Unicorn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since
 Ctesias got his information while living in
Ctesias got his information while living in

 One traditional method of hunting unicorns involved entrapment by a virgin.
In one of his notebooks
One traditional method of hunting unicorns involved entrapment by a virgin.
In one of his notebooks
Zapolyia siedmiogrodzki2.png, Arms of John, King of Hungary (16th century)
Roxburghshire arms .png, Arms of the County of Roxburgh, Scotland
Blason ville fr SaintLo (Manche).svg, Arms of Saint-Lô,
Unicorns as supporters:
Licorne Edimbourg Scotland.JPG, Scottish unicorn, flag and shield carved at Holyrood Palace, Edinburgh
Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom.svg, Royal arms of
 By the beginning of the 21st Century, unicorns became a queer icon, second only to the rainbow flag, symbolizing queerness. The
By the beginning of the 21st Century, unicorns became a queer icon, second only to the rainbow flag, symbolizing queerness. The

 An animal called the '' re'em'' ( he, רְאֵם) is mentioned in several places in the
An animal called the '' re'em'' ( he, רְאֵם) is mentioned in several places in the
 The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since
The unicorn is a legendary creature that has been described since antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
as a beast with a single large, pointed, spiraling horn projecting from its forehead.
In European literature and art, the unicorn has for the last thousand years or so been depicted as a white horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
-like or goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
-like animal with a long straight horn with spiralling grooves, cloven hooves, and sometimes a goat's beard. In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
, it was commonly described as an extremely wild woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with trees, or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunlight and limited shade (see ...
creature, a symbol of purity and grace, which could be captured only by a virgin. In encyclopedias, its horn was described as having the power to render poisoned water potable and to heal sickness. In medieval and Renaissance times, the tusk of the narwhal was sometimes sold as a unicorn horn.
A bovine type of unicorn is thought by some scholars to have been depicted in seals of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
Indus Valley civilization, the interpretation remaining controversial. An equine form of the unicorn was mentioned by the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
in accounts of natural history by various writers, including Ctesias, Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
, Pliny the Younger, Aelian and Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
. The Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
also describes an animal, the re'em, which some translations render as ''unicorn''.
The unicorn continues to hold a place in popular culture. It is often used as a symbol of fantasy or rarity.
History
Indus Valley civilization
A creature with a single horn, conventionally called a unicorn, is the most common image on the soapstone stamp seals of theBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
Indus Valley civilization ("IVC"), from the centuries around 2000 BC. It has a body more like a cow than a horse, and a curved horn that goes forward, then up at the tip. The mysterious feature depicted coming down from the front of the back is usually shown; it may represent a harness or other covering. Typically the unicorn faces a vertical object with at least two stages; this is variously described as a "ritual offering stand", an incense burner, or a manger. The animal is always in profile on Indus seals, but the theory that it represents animals with two horns, one hiding the other, is disproved by a (much smaller) number of small terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based unglazed or glazed ceramic where the fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, and architecture, terra ...
unicorns, probably toys, and the profile depictions of bulls, where both horns are clearly shown. It is thought that the unicorn was the symbol of a powerful "clan or merchant community", but may also have had some religious significance.
In South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
the unicorn is only seen during the IVC period — it disappears in South Asian art ever since. Jonathan Mark Kenoyer notes the IVC unicorn to not have any "direct connection" with later unicorn motifs observed in other parts of world; nonetheless it remains possible that the IVC unicorn had contributed to later myths of fantastical one-horned creatures in West Asia.
Classical antiquity
Unicorns are not found inGreek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities o ...
, but rather in the accounts of natural history, for Greek writers of natural history were convinced of the reality of unicorns, which they believed lived in India, a distant and fabulous realm for them. The earliest description is from Ctesias, who in his book '' Indika'' ("On India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
") described them as wild ass The wild asses (''Asinus'') are a subgenus of single toed grazing ungulates. Its species are:
*African wild ass ''Equus africanus''
**Nubian wild ass ''Equus africanus africanus'' (likely ancestor of the domestic donkey)
**Somali wild ass ''Equus a ...
es, fleet of foot, having a horn a cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding ...
and a half () in length, and colored white, red and black. Unicorn meat was said to be too bitter to eat.
 Ctesias got his information while living in
Ctesias got his information while living in Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Unicorns on a relief sculpture have been found at the ancient Persian capital of Persepolis in Iran. Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
must be following Ctesias when he mentions two one-horned animals, the oryx
''Oryx'' is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes. Their pelage is pale with contrasting dark markings in the face and on the legs, and their long horns are almost straight. The exception is the scimitar oryx, which ...
(a kind of antelope) and the so-called "Indian ass" (ἰνδικὸς ὄνος).
Antigonus of Carystus also wrote about the one-horned "Indian ass".
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called " Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could s ...
says that in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
there were one-horned horses with stag-like heads.
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
mentions the oryx and an Indian ox (perhaps a Greater one-horned rhinoceros) as one-horned beasts, as well as "a very fierce animal called the monoceros which has the head of the stag, the feet of the elephant
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantida ...
, and the tail of the boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The species is ...
, while the rest of the body is like that of the horse; it makes a deep lowing noise, and has a single black horn, which projects from the middle of its forehead, two cubits [] in length." In ''On the Nature of Animals'' (''Περὶ Ζῴων Ἰδιότητος'', ''De natura animalium''), Aelian, quoting Ctesias, adds that India produces also a one-horned horse (iii. 41; iv. 52), and says (xvi. 20) that the ''monoceros
Monoceros ( Greek: Μονόκερως, "unicorn") is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century Dutch cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the nort ...
'' ( el, μονόκερως) was sometimes called ''cartazonos'' ( el, καρτάζωνος), which may be a form of the Arabic '' karkadann'', meaning "rhinoceros
A rhinoceros (; ; ), commonly abbreviated to rhino, is a member of any of the five extant species (or numerous extinct species) of odd-toed ungulates in the family Rhinocerotidae. (It can also refer to a member of any of the extinct specie ...
".
Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes ( grc-x-koine, Κοσμᾶς Ἰνδικοπλεύστης, lit=Cosmas who sailed to India; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a Greek merchant and later hermit from Alexandria of Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who ma ...
, a merchant of Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
who lived in the 6th century, made a voyage to India and subsequently wrote works on cosmography. He gives a description of a unicorn based on four brass figures in the palace of the King of Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
. He states, from report, that "it is impossible to take this ferocious beast alive; and that all its strength lies in its horn. When it finds itself pursued and in danger of capture, it throws itself from a precipice, and turns so aptly in falling, that it receives all the shock upon the horn, and so escapes safe and sound".
Middle Ages and Renaissance

Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
knowledge of the fabulous beast stemmed from biblical
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of ...
and ancient sources, and the creature was variously represented as a kind of wild ass The wild asses (''Asinus'') are a subgenus of single toed grazing ungulates. Its species are:
*African wild ass ''Equus africanus''
**Nubian wild ass ''Equus africanus africanus'' (likely ancestor of the domestic donkey)
**Somali wild ass ''Equus a ...
, goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
, or horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
.
The predecessor of the medieval bestiary
A bestiary (from ''bestiarum vocabulum'') is a compendium of beasts. Originating in the ancient world, bestiaries were made popular in the Middle Ages in illustrated volumes that described various animals and even rocks. The natural history ...
, compiled in Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
and known as ''Physiologus
The ''Physiologus'' () is a didactic Christian text written or compiled in Greek by an unknown author, in Alexandria; its composition has been traditionally dated to the 2nd century AD by readers who saw parallels with writings of Clement of A ...
'' (''Φυσιολόγος''), popularized an elaborate allegory in which a unicorn, trapped by a maiden (representing the Virgin Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
), stood for the Incarnation
Incarnation literally means ''embodied in flesh'' or ''taking on flesh''. It refers to the conception and the embodiment of a deity or spirit in some earthly form or the appearance of a god as a human. If capitalized, it is the union of divinit ...
. As soon as the unicorn sees her, it lays its head on her lap and falls asleep. This became a basic emblematic tag that underlies medieval notions of the unicorn, justifying its appearance in both secular and religious art. The unicorn is often shown hunted, raising parallels both with vulnerable virgins and sometimes the Passion of Christ. The myths refer to a beast with one horn that can only be tamed by a virgin; subsequently, some writers translated this into an allegory for Christ's relationship with the Virgin Mary.
The unicorn also figured in courtly terms: for some 13th-century French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
authors such as Thibaut of Champagne and Richard de Fournival
Richard de Fournival or Richart de Fornival (1201 – ?1260) was a medieval philosopher and trouvère perhaps best known for the '' Bestiaire d'amour'' ("The Bestiary of Love").
Life
Richard de Fournival was born in Amiens on October 10, 1201. ...
, the lover is attracted to his lady as the unicorn is to the virgin. With the rise of humanism
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
, the unicorn also acquired more orthodox secular meanings, emblematic of chaste love and faithful marriage. It plays this role in Petrarch
Francesco Petrarca (; 20 July 1304 – 18/19 July 1374), commonly anglicized as Petrarch (), was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.
Petrarch's rediscovery of Cicero's letters is often credited ...
's ''Triumph of Chastity'', and on the reverse of Piero della Francesca's portrait of Battista Strozzi, paired with that of her husband Federico da Montefeltro (painted 1472–74), Bianca's triumphal car is drawn by a pair of unicorns.
However, when the unicorn appears in the medieval legend of '' Barlaam and Josaphat'', ultimately derived from the life of the Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism.
According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in L ...
, it represents death, as the '' Golden Legend'' explains. Unicorns in religious art largely disappeared after they were condemned by Molanus
Joannes Molanus (1533–1585), often cited simply as Molanus, is the Latinized name of Jan Vermeulen or Van der Meulen, an influential Counter Reformation Catholic theologian of Louvain University, where he was Professor of Theology, and Rector ...
after the Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
.
The unicorn, tamable only by a virgin woman, was well established in medieval lore by the time Marco Polo described them as "scarcely smaller than elephants. They have the hair of a buffalo and feet like an elephant's. They have a single large black horn in the middle of the forehead... They have a head like a wild boar's… They spend their time by preference wallowing in mud and slime. They are very ugly brutes to look at. They are not at all such as we describe them when we relate that they let themselves be captured by virgins, but clean contrary to our notions." It is clear that Marco Polo was describing a rhinoceros.
Alicorn
The horn itself and the substance it was made of was called alicorn, and it was believed that the horn holds magical and medicinal properties. The Danish physician Ole Worm determined in 1638 that the alleged alicorns were the tusks of narwhals. Such beliefs were examined wittily and at length in 1646 by Sir Thomas Browne in his ''Pseudodoxia Epidemica
''Pseudodoxia Epidemica or Enquiries into very many received tenents and commonly presumed truths'', also known simply as ''Pseudodoxia Epidemica'' or ''Vulgar Errors'', is a work by Thomas Browne challenging and refuting the "vulgar" or common ...
''.
False alicorn powder, made from the tusks of narwhals or horns of various animals, was sold in Europe for medicinal purposes as late as 1741. The alicorn was thought to cure many diseases and have the ability to detect poisons, and many physicians would make "cures" and sell them. Cups were made from alicorn for kings and given as a gift; these were usually made of ivory or walrus ivory. Entire horns were very precious in the Middle Ages and were often really the tusks of narwhals.
Entrapment
 One traditional method of hunting unicorns involved entrapment by a virgin.
In one of his notebooks
One traditional method of hunting unicorns involved entrapment by a virgin.
In one of his notebooks Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested on ...
wrote:
The unicorn, through its intemperance and not knowing how to control itself, for the love it bears to fair maidens forgets its ferocity and wildness; and laying aside all fear it will go up to a seated damsel and go to sleep in her lap, and thus the hunters take it.The famous late
Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
series of seven tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven by hand on a loom. Tapestry is weft-faced weaving, in which all the warp threads are hidden in the completed work, unlike most woven textiles, where both the warp and the weft threads ma ...
hangings ''The Hunt of the Unicorn
''The Hunt of the Unicorn'' or the ''Unicorn Tapestries'' (french: La Chasse à la licorne) is a series of seven tapestries made in the South Netherlands around 1495–1505, and now in The Cloisters in New York. They were possibly designed in ...
'' are a high point in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an tapestry manufacture, combining both secular and religious themes. The tapestries now hang in the Cloisters division of the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. In the series, richly dressed noblemen
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
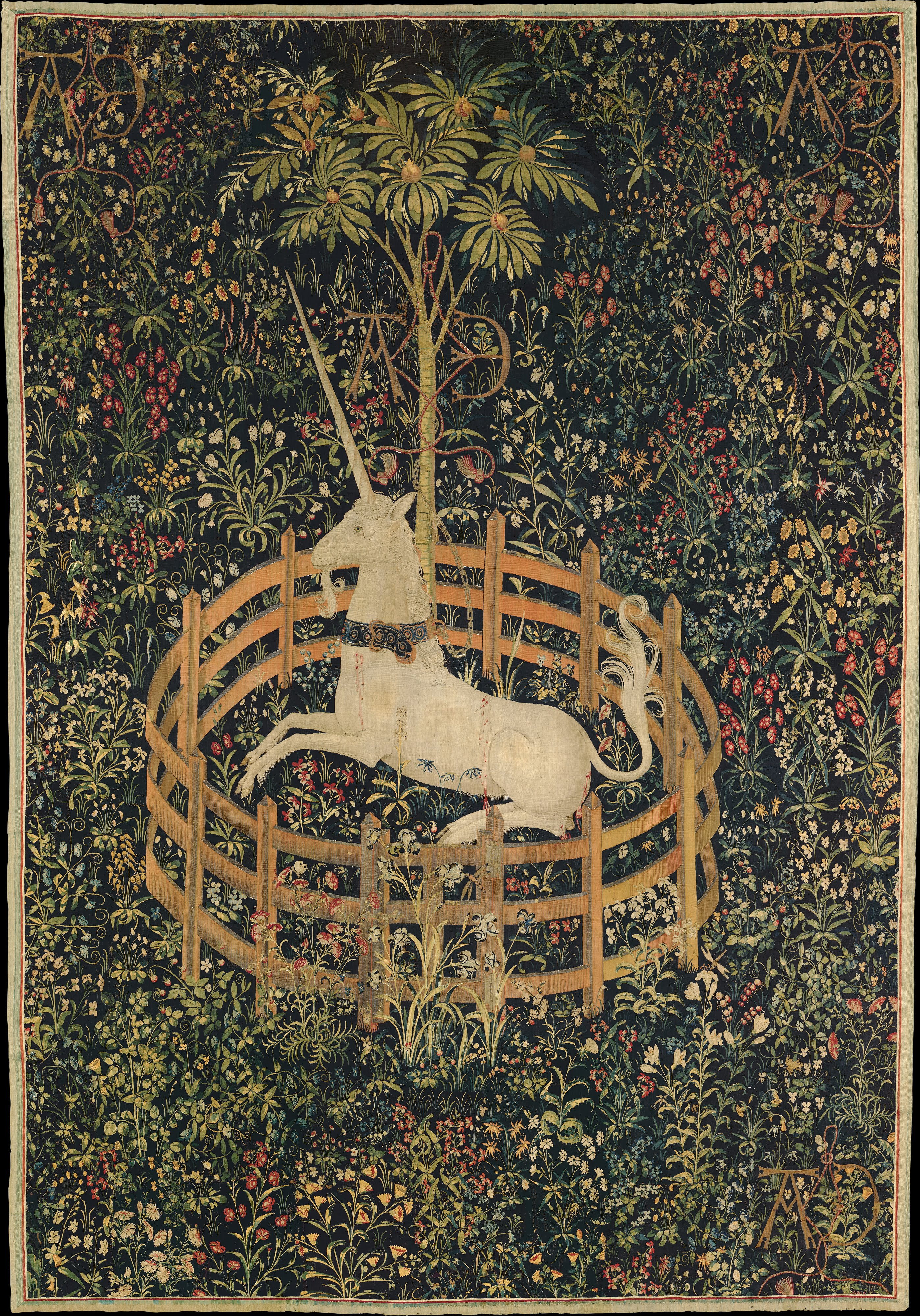
, accompanied by huntsmen and hounds, pursue a unicorn against '' mille-fleur'' backgrounds or settings of buildings and gardens. They bring the animal to bay with the help of a maiden who traps it with her charms, appear to kill it, and bring it back to a castle; in the last and most famous panel, "The Unicorn in Captivity", the unicorn is shown alive again and happy, chained to a pomegranate tree surrounded by a fence, in a field of flowers. Scholars conjecture that the red stains on its flanks are not blood but rather the juice from pomegranates, which were a symbol of fertility. However, the true meaning of the mysterious resurrected unicorn in the last panel is unclear. The series was woven about 1500 in the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
, probably Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
or Liège, for an unknown patron. A set of six engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an in ...
s on the same theme, treated rather differently, were engraved by the French artist Jean Duvet
Jean Duvet (1485 – after 1562) was a French Renaissance goldsmith and engraver, now best known for his engravings. He was the first significant French printmaker. He produced about seventy-three known plates, that convey a highly persona ...
in the 1540s.
Another famous set of six tapestries of '' Dame à la licorne'' ("Lady with the unicorn") in the Musée de Cluny
The Musée de Cluny ("Cluny Museum", ), also known as Musée national du Moyen Âge – Thermes et hôtel de Cluny ("National Museum of the Middle Ages – Cluny thermal baths and mansion"), is a museum of the Middle Ages in Paris, ...
, Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
, were also woven in the Southern Netherlands
The Southern Netherlands, also called the Catholic Netherlands, were the parts of the Low Countries belonging to the Holy Roman Empire which were at first largely controlled by Habsburg Spain (Spanish Netherlands, 1556–1714) and later by the A ...
before 1500, and show the five senses (the gateways to temptation) and finally Love ("A mon seul desir" the legend reads), with unicorns featured in each piece. Facsimiles of these unicorn tapestries were woven for permanent display in Stirling Castle, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, to take the place of a set recorded in the castle in a 16th-century inventory.
A rather rare, late-15th-century, variant depiction of the '' hortus conclusus'' in religious art combined the Annunciation to Mary
The Annunciation (from Latin '), also referred to as the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary, the Annunciation of Our Lady, or the Annunciation of the Lord, is the Christian celebration of the biblical tale of the announcement by the ange ...
with the themes of the ''Hunt of the Unicorn'' and ''Virgin and Unicorn'', so popular in secular art. The unicorn already functioned as a symbol of the Incarnation
Incarnation literally means ''embodied in flesh'' or ''taking on flesh''. It refers to the conception and the embodiment of a deity or spirit in some earthly form or the appearance of a god as a human. If capitalized, it is the union of divinit ...
and whether this meaning is intended in many ''prima facie'' secular depictions can be a difficult matter of scholarly interpretation. There is no such ambiguity in the scenes where the archangel Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity and Islam), Gabriel (); Greek: grc, Γαβριήλ, translit=Gabriḗl, label=none; Latin: ''Gabriel''; Coptic: cop, Ⲅⲁⲃⲣⲓⲏⲗ, translit=Gabriêl, label=none; Amharic: am, ገብ� ...
is shown blowing a horn, as hounds chase the unicorn into the Virgin's arms, and a little Christ Child descends on rays of light from God the Father. The Council of Trent
The Council of Trent ( la, Concilium Tridentinum), held between 1545 and 1563 in Trent (or Trento), now in northern Italy, was the 19th ecumenical council of the Catholic Church. Prompted by the Protestant Reformation, it has been described a ...
finally banned this somewhat over-elaborated, if charming, depiction, partly on the grounds of realism, as no one now believed the unicorn to be a real animal.
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
scholars describe unicorns being captured by a hunter standing in front of a tree, the unicorn goaded into charging; the hunter would step aside the last moment and the unicorn would embed its horn deeply into the tree (See annotations of Timon of Athens, Act 4, scene 3, c. line 341: "wert thou the unicorn, pride and wrath would confound thee and make thine own self the conquest of thy fury".)
Heraldry
Inheraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known bran ...
, a unicorn is often depicted as a horse with a goat's cloven hooves and beard, a lion's tail, and a slender, spiral horn on its forehead (non-equine attributes may be replaced with equine ones, as can be seen from the following gallery). Whether because it was an emblem of the Incarnation or of the fearsome animal passions of raw nature, the unicorn was not widely used in early heraldry, but became popular from the 15th century. Though sometimes shown collared and chained, which may be taken as an indication that it has been tamed or tempered, it is more usually shown collared with a broken chain attached, showing that it has broken free from its bondage.
Scotland
In heraldry the unicorn is best known as a symbol ofScotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
: the unicorn was believed to be the natural enemy of the lion – a symbol that the English royals had adopted around a hundred years before Two unicorns supported the royal arms
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varia ...
of the King of Scots
The monarch of Scotland was the head of state of the Kingdom of Scotland. According to tradition, the first King of Scots was Kenneth I MacAlpin (), who founded the state in 843. Historically, the Kingdom of Scotland is thought to have gro ...
and Duke of Rothesay, and since the 1707 union of England and Scotland, the royal arms of the United Kingdom
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varia ...
have been supported by a unicorn along with an English lion. Two versions of the royal arms exist: that used in Scotland gives more emphasis to the Scottish elements, placing the unicorn on the left and giving it a crown, whereas the version used in England and elsewhere gives the English elements more prominence. John Guillim
John Guillim (c. 1565 – 7 May 1621) of Minsterworth, Gloucestershire, was an antiquarian and officer of arms at the College of Arms in London. He is best remembered for his monumental work on heraldry, ''A Display of Heraldry'', first pu ...
, in his book; ''A Display of Heraldry'', has illustrated the unicorn as a symbol of power, honor and respect.
Golden coins known as the unicorn and half-unicorn, both with a unicorn on the obverse, were used in Scotland in the 15th and 16th century. In the same realm, carved unicorns were often used as finials on the pillars of Mercat crosses, and denoted that the settlement was a royal burgh
A royal burgh () was a type of Scottish burgh which had been founded by, or subsequently granted, a royal charter. Although abolished by law in 1975, the term is still used by many former royal burghs.
Most royal burghs were either created by ...
. Certain noblemen such as the Earl of Kinnoull were given special permission to use the unicorn in their arms, as an augmentation of honour. The crest for Clan Cunningham bears a unicorn head.
Gallery
Unicorns as heraldic charges:France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
Líšnice.svg, Arms of Líšnice, Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
Schwäbisch Gmünd Wappen.svg, Arms of Schwäbisch Gmünd
Schwäbisch Gmünd (, until 1934: Gmünd; Swabian: ''Gmẽẽd'' or ''Gmend'') is a city in the eastern part of the German state of Baden-Württemberg. With a population of around 60,000, the city is the second largest in the Ostalb district and ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
LTU Merkinė COA.svg, Arms of Merkinė
Merkinė is a town in the Dzūkija National Park in Lithuania, located at the confluence of the Merkys, Stangė, and Nemunas rivers. Merkinė is one of the oldest settlements in Lithuania. The first settlers inhabited the confluence of Merkys an ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
Queen Elizabeth II
Elizabeth II (Elizabeth Alexandra Mary; 21 April 1926 – 8 September 2022) was Queen of the United Kingdom and other Commonwealth realms from 6 February 1952 until her death in 2022. She was queen regnant of 32 sovereign states during ...
, as used in England
Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (Scotland).svg, Royal arms of Queen Elizabeth II as used in Scotland
Coat of arms of the President of Lithuania (2).svg, Coat of arms of Lithuania as used by President
Coat of arms of Nova Scotia.svg, Coat of arms of Nova Scotia
A coat typically is an outer garment for the upper body as worn by either gender for warmth or fashion. Coats typically have long sleeves and are open down the front and closing by means of buttons, zippers, hook-and-loop fasteners, toggles, ...
Queer culture
 By the beginning of the 21st Century, unicorns became a queer icon, second only to the rainbow flag, symbolizing queerness. The
By the beginning of the 21st Century, unicorns became a queer icon, second only to the rainbow flag, symbolizing queerness. The rainbow flag
A rainbow flag is a multicolored flag consisting of the colors of the rainbow. The designs differ, but many of the colors are based on the spectral colors of the visible light spectrum.
The LGBT flag introduced in 1978 is the most recognize ...
, created by American artist Gilbert Baker in 1978 as a joyous symbol of the diversity of the queer community, became prominent during the gay rights protests of the 1970s and 1980s. Unicorns, which were intrinsically linked to rainbows since the Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
, became symbol of the queer community.
There is no consensus on how the unicorn became a gay icon. Alice Fisher, an editor of Observer Design magazine, notes that the values of a unicorn – as rare and magical – have resulted in the word being used with various connotations. However, she argues that the Victorian association between rainbows and unicorns has resulted in unicorns becoming a queer icon.
When directly asked, queer people give different answers. There are compelling stories about their own close personal relationship with unicorns. They often relate to one or more of the following aspects: uniqueness, magical quality, elusiveness and gender fluidity.
Queer individuals tend to relate to the unicorn because of their unique sexual orientation and gender identity. A New Orleans journalist, Tracey Anne Duncan, described her connection to unicorn when she watched ''The Last Unicorn'' as a child. In the film, the protagonist believed she was one of a kind throughout her life. Tracey was able to relate to that feeling, even though she didn't really know what "her kind" was at that time.
The unicorn is an imaginary animal that lives in a world of myths and legends. Queer people, whose existence seems to blur the lines between societal norms of masculinity and femininity, may feel like they don't fully belong in this world. It explains their interests in mythical creatures such as unicorns, mermaids, and fairies.
Some argue that the gender fluidity of the unicorn makes it a suitable representation of the LGBT community. In ancient myths, the unicorn is portrayed as male, whereas in the modern times, it is depicted as a female creature.
Similar animals in religion and myth
Biblical

 An animal called the '' re'em'' ( he, רְאֵם) is mentioned in several places in the
An animal called the '' re'em'' ( he, רְאֵם) is mentioned in several places in the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' aurochs (''Bos primigenius''); this view is further supported by the Assyrian cognate word ''rimu,'' which is often used as a metaphor of strength, and is depicted as a powerful, fierce, wild mountain bull with large horns. This animal was often depicted in ancient
 The '' qilin'' (), a creature in
The '' qilin'' (), a creature in
American Museum of Natural History, ''Mythic Creatures'': Unicorns, West and East
Pascal Gratz, ''De Monocerote – Zur Rezeptionsgeschichte des Einhorns''
(PDF, German)
* {{Authority control National symbols of Scotland National symbols of the United Kingdom LGBT symbols Human gender and sexuality symbols
'' aurochs (''Bos primigenius''); this view is further supported by the Assyrian cognate word ''rimu,'' which is often used as a metaphor of strength, and is depicted as a powerful, fierce, wild mountain bull with large horns. This animal was often depicted in ancient
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
n art in profile, with only one horn visible.
The translators of the Authorized King James Version of the Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus ...
(1611) followed the Greek Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond t ...
(''monokeros'') and the Latin Vulgate (''unicornis'') and employed ''unicorn'' to translate ''re'em'', providing a recognizable animal that was proverbial for its untamable nature. The American Standard Version translates this term "wild ox" in each case.
* "God brought them out of Egypt; he hath as it were the strength of an unicorn."—
* "God brought him forth out of Egypt; he hath as it were the strength of an unicorn."—
* "His glory is like the firstling of his bullock, and his horns are like the horns of unicorns: with them he shall push the people together to the ends of the earth."—
* "Will the unicorn be willing to serve thee, or abide by thy crib? Canst thou bind the unicorn with his band in the furrow? or will he harrow the valleys after thee? Wilt thou trust him, because his strength is great? or wilt thou leave thy labour to him? Wilt thou believe him, that he will bring home thy seed, and gather it into thy barn?"—
* "Save me from the lion's mouth; for thou hast heard me from the horns of unicorns."—
* "He maketh them he cedars of Lebanon
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
also to skip like a calf; Lebanon and Sirion like a young unicorn."—
* "But my horn shalt thou exalt like the horn of the unicorn: I shall be anointed with fresh oil."—
* "And the unicorns shall come down with them, and the bullocks with their bulls; and their land shall be soaked with blood, and their dust made fat with fatness."—
The classical Jewish understanding of the Bible did not identify the ''Re'em'' animal as the unicorn. However, some rabbis in the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
debate the proposition that the '' Tahash'' animal (Exodus 25, 26, 35, 36 and 39; Numbers 4; and Ezekiel 16:10) was a domestic, single-horned kosher creature that existed in Moses' time, or that it was similar to the ''keresh'' animal described in Morris Jastrow
Marcus Jastrow (June 5, 1829 – October 13, 1903) was a German-born American Talmudic scholar, most famously known for his authorship of the popular and comprehensive ''Dictionary of the Targumim, Talmud Babli, Talmud Yerushalmi and Midrashic L ...
's Talmudic dictionary as "a kind of antelope, unicorn".
Chinese mythology
 The '' qilin'' (), a creature in
The '' qilin'' (), a creature in Chinese mythology
Chinese mythology () is mythology that has been passed down in oral form or recorded in literature in the geographic area now known as Greater China. Chinese mythology includes many varied myths from regional and cultural traditions.
Much of ...
, is sometimes called "the Chinese unicorn", and some ancient accounts describe a single horn as its defining feature. However, it is more accurately described as a hybrid animal that looks less unicorn than chimera, with the body of a deer, the head of a lion, green scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
and a long forwardly-curved horn. The Japanese version (''kirin'') more closely resembles the Western unicorn, even though it is based on the Chinese ''qilin''. The Quẻ Ly of Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making ...
ese myth, similarly sometimes mistranslated "unicorn" is a symbol of wealth and prosperity that made its first appearance during the Duong Dynasty, about 600 CE, to Emperor Duong Cao To, after a military victory which resulted in his conquest of Tây Nguyên. In November 2012 the History Institute of the DPRK Academy of Social Sciences, as well as the Korea News Service, reported that the Kiringul
Kiringul () is a cave in North Korea said to have been the home of the '' kirin'' (''Qilin'' in Chinese), a mythical chimeric beast that was reputedly ridden by King Dongmyeong of Goguryeo in the 1st century BC.
In November 2012, the state-owne ...
had been found, which is associated with a kirin ridden by King Dongmyeong of Goguryeo
Chumo ( Hangul: 추모, Hanja: 鄒牟), posthumously Chumo the Holy ( Hangul: 추모성왕, Hanja: 鄒牟聖王), was the founding monarch of the kingdom of Goguryeo, and was worshipped as a god-king by the people of Goguryeo and Goryeo. ' ...
.
Beginning in the Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
, the ''qilin'' became associated with giraffes, after Zheng He
Zheng He (; 1371–1433 or 1435) was a Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat, fleet admiral, and court eunuch during China's early Ming dynasty. He was originally born as Ma He in a Muslim family and later adopted the surname Zheng conferr ...
's voyage to East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historica ...
brought a pair of the long-necked animals and introduced them at court in Nanjing
Nanjing (; , Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Map Romanization, alternately romanized as Nanking, is the capital of Jiangsu Provinces of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is a sub-provincial city, a megacity, and t ...
as ''qilin''. The resemblance to the ''qilin'' was noted in the giraffe's ossicones (bony protrusions from the skull resembling horns), graceful movements, and peaceful demeanor.
Shanhaijing (117) also mentioned ''Bo''-horse (), a chimera horse with ox tail, single horn, white body, and its sound like person calling. The creature is lived at Honest-head Mountain. Guo Pu in his ''jiangfu'' said that ''Bo''-horse able to walk on water. Another similar creature also mentioned in Shanhaijing (80) to live in Mount Winding-Centre as ''Bo'' (), but with black tail, tiger's teeth and claws, and also devour leopards and tigers.
See also
* Al-mi'raj (unicorn-like creature in Islamic mythology) *Bestiary
A bestiary (from ''bestiarum vocabulum'') is a compendium of beasts. Originating in the ancient world, bestiaries were made popular in the Middle Ages in illustrated volumes that described various animals and even rocks. The natural history ...
* Elasmotherium (extinct rhinoceros species known as "Siberian unicorn")
* Invisible Pink Unicorn
The Invisible Pink Unicorn (IPU) is the goddess of a parody religion used to satirize theistic beliefs, taking the form of a unicorn that is paradoxically both invisible and pink. She is a rhetorical illustration used by atheists and other reli ...
(a modern satirical religious symbol)
* '' The Last Unicorn'' and its film adaption
A film adaptation is the transfer of a work or story, in whole or in part, to a feature film. Although often considered a type of derivative work, film adaptation has been conceptualized recently by academic scholars such as Robert Stam as a dial ...
* '' Legend (1985 film)
* List of unicorns
* Monoceros
Monoceros ( Greek: Μονόκερως, "unicorn") is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century Dutch cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the nort ...
(constellation)
* Okapi (real animal once known as "African unicorn")
* '' Phoebe and Her Unicorn''
* '' Planet Unicorn''
* Sin-you (mythology)
* "The Unicorn" (song)
* "The Unicorn in the Garden
"The Unicorn in the Garden" is a short story written by James Thurber. One of the most famous of Thurber's humorous modern fables, it first appeared in ''The New Yorker'' on October 21, 1939; and was first collected in his book ''Fables for Our Ti ...
" – short story
* Unicorn Trend (pop-culture phenomenon)
* Winged unicorn
A winged unicorn (cerapter, flying unicorn, pegacorn, or unisus) is a fictional ungulate, typically portrayed as a horse, with wings like Pegasus and the horn of a unicorn. In some literature and media, it has been referred to as an alicorn, a ...
References
*Hall, James, ''A History of Ideas and Images in Italian Art'', 1983, John Murray, London,External links
American Museum of Natural History, ''Mythic Creatures'': Unicorns, West and East
Pascal Gratz, ''De Monocerote – Zur Rezeptionsgeschichte des Einhorns''
(PDF, German)
* {{Authority control National symbols of Scotland National symbols of the United Kingdom LGBT symbols Human gender and sexuality symbols