USDA soil taxonomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
USDA soil taxonomy (ST) developed by the
File:Alfisol.jpg, Alfisol
File:Andisol.jpg, Andisol
File:Aridisol.jpg, Aridisol
File:Entisol.jpg, Entisol
File:Gelisol.jpg, Gelisol
File:Histosol.jpg, Histosol
File:Inzeptisol.jpg, Inceptisol
File:Mollisol.jpg, Mollisol
File:Oxisol.jpg, Oxisol
File:Spodosol.jpg, Spodosol
File:Ultisol.jpg, Ultisol
File:Vertisol.jpg, Vertisol
The percentages listed above are for land area free of ice. "Soils of Mountains", which constitute the balance (11.6%), have a mixture of those listed above, or are classified as "Rugged Mountains" which have no soil.
The above soil orders in sequence of increasing degree of development are Entisols, Inceptisols, Aridisols, Mollisols, Alfisols, Spodosols, Ultisols, and Oxisols. Histosols and Vertisols may appear in any of the above at any time during their development.
The soil suborders within an order are differentiated on the basis of soil properties and horizons which depend on soil moisture and temperature. Forty-seven suborders are recognized in the United States.
The soil great group category is a subdivision of a suborder in which the kind and sequence of soil horizons distinguish one soil from another. About 185 great groups are recognized in the United States. Horizons marked by clay, iron, humus and hard pans and soil features such as the expansion-contraction of clays (that produce self-mixing provided by clay), temperature, and marked quantities of various salts are used as distinguishing features.
The great group categories are divided into three kinds of ''soil subgroups'': typic, intergrade and extragrade. A typic subgroup represents the basic or 'typical' concept of the great group to which the described subgroup belongs. An intergrade subgroup describes the properties that suggest how it grades towards (is similar to) soils of other soil great groups, suborders or orders. These properties are not developed or expressed well enough to cause the soil to be included within the great group towards which they grade, but suggest similarities. Extragrade features are aberrant properties which prevent that soil from being included in another soil classification. About 1,000 soil subgroups are defined in the United States.
A ''soil family'' category is a group of soils within a subgroup and describes the physical and chemical properties which affect the response of soil to agricultural management and engineering applications. The principal characteristics used to differentiate soil families include texture, mineralogy, pH, permeability, structure, consistency, the locale's precipitation pattern, and soil temperature. For some soils the criteria also specify the percentage of silt, sand and coarse fragments such as gravel, cobbles and rocks. About 4,500 soil families are recognised in the United States.
A family may contain several ''soil series'' which describe the physical location using the name of a prominent physical feature such as a river or town near where the soil sample was taken. An example would be Merrimac for the
 Name of soil orders in soil taxonomy with their major characteristics:
*
Name of soil orders in soil taxonomy with their major characteristics:
*
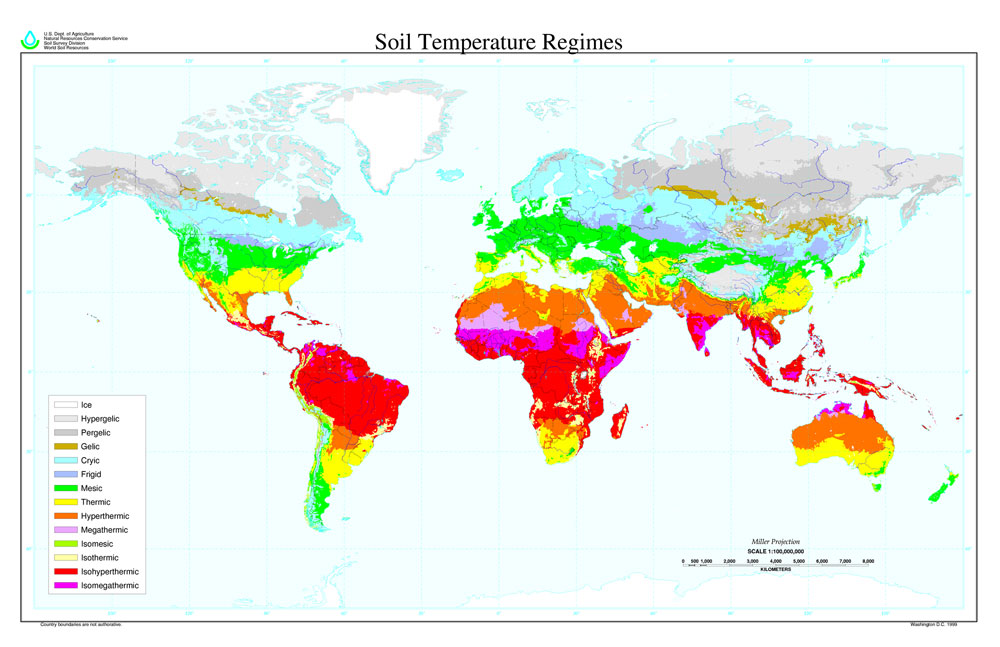 Soil temperature regimes, such as frigid, mesic, and thermic, are used to classify soils at some of the lower levels of the Soil Taxonomy. The cryic temperature regime distinguishes some higher-level groups. These regimes are based on the mean annual soil temperature (MAST), mean summer temperature, and the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures all at a soil depth of 50 cm. It is normally assumed that the MAST (in °C) equals the sum of the mean annual air temperature plus 2 °C. If the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures is less than 6 °C, then add "Iso" at the front of the name of the Soil Temperature Class.
Soil temperature regimes, such as frigid, mesic, and thermic, are used to classify soils at some of the lower levels of the Soil Taxonomy. The cryic temperature regime distinguishes some higher-level groups. These regimes are based on the mean annual soil temperature (MAST), mean summer temperature, and the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures all at a soil depth of 50 cm. It is normally assumed that the MAST (in °C) equals the sum of the mean annual air temperature plus 2 °C. If the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures is less than 6 °C, then add "Iso" at the front of the name of the Soil Temperature Class.

 The soil moisture regime, often reflective of climatic factors, is a major determinant of the productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, including agricultural systems. The soil moisture regimes are defined based on the levels of the groundwater table and the amounts of soil water available to plants during a given year in a particular region. Several moisture regime classes are used to characterize soils. These categories are terminology modifiers at the soil suborder level of characterization.
The soil moisture regime, often reflective of climatic factors, is a major determinant of the productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, including agricultural systems. The soil moisture regimes are defined based on the levels of the groundwater table and the amounts of soil water available to plants during a given year in a particular region. Several moisture regime classes are used to characterize soils. These categories are terminology modifiers at the soil suborder level of characterization.
USDA / NRCS soil taxonomy webpageSoil taxonomy documentUSDA-NRCS Web Soil Survey
{{Soil science topics Taxonomy Soil science Types of soil Taxonomy, USDA Land management in the United States zh:土壤#美國新分類法
United States Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of comme ...
and the National Cooperative Soil Survey provides an elaborate classification of soil types according to several parameters (most commonly their properties) and in several levels: ''Order'', ''Suborder'', ''Great Group'', ''Subgroup'', ''Family'', and '' Series''. The classification was originally developed by Guy Donald Smith, former director of the U.S. Department of Agriculture's soil survey investigations.
Discussion
A taxonomy is an arrangement in a systematic manner; the USDA soil taxonomy has six levels of classification. They are, from most general to specific: order, suborder, great group, subgroup, family and series. Soil properties that can be measured quantitatively are used in this classification system – they include: depth, moisture, temperature, texture, structure, cation exchange capacity, base saturation, clay mineralogy, organic matter content and salt content. There are 12 soil orders (the top hierarchical level) in soil taxonomy. The names of the orders end with the suffix ''-sol''. The criteria for the different soil orders include properties that reflect major differences in the genesis of soils. The orders are: *Alfisol
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron ( ...
– soils with aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
. They have horizons of clay accumulation, and form where there is enough moisture and warmth for at least three months of plant growth. They constitute 10% of soils worldwide.
* Andisol
In USDA soil taxonomy, Andisols are soils formed in volcanic ash and defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite. In the World Reference Base for Soil Re ...
– volcanic ash soils. They are young and very fertile. They cover 1% of the world's ice-free surface.
* Aridisol
Arid soils (or desert soils) are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Aridisols (from the Latin ''aridus'', for "dry", and ''solum'') form in an arid or semi-arid climate. Aridisols dominate the deserts and xeric shrublands, which occupy about one ...
– dry soils forming under desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
conditions which have fewer than 90 consecutive days of moisture during the growing season and are nonleached. They include nearly 12% of soils on Earth. Soil formation is slow, and accumulated organic matter is scarce. They may have subsurface zones of caliche or duripan A duripan is a diagnostic soil horizon of the USDA soil taxonomy that is cemented by illuvial silica into a subsurface hardpan. Similar to a fragipan, Petrocalcic Horizon and petrogypsic horizon, it is firmly cemented and restricts soil managemen ...
. Many aridisols have well-developed Bt horizons showing clay movement from past periods of greater moisture.
* Entisol – recently formed soils that lack well-developed horizons. Commonly found on unconsolidated river and beach sediments of sand and clay or volcanic ash, some have an A horizon on top of bedrock. They are 18% of soils worldwide.
* Gelisol – permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
soils with permafrost within two metres of the surface or gelic materials and permafrost within one metre. They constitute 9% of soils worldwide.
* Histosol – organic soils, formerly called bog soils, are 1% of soils worldwide.
* Inceptisol – young soils. They have subsurface horizon formation but show little eluviation and illuviation. They constitute 15% of soils worldwide.
* Mollisol – soft, deep, dark fertile soil formed in grasslands and some hardwood forests with very thick A horizons. They are 7% of soils worldwide.
* Oxisol
Oxisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy, best known for their occurrence in tropical rain forest within 25 degrees north and south of the Equator. In the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB), they belong mainly to the ferralsols, ...
– are heavily weathered, are rich in iron and aluminum oxides (sesquioxides
A sesquioxide is an oxide of an element (or radical), where the ratio between the number of atoms of that element and the number of atoms of oxygen is 2:3. For example, aluminium oxide and phosphorus(III) oxide are sesquioxides.
Many sesquioxid ...
) or kaolin
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedra ...
but low in silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is ...
. They have only trace nutrients due to heavy tropical rainfall and high temperatures and low CEC of the remaining clays. They are 8% of soils worldwide.
* Spodosol – acid soils with organic colloid layer complexed with iron and aluminium leached from a layer above. They are typical soils of coniferous and deciduous forest
In the fields of horticulture and Botany, the term ''deciduous'' () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals ...
s in cooler climates. They constitute 4% of soils worldwide.
* Ultisol
Ultisols, commonly known as red clay soils, are one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continu ...
– acid soils in the humid tropics and subtropics, which are depleted in calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmos ...
(important plant nutrients). They are highly weathered, but not as weathered as Oxisols. They make up 8% of the soil worldwide.
* Vertisol – inverted soils. They are clay-rich and tend to swell when wet and shrink upon drying, often forming deep cracks into which surface layers can fall. They are difficult to farm or to construct roads and buildings due to their high expansion rate. They constitute 2% of soils worldwide.
Merrimack River
The Merrimack River (or Merrimac River, an occasional earlier spelling) is a river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Mas ...
in New Hampshire. More than 14,000 soil series are recognised in the United States. This permits very specific descriptions of soils.
A ''soil phase of series'', originally called 'soil type' describes the soil surface texture, slope, stoniness, saltiness, erosion, and other conditions.
Soil Orders
 Name of soil orders in soil taxonomy with their major characteristics:
*
Name of soil orders in soil taxonomy with their major characteristics:
* Alfisols
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron ...
: Must have argillic, natric, or kandic horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
; high-to-medium base saturation; moderately weathered; commonly form under boreal or broadleaf forests; rich in iron and aluminum; common in humid areas, semi-tropics, and mediterranean climates; 9.6% of global and 14.5% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Andisols
In USDA soil taxonomy, Andisols are soils formed in volcanic ash and defined as soils containing high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, including allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite. In the World Reference Base for Soil Re ...
: Form from volcanic ejecta, dominated by allophane or Al-humic complexes; Must have andic soil properties: high in poorly crystalline Fe and Al minerals, high in phosphorus, low bulk density, and high proportions of glass and amorphous colloidal materials, such as allophane, imogolite and ferrihydrite
Ferrihydrite (Fh) is a widespread hydrous ferric oxyhydroxide mineral at the Earth's surface, and a likely constituent in extraterrestrial materials. It forms in several types of environments, from freshwater to marine systems, aquifers to hy ...
; high organic matter content, sometimes melanic epipedon; 0.7% of global and 1.7% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Aridisols: Dry soil (i.e., must have aridic moisture regime); ochric epipedon is common; Sometimes argillic or natric horizon; must have some diagnostic subsurface horizon; commonly in deserts; 12.7% of global and 8.8% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Entisols
Entisols are soils defined in USDA soil taxonomy that do not show any profile development other than an A horizon. An entisol has no diagnostic horizons, and most are basically unaltered from their parent material, which can be unconsolidated s ...
: Least soil profile development; ochric epipedon is common; no B horizons; most common order by surface area (16.3% of global and 12.2% of U.S. ice-free land).
* Gelisols
Gelisols are an order in USDA soil taxonomy. They are soils of very cold climates which are defined as containing permafrost within two meters of the soil surface. The word "Gelisol" comes from the Latin ''gelare'' meaning "to freeze", a ref ...
: Soils with permafrost within 100 cm or cryoturbation (frost churning) within 100 cm plus permafrost within 200 cm; commonly at high latitudes and elevations; 8.6% of global and 7.5% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Histosols: Must have histic epipedon; usually aquic soil moisture regime; no diagnostic subsurface horizons; rapid decomposition when aerated; peat or bog; >20% organic matter; organic soil materials extending down to an impermeable layer or with an organic layer that is more than 40 cm thick and without andic properties; commonly in wetlands (swamps, marshes, etc.); 1.2% of global and 1.3% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Inceptisols
Inceptisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. They form quickly through alteration of parent material. They are more developed than Entisols. They have no accumulation of clays, iron oxide, aluminium oxide or organic matter. They have an ...
: Similar to entisol, but beginning of a B horizon is evident; no diagnostic subsurface horizons; on landscapes continuously eroded or young deposits; cambic, sulfuric, calcic, gypsic, petrocalcic, or petrogypsic horizon, or with a mollic, umbric, or histic epipedon, or with an exchangeable sodium percentage of >15% or fragipan; 9.9% of global & 9.1% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Mollisols: Must have mollic epipedon; high base saturation of >50%; dark soils; some with argillic or natric horizons; common in grasslands; 6.9% of global and 22.4% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Oxisols: Most soil profile development; must have oxic horizon within 150 cm of soil surface; low nutrient availability; no argillic horizon; highly weathered; dominated by end-member clays, Al and Fe oxides; commonly in old landscapes in tropics; 7.6% of global and <0.01% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Spodosols
In soil science, podzols are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathland, which is often a construct of huma ...
: Must have spodic horizon within 2 m of soil surface and without andic properties; Usually have albic horizon; high in Fe, Al oxides and humus accumulation; acidic soils; common in coniferous or boreal forests; 2.6% of global and 3.3% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Ultisols
Ultisols, commonly known as red clay soils, are one of twelve soil orders in the United States Department of Agriculture soil taxonomy. The word "Ultisol" is derived from "ultimate", because Ultisols were seen as the ultimate product of continu ...
: Must have argillic or kandic horizon; Low base saturation of <35% at 2 m depth or 75 cm below a fragipan; common in subtropical regions; often known as red clay soils; 8.5% of global & 9.6% of U.S. ice-free land.
* Vertisols: Usually mollic epipedon; high in shrinking and swelling clays; >30% clay to a depth of 50 cm; deep cracks (called gilgai) form when soil dries; form from parent material high in clay (e.g., shales, basins, exposed Bt horizons of old soils); 2.4% of global and 1.7% of U.S. ice-free land.
Soil Type Classification Examples
Order: Entisols :Suborder: Fluvents ::Great Group: Torrifluvents :::Subgroup: Typic Torrifluvents ::::Family: Fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, calcareous, Typic Torrifluvents :::::Series: Jocity, Youngston. Order:Alfisols
Alfisols are a soil order in USDA soil taxonomy. Alfisols form in semi-arid to humid areas, typically under a hardwood forest cover. They have a clay-enriched subsoil and relatively high native fertility. "Alf" refers to aluminium (Al) and iron ...
:Suborder: Xeralfs
::Great Group: Durixeralfs
:::Subgroup: Abruptic Durixeralfs
::::Family: Fine, Mixed, Active, thermic Abruptic Durixeralfs
:::::Series: San Joaquin (soil)
San Joaquin is an officially designated state insignia, the state soil of the U.S. state of California.
The California Central Valley has more than 500,000 acres (2,000 km²) of San Joaquin soils, named for the south end of that valley. Th ...
Soil temperature regimes
 Soil temperature regimes, such as frigid, mesic, and thermic, are used to classify soils at some of the lower levels of the Soil Taxonomy. The cryic temperature regime distinguishes some higher-level groups. These regimes are based on the mean annual soil temperature (MAST), mean summer temperature, and the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures all at a soil depth of 50 cm. It is normally assumed that the MAST (in °C) equals the sum of the mean annual air temperature plus 2 °C. If the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures is less than 6 °C, then add "Iso" at the front of the name of the Soil Temperature Class.
Soil temperature regimes, such as frigid, mesic, and thermic, are used to classify soils at some of the lower levels of the Soil Taxonomy. The cryic temperature regime distinguishes some higher-level groups. These regimes are based on the mean annual soil temperature (MAST), mean summer temperature, and the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures all at a soil depth of 50 cm. It is normally assumed that the MAST (in °C) equals the sum of the mean annual air temperature plus 2 °C. If the difference between mean summer and winter temperatures is less than 6 °C, then add "Iso" at the front of the name of the Soil Temperature Class.
Soil moisture regimes

 The soil moisture regime, often reflective of climatic factors, is a major determinant of the productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, including agricultural systems. The soil moisture regimes are defined based on the levels of the groundwater table and the amounts of soil water available to plants during a given year in a particular region. Several moisture regime classes are used to characterize soils. These categories are terminology modifiers at the soil suborder level of characterization.
The soil moisture regime, often reflective of climatic factors, is a major determinant of the productivity of terrestrial ecosystems, including agricultural systems. The soil moisture regimes are defined based on the levels of the groundwater table and the amounts of soil water available to plants during a given year in a particular region. Several moisture regime classes are used to characterize soils. These categories are terminology modifiers at the soil suborder level of characterization.
See also
* 1938 USDA soil taxonomy * FAO soil classification *International Committee on Anthropogenic Soils The International Committee on Anthropogenic Soils (ICOMANTH) defines its mission as follows. ''"ICOMANTH is charged with defining appropriate classes in soil taxonomy for soils that have their major properties derived from human activities. The c ...
(ICOMANTH The International Committee on Anthropogenic Soils (ICOMANTH) defines its mission as follows. ''"ICOMANTH is charged with defining appropriate classes in soil taxonomy for soils that have their major properties derived from human activities. The c ...
)
* Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former ...
* Soil classification
* Soil horizon
* Soil in the United States
* World Reference Base for Soil Resources
References
External links
USDA / NRCS soil taxonomy webpage
{{Soil science topics Taxonomy Soil science Types of soil Taxonomy, USDA Land management in the United States zh:土壤#美國新分類法