V-2 rocket on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The V-2 (german: Vergeltungswaffe 2, lit=Retaliation Weapon 2), with the technical name ''
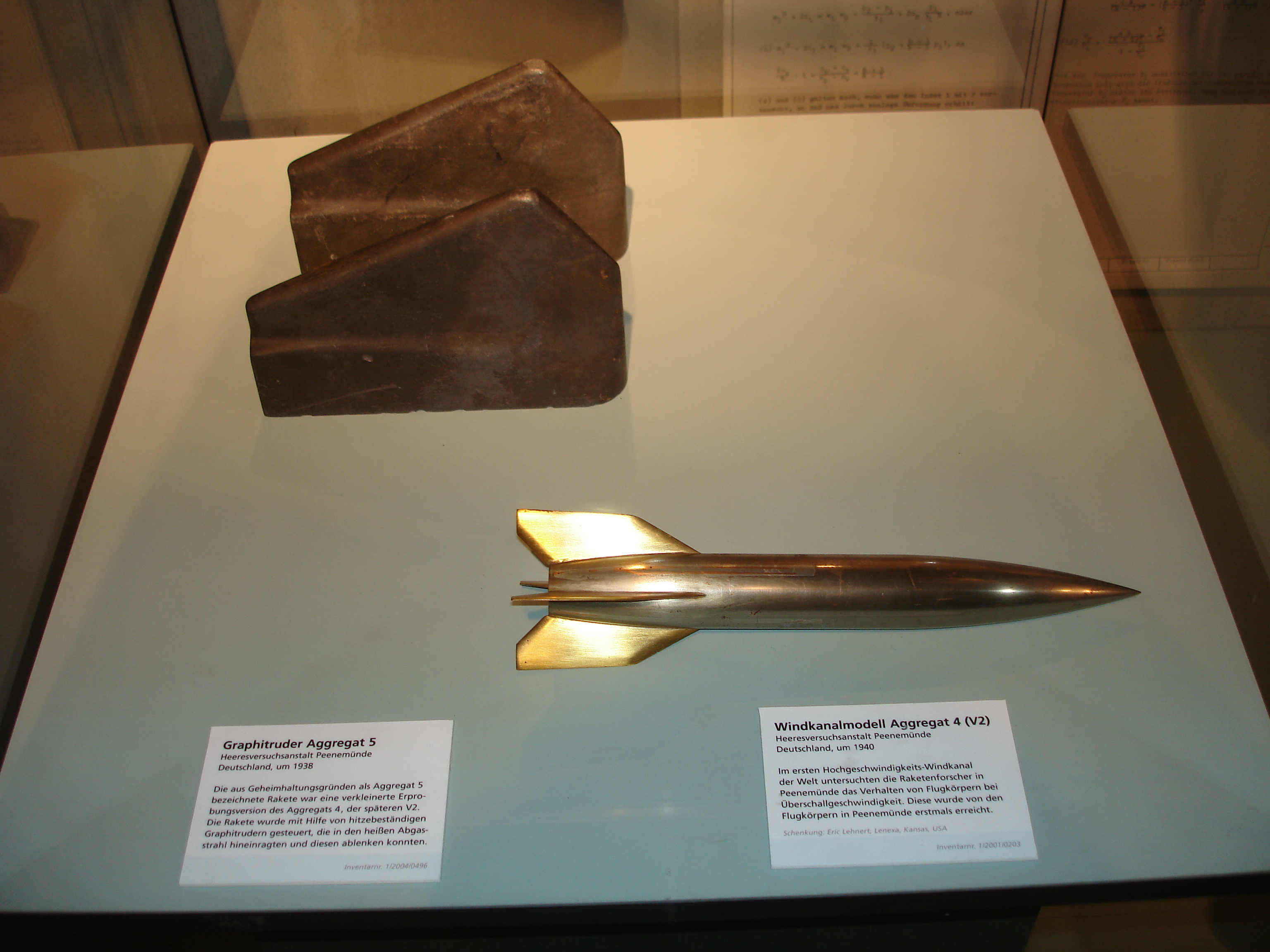
 In the late 1920s, a young Wernher von Braun bought a copy of Hermann Oberth's book, '' Die Rakete zu den Planetenräumen'' (''The Rocket into Interplanetary Spaces''). The world's first large-scale experimental rocket program was Opel-RAK under the leadership of Fritz von Opel and Max Valier, a collaborator of Oberth, during the late 1920s leading to the first manned rocket cars and rocket planes, which paved the way for the Nazi era V2 program and US and Soviet activities from 1950 onwards. The Opel RAK program and the spectacular public demonstrations of ground and air vehicles drew large crowds, as well as caused global public excitement as so-called "Rocket Rumble" and had a large long-lasting impact on later spaceflight pioneers, in particular on Wernher von Braun. The
In the late 1920s, a young Wernher von Braun bought a copy of Hermann Oberth's book, '' Die Rakete zu den Planetenräumen'' (''The Rocket into Interplanetary Spaces''). The world's first large-scale experimental rocket program was Opel-RAK under the leadership of Fritz von Opel and Max Valier, a collaborator of Oberth, during the late 1920s leading to the first manned rocket cars and rocket planes, which paved the way for the Nazi era V2 program and US and Soviet activities from 1950 onwards. The Opel RAK program and the spectacular public demonstrations of ground and air vehicles drew large crowds, as well as caused global public excitement as so-called "Rocket Rumble" and had a large long-lasting impact on later spaceflight pioneers, in particular on Wernher von Braun. The  By late 1941, the Army Research Center at Peenemünde possessed the technologies essential to the success of the A-4. The four key technologies for the A-4 were large liquid-fuel rocket engines, supersonic aerodynamics, gyroscopic guidance and rudders in jet control. At the time,
By late 1941, the Army Research Center at Peenemünde possessed the technologies essential to the success of the A-4. The four key technologies for the A-4 were large liquid-fuel rocket engines, supersonic aerodynamics, gyroscopic guidance and rudders in jet control. At the time,
 The A-4 used a 75%
The A-4 used a 75%
Aggregat
The Aggregat series (German for "Aggregate") was a set of ballistic missile designs developed in 1933–1945 by a research program of Nazi Germany's Armed Forces ( Wehrmacht). Its greatest success was the A4, more commonly known as the V-2.
...
4'' (A-4), was the world’s first long-range guided ballistic missile
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within t ...
. The missile, powered by a liquid-propellant rocket engine, was developed during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
in Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
as a "vengeance weapon" and assigned to attack Allied cities as retaliation for the Allied bombings of German cities. The rocket also became the first artificial object to travel into space by crossing the Kármán line (edge of space) with the vertical launch of MW 18014 on 20 June 1944.
Research into military use of long-range rockets began when the graduate studies of Wernher von Braun attracted the attention of the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
. A series of prototypes culminated in the A-4, which went to war as the . Beginning in September 1944, over 3,000 were launched by the Wehrmacht against Allied targets, first London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and later Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
and Liège. According to a 2011 BBC documentary, the attacks from resulted in the deaths of an estimated 9,000 civilians and military personnel, and a further 12,000 forced laborers and Nazi concentration camps
From 1933 to 1945, Nazi Germany operated more than a thousand concentration camps, (officially) or (more commonly). The Nazi concentration camps are distinguished from other types of Nazi camps such as forced-labor camps, as well as con ...
prisoners died as a result of their forced participation in the production of the weapons."Am Anfang war die V2. Vom Beginn der Weltraumschifffahrt in Deutschland". In: Utz Thimm (ed.): ''Warum ist es nachts dunkel? Was wir vom Weltall wirklich wissen''. Kosmos, 2006, p. 158, .
The rockets travelled at supersonic speed, impacted without audible warning, and proved unstoppable, as no effective defense existed. Teams from the Allied forces—the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
—raced to seize key Nazi manufacturing facilities, procure the Nazis' missile technology, and capture the V-2’s launching sites. Von Braun and over 100 key personnel surrendered to the Americans, and many of the original team ended up working at the Redstone Arsenal. The US also captured enough hardware to build approximately 80 of the missiles. The Soviets gained possession of the manufacturing facilities after the war, re-established production, and moved it to the Soviet Union.
Development history

Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
ended these activities. Von Opel left Germany in 1930 and emigrated later to France and Switzerland.
Starting in 1930, von Braun attended the Technical University of Berlin, where he assisted Oberth in liquid-fueled rocket motor tests. Von Braun was working on his doctorate when the Nazi Party
The Nazi Party, officially the National Socialist German Workers' Party (german: Nationalsozialistische Deutsche Arbeiterpartei or NSDAP), was a far-right political party in Germany active between 1920 and 1945 that created and supported t ...
gained power in Germany. An artillery captain, Walter Dornberger, arranged an Ordnance Department research grant for von Braun, who from then on worked next to Dornberger's existing solid-fuel rocket test site at Kummersdorf. Von Braun's thesis, ''Construction, Theoretical, and Experimental Solution to the Problem of the Liquid Propellant Rocket'' (dated 16 April 1934), was kept classified by the German Army and was not published until 1960. By the end of 1934, his group had successfully launched two rockets that reached heights of .
At the time, Germany was highly interested in American physicist Robert H. Goddard's research. Before 1939, German engineers and scientists occasionally contacted Goddard directly with technical questions. Von Braun used Goddard's plans from various journals and incorporated them into the building of the ''Aggregate
Aggregate or aggregates may refer to:
Computing and mathematics
* collection of objects that are bound together by a root entity, otherwise known as an aggregate root. The aggregate root guarantees the consistency of changes being made within the ...
'' (A) series of rocket
A rocket (from it, rocchetto, , bobbin/spool) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using the surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entir ...
s, named for the German word for mechanism or mechanical system.
Following successes at Kummersdorf with the first two Aggregate series rockets, Braun and Walter Riedel began thinking of a much larger rocket in the summer of 1936, based on a projected thrust engine. In addition, Dornberger specified the military requirements needed to include a 1-ton payload, a range of 172 miles with a dispersion of 2 or 3 miles, and transportable using road vehicles.
After the A-4 project was postponed due to unfavorable aerodynamic stability testing of the A-3 in July 1936, English translation 1954.
Braun specified the A-4 performance in 1937, and, after an "extensive" series of test firings of the A-5 scale test model,Christopher, p.111. using a motor redesigned from the troublesome A-3 by Walter Thiel, A-4 design and construction was ordered 1938–39. During 28–30 September 1939, (English: ''The Day of Wisdom'') conference met at Peenemünde to initiate the funding of university research to solve rocket problems.
 By late 1941, the Army Research Center at Peenemünde possessed the technologies essential to the success of the A-4. The four key technologies for the A-4 were large liquid-fuel rocket engines, supersonic aerodynamics, gyroscopic guidance and rudders in jet control. At the time,
By late 1941, the Army Research Center at Peenemünde possessed the technologies essential to the success of the A-4. The four key technologies for the A-4 were large liquid-fuel rocket engines, supersonic aerodynamics, gyroscopic guidance and rudders in jet control. At the time, Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
was not particularly impressed by the V-2; he opined that it was merely an artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during si ...
shell with a longer range and much higher cost.
In early September 1943, Braun promised the Long-Range Bombardment Commission that the A-4 development was "practically complete/concluded", but even by the middle of 1944, a complete A-4 parts list was still unavailable. Hitler was sufficiently impressed by the enthusiasm of its developers, and needed a " wonder weapon" to maintain German morale, so he authorized its deployment in large numbers.
The V-2s were constructed at the Mittelwerk site by prisoners
A prisoner (also known as an inmate or detainee) is a person who is deprived of liberty against their will. This can be by confinement, captivity, or forcible restraint. The term applies particularly to serving a prison sentence in a prison.
...
from Mittelbau-Dora, a concentration camp where 20,000 prisoners died.
In 1943, the Austrian resistance group around Heinrich Maier managed to send exact drawings of the V-2 rocket to the American Office of Strategic Services. Location sketches of V-rocket manufacturing facilities, such as those in Peenemünde, were also sent to the Allied general staff in order to enable Allied bombers to carry out airstrike
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The off ...
s. This information was particularly important for Operation Crossbow and Operation Hydra, both preliminary missions for Operation Overlord
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Norm ...
. The group was gradually captured by the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
and most of the members were executed.
Technical details
 The A-4 used a 75%
The A-4 used a 75% ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
/25% water mixture ( ''B-Stoff'') for fuel and liquid oxygen
Liquid oxygen—abbreviated LOx, LOX or Lox in the aerospace, submarine and gas industries—is the liquid form of molecular oxygen. It was used as the oxidizer in the first liquid-fueled rocket invented in 1926 by Robert H. Goddard, an app ...
(LOX) ( ''A-Stoff'') for oxidizer
An oxidizing agent (also known as an oxidant, oxidizer, electron recipient, or electron acceptor) is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or " accepts"/"receives" an electron from a (called the , , or ). In other words, an oxi ...
. The water reduced the flame temperature, acted as a coolant by turning to steam and augmented the thrust, tended to produce a smoother burn, and reduced thermal stress.
Rudolf Hermann's supersonic wind tunnel
A supersonic wind tunnel is a wind tunnel that produces supersonic speeds (1.2< M<5)
The Mach number and flow are determined by the was used to measure the A-4's aerodynamic characteristics and center of pressure, using a model of the A-4 within a 40 square centimeter chamber. Measurements were made using a Mach 1.86 blowdown nozzle on 8 August 1940. Tests at Mach numbers 1.56 and 2.5 were made after 24 September 1940.
At launch the A-4 propelled itself for up to 65 seconds on its own power, and a program motor held the inclination at the specified angle until engine shutdown, after which the rocket continued on a ballistic free-fall trajectory. The rocket reached a height of or 264,000 ft after shutting off the engine.
The fuel and oxidizer pumps were driven by a steam turbine, and the steam was produced by concentrated  The V-2 was guided by four external rudders on the tail fins, and four internal
The V-2 was guided by four external rudders on the tail fins, and four internal 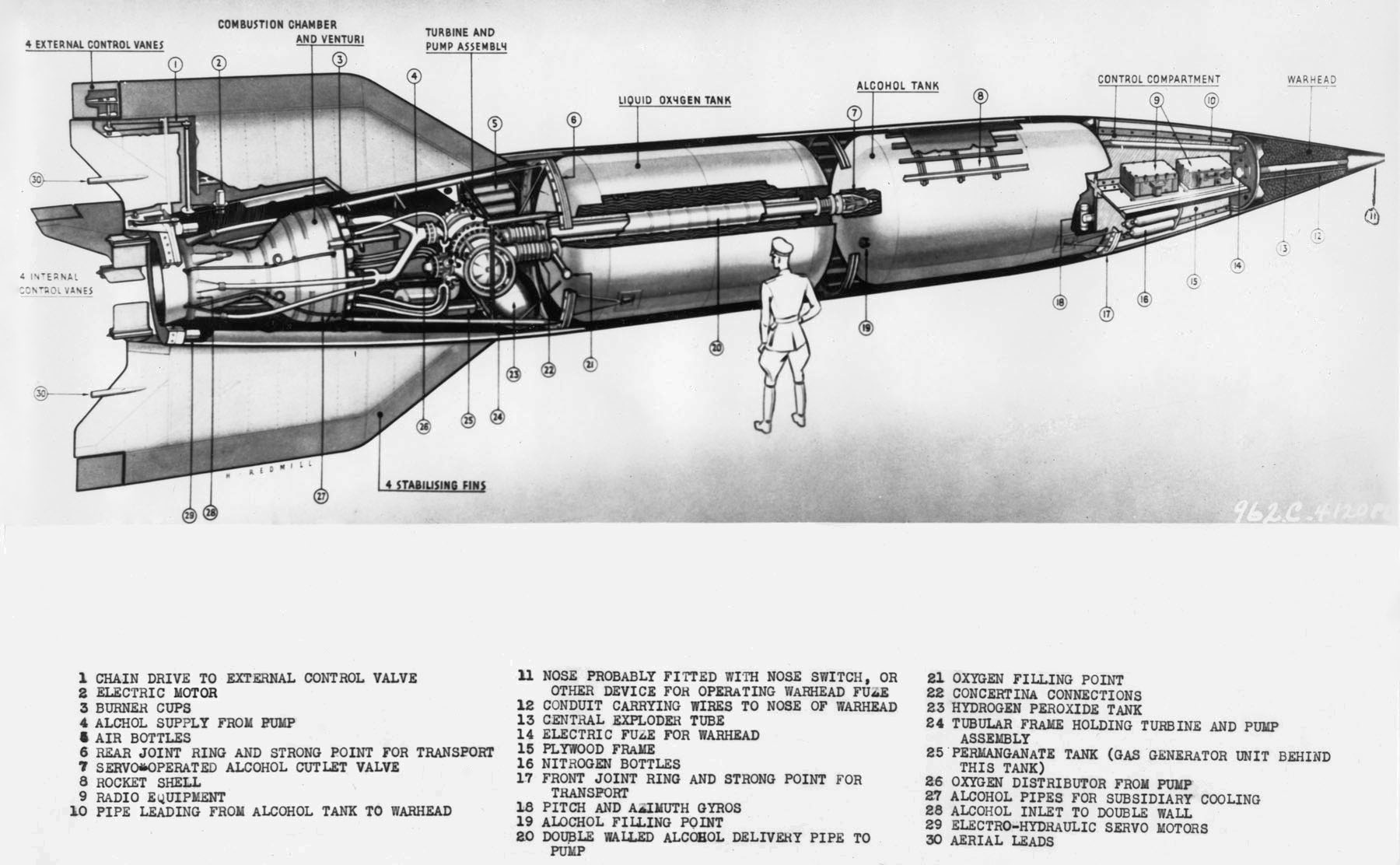 The original German designation of the rocket was "V2", unhyphenated – exactly as used for any Third Reich-era "second prototype" example of an RLM-registered German aircraft design – but U.S. publications such as ''
The original German designation of the rocket was "V2", unhyphenated – exactly as used for any Third Reich-era "second prototype" example of an RLM-registered German aircraft design – but U.S. publications such as ''
 Two test launches were recovered by the Allies: the Bäckebo rocket, the remnants of which landed in Sweden on 13 June 1944, and one recovered by the Polish resistance on 30 May 1944 from
Two test launches were recovered by the Allies: the Bäckebo rocket, the remnants of which landed in Sweden on 13 June 1944, and one recovered by the Polish resistance on 30 May 1944 from
 On 27 March 1942, Dornberger proposed production plans and the building of a launching site on the Channel coast. In December, Speer ordered Major Thom and Dr. Steinhoff to reconnoiter the site near Watten. Assembly rooms were established at Peenemünde and in the
On 27 March 1942, Dornberger proposed production plans and the building of a launching site on the Channel coast. In December, Speer ordered Major Thom and Dr. Steinhoff to reconnoiter the site near Watten. Assembly rooms were established at Peenemünde and in the
 Following the Operation Crossbow bombing, initial plans for launching from the massive underground Watten,
Following the Operation Crossbow bombing, initial plans for launching from the massive underground Watten,
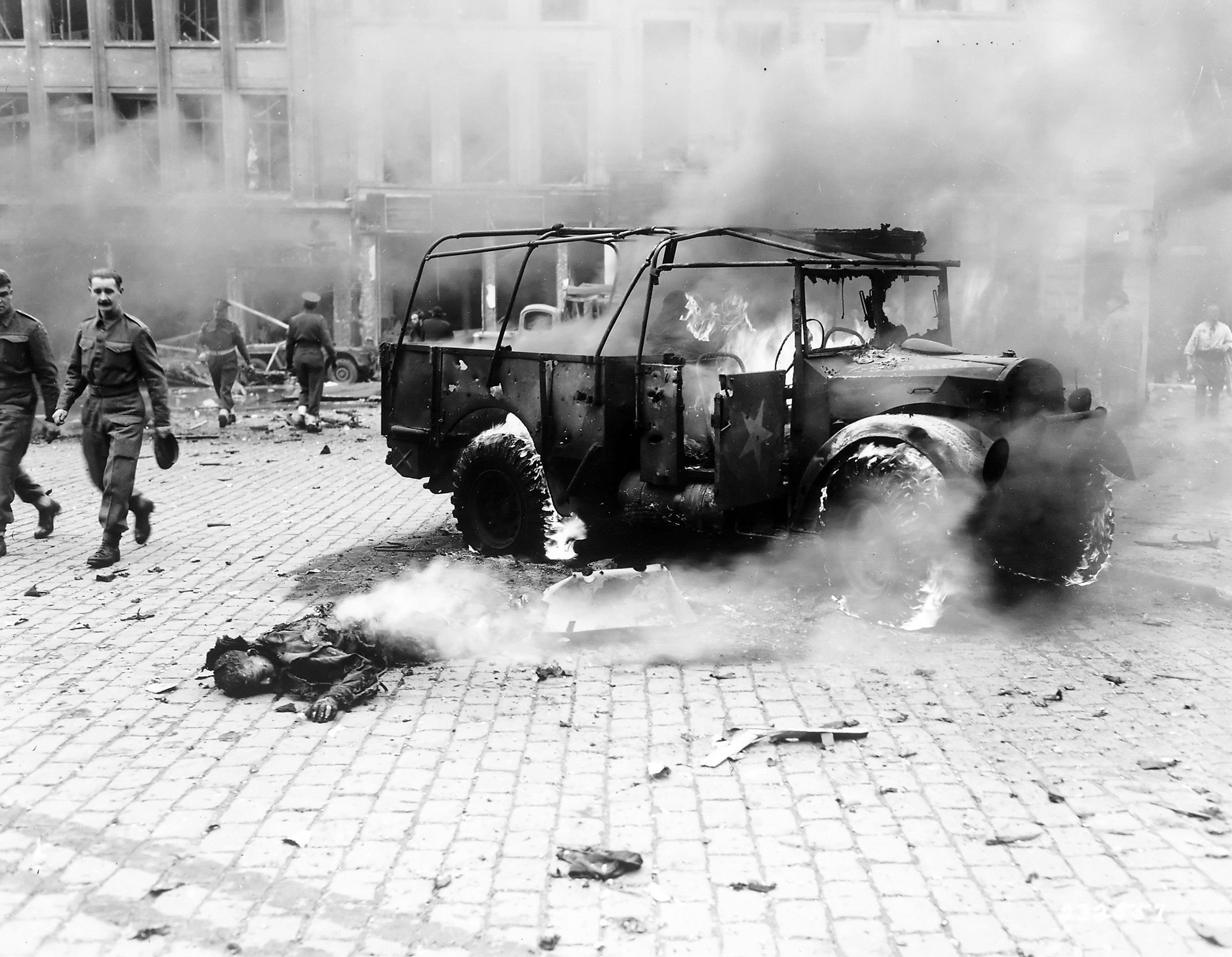 The LXV ''Armeekorps'' z.b.V. formed during the last days of November 1943 in France commanded by ''General der Artillerie'' z.V.
The LXV ''Armeekorps'' z.b.V. formed during the last days of November 1943 in France commanded by ''General der Artillerie'' z.V. 
 The final two rockets exploded on 27 March 1945. One of these was the last V-2 to kill a British civilian and the final civilian casualty of the war on British soil: Ivy Millichamp, aged 34, killed in her home in Kynaston Road,
The final two rockets exploded on 27 March 1945. One of these was the last V-2 to kill a British civilian and the final civilian casualty of the war on British soil: Ivy Millichamp, aged 34, killed in her home in Kynaston Road,

"Britain and Ballistic Missile Defence, 1942–2002"
, pp. 20–28.
 In October 1945, '' Operation Backfire'' assembled a small number of V-2 missiles and launched three of them from a site in northern Germany. The engineers involved had already agreed to move to the US when the test firings were complete. The Backfire report, published in January 1946, contains extensive technical documentation of the rocket, including all support procedures, tailored vehicles and fuel composition.
In 1946, the
In October 1945, '' Operation Backfire'' assembled a small number of V-2 missiles and launched three of them from a site in northern Germany. The engineers involved had already agreed to move to the US when the test firings were complete. The Backfire report, published in January 1946, contains extensive technical documentation of the rocket, including all support procedures, tailored vehicles and fuel composition.
In 1946, the

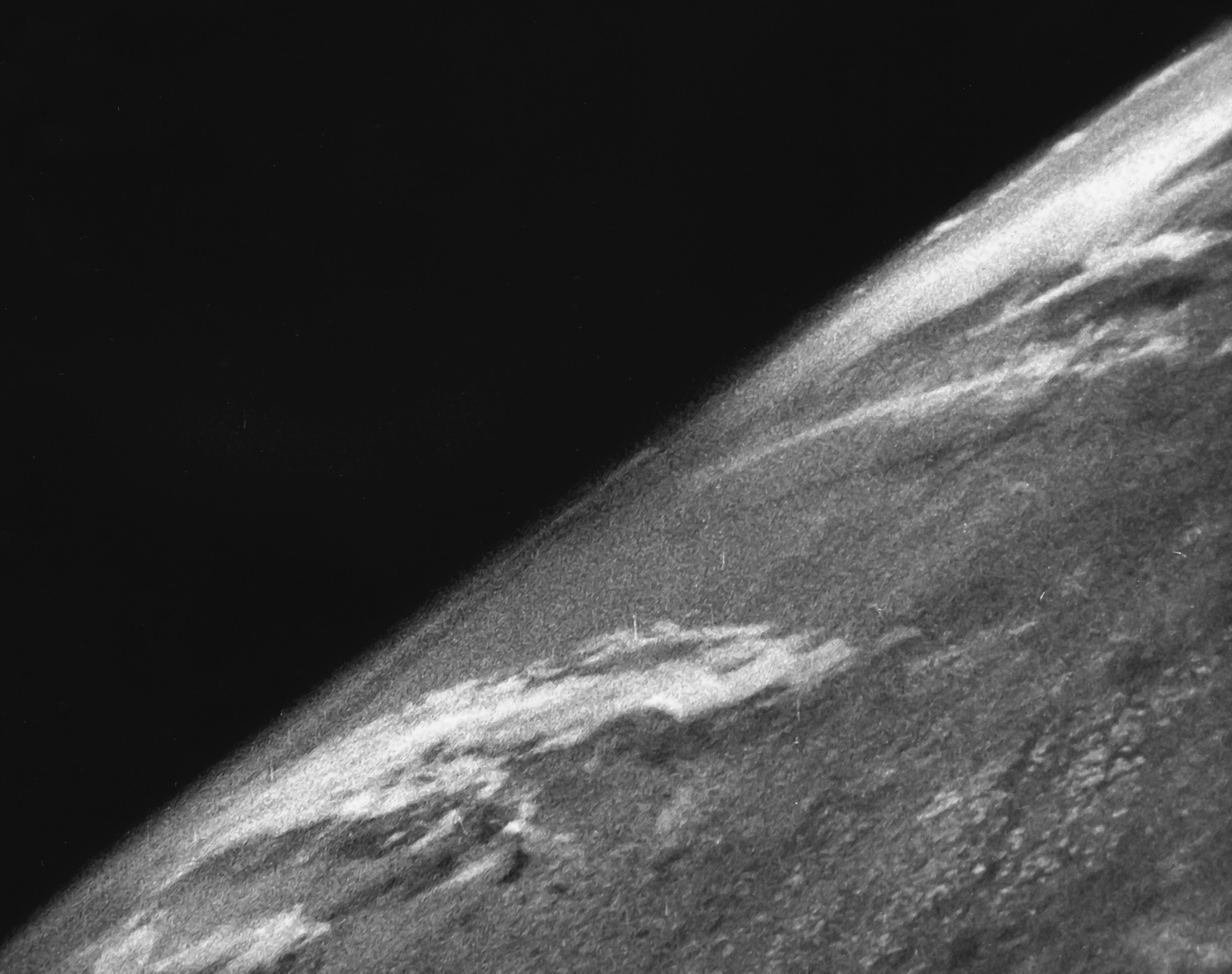 Only 68 percent of the V-2 trials were considered successful. A supposed V-2 launched on 29 May 1947 landed near Juarez, Mexico and was actually a Hermes B-1 vehicle.
The U.S. Navy attempted to launch a German V-2 rocket at sea—one test launch from the aircraft carrier USS ''Midway'' was performed on 6 September 1947 as part of the Navy's Operation Sandy. The test launch was a partial success; the V-2 went off the pad but splashed down in the ocean only some from the carrier. The launch setup on the Midway's deck is notable in that it used foldaway arms to prevent the missile from falling over. The arms pulled away just after the engine ignited, releasing the missile. The setup may look similar to the R-7 launch procedure but in the case of the R-7 the trusses hold the full weight of the rocket, rather than just reacting to side forces.
The PGM-11 Redstone rocket is a direct descendant of the V-2.
Only 68 percent of the V-2 trials were considered successful. A supposed V-2 launched on 29 May 1947 landed near Juarez, Mexico and was actually a Hermes B-1 vehicle.
The U.S. Navy attempted to launch a German V-2 rocket at sea—one test launch from the aircraft carrier USS ''Midway'' was performed on 6 September 1947 as part of the Navy's Operation Sandy. The test launch was a partial success; the V-2 went off the pad but splashed down in the ocean only some from the carrier. The launch setup on the Midway's deck is notable in that it used foldaway arms to prevent the missile from falling over. The arms pulled away just after the engine ignited, releasing the missile. The setup may look similar to the R-7 launch procedure but in the case of the R-7 the trusses hold the full weight of the rocket, rather than just reacting to side forces.
The PGM-11 Redstone rocket is a direct descendant of the V-2.
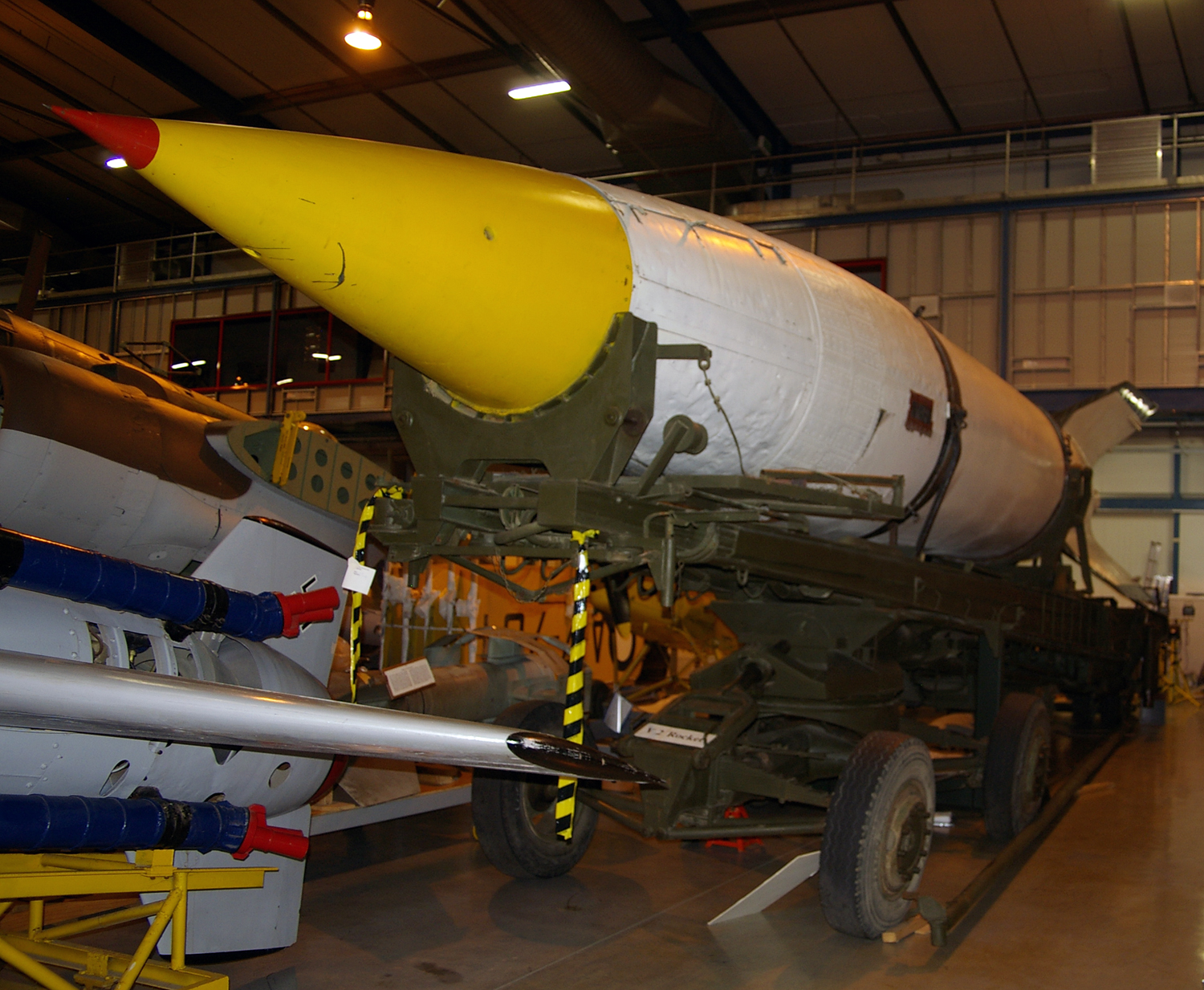 At least 20 V-2s still existed in 2014.
At least 20 V-2s still existed in 2014.
 * One at the
* One at the
"V-2 Rocket".
''National Museum of the United States Air Force''. Retrieved: 3 January 2017. (one was transferred from United States Army Ordnance Museum in Aberdeen, Maryland around 2005 when the museum closed).
* Combustion chambers and other components plus a U.S. built engine at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center in Dulles, Virginia.
* One engine at the Museum of Science and Industry in Chicago.
* One rocket body at Picatinny Arsenal in Dover, New Jersey.
* One engine in the Auburn University Engineering Lab
* One engine in the Exhibit Hall adjacent to the Blockhouse building on the Historic Cape Canaveral Tour in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
* One engine at Parks College of Engineering, Aviation and Technology in St. Louis, Missouri
* One engine and tail section at New Mexico Museum of Space History in Alamogordo, New Mexico
"The German A4 Rocket (Main Title)"
Information Film of Operation Backfire from IWM
* ttps://books.google.com/books?id=miQDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA124 '"Chute Saves Rockets Secrets" September 1947, ''
Reconstruction, restoration & refurbishment of a V-2 rocket
spherical panoramas of the process and milestones.
Hermann Ludewig Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
Files of Hermann Ludewig, Deputy of Design Chief and later Chief of Acceptance and Inspection on the V-2 program {{authority control * . 1944 in Germany 1944 in military history 1944 in science German inventions of the Nazi period Operation Crossbow Operation Paperclip Peenemünde Army Research Center and Airfield Rockets and missiles Short-range ballistic missiles Space programme of Germany Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1944 Wernher von Braun World War II guided missiles of Germany
hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3 ...
(T-Stoff
T-Stoff (; 'substance T') was a stabilised high test peroxide used in Germany during World War II. T-Stoff was specified to contain 80% (occasionally 85%) hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), remainder water, with traces (<0.1%) of stabilisers. Stabiliser ...
) with sodium permanganate (Z-Stoff
Z-Stoff (, "substance Z") was a name for calcium permanganate or sodium permanganate mixed in water. It was normally used as a catalyst for T-Stoff ( high-test peroxide) in military rocket programs by Nazi Germany during World War II.
Z-Stoff wa ...
) catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
. Both the alcohol and oxygen tanks were an aluminum-magnesium alloy.
The turbopump, rotating at 4000 rpm, forced the alcohol and oxygen into the combustion chamber at 125 liters (33 US gallons) per second, where they were ignited by a spinning electrical igniter. Thrust increased from 8 tons during this preliminary stage whilst the fuel was gravity-fed, before increasing to 25 tons as the turbopump pressurised the fuel, lifting the 13.5 ton rocket. Combustion gases exited the chamber at , and a speed of 2000 m (6500 feet) per second. The oxygen to fuel mixture was 1.0:0.85 at 25 tons of thrust, but as ambient pressure
Ambient or Ambiance or Ambience may refer to:
Music and sound
* Ambience (sound recording), also known as atmospheres or backgrounds
* Ambient music, a genre of music that puts an emphasis on tone and atmosphere
* ''Ambient'' (album), by Moby
* ...
decreased with flight altitude, thrust increased until it reached 29 tons.Zaloga 2003 p19 The turbopump assembly contained two centrifugal pumps, one for the alcohol, and one for the oxygen, both connected to a common shaft. Hydrogen peroxide converted to steam, using a sodium permanganate catalyst powered the pump, which delivered 55 kg (120 pounds) of alcohol and 68 kg (150 pounds) of liquid oxygen per second to a combustion chamber at 1.5 MPa (210 psi).
Dr. Thiel's development of the 25 ton rocket motor relied on pump feeding, rather than on the earlier pressure feeding. The motor used centrifugal injection, while using both regenerative cooling and film cooling. Film cooling admitted alcohol into the combustion chamber and exhaust nozzle under slight pressure through four rings of small perforations. The mushroom-shaped injection head was removed from the combustion chamber to a mixing chamber, the combustion chamber was made more spherical while being shortened from 6 to 1 foot in length, and the connection to the nozzle was made cone shaped. The resultant 1.5 ton chamber operated at a combustion pressure of 1.52 MPa (220 psi). Thiel's 1.5 ton chamber was then scaled up to a 4.5 ton motor by arranging three injection heads above the combustion chamber. By 1939, eighteen injection heads in two concentric circles at the head of the 3 mm (0.12-inch) thick sheet-steel chamber, were used to make the 25 ton motor.
The warhead was another source of trouble. The explosive employed was amatol 60/40 detonated by an electric contact fuze. Amatol had the advantage of stability, and the warhead was protected by a thick layer of glass wool
Glass wool is an insulating material made from glass fiber arranged using a binder into a texture similar to wool. The process traps many small pockets of air between the glass, and these small air pockets result in high thermal insulation pro ...
, but even so it could still explode in the re-entry phase. The warhead weighed and contained of explosive. The warhead's percentage by weight that was explosive was 93%, a very high percentage when compared with other types of munition.
A protective layer of glass wool was also used for the fuel tanks so the A-4 did not have a tendency to form ice, a problem which plagued other early ballistic missiles such as the balloon tank
A balloon tank is a style of propellant tank used in the SM-65 Atlas intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and Centaur upper stage that does not use an internal framework, but instead relies on a positive internal pressurization to keep i ...
-design SM-65 Atlas which entered US service in 1959. The tanks held of ethyl alcohol and of oxygen.
 The V-2 was guided by four external rudders on the tail fins, and four internal
The V-2 was guided by four external rudders on the tail fins, and four internal graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on la ...
vanes in the jet stream at the exit of the motor. These 8 control surfaces were controlled by Helmut Hölzer )
, image = File:HolzerHelmut Huntsville.jpg
, image_size = 100px
, caption = Helmut Hölzer in Huntsville, Alabama
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bad Liebenstein, Thüringen, German Empire
, death_date =
, death_place = Huntsville, Alabama ...
's analog computer, the , via electrical-hydraulic servomotors, based on electrical signals from the gyros. The Siemens ''Vertikant'' LEV-3 guidance system consisted of two free gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rot ...
s (a horizontal for pitch and a vertical with two degrees of freedom for yaw and roll) for lateral stabilization, coupled with a PIGA accelerometer, or the Walter Wolman radio control system, to control engine cutoff at a specified velocity. Other gyroscopic systems used in the A-4 included Kreiselgeräte's SG-66 and SG-70. The V-2 was launched from a pre-surveyed location, so the distance and azimuth
An azimuth (; from ar, اَلسُّمُوت, as-sumūt, the directions) is an angular measurement in a spherical coordinate system. More specifically, it is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north.
Mathematical ...
to the target were known. Fin 1 of the missile was aligned to the target azimuth.
Some later V-2s used " guide beams", radio signals transmitted from the ground, to keep the missile on course, but the first models used a simple analog computer that adjusted the azimuth for the rocket, and the flying distance was controlled by the timing of the engine cut-off, ''Brennschluss
Brennschluss (a loanword, from the German ''Brennschluss'') is either the cessation of fuel burning in a rocket or the time that the burning ceases: the cessation may result from the consumption of the propellants, from deliberate shutoff, or fro ...
'', ground-controlled by a Doppler system or by different types of on-board integrating accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acce ...
s. Thus, range was a function of engine burn time, which ended when a specific velocity was achieved. Just before engine cutoff, thrust was reduced to eight tons, in an effort to avoid any water hammer problems a rapid cutoff could cause.
Dr. Friedrich Kirchstein of Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', ''E ...
of Berlin developed the V-2 radio control for motor-cut-off (german: Brennschluss). For velocity measurement, Professor Wolman of Dresden created an alternative of his Doppler tracking system in 1940–41, which used a ground signal transponded by the A-4 to measure the velocity of the missile. By 9 February 1942, Peenemünde engineer Gerd had documented the radio interference area of a V-2 as around the "Firing Point", and the first successful A-4 flight on 3 October 1942, used radio control for . Although Hitler commented on 22 September 1943 that "It is a great load off our minds that we have dispensed with the radio guiding-beam; now no opening remains for the British to interfere technically with the missile in flight", about 20% of the operational V-2 launches were beam-guided. The Operation Pinguin V-2 offensive began on 8 September 1944, when (English: 'Training and Testing Battery 444') launched a single rocket guided by a radio beam directed at Paris. Wreckage of combat V-2s occasionally contained the transponder for velocity and fuel cutoff.
The painting of the operational V-2s was mostly a ragged-edged pattern with several variations, but at the end of the war a plain olive green rocket also appeared. During tests the rocket was painted in a characteristic black-and-white chessboard pattern, which aided in determining if the rocket was spinning around its longitudinal axis.
 The original German designation of the rocket was "V2", unhyphenated – exactly as used for any Third Reich-era "second prototype" example of an RLM-registered German aircraft design – but U.S. publications such as ''
The original German designation of the rocket was "V2", unhyphenated – exactly as used for any Third Reich-era "second prototype" example of an RLM-registered German aircraft design – but U.S. publications such as ''Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for growth, reaction to stimuli, metabolism, energy ...
'' magazine were using the hyphenated form "V-2" as early as December 1944.
Testing
The first successful test flight was on 3 October 1942, reaching an altitude of . On that day, Walter Dornberger declared in a speech at Peenemünde: Two test launches were recovered by the Allies: the Bäckebo rocket, the remnants of which landed in Sweden on 13 June 1944, and one recovered by the Polish resistance on 30 May 1944 from
Two test launches were recovered by the Allies: the Bäckebo rocket, the remnants of which landed in Sweden on 13 June 1944, and one recovered by the Polish resistance on 30 May 1944 from Blizna :''See also Blizna, Podlaskie Voivodeship. For the Polish film of this name see The Scar (1976 film).''
Blizna is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ostrów, within Ropczyce-Sędziszów County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in sou ...
and transported to the UK during Operation Most III. The highest altitude reached during the war was (20 June 1944). Test launches of V-2 rockets were made at Peenemünde, Blizna and Tuchola Forest, and after the war, at Cuxhaven by the British, White Sands Proving Grounds
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Pa ...
and Cape Canaveral by the U.S., and Kapustin Yar by the USSR.
Various design issues were identified and solved during V-2 development and testing:
:* To reduce tank pressure and weight, high flow turbopumps were used to boost pressure.
:* A short and lighter combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is part of an internal combustion engine in which the fuel/air mix is burned. For steam engines, the term has also been used for an extension of the firebox which is used to allow a more complete combustion process.
Intern ...
without burn-through was developed by using centrifugal injection nozzles, a mixing compartment, and a converging nozzle to the throat for homogeneous combustion.
:* Film cooling was used to prevent burn-through at the nozzle throat.
:* Relay contacts were made more durable to withstand vibration and prevent thrust cut-off just after lift-off.
:* Ensuring that the fuel pipes had tension-free curves reduced the likelihood of explosions at .
:* Fins were shaped with clearance to prevent damage as the exhaust jet expanded with altitude.
:* To control trajectory at liftoff and supersonic speeds, heat-resistant graphite vanes were used as rudders in the exhaust jet.
Air burst problem
Through mid-March 1944, only four of the 26 successful Blizna launches had satisfactorily reached theSarnaki
Sarnaki is a village in Łosice County, Masovian Voivodeship, in east-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Sarnaki. It lies approximately north-east of Łosice and east of Warsaw
Warsaw ( ...
target area due to in-flight breakup () on re-entry into the atmosphere. (As mentioned above, one rocket was collected by the Polish Home Army
The Home Army ( pl, Armia Krajowa, abbreviated AK; ) was the dominant resistance movement in German-occupied Poland during World War II. The Home Army was formed in February 1942 from the earlier Związek Walki Zbrojnej (Armed Resistance) es ...
, with parts of it transported to London for tests.) Initially, the German developers suspected excessive alcohol tank pressure, but by April 1944, after five months of test firings, the cause was still not determined. Major-General Rossmann, the Army Weapons Office department chief, recommended stationing observers in the target area – May/June, Dornberger and von Braun set up a camp at the centre of the Poland target zone. After moving to the Heidekraut, SS Mortar Battery 500 of the 836th Artillery Battalion (Motorized) was ordered on 30 August to begin test launches of eighty 'sleeved' rockets. Testing confirmed that the so-called 'tin trousers' – a tube designed to strengthen the forward end of the rocket cladding – reduced the likelihood of air bursts.
Production
 On 27 March 1942, Dornberger proposed production plans and the building of a launching site on the Channel coast. In December, Speer ordered Major Thom and Dr. Steinhoff to reconnoiter the site near Watten. Assembly rooms were established at Peenemünde and in the
On 27 March 1942, Dornberger proposed production plans and the building of a launching site on the Channel coast. In December, Speer ordered Major Thom and Dr. Steinhoff to reconnoiter the site near Watten. Assembly rooms were established at Peenemünde and in the Friedrichshafen
Friedrichshafen ( or ; Low Alemannic: ''Hafe'' or ''Fridrichshafe'') is a city on the northern shoreline of Lake Constance (the ''Bodensee'') in Southern Germany, near the borders of both Switzerland and Austria. It is the district capital (''K ...
facilities of Zeppelin Works. In 1943, a third factory, Raxwerke, was added.
On 22 December 1942, Hitler signed the order for mass production, when Albert Speer
Berthold Konrad Hermann Albert Speer (; ; 19 March 1905 – 1 September 1981) was a German architect who served as the Minister of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany during most of World War II. A close ally of Adolf Hitler, h ...
assumed final technical data would be ready by July 1943. However, many issues still remained to be solved even by the autumn of 1943.
On 8 January 1943, Dornberger and von Braun met with Speer. Speer stated, "As head of the Todt organisation I will take it on myself to start at once with the building of the launching site on the Channel coast," and established an A-4 production committee under Degenkolb.
On 26 May 1943, the Long-Range Bombardment Commission, chaired by AEG
Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG (AEG; ) was a German producer of electrical equipment founded in Berlin as the ''Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität'' in 1883 by Emil Rathenau. During the Second World War, ...
director Petersen, met at Peenemünde to review the V-1 and V-2 automatic long-range weapons. In attendance were Speer, Air Marshal Erhard Milch, Admiral Karl Dönitz, Col. General Friedrich Fromm, and Karl Saur
Karl-Otto Saur (February 16, 1902 in Düsseldorf – July 28, 1966 in Pullach) was a high ranking official in the Reich Ministry of Armaments and War Production in Nazi Germany and was named as ''Reichsminister'' of Munitions in Adolf Hitl ...
. Both weapons had reached the final stage of development, and the commission decided to recommend to Hitler that both weapons be put into mass production. As Dornberger observed, "The disadvantages of the one would be compensated by the other's advantages."
On 7 July 1943, Major General Dornberger, von Braun, and Dr. Steinhof briefed Hitler in his Wolf's Lair. Also in attendance were Speer, Wilhelm Keitel, and Alfred Jodl
Alfred Josef Ferdinand Jodl (; 10 May 1890 – 16 October 1946) was a German '' Generaloberst'' who served as the chief of the Operations Staff of the '' Oberkommando der Wehrmacht'' – the German Armed Forces High Command – throughout Worl ...
. The briefing included von Braun narrating a film showing the successful launch on 3 October 1942, with scale models of the Channel coast firing bunker, and supporting vehicles, including the . Hitler then gave Peenemünde top priority in the German armaments program stating, "Why was it I could not believe in the success of your work? if we had had these rockets in 1939 we should never have had this war..." Hitler also wanted a second launch bunker built.
Saur planned to build 2,000 rockets per month, between the existing three factories and the Nordhausen Mittelwerk factory being built. However, alcohol production was dependent upon the potato harvest.
A production line was nearly ready at Peenemünde when the Operation Hydra attack occurred. The main targets of the attack included the test stands, the development works, the Pre-Production Works, the settlement where the scientists and technicians lived, the Trassenheide camp, and the harbor sector. According to Dornberger, "Serious damage to the works, contrary to first impressions, was surprisingly small." Work resumed after a delay of four to six weeks, and because of camouflage to mimic complete destruction, there were no more raids over the next nine months. The raid resulted in 735 lives lost, with heavy losses at Trassenheide, while 178 were killed in the settlement, including Dr. Thiel, his family, and Chief Engineer Walther. The Germans eventually moved production to the underground ''Mittelwerk'' in the Kohnstein where 5,200 V-2 rockets were built with the use of forced labour.
Launch sites
 Following the Operation Crossbow bombing, initial plans for launching from the massive underground Watten,
Following the Operation Crossbow bombing, initial plans for launching from the massive underground Watten, Wizernes
Wizernes (; vls, Wezerne) is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department, northern France. It lies southwest of Saint-Omer on the banks of the river Aa at the D928 and D211 road junction. The commune is twinned with Ensdorf, Germany.
Populat ...
and Sottevast
Sottevast () is a commune in Normandy in north-western France.
Sottevast in World War II
During World War II, there was a German storage and servicing bunker for V-weapons near Sottevast. The site was captured by the 504th Parachute Infantry ...
bunkers or from fixed pads such as near the Château du Molay were dropped in favour of mobile launching. Eight main storage dumps were planned and four had been completed by July 1944 (the one at Mery-sur-Oise was begun in August 1943 and completed by February 1944). The missile could be launched practically anywhere, roads running through forests being a particular favourite. The system was so mobile and small that only one was ever caught in action by Allied aircraft, during the Operation Bodenplatte attack on 1 January 1945 near Lochem by a USAAF 4th Fighter Group aircraft, although Raymond Baxter described flying over a site during a launch and his wingman firing at the missile without hitting it.
It was estimated that a sustained rate of 350 V-2s could be launched per week, with 100 per day at maximum effort, given sufficient supply of the rockets.
Operational history
 The LXV ''Armeekorps'' z.b.V. formed during the last days of November 1943 in France commanded by ''General der Artillerie'' z.V.
The LXV ''Armeekorps'' z.b.V. formed during the last days of November 1943 in France commanded by ''General der Artillerie'' z.V. Erich Heinemann
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization).
The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse ''* ain ...
was responsible for the operational use of V-2. Three launch battalions were formed in late 1943, ''Artillerie Abteilung'' 836 (Mot.), Grossborn, Artillerie Abteilung 485 (Mot.), Naugard, and ''Artillerie Abteilung'' 962 (''Mot.''). Combat operations commenced in Sept. 1944, when training Batterie 444 deployed. On 2 September 1944, the SS ''Werfer-Abteilung'' 500 was formed, and by October, the SS under the command of SS Lt. Gen Hans Kammler, took operational control of all units. He formed ''Gruppe Sud'' with Art. Abt. 836, Merzig, and ''Gruppe Nord'' with Art. Abt. 485 and ''Batterie'' 444, Burgsteinfurt
Steinfurt (; Westphalian: ''Stemmert'') is a city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is the capital of the district of Steinfurt. From roughly 1100-1806, it was the capital of the County of Steinfurt.
Geography
Steinfurt is situated north ...
and The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital o ...
.
After Hitler's 29 August 1944 declaration to begin V-2 attacks as soon as possible, the offensive began on 7 September 1944 when two were launched at Paris (which the Allies had liberated less than two weeks earlier), but both crashed soon after launch. On 8 September a single rocket was launched at Paris, which caused modest damage near Porte d'Italie
Porte d'Italie is one of the city gates of Paris, located in the 13th arrondissement, at the intersection of Avenue d'Italie, Boulevard Massena, Avenue de la Porte d'Italie and street Kellermann, facing the Kremlin-Bicetre.
The "gate of Italy" ...
. Two more launches by the 485th followed, including one from The Hague against London on the same day at 6:43 pm. – the first landed at Staveley Road, Chiswick, killing 63-year-old Mrs. Ada Harrison, three-year-old Rosemary Clarke, and Sapper
A sapper, also called a pioneer or combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparin ...
Bernard Browning on leave from the Royal Engineers, and one that hit Epping with no casualties. Upon hearing the double-crack of the supersonic rocket (London's first ever), Duncan Sandys and Reginald Victor Jones looked up from different parts of the city and exclaimed "That was a rocket!", and a short while after the double-crack, the sky was filled with the sound of a heavy body rushing through the air.
The British government, concerned about spreading panic or giving away vital intelligence to German forces, initially attempted to conceal the cause of the explosions by making no official announcement, and euphemistically blaming them on defective gas mains. The public did not believe this explanation and therefore began referring to the V-2s as "flying gas mains". The Germans themselves finally announced the V-2 on 8 November 1944 and only then, on 10 November 1944, did Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
inform Parliament, and the world, that England had been under rocket attack "for the last few weeks".
In September 1944, control of the V-2 mission was taken over by the Waffen-SS and Division z.V.
Positions of the German launch units changed a number of times. For example, ''Artillerie Init 444'' arrived in the southwest Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
(in Zeeland) in September 1944. From a field near the village of Serooskerke, five V-2s were launched on 15 and 16 September, with one more successful and one failed launch on the 18th. That same date, a transport carrying a missile took a wrong turn and ended up in Serooskerke itself, giving a villager the opportunity to surreptitiously take some photographs of the weapon; these were smuggled to London by the Dutch Resistance. After that the unit moved to the woods near Rijs, Gaasterland in the northwest Netherlands, to ensure that the technology did not fall into Allied hands. From Gaasterland V-2s were launched against Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line ...
and Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
from 25 September (London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
being out of range). Because of their inaccuracy, these V-2s did not hit their target cities. Shortly after that only London and Antwerp remained as designated targets as ordered by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
himself, Antwerp being targeted in the period of 12 to 20 October, after which time the unit moved to The Hague.

Targets
Over the following months about 3,172 V-2 rockets were fired at the following targets: :Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
, 1,664: Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
(1,610), Liège (27), Hasselt (13), Tournai (9), Mons
Mons (; German and nl, Bergen, ; Walloon and pcd, Mont) is a city and municipality of Wallonia, and the capital of the province of Hainaut, Belgium.
Mons was made into a fortified city by Count Baldwin IV of Hainaut in the 12th century. T ...
(3), Diest (2)
: United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, 1,402: London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
(1,358), Norwich
Norwich () is a cathedral city and district of Norfolk, England, of which it is the county town. Norwich is by the River Wensum, about north-east of London, north of Ipswich and east of Peterborough. As the seat of the Episcopal see, See of ...
(43), Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line ...
(1)
: France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, 76: Lille
Lille ( , ; nl, Rijsel ; pcd, Lile; vls, Rysel) is a city in the northern part of France, in French Flanders. On the river Deûle, near France's border with Belgium, it is the capital of the Hauts-de-France region, the prefecture of the No ...
(25), Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
(22), Tourcoing
Tourcoing (; nl, Toerkonje ; vls, Terkoeje; pcd, Tourco) is a city in northern France on the Belgian border. It is designated municipally as a commune within the department of Nord. Located to the north-northeast of Lille, adjacent to Roubaix, ...
(19), Arras (6), Cambrai
Cambrai (, ; pcd, Kimbré; nl, Kamerijk), formerly Cambray and historically in English Camerick or Camericke, is a city in the Nord department and in the Hauts-de-France region of France on the Scheldt river, which is known locally as the ...
(4)
: Netherlands, 19: Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the ...
(19)
: Germany, 11: Remagen (11)
Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
, Belgium was a target for a large number of V-weapon attacks from October 1944 through to the virtual end of the war in March 1945, leaving 1,736 dead and 4,500 injured in greater Antwerp. Thousands of buildings were damaged or destroyed as the city was struck by 590 direct hits. The largest loss of life by a single rocket attack during the war came on 16 December 1944, when the roof of the crowded Cine Rex was struck, leaving 567 dead and 291 injured.
An estimated 2,754 civilians were killed in London by V-2 attacks with another 6,523 injured, which is two people killed per V-2 rocket. However, this understates the potential of the V-2, since many rockets were misdirected and exploded harmlessly. Accuracy increased over the course of the war, particularly for batteries where the (radio guide beam) system was used. Missile strikes that found targets could cause large numbers of deaths – 160 were killed and 108 seriously injured in one explosion at 12:26 pm on 25 November 1944, at a Woolworth's
Woolworth, Woolworth's, or Woolworths may refer to:
Businesses
* F. W. Woolworth Company, the original US-based chain of "five and dime" (5¢ and 10¢) stores
* Woolworths Group (United Kingdom), former operator of the Woolworths chain of shop ...
department store in New Cross, south-east London.
British intelligence sent false reports via their Double-Cross System implying that the rockets were over-shooting their London target by . This tactic worked; more than half of the V-2s aimed at London landed outside the London Civil Defence Region.Jones RV; Most Secret War 1978 Most landed on less-heavily populated areas in Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
due to erroneous recalibration. For the remainder of the war, British intelligence kept up the ruse by repeatedly sending bogus reports implying that the rockets were now striking the British capital with heavy loss of life.Blitz Street; Channel 4, 10 May 2010
Possible use during Operation Bodenplatte
At least one V-2 missile on a mobile '' Meillerwagen'' launch trailer was observed being elevated to launch position by a USAAF 4th Fighter Group pilot defending against the massive New Year's Day 1945 Operation Bodenplatte strike by the Luftwaffe over the northern German attack route near the town of Lochem on 1 January 1945. Possibly, from the potential sighting of the American fighter by the missile's launch crew, the rocket was quickly lowered from a near launch-ready 85° elevation to 30°.Tactical use on German target
After the US Army captured the Ludendorff Bridge during theBattle of Remagen
The Battle of Remagen was an 18-day battle during the Allied invasion of Germany in World War II from 7 to 25 March 1945 when American forces unexpectedly captured the Ludendorff Bridge over the Rhine intact. They were able to hold it against ...
on 7 March 1945, the Germans were desperate to destroy it. On 17 March 1945, they fired eleven V-2 missiles at the bridge, their first use against a tactical target and the only time they were fired on a German target during the war. They could not employ the more accurate device because it was oriented towards Antwerp and could not be easily adjusted for another target. Fired from near Hellendoorn, the Netherlands, one of the missiles landed as far away as Cologne, to the north, while one missed the bridge by only . They also struck the town of Remagen, destroying a number of buildings and killing at least six American soldiers.
Final use
 The final two rockets exploded on 27 March 1945. One of these was the last V-2 to kill a British civilian and the final civilian casualty of the war on British soil: Ivy Millichamp, aged 34, killed in her home in Kynaston Road,
The final two rockets exploded on 27 March 1945. One of these was the last V-2 to kill a British civilian and the final civilian casualty of the war on British soil: Ivy Millichamp, aged 34, killed in her home in Kynaston Road, Orpington
Orpington is a town and area in south east London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley. It is 13.4 miles (21.6 km) south east of Charing Cross.
On the south-eastern edge of the Greater London Built-up Area, it is south of St ...
in Kent. A scientific reconstruction carried out in 2010 demonstrated that the V-2 creates a crater wide and deep, ejecting approximately 3,000 tons of material into the air.
Countermeasures
Big Ben and Crossbow
Unlike the V-1, the V-2's speed and trajectory made it practically invulnerable to anti-aircraft guns and fighters, as it dropped from an altitude of at up to three times the speed of sound at sea level (approximately 3550 km/h). Nevertheless, the threat of what was then code-named "Big Ben" was great enough that efforts were made to seek countermeasures. The situation was similar to the pre-war concerns about manned bombers and led to a similar solution, the formation of the Crossbow Committee, to collect, examine and develop countermeasures. Early on, it was believed that the V-2 employed some form of radio guidance, a belief that persisted in spite of several rockets being examined without discovering anything like a radio receiver. This led to efforts to jam this non-existent guidance system as early as September 1944, using both ground and air-based jammers flying over the UK. In October, a group had been sent to jam the missiles during launch. By December it was clear these systems were having no obvious effect, and jamming efforts ended.Jeremy Stocker"Britain and Ballistic Missile Defence, 1942–2002"
, pp. 20–28.
Anti-aircraft gun system
General Frederick Alfred Pile, commander of Anti-Aircraft Command, studied the problem and proposed that enough anti-aircraft guns were available to produce a barrage of fire in the rocket's path, but only if provided with a reasonable prediction of the trajectory. The first estimates suggested that 320,000 shells would have to be fired for each rocket. About 2% of these were expected to fall back to the ground, almost 90 tons of rounds, which would cause far more damage than the missile. At a 25 August 1944 meeting of the Crossbow Committee, the concept was rejected. Pile continued studying the problem, and returned with a proposal to fire only 150 shells at a single rocket, with those shells using a new fuse that would greatly reduce the number that fell back to Earth unexploded. Some low-level analysis suggested that this would be successful against 1 in 50 rockets, provided that accurate trajectories were forwarded to the gunners in time. Work on this basic concept continued and developed into a plan to deploy a large number of guns in Hyde Park that were provided with pre-configured firing data for grids of the London area. After the trajectory was determined, the guns would aim and fire between 60 and 500 rounds. At a Crossbow meeting on 15 January 1945 Pile's updated plan was presented with some strong advocacy from Roderic Hill andCharles Drummond Ellis
Sir Charles Drummond Ellis (b. Hampstead, 11 August 1895; died Cookham 10 January 1980) was an English physicist and scientific administrator. His work on the magnetic spectrum of the beta-rays helped to develop a better understanding of nuclear ...
. However, the Committee suggested that a test not be carried out as no technique for tracking the missiles with sufficient accuracy had yet been developed. By March this had changed significantly, with 81% of incoming missiles correctly allotted to the grid square each fell into, or the one beside it. At a 26 March meeting the plan moved ahead, and Pile was directed to a subcommittee with RV Jones and Ellis to further develop the statistics. Three days later the team returned a report stating that if the guns fired 2,000 rounds at a missile there was a 1 in 60 chance of shooting it down. Plans for an operational test began, but as Pile later put it, "Monty
Monty is a masculine given name, often a short form of Montgomery, Montague and other similar names. It is also a surname.
Notable people with the name or nickname include:
First name Nickname
*Bernard Montgomery (1887–1976), British Second ...
beat us to it", as the attacks ended with the Allied liberation of their launching areas.
With the Germans no longer in control of any part of the continent that could be used as a launching site capable of striking London, they turned their attention to Antwerp. Plans were made to move the Pile system to protect that city, but the war ended before anything could be done.
Direct attack and disinformation
The only effective defences against the V-2 campaign were to destroy the launch infrastructure—expensive in terms of bomber resources and casualties—or to cause the Germans to aim at the wrong place throughdisinformation
Disinformation is false information deliberately spread to deceive people. It is sometimes confused with misinformation, which is false information but is not deliberate.
The English word ''disinformation'' comes from the application of the ...
. The British were able to convince the Germans to direct V-1s and V-2s aimed at London to less populated areas east of the city. This was done by sending deceptive reports on the sites hit and damage caused via the German espionage network in Britain, which was secretly controlled by the British (the Double-Cross System).
According to the BBC television presenter Raymond Baxter, who served with the RAF during the war, in February 1945 his squadron was carrying out a mission against a V2 launch site, when one missile was launched in front of them. One member of Baxter's squadron opened fire on it, without effect.
On 3 March 1945 the Allies attempted to destroy V-2s and launching equipment in the "Haagse Bos" in The Hague by a large-scale bombardment, but due to navigational errors the Bezuidenhout
Bezuidenhout (; en, "South of the Wood") is the neighborhood ( nl, wijk) southeast of the Haagse Bos neighborhood of The Hague in the Netherlands. Bezuidenhout includes the Beatrixkwartier financial area near the Central Station and streets ...
quarter was destroyed, killing 511 Dutch civilians.
Assessment
The German V-weapons (V-1 and V-2) cost the equivalent of around US$500 million. Given the relatively smaller size of the German economy, this represented an industrial effort on par but slightly less than that of the U.S. Manhattan Project that produced the atomic bomb. 6,048 V-2s were built, at a cost of approximately ( in 2011) each; 3,225 were launched. SS General Hans Kammler, who as anengineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considerin ...
had constructed several concentration camps including Auschwitz, had a reputation for brutality and had originated the idea of using concentration camp prisoners as slave laborers in the rocket program. More people died manufacturing the V-2 than were killed by its deployment.
The V-2 consumed a third of Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
's fuel alcohol production and major portions of other critical technologies: to distil the fuel alcohol for one V-2 launch required 30 tonnes of potatoes at a time when food was becoming scarce. Due to a lack of explosives, some warheads were simply filled in with concrete, using the kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acce ...
alone for destruction, and sometimes the warhead contained photographic propaganda of German citizens who had died in Allied bombings.
The psychological effect of the V-2 was considerable, as the V-2, traveling faster than the speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled per unit of time by a sound wave as it propagates through an elastic medium. At , the speed of sound in air is about , or one kilometre in or one mile in . It depends strongly on temperature as we ...
, gave no warning before impact (unlike bombing planes or the V-1 Flying Bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buzz bomb or doodlebug and in Germany ...
, which made a characteristic buzzing sound). There was no effective defence and no risk of pilot or crew casualties. An example of the impression it made is in the reaction of American pilot and future nuclear strategist and Congressional aide William Liscum Borden, who in November 1944 while returning from a nighttime mission over Holland saw a V-2 in flight on its way to strike London: "It resembled a meteor, streaming red sparks and whizzing past us as though the aircraft were motionless. I became convinced that it was only a matter of time until rockets would expose the United States to direct, transoceanic attack."
With the war all but lost, regardless of the factory output of conventional weapons, the Nazis resorted to V-weapons as a tenuous last hope to influence the war militarily (hence Antwerp as V-2 target), as an extension of their desire to "punish" their foes and most importantly to give hope to their supporters with their miracle weapon. The V-2 had no effect on the outcome of the war, but it led to the ICBMs
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
, which in turn were used for space exploration.
Unfulfilled plans
A submarine-towed launch platform was tested successfully, making it the prototype forsubmarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead ...
s. The project codename was ("Test stand XII"), sometimes called the rocket U-boat. If deployed, it would have allowed a U-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
to launch V-2 missiles against United States cities, though only with considerable effort (and limited effect).
Hitler, in July 1944 and Speer, in January 1945, made speeches alluding to the scheme, though Germany did not possess the capability to fulfill these threats. These schemes were met by the Americans with Operation Teardrop.
While interned after the war by the British at CSDIC camp 11, Dornberger was recorded saying that he had begged the Führer to stop the V-weapon propaganda, because nothing more could be expected from one ton of explosive. To this Hitler had replied that ''Dornberger'' might not expect more, but ''he'' (Hitler) certainly did.
According to decrypted messages from the Japanese embassy in Germany, twelve dismantled V-2 rockets were shipped to Japan. These left Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectu ...
in August 1944 on the transport U-boats and , which reached Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital city, capital and list of Indonesian cities by population, largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coa ...
in December 1944. A civilian V-2 expert was a passenger on ', bound for Japan in May 1945 when the war ended in Europe. The fate of these V-2 rockets is unknown.
Post-war use
At the end of the war, a race began between the United States and theUSSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
to retrieve as many V-2 rockets and staff as possible. Three hundred rail-car loads of V-2s and parts were captured and shipped to the United States and 126 of the principal designers, including Wernher von Braun and Walter Dornberger, were in American hands. Von Braun, his brother Magnus von Braun, and seven others decided to surrender to the United States military (Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from the former Nazi Germany to the U.S. for government employment after the end of World War ...
) to ensure they were not captured by the advancing Soviets or shot dead by the Nazis to prevent their capture.
After the Nazi defeat, German engineers were moved to the United States, the United Kingdom and the USSR, where they further developed the V-2 rocket for military and civilian purposes. The V-2 rocket also laid the foundation for the liquid fuel missiles and space launchers used later.
Britain
 In October 1945, '' Operation Backfire'' assembled a small number of V-2 missiles and launched three of them from a site in northern Germany. The engineers involved had already agreed to move to the US when the test firings were complete. The Backfire report, published in January 1946, contains extensive technical documentation of the rocket, including all support procedures, tailored vehicles and fuel composition.
In 1946, the
In October 1945, '' Operation Backfire'' assembled a small number of V-2 missiles and launched three of them from a site in northern Germany. The engineers involved had already agreed to move to the US when the test firings were complete. The Backfire report, published in January 1946, contains extensive technical documentation of the rocket, including all support procedures, tailored vehicles and fuel composition.
In 1946, the British Interplanetary Society
The British Interplanetary Society (BIS), founded in Liverpool in 1933 by Philip E. Cleator, is the oldest existing space advocacy organisation in the world. Its aim is exclusively to support and promote astronautics and space exploration.
S ...
proposed an enlarged man-carrying version of the V-2, called Megaroc. It could have enabled sub-orbital spaceflight similar to, but at least a decade earlier than, the Mercury-Redstone
The Mercury-Redstone Launch Vehicle, designed for NASA's Project Mercury, was the first American crewed space booster. It was used for six sub-orbital Mercury flights from 1960–1961; culminating with the launch of the first, and 11 weeks ...
flights of 1961.
United States

Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip was a secret United States intelligence program in which more than 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians were taken from the former Nazi Germany to the U.S. for government employment after the end of World War ...
recruited German engineers and Special Mission V-2 transported the captured V-2 parts to the United States. At the close of the Second World War, over 300 rail cars filled with V-2 engines, fuselage
The fuselage (; from the French ''fuselé'' "spindle-shaped") is an aircraft's main body section. It holds crew, passengers, or cargo. In single-engine aircraft, it will usually contain an engine as well, although in some amphibious aircraft t ...
s, propellant tanks, gyroscopes, and associated equipment were brought to the railyards in Las Cruces, New Mexico, so they could be placed on trucks and driven to the White Sands Proving Grounds
White Sands Missile Range (WSMR) is a United States Army military testing area and firing range located in the US state of New Mexico. The range was originally established as the White Sands Proving Ground on 9July 1945. White Sands National Pa ...
, also in New Mexico.
In addition to V-2 hardware, the U.S. Government delivered German mechanization equations for the V-2 guidance, navigation, and control systems, as well as for advanced development concept vehicles, to U.S. defence contractors for analysis. In the 1950s some of these documents were useful to U.S. contractors in developing direction cosine matrix transformations and other inertial navigation architecture concepts that were applied to early U.S. programs such as the Atlas and Minuteman guidance systems as well as the Navy's Subs Inertial Navigation System.
A committee was formed with military and civilian scientists to review payload proposals for the reassembled V-2 rockets. This led to an eclectic array of experiments that flew on V-2s and paved the way for American manned space exploration. Devices were sent aloft to sample the air at all levels to determine atmospheric pressures and to see what gases were present. Other instruments measured the level of cosmic radiation
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our ow ...
.
 Only 68 percent of the V-2 trials were considered successful. A supposed V-2 launched on 29 May 1947 landed near Juarez, Mexico and was actually a Hermes B-1 vehicle.
The U.S. Navy attempted to launch a German V-2 rocket at sea—one test launch from the aircraft carrier USS ''Midway'' was performed on 6 September 1947 as part of the Navy's Operation Sandy. The test launch was a partial success; the V-2 went off the pad but splashed down in the ocean only some from the carrier. The launch setup on the Midway's deck is notable in that it used foldaway arms to prevent the missile from falling over. The arms pulled away just after the engine ignited, releasing the missile. The setup may look similar to the R-7 launch procedure but in the case of the R-7 the trusses hold the full weight of the rocket, rather than just reacting to side forces.
The PGM-11 Redstone rocket is a direct descendant of the V-2.
Only 68 percent of the V-2 trials were considered successful. A supposed V-2 launched on 29 May 1947 landed near Juarez, Mexico and was actually a Hermes B-1 vehicle.
The U.S. Navy attempted to launch a German V-2 rocket at sea—one test launch from the aircraft carrier USS ''Midway'' was performed on 6 September 1947 as part of the Navy's Operation Sandy. The test launch was a partial success; the V-2 went off the pad but splashed down in the ocean only some from the carrier. The launch setup on the Midway's deck is notable in that it used foldaway arms to prevent the missile from falling over. The arms pulled away just after the engine ignited, releasing the missile. The setup may look similar to the R-7 launch procedure but in the case of the R-7 the trusses hold the full weight of the rocket, rather than just reacting to side forces.
The PGM-11 Redstone rocket is a direct descendant of the V-2.
USSR
TheUSSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
also captured a number of V-2s and staff, letting them stay in Germany for a time. The first work contracts were signed in the middle of 1945. In October 1946 (as part of Operation Osoaviakhim) they were obliged to move to Branch 1 of NII-88 on Gorodomlya Island in Lake Seliger where Helmut Gröttrup headed up a group of 150 engineers. In October 1947, a group of German scientists supported the USSR in launching rebuilt V-2s in Kapustin Yar. The German team was indirectly overseen by Sergei Korolev, the "chief designer" of the Soviet rocketry program.
The first Soviet missile was the R-1, a duplicate of the V-2 completely manufactured in Soviet Union, which was first launched in October 1948. From 1947 until the end of 1950, the German team elaborated concepts and improvements for extended payload and range under the projects G-1, G-2 and G-4. The German team had to remain on Gorodomlya island until as late as 1952 and 1953. In parallel, Soviet work was focused on larger missiles, the R-2 and R-5, based on further developing the V-2 technology with using ideas of the German concept studies. Details of Soviet achievements were unknown to the German team and completely underestimated by Western intelligence until, in November 1957, the Sputnik 1 satellite was successfully launched to orbit by the Sputnik rocket based on R-7, the world's first intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapo ...
.
In the autumn of 1945, the group led by M. Tikhonravov K. and N. G. Chernyshov at NII-4 rocket artillery institute of the USSR Academy of Sciences developed on their own initiative the first stratospheric rocket project. VR-190 called for vertical flight of two pilots to an altitude of 200 km using captured German V-2 rockets.
China
The first Chinese Dongfeng missile, the DF-1 was a licensed copy of the Soviet R-2.Surviving V-2 examples and components
 At least 20 V-2s still existed in 2014.
At least 20 V-2s still existed in 2014.
Australia
* One at the Australian War Memorial, Canberra, including a complete '' Meillerwagen'' transporter. The rocket has the most complete set of guidance components of all surviving A4s. The is the most complete of the three examples known to exist. Another A4 was on display at the RAAF Museum at Point Cook outside Melbourne. Both rockets now reside in Canberra.Netherlands
* One example, partly skeletonized, is in the collection of theNationaal Militair Museum
The Nationaal Militair Museum (NMM) is a military museum in Soesterberg, Netherlands. It focuses on the history of the Dutch Armed Forces with emphasis on the Royal Netherlands Army and the Royal Netherlands Air Force. The Stichting Koninklijke De ...
. In this collection are also a launching table and some loose parts, as well as the remains of a V-2 that crashed in The Hague immediately after launch.
Poland
* Several large components, like hydrogen peroxide tank and reaction chamber, the propellant turbopump and the HWK rocket engine chamber (partly cut-out) are displayed at the Polish Aviation Museum in Kraków * A reconstruction of a V-2 missile containing multiple original recovered parts is on display at the Armia Krajowa Museum in Kraków.France
* One engine at inToulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
.
* V-2 display including engine, parts, rocket body and many documents and photographs relating to the development and use at La Coupole museum, Wizernes, Pas de Calais.
* One rocket body no engine, one complete engine, one lower engine section and one wrecked engine on display at ''La Coupole'' museum
* One engine complete with steering pallets, feed lines and tank bottoms, plus one cut-out thrust chamber and one cut-out turbopump at the Snecma (Space Engines Div.) museum in Vernon
* One complete rocket in WWII wing of the Musée de l'Armée (Army Museum) in Paris.
Germany
* One engine at theDeutsches Museum
The Deutsches Museum (''German Museum'', officially (English: ''German Museum of Masterpieces of Science and Technology'')) in Munich, Germany, is the world's largest museum of science and technology, with about 28,000 exhibited objects from ...
in Munich
Munich ( ; german: München ; bar, Minga ) is the capital and most populous city of the German state of Bavaria. With a population of 1,558,395 inhabitants as of 31 July 2020, it is the third-largest city in Germany, after Berlin and ...
(In fact at the out-station of the Deutsches Museum at Schleissheim).
* One engine at the German Museum of Technology in Berlin.
* One engine at the Deutsches Historisches Museum in Berlin.
* One rusty engine in the original V-2 underground production facilities at the Dora-Mittelbau concentration camp memorial site.
* One rusty engine in Buchenwald concentration camp
* One replica was constructed for the Historical and Technical Information Centre in Peenemünde,The Peenemünde replica incorporates many original components along with re-manufactured ones and was put together by a group that included Reinhold Krüger, who worked as an apprentice at Peenemünde during the war. where it is displayed near what remains of the factory where it was built.
United Kingdom
 * One at the
* One at the Science Museum
A science museum is a museum devoted primarily to science. Older science museums tended to concentrate on static displays of objects related to natural history, paleontology, geology, industry and industrial machinery, etc. Modern trends in ...
, London.
* One, on loan from Cranfield University, at the Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military ...
, London.
* The RAF Museum has two rockets, one of which is displayed at its Cosford site. The Museum also owns a , a , a Strabo crane, and a firing table with towing dolly.
* One at the Royal Engineers Museum in Chatham, Kent
Chatham ( ) is a town located within the Medway unitary authority in the ceremonial county of Kent, England. The town forms a conurbation with neighbouring towns Gillingham, Rochester, Strood and Rainham.
The town developed around Chatham ...
.
* A propulsion unit (minus injectors) is in Norfolk and Suffolk Aviation Museum near Bungay
* A complete turbo-pump is at Solway Aviation Museum, Carlisle Airport as part of the Blue Streak Rocket exhibition.
* The venturi segment of one discovered in April 2012 was donated to the Harwich Sailing Club after they found it buried in a mudflat.
* Fuel combustion chamber recovered from the sea near Clacton at the East Essex Aviation Museum, St Oysth
* A gyroscope unit is on display at the National Space Centre in Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
.
* A turbo pump unit on display at the National Space Centre in Leicester.
* A steam generating chamber on display at the National Space Centre in Leicester.
United States
; Complete missiles * One at theFlying Heritage Collection
The Flying Heritage & Combat Armor Museum is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization dedicated to the display and preservation of rare military aircraft, tanks and other military equipment. The plan is for the museum to reopen in 2023.
On rotation in t ...
, Everett, Washington
* One at the National Museum of the United States Air Force, including complete , Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County, Ohio, Greene County. The 2020 United S ...
.
* One (chessboard-painted) at the Cosmosphere
Cosmosphere is a space museum and STEM education center in Hutchinson, Kansas, United States. It was previously known as the Kansas Cosmosphere. The museum houses over 13,000 spaceflight artifacts—the largest combined collection of US and R ...
in Hutchinson, Kansas.
* One at the National Air and Space Museum, Washington, D.C.
* One at the Fort Bliss
Fort Bliss is a United States Army post in New Mexico and Texas, with its headquarters in El Paso, Texas. Named in honor of William Wallace Smith Bliss, LTC William Bliss (1815–1853), a mathematics professor who was the son-in-law of President ...
Air Defense Museum, El Paso, Texas
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the ...
.
* One (yellow and black) at Missile Park, White Sands Missile Range in White Sands, New Mexico
White Sands is a census-designated place (CDP) in Doña Ana County, New Mexico, United States. It consists of the main residential area on the White Sands Missile Range. As of the 2010 census the population of the CDP was 1,651. It is part of ...
.The White Sands Missile Range exhibit is Mittelwerk rocket #FZ04/20919 captured during Special Mission V-2 and is painted with a yellow and black paint scheme resembling that of the first V-2 launched at WSMR on 16 April 1946.
* One at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in ...
.
* One at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in ...
.
; Components
* One engine at the Stafford Air & Space Museum in Weatherford, Oklahoma.
* One engine at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center in Huntsville, Alabama
Huntsville is a city in Madison County, Limestone County, and Morgan County, Alabama, United States. It is the county seat of Madison County. Located in the Appalachian region of northern Alabama, Huntsville is the most populous city in ...
.
* Two engines at the National Museum of the United States Air Force''National Museum of the United States Air Force''. Retrieved: 3 January 2017.
See also
*V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb (german: Vergeltungswaffe 1 "Vengeance Weapon 1") was an early cruise missile. Its official Reich Aviation Ministry () designation was Fi 103. It was also known to the Allies as the buzz bomb or doodlebug and in Germany ...
* V-3 cannon
Notes
References
* 24,000 fighters could have been produced instead of the inaccurate V-weapons. * * (Alternately: ''Impact: An Operational History of Germany's V Weapons in World War II''.) Staplehurst, Kent: Spellmount Publishers. . Da Capo Press; Reprint edition, 2003: . * * * *Further reading
* Dungan, Tracy D. (2005). ''V-2: A Combat History of the First Ballistic Missile''. Westholme Publishing. . * Hall, Charlie (2022). 'Flying Gas Mains': Rumour, Secrecy, and Morale during the V-2 Bombardment of Britain', ''Twentieth Century British History'', 33:1, pp. 52-79. * Huzel, Dieter K. (ca. 1965). ''Peenemünde to Canaveral''. Prentice Hall Inc. * Piszkiewicz, Dennis (1995). ''The Nazi Rocketeers: Dreams of Space and Crimes of War''. Westport, Conn.: Praeger. .External links
"The German A4 Rocket (Main Title)"
Information Film of Operation Backfire from IWM
* ttps://books.google.com/books?id=miQDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA124 '"Chute Saves Rockets Secrets" September 1947, ''
Popular Science
''Popular Science'' (also known as ''PopSci'') is an American digital magazine carrying popular science content, which refers to articles for the general reader on science and technology subjects. ''Popular Science'' has won over 58 awards, incl ...
'' article on US use of V-2 for scientific research
Reconstruction, restoration & refurbishment of a V-2 rocket
spherical panoramas of the process and milestones.
Hermann Ludewig Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
Files of Hermann Ludewig, Deputy of Design Chief and later Chief of Acceptance and Inspection on the V-2 program {{authority control * . 1944 in Germany 1944 in military history 1944 in science German inventions of the Nazi period Operation Crossbow Operation Paperclip Peenemünde Army Research Center and Airfield Rockets and missiles Short-range ballistic missiles Space programme of Germany Weapons and ammunition introduced in 1944 Wernher von Braun World War II guided missiles of Germany