vegg'' (Old Carnival)
In the village of Grosio, theCarnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival t ...
is celebrated, unlike the rest of Valtellina, on the first Sunday of Lent
Lent ( la, Quadragesima, 'Fortieth') is a solemn religious moveable feast#Lent, observance in the liturgical calendar commemorating the 40 days Jesus spent fasting in the desert and enduring Temptation of Jesus, temptation by Satan, according ...
, according to the Ambrosian calendar in force before the Gregorian reform
The Gregorian Reforms were a series of reforms initiated by Pope Gregory VII and the circle he formed in the papal curia, c. 1050–80, which dealt with the moral integrity and independence of the clergy. The reforms are considered to be na ...
. For this reason, it is called ''Carneval vegg'' ("Old Carnival").
In the past, it was customary for people to gather all together to dance, sing, eat and drink. Being an agricultural ritual that represents the death of winter and the beginning of summer, Carnival officially began on January 17th with the parade of the blessed cattle adorned with coloured ribbons. It included numerous bonfire
A bonfire is a large and controlled outdoor fire, used either for informal disposal of burnable waste material or as part of a celebration.
Etymology
The earliest recorded uses of the word date back to the late 15th century, with the Catho ...
s, with which the paths were cleared to facilitate the passage of farmers, their agricultural vehicles and their livestock. A straw puppet with horns on his head representing the Carnival was also burnt.
Nowadays, the districts of the towns challenge each other to the sound of allegorical floats, and the parade is attended by traditional masks, eight characters representing traditions, past events, and moments of everyday life: the Old Carnival, a bearded and joyful man dressed as a mountaineer, and Lean Lent, a thin woman dressed in a humble way, with a dark handkerchief on her head and an empty basket on her arm, represent the transition from the glories of Carnival to Lenten fasts. They are accompanied by the Paralytic, the Bear Handler, a funny shepherd who dances and rolls on the ground named Toni, an old man with the butt covered with Nutella, a hunchbacked mountaineer whose hump is filled with chestnut urchins, and Bernarda, a man disguised as a baby put in a pannier supported by a fake old woman, and accompanied by another man dressed as a farmer).
During the Carnival period, ''manzòli'' or ''manzòla'', white flour and buckwheat
Buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum''), or common buckwheat, is a flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae cultivated for its grain-like seeds and as a cover crop. The name "buckwheat" is used for several other species, such as ''Fagop ...
pancake
A pancake (or hotcake, griddlecake, or flapjack) is a flat cake, often thin and round, prepared from a starch-based batter that may contain eggs, milk and butter and cooked on a hot surface such as a griddle or frying pan, often frying w ...
s mixed with slices of cheese and cut into the shape of a calf
Calf most often refers to:
* Calf (animal), the young of domestic cattle.
* Calf (leg), in humans (and other primates), the back portion of the lower leg
Calf or calves may also refer to:
Biology and animal byproducts
*Veal, meat from calves
*C ...
were eaten to propitiate the abundance of livestock parts.
The ''Carneval di Mat'' (Carnival of the fools)
InBormio
Bormio ( lmo, Bormi, rm, italic=yes, , german: Worms im Veltlintal) is a town and ''comune'' with a population of about 4,100 located in the Province of Sondrio, Lombardy region of the Alps in northern Italy.
The centre of the upper Valtellina ...
, during the day of the Carnival of the Fools, the Mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well ...
hands over his power to the ''Podestà di Mat'' (Podestà
Podestà (, English: Potestate, Podesta) was the name given to the holder of the highest civil office in the government of the cities of Central and Northern Italy during the Late Middle Ages. Sometimes, it meant the chief magistrate of a city ...
of the Fools) to Harlequin
Harlequin (; it, Arlecchino ; lmo, Arlechin, Bergamasque pronunciation ) is the best-known of the '' zanni'' or comic servant characters from the Italian '' commedia dell'arte'', associated with the city of Bergamo. The role is traditional ...
, and to the ''Compagnia di Mat'' ("the Company of the Fools") who give a public reading of the gossip and complaints that citizens have deposited in a box placed in the square of the Kuerc. The festival also includes a parade along the streets of the historic centre led by the Harlequins of the Company of Mat, with children escorting the Podestà.

''La'' ''coscrizione'' (the conscription)
Theconscription
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to Ancient history, antiquity and it continues in some countries to th ...
was originally a celebration on the occasion of the call to the draft: the tradition seems to have originated in the second half of the nineteenth century
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium.
The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolish ...
with the unification of Italy
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
when adults were forced to do military service in the Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
. The feast of the conscripts of eighteen-year-olds was therefore a kind of rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of social status, status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisat ...
to adulthood. Today is simply the celebration of the coming of age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from being a child to being an adult. The specific age at which this transition takes place varies between societies, as does the nature of the change. It can be a simple legal convention or can ...
.
The duration of the celebration varied from town to town: in Grosio the conscription could last up to ten days, during which the boys and girls met in bars, taverns, or in places specially set up for the purpose. The conscripts had the task of embroidering on the tricolour flag
A tricolour () or tricolor () is a type of flag or banner design with a triband design which originated in the 16th century as a symbol of republicanism, liberty, or revolution. The flags of France, Italy, Romania, Mexico, and Ireland were ...
the symbol and possibly the motto that the group had chosen. On the walls of the villages, it was customary to write ''W LA CLASSE...'' ("cheers to the year...") followed by the year of birth: nowadays, conscripts hang a tricolour banner with the same wording and the names (or nicknames) of the members of the group.
The feast of the conscripts is particularly felt in Alta Valtellina: in Grosio, for a week, the conscripts meet in a club to celebrate and travel through the streets of the town in a car from which the flag decorated with the symbol of the group waves. On New Year's Eve, amid fireworks
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices ...
and the noise of whistles, cowbell
A cowbell (or cow bell) is a bell worn around the neck of free-roaming livestock so herders can keep track of an animal via the sound of the bell when the animal is grazing out of view in hilly landscapes or vast plains. Although they are t ...
s, motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle Steering, steered by a Motorcycle handlebar, handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: Long-distance ...
s, and tractor
A tractor is an engineering vehicle specifically designed to deliver a high tractive effort (or torque) at slow speeds, for the purposes of hauling a trailer or machinery such as that used in agriculture, mining or construction. Most commo ...
s, they entrust the flag to conscripts one year younger, after having it blessed in church. Each group chooses different coloured sweatshirts and decorates the tricolour with a symbol
A symbol is a mark, sign, or word that indicates, signifies, or is understood as representing an idea, object, or relationship. Symbols allow people to go beyond what is known or seen by creating linkages between otherwise very different conc ...
that represents the group's motto or identity.

''I Pasquali''
The ''Pasquali'' are allegorical floats with a religious theme, prepared during the winter by the various districts of Bormio (Buglio, Combo, Dossiglio, Dossorovina and Maggiore) forEaster
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samue ...
(Pasqua meaning Easter in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
). On Easter day, the Pasquali are carried on the shoulders of the boys and are accompanied by a band, folk groups, women, seniors, and children who embellish the parade with flowers and other small crafts. Everyone wears the traditional red, black and white costume. After having followed the entire Via Roma and upon arrival at the Piazza del Kuerc (the main square of the town) the ancient bell called Bajona starts tolling and a jury draws up a ranking of the best Pasquali. At the end of the parade, the floats are exhibited in Piazza del Kuerc where they stay until Easter Monday.
''Il Palio delle Contrade''
Born in 1963, the ''Palio delle Contrade'' sees the inhabitants of the five districts of Bormio compete against each other, divided according to age, in downhill, cross-country, combined, and relay races. The cross-country race takes place through the streets of the town, covered with snow for the purpose.Wines
 In Valtellina, wines are produced mainly from ''Chiavennasca'' (the local name of
In Valtellina, wines are produced mainly from ''Chiavennasca'' (the local name of Nebbiolo
Nebbiolo (, ; pms, nebieul ) is an Italian red wine grape variety predominantly associated with its native Piedmont region, where it makes the '' Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita'' (DOCG) wines of Barolo, Barbaresco, Roero ...
grape variety
This list of grape varieties includes cultivated grapes, whether used for wine, or eating as a table grape, fresh or dried ( raisin, currant, sultana). For a complete list of all grape species including those unimportant to agriculture, see ...
) with other minor varieties such as Rossola nera
Rossola nera is a red Italian wine grape variety that has been growing in the Valtellina region of Lombardy since at least the 17th century. In 2004 DNA profiling determined that the grape has a parent-offspring relationship with the Piedmont wine ...
permitted up to 20% for the ''Denominazione di origine controllata
The following four classifications of wine constitute the Italian system of labelling and legally protecting Italian wine:
* ''Denominazione di origine'' (DO, rarely used; ; English: “designation of origin”),
* ''Indicazione geografica tipi ...
'' (DOC) and 10% for the '' Denominazione di Origine Controllata e Garantita'' (DOCG). Grapes are limited to a harvest
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most l ...
yield of 12 tonnes per hectare. The finished wine must be aged for at least two years prior to release (three years if a ''Riserva
Reserve wine is wine of a higher quality than usual, a wine that has been aged before sale, or both. Traditionally, winemakers would reserve some of their best wine rather than sell it immediately, coining the term.
In some countries the use of t ...
'' bottling) with a minimum alcohol level
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as ABV, abv, or alc/vol) is a standard measure of how much alcohol (ethanol) is contained in a given volume of an alcoholic beverage (expressed as a volume percent). It is defined as the number of millilitres (mL) o ...
of at least 11%. Yields for the DOCG wines are further restricted to a maximum of 8 tonnes/ha. While the aging requirements are the same as the DOC, the minimum alcohol level for the DOCG wine is 12%.P. Saunders ''Wine Label Language'' pg 143 Firefly Books 2004
The best-known villages for red wines are: Grumello, Sassella, Inferno, Valgella, and Maroggia
Maroggia is a former municipality in the district of Lugano in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. On 10 April 2022, the former municipalities of Maroggia, Melano and Rovio merged to form the new municipality of Val Mara.
History
Maroggia is ...
. The village names are normally indicated on the label. Additionally there is an Amarone style DOCG wine called Sforzato (Sfursat).
Tourism
One of the most notable tourist attractions of the area is the Bernina Line (“Trenino Rosso”) of theRhaetian Railway
The Rhaetian Railway (german: Rhätische Bahn; it, Ferrovia retica; rm, Viafier retica), abbreviated RhB, is a Swiss transport company that owns the largest network of all private railway operators in Switzerland. Headquartered in Chur, the Rh ...
, which links the town of Tirano in the Valtellina with St. Moritz in Graubünden, Switzerland via the Bernina Pass. The mountains of the Valtellina offer numerous possibilities for sport activities: skiing and winter sports in Bormio
Bormio ( lmo, Bormi, rm, italic=yes, , german: Worms im Veltlintal) is a town and ''comune'' with a population of about 4,100 located in the Province of Sondrio, Lombardy region of the Alps in northern Italy.
The centre of the upper Valtellina ...
, Aprica
Aprica ( lmo, Abriga) is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Sondrio, Lombardy, northern Italy. It is located on the eponymous pass, the most favourable one connecting Valtellina to Val Camonica.
Its main source of income is tourism, us ...
or Livigno
Livigno (; local lmo, Livígn ; german: Luwin) is a town, ''comune'' and a special-administered territory in the province of Sondrio, in the region of Lombardy, Italy, located in the Italian Alps, near the Swiss border.
History
Livigno's firs ...
, hiking and biking in the same locations and especially in the secondary valleys, and rock climbing in the Val Masino
Val Masino (Western Lombard dialect, Western Lombard: ''Val Màsen'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Sondrio in the Italy, Italian region Lombardy, located about northeast of Milan and about northwest of Sondrio, on the border ...
.
The Rupe Magna, a unique large rock with more than 5,000 engraved figures dating from between the 4th and 1st millennia BCE, can be found at the Rock Engraving Park in Grosio. Val Poschiavo
In the lower part of the Val Poschiavo, the valley in the Graubünden canton ofSwitzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
that descends into the Valtellina at Tirano, similar wines are produced - but under different regulations such as appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical bo ...
and the allowance of sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or do ...
addition, or chaptalization.
Notable people
Born in Valtellina: * Achille Compagnoni (Mountaineer) *Deborah Compagnoni
Deborah Compagnoni (; born 4 June 1970) is an Italian former Alpine skier who won three gold medals at the 1992, 1994, and 1998 Winter Olympics.
Biography
Deborah Compagnoni was born in Bormio, northern Lombardy, and skied with the G.S. Forest ...
(Alpine skier)
* Arianna Fontana
Arianna Fontana OMRI (born 14 April 1990) is an Italian short track speed skater, who has won eleven Olympic medals among these two gold medals in the 500m short track, one at the 2018 Winter Olympics in Pyeongchang and the second one at the 20 ...
(Short track speed skater)
* Marco De Gasperi
Marco De Gasperi (born 5 April 1977) is an Italian male mountain runner, sky runner and long-distance runner.
Biography
He won five gold medals at senior level (from 1997 to 2007) and one at junior level (1996), at the World Mountain Running Cha ...
(Athlete, Skyrunner)
* Fabio Meraldi
Fabio Meraldi (born 5 August 1965) is an Italian ski mountaineer, mountain guide and mountain runner.
Meraldi was born in Valtellina. He passed the mountain guide training at the age of 20, and participated in various mountain tours, sky running a ...
(Ski mountaineer)
* Giuseppe Piazzi
Giuseppe Piazzi ( , ; 16 July 1746 – 22 July 1826) was an Italian Catholic priest of the Theatine order, mathematician, and astronomer. He established an observatory at Palermo, now the '' Osservatorio Astronomico di Palermo – Giuseppe S ...
(Priest, mathematician and astronomer)
* Giulio Tremonti
Giulio Tremonti () (born 18 August 1947) is an Italian politician. He served in the government of Italy as Minister of Economy and Finance under Prime Minister Silvio Berlusconi from 1994 to 1995, from 2001 to 2004, from 2005 to 2006, and from 20 ...
(Politician)
* Luigi Torelli
Luigi Torelli (9 February 1810 – 14 November 1887) was born in Villa di Tirano, in the Valtellina of Lombardy, at the time part of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy.
Being a patriot, he took part in the Five Days of Milan, most noted in drivi ...
(Patriot)
See also
*Valtellina disaster
The Val Pola landslide (Val Pola rock avalanche) happened in Valtellina, Lombardy, Northern Italian Alps, on July 28, 1987 and resulted in the Valtellina disaster (destruction of villages, road closure, and flooding threat) with a total cost of ...
References
Further reading: F Pieth: Bündnergeschichte, 1982,External links
An extensive history of the Valtellina area
Tourist information
{{Authority control Valleys of the Alps Valleys of Lombardy Geographical, historical and cultural regions of Italy Wine regions of Italy Wine regions of Switzerland