USKOK on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
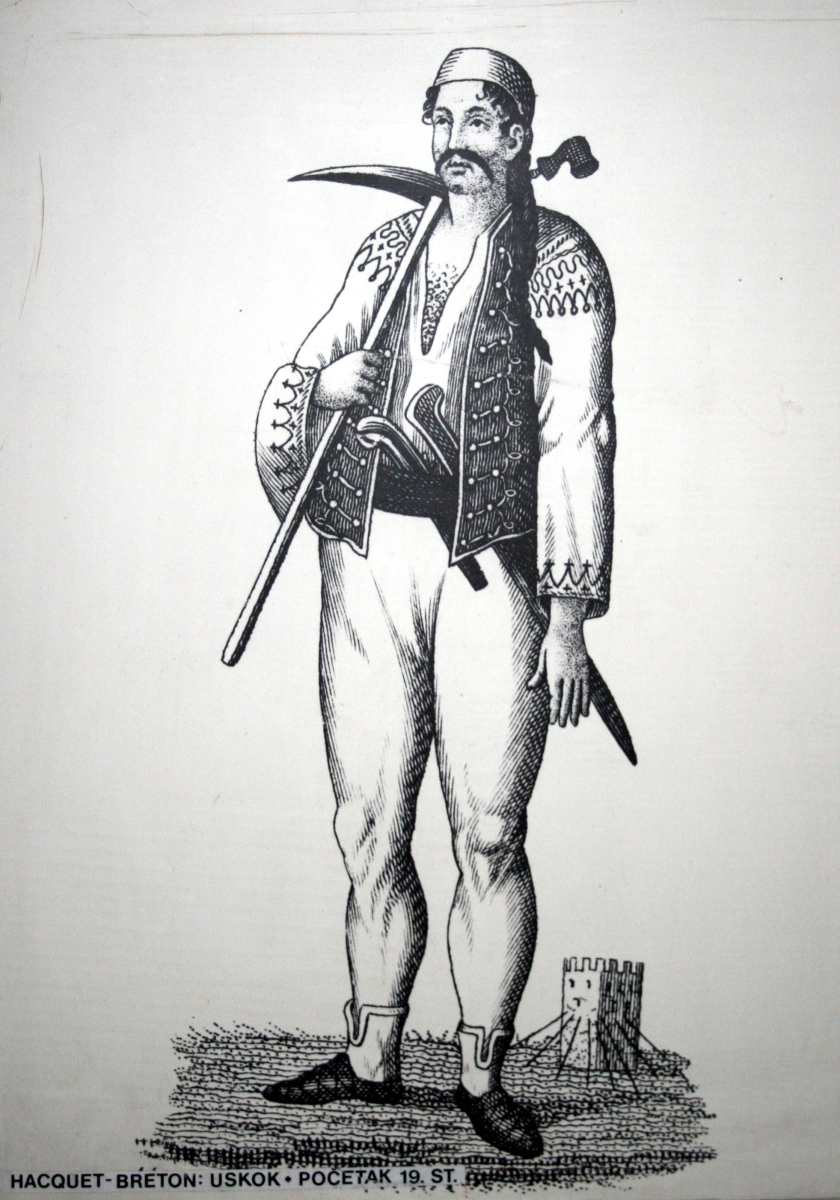
 The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a
The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a
R. W. SETON -WATSON:The southern Slav question and the Habsburg Monarchy page 18
who obtained the Croatian crown in 1527, Kružić and his freebooting Uskoks were a law unto themselves. After Petar Kružić's death, and the lack of water supply, the defenders of Klis finally surrendered to the Ottomans in exchange for their freedom. On March 12, 1537, the town and fortress was given up to the Ottomans, many of the citizens left the town while the Uskoks went to the city of
 Beginning as inland pirates, the Uskoci shortly turned to the seas once realizing the full potential of the geography of Senj. The land was protected by thick forests and mountains while the jagged cliffs near the seas prevented warships from entering. The seas in the Gulf of Quarnero were quite rough, which posed navigational hazards as further protection from their enemies. Uskoks began their attacks upon Turkish ships with boats large enough to hold thirty to fifty men.
After 1540, however, Venice, as mistress of the seas, guaranteed the safety of Ottoman merchant vessels, and provided them with an escort of galleys. The uskoks retaliated by ravaging the Venetian islands of
Beginning as inland pirates, the Uskoci shortly turned to the seas once realizing the full potential of the geography of Senj. The land was protected by thick forests and mountains while the jagged cliffs near the seas prevented warships from entering. The seas in the Gulf of Quarnero were quite rough, which posed navigational hazards as further protection from their enemies. Uskoks began their attacks upon Turkish ships with boats large enough to hold thirty to fifty men.
After 1540, however, Venice, as mistress of the seas, guaranteed the safety of Ottoman merchant vessels, and provided them with an escort of galleys. The uskoks retaliated by ravaging the Venetian islands of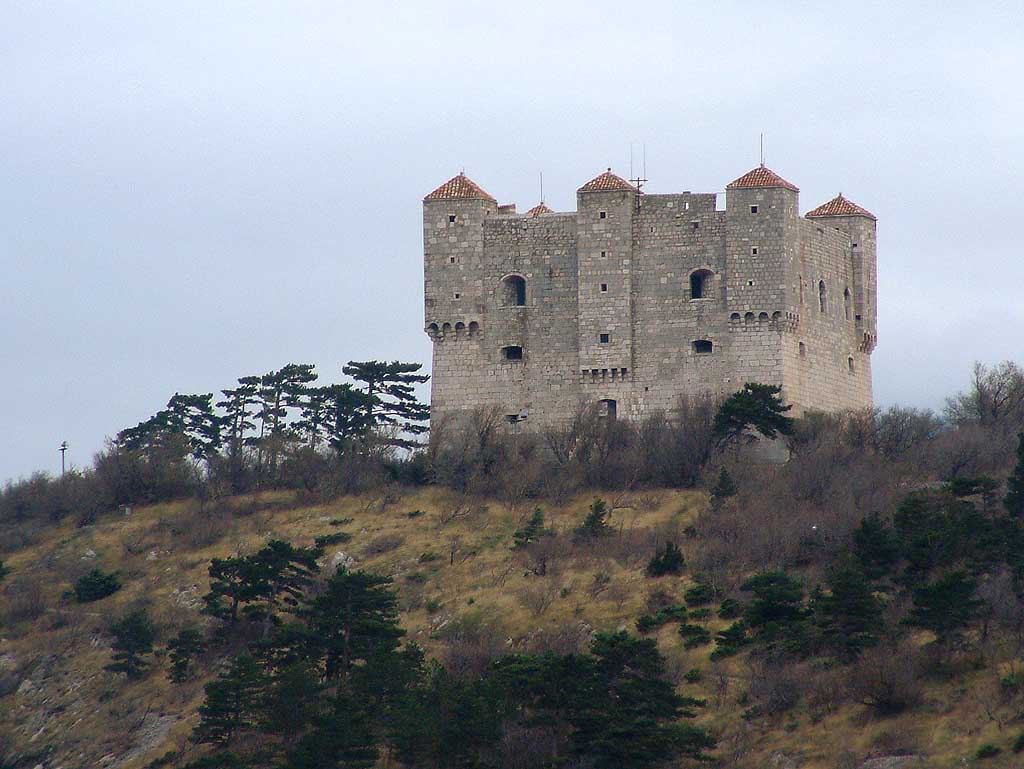  After 1561 the Uskoci attacked Christian shipping in Dubrovnik with numbers never exceeding 2000 men. By 1573 the Uskoks caused considerable concern in Venice with frequent attacks once Venetian attempts of protection had proven to be ineffective. The following years led the reputation of the Uskoks to spread, becoming the resort of refugees and outlaws of all kinds from all nations.
Meanwhile, the corsairs of
After 1561 the Uskoci attacked Christian shipping in Dubrovnik with numbers never exceeding 2000 men. By 1573 the Uskoks caused considerable concern in Venice with frequent attacks once Venetian attempts of protection had proven to be ineffective. The following years led the reputation of the Uskoks to spread, becoming the resort of refugees and outlaws of all kinds from all nations.
Meanwhile, the corsairs of  A raid by the Uskoks upon Istria resulted in an agreement between Venice and Austria, and Count Joseph de Rabatta was appointed to act as commissioner to those in Senj as well as the chief negotiator with the Venetians. Rabatta came to Senj in 1600 with a strong bodyguard detail, and was very energetic. His time ruling over the Uskoks was brutal where many Uskoks were hung or sent to fight in the Turkish war, revealing his favor towards the Venetian side. He soon lost all military support, giving the Uskoks the opportunity to overthrow his rule and was ultimately killed in January 1602, enabling Senj to return to its usual state, with the fugitive Uskoks returning to Senj where they resumed their acts of piracy.
A raid by the Uskoks upon Istria resulted in an agreement between Venice and Austria, and Count Joseph de Rabatta was appointed to act as commissioner to those in Senj as well as the chief negotiator with the Venetians. Rabatta came to Senj in 1600 with a strong bodyguard detail, and was very energetic. His time ruling over the Uskoks was brutal where many Uskoks were hung or sent to fight in the Turkish war, revealing his favor towards the Venetian side. He soon lost all military support, giving the Uskoks the opportunity to overthrow his rule and was ultimately killed in January 1602, enabling Senj to return to its usual state, with the fugitive Uskoks returning to Senj where they resumed their acts of piracy.
 Up until 1611 the Uskoks were relatively undisturbed. Piracy was strictly forbidden at this point but it was tolerated in order to avoid payment of subsidies owed to those of Senj. A Venetian squadron intercepted an Uskok fleet in the spring of 1613 in response to the complaints regarding Uskok activity and, as reported, sixty Uskoks were beheaded with their heads then displayed in St. Mark's Square. In response to this offense the Uskok captured a galley of Venetians, slaughtered the crew, and used the blood of the victims to flavor their bread.
The uskoks would conduct such acts up until 1615 when their piracy went so far as creating an open war between Venice and Austria. Venice, frustrated with the piracy, launched an attack after the Archduke Ferdinand of Styria refused to reprimand the Uskoks. A peace treaty was signed in autumn 1617 which arranged for the Uskoks to be disbanded, as well as their ships and fortresses be destroyed. An agreement between the Habsburgs and Venetians in 1618 expelled the Uskoks from Senj, prompting migrations of Uskok families into the hinterland.
The Venetians nominated Marko Srdanovic Knew of Omis. Marko was born Srdan Kacic but the last name was changed to Srdanovic. This was because the Ottomans had given an order to kill every Kacic of the Omis Pirates.
Up until 1611 the Uskoks were relatively undisturbed. Piracy was strictly forbidden at this point but it was tolerated in order to avoid payment of subsidies owed to those of Senj. A Venetian squadron intercepted an Uskok fleet in the spring of 1613 in response to the complaints regarding Uskok activity and, as reported, sixty Uskoks were beheaded with their heads then displayed in St. Mark's Square. In response to this offense the Uskok captured a galley of Venetians, slaughtered the crew, and used the blood of the victims to flavor their bread.
The uskoks would conduct such acts up until 1615 when their piracy went so far as creating an open war between Venice and Austria. Venice, frustrated with the piracy, launched an attack after the Archduke Ferdinand of Styria refused to reprimand the Uskoks. A peace treaty was signed in autumn 1617 which arranged for the Uskoks to be disbanded, as well as their ships and fortresses be destroyed. An agreement between the Habsburgs and Venetians in 1618 expelled the Uskoks from Senj, prompting migrations of Uskok families into the hinterland.
The Venetians nominated Marko Srdanovic Knew of Omis. Marko was born Srdan Kacic but the last name was changed to Srdanovic. This was because the Ottomans had given an order to kill every Kacic of the Omis Pirates.
 Today, a historical unit of uskoks called ''Kliški uskoci'' ("Uskoks of
Today, a historical unit of uskoks called ''Kliški uskoci'' ("Uskoks of Archduke Karl von Habsburg honored Kliški uskoci
/ref> One Special Forces unit of Special Operations Command of
Historical Unit Kliški uskoci - About Uskoks
* * * {{Authority control Military history of Croatia Military history of the Republic of Venice Piracy in the Mediterranean Military history of Slovenia History of Dalmatia 16th- and 17th-century warrior types Croatia under Habsburg rule Army of the Habsburg Monarchy
 The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a
The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a guerrilla war
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, raids, petty warfare, hit-and-run tactics ...
against the Ottomans, and they formed small units and rowed swift boats. Since the uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual subsidy, they resorted to acts of piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
.
The exploits of the Uskoks contributed to a renewal of war between Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 bridges. The isla ...
and the Ottoman Empire (1571–1573). An extremely curious picture of contemporary manners is presented by the Venetian agents, whose reports on this war resemble a knightly chronicle of the Middle Ages. These chronicles contain information pertaining to single combat
Single combat is a duel between two single warriors which takes place in the context of a battle between two armies.
Instances of single combat are known from Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages. The champions were often combatants who repre ...
s, tournaments and other chivalrous adventures.
Many of these troops served abroad. After a series of incidents that escalated into the Uskok War
The Uskok War, also known as the War of Gradisca, was fought by the Austrians, Croats, and Spanish on one side and the Venetians, Dutch, and English on the other. It is named for the Uskoks, soldiers from Croatia used by the Austrians for irreg ...
(1615–1618), the Uskok activity in their stronghold of Senj
Senj (; it, Segna, la, Senia, Hungarian and german: Zengg) is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains.
The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj) whic ...
mostly ceased.
Name
Etymologically, the word ''uskoci'' itself means "the ones who jumped in" ("the ones who ambushed") in South Slavic languages. TheSerbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian, t ...
transliteration is , and Slovene is . In other languages, the term became a loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
as well — german: Uskoken, hu, Uszkókok, it, Uscocchi.
History
Early period
TheOttoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina was a process that started roughly in 1386, when the first Ottoman attacks on the Kingdom of Bosnia took place. In 1451, more than 65 years after its initial attacks, the Ottoman Empire officially est ...
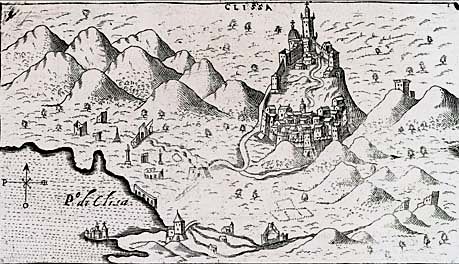
during the early years of the 16th century drove large numbers of ethnic Croats from their homes, which in the town of Klis
Klis ( hr, Klis, it, Clissa, tr, Kilis) is a Croatian municipality located around a mountain fortress bearing the same name. It is located in the region of Dalmatia, located just northeast of Solin and Split near the eponymous mountain pass. I ...
prompted the formation of the ''Uskok'' military. Large numbers of fugitives from Herzegovina, Dalmatia, and Bosnia fleeing the Ottomans, joined the ranks of the Uskok bands. In 1522 the border territory of Senj was taken over by the Habsburgs under the authority of Archduke Ferdinand, forming a state-controlled Militärgrenze, or Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and ...
. The Austrian Emperor Ferdinand I
Ferdinand I ( es, Fernando I; 10 March 1503 – 25 July 1564) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1556, King of Bohemia, Hungary, and Croatia from 1526, and Archduke of Austria from 1521 until his death in 1564.Milan Kruhek: Cetin, grad izbornog sabo ...
instituted a system of planting colonies of defenders along the Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and ...
. Moreover, the Uskoks were promised an annual subsidy in return for their services. Owing to its location, Klis Fortress
) from Vrana, in the name of Bosnian King Tvrtko I
* 1394–1401 Ban Nikola II Gorjanski in the name of Sigismund
* 1401–1434 Croatian noble Prince Ivaniš Nelipić
* 1434–1436 Croatian noble and Ban of Croatia Ivan Frankopan, at that ...
was an important defensive position which stands on the route by which the Ottomans could penetrate the mountain barrier separating the coastal lowlands from around Split
Split(s) or The Split may refer to:
Places
* Split, Croatia, the largest coastal city in Croatia
* Split Island, Canada, an island in the Hudson Bay
* Split Island, Falkland Islands
* Split Island, Fiji, better known as Hạfliua
Arts, entertai ...
in Croatia, from Ottoman-held Bosnia. Numerous refugees from Ottoman areas began settling along this territory, crossing the border to escape Ottoman attacks. Christian guerilla resistance in Ottoman-occupied areas of Dalmatia and Bosnia caused these people to flee and settle down, first at the fortress of Klis along the Military Frontier, then at Senj. A body of these "uskoks" led by Croatian captain Petar Kružić
Petar Kružić (died 1537) was a Croatian knez, captain, soldier and defender of Klis, and the captain of Senj.
In the early 16th century Petar Kružić ''(knez of Klis)'' defended the Klis Fortress against Turk invasion. He died in 1537 ...
used the base at Klis both to hold the Turks at bay, and to engage in marauding and piracy against coastal shipping. Although nominally accepting the sovereignty of the Habsburg Emperor Ferdinand I,In 1527, the Croatian nobles elected Ferdinand I, Archduke of Austria as their king, and confirmed the succession to him and his heirs. In return for the throne Archduke Ferdinand promised to respect the historic rights, freedoms, laws and customs the Croats had when united with the Hungarian kingdom and to defend Croatia from Ottoman invasion.R. W. SETON -WATSON:The southern Slav question and the Habsburg Monarchy page 18
who obtained the Croatian crown in 1527, Kružić and his freebooting Uskoks were a law unto themselves. After Petar Kružić's death, and the lack of water supply, the defenders of Klis finally surrendered to the Ottomans in exchange for their freedom. On March 12, 1537, the town and fortress was given up to the Ottomans, many of the citizens left the town while the Uskoks went to the city of
Senj
Senj (; it, Segna, la, Senia, Hungarian and german: Zengg) is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains.
The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj) whic ...
on the Adriatic coast, where they continued fighting the Ottomans. They may have started to gather around Senj as early as 1520 (Bracewell 1992). The Ottoman raids and destruction brought Senj natives together with those from the Habsburg lands, Dalmatians, Ragusans and Italians. At Senj, the Klis Uskoks were soon joined by other refugees from Novi Vinodolski
Novi Vinodolski (, often also called Novi or ''Novi del Vinodol'' o ''Novi in Valdivino'' in Italian) is a town on the Adriatic Sea coast in Croatia, located south of Crikvenica, Selce and Bribir and north of Senj. The population of Novi is 3,988 ...
in northwestern Croatia, from Otočac
Otočac () is a town in Croatia, former bishopric and present Latin Catholic titular see. It lies in the northwestern part of Lika region, in the Gacka river valley. The population of the administrative area of the Town of Otočac was 9,778 in ...
on the Gacka River, and from other Croatian towns and villages.
The new Uskok stronghold, screened by mountains and forests, was unassailable by cavalry or artillery. However, the fortress was admirably suitable to the lightly armed uskoks who were excellent in guerrilla warfare. The Martolos
The ''martolos'' was an internal security force of the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans ('' Rumelia''), mostly active between the 15th to 17th centuries. It initially constituted out of the local mostly Christian populations (Rum Millet), but over ti ...
were employed by the Ottomans to discourage Uskok penetration of Turkish territory, which was not very profitable anyhow. Since the uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual subsidy, they resorted to acts of piracy. Large galleys could not anchor in the bay of Senj, which is shallow and exposed to sudden gales. So, the uskoks fitted out a fleet of swift boats, which were light enough to navigate the smallest creeks and inlets of the shores of Illyria. Moreover, these boats were helpful in providing the uskoks a temporary landing on shore. With these they were able to attack numerous commercial areas on the Adriatic. The uskoks saw their ranks swell as outlaws from all nations joined them. Eventually, the whole city of Senj lived from piracy. The expeditions were blessed in the local church and the monasteries of the Dominicans and the Franciscan
, image = FrancescoCoA PioM.svg
, image_size = 200px
, caption = A cross, Christ's arm and Saint Francis's arm, a universal symbol of the Franciscans
, abbreviation = OFM
, predecessor =
, ...
s received tithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more ...
s from the loot.
After the War of the Holy League in 1537 against the Ottoman Empire, a truce between Venice and the Ottomans was created in 1539. This led to the evacuation of all Uskoks in Dalmatia in 1541 where they had been defending a Christian enclave in the mountains during the war. Throughout the following years the Habsburgs were at arms with the Turks, giving the Uskoks the opportunity to repeatedly raid Bosnia and Dalmatia. The Uskoks were able to continue doing so up until 1547 when peace was established between the two, forcing the Uskoks to find other ways of making ends meet. As with other Slavic pirates, the Uskok territory was not suitable for any form of agriculture, forcing them to turn to piracy once more.
Ottoman invasion and Venice
 Beginning as inland pirates, the Uskoci shortly turned to the seas once realizing the full potential of the geography of Senj. The land was protected by thick forests and mountains while the jagged cliffs near the seas prevented warships from entering. The seas in the Gulf of Quarnero were quite rough, which posed navigational hazards as further protection from their enemies. Uskoks began their attacks upon Turkish ships with boats large enough to hold thirty to fifty men.
After 1540, however, Venice, as mistress of the seas, guaranteed the safety of Ottoman merchant vessels, and provided them with an escort of galleys. The uskoks retaliated by ravaging the Venetian islands of
Beginning as inland pirates, the Uskoci shortly turned to the seas once realizing the full potential of the geography of Senj. The land was protected by thick forests and mountains while the jagged cliffs near the seas prevented warships from entering. The seas in the Gulf of Quarnero were quite rough, which posed navigational hazards as further protection from their enemies. Uskoks began their attacks upon Turkish ships with boats large enough to hold thirty to fifty men.
After 1540, however, Venice, as mistress of the seas, guaranteed the safety of Ottoman merchant vessels, and provided them with an escort of galleys. The uskoks retaliated by ravaging the Venetian islands of Krk
Krk (; it, Veglia; ruo, Krk; dlm, label= Vegliot Dalmatian, Vikla; la, Curicta; grc-gre, Κύρικον, Kyrikon) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kot ...
, Rab
Rab �âːb( dlm, Arba, la, Arba, it, Arbe, german: Arbey) is an island in the northern Dalmatia region in Croatia, located just off the northern Croatian coast in the Adriatic Sea.
The island is long, has an area of and 9,328 inhabitants (2 ...
and Pag. Moreover, they utilized the Venetian territories in Dalmatia as a springboard in order to launch attacks against the Ottomans.
 After 1561 the Uskoci attacked Christian shipping in Dubrovnik with numbers never exceeding 2000 men. By 1573 the Uskoks caused considerable concern in Venice with frequent attacks once Venetian attempts of protection had proven to be ineffective. The following years led the reputation of the Uskoks to spread, becoming the resort of refugees and outlaws of all kinds from all nations.
Meanwhile, the corsairs of
After 1561 the Uskoci attacked Christian shipping in Dubrovnik with numbers never exceeding 2000 men. By 1573 the Uskoks caused considerable concern in Venice with frequent attacks once Venetian attempts of protection had proven to be ineffective. The following years led the reputation of the Uskoks to spread, becoming the resort of refugees and outlaws of all kinds from all nations.
Meanwhile, the corsairs of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
were free to raid the unprotected southern shores of Italy. Venice was besieged with complaints from the Porte
Porte may refer to:
*Sublime Porte, the central government of the Ottoman empire
*Porte, Piedmont, a municipality in the Piedmont region of Italy
*John Cyril Porte, British/Irish aviator
*Richie Porte, Australian professional cyclist who competes ...
, the Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
, and the Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning " ...
of Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
with his sovereign, the King of Spain. A Venetian appeal to Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
for help met with little success, and the offenses of the uskoks against the Venetians were outweighed by their attacks against the Ottomans. Minuccio Minucci, a Venetian envoy at Graz, states that a share of the uskoks' spoils of silk, velvet and jewels, went to the ladies of the Archducal Court of Graz, where important matters between Venice and Austria were negotiated.
From 1577 onwards, Venice endeavored to crush the pirates without offending Austria, enlisting Albanians in place of their Dalmatian crews, who feared reprisals at home. For a time the uskoks only ventured forth at night, during the winter season and even during stormy weather.
In 1592, following the fall of Bihać, a strong Ottoman army invaded further into Croatia hoping to capture Senj. Led by Telli Hasan Pasha
Hasan Predojević ( 1530 – 22 June 1593), also known as Telli Hasan Pasha ( tr, Telli Hasan Paşa), was the fifth Ottoman beylerbey ( vali) of Bosnia and a notable Ottoman Bosnian military commander, who led an invasion of the Habsburg Kingdo ...
, the beylerbey of Bosnia, the Ottomans managed to capture a number of uskok settlements, killing and enslaving the population. However, the army was routed and dispersed in the following year. Austria was involved in war with the Ottomans and the Venetian admiral Giovanni Bembo
Giovanni Bembo (21 August 1543 – 16 March 1618) was the 92nd Doge of Venice, reigning from his election on 2 December 1615 until his death. His reign is notable for Venetian victories during the War of Gradisca (1617) and for the Bedmar Plo ...
blockaded Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into prov ...
and Rijeka (Fiume), where the pirates forwarded their booty for sale. They also erected two forts to command the passages from Senj to the open sea. In 1600, the Prince of Senj was Mickael Radic. The Duke Micheal Radic, appointed as Prince of Senj on 1 December 1600 by King Rudolf in Graz. Prince Radic was Prince of Senj. Radic family is a Native noble family from Lika region; members of the family were Uskok military leaders at the headquarters in Senj.
 A raid by the Uskoks upon Istria resulted in an agreement between Venice and Austria, and Count Joseph de Rabatta was appointed to act as commissioner to those in Senj as well as the chief negotiator with the Venetians. Rabatta came to Senj in 1600 with a strong bodyguard detail, and was very energetic. His time ruling over the Uskoks was brutal where many Uskoks were hung or sent to fight in the Turkish war, revealing his favor towards the Venetian side. He soon lost all military support, giving the Uskoks the opportunity to overthrow his rule and was ultimately killed in January 1602, enabling Senj to return to its usual state, with the fugitive Uskoks returning to Senj where they resumed their acts of piracy.
A raid by the Uskoks upon Istria resulted in an agreement between Venice and Austria, and Count Joseph de Rabatta was appointed to act as commissioner to those in Senj as well as the chief negotiator with the Venetians. Rabatta came to Senj in 1600 with a strong bodyguard detail, and was very energetic. His time ruling over the Uskoks was brutal where many Uskoks were hung or sent to fight in the Turkish war, revealing his favor towards the Venetian side. He soon lost all military support, giving the Uskoks the opportunity to overthrow his rule and was ultimately killed in January 1602, enabling Senj to return to its usual state, with the fugitive Uskoks returning to Senj where they resumed their acts of piracy.
 Up until 1611 the Uskoks were relatively undisturbed. Piracy was strictly forbidden at this point but it was tolerated in order to avoid payment of subsidies owed to those of Senj. A Venetian squadron intercepted an Uskok fleet in the spring of 1613 in response to the complaints regarding Uskok activity and, as reported, sixty Uskoks were beheaded with their heads then displayed in St. Mark's Square. In response to this offense the Uskok captured a galley of Venetians, slaughtered the crew, and used the blood of the victims to flavor their bread.
The uskoks would conduct such acts up until 1615 when their piracy went so far as creating an open war between Venice and Austria. Venice, frustrated with the piracy, launched an attack after the Archduke Ferdinand of Styria refused to reprimand the Uskoks. A peace treaty was signed in autumn 1617 which arranged for the Uskoks to be disbanded, as well as their ships and fortresses be destroyed. An agreement between the Habsburgs and Venetians in 1618 expelled the Uskoks from Senj, prompting migrations of Uskok families into the hinterland.
The Venetians nominated Marko Srdanovic Knew of Omis. Marko was born Srdan Kacic but the last name was changed to Srdanovic. This was because the Ottomans had given an order to kill every Kacic of the Omis Pirates.
Up until 1611 the Uskoks were relatively undisturbed. Piracy was strictly forbidden at this point but it was tolerated in order to avoid payment of subsidies owed to those of Senj. A Venetian squadron intercepted an Uskok fleet in the spring of 1613 in response to the complaints regarding Uskok activity and, as reported, sixty Uskoks were beheaded with their heads then displayed in St. Mark's Square. In response to this offense the Uskok captured a galley of Venetians, slaughtered the crew, and used the blood of the victims to flavor their bread.
The uskoks would conduct such acts up until 1615 when their piracy went so far as creating an open war between Venice and Austria. Venice, frustrated with the piracy, launched an attack after the Archduke Ferdinand of Styria refused to reprimand the Uskoks. A peace treaty was signed in autumn 1617 which arranged for the Uskoks to be disbanded, as well as their ships and fortresses be destroyed. An agreement between the Habsburgs and Venetians in 1618 expelled the Uskoks from Senj, prompting migrations of Uskok families into the hinterland.
The Venetians nominated Marko Srdanovic Knew of Omis. Marko was born Srdan Kacic but the last name was changed to Srdanovic. This was because the Ottomans had given an order to kill every Kacic of the Omis Pirates.
Uskok migrations
The pirates and their families were, accordingly, transported to the interior, where they gave their name to the "Uskoken Gebirge", a group of mountains on the borders of Carniola now called Žumberak. They were also settled in the nearbyWhite Carniola
White Carniola ( sl, Bela krajina; german: Weißkrain or ''Weiße Mark'') is a traditional region in southeastern Slovenia on the border with Croatia. Due to its smallness, it is often considered a subunit of the broader Lower Carniola region, alt ...
and Kostel in what is now Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. Their presence has also been traced near Učka
The Učka ([], it, Monte Maggiore) is a mountain range in western Croatia. It rises behind the Opatija riviera, on the eastern side of the Istrian peninsula.
It forms a single morphological unit together with the Ćićarija range which stretche ...
in Istria, where such significant family names as Novlian (from Novi Vinodolski
Novi Vinodolski (, often also called Novi or ''Novi del Vinodol'' o ''Novi in Valdivino'' in Italian) is a town on the Adriatic Sea coast in Croatia, located south of Crikvenica, Selce and Bribir and north of Senj. The population of Novi is 3,988 ...
), Ottocian (from Otočac
Otočac () is a town in Croatia, former bishopric and present Latin Catholic titular see. It lies in the northwestern part of Lika region, in the Gacka river valley. The population of the administrative area of the Town of Otočac was 9,778 in ...
) and Clissan (from Klis
Klis ( hr, Klis, it, Clissa, tr, Kilis) is a Croatian municipality located around a mountain fortress bearing the same name. It is located in the region of Dalmatia, located just northeast of Solin and Split near the eponymous mountain pass. I ...
, older orthography), were noted by Italian historian in 1879.
Origin of Uskoks from Senj
Determining the exact national or ethnic composition of the Uskoks from Senj is extremely difficult since it is rarely recorded nationality of the Uskoks, (most commonly terms for Uskoks are "Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, ...
", "Slavs", " Morlachs") Venetians are described Uskoks as Croats, Habsburg sources also identify Uskoks as Croats. The observers and same Uskoks used terms national and ethnic identity as a way to describe the origin of Uskoks. They use terms Croat, Slav and Morlach to connect the Uskoks with the rest population of the islands, the coast and the hinterland, but also to show difference between those Uskoks which belonged to other nationalities, Vlachs, Italians, Albanians, Germans and others. Venetian Republic at the end of the 16th century are concerned about the excellent relations between the Venetian Dalmatian peoples and Uskoks. According to them such relationships existed because of belonging to the same people. There were many Albanians among Uskoks as well and many islanders from Krk
Krk (; it, Veglia; ruo, Krk; dlm, label= Vegliot Dalmatian, Vikla; la, Curicta; grc-gre, Κύρικον, Kyrikon) is a Croatian island in the northern Adriatic Sea, located near Rijeka in the Bay of Kvarner and part of Primorje-Gorski Kot ...
, Pag, Rab
Rab �âːb( dlm, Arba, la, Arba, it, Arbe, german: Arbey) is an island in the northern Dalmatia region in Croatia, located just off the northern Croatian coast in the Adriatic Sea.
The island is long, has an area of and 9,328 inhabitants (2 ...
and residents of other Dalmatian islands. All Uskoks were Catholics, while newcomers to Senj Orthodox or Muslims immediately became Catholics. Uskoks marrying women from Senj area and much less from area of Venetian and Turkish Dalmatia The arrival and occurrence of the Uskoks cannot be identified with the migration of the Vlachs.
Uskok Code
As a group whose central reason for being brought together was Christianity, the Uskoks' explanation for piracy and warfare rested in their religion. These people felt they were fighting a holy war against the Muslim enemy in defense of the boundaries of Christendom. Seeing that these people were once refugees from Ottoman nations, they were given no choice but to leave in order to continue following the religion they had been their entire lives. The Uskok people established a code to follow, holding Senj honor and its values in a central place of that code. Honor is what they believed to be the most important quality that a hero could have, which all Uskoks strived to be. Other important aspects of the Uskok heroic honor were loyalty to their city, army, and band; honorable attention to every knight and obligation; readiness to lay down their lives or spill their blood in time of war; experience in warfare; ability to benefit their city; success and glory in duels with the Turks and other enemies of the Christian faith; and severity in punishing those who were disobedient or rebellious. It was also made known the Uskok qualities that would cancel out one's honor: reluctance to shed one's own blood; failure to engage the enemy in battle; groundless boasting; avoidance of risks on the frontier; failure to take prisoners, trophies, or booty; meanness in rewards to comrades or spies; the absence of any general recognition of one's manliness; and the lack of battle scars or wounds. From these principles it is clear that the Uskoks admired the strength and arrogance of a hero and despised the weakness displayed by a coward. The importance of these principles was instilled in boys at a young age. Taught to take part in competitions, they would test their strength and dexterity through racing, fighting, and throwing stones at one another until blood ran. Over time, this code would be broken, ignored, and overlooked as the Uskok attitude and motives would change.Legacy
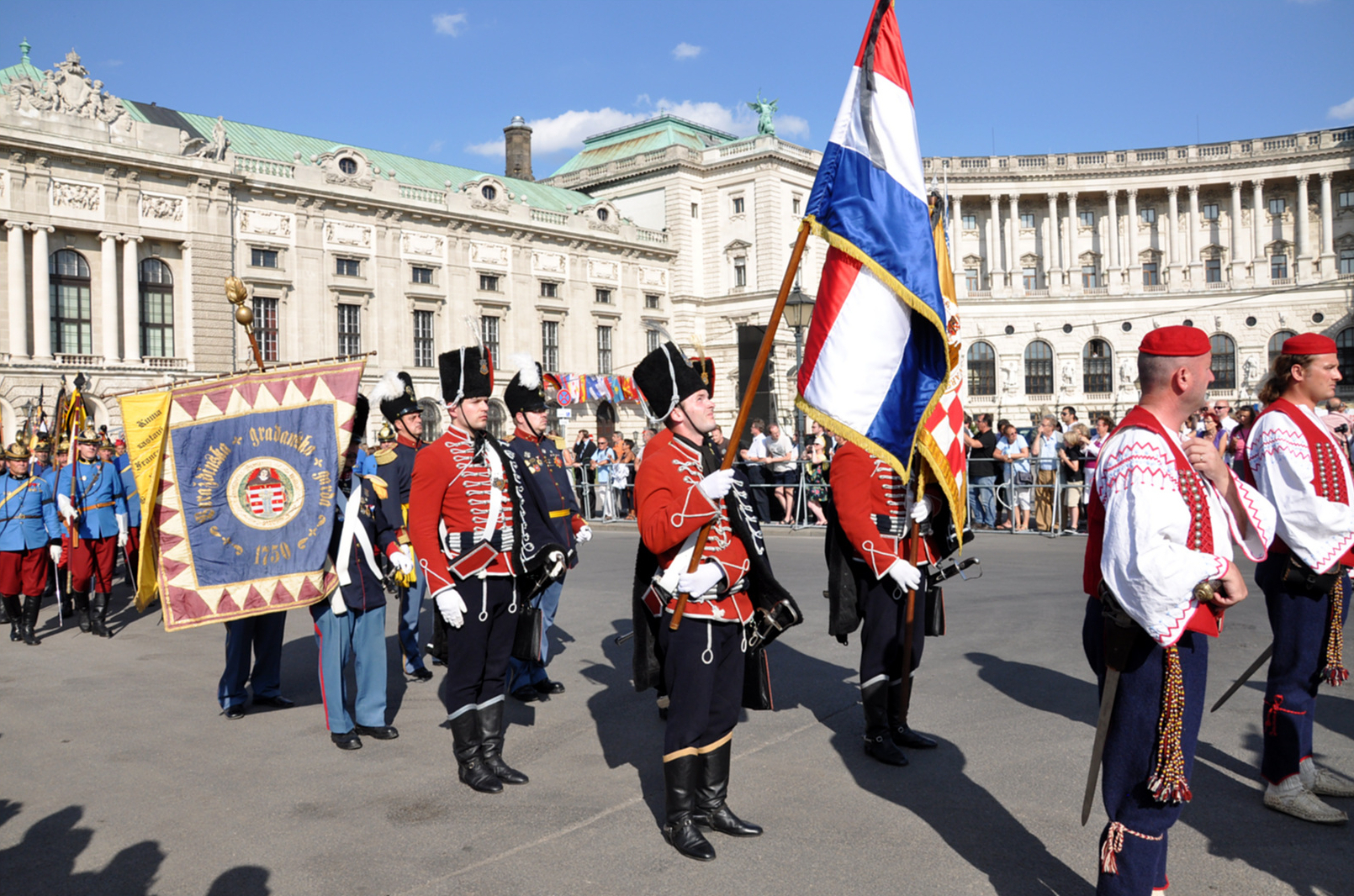
 Today, a historical unit of uskoks called ''Kliški uskoci'' ("Uskoks of
Today, a historical unit of uskoks called ''Kliški uskoci'' ("Uskoks of Klis
Klis ( hr, Klis, it, Clissa, tr, Kilis) is a Croatian municipality located around a mountain fortress bearing the same name. It is located in the region of Dalmatia, located just northeast of Solin and Split near the eponymous mountain pass. I ...
" , ) exists as a ceremonial regiment in honour of the national legacy of uskoks in Croatia. The unit of Klis Uskoks is founded by Croatian war veterans. After the Croatian War for Independence, the former soldiers wanted to revitalize the historical and cultural heritage of Klis, the town whose bloody history gave much inspiration during the war. The veterans participate in historical and cultural events to renew the memory of the Uskoks of Klis. They were among the six historic Croatian military units represented at the funeral of Otto von Habsburg in July 2011./ref> One Special Forces unit of Special Operations Command of
Croatian Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Croatia ( hr, Oružane snage Republike Hrvatske – OSRH) is the military service of Croatia.
The President is the Armed Forces Commander-in-Chief, and exercises administrative powers in times of war by giv ...
is called Commando Uskok Company (''Komando uskočka satnija'').
Notable uskoci
*Petar Kružić
Petar Kružić (died 1537) was a Croatian knez, captain, soldier and defender of Klis, and the captain of Senj.
In the early 16th century Petar Kružić ''(knez of Klis)'' defended the Klis Fortress against Turk invasion. He died in 1537 ...
*Ivan Lenković
Ivan Lenković (died 22 June 1569) was a Habsburg Croatian army general and the leader of the Uskoks. He carried the title of baron. He is noted for the construction of Nehaj Fortress and as a captain of the Senj area.Bousfield (2003), p. 227. ...
*Nikola Jurišić
Baron Nikola Jurišić ( hu, Jurisich Miklós; – 1545) was a Croatian nobleman, soldier, and diplomat.
Early life
Jurišić was born in Senj, Croatia.
He is first mentioned in 1522 as an officer of Ferdinand I of Habsburg's troops deployed ...
* Krsto Delišimunović
* Petar Mrkonjić
*Ivo Senjanin
Ivan Vlatković ( 1571 – 1612), known in folklore as Ivo Senjanin ("Ivo of Senj"), was a Habsburg Croatian uskok who led numerous military exploits against the Ottoman Empire. Due to few historical sources, much of what is known about him today ...
* Đure Daničić
See also
*Hajduk
A hajduk ( hu, hajdúk, plural of ) is a type of irregular infantry found in Central and parts of Southeast Europe from the late 16th to mid 19th centuries. They have reputations ranging from bandits to freedom fighters depending on time, p ...
* Morlachs
* Croats of Belgium
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
*See Minuccio Minucci, ''Historia degli Uscochi'' (Venice, 1603); enlarged by Paolo Sarpi, and translated into French as a supplement to Amelot de la Houssaye's ''Histoire du gouvernement de Venise'' (Amsterdam, 1/05). Minucci was one of the Venetian envoys at Graz. *See also the conciser narratives in C. de Franceschi's ''L'Istria'', chap. 37 (Parenzo, 1879); and T. G. Jackson's ''Dalmatia, the Quarnero and Istria'', chap. 27 (Oxford, 1887). *Wendy Bracewell also published a study of the Uskok women in a collection titled "Žene u Hrvatskoj" in 2004Historical Unit Kliški uskoci - About Uskoks
External links
* * * {{Authority control Military history of Croatia Military history of the Republic of Venice Piracy in the Mediterranean Military history of Slovenia History of Dalmatia 16th- and 17th-century warrior types Croatia under Habsburg rule Army of the Habsburg Monarchy