Uriankhai on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
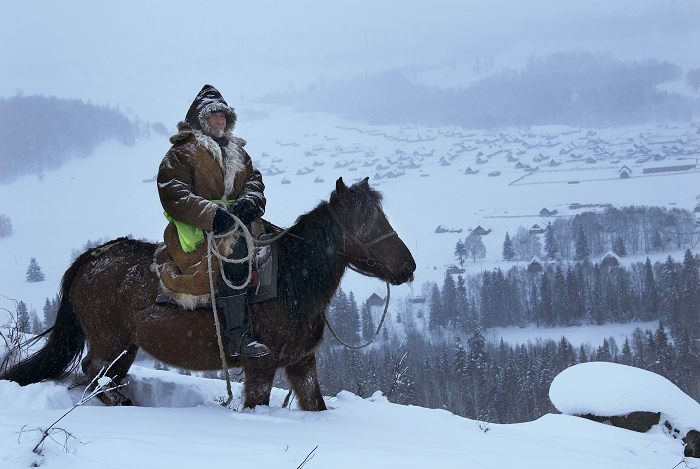

 Uriankhai ( traditional Mongolian: , Mongolian Cyrillic: урианхай; sah, урааҥхай; zh, t=烏梁海, s=乌梁海, p=Wūliánghǎi), Uriankhan (, урианхан) or Uriankhat (, урианхад), is a term of address applied by the
Uriankhai ( traditional Mongolian: , Mongolian Cyrillic: урианхай; sah, урааҥхай; zh, t=烏梁海, s=乌梁海, p=Wūliánghǎi), Uriankhan (, урианхан) or Uriankhat (, урианхад), is a term of address applied by the



 Uriankhai ( traditional Mongolian: , Mongolian Cyrillic: урианхай; sah, урааҥхай; zh, t=烏梁海, s=乌梁海, p=Wūliánghǎi), Uriankhan (, урианхан) or Uriankhat (, урианхад), is a term of address applied by the
Uriankhai ( traditional Mongolian: , Mongolian Cyrillic: урианхай; sah, урааҥхай; zh, t=烏梁海, s=乌梁海, p=Wūliánghǎi), Uriankhan (, урианхан) or Uriankhat (, урианхад), is a term of address applied by the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
to a group of forest peoples of the North, who include the Turkic-speaking Tuvans and Yakuts, while sometimes it is also applied to the Mongolian-speaking Altai Uriankhai. The Uriankhai included the western forest Uriankhai tribe and the transbaikal Uriankhai tribe, with the former recorded in Chinese sources as 兀良哈 (pinyin
Hanyu Pinyin (), often shortened to just pinyin, is the official romanization system for Standard Mandarin Chinese in China, and to some extent, in Singapore and Malaysia. It is often used to teach Mandarin, normally written in Chinese fo ...
: ''Wùliánghā'').
History
The name "Uriankhai' means "uria" (motto, war motto) andkhan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
(lord) in Mongolian. The Mongols applied the name to all the forest peoples and, later, to Tuvans. They were classified by the Mongols as Darligin Mongols.
At the beginning of the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), the Uriankhai were located in central Mongolia.
In 13th century Yuan China, Rashid-al-Din Hamadani described the Forest Uriyankhai as extremely isolated Siberian forest people living in birch bark
Birch bark or birchbark is the bark of several Eurasian and North American birch trees of the genus ''Betula''.
The strong and water-resistant cardboard-like bark can be easily cut, bent, and sewn, which has made it a valuable building, craftin ...
tents and hunting on skis. Despite the similarity in name to the famous Uriyankhan clan of the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member ...
, Rashid states that they had no connection.C.P.Atwood ''Encyclopedia of Mongolia and the Mongol Empire'', 2004 p.9 During the Ming dynasty, the Jurchens were known among the Chinese as "forest people" (using the Jurchen word, ''Woji''), and this connotation later transferred to the Chinese rendering of Uriankhai, ''Wulianghai''.
In the mid-14th century, they lived in Liaoyang in Northeast China
Northeast China or Northeastern China () is a geographical region of China, which is often referred to as "Manchuria" or "Inner Manchuria" by surrounding countries and the West. It usually corresponds specifically to the three provinces east of ...
. In 1375, Naghachu Naghachu ( mn, Naγaču, script=Latn; ; d. 1388), also written as Nahacu, was an ethnic Mongol leader and general of the Northern Yuan in Manchuria, which was under Liaoyang province of the former Yuan dynasty. Originally a Yuan official, he had w ...
, Uriankhai leader of the Mongol-led Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later Ji ...
in Liaoyang, invaded the Liaodong Peninsula to restore the Mongols to power. Although he continued to hold southern Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym " Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East (Outer M ...
, the Ming military campaign against Naghachu ended with his surrender in 1388. After the rebellion of the northern Uriankhai people, they were conquered by Dayan Khan in 1538 and mostly annexed by the northern Khalkha
The Khalkha ( Mongolian: mn, Халх, Halh, , zh, 喀爾喀) have been the largest subgroup of Mongol people in modern Mongolia since the 15th century. The Khalkha, together with Chahars, Ordos and Tumed, were directly ruled by Borjigin k ...
. Batmunkh Dayan Khan dissolved Uriankhai tumen.
The second group of Uriankhai (Uriankhai of the Khentii Mountains) lived in central Mongolia and they started moving to the Altai Mountains in the beginning of the 16th century. Some groups migrated from the Khentii Mountains to Khövsgöl Province during the course of the Northern Yuan dynasty
The Northern Yuan () was a dynastic regime ruled by the Mongol Borjigin clan based in the Mongolian Plateau. It existed as a rump state after the collapse of the Yuan dynasty in 1368 and lasted until its conquest by the Jurchen-led Later Ji ...
(1368-1635).
By the early 17th century the term Uriankhai was a general Mongolian term for all the dispersed bands to the northwest, whether Samoyedic, Turkic, or Mongol in origin. In 1757 the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
organized its far northern frontier into a series of Uriankhai banners: the Khövsgöl Nuur Uriankhai, Tannu Uriankhai
Tannu Uriankhai ( tyv, Таңды Урянхай, ; mn, Тагна Урианхай, Tagna Urianhai, ; ) is a historical region of the Mongol Empire (and its principal successor, the Yuan dynasty) and, later, the Qing dynasty. The territory ...
; Kemchik, Salchak, and Tozhu (all Tuvans); and Altai people. Tuvans in Mongolia are called Monchoogo Uriankhai (cf. Tuvan ''Monchak'' < Kazakh ''monshak'' "necklace") by Mongolians. Another group of Uriankhai in Mongolia (in Bayan-Ölgii and Khovd Provinces) are called Altai Uriankhai. These were apparently attached to the Oirats. A third group of Mongolian Uriankhai were one of the 6 tumens of Dayan Khan in Eastern Mongolia. These last two Uriankhai groups are said to be descendants of the Uriankhan tribe from which came Jelme and his more famous cousin Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''Sübügätäi'' or ''Sübü'ätäi''; Modern Mongolian: Сүбээдэй, ''Sübeedei''. ; ; c. 1175–1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan. He directe ...
. The clan names of the Altai Uriankhai, Khövsgöl Nuur Uriankhai and Tuvans are different. There are no Turkic or Samoyedic clans among the Altai or Khövsgöl Uriankhais.
A variation of the name, Uraŋxai Sakha, was an old name for the Yakuts. Russian Pavel Nebolsin documented the ''Urankhu'' clan of Volga Kalmyks in the 1850s. The existence of the Uriankhai was documented by the Koreans, who called them by the borrowed name Orangkae (, "savages"), especially in context of their attacks against the Siniticized world in the 14th and 15th centuries.
Some Uriankhais still live in the Khentii Mountains.
The Taowen, Huligai, and Wodolian Jurchen tribes lived in the area of Heilongjiang in Yilan during the Yuan dynasty when it was part of Liaoyang province and governed as a circuit. These tribes became the Jianzhou Jurchens in the Ming dynasty and the Taowen and Wodolian were mostly real Jurchens. In the Jin dynasty, the Jin Jurchens did not regard themselves as the same ethnicity as the Hurka people who became the Huligai. Uriangqa was used as a name in the 1300s by Jurchen migrants in Korea from Ilantumen because the Uriangqa influenced the people at Ilantumen. Bokujiang, Tuowulian, Woduolian, Huligai, Taowan separately made up 10,000 households and were the divisions used by the Yuan dynasty to govern the people along the Wusuli river and Songhua area.
Notable people
*Aju
Aju (or Achu; Khalkha Mongolian: ; ) (1227–1287) was a general and chancellor of the Mongol Empire and the Yuan dynasty. He was from the Jarchud clan of the Mongol Uriankhai. His father was Yuan dynasty general Uriyangkhadai and his grandfather ...
* Jelme
*Naghachu Naghachu ( mn, Naγaču, script=Latn; ; d. 1388), also written as Nahacu, was an ethnic Mongol leader and general of the Northern Yuan in Manchuria, which was under Liaoyang province of the former Yuan dynasty. Originally a Yuan official, he had w ...
*Subutai
Subutai (Classical Mongolian: ''Sübügätäi'' or ''Sübü'ätäi''; Modern Mongolian: Сүбээдэй, ''Sübeedei''. ; ; c. 1175–1248) was a Mongol general and the primary military strategist of Genghis Khan and Ögedei Khan. He directe ...
* Uriyangkhadai
Notes