U.S. presidential election, 1996 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The 1996 United States presidential election was the 53rd quadrennial
File:Bill Clinton.jpg,
File:Lyndon LaRouche (cropped).jpg,
With the advantage of incumbency,
File:Bob Dole, PCCWW photo portrait.JPG,
File:Patrickjbuchanan.JPG,
File:Steve Forbes.jpg,
File:Lamar Alexander 2.jpg,
File:Alan Keyes (1).jpg,
File:Dick Lugar official photo.jpg,
File:PhilGramm (1).jpg,
File:RobertDornan.jpg,
File:Arlen Specter official portrait.jpg,
File:Pete Wilson meeting with Les Aspin, Feb 3, 1993 - cropped to Wilson.JPEG,
A number of Republican candidates entered the field to challenge the incumbent Democratic president,

File:RossPerotColor.jpg, Party Founder Ross Perot, from
The United States Reform Party had great difficulty in finding a candidate willing to run in the general election.
 Libertarian candidates
*
Libertarian candidates
*
 The
The
 The
The
 The U.S. Taxpayers Party had run its first presidential ticket in 1992, it being head by Howard Phillips who had failed to find any prominent conservative willing to take the mantle. In 1996 the situation ultimately proved the same, though Pat Buchanan for a time was widely speculated to be planning on bolting to the Taxpayers' Party should the expected Republican nominee, Senator Bob Dole, name a pro-choice running-mate. When Jack Kemp, who opposed abortion, was tapped for the position Buchanan agreed to endorse the Republican ticket. Again, Phillips found himself at a temporary post that was made permanent, with Herbert Titus being nominated for the Vice Presidency.
Phillips and Titus drew 182,820 votes (0.2% of the popular vote).
The U.S. Taxpayers Party had run its first presidential ticket in 1992, it being head by Howard Phillips who had failed to find any prominent conservative willing to take the mantle. In 1996 the situation ultimately proved the same, though Pat Buchanan for a time was widely speculated to be planning on bolting to the Taxpayers' Party should the expected Republican nominee, Senator Bob Dole, name a pro-choice running-mate. When Jack Kemp, who opposed abortion, was tapped for the position Buchanan agreed to endorse the Republican ticket. Again, Phillips found himself at a temporary post that was made permanent, with Herbert Titus being nominated for the Vice Presidency.
Phillips and Titus drew 182,820 votes (0.2% of the popular vote).
 With respect to the issues, Dole promised a 15% across-the-board reduction in
With respect to the issues, Dole promised a 15% across-the-board reduction in
1996 Official Presidential General Election Results
'' Source (popular and electoral vote)
'' unofficial Secondary Source (Popular Vote): Voting age population: 196,498,000 Percent of voting age population casting a vote for President: 49.00%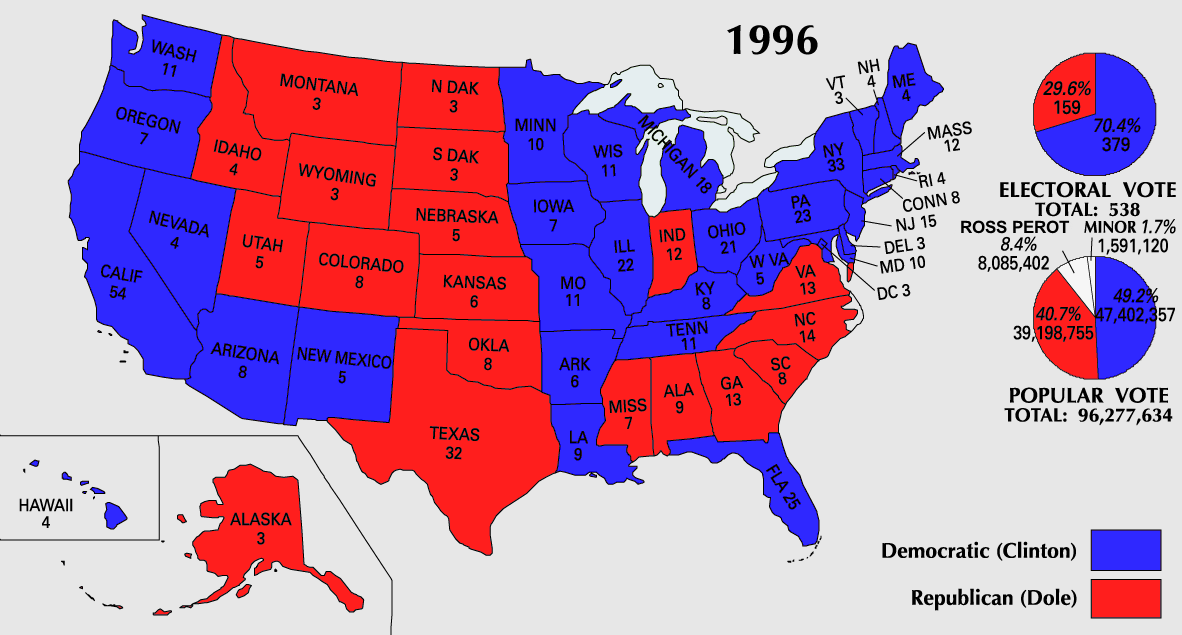
Image:1996prescountymap2.PNG, Election results by county.
Image:1996 Presidential Election, Results by Congressional District.png, Results by congressional district.
Image:1996 United States presidential election results map by county.svg, Results by county, shaded according to winning candidate's percentage of the vote.
1996 Presidential General Election Data - National
Uselectionatlas.org.
online
*
* (as of 1996) *
(still active as of February 2021) ; Other links
The Election Wall's 1996 Election Video Page
1996 popular vote by states
1996 popular vote by states (with bar graphs)
* – MTV pages on the election * *Documentary about the 1996 Vice Presidential Candidates
"Running Mate,"
1996-10-01, The Walter J. Brown Media Archives & Peabody Awards Collection at the
presidential election
A presidential election is the election of any head of state whose official title is President.
Elections by country
Albania
The president of Albania is elected by the Assembly of Albania who are elected by the Albanian public.
Chile
The pre ...
, held on Tuesday, November 5, 1996. Incumbent Democratic President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
defeated former Senate Majority Leader Bob Dole, the Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
nominee, and Ross Perot, the Reform Party nominee.
Clinton and Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on ...
Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic no ...
were re-nominated without incident by the Democratic Party. Numerous candidates entered the 1996 Republican primaries, with Dole considered the early front-runner. Dole clinched the nomination after defeating challenges by publisher Steve Forbes
Malcolm Stevenson Forbes Jr. (; born July 18, 1947) is an American publishing executive and politician who is the editor-in-chief of ''Forbes'', a business magazine. He is the son of longtime ''Forbes'' publisher Malcolm Forbes and the grandso ...
and paleoconservative
Paleoconservatism is a political philosophy and variety of conservatism in the United States stressing American nationalism, Christian ethics, regionalism, and traditionalist conservatism. Paleoconservatism's concerns overlap with those of the ...
leader Pat Buchanan. Dole's running mate was Jack Kemp, a former Congressman and football player who had served as the Housing Secretary under President George H. W. Bush. Ross Perot, who had won 18.9% of the popular vote as an independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
candidate in the 1992 election, ran as the candidate of the Reform Party. Perot received less media attention in 1996 and was excluded from the presidential debates.
Clinton's chances of winning were initially considered slim in the middle of his term, as his party had lost both the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
and the Senate in 1994
File:1994 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The 1994 Winter Olympics are held in Lillehammer, Norway; The Kaiser Permanente building after the 1994 Northridge earthquake; A model of the MS Estonia, which sank in the Baltic Sea; Nelson ...
for the first time in decades. He was able to regain ground as the economy began to recover from the early 1990s recession with a relatively stable world stage. Clinton tied Dole to Newt Gingrich, the unpopular Republican Speaker of the House, and warned that Republicans would increase the deficit and slash spending on popular programs like Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifical ...
and Medicare. Dole promised an across-the-board 15% reduction in federal income taxes and labeled Clinton as a member of the "spoiled" Baby Boomer
Baby boomers, often shortened to boomers, are the Western demographic cohort following the Silent Generation and preceding Generation X. The generation is often defined as people born from 1946 to 1964, during the mid-20th century baby boom. ...
generation. Dole's age was a persistent issue in the election, and gaffes by Dole exacerbated the issue for his campaign.
Clinton maintained a consistent polling edge over Dole, and he won re-election with a substantial margin in the popular vote and the Electoral College. Clinton became the first Democrat since Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
to win two straight presidential elections. Dole won 40.7% of the popular vote and 159 electoral votes, while Perot won 8.4% of the popular vote. Despite Dole's defeat, the Republican Party was able to maintain majorities in both the House of Representatives
House of Representatives is the name of legislative bodies in many countries and sub-national entitles. In many countries, the House of Representatives is the lower house of a bicameral legislature, with the corresponding upper house often c ...
and the Senate. Voter turnout was registered at 49.0%, the lowest for a presidential election since 1924
Events
January
* January 12 – Gopinath Saha shoots Ernest Day, whom he has mistaken for Sir Charles Tegart, the police commissioner of Calcutta, and is arrested soon after.
* January 20– 30 – Kuomintang in China holds ...
.
Five states switched party predominance in 1996 with their presidential voting: Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
, Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
were flipped by Senator Dole, while Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
were flipped by President Clinton. This is also the last time a third-party candidate finished with over 5% of the vote nationwide.
Background
In 1995, the Republican Party was riding high on the significant gains made in the 1994 mid-term elections. In those races, the Republicans, led by whip Newt Gingrich, captured the majority of seats in the House for the first time in forty years and the majority of seats in the Senate for the first time in eight years. Gingrich becameSpeaker of the House
The speaker of a deliberative assembly, especially a legislative body, is its presiding officer, or the chair. The title was first used in 1377 in England.
Usage
The title was first recorded in 1377 to describe the role of Thomas de Hungerf ...
, while Bob Dole was elevated to Senate Majority leader
The positions of majority leader and minority leader are held by two United States senators and members of the party leadership of the United States Senate. They serve as the chief spokespersons for their respective political parties holding t ...
.
The Republicans of the 104th Congress
The 104th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It met in Washington, D.C. from January 3, 19 ...
pursued an ambitious agenda, highlighted by their Contract with America
The Contract with America was a legislative agenda advocated for by the Republican Party during the 1994 congressional election campaign. Written by Newt Gingrich and Dick Armey, and in part using text from former President Ronald Reagan's 19 ...
, but were often forced to compromise with President Clinton, who wielded veto power
A veto is a legal power to unilaterally stop an official action. In the most typical case, a president or monarch vetoes a bill to stop it from becoming law. In many countries, veto powers are established in the country's constitution. Veto pow ...
. A budget impasse between Congress and the Clinton Administration eventually resulted in a government shutdown. Clinton, meanwhile, was praised for signing the GOP's welfare reform, and other notable bills, but was forced to abandon his own health care plan.
Democratic Party nomination
Democratic Candidates *Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
, President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
* Lyndon LaRouche
Lyndon Hermyle LaRouche Jr. (September 8, 1922 – February 12, 2019) was an American political activist who founded the LaRouche movement and its main organization the National Caucus of Labor Committees (NCLC). He was a prominent conspira ...
, Activist from Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
* Jimmy Griffin
James Arthur Griffin (August 10, 1943 – January 11, 2005) was an American singer, guitarist and songwriter, best known for his work with the 1970s soft rock band Bread. He won an Academy Award for Best Original Song in 1970 as co-writer ...
, Former Mayor of Buffalo from New York
Candidates gallery
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
's path to renomination by the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
was uneventful. At the 1996 Democratic National Convention
The 1996 Democratic National Convention was held at the United Center in Chicago, Illinois, from August 26 to August 29, 1996. President Bill Clinton and Vice President Al Gore were nominated for reelection. This was the first national conven ...
, Clinton and incumbent Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on ...
Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic no ...
were renominated with token opposition. Formerly incarcerated fringe candidate Lyndon LaRouche
Lyndon Hermyle LaRouche Jr. (September 8, 1922 – February 12, 2019) was an American political activist who founded the LaRouche movement and its main organization the National Caucus of Labor Committees (NCLC). He was a prominent conspira ...
won a few Arkansas delegates who were barred from the convention. Jimmy Griffin
James Arthur Griffin (August 10, 1943 – January 11, 2005) was an American singer, guitarist and songwriter, best known for his work with the 1970s soft rock band Bread. He won an Academy Award for Best Original Song in 1970 as co-writer ...
, former Mayor of Buffalo, New York
The following is a list of people who have served as mayors of the city of Buffalo in the U.S. state of New York.
List of mayors
Number of mayors by party affiliation
History
In 1853, the charter of the city was amended to include the tow ...
, mounted a brief campaign but withdrew after a poor showing in the New Hampshire primary. Former Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
governor Bob Casey contemplated a challenge to Clinton, but health problems forced Casey to abandon a bid.
Clinton easily won primaries nationwide, with margins consistently higher than 80%.
Popular primaries vote:
* Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
(inc.) – 9,730,184 (88.5%)
* Lyndon LaRouche
Lyndon Hermyle LaRouche Jr. (September 8, 1922 – February 12, 2019) was an American political activist who founded the LaRouche movement and its main organization the National Caucus of Labor Committees (NCLC). He was a prominent conspira ...
– 597,081 (5.4%)
* Unpledged – 423,265 (3.8%)
Convention tally:
* Bill Clinton (inc.) – 4,277
* Not voting – 12
Republican Party nomination
Republican Candidates * Bob Dole, U.S. Senator fromKansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
and Republican nominee for Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
in 1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 ...
* Pat Buchanan, conservative columnist from Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
* Steve Forbes
Malcolm Stevenson Forbes Jr. (; born July 18, 1947) is an American publishing executive and politician who is the editor-in-chief of ''Forbes'', a business magazine. He is the son of longtime ''Forbes'' publisher Malcolm Forbes and the grandso ...
, newspaper and magazine publisher from New York
* Lamar Alexander
Andrew Lamar Alexander Jr. (born July 3, 1940) is a retired American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 2003 to 2021. A member of the Republican Party, he also was the 45th governor of Tennessee from ...
, former Governor of Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
* Phil Gramm, U.S. Senator from Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
* Alan Keyes
Alan Lee Keyes (born August 7, 1950) is an American politician, political activist, author, and perennial candidate who served as the Assistant Secretary of State for International Organization Affairs from 1985 to 1987. A member of the Repub ...
, former U.S. ECOSOC
The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC; french: links=no, Conseil économique et social des Nations unies, ) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, responsible for coordinating the economic and social fields ...
Ambassador from Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
* Richard Lugar, U.S. Senator from Indiana
Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States. Its capital and largest city is Indianapolis. Indiana was admitted to the United States as the 19th s ...
* Bob Dornan
Robert Kenneth Dornan (born April 3, 1933) is an American politician and actor from California. A Republican, Dornan served in the United States House of Representatives from 1977 to 1983 and from 1985 to 1997. He has become well known for public ...
, U.S. Representative from California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
* Arlen Specter
Arlen Specter (February 12, 1930 – October 14, 2012) was an American lawyer, author and politician who served as a United States Senator from Pennsylvania from 1981 to 2011. Specter was a Democrat from 1951 to 1965, then a Republican fr ...
, U.S. Senator from Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
* Pete Wilson
Peter Barton Wilson (born August 23, 1933) is an American attorney and politician who served as the 36th governor of California from 1991 to 1999. A member of the Republican Party, he also served as a United States senator from California betw ...
, Governor of California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
* Morry Taylor, CEO from Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
Candidates gallery
Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
.
The fragmented field of candidates debated issues such as a flat tax and other tax cut proposals, and a return to supply-side economic policies popularized by Ronald Reagan. More attention was drawn to the race by the budget stalemate in 1995 between Congress and the President, which caused temporary shutdowns and slowdowns in many areas of federal government service.
Former Secretary of Labor Lynn Martin of Illinois, who served in the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
from Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
's 16th
16 (sixteen) is the natural number following 15 and preceding 17. 16 is a composite number, and a square number, being 42 = 4 × 4. It is the smallest number with exactly five divisors, its proper divisors being , , and .
In English speech, ...
District and was the 1990 Republican U.S. Senate nominee losing to incumbent Paul Simon conducted a bid for most of 1995, but withdrew before the Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
caucuses as polls showed her languishing far behind. She participated in a number of primary Presidential debates before withdrawing. Martin's predecessor in Congress, John Anderson had made first a Republican then Independent Presidential bid in 1980. Also, Simon who defeated Martin for the U.S. Senate had run for president as a Democrat in 1988.
Former U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
General Colin Powell was widely courted as a potential Republican nominee. However, on November 8, 1995, Powell announced that he would not seek the nomination. Former Secretary of Defense and future Vice President of the United States
The vice president of the United States (VPOTUS) is the second-highest officer in the executive branch of the U.S. federal government, after the president of the United States, and ranks first in the presidential line of succession. The vice ...
Dick Cheney was touted by many as a possible candidate for the presidency, but he declared his intentions not to run in early 1995. Former and future Defense Secretary
The United States secretary of defense (SecDef) is the head of the United States Department of Defense, the executive department of the U.S. Armed Forces, and is a high ranking member of the federal cabinet. DoDD 5100.1: Enclosure 2: a The ...
Donald Rumsfeld formed a presidential campaign exploratory committee, but declined to formally enter the race. Former Secretary of State James A. Baker III and former Secretary of Education
An education ministry is a national or subnational government agency politically responsible for education. Various other names are commonly used to identify such agencies, such as Ministry of Education, Department of Education, and Ministry of Pub ...
William Bennett
William John Bennett (born July 31, 1943) is an American conservative politician and political commentator who served as secretary of education from 1985 to 1988 under President Ronald Reagan. He also held the post of director of the Office of ...
both flirted with bids, both even set up exploratory committees, for a number of months but both finally declared within days of each other they would not run either.
Primaries and convention
Ahead of the 1996 primary contest, Republican Leader of the United States Senate and former vice-presidential candidate Bob Dole was seen as the most likely winner. However,Steve Forbes
Malcolm Stevenson Forbes Jr. (; born July 18, 1947) is an American publishing executive and politician who is the editor-in-chief of ''Forbes'', a business magazine. He is the son of longtime ''Forbes'' publisher Malcolm Forbes and the grandso ...
finished first in Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
and Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
while paleoconservative
Paleoconservatism is a political philosophy and variety of conservatism in the United States stressing American nationalism, Christian ethics, regionalism, and traditionalist conservatism. Paleoconservatism's concerns overlap with those of the ...
firebrand Pat Buchanan managed early victories in Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S. ...
and Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, in addition to a strong second place in the Iowa caucuses
The Iowa caucuses are biennial electoral events for members of the Democratic and Republican parties in the U.S. state of Iowa. Unlike primary elections in most other U.S. states, where registered voters go to polling places to cast ballot ...
and a surprising victory in the small but key New Hampshire primary. Buchanan's New Hampshire win alarmed the Republican "establishment" sufficiently as to provoke prominent Republicans to quickly coalesce around Dole, and Dole won every primary starting with North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota and Dakota Sioux Native American tribes, who comprise a large porti ...
. Dole resigned his Senate seat on June 11 and the Republican National Convention formally nominated Dole on August 15, 1996, for president.
Popular primaries vote:
* Bob Dole – 8,427,601 (59.2%)
* Pat Buchanan – 3,021,935 (21.2%)
* Steve Forbes
Malcolm Stevenson Forbes Jr. (; born July 18, 1947) is an American publishing executive and politician who is the editor-in-chief of ''Forbes'', a business magazine. He is the son of longtime ''Forbes'' publisher Malcolm Forbes and the grandso ...
– 1,425,998 (10.0%)
* Lamar Alexander
Andrew Lamar Alexander Jr. (born July 3, 1940) is a retired American lawyer and politician who served as a United States Senator from Tennessee from 2003 to 2021. A member of the Republican Party, he also was the 45th governor of Tennessee from ...
– 495,590 (3.5%)
* Alan Keyes
Alan Lee Keyes (born August 7, 1950) is an American politician, political activist, author, and perennial candidate who served as the Assistant Secretary of State for International Organization Affairs from 1985 to 1987. A member of the Repub ...
– 449,536 (3.2%)
* Richard Lugar – 127,111 (0.9%)
* Unpledged – 123,765 (0.9%)
* Phil Gramm – 71,457 (0.5%)
* Bob Dornan
Robert Kenneth Dornan (born April 3, 1933) is an American politician and actor from California. A Republican, Dornan served in the United States House of Representatives from 1977 to 1983 and from 1985 to 1997. He has become well known for public ...
– 42,141 (0.3%)
* Morry Taylor – 21,180 (0.1%)
Convention tally:
* Bob Dole – 1928
* Pat Buchanan – 43
* Phil Gramm – 2
* Alan Keyes – 1
* Robert Bork – 1
* Not voting – 15
Former Representative and Housing Secretary Jack Kemp was nominated by acclamation for vice president, the following day. This was the only Republican ticket between 1980 and 2008 that did not include a member of the Bush family
The Bush family is an American dynastic family that is prominent in the fields of American politics, news, sports, entertainment, and business. They were the first family of the United States from 1989 to 1993 and again from 2001 to 2009, and w ...
.
Reform Party nomination
Candidates gallery
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
File:Richard Lamm.jpg, Former Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Richard Lamm
Richard Douglas Lamm (August 3, 1935 – July 29, 2021) was an American politician, writer, and attorney. He served three terms as 38th Governor of Colorado as a Democrat (1975–1987) and ran for the Reform Party's nomination for Preside ...
of Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
Lowell Weicker
Lowell Palmer Weicker Jr. (; born May 16, 1931) is an American politician who served as a U.S. Representative, U.S. Senator, and the 85th Governor of Connecticut. He unsuccessfully sought the Republican nomination for president in 1980. He was ...
, Tim Penny
Timothy Joseph Penny (born November 19, 1951) is an American author, musician, and former politician from Minnesota. Penny was a Democratic-Farmer-Labor member of the United States House of Representatives, 1983–1995, representing Minnesota' ...
, David Boren
David Lyle Boren (born April 21, 1941) is a retired American lawyer and politician from the state of Oklahoma. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as 21st governor of Oklahoma from 1975 to 1979 and three terms in the United States Sen ...
and Richard Lamm
Richard Douglas Lamm (August 3, 1935 – July 29, 2021) was an American politician, writer, and attorney. He served three terms as 38th Governor of Colorado as a Democrat (1975–1987) and ran for the Reform Party's nomination for Preside ...
were among those who toyed with the notion of seeking its presidential nomination, though all but Lamm decided against it; Lamm had himself come close to withdrawing his name from consideration. Lamm designated Ed Zschau as his vice presidential candidate.
Ultimately, the Reform Party nominated its founder Ross Perot from Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
in its first election as an official political party. Although Perot easily won the nomination, his victory at the party's national convention led to a schism as supporters of Lamm accused him of rigging the vote to prevent them from casting their ballots. This faction walked out of the national convention and eventually formed their own group, the American Reform Party, and attempted to convince Lamm to run as an Independent in the general election; Lamm declined, pointing out a promise he made before running that he would respect the Party's final decision.
Economist Pat Choate
Pat Choate (; born April 27, 1941) is an American economist who is most known for being the 1996 Reform Party candidate for Vice President of the United States, the running-mate of Ross Perot. Following the 1996 election, the Federal Election Co ...
was nominated for Vice President
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on ...
.
Minor parties and independents
Parties in this section obtained ballot access in enough states to theoretically obtain the minimum number of electoral votes needed to win the election. Individuals included in this section completed one or more of the following actions: received, or formally announced their candidacy for, the presidential nomination of athird party
Third party may refer to:
Business
* Third-party source, a supplier company not owned by the buyer or seller
* Third-party beneficiary, a person who could sue on a contract, despite not being an active party
* Third-party insurance, such as a V ...
; formally announced intention to run as an independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
candidate and obtained enough ballot access to win the election; filed as a third party or non-affiliated candidate with the FEC (for other than exploratory purposes). Within each party, candidates are listed alphabetically by surname.
Libertarian Party nomination
Harry Browne
Harry Edson Browne (June 17, 1933 – March 1, 2006) was an American writer, politician, and investment advisor. He was the Libertarian Party's Presidential nominee in the U.S. elections of 1996 and 2000. He authored 12 books that in total hav ...
– writer and investment analyst from Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
* Rick Tompkins – former candidate for Senator from Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
* Irwin Schiff
Irwin Allen Schiff (; February 23, 1928 – October 16, 2015) was an American libertarian and tax resistance advocate known for writing and promoting literature in which he argued that the income tax in the United States is illegal and unconstitu ...
– writer and prominent figure in the tax protester movement from Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, ...
* Douglas J. Ohmen – political activist from California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
* Jeffrey Diket – political activist from Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
The Libertarian Party
Active parties by country
Defunct parties by country
Organizations associated with Libertarian parties
See also
* Liberal parties by country
* List of libertarian organizations
* Lists of political parties
Lists of political part ...
nominated free-market writer and investment analyst, Harry Browne
Harry Edson Browne (June 17, 1933 – March 1, 2006) was an American writer, politician, and investment advisor. He was the Libertarian Party's Presidential nominee in the U.S. elections of 1996 and 2000. He authored 12 books that in total hav ...
from Tennessee, and selected Jo Jorgensen
Jo Jorgensen (born May 1, 1957) is an American libertarian political activist and academic. Jorgensen was the Libertarian Party's nominee for president of the United States in the 2020 election, in which she finished third in the popular vot ...
from South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
as his running-mate. Browne and Jorgensen drew 485,798 votes (0.5% of the popular vote).
Green Party nomination
Green Party of the United States
The Green Party of the United States (GPUS) is a federation of Green state political parties in the United States. The party promotes green politics, specifically environmentalism; nonviolence; social justice; participatory democracy, grassroot ...
– Ralph Nader
Ralph Nader (; born February 27, 1934) is an American political activist, author, lecturer, and attorney noted for his involvement in consumer protection, environmentalism, and government reform causes.
The son of Lebanese immigrants to the U ...
of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its capita ...
was drafted as a candidate for President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States ...
on the Green Party ticket. He was not formally nominated by the Green Party USA, which was, at the time, the largest national Green group; instead, he was nominated independently by various state Green parties (in some areas, he appeared on the ballot as an independent). Nader vowed to spend only $5,000 in his election campaign (to avoid having to file a financial statement with the FEC). Winona LaDuke
Winona LaDuke (born August 18, 1959) is an American economist, environmentalist, writer and industrial hemp grower, known for her work on tribal land claims and preservation, as well as sustainable development.
In 1996 and 2000, she ran for Vice ...
, a Native American activist and economist from Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
, was named as his running-mate. In Iowa
Iowa () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States, bordered by the Mississippi River to the east and the Missouri River and Big Sioux River to the west. It is bordered by six states: Wisconsin to the northeast, Illinois to th ...
and Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
, Anne Goeke was listed as Nader's running mate; in New Jersey it was Madelyn Hoffman and in New York it was Muriel Tillinghast.
Nader and his running mates drew 685,128 votes (0.71% of the popular vote).
Natural Law Party nomination
Natural Law Party
The Natural Law Party (NLP) is a transnational party founded in 1992 on "the principles of Transcendental Meditation", the laws of nature, and their application to all levels of government. At its peak, it was active in up to 74 countries; it con ...
for a second time nominated scientist and researcher John Hagelin
John Samuel Hagelin (born June 9, 1954) is the leader of the Transcendental Meditation (TM) movement in the United States. He is president of the Maharishi University of Management (MUM) in Fairfield, Iowa, and honorary chair of its board of t ...
for president and Mike Tompkins for vice president. The party platform included preventive health care, sustainable agriculture and renewable energy technologies. During his campaigns, Hagelin favored abortion rights without public financing, campaign finance law reform, improved gun control, a flat tax, the eradication of PACs, a ban on soft money
The financing of electoral campaigns in the United States happens at the federal, state, and local levels by contributions from individuals, corporations, political action committees, and sometimes the government. Campaign spending has risen ...
contributions, and school vouchers
A school voucher, also called an education voucher in a voucher system, is a certificate of government funding for students at schools chosen by themselves or their parents. Funding is usually for a particular year, term, or semester. In some cou ...
, and was a believer in "yogic flying
The Transcendental Meditation technique (abbreviated as TM) is the technique associated with the practice of Transcendental Meditation developed by the Indian spiritual figure Maharishi Mahesh Yogi. The practice involves the use of a private m ...
."
Hagelin and Tompkins drew 113,671 votes (0.1% of the popular vote).
U.S. Taxpayers' Party nomination
General election
Campaign
Without meaningful primary opposition, Clinton was able to focus on the general election early, whileDole
Dole may refer to:
Places
* Dole, Ceredigion, Wales
* Dole, Idrija, Slovenia
* Dole, Jura, France
** Arrondissement of Dole
* Dole (Kladanj), a village at the entity line of Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina-Republika Srpska
* Dole, Ljubušk ...
was forced to move to the right and spend his campaign reserves fighting off challengers. Political adviser Dick Morris
Richard Samuel Morris (born November 28, 1948) is an American political author and commentator who previously worked as a pollster, political campaign consultant, and general political consultant.
A friend and advisor to Bill Clinton during ...
urged Clinton to raise huge sums of campaign funds via soft money
The financing of electoral campaigns in the United States happens at the federal, state, and local levels by contributions from individuals, corporations, political action committees, and sometimes the government. Campaign spending has risen ...
for an unprecedented early TV blitz of swing states promoting Clinton's agenda and record. As a result, Clinton could run a campaign through the summer defining his opponent as an aged conservative far from the mainstream before Dole was in a position to respond. Compared to the 50-year-old Clinton, then 73-year-old Dole appeared especially old and frail, as illustrated by an embarrassing fall off a stage during a campaign event in Chico, California
Chico ( ; Spanish for "little") is the most populous city in Butte County, California. Located in the Sacramento Valley region of Northern California, the city had a population of 101,475 in the 2020 census, reflecting an increase from 86,18 ...
. Dole further enhanced this contrast on September 18 when he made a reference to a no-hitter thrown the day before by Hideo Nomo
is a Japanese former baseball pitcher who played in Nippon Professional Baseball (NPB) and Major League Baseball (MLB). He achieved early success in his native country, where he played with the Kintetsu Buffaloes from to . He then exploited a l ...
of the " Brooklyn Dodgers", a team that had left Brooklyn for Los Angeles 38 years earlier. A few days later Dole would make a joke about the remark by saying, "And I'd like to congratulate the St. Louis Cardinals
The St. Louis Cardinals are an American professional baseball team based in St. Louis. The Cardinals compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) Central division. Since the 2006 season, the Cardinals ha ...
on winning the N.L. Central. Notice I said the St. Louis Cardinals, not the St. Louis Browns
The St. Louis Browns were a Major League Baseball team that originated in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, as the Milwaukee Brewers. A charter member of the American League (AL), the Brewers moved to St. Louis, Missouri, after the 1901 season, where they p ...
." (The Browns had left St. Louis after the 1954 season to become the Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. As one of the American League's eight charter ...
.)
Dole chose to focus on Clinton as being "part of the spoiled baby boomer generation" and stating, "My generation won orld War II and we may need to be called to service one last time." Although his message won appeal with older voters, surveys found that his age was widely held as a liability and his frequent allusions to WWII and the Great Depression in speeches and campaign ads "unappealing" to younger voters. To prove that he was still healthy and active, Dole released all of his medical records to the public and published photographs of himself running on a treadmill
A treadmill is a device generally used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. Treadmills were introduced before the development of powered machines to harness the power of animals or humans to do work, often a type o ...
. After the falling incident in California, he joked that he "was trying to do that new Democratic dance, the macarena."
The Clinton campaign avoided mentioning Dole's age directly, instead choosing to confront it in more subtle ways such as the campaign slogan "Building Bridges to the Future" in contrast to the Republican candidate's frequent remarks that he was a "bridge to the past", before the social upheavals of the 1960s. Clinton, without actually calling Dole old, questioned the age of his ideas. With respect to the issues, Dole promised a 15% across-the-board reduction in
With respect to the issues, Dole promised a 15% across-the-board reduction in income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
rates and made former Congressman and supply side
Supply-side economics is a Macroeconomics, macroeconomic theory that postulates economic growth can be most effectively fostered by Tax cuts, lowering taxes, Deregulation, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-sid ...
advocate Jack Kemp his running mate. Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
framed the narrative against Dole early, painting him as a mere clone of unpopular House Speaker Newt Gingrich, warning America that Bob Dole would work in concert with the Republican Congress to slash popular social programs, like Medicare and Social Security, dubbed by Clinton as "Dole-Gingrich". Bob Dole's tax-cut plan found itself under attack from the White House, who said it would "blow a hole in the deficit," which had been cut nearly in half during his opponent's term.
The televised debates featured only Dole and Clinton, locking out Perot and the other minor candidates from the discussion. Perot, who had been allowed to participate in the 1992 debates, would eventually take his case to court, seeking damages from not being in the debate, as well as citing unfair coverage from the major media outlets.
In a first for either major party in a presidential election, both the Clinton and Dole campaigns had official websites. Dole invited viewers to visit his "homepage" at the end of the first debate.
Throughout the campaign, Clinton maintained leads in the polls over Dole and Perot, generally by large margins. In October, Republican National Committee
The Republican National Committee (RNC) is a U.S. Political action committee, political committee that assists the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party of the United States. It is responsible for developing and promoting the Republi ...
"operatives urg dtheir party's Congressional candidates to cut loose from Bob Dole and press voters to maintain a Republican majority" and spent $4 million on advertising in targeted districts.
Presidential debates
Three debates, organized by theCommission on Presidential Debates
The Commission on Presidential Debates (CPD) is a nonprofit corporation established in 1987 under the joint sponsorship of the Democratic and Republican political parties in the United States. The CPD sponsors and produces debates for U.S. pre ...
, took place—two between the presidential candidates and one between the vice presidential candidates:
Campaign donations controversy
In late September 1995, questions arose regarding the Democratic National Committee's fund-raising practices. In February the following year, China's alleged role in the campaign finance controversy first gained public attention after ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
'' published a story stating that a U.S. Department of Justice
The United States Department of Justice (DOJ), also known as the Justice Department, is a federal executive department of the United States government tasked with the enforcement of federal law and administration of justice in the United State ...
investigation had discovered evidence that agents of China sought to direct contributions from foreign sources to the DNC before the 1996 presidential campaign. The paper wrote that intelligence information had showed the Chinese Embassy in Washington, D.C. was used for coordinating contributions to the DNC in violation of U.S. law forbidding non-American citizens from giving monetary donations to U.S. politicians and political parties. Seventeen people were eventually convicted for fraud or for funneling Asian funds into the U.S. elections.
One of the more notable events learned involved Vice President Al Gore
Albert Arnold Gore Jr. (born March 31, 1948) is an American politician, businessman, and environmentalist who served as the 45th vice president of the United States from 1993 to 2001 under President Bill Clinton. Gore was the Democratic no ...
and a fund-raising event held at Hsi Lai Temple in Hacienda Heights, California. The Temple event was organized by DNC fund-raisers John Huang
John Huang (, born 1945) is a major figure in the 1996 United States campaign finance controversy. He worked for Lippo Bank in California and Worthen Bank in Arkansas, and as deputy assistant secretary for international economic affairs in U.S. ...
and Maria Hsia. It is illegal under U.S. law for religious organizations to donate money to politicians or political groups due to their tax-exempt status. The U.S. Justice Department alleged Hsia facilitated $100,000 in illegal contributions to the 1996 Clinton-Gore re-election campaign through her efforts at the Temple. Hsia was eventually convicted by a jury in March 2000. The DNC eventually returned the money donated by the Temple's monks and nuns. Twelve nuns and employees of the Temple refused to answer questions by pleading the Fifth Amendment when they were subpoena
A subpoena (; also subpœna, supenna or subpena) or witness summons is a writ issued by a government agency, most often a court, to compel testimony by a witness or production of evidence under a penalty for failure. There are two common types of ...
ed to testify before Congress in 1997.
Results
On election day, President Clinton won a decisive victory over Dole, becoming the first Democrat to win two consecutive presidential elections sinceFranklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
in 1936
Events
January–February
* January 20 – George V of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India, dies at his Sandringham Estate. The Prince of Wales succeeds to the throne of the United Kingdom as King E ...
, 1940
A calendar from 1940 according to the Gregorian calendar, factoring in the dates of Easter and related holidays, cannot be used again until the year 5280.
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* Januar ...
, and 1944
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 2 – WWII:
** Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in Nor ...
. In the popular vote, he out-polled Dole by over 8.2 million votes. The Electoral College map did not change much from the previous election, with the Democratic incumbent winning 379 votes to the Republican ticket's 159. In the West, Dole managed to narrowly win Colorado and Montana (both had voted for Clinton four years earlier), while Clinton became the first Democrat to win Arizona since Harry Truman in 1948. In the South, Clinton won Florida, a state he had failed to win in 1992, but lost Georgia, a state that he had carried. The election helped to cement Democratic presidential control in California, Vermont, Maine, Illinois, New Jersey and Connecticut; all went on to vote Democratic in every subsequent presidential election after having voted Republican in the five prior to 1992. 1996 marked the first time that Vermont voted for a Democrat in two successive elections. Pennsylvania and Michigan both voted Democratic, and would remain in the Democratic presidential fold until 2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff, impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses duri ...
.
Although Clinton's margin of victory in the popular vote was slightly greater than that of George H.W. Bush eight years prior, he won fewer states and electoral votes, in part due to his relatively poor performance in areas of low population density – a precursor of the trend where future Democratic contenders for the presidency perform very well in populous metropolitan areas but vastly underperform in rural counties.
Reform Party nominee Ross Perot won approximately 8% of the popular vote. His vote total was less than half of his performance in 1992. The 1996 national exit poll showed that just as in 1992, Perot drew supporters from Clinton and Dole equally. In polls directed at Perot voters as to who would be a second choice, Clinton consistently held substantial leads. Perot's best showing was in states that tended to strongly favor either Clinton (such as Maine) or Dole (particularly Montana, though the margin of victory there was much closer). Perot once again received his lowest amount of support in the South.
Although Clinton is a native of Arkansas, and his running mate hailed from Tennessee, the Democratic ticket again carried just four of the eleven states of the former Confederacy. This tied Clinton's 1992 run for the weakest performance by a winning Democratic presidential candidate in the region before 2000 (in terms of states won). Clinton's performance seems to have been part of a broader decline in support for the Democratic Party in the South. In the 2000
File:2000 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Protests against Bush v. Gore after the 2000 United States presidential election; Heads of state meet for the Millennium Summit; The International Space Station in its infant form as seen from S ...
and 2004 elections, the Democrats would fail to carry even one of the former Confederate states, contributing to their defeat both times. This completed the Republican takeover of the American South, a region in which Democrats had held a near monopoly from 1880
Events
January–March
* January 22 – Toowong State School is founded in Queensland, Australia.
* January – The international White slave trade affair scandal in Brussels is exposed and attracts international infamy.
* February � ...
to 1948. However, in 2008
File:2008 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Lehman Brothers went bankrupt following the Subprime mortgage crisis; Cyclone Nargis killed more than 138,000 in Myanmar; A scene from the opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics in Beijing; ...
, the Democrats were able to win three former Confederate states (Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
, and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
), but that was still worse than Clinton's performances in both 1992 and 1996. Since 1984
Events
January
* January 1 – The Bornean Sultanate of Brunei gains full independence from the United Kingdom, having become a British protectorate in 1888.
* January 7 – Brunei becomes the sixth member of the Association of Southeas ...
, no winning presidential candidate has surpassed Bill Clinton's 8.5 percentage popular vote margin, or his 220 electoral vote margin since 1988
File:1988 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The oil platform Piper Alpha explodes and collapses in the North Sea, killing 165 workers; The USS Vincennes (CG-49) mistakenly shoots down Iran Air Flight 655; Australia celebrates its Bicenten ...
. Additionally, since 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarc ...
, no other Democratic presidential candidate has surpassed Clinton's electoral vote margin and, except Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
in that election, no Democratic presidential candidate has surpassed Clinton's 8.5 percentage popular vote margin since 1940.
The election was also notable for the fact that for the first time in U.S. history the winner was elected without winning the male vote and the third time in U.S. history that a candidate was elected president twice without receiving an absolute majority of the popular vote in either election (Grover Cleveland
Stephen Grover Cleveland (March 18, 1837June 24, 1908) was an American lawyer and politician who served as the 22nd and 24th president of the United States from 1885 to 1889 and from 1893 to 1897. Cleveland is the only president in American ...
and Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson (December 28, 1856February 3, 1924) was an American politician and academic who served as the 28th president of the United States from 1913 to 1921. A member of the Democratic Party, Wilson served as the president of ...
are the others, although all three won pluralities, i.e. the most votes).
Clinton was the first Democrat to win re-election to the presidency since Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
, and the first Southern Democrat to win re-election since Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
in 1832
Events
January–March
* January 6 – Abolitionist William Lloyd Garrison founds the New-England Anti-Slavery Society.
* January 13 – The Christmas Rebellion of slaves is brought to an end in Jamaica, after the island's white plant ...
. Following the 2020 election, 1996 remains the last time the following states voted Democratic: Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
, Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, and West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
. Clinton also remains the last presidential candidate of either party to win at least one county in every state and the last Democrat to win a majority or plurality in Ross County, Ohio
Ross County is a county in the Appalachian region of the U.S. state of Ohio. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 77,093. Its county seat is Chillicothe, the first and third capital of Ohio. Established on August 20, 1798, th ...
, Spokane County, Washington
Spokane County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, its population was 539,339, making it the fourth-most populous county in Washington. The largest city and county seat is Spokane, the second largest cit ...
, Pinal and Gila Counties, Arizona, Washington County, Arkansas
Washington County is a regional economic, educational, and cultural hub in the Northwest Arkansas region. Created as Arkansas's 17th county on November 30, 1848, Washington County has 13 incorporated municipalities, including Fayetteville, the ...
, Westmoreland County, Pennsylvania
Westmoreland County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 364,663. The county seat is Greensburg. Formed from, successively, Lancaster, Northumberland, and later Bedford co ...
, Oneida County, New York
Oneida County is a county in the state of New York, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 232,125. The county seat is Utica. The name is in honor of the Oneida, one of the Five Nations of the Iroquois League or ''Haudenos ...
and Anoka County, Minnesota
Anoka County ( ) is the fourth-most-populous county in the U.S. state of Minnesota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 363,887. The county seat and namesake of the county is the city of Anoka, which is derived from the Dakota word '' ...
. Clinton was also the last Democrat to win Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
until 2020.
Official Source (Popular Vote)1996 Official Presidential General Election Results
'' Source (popular and electoral vote)
'' unofficial Secondary Source (Popular Vote): Voting age population: 196,498,000 Percent of voting age population casting a vote for President: 49.00%

Results by state
Uselectionatlas.org.
Maine and Nebraska district results
†Maine and Nebraska each allow for their electoral votes to be split between candidates. In both states, two electoral votes are awarded to the winner of the statewide race and one electoral vote is awarded to the winner of each congressional district.Close states
State where the margin of victory was under 1% (8 electoral votes): # Kentucky, 0.96% (13,331 votes) States where the margin of victory was under 5% (109 electoral votes): # Nevada, 1.02% (4,730 votes) # Georgia, 1.17% (26,994 votes) # Colorado, 1.37% (20,696 votes) # Virginia, 1.96% (47,290 votes) # Arizona, 2.22% (31,215 votes) # Tennessee, 2.41% (45,616 votes) # Montana, 2.88% (11,730 votes) # South Dakota, 3.46% (11,210 votes) # North Carolina, 4.69% (118,089 votes) # Texas, 4.93% (276,484 votes) States where the margin of victory was between 5% and 10% (143 electoral votes): # Mississippi, 5.13% (45,816 votes) # Indiana, 5.58% (119,269 votes) # Florida, 5.70% (302,334 votes) # South Carolina, 6.04% (69,407 votes) # Missouri, 6.30% (135,919 votes) # Ohio, 6.36% (288,339 votes) # North Dakota, 6.81% (18,145 votes) # Alabama, 6.96% (106,879 votes) # New Mexico, 7.32% (40,744 votes) # Oklahoma, 7.81% (94,210 votes) # Oregon, 8.09% (111,489 votes) # Pennsylvania, 9.20% (414,650 votes) (tipping point state) # New Hampshire, 9.95% (49,682 votes)Statistics
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Democratic) #Starr County, Texas
Starr County is located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 65,920. Its county seat is Rio Grande City. The county was created in 1848. It is named for James Harper Starr, who served as Secretary of the Treasu ...
86.94%
# Bronx County, New York
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Yo ...
85.80%
# Macon County, Alabama
Macon County is a county located in the east central part of the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 19,532. Its county seat is Tuskegee. Its name is in honor of Nathaniel Macon, a member of the United States Senat ...
85.55%
# Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
85.19%
# Duval County, Texas
Duval County is a county located in the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 9,831. The county seat is San Diego. The county was founded in 1858 and later organized in 1876. It is named for Burr H. Duval, a soldier in ...
84.94%
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Republican)
# Ochiltree County, Texas
Ochiltree County ( ) is a county located in the panhandle of the U.S. state of Texas. As of the 2020 census, its population was 10,015. The county seat is Perryton. The county was created in 1876 and organized in 1889. and is named for W ...
79.20%
# Russell County, Kansas
Russell County (standard abbreviation: RS) is a county in the U.S. state of Kansas. As of the 2020 census, the population was 6,691. The largest city and county seat is Russell. Russell, the county seat, was the home of former U.S. Senate Maj ...
78.98%
# Glasscock County, Texas 78.93%
# Hayes County, Nebraska
Hayes County is a county in the U.S. state of Nebraska. As of the 2010 United States Census, the population was 967. Its county seat is Hayes Center. The county was created in 1877, and was organized in 1884. It was named for Rutherford B. Haye ...
77.02%
# Sioux County, Iowa
Sioux County is a county located in the U.S. state of Iowa. As of the 2020 census, the population was 35,872. Its county seat is Orange City. Its largest city is Sioux Center.
History
Sioux County was formed on January 15, 1851. It has been ...
77.00%
Counties with Highest Percent of Vote (Other)
# Mineral County, Montana
Mineral County is a county located in the U.S. state of Montana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 4,535. Its county seat is Superior.
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which i ...
23.72%
# Grant County, North Dakota
Grant County is a county in the U.S. state of North Dakota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 2,301. Its county seat is Carson.
History
The territory of Grant County was part of Morton County until 1916. On November 7 the county vote ...
21.55%
# Shoshone County, Idaho
Shoshone County is a county in the U.S. state of Idaho. As of the 2020 census, the population was 13,169. The largest city is Kellogg. The county was established in 1864, named for the Native American Shoshone tribe.
Shoshone County is co ...
21.55%
# Sanders County, Montana
Sanders County is a county in the U.S. state of Montana. As of the 2020 census, the population was 12,400. Its county seat is Thompson Falls. The county was founded in 1905.
It has an annual county fair with rodeo at Plains.
Geography
Acc ...
21.24%
# Billings County, North Dakota
Billings County is a county in the U.S. state of North Dakota. As of the 2020 census, the population was 945, making it the second-least populous county in North Dakota. Its county seat and only incorporated place is Medora.
The Territorial ...
21.10%
Voter demographics
Source: Voter News Service exit poll, reported in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'', November 10, 1996, 28.
Polling controversy
The polling in the election was criticized by Everett Carll Ladd, who argued that "polls had overestimated Clinton's lead during the campaign and had thereby dampened interest in the election." Others such as Warren J. Mitofsky rebutted Ladd's view; in an analysis in ''Public Opinion Quarterly
''Public Opinion Quarterly'' is an academic journal published by Oxford University Press for the American Association for Public Opinion Research, covering communication studies and political science. It was established in 1937 and according to t ...
'', Mitofsky wrote that "1996 was not the best but was far from the worst year for the polls", with accuracy surpassing the polling in 1948 and in 1980. Because Clinton won the election by a comfortable margin, there was no major reaction towards the impreciseness of the polls.
See also
*List of presidents of the United States
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year Term of office, term via the United States Electoral College, Electoral College. The officeholder leads the ...
* Second inauguration of Bill Clinton
The second inauguration of Bill Clinton as president of the United States was held on Monday, January 20, 1997, at the West Front of the United States Capitol Building in Washington, D.C. This was the 53rd inauguration and marked the commencemen ...
* Newspaper endorsements in the 1996 United States presidential election
During the 1996 United States presidential election, newspapers, magazines, and other publications made general election endorsements.
According to ''Editor & Publisher'', based on responses to their quadrennial poll, Bob Dole received a total o ...
* 1996 United States gubernatorial elections
United States gubernatorial elections were held on November 5, 1996, in 11 states and two territories. Going into the elections, seven of the seats were held by Democrats and four by Republicans. Democrats picked up the open seat in New Hampshir ...
* 1996 United States House of Representatives elections
The 1996 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives on November 5, 1996, which coincided with the re-election of President Bill Clinton. Democrats won the popular vote by almos ...
* 1996 United States Senate elections
The 1996 United States Senate elections coincided with the presidential election of the same year, in which Democrat Bill Clinton was re-elected president.
Despite the re-election of Clinton and Gore, and despite Democrats picking up a net two ...
Notes
References
Further reading
Books
* * * * * * * *Journals
* Immelman, Aubrey. "The political personalities of 1996 US presidential candidates Bill Clinton and Bob Dole." ''Leadership Quarterly'' 9.3 (1998): 335–366online
*
Web references
* *External links
; Campaign websites* (as of 1996) *
(still active as of February 2021) ; Other links
The Election Wall's 1996 Election Video Page
1996 popular vote by states
1996 popular vote by states (with bar graphs)
* – MTV pages on the election * *Documentary about the 1996 Vice Presidential Candidates
"Running Mate,"
1996-10-01, The Walter J. Brown Media Archives & Peabody Awards Collection at the
University of Georgia
, mottoeng = "To teach, to serve, and to inquire into the nature of things.""To serve" was later added to the motto without changing the seal; the Latin motto directly translates as "To teach and to inquire into the nature of things."
, establ ...
, American Archive of Public Broadcasting
The American Archive of Public Broadcasting (AAPB) is a collaboration between the Library of Congress and WGBH Educational Foundation, founded through the efforts of the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. The AAPB is a national effort to digital ...
{{Authority control
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Bill Clinton
Al Gore
Ross Perot
Bob Dole
November 1996 events in the United States
Foreign electoral intervention
Jack Kemp