Ultraviolet light and cancer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The
The
 UVB radiation with a wavelength of 290–315 nanometers penetrates uncovered skin and converts cutaneous 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which in turn becomes vitamin D3. UVB radiation does not penetrate glass, so exposure to sunshine indoors through a window does not produce vitamin D. Time of day, time of year, geographic latitude, ground altitude, cloud cover, smog, skin
UVB radiation with a wavelength of 290–315 nanometers penetrates uncovered skin and converts cutaneous 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which in turn becomes vitamin D3. UVB radiation does not penetrate glass, so exposure to sunshine indoors through a window does not produce vitamin D. Time of day, time of year, geographic latitude, ground altitude, cloud cover, smog, skin  Using satellite data, measurements from the European Space Agency produce similar maps expressed in units of the widely followed
Using satellite data, measurements from the European Space Agency produce similar maps expressed in units of the widely followed  Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is a source of vitamin D. One minimal erythemal dose of sunlight UV radiation provides the equivalent of about 20,000 IU of vitamin D2, taken as an oral supplement. If an adult's arms and legs are exposed to a half minimal erythemal UV radiation, it is the same as taking 3,000 IU of vitamin D3 through an oral supplement. This exposure of 10–15 minutes, on a frequency of two to three times per week, will cause the adult's skin to produce enough vitamin D. It is not necessary to expose the face to the UV, as facial skin provides little vitamin D3. Individuals whose metabolism makes taking oral vitamin D ineffective are able, through exposure to an ultraviolet lamp that emits
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is a source of vitamin D. One minimal erythemal dose of sunlight UV radiation provides the equivalent of about 20,000 IU of vitamin D2, taken as an oral supplement. If an adult's arms and legs are exposed to a half minimal erythemal UV radiation, it is the same as taking 3,000 IU of vitamin D3 through an oral supplement. This exposure of 10–15 minutes, on a frequency of two to three times per week, will cause the adult's skin to produce enough vitamin D. It is not necessary to expose the face to the UV, as facial skin provides little vitamin D3. Individuals whose metabolism makes taking oral vitamin D ineffective are able, through exposure to an ultraviolet lamp that emits

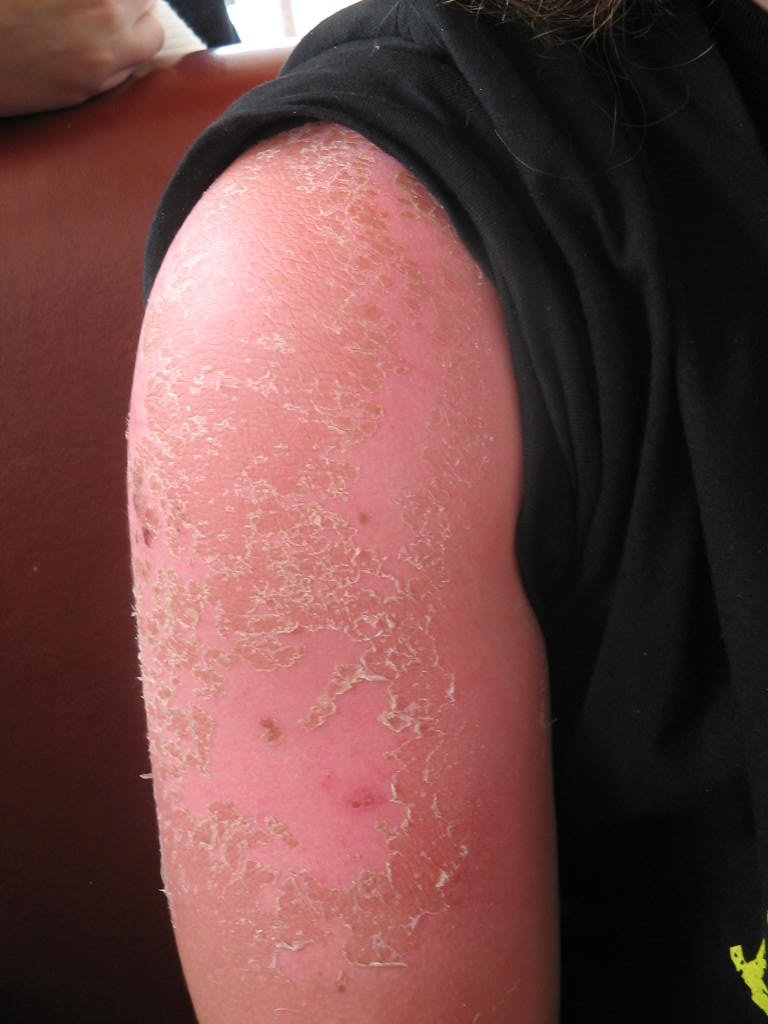 Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation present in sunlight is an environmental human
Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation present in sunlight is an environmental human
Position statement on vitamin D.
November 1, 2008. Short-term over-exposure causes the pain and itching of
 There are currently no recommendations on a safe level of total lifetime sun exposure. According to epidemiologist Robyn Lucas at
There are currently no recommendations on a safe level of total lifetime sun exposure. According to epidemiologist Robyn Lucas at
 The
The ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
in sunlight has both positive and negative health effects, as it is required for the synthesis of vitamin D3 and is a mutagen. A dietary supplement can supply vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
without this mutagenic effect, but supplementation offers limited bioavailability and no synthesis of subdermal nitric oxide. Vitamin D has been suggested as having a wide range of positive health effects, which include strengthening bones and possibly inhibiting the growth of some cancers. UV exposure also has positive effects for endorphin
Endorphins (contracted from endogenous morphine) are chemical signals in the brain that block the perception of pain and increase feelings of wellbeing. They are produced and stored in an area of the brain known as the pituitary gland.
Hist ...
levels, and possibly for protection against multiple sclerosis. Abundant visible light to the eyes gives health benefits through its association with the timing of melatonin synthesis, maintenance of normal and robust circadian rhythms, and reduced risk of seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset, in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year.
Common symptoms include sleeping too much, having li ...
.
Long-term sunlight exposure is known to be associated with the development of some types of skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC) ...
, skin aging
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to ...
, immune suppression, eye diseases such as cataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
and maybe macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, som ...
. Conversely, long-term sun avoidance is associated with increased all-cause mortality and increased mortality risk from cardiovascular disease (CVD) and non-CVD/noncancer related disease.
Since UV rays, and therefore sunlight and sunlamps, are carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive subs ...
s that also have health benefits, a number of public health organizations state that there needs to be a balance between the risks of having too much sunlight or too little. There is a general consensus that sunburn should always be avoided.
Synthesis of vitamin D3
 UVB radiation with a wavelength of 290–315 nanometers penetrates uncovered skin and converts cutaneous 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which in turn becomes vitamin D3. UVB radiation does not penetrate glass, so exposure to sunshine indoors through a window does not produce vitamin D. Time of day, time of year, geographic latitude, ground altitude, cloud cover, smog, skin
UVB radiation with a wavelength of 290–315 nanometers penetrates uncovered skin and converts cutaneous 7-dehydrocholesterol to previtamin D3, which in turn becomes vitamin D3. UVB radiation does not penetrate glass, so exposure to sunshine indoors through a window does not produce vitamin D. Time of day, time of year, geographic latitude, ground altitude, cloud cover, smog, skin melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
content, and sunscreen are among the factors that greatly affect UV intensity and vitamin D synthesis, making it difficult to provide general guidelines. It has been suggested by some researchers, for example, that adequate amounts of vitamin D can be produced with moderate sun exposure to the face, arms and legs, averaging 5–30 minutes twice per week without sunscreen. (The darker the complexion, or the weaker the sunlight, the more minutes of exposure are needed, approximating 25% of the time for minimal sunburn. Vitamin D overdose is impossible from UV exposure; the skin reaches an equilibrium where the vitamin degrades as fast as it is created.) Individuals with limited sun exposure need to include good sources of vitamin D in their diet or take a supplement.
The only way to quantify adequate levels of vitamin D is with a serum 25(OH)D3 (calcifediol
Calcifediol, also known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (abbreviated 25(OH)D3), is a form of vitamin D produced in the liver by hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylas ...
) test. In the United States, serum 25(OH)D3 was below the recommended level for more than a third of white men in a 2005 study, with serum levels even lower in women and in most minorities. This indicates that vitamin D deficiency may be a common problem in the US. Australia and New Zealand have had similar findings, which indicate insufficient protection against rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
for children and osteoporosis for adults.
Over the past several years, levels of ultraviolet radiation have been tracked at over 30 sites across North America as part of the United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
's UVB Monitoring and Research Program at Colorado State University. The first map at right shows levels of UVB radiation in June 2008, expressed in Vitamin D Equivalents.
 Using satellite data, measurements from the European Space Agency produce similar maps expressed in units of the widely followed
Using satellite data, measurements from the European Space Agency produce similar maps expressed in units of the widely followed UV Index
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general ...
, for locations around the world. Effects of UV-radiation at high latitudes, where snow stays on the ground into early summer and the sun then remains at a low position even at its zenith, have been reviewed by Meyer-Rochow.
 Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is a source of vitamin D. One minimal erythemal dose of sunlight UV radiation provides the equivalent of about 20,000 IU of vitamin D2, taken as an oral supplement. If an adult's arms and legs are exposed to a half minimal erythemal UV radiation, it is the same as taking 3,000 IU of vitamin D3 through an oral supplement. This exposure of 10–15 minutes, on a frequency of two to three times per week, will cause the adult's skin to produce enough vitamin D. It is not necessary to expose the face to the UV, as facial skin provides little vitamin D3. Individuals whose metabolism makes taking oral vitamin D ineffective are able, through exposure to an ultraviolet lamp that emits
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun is a source of vitamin D. One minimal erythemal dose of sunlight UV radiation provides the equivalent of about 20,000 IU of vitamin D2, taken as an oral supplement. If an adult's arms and legs are exposed to a half minimal erythemal UV radiation, it is the same as taking 3,000 IU of vitamin D3 through an oral supplement. This exposure of 10–15 minutes, on a frequency of two to three times per week, will cause the adult's skin to produce enough vitamin D. It is not necessary to expose the face to the UV, as facial skin provides little vitamin D3. Individuals whose metabolism makes taking oral vitamin D ineffective are able, through exposure to an ultraviolet lamp that emits UV-B
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
radiation, to achieve a 25 (OH) D blood level.
Three benefits of UV exposure are production of vitamin D, improvement in mood, and increased energy.
UVB induces production of vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
in the skin at rates of up to 1,000 IUs per minute. This vitamin helps to regulate calcium metabolism (vital for the nervous system and bone health), immunity, cell proliferation, insulin secretion, and blood pressure. In low and middle income countries, foods fortified with vitamin D are "practically nonexistent." Most people in the world depend on the sun to get vitamin D, and elderly populations in low UVB countries experience higher rates of cancer.
There are not many foods that naturally have vitamin D. Examples are cod liver oil and oily fish. If people cannot get sunlight, then they will need 1,000 IU of vitamin D per day to stay healthy. A person would have to eat oily fish three or four times per week in order to get enough vitamin D from that food source alone.
People with higher levels of vitamin D tend to have lower rates of diabetes, heart disease, and stroke and tend to have lower blood pressure. However, it has been found that vitamin D supplementation does not improve cardiovascular health or metabolism, so the link with vitamin D must be in part indirect. People who get more sun are generally healthier, and also have higher vitamin D levels. It has been found that ultraviolet radiation (even UVA) produces nitric oxide (NO) in the skin, and nitric oxide can lower blood pressure. High blood pressure increases the risk of stroke and heart disease. Although long-term exposure to ultraviolet contributes to non-melanoma skin cancers that are rarely fatal, it has been found in a Danish study that those who get these cancers were less likely to die during the study, and were much less likely to have a heart attack, than those who did not have these cancers.
People in certain situations, such as people with intellectual disabilities and neurodevelopmental disorders who stay inside most of the time have low vitamin D levels. Getting enough vitamin D can help stave off "autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular disease, many types of cancer, dementia, types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, and respiratory tract infections."
Fetuses and children who do not get enough vitamin D can result in "growth retardation and skeletal deformities."
Lower prevalence of multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is least prevalent in the sunniest regions. Exposure to the ultraviolet-B radiation of sunlight appears to be most important and this may operate via vitamin D synthesis.Risks to skin

carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive subs ...
. The toxic effects of UV from natural sunlight and therapeutic artificial lamps are a major concern for human health. The major acute effects of UV irradiation on normal human skin comprise sunburn inflammation erythema
Erythema (from the Greek , meaning red) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not asso ...
, tanning
Tanning may refer to:
*Tanning (leather), treating animal skins to produce leather
*Sun tanning, using the sun to darken pale skin
**Indoor tanning, the use of artificial light in place of the sun
**Sunless tanning, application of a stain or dye t ...
, and local or systemic immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reacti ...
. The most deadly form, malignant melanoma, is mostly caused by indirect DNA damage from UVA radiation. This can be seen from the absence of a direct UV signature mutation in 92% of all melanoma. UVC is the highest-energy, most-dangerous type of ultraviolet radiation, and causes adverse effects that can variously be mutagenic or carcinogenic.
Despite the importance of the sun to vitamin D synthesis, it is prudent to limit the exposure of skin to UV radiation from sunlight and from tanning bed
Indoor tanning involves using a device that emits ultraviolet radiation to produce a cosmetic tan. Typically found in tanning salons, gyms, spas, hotels, and sporting facilities, and less often in private residences, the most common device is a ho ...
s. According to the National Toxicology Program Report on Carcinogens from the US Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
, broad-spectrum UV radiation is a carcinogen whose DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA d ...
is thought to contribute to most of the estimated 1.5 million skin cancers and the 8,000 deaths due to metastatic
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, ...
melanoma that occur annually in the United States. The use of sunbeds is reported by the World Health Organization to be responsible for over 450,000 cases of non-melanoma skin cancer and over 10,000 cases of melanoma every year in the U.S., Europe, as well as Australia. Lifetime cumulative UV exposure to skin is also responsible for significant age-associated dryness, wrinkling, elastin and collagen damage, freckling, IGH, age spots and other cosmetic changes. The American Academy of Dermatology advises that photoprotective measures be taken, including the use of sunscreen, whenever one is exposed to the sun.American Academy of DermatologyPosition statement on vitamin D.
November 1, 2008. Short-term over-exposure causes the pain and itching of
sunburn
Sunburn is a form of radiation burn that affects living tissue, such as skin, that results from an overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, usually from the Sun. Common symptoms in humans and animals include: red or reddish skin that is h ...
, which in extreme cases can produce more-severe effects like blistering.
Several countries (such as Australia) provide public forecasts of UV irradiation in the form of the UV Index
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general ...
. The index can be used as a guide to the public of dangers from over-exposure to sunlight, especially around noon, when direct sunlight is at its most intense.
Benefits of optic exposure
Light to the eyes, primarily blue-wavelength light, is important for the entrainment and maintenance of robust circadian rhythms. Exposure to sunlight in the morning is particularly effective; it leads to earlier melatonin onset in the evening and makes it easier to fall asleep. Bright morning light has been shown to be effective againstinsomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder in which people have trouble sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low energy, ...
, premenstrual syndrome and seasonal affective disorder
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a mood disorder subset, in which people who have normal mental health throughout most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year.
Common symptoms include sleeping too much, having li ...
(SAD).
Effects on eyes
Prolonged optical exposure to sunlight, especially intense ultraviolet light, may be linked to corticalcataracts
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble w ...
, and high levels of visible light is maybe linked to macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, som ...
.
However, significant daily exposure to bright light may be necessary for children to avoid myopia (nearsightedness).
Short-term over-exposure can cause snow blindness
Photokeratitis or ultraviolet keratitis is a painful eye condition caused by exposure of insufficiently protected eyes to the ultraviolet (UV) rays from either natural (e.g. intense sunlight) or artificial (e.g. the electric arc during welding) ...
, which is analogous to sunburn of the cornea, or can cause solar retinopathy, which is long-lasting retinal damage and vision impairment from sungazing
Sungazing is the dangerous practice of looking directly into the Sun. It is sometimes done as part of a spiritual or religious practice, most often near dawn or dusk. The human eye is very sensitive, and exposure to direct sunlight can lead to ...
.
Frequent exposure to the sun can cause yellow non-cancerous bumps on the middle part of the sclera of the eye, called pingueculae. It is most common in younger people, mainly those who spend a lot of their time outdoors and do not protect their eyes from UV rays. To decrease the risk of developing pingueculae, it may be wise to wear sunglasses when outdoors, even on overcast days.
Folate degradation
Blood levels offolate
Folate, also known as vitamin B9 and folacin, is one of the B vitamins. Manufactured folic acid, which is converted into folate by the body, is used as a dietary supplement and in food fortification as it is more stable during processing an ...
, a nutrient vital for fetal development, can be degraded by UV radiation, raising concerns about sun exposure for pregnant women. Lifespan and fertility can be adversely affected for individuals born during peaks of the 11-year solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surfa ...
, possibly because of UV-related folate deficiency
Folate deficiency, also known as vitamin B9 deficiency, is a low level of folate and derivatives in the body. Signs of folate deficiency are often subtle. A low number of red blood cells (anemia) is a late finding in folate deficiency and folate ...
during gestation.
Safe level of sun exposure
According to a 2007 study submitted by theUniversity of Ottawa
The University of Ottawa (french: Université d'Ottawa), often referred to as uOttawa or U of O, is a bilingual public research university in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is located on directly to the northeast of Downtown Ottaw ...
to the US Department of Health and Human Services, there is not enough information to determine a safe level of sun exposure that imposes minimal risk of skin cancer. In addition, there is not yet conclusive evidence on which components of ultraviolet radiation (UVA, UVB, UVC) are actually carcinogenic. UVC is almost completely absorbed by the atmosphere and does not reach the surface in any appreciable quantity. As a result, only the broad-spectrum combination (UVA, UVB, UVC) known as "ultraviolet radiation" is listed as a carcinogen; the components are only "likely to become" known carcinogens. Solar radiation (sunlight) and sunlamps are listed as carcinogens because they contain ultraviolet radiation.
Lifetime sun exposure
 There are currently no recommendations on a safe level of total lifetime sun exposure. According to epidemiologist Robyn Lucas at
There are currently no recommendations on a safe level of total lifetime sun exposure. According to epidemiologist Robyn Lucas at Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public research university located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton encompasses seven teaching and research colleges, in addition to several national academies an ...
, analysis of lifespan versus disease shows that far more lives worldwide could be lost to diseases caused by lack of sunlight than to those caused by too much, and it is inappropriate to recommend total avoidance of sunlight.
Over thousands of years, in many climate zones, genetic selection has helped indigenous human populations adapt toward skin pigmentation levels that provide a healthy level of UV exposure. This largely explains the tendency toward darker-skinned populations in the sunniest tropical environments, and lighter skin tones in less-sunny regions and for those who most need vitamin D for rapid bone growth, specifically children and reproductive-age women. The map to the right illustrates the geographic distribution of skin color for native populations prior to 1940, based on von Luschan's chromatic scale
Von Luschan's chromatic scale (VLS) is a method of classifying skin color. It is also called the von Luschan scale or von Luschan's scale. It is named after its inventor, Felix von Luschan. The equipment consists of 36 opaque glass tiles which ...
. These long-term adaptations for optimal health can be confounded by patterns of food, clothing and shelter, especially at a time when large populations have migrated far from the climates for which their skin was genetically adapted.
See also
*Fluorescent lamps and health
Fluorescent lamps have been suggested to affect human health in various ways.
Flicker effects
New lighting systems have not used magnetic ballasts since the turn of the century, however some older installations still remain. Fluorescent lamps with ...
*Heat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstroke, ...
*Photosensitivity in humans
Light sensitivity or photosensitivity refers to a notable or increased reactivity to light. Apart from vision, human beings have many physiological and psychological responses to light. In rare individuals an atypical response may result in seriou ...
*UV Index
The ultraviolet index, or UV index, is an international standard measurement of the strength of the sunburn-producing ultraviolet (UV) radiation at a particular place and time. It is primarily used in daily and hourly forecasts aimed at the general ...
*High-energy visible light
High-energy visible light (HEV light) is high-frequency, high-energy light in the violet/blue band from 400 to 450 nm in the visible spectrum,
which has a number of biological effects, including those on the eye.
HEV light may be a cause ...
References
{{Health effects ofSun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
Sun tanning
Vitamin D