US Exploring Expedition on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
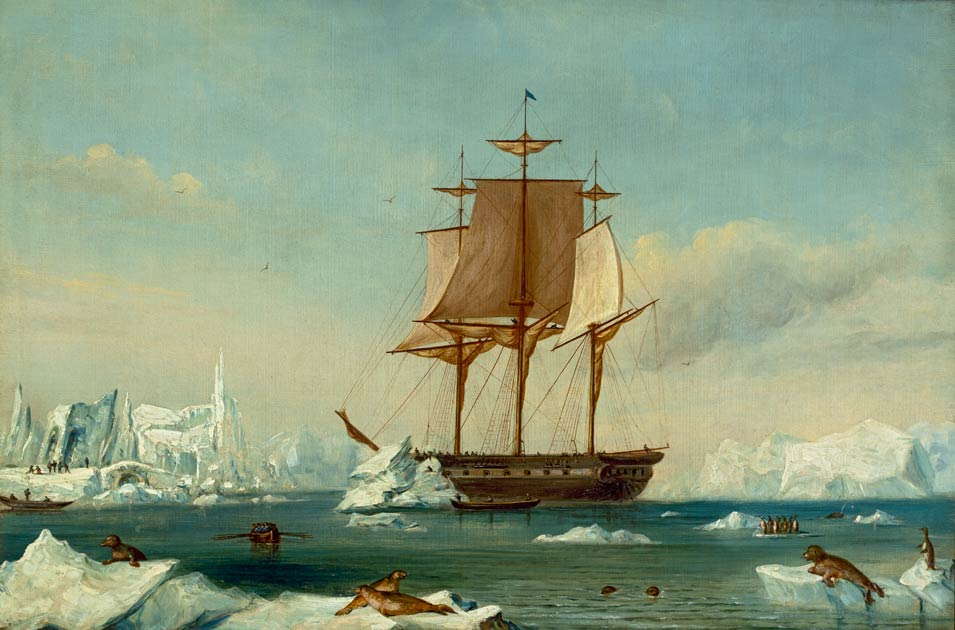 The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the
 The Squadron did not leave Rio de Janeiro until January 6, 1839, arriving at the mouth of the Río Negro on January 25. On February 19, the squadron joined the ''Relief'', ''Flying Fish'', and ''Sea Gull'' in Orange Harbor, Hoste Island, after passing through
The Squadron did not leave Rio de Janeiro until January 6, 1839, arriving at the mouth of the Río Negro on January 25. On February 19, the squadron joined the ''Relief'', ''Flying Fish'', and ''Sea Gull'' in Orange Harbor, Hoste Island, after passing through  The expedition then visited
The expedition then visited
 On August 9, after three months of surveying, the squadron met off Macuata. The ''Vincennes'' and ''Peacock'' proceeded onwards to the Sandwich Islands, with the ''Flying Fish'' and ''Porpoise'' to meet them in
On August 9, after three months of surveying, the squadron met off Macuata. The ''Vincennes'' and ''Peacock'' proceeded onwards to the Sandwich Islands, with the ''Flying Fish'' and ''Porpoise'' to meet them in
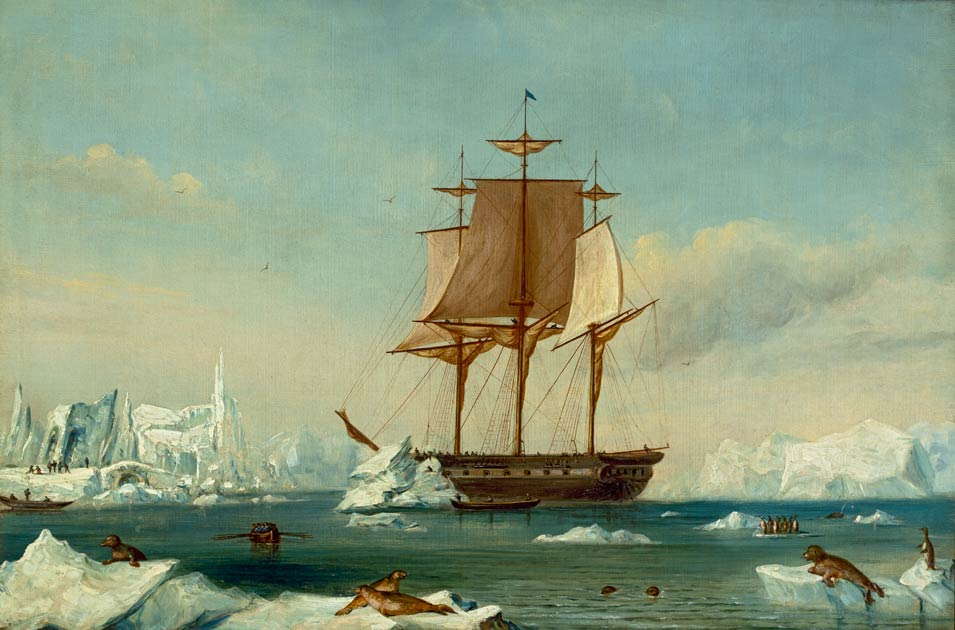 The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby Jones
Thomas ''ap'' Catesby Jones (24 April 1790 – 30 May 1858) was a U.S. Navy commissioned officer during the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War.
Early life and education
Thomas ap Catesby Jones was born on 24 April 1790 in Westm ...
. Funding for the original expedition was requested by President John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States ...
in 1828; however, Congress would not implement funding until eight years later. In May 1836, the oceanic exploration voyage was finally authorized by Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
and created by President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
.
The expedition is sometimes called the U.S. Ex. Ex. for short, or the Wilkes Expedition in honor of its next appointed commanding officer, United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
Lieutenant Charles Wilkes
Charles Wilkes (April 3, 1798 – February 8, 1877) was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842).
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), he commanded ' during the ...
. The expedition was of major importance to the growth of science in the United States, in particular the then-young field of oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynami ...
. During the event, armed conflict between Pacific islanders and the expedition was common and dozens of natives were killed in action, as well as a few Americans.
Preparations
Through the lobbying efforts of Jeremiah N. Reynolds, theUnited States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
passed a resolution on May 21, 1828, requesting President John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States ...
to send a ship to explore the Pacific. Adams was keen on the resolution and ordered his Secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the se ...
to ready a ship, the ''Peacock''. The House voted an appropriation in December but the bill stalled in the US Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and po ...
in February 1829. Then, under President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, Congress passed legislation in 1836 approving the exploration mission. Again, the effort stalled under Secretary of the Navy Mahlon Dickerson
Mahlon Dickerson (April 17, 1770 – October 5, 1853) was a justice of the Supreme Court of New Jersey, the seventh governor of New Jersey, United States Senator from New Jersey, the 10th United States Secretary of the Navy and a United States ...
until President Van Buren assumed office and pushed the effort forward.
Originally, the expedition was under the command Commodore Jones, but he resigned in November 1837, frustrated with all of the procrastination. Secretary of War Joel Roberts Poinsett, in April 1838, then assigned command to Wilkes, after more senior officers refused the command. Wilkes had a reputation for hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the prima ...
, geodesy
Geodesy ( ) is the Earth science of accurately measuring and understanding Earth's figure (geometric shape and size), orientation in space, and gravity. The field also incorporates studies of how these properties change over time and equival ...
, and magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles ...
. Additionally, Wilkes had received mathematics training from Nathaniel Bowditch
Nathaniel Bowditch (March 26, 1773 – March 16, 1838) was an early American mathematician remembered for his work on ocean navigation. He is often credited as the founder of modern maritime navigation; his book '' The New American Practical Navi ...
, triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
methods from Ferdinand Hassler
Ferdinand Rudolph Hassler (October 6, 1770 – November 20, 1843) was a Swiss-American surveyor who is considered the forefather of both the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and the National Institute of Standards and Tech ...
, and geomagnetism from James Renwick.
Personnel included naturalists, botanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek wo ...
s, a mineralogist
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proce ...
, a taxidermist, and a philologist
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics (with especially strong ties to etymology). Philology is also defined ...
. They were carried aboard the sloops-of-war (780 tons), and (650 tons), the brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part ...
(230 tons), the full-rigged ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three s ...
''Relief'', which served as a store-ship, and two schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoo ...
s, ''Sea Gull'' (110 tons) and (96 tons), which served as tenders.
On the afternoon of August 18, 1838, the vessels weighed anchor and set to sea under full sail. By 0730 the next morning, they had passed the lightship off Willoughby Spit and discharged the pilot. The fleet then headed to Madeira
)
, anthem = ( en, "Anthem of the Autonomous Region of Madeira")
, song_type = Regional anthem
, image_map=EU-Portugal_with_Madeira_circled.svg
, map_alt=Location of Madeira
, map_caption=Location of Madeira
, subdivision_type=Sovereign st ...
, taking advantage of the prevailing winds.
Coincidentally, Commodore George C. Read
George Campbell Read (January 9, 1788August 22, 1862) was a United States Naval officer who served on Old Ironsides during the War of 1812 and commanded vessels in actions off the Barbary Coast and India. Read eventually rose to the rank of ...
in command of the East India Squadron
The East India Squadron, or East Indies Squadron, was a squadron of American ships which existed in the nineteenth century, it focused on protecting American interests in the Far East while the Pacific Squadron concentrated on the western coast ...
aboard the flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
frigate USS ''Columbia'', together with the frigate USS ''John Adams'', were at the time in the process of circumnavigating the globe when the ships paused for the second Sumatran punitive expedition, which required no detour.
Ships and personnel
The expedition consisted of nearly 350 men, many of whom were not assigned to any specific vessel. Others served on more than one vessel.Ships
* –sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' en ...
, 780 tons, 18 guns, flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
* – sloop-of-war, 650 tons, 22 guns
* – full-rigged ship
A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel's sail plan with three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. A full-rigged ship is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged. Such vessels also have each mast stepped in three s ...
, 468 tons, 7 guns
* – brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part ...
, 230 tons, 10 guns
* – schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoo ...
, 110 tons, 2 guns
* – schooner, 96 tons, 2 guns
* – brig, 250 tons, 2 guns
Command
*Charles Wilkes
Charles Wilkes (April 3, 1798 – February 8, 1877) was an American naval officer, ship's captain, and explorer. He led the United States Exploring Expedition (1838–1842).
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), he commanded ' during the ...
– Expedition commander and commandant of ''Vincennes''
* Cadwalader Ringgold – Lieutenant commandant of ''Porpoise''
* Andrew K. Long – Lieutenant commandant of ''Relief''
* William L. Hudson – Commandant
Commandant ( or ) is a title often given to the officer in charge of a military (or other uniformed service) training establishment or academy. This usage is common in English-speaking nations. In some countries it may be a military or police ran ...
of ''Peacock''
* Samuel R. Knox – Commandant of ''Flying Fish''
* James W. E. Reid – Commandant of ''Sea Gull''
Naval officers
* James Alden – Lieutenant *Daniel Ammen
Daniel Ammen (May 15, 1820 – July 11, 1898) was a U.S. naval officer during the American Civil War and the postbellum period, as well as a prolific author. His last assignment in the Navy was Chief of the Bureau of Navigation.
Early care ...
- Passed midshipman
* Thomas A. Budd – Lieutenant and cartographer
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an ...
* Simon F. Blunt – Passed midshipman
* Augustus Case – Lieutenant
* George Colvocoresses – Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Af ...
* Edwin De Haven – Acting Master
* Henry Eld – Midshipman
* George F. Emmons – Lieutenant
* Charles Guillou – Assistant surgeon
* William L. Maury – Lieutenant
* William Reynolds – Passed midshipman
* Richard R. Waldron – Purser
A purser is the person on a ship principally responsible for the handling of money on board. On modern merchant ships, the purser is the officer responsible for all administration (including the ship's cargo and passenger manifests) and supply. ...
* Thomas W. Waldron – Captain's clerk
Scientific corps
* Alfred T. Agate – Artist * James Drayton – Artist * William Brackenridge – Assistantbotanist
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek wo ...
* Joseph P. Couthouy – Conchologist
Conchology () is the study of mollusc shells. Conchology is one aspect of malacology, the study of molluscs; however, malacology is the study of molluscs as whole organisms, whereas conchology is confined to the study of their shells. It incl ...
* James D. Dana – Mineralogist
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proce ...
and geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althou ...
* Horatio Hale
Horatio Emmons Hale (May 3, 1817 – December 28, 1896) was an American-Canadian ethnologist, philologist and businessman. He is known for his study of languages as a key for classifying ancient peoples and being able to trace their migrations. ...
– Philologist
Philology () is the study of language in oral and written historical sources; it is the intersection of textual criticism, literary criticism, history, and linguistics (with especially strong ties to etymology). Philology is also defined ...
* Titian Peale – Naturalist
* Charles Pickering – Naturalist
* William Rich – Botanist
History
Expedition
First part
Wilkes was to search for vigias, or shoals, as reported by John Purdy, but failed to corroborate those claims for the locations given. The squadron arrived in the Madeira Islands on September 16, 1838, and Porto Praya on October 6. The ''Peacock'' arrived at Rio de Janeiro on November 21, and the ''Vincennes'' with brigs and schooners on November 24. However, the ''Relief'' did not arrive until the November 27, setting a record for slowness, 100 days. While there, they used Enxados Island in Guanabara Bay for an observatory and naval yard for repair and refitting. The Squadron did not leave Rio de Janeiro until January 6, 1839, arriving at the mouth of the Río Negro on January 25. On February 19, the squadron joined the ''Relief'', ''Flying Fish'', and ''Sea Gull'' in Orange Harbor, Hoste Island, after passing through
The Squadron did not leave Rio de Janeiro until January 6, 1839, arriving at the mouth of the Río Negro on January 25. On February 19, the squadron joined the ''Relief'', ''Flying Fish'', and ''Sea Gull'' in Orange Harbor, Hoste Island, after passing through Le Maire Strait
The Le Maire Strait (''Estrecho de le Maire'') (also the Straits Lemaire) is a sea passage between Isla de los Estados and the eastern extremity of the Argentine portion of Tierra del Fuego.
History
Jacob Le Maire and Willem Schouten discov ...
. While there, the expedition came in contact with the Fuegians. Wilkes sent an expedition south in an attempt to exceed Captain Cook's farthest point south, 71°10'.
The ''Flying Fish'' reached 70° on March 22, in the area about north of Thurston Island
Thurston Island is an ice-covered, glacially dissected island, long, wide and in area, lying a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. It is the third-largest island of Antarctica, after Alexander Island and Berkner Isl ...
, and what is now called Cape Flying Fish
Cape Flying Fish (, also known as Cape Dart) is an ice-covered cape which forms the western extremity of Thurston Island. It was discovered by Richard E. Byrd and members of the US Antarctic Program in a flight from the USS ''Bear'' in Februar ...
, and the Walker Mountains. The squadron joined the ''Peacock'' in Valparaiso on May 10, but the ''Sea Gull'' was reported missing. On June 6, the squadron arrived at San Lorenzo
San Lorenzo is the Italian and Spanish name for Lawrence of Rome, Saint Lawrence, the 3rd-century Christian martyr, and may refer to:
Places Argentina
* San Lorenzo, Santa Fe
* San Lorenzo Department, Chaco
* Monte San Lorenzo, a mountain on t ...
, off Callao
Callao () is a Peruvian seaside city and region on the Pacific Ocean in the Lima metropolitan area. Callao is Peru's chief seaport and home to its main airport, Jorge Chávez International Airport. Callao municipality consists of the whole Cal ...
for repair and provisioning, while Wilkes dispatched the ''Relief'' homewards on June 21. Leaving South America on July 12, the expedition reached Reao
Reao or Natūpe is an atoll in the eastern expanses of the Tuamotu group in French Polynesia. The closest land is Pukarua Atoll, located 48 km to the WNW.
Reao is 24.5 km long and its maximum width is 5 km. The whole length of ...
of the Tuamotu Group on August 13, and Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austra ...
on September 11. They departed Tahiti on October 10.
 The expedition then visited
The expedition then visited Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Australia. In December 1839, the expedition sailed from Sydney into the Antarctic Ocean and reported the discovery of the Antarctic continent on January 16, 1840, when Henry Eld and William Reynolds aboard the ''Peacock'' sighted Eld Peak and Reynolds Peak along the George V Coast
George V Coast () is that portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between Point Alden, at 148°2′E, and Cape Hudson, at 153°45′E.
Portions of this coast were sighted by the US Exploring Expedition in 1840. It was explored by members of t ...
. On the January 19, Reynolds spotted Cape Hudson Mawson Peninsula () is a high (), narrow, ice-covered peninsula on the George V Coast, on the west side of the Slava Ice Shelf, Antarctica, terminating in Cape Hudson. It extends for over in a northwesterly direction. The peninsula was photographed ...
. On January 25, the ''Vincennes'' sighted the mountains behind the Cook Ice Shelf
Cook Ice Shelf is an ice shelf about wide, occupying a deep recession of the coastline between Cape Freshfield and Cape Hudson, to the east of Deakin Bay.
This bay was discovered by the US Exploring Expedition in 1840, and referred to by Wil ...
, similar peaks at Piner Bay on January 30, and had covered of coastline by February 12, from 140° 30' E. to 112° 16' 12"E., when Wilkes acknowledged they had "discovered the Antarctic Continent." Named Wilkes Land
Wilkes Land is a large district of land in eastern Antarctica, formally claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory, though the validity of this claim has been placed for the period of the operation of the Antarctic Treaty ...
, it includes Claire Land, Banzare Land, Sabrina Land, Budd Land
Budd Coast (), part of Wilkes Land, is that portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between the Hatch Islands, at 109°16'E, and Cape Waldron, at 115°33'E. It was discovered in February 1840 by the U.S. Exploring Expedition (1838–42) under ...
, and Knox Land. They charted of Antarctic coastline to a westward goal of 105° E., the edge of Queen Mary Land
Queen Mary Land or the Queen Mary Coast () is the portion of the coast of Antarctica lying between Cape Filchner, in 91° 54' E, and Cape Hordern, at 100° 30' E. It is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory.
It wa ...
, before departing to the north again on February 21.
The ''Porpoise'' came across the French expedition of Jules Dumont d'Urville
Jules Sébastien César Dumont d'Urville (; 23 May 1790 – 8 May 1842) was a French explorer and naval officer who explored the south and western Pacific, Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica. As a botanist and cartographer, he gave his nam ...
on January 30. However, due to a misunderstanding of each other's intentions, the Porpoise and Astrolabe
An astrolabe ( grc, ἀστρολάβος ; ar, ٱلأَسْطُرلاب ; persian, ستارهیاب ) is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclin ...
were unable to communicate. In February 1840, some of the expedition were present at the initial signing of the Treaty of Waitangi in New Zealand. Some of the squadron then proceeded back to Sydney for repairs, while the rest visited the Bay of Islands, before arriving in Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
in April. At Nuku'alofa they met King Josiah (Aleamotu'a), and the George (Taufa'ahau), chief of Ha'apai, before proceeding onwards to Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
on May 4. The ''Porpoise'' surveyed the Low Archipelago, while the ''Vincennes'' and ''Peacock'' proceeded onwards to Ovalau, where they signed a commercial treaty with Tanoa Visawaqa
Ratu Tanoa Visawaqa (pronounced ) (died on 8 December 1852) was a Fijian Chieftain who held the title 5th Vunivalu of Bau. With Adi Savusavu, one of his nine wives, he was the father of Ratu Seru Epenisa Cakobau, who succeeded in unifying Fiji w ...
in Levuka. Edward Belcher's visited Ovalau at the same time. Hudson was able to capture Vendovi, after holding his brothers Cocanauto, Qaraniqio, and Tui Dreketi ( Roko Tui Dreketi or King of Rewa Province) hostage. Vendovi was deemed responsible for the attack against US sailors on Ono Island in 1836. Vendovi was taken back to the US, but died shortly after his arrival in New York. His skull was then added to the expedition collections and put on display in the Patent Office building in Washington, D.C.
In July 1840, two members of the party, Lieutenant Underwood and Wilkes' nephew, Midshipman
A midshipman is an officer of the lowest rank, in the Royal Navy, United States Navy, and many Commonwealth navies. Commonwealth countries which use the rank include Canada (Naval Cadet), Australia, Bangladesh, Namibia, New Zealand, South Af ...
Wilkes Henry, were killed while bartering for food in western Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consis ...
's Malolo
Malolo is an inhabited volcanic island in the Pacific Ocean, near Fiji. Malolo was used as a tribe name in Survivor: Ghost Island. Malolo Island is the largest of the Mamanuca Islands and is home to two villages.
History
Malolo was one of the ...
Island. The cause of this event remains equivocal. Immediately prior to their deaths, the son of the local chief, who was being held as a hostage by the Americans, escaped by jumping out of the boat and running through the shallow water for shore. The Americans fired over his head. According to members of the expedition party on the boat, his escape was intended as a prearranged signal by the Fijians to attack. According to those on shore, the shooting actually precipitated the attack on the ground. The Americans landed sixty sailors to attack the hostile natives. Close to eighty Fijians were killed in the resulting American reprisal and two villages were burned to the ground.
Return route
 On August 9, after three months of surveying, the squadron met off Macuata. The ''Vincennes'' and ''Peacock'' proceeded onwards to the Sandwich Islands, with the ''Flying Fish'' and ''Porpoise'' to meet them in
On August 9, after three months of surveying, the squadron met off Macuata. The ''Vincennes'' and ''Peacock'' proceeded onwards to the Sandwich Islands, with the ''Flying Fish'' and ''Porpoise'' to meet them in Oahu
Oahu () ( Hawaiian: ''Oʻahu'' ()), also known as "The Gathering Place", is the third-largest of the Hawaiian Islands. It is home to roughly one million people—over two-thirds of the population of the U.S. state of Hawaii. The island of O ...
by October. Along the way, Wilkes named the Phoenix Group
Phoenix Group Holdings plc (formerly Pearl Group plc) is a provider of insurance services based in London, England. It is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
History
The company was founded in 185 ...
and made a stop at the Palmyra Atoll, making their group the first scientific expedition in history to visit Palmyra. While in Hawaii, the officers were welcomed by Governor Kekuanaoa, King Kamehameha III
Kamehameha III (born Kauikeaouli) (March 17, 1814 – December 15, 1854) was the third king of the Kingdom of Hawaii from 1825 to 1854. His full Hawaiian name is Keaweaweula Kīwalaō Kauikeaouli Kaleiopapa and then lengthened to Keaweaweula Kī ...
, his aide William Richards, and the journalist James Jackson Jarves
James Jackson Jarves (1818–1888) was an American newspaper editor, and art critic who is remembered above all as the first American art collector to buy Italian primitives and Old Masters.
Life and career
Jarves was the editor of an early wee ...
. The expedition surveyed Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest islan ...
, Oahu, Hawaii, and the peak of Mauna Loa
Mauna Loa ( or ; Hawaiian: ; en, Long Mountain) is one of five volcanoes that form the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The largest subaerial volcano (as opposed to subaqueous volcanoes) in both mass and ...
. The ''Porpoise'' was dispatched in November to survey several of the Tuamotus, including Aratika, Kauehi, Raraka, and Katiu
Katiu, or Taungataki, is an atoll of the central Tuamotu Archipelago in French Polynesia. It is located west of Makemo Atoll's westernmost point. It measures in length with a maximum width of . Its total area, including the lagoon is and a l ...
, before proceeding onwards to Penrhyn Penryn is a Cornish word meaning 'headland' that may refer to:
*Penryn, Cornwall, United Kingdom, a town of about 7,000 on the Penryn River
**Penryn railway station, a station on the Maritime Line between Truro and Falmouth Docks, and serves the t ...
and returning to Oahu on 24 March.
On April 5, 1841, the squadron departed Honolulu, the ''Porpoise'' and ''Vincennes'' for the Pacific Northwest, the ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' to resurvey Samoa, before rejoining the squadron. Along the way, the ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' surveyed Jarvis Island, Enderbury Island
Enderbury Island, also known as Ederbury Island or Guano Island, is a small, uninhabited atoll 63 km ESE of Kanton Island in the Pacific Ocean at . It is about 1 mile (1.6 km) wide and 3 miles (4.8 km) long, with a reef stretchin ...
, the Tokelau Islands, and Fakaofo
Fakaofo, formerly known as Bowditch Island, is a South Pacific Ocean atoll located in the Tokelau Group. The actual land area is only about 3 km2 (1.1 sq mi), consisting of islets on a coral reef surrounding a central lagoon of some 45 ...
. The ''Peacock'' followed this with surveys of the Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northea ...
islands of Nukufetau
Nukufetau is an atoll that is part of the nation of Tuvalu. The atoll was claimed by the US under the Guano Islands Act some time in the 19th century and was ceded in a treaty of friendship concluded in 1979 and coming into force in 1983. It has ...
, Vaitupu, and Nanumanga in March, followed by Tabiteuea in April. Also in April, the ''Peacock'' surveyed the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
of Nonouti
Nonouti is an atoll and district of Kiribati. The atoll is located in the Southern Gilbert Islands, 38 km north of Tabiteuea, and 250 km south of Tarawa. The atoll is the third largest in the Gilbert Islands and is the island where the ...
, Aranuka
Aranuka is an atoll of Kiribati, located just north of the equator, in the Gilbert Islands. It has an area of and a population of 1,057 in 2010. By local tradition, Aranuka is the central island of the Gilbert group.
Geography
Aranuka is a ...
, Maiana
Maiana is an atoll in Kiribati and is one of the Central Gilbert Islands. Maiana is south of the capital island of South Tarawa and has a population of 1,982 . The northern and eastern sides of the atoll are a single island, whilst the western e ...
, Abemama
Abemama (Apamama) is an atoll, one of the Gilberts group in Kiribati, and is located southeast of Tarawa and just north of the Equator. Abemama has an area of and a population of 3,299 . The islets surround a deep lagoon. The eastern part o ...
, Kuria, Tarawa
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
'' After making another search, the man was not found and the natives began arming themselves. Lieutenant Walker returned his force to the ship, to converse with Hudson, who ordered Walker to return to shore and demand the return of the sailor. Walker then reboarded his boats with his landing party and headed to shore. Walker shouted his demand and the natives charged for him, forcing the boats to turn back to the ships. It was decided on the next day that the Americans would bombard the hostiles and land again. While doing this, a force of around 700 Gilbertese warriors opposed the American assault, but were defeated after a long battle. No Americans were hurt, but twelve natives were killed and others were wounded, and two villages were also destroyed. A similar episode occurred two months before in February when the ''Peacock'' and the ''Flying Fish'' briefly bombarded the island of
After making another search, the man was not found and the natives began arming themselves. Lieutenant Walker returned his force to the ship, to converse with Hudson, who ordered Walker to return to shore and demand the return of the sailor. Walker then reboarded his boats with his landing party and headed to shore. Walker shouted his demand and the natives charged for him, forcing the boats to turn back to the ships. It was decided on the next day that the Americans would bombard the hostiles and land again. While doing this, a force of around 700 Gilbertese warriors opposed the American assault, but were defeated after a long battle. No Americans were hurt, but twelve natives were killed and others were wounded, and two villages were also destroyed. A similar episode occurred two months before in February when the ''Peacock'' and the ''Flying Fish'' briefly bombarded the island of  The ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' arrived off Cape Disappointment on July 17. However, the ''Peacock'' went aground while attempting to enter the Columbia River and was soon lost, though with no loss of life. The crew was able to lower six boats and get everyone into Baker's Bay, along with their journals, surveys, the chronometers, and some of Agate's sketches. A one-eyed Indian named George then guided the ''Flying Fish'' into the same bay.
There, the crew set up "Peacockville", assisted by James Birnie of the
The ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' arrived off Cape Disappointment on July 17. However, the ''Peacock'' went aground while attempting to enter the Columbia River and was soon lost, though with no loss of life. The crew was able to lower six boats and get everyone into Baker's Bay, along with their journals, surveys, the chronometers, and some of Agate's sketches. A one-eyed Indian named George then guided the ''Flying Fish'' into the same bay.
There, the crew set up "Peacockville", assisted by James Birnie of the
Alfred Agate Collection
at
US Exploring Expedition
– at
Video of Dr. Adrienne Kaeppler
discussing the
collections from the expedition
Charles L. Erskine's Panorama Lecture
at Dartmouth College Library {{Authority control 1838 in the United States 1839 in Antarctica Artifacts in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution Circumnavigations Exploration of North America Explorers of the United States Global expeditions History of science and technology in the United States Military expeditions of the United States Oceanography Pacific expeditions Pacific Ocean United States Navy in the 19th century
''
Marakei
Marakei is a small atoll in the North Gilbert Islands. It consists of a central lagoon with numerous deep basins, surrounded by two large islands separated by two narrow channels. The atoll covers approximately .
Geography
Marakei's total land ...
, Butaritari, and Makin, before returning to Ohau on June 13. The ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' then left for the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
on June 21.
In April 1841, USS ''Peacock'', under Lieutenant William L. Hudson, and USS ''Flying Fish'', surveyed Drummond's Island, which was named for an American of the expedition. Lieutenant Hudson heard from a member of his crew that a ship had wrecked off the island and her crew massacred by the Gilbertese. A woman and her child were said to be the only survivors, so Hudson decided to land a small force of marines and sailors, under William M. Walker
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of ...
, to search the island. Initially, the natives were peaceful and the Americans were able to explore the island, without results. It was when the party was returning to their ship that Hudson noticed a member of his crew was missing.
 After making another search, the man was not found and the natives began arming themselves. Lieutenant Walker returned his force to the ship, to converse with Hudson, who ordered Walker to return to shore and demand the return of the sailor. Walker then reboarded his boats with his landing party and headed to shore. Walker shouted his demand and the natives charged for him, forcing the boats to turn back to the ships. It was decided on the next day that the Americans would bombard the hostiles and land again. While doing this, a force of around 700 Gilbertese warriors opposed the American assault, but were defeated after a long battle. No Americans were hurt, but twelve natives were killed and others were wounded, and two villages were also destroyed. A similar episode occurred two months before in February when the ''Peacock'' and the ''Flying Fish'' briefly bombarded the island of
After making another search, the man was not found and the natives began arming themselves. Lieutenant Walker returned his force to the ship, to converse with Hudson, who ordered Walker to return to shore and demand the return of the sailor. Walker then reboarded his boats with his landing party and headed to shore. Walker shouted his demand and the natives charged for him, forcing the boats to turn back to the ships. It was decided on the next day that the Americans would bombard the hostiles and land again. While doing this, a force of around 700 Gilbertese warriors opposed the American assault, but were defeated after a long battle. No Americans were hurt, but twelve natives were killed and others were wounded, and two villages were also destroyed. A similar episode occurred two months before in February when the ''Peacock'' and the ''Flying Fish'' briefly bombarded the island of Upolu
Upolu is an island in Samoa, formed by a massive basaltic shield volcano which rises from the seafloor of the western Pacific Ocean. The island is long and in area, making it the second largest of the Samoan Islands by area. With approxi ...
, Samoa following the death of an American merchant sailor on the island.
The ''Vincennes'' and ''Porpoise'' reached Cape Disappointment on April 28, 1841, but then headed north to the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Port Discovery, and Fort Nisqually
Fort Nisqually was an important fur trading and farming post of the Hudson's Bay Company in the Puget Sound area, part of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department. It was located in what is now DuPont, Washington. Today it is a living h ...
, where they were welcomed by William Henry McNeill
William Henry McNeill (7 July 1803 – 4 September 1875) was best known for his 1830 expedition as the captain of the brig ''Llama'' (also spelled ''Lama''), which sailed from Boston, Massachusetts, United States, around Cape Horn, to the Pacific ...
and Alexander Caulfield Anderson. The ''Porpoise'' surveyed the Admiralty Inlet, while boats from the ''Vincennes'' surveyed Hood Canal, and the coast northwards to the Fraser River
The Fraser River is the longest river within British Columbia, Canada, rising at Fraser Pass near Blackrock Mountain in the Rocky Mountains and flowing for , into the Strait of Georgia just south of the City of Vancouver. The river's annual ...
. Wilkes visited Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805–1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approxi ...
, John McLoughlin
John McLoughlin, baptized Jean-Baptiste McLoughlin, (October 19, 1784 – September 3, 1857) was a French-Canadian, later American, Chief Factor and Superintendent of the Columbia District of the Hudson's Bay Company at Fort Vancouver fr ...
at Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of ...
, and William Cannon
William Cannon (March 15, 1809 – March 1, 1865) was an American merchant and politician from Bridgeville, in Sussex County, Delaware. He was a member of the Democratic Party and later the Republican Party, who served in the Delaware General ...
on the Willamette River
The Willamette River ( ) is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward b ...
, while he sent Lt. Johnson on an expedition to Fort Okanogan
Fort Okanogan (also spelled Fort Okanagan) was founded in 1811 on the confluence of the Okanogan and Columbia Rivers as a fur trade outpost. Originally built for John Jacob Astor’s Pacific Fur Company, it was the first American-owned settle ...
, Fort Colvile and Fort Nez Perces, where they met Marcus Whitman. Like his predecessor, British explorer George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are ...
, Wilkes spent a good deal of time near Bainbridge Island
Bainbridge Island is a city and island in Kitsap County, Washington. It is located in Puget Sound. The population was 23,025 at the 2010 census and an estimated 25,298 in 2019, making Bainbridge Island the second largest city in Kitsap County. ...
. He noted the bird-like shape of the harbor at Winslow and named it Eagle Harbor. Continuing his fascination with bird names, he named Bill Point and Wing Point. Port Madison, Washington
The Port Madison Native Reservation is an Indigenous Reservation in the U.S. state of Washington belonging to the Suquamish Tribe, a federally recognized indigenous nation and signatory to the Treaty of Point Elliott of 1855.
Location
The reser ...
and Points Monroe and Jefferson were named in honor of former United States presidents. Port Ludlow was assigned to honor Lieutenant Augustus Ludlow __NOTOC__
Augustus C. Ludlow (1 January 1792 – 13 June 1813) was an officer in the United States Navy during the War of 1812.
Ludlow was born in Newburgh, New York. He was appointed midshipman April 2, 1804, and commissioned lieutenant June 3, 18 ...
, who lost his life during the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It be ...
.
 The ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' arrived off Cape Disappointment on July 17. However, the ''Peacock'' went aground while attempting to enter the Columbia River and was soon lost, though with no loss of life. The crew was able to lower six boats and get everyone into Baker's Bay, along with their journals, surveys, the chronometers, and some of Agate's sketches. A one-eyed Indian named George then guided the ''Flying Fish'' into the same bay.
There, the crew set up "Peacockville", assisted by James Birnie of the
The ''Peacock'' and ''Flying Fish'' arrived off Cape Disappointment on July 17. However, the ''Peacock'' went aground while attempting to enter the Columbia River and was soon lost, though with no loss of life. The crew was able to lower six boats and get everyone into Baker's Bay, along with their journals, surveys, the chronometers, and some of Agate's sketches. A one-eyed Indian named George then guided the ''Flying Fish'' into the same bay.
There, the crew set up "Peacockville", assisted by James Birnie of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
, and the American Methodist Mission at Point Adams. They also traded with the local Clatsop and Chinookan Indians over the next three weeks, while surveying the channel, before journeying to Fort George and a reunion with the rest of the squadron. This prompted Wilkes to send the ''Vincennes'' to San Francisco Bay, while he continued to survey Grays Harbor Grays Harbor is an estuarine bay located north of the mouth of the Columbia River, on the southwest Pacific coast of Washington state, in the United States of America. It is a ria, which formed at the end of the last ice age, when sea levels floo ...
.
From the area of modern-day Portland, Wilkes sent an overland party of 39 southwards, led by Emmons, but guided by Joseph Meek. The group included Agate, Eld, Colvocoresses, Brackenridge, Rich, Peale, Stearns, and Dana, and proceeded along an inland route to Fort Umpqua
Fort Umpqua was a trading post built by the Hudson's Bay Company in the company's Columbia District (or Oregon Country), in what is now the U.S. state of Oregon. It was first established in 1832 and moved and rebuilt in 1836.; online aGoogle Books/ ...
, Mount Shasta
Mount Shasta ( Shasta: ''Waka-nunee-Tuki-wuki''; Karuk: ''Úytaahkoo'') is a potentially active volcano at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California. At an elevation of , it is the second-highest peak in the Cascad ...
, the Sacramento River
The Sacramento River ( es, Río Sacramento) is the principal river of Northern California in the United States and is the largest river in California. Rising in the Klamath Mountains, the river flows south for before reaching the Sacramento� ...
, John Sutter's New Helvetia, and then onwards to San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a large tidal estuary in the U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the big cities of San Francisco, San Jose, and Oakland.
San Francisco Bay drains water f ...
. They departed September 7, and arrived aboard the ''Vincennes'' in Sausalito on October 23, having traveled along the Siskiyou Trail.
Wilkes arrived with the ''Porpoise'' and ''Oregon'', while the ''Flying Fish'' was to rendezvous with the squadron in Honolulu. The squadron surveyed San Francisco and its tributaries, and later produced a map of "Upper California". The expedition then headed back out on October 31, arriving Honolulu on November 17, and departing on November 28. They included a visit to Wake Island
Wake Island ( mh, Ānen Kio, translation=island of the kio flower; also known as Wake Atoll) is a coral atoll in the western Pacific Ocean in the northeastern area of the Micronesia subregion, east of Guam, west of Honolulu, southeast of T ...
, and returned by way of the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, Borneo
Borneo (; id, Kalimantan) is the third-largest island in the world and the largest in Asia. At the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia, in relation to major Indonesian islands, it is located north of Java, west of Sulawesi, and e ...
, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
, and the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
, reaching New York on June 10, 1842.
The expedition was plagued by poor relationships between Wilkes and his subordinate officers throughout. Wilkes' self-proclaimed status as captain and commodore, accompanied by the flying of the requisite pennant and the wearing of a captain's uniform while being commissioned only as a Lieutenant, rankled heavily with other members of the expedition of similar real rank. His apparent mistreatment of many of his subordinates, and indulgence in punishments such as " flogging round the fleet" resulted in a major controversy on his return to America. Wilkes was court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
led on his return, but was acquitted on all charges except that of illegally punishing men in his squadron.
Significance
The Wilkes Expedition played a major role in the development of 19th-century science, particularly in the growth of the American scientific establishment. Many of the species and other items found by the expedition helped form the basis of collections at the newSmithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
.
With the help of the expedition's scientists, derisively called "''clam digger''s" and "''bug catchers''" by navy crew members, 280 islands, mostly in the Pacific, were explored, and over of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
were mapped. Of no less importance, over 60,000 plant and bird specimens were collected. A staggering amount of data and specimens were collected during the expedition, including the seeds of 648 species, which were later traded, planted, and sent throughout the country. Dried specimens were sent to the National Herbarium, now a part of the Smithsonian Institution. There were also 254 live plants, which mostly came from the home stretch of the journey, that were placed in a newly constructed greenhouse in 1850, which later became the United States Botanic Garden.
Alfred Thomas Agate
Alfred Thomas Agate (February 14, 1812 – January 5, 1846) was a noted American artist, painter and miniaturist.
Agate lived in New York from 1831 to 1838. He studied with his brother, Frederick Styles Agate, a portrait and historical painter ...
, engraver and illustrator, created an enduring record of traditional cultures such as the illustrations made of the dress and tattoo patterns of natives of the Ellice Islands (now Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northea ...
).
A collection of artifacts from the expedition also went to the National Institute for the Promotion of Science, a precursor of the Smithsonian Institution. These joined artifacts from American history as the first artifacts in the Smithsonian collection.
Published works
For a short time Wilkes was attached to the Office of Coast Survey, but from 1844 to 1861 he was chiefly engaged in preparing the expedition report. Twenty-eight volumes were planned, but only nineteen were published. Of these, Wilkes wrote the multi-volume ''Narrative of the United States exploring expedition, during 1838, 1839, 1840, 1841, 1842'', ''Hydrography'', and ''Meteorology''. The ''Narrative'' concerns the customs, political and economic conditions of many places then little-known. Other contributions were three reports by James Dwight Dana on ''Zoophytes'', ''Geology'', and ''Crustacea''. In addition to shorter articles and reports, Wilkes published ''Western America, including California and Oregon'', and ''Theory of the Winds''. TheSmithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
digitized the five volume narrative and the accompanying scientific volumes. The mismanagement that plagued the expedition prior to its departure continued after its completion. By June 1848, many of the specimens had been lost or damaged and many remained unidentified. In 1848 Asa Gray
Asa Gray (November 18, 1810 – January 30, 1888) is considered the most important American botanist of the 19th century. His ''Darwiniana'' was considered an important explanation of how religion and science were not necessarily mutually excl ...
was hired to work on the botanical specimens, and published the first volume of the report on botany in 1854, but Wilkes was unable to secure the funding for the second volume.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ** * *External links
Alfred Agate Collection
at
Naval History and Heritage Command
The Naval History and Heritage Command, formerly the Naval Historical Center, is an Echelon II command responsible for the preservation, analysis, and dissemination of U.S. naval history and heritage located at the historic Washington Navy Yard. ...
US Exploring Expedition
– at
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
Libraries Digital Collections
Video of Dr. Adrienne Kaeppler
discussing the
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums and education and research centers, the largest such complex in the world, created by the U.S. government "for the increase and diffusion of knowledge". Found ...
br>Anthropologycollections from the expedition
Charles L. Erskine's Panorama Lecture
at Dartmouth College Library {{Authority control 1838 in the United States 1839 in Antarctica Artifacts in the collection of the Smithsonian Institution Circumnavigations Exploration of North America Explorers of the United States Global expeditions History of science and technology in the United States Military expeditions of the United States Oceanography Pacific expeditions Pacific Ocean United States Navy in the 19th century