The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by
other names) was a
civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. It was fought between the
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
("the North") and the
Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
s that had
seceded. The central
cause of the war was the dispute over whether
slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.
Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the
1860 U.S. presidential election of
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern
slave states
In the United States before 1865, a slave state was a state in which slavery and the internal or domestic slave trade were legal, while a free state was one in which they were not. Between 1812 and 1850, it was considered by the slave states ...
responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President
Jefferson Davis, the Confederacy ultimately came to control over half of U.S. territory in eleven of the 34 U.S. states that then existed. Four years of intense combat, mostly in the South, ensued.
During 1861–1862 in the
war's Western Theater, the Union made significant permanent gainsthough in the
war's Eastern Theater the conflict was inconclusive. The abolition of slavery became a war goal on January 1, 1863, when Lincoln issued the
Emancipation Proclamation and declared all slaves in states in rebellion to be free, affecting more than 3.5 million of the 4 million enslaved people in the country. To the west, the Union destroyed the Confederate's river navy by the summer of 1862, then much of its western armies, and seized
. The successful 1863 Union
siege of Vicksburg
The siege of Vicksburg (May 18 – July 4, 1863) was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Maj. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mis ...
split the Confederacy in two at the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
. In 1863, Confederate General
Robert E. Lee's incursion north ended at the
Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
. Western successes led to General
Ulysses S. Grant's command of all Union armies in 1864. Inflicting an ever-tightening
naval blockade of Confederate ports, the Union marshaled resources and manpower to attack the Confederacy from all directions. This led to the
fall of Atlanta in 1864 to Union General
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
, followed by
his march to the sea. The last significant battles raged around the ten-month
Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the Siege of Petersburg, it was not a cla ...
, gateway to the Confederate capital of
Richmond. The Confederates abandoned Richmond, and on April 9, 1865, Lee surrendered to Grant following the
Battle of Appomattox Court House, setting in motion the end of the war.
A wave of Confederate surrenders followed. On April 14, just five days after Lee's surrender,
Lincoln was assassinated. As a practical matter, the war ended with the May 26 surrender of the
Department of the Trans-Mississippi but the
conclusion of the American Civil War lacks a clear and precise historical end date. Confederate ground forces continued surrendering past the May 26 surrender date until June 23. By the end of the war, much of the South's infrastructure was destroyed, especially its railroads. The Confederacy collapsed, slavery was abolished, and four million enslaved black people were freed. The war-torn nation then entered the
Reconstruction era in an attempt to rebuild the country, bring the former Confederate states back into the United States, and grant
civil rights
Civil and political rights are a class of rights that protect individuals' freedom from infringement by governments, social organizations, and private individuals. They ensure one's entitlement to participate in the civil and political life o ...
to freed slaves.
The Civil War is one of the most extensively studied and
written about episodes in
U.S. history. It remains the subject of cultural and
historiographical debate. Of particular interest is the persisting myth of the
Lost Cause of the Confederacy
The Lost Cause of the Confederacy (or simply Lost Cause) is an American pseudohistorical negationist mythology that claims the cause of the Confederate States during the American Civil War was just, heroic, and not centered on slavery. Fir ...
. The American Civil War was among the first wars to utilize
industrial warfare. Railroads, the
telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
, steamships, the
ironclad warship, and mass-produced weapons were all widely used during the war. In total, the war left between 620,000 and 750,000 soldiers dead, along with an undetermined number of
civilian casualties
Civilian casualties occur when civilians are killed or injured by non-civilians, mostly law enforcement officers, military personnel, rebel group forces, or terrorists. Under the law of war, it refers to civilians who perish or suffer wounds as ...
, making the Civil War the deadliest military conflict in American history. The technology and brutality of the Civil War foreshadowed the coming
World Wars
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
.
Causes of secession

The causes behind Southern states' decision to secede were complex and have been historically controversial; most academic scholars identify slavery as the central cause of the war. The causes are further complicated by some
historical revisionists who have tried to offer a variety of reasons for the war. Slavery was the central source of escalating political tension in the
1850s. The
Republican Party was determined to prevent any spread of slavery to the territories, which, after they were admitted as states, would give the North greater representation in Congress and the Electoral College. Many Southern leaders had threatened secession if the Republican candidate, Lincoln, won the
1860 election. After Lincoln won, many Southern leaders felt that disunion was their only option, fearing that the loss of representation would hamper their ability to enact pro-slavery laws and policies. In his
second inaugural address, Lincoln said that "slaves constituted a peculiar and powerful interest. All knew that this interest was, somehow, the cause of the war. To strengthen, perpetuate, and extend this interest was the object for which the insurgents would rend the Union, even by war; while the government claimed no right to do more than to restrict the territorial enlargement of it."
Slavery
Disagreements among states about the future of slavery were the main cause of disunion and the subsequent war itself. Slavery had been a controversial issue during the framing of the
Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
but had been left unsettled. The issue of slavery had confounded the nation since its inception, and increasingly separated the United States into a slaveholding South and a free North. The issue was exacerbated by the rapid territorial expansion of the country, which repeatedly brought to the fore the issue of whether new territory should be slaveholding or free. The issue had dominated politics for decades leading up to the war. Key attempts to solve the issue included the
Missouri Compromise and the
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Am ...
, but these only postponed an inevitable showdown over slavery.
The motivations of the average person were not necessarily those of their faction; some Northern soldiers were indifferent on the subject of slavery, but a general pattern can be established. Confederate soldiers fought the war primarily to protect a Southern society of which slavery was an integral part. Opponents of slavery considered slavery an anachronistic evil incompatible with
republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology centered on citizenship in a state organized as a republic. Historically, it emphasises the idea of self-rule and ranges from the rule of a representative minority or oligarchy to popular sovereignty. It ...
. The strategy of the anti-slavery forces was containment—to stop the expansion of slavery and thereby put it on a path to ultimate extinction. The slaveholding interests in the South denounced this strategy as infringing upon their constitutional rights. Southern whites believed that the emancipation of slaves would destroy the South's economy, because of the large amount of capital invested in slaves and fears of integrating the ex-slave black population. In particular, many Southerners feared a repeat of the
1804 Haiti massacre
The 1804 Haiti massacre also known as the 1804 Haitian Genocide or simply the Haitian Genocide was carried out by Afro-Haitian soldiers, mostly former slaves, under orders from Jean-Jacques Dessalines against the remaining European population in ...
(referred to at the time as "the horrors of Santo Domingo"),
in which former slaves systematically murdered most of what was left of the country's white population—including men, women, children, and even many sympathetic to abolition—after the
successful slave revolt in Haiti. Historian
Thomas Fleming points to the historical phrase "a disease in the public mind" used by critics of this idea and proposes it contributed to the segregation in the
Jim Crow era following emancipation. These fears were exacerbated by the
1859 attempt of
John Brown to instigate an armed slave rebellion in the South.
Abolitionists

The
abolitionists—those advocating the end of slavery—were active in the decades leading up to the Civil War. They traced their philosophical roots back to the
Puritans
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to purify the Church of England of Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should become more Protestant. ...
, who believed that slavery was morally wrong. One of the early Puritan writings on this subject was ''The Selling of Joseph,'' by
Samuel Sewall in 1700. In it, Sewall condemned slavery and the slave trade and refuted many of the era's typical justifications for slavery.
[McCullough, David. ''John Adams,'' pp. 132–3, Simon & Schuster, New York, New York, 2001. .]
The
American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revoluti ...
and the cause of liberty added tremendous impetus to the abolitionist cause. Slavery, which had been around for thousands of years, was considered normal and was not a significant issue of public debate prior to the Revolution. The Revolution changed that and made it into an issue that had to be addressed. As a result, during and shortly after the Revolution, the Northern states quickly started outlawing slavery. Even in Southern states, laws were changed to limit slavery and facilitate
manumission
Manumission, or enfranchisement, is the act of freeing enslaved people by their enslavers. Different approaches to manumission were developed, each specific to the time and place of a particular society. Historian Verene Shepherd states that t ...
. The amount of
indentured servitude dropped dramatically throughout the country. An
Act Prohibiting Importation of Slaves sailed through Congress with little opposition. President
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 1801 to 1809. He was previously the natio ...
supported it, and it went into effect on January 1, 1808, which was the first day that the Constitution (Article I, section 9, clause 1) permitted Congress to prohibit the importation of slaves.
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
and
James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for h ...
each helped found manumission societies. Influenced by the Revolution, many slave owners freed their slaves, but some, such as
George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
, did so only in their wills. The number of free black people as a proportion of the black population in the
upper South
The Upland South and Upper South are two overlapping cultural and geographic subregions in the inland part of the Southern and lower Midwestern United States. They differ from the Deep South and Atlantic coastal plain by terrain, history, econom ...
increased from less than 1 percent to nearly 10 percent between 1790 and 1810 as a result of these actions.
[Wilson, ''Black Codes'' (1965), p. 15. "By 1775, inspired by those 'self-evident' truths which were to be expressed by the ]Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of th ...
, a considerable number of colonists felt that the time had come to end slavery and give the free Negroes some fruits of liberty. This sentiment, added to economic considerations, led to the immediate or gradual abolition of slavery in six northern states, while there was a swelling flood of private manumissions in the South. Little actual gain was made by the free Negro even in this period, and by the turn of the century, the downward trend had begun again. Thereafter the only important change in that trend before the Civil War was that after 1831 the decline in the status of the free Negro became more precipitate."
The establishment of the
Northwest Territory as "free soil"—no slavery—by
Manasseh Cutler
Manasseh Cutler (May 13, 1742 – July 28, 1823) was an American clergyman involved in the American Revolutionary War. He was influential in the passage of the Northwest Ordinance of 1787 and wrote the section prohibiting slavery in the Nort ...
and
Rufus Putnam
Brigadier-General Rufus Putnam (April 9, 1738 – May 4, 1824) was an American military officer who fought during the French and Indian War and the American Revolutionary War. As an organizer of the Ohio Company of Associates, he was instrumenta ...
(who both came from Puritan New England) would also prove crucial. This territory (which became the states of Ohio, Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, Wisconsin and part of Minnesota) doubled the size of the United States.

In the decades leading up to the Civil War, abolitionists, such as
Theodore Parker,
Ralph Waldo Emerson
Ralph Waldo Emerson (May 25, 1803April 27, 1882), who went by his middle name Waldo, was an American essayist, lecturer, philosopher, abolitionist, and poet who led the transcendentalist movement of the mid-19th century. He was seen as a champ ...
,
Henry David Thoreau and
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became ...
, repeatedly used the Puritan heritage of the country to bolster their cause. The most radical anti-slavery newspaper, ''
The Liberator,'' invoked the Puritans and Puritan values over a thousand times. Parker, in urging New England congressmen to support the abolition of slavery, wrote, "The son of the Puritan . . . is sent to Congress to stand up for Truth and Right." Literature served as a means to spread the message to common folks. Key works included ''
Twelve Years a Slave
''Twelve Years a Slave'' is an 1853 memoir and slave narrative by American Solomon Northup as told to and written by David Wilson. Northup, a black man who was born free in New York state, details himself being tricked to go to Washington, D. ...
'', the
''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass'', ''
American Slavery as It Is'', and the most important: ''
Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U ...
'', the best-selling book of the 19th century aside from the Bible.
["The Sentimental Novel: The Example of Harriet Beecher Stowe" by Gail K. Smith, ''The Cambridge Companion to Nineteenth-Century American Women's Writing'' by Dale M. Bauer and Philip Gould, Cambridge University Press, 2001, p. 221]
Book preview
.
A more unusual abolitionist than those named above was
Hinton Rowan Helper, whose 1857 book, ''
The Impending Crisis of the South
''The Impending Crisis of the South: How to Meet It'' is an 1857 book by Hinton Rowan Helper, who declares himself a proud Southerner. It was written mostly in Baltimore, but it would have been illegal to publish it there, as he pointed out. It wa ...
: How to Meet It'', "
en more perhaps than ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' ... fed the fires of sectional controversy leading up to the Civil War." A Southerner and a virulent racist, Helper was nevertheless an abolitionist because he believed, and showed with statistics, that slavery "impeded the progress and prosperity of the South, ... dwindled our commerce, and other similar pursuits, into the most contemptible insignificance; sunk a large majority of our people in galling poverty and ignorance, ...
ndentailed upon us a humiliating dependence on the Free States...."
By 1840 more than 15,000 people were members of abolitionist societies in the United States. Abolitionism in the United States became a popular expression of
moralism
Moralism is any philosophy with the central focus of applying moral judgements. The term is commonly used as a pejorative to mean "being overly concerned with making moral judgments or being illiberal in the judgments one makes".
Moralism has s ...
, and led directly to the Civil War. In churches, conventions and newspapers, reformers promoted an absolute and immediate rejection of slavery.
Support for abolition among the religious was not universal though. As the war approached, even the main denominations split along political lines, forming rival Southern and Northern churches. For example, in 1845 the
Baptists split into the
Northern Baptists and
Southern Baptists
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wo ...
over the issue of slavery.
Abolitionist sentiment was not strictly religious or moral in origin. The
Whig Party became increasingly opposed to slavery because it saw it as inherently against the ideals of capitalism and the free market. Whig leader
William H. Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
(who would serve as Lincoln's secretary of state) proclaimed that there was an "irrepressible conflict" between slavery and free labor, and that slavery had left the South backward and undeveloped. As the Whig party dissolved in the 1850s, the mantle of abolition fell to its newly formed successor, the
Republican Party.
Territorial crisis
Manifest destiny heightened the conflict over slavery. Each new territory acquired had to face the thorny question of whether to allow or disallow the "peculiar institution". Between 1803 and 1854, the United States achieved a vast expansion of territory through purchase, negotiation, and conquest. At first, the new states carved out of these territories entering the union were apportioned equally between slave and free states. Pro- and anti-slavery forces collided over the territories west of the Mississippi.
The
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War, also known in the United States as the Mexican War and in Mexico as the (''United States intervention in Mexico''), was an armed conflict between the United States and Mexico from 1846 to 1848. It followed the 1 ...
and its aftermath was a key territorial event in the leadup to the war. As the
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 ...
finalized the conquest of northern Mexico west to
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
in 1848, slaveholding interests looked forward to expanding into these lands and perhaps Cuba and Central America as well. Prophetically, Ralph Waldo Emerson wrote that "Mexico will poison us", referring to the ensuing divisions around whether the newly conquered lands would end up slave or free. Northern free-soil interests vigorously sought to curtail any further expansion of slave territory. The
Compromise of 1850
The Compromise of 1850 was a package of five separate bills passed by the United States Congress in September 1850 that defused a political confrontation between slave and free states on the status of territories acquired in the Mexican–Am ...
over California balanced a free-soil state with a stronger
federal fugitive slave law for a political settlement after four years of strife in the 1840s. But the states admitted following
California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
were all free:
Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
(1858),
Oregon
Oregon () is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. T ...
(1859), and
Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to th ...
(1861). In the Southern states, the question of the territorial expansion of slavery westward again became explosive. Both the South and the North drew the same conclusion: "The power to decide the question of slavery for the territories was the power to determine the future of slavery itself."
By 1860, four doctrines had emerged to answer the question of federal control in the territories, and they all claimed they were sanctioned by the Constitution, implicitly or explicitly. The first of these theories, represented by the
Constitutional Union Party, argued that the
Missouri Compromise apportionment of territory north for free soil and south for slavery should become a constitutional mandate. The failed
Crittenden Compromise of 1860 was an expression of this view.
The second doctrine of congressional preeminence was championed by Abraham Lincoln and the Republican Party. It insisted that the Constitution did not bind legislators to a policy of balance—that slavery could be excluded in a territory, as it was in the
Northwest Ordinance of 1787, at the discretion of Congress. Thus Congress could restrict human bondage, but never establish it. The ill-fated
Wilmot Proviso
The Wilmot Proviso was an unsuccessful 1846 proposal in the United States Congress to ban slavery in territory acquired from Mexico in the Mexican–American War. The conflict over the Wilmot Proviso was one of the major events leading to the ...
announced this position in 1846. The Proviso was a pivotal moment in national politics, as it was the first time slavery had become a major congressional issue based on sectionalism, instead of party lines. Its support by Northern Democrats and Whigs, and opposition by Southerners, was a dark omen of coming divisions.
Senator
Stephen A. Douglas proclaimed the third doctrine: territorial or "popular" sovereignty, which asserted that the settlers in a territory had the same rights as states in the Union to establish or disestablish slavery as a purely local matter. The
Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 legislated this doctrine. In the Kansas Territory, years of
pro- and anti-slavery violence and political conflict erupted. The U.S. House of Representatives voted to admit Kansas as a free state in early 1860, but its admission did not pass the Senate until January 1861, after the departure of Southern senators.
[ Finteg.]
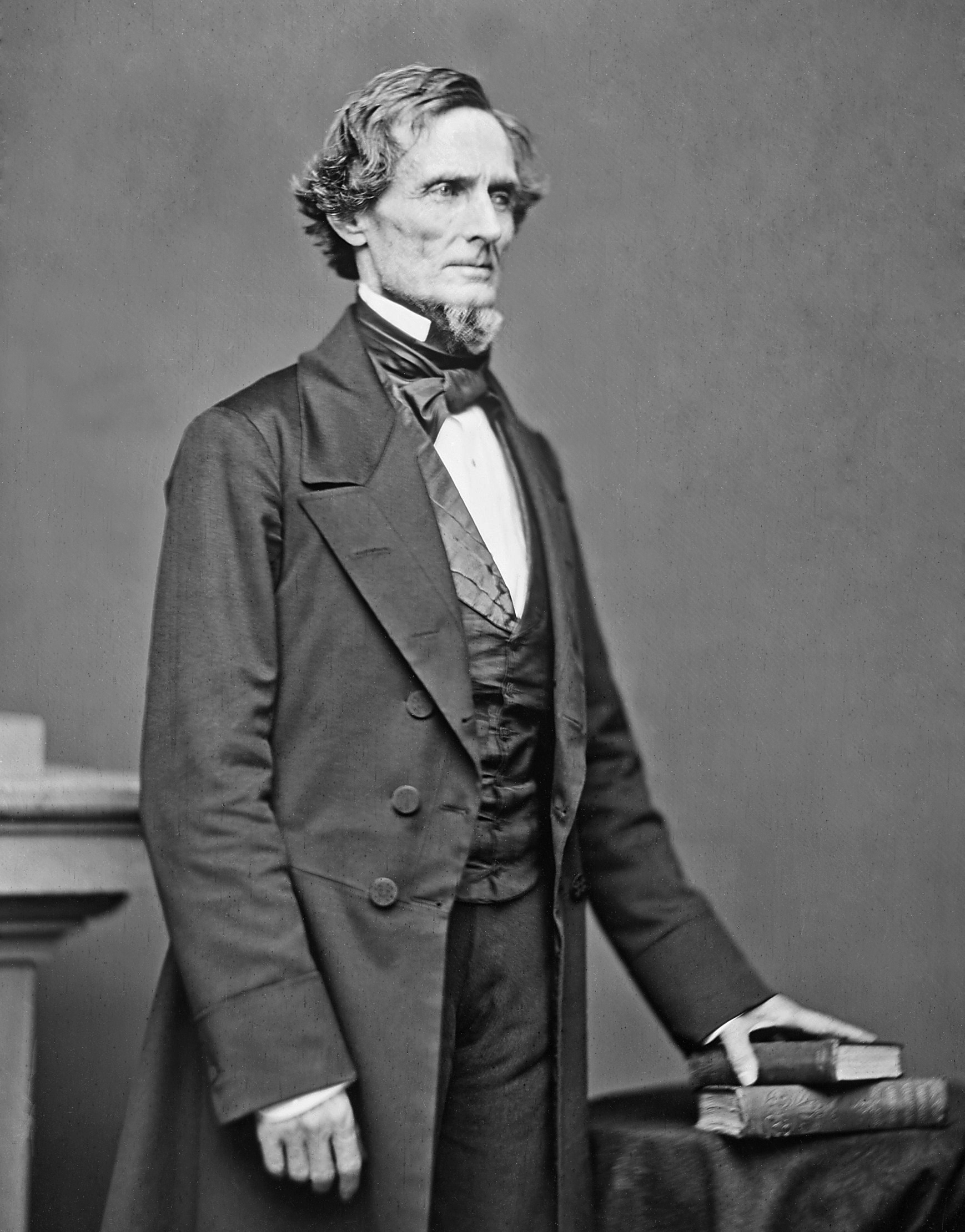
The fourth doctrine was advocated by Mississippi Senator (and soon to be Confederate President)
Jefferson Davis. It was one of state sovereignty ("states' rights"), also known as the "Calhoun doctrine", named after the South Carolinian political theorist and statesman
John C. Calhoun. Rejecting the arguments for federal authority or self-government, state sovereignty would empower states to promote the expansion of slavery as part of the federal union under the U.S. Constitution. These four doctrines comprised the dominant ideologies presented to the American public on the matters of slavery, the territories, and the U.S. Constitution before the 1860 presidential election.
States' rights
A long-running dispute over the origin of the Civil War is to what extent states' rights triggered the conflict. The consensus among historians is that the Civil War was fought about states' rights.
But the issue is frequently referenced in popular accounts of the war and has much traction among Southerners. The South argued that just as each state had decided to join the Union, a state had the right to secede—leave the Union—at any time. Northerners (including pro-slavery President Buchanan) rejected that notion as opposed to the will of the
Founding Fathers, who said they were setting up a perpetual union.
Historian James McPherson points out that even if Confederates genuinely fought over states' rights, it boiled down to states' right to slavery. McPherson writes concerning states' rights and other non-slavery explanations:
States' rights was an ideology formulated and applied as a means of advancing slave state interests through federal authority. As historian Thomas L. Krannawitter points out, the "Southern demand for federal slave protection represented a demand for an unprecedented expansion of Federal power." Before the Civil War, the Southern states supported the use of federal powers to enforce and extend slavery, as with the
Fugitive Slave Act of 1850 and the ''
Dred Scott v. Sandford
''Dred Scott v. Sandford'', 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, enslaved or free; th ...
'' decision.
The faction that pushed for secession often infringed on states' rights. Because of the overrepresentation of pro-slavery factions in the federal government, many Northerners, even non-abolitionists, feared the
Slave Power conspiracy.
Some Northern states resisted the enforcement of the Fugitive Slave Act. Historian
Eric Foner
Eric Foner (; born February 7, 1943) is an American historian. He writes extensively on American political history, the history of freedom, the early history of the Republican Party, African-American biography, the American Civil War, Reconstruc ...
states that the act "could hardly have been designed to arouse greater opposition in the North. It overrode numerous state and local laws and legal procedures and 'commanded' individual citizens to assist, when called upon, in capturing runaways." He continues, "It certainly did not reveal, on the part of slaveholders, sensitivity to states' rights."
According to historian
Paul Finkelman, "the southern states mostly complained that the northern states were asserting their states' rights and that the national government was not powerful enough to counter these northern claims."
The
Confederate Constitution also "federally" required slavery to be legal in all Confederate states and claimed territories.
Sectionalism
Sectionalism
Sectionalism is loyalty to one's own region or section of the country, rather than to the country as a whole.
Sectionalism occurs in many countries, such as in the United Kingdom, most notably in the constituent nation of Scotland, where various ...
resulted from the different economies, social structure, customs, and political values of the North and South.
Regional tensions came to a head during the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, resulting in the
Hartford Convention
The Hartford Convention was a series of meetings from December 15, 1814, to January 5, 1815, in Hartford, Connecticut, United States, in which the New England Federalist Party met to discuss their grievances concerning the ongoing War of 1812 and ...
, which manifested Northern dissatisfaction with a foreign trade embargo that affected the industrial North disproportionately, the
Three-Fifths Compromise, dilution of Northern power by new states, and a succession of
Southern presidents. Sectionalism increased steadily between 1800 and 1860 as the North, which phased slavery out of existence, industrialized, urbanized, and built prosperous farms, while the
deep South concentrated on plantation agriculture based on slave labor, together with
subsistence agriculture for poor whites. In the 1840s and 1850s, the issue of accepting slavery (in the guise of rejecting slave-owning bishops and missionaries) split the nation's largest religious denominations (the Methodist, Baptist, and Presbyterian churches) into separate Northern and Southern denominations.
Historians have debated whether economic differences between the mainly industrial North and the mainly agricultural South helped cause the war. Most historians now disagree with the
economic determinism
Economic determinism is a socioeconomic theory that economic relationships (such as being an owner or capitalist, or being a worker or proletarian) are the foundation upon which all other societal and political arrangements in society are based. ...
of historian
Charles A. Beard in the 1920s, and emphasize that Northern and Southern economies were largely complementary. While socially different, the sections economically benefited each other.
Protectionism
Owners of slaves preferred low-cost manual labor with no mechanization. Northern manufacturing interests supported tariffs and protectionism while Southern planters demanded free trade. The Democrats in Congress, controlled by Southerners, wrote the tariff laws in the 1830s, 1840s, and 1850s, and kept reducing rates so that the 1857 rates were the lowest since 1816. The Republicans called for an increase in tariffs in the 1860 election. The increases were only enacted in 1861 after Southerners resigned their seats in Congress.
The tariff issue was a Northern grievance. However,
neo-Confederate writers have claimed it as a Southern grievance. In 1860–61 none of the groups that proposed compromises to head off secession raised the tariff issue. Pamphleteers from the North and the South rarely mentioned the tariff.
Nationalism and honor

Nationalism was a powerful force in the early 19th century, with famous spokesmen such as
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
and
Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison ...
. While practically all Northerners supported the Union, Southerners were split between those loyal to the entirety of the United States (called "
Southern Unionists
In the United States, Southern Unionists were white Southerners living in the Confederate States of America opposed to secession. Many fought for the Union during the Civil War. These people are also referred to as Southern Loyalists, Union Lo ...
") and those loyal primarily to the Southern region and then the Confederacy.
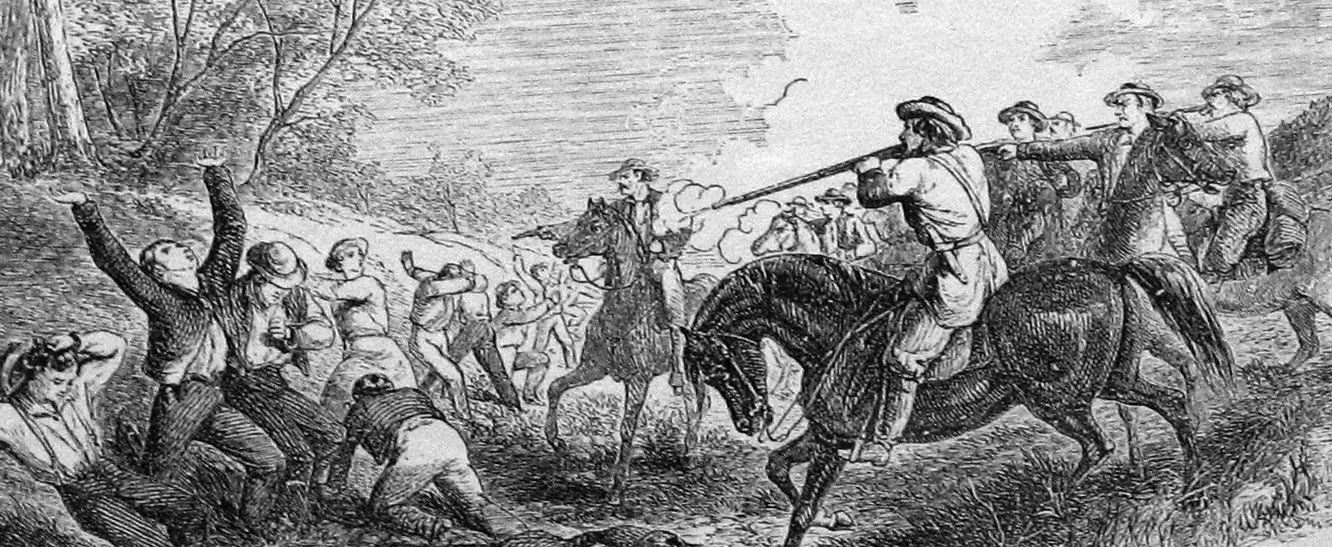
Perceived insults to Southern collective honor included the enormous popularity of ''Uncle Tom's Cabin,'' and the actions of abolitionist
John Brown in trying to incite a
rebellion of slaves in 1859.
While the South moved towards a Southern nationalism, leaders in the North were also becoming more nationally minded, and they rejected any notion of splitting the Union. The Republican national electoral platform of 1860 warned that Republicans regarded disunion as
treason
Treason is the crime of attacking a state authority to which one owes allegiance. This typically includes acts such as participating in a war against one's native country, attempting to overthrow its government, spying on its military, its diplo ...
and would not tolerate it.
The South ignored the warnings; Southerners did not realize how ardently the North would fight to hold the Union together.
Lincoln's election
The election of Abraham Lincoln in November 1860 was the final trigger for secession. Southern leaders feared that Lincoln would stop the expansion of slavery and put it on a course toward extinction. However, Lincoln would not be inaugurated until five months after the election, which gave the South time to secede and prepare for war in the winter and spring of 1861.
According to Lincoln, the American people had shown that they had been successful in ''establishing'' and ''administering'' a republic, but a third challenge faced the nation: ''maintaining'' a republic based on the people's vote, in the face of an attempt to destroy it.
Outbreak of the war
Secession crisis
The election of Lincoln provoked the legislature of
South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
to call a state convention to consider secession. Before the war, South Carolina did more than any other Southern state to advance the notion that a state had the right to
nullify federal laws, and even to secede from the United States. The convention unanimously voted to secede on December 20, 1860, and adopted
a secession declaration. It argued for states' rights for slave owners in the South, but contained a complaint about states' rights in the North in the form of opposition to the
Fugitive Slave Act, claiming that Northern states were not fulfilling their federal obligations under the Constitution. The "cotton states" of
Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
,
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
,
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
, Georgia, Louisiana, and
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
followed suit, seceding in January and February 1861.

Among the ordinances of secession passed by the individual states, those of three—Texas, Alabama, and Virginia—specifically mentioned the plight of the "slaveholding states" at the hands of Northern abolitionists. The rest make no mention of the slavery issue and are often brief announcements of the dissolution of ties by the legislatures. However, at least four states—South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, and Texas
[The text o]
''A Declaration of the Causes which Impel the State of Texas to Secede from the Federal Union''
. Retrieved November 28, 2012.—also passed lengthy and detailed explanations of their reasons for secession, all of which laid the blame squarely on the movement to abolish slavery and that movement's influence over the politics of the Northern states. The Southern states believed slaveholding was a constitutional right because of the
Fugitive Slave Clause of the Constitution. These states agreed to form a new federal government, the
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
, on February 4, 1861. They took control of federal forts and other properties within their boundaries with little resistance from outgoing President
James Buchanan, whose term ended on March 4, 1861. Buchanan said that the
Dred Scott decision
''Dred Scott v. Sandford'', 60 U.S. (19 How.) 393 (1857), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that held the U.S. Constitution did not extend American citizenship to people of black African descent, enslaved or free; th ...
was proof that the South had no reason for secession, and that the Union "was intended to be perpetual", but that "The power by force of arms to compel a State to remain in the Union" was not among the "enumerated powers granted to Congress".
One-quarter of the U.S. Army—the entire garrison in Texas—was surrendered in February 1861 to state forces by its commanding general,
David E. Twiggs, who then joined the Confederacy.
As Southerners resigned their seats in the Senate and the House, Republicans were able to pass projects that had been blocked by Southern senators before the war. These included the
Morrill Tariff, land grant colleges (the
Morrill Act
The Morrill Land-Grant Acts are United States statutes that allowed for the creation of land-grant colleges in U.S. states using the proceeds from sales of federally-owned land, often obtained from indigenous tribes through treaty, cession, or s ...
), a
Homestead Act
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of t ...
, a transcontinental railroad (the
Pacific Railroad Acts The Pacific Railroad Acts of 1862 were a series of acts of Congress that promoted the construction of a "transcontinental railroad" (the Pacific Railroad) in the United States through authorizing the issuance of government bonds and the grants of ...
),
the
National Bank Act
The National Banking Acts of 1863 and 1864 were two United States federal banking acts that established a system of national banks, and created the United States National Banking System. They encouraged development of a national currency backed by ...
, the authorization of
United States Note
A United States Note, also known as a Legal Tender Note, is a type of paper money that was issued from 1862 to 1971 in the U.S. Having been current for 109 years, they were issued for longer than any other form of U.S. paper money. They were k ...
s by the
Legal Tender Act of 1862, and the ending of
slavery in the District of Columbia
The slave trade in the District of Columbia was legal from its creation until 1850, when the trade in enslaved people in the District was outlawed as part of the Compromise of 1850. That restrictions on slavery in the District were probably coming ...
. The
Revenue Act of 1861
The Revenue Act of 1861, formally cited as Act of August 5, 1861, Chap. XLV, 12 Stat. 292', included the first U.S. Federal income tax statute (seSec.49. The Act, motivated by the need to fund the Civil War, imposed an income tax to be "levied, c ...
introduced the
income tax
An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities (taxpayers) in respect of the income or profits earned by them (commonly called taxable income). Income tax generally is computed as the product of a tax rate times the taxable income. Tax ...
to help finance the war.
In December 1860, the
Crittenden Compromise was proposed to re-establish the
Missouri Compromise line by constitutionally banning slavery in territories to the north of the line while guaranteeing it to the south. The adoption of this compromise likely would have prevented the secession of the Southern states, but Lincoln and the Republicans rejected it. Lincoln stated that any compromise that would extend slavery would in time bring down the Union. A pre-war February
Peace Conference of 1861 met in Washington, proposing a solution similar to that of the Crittenden compromise; it was rejected by Congress. The Republicans proposed an
alternative compromise to not interfere with slavery where it existed but the South regarded it as insufficient. Nonetheless, the remaining eight slave states rejected pleas to join the Confederacy following a two-to-one no-vote in Virginia's First Secessionist Convention on April 4, 1861.

On March 4, 1861, Abraham Lincoln was sworn in as president. In his
inaugural address
In government and politics, inauguration is the process of swearing a person into office and thus making that person the incumbent. Such an inauguration commonly occurs through a formal ceremony or special event, which may also include an inaugur ...
, he argued that the Constitution was a ''
more perfect union'' than the earlier
Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
, that it was a binding contract, and called any secession "legally void".
He had no intent to invade Southern states, nor did he intend to end slavery where it existed, but said that he would use force to maintain possession of federal property,
including forts, arsenals, mints, and customhouses that had been seized by the Southern states. The government would make no move to recover post offices, and if resisted, mail delivery would end at state lines. Where popular conditions did not allow peaceful enforcement of federal law, U.S. marshals and judges would be withdrawn. No mention was made of bullion lost from U.S. mints in Louisiana, Georgia, and North Carolina. He stated that it would be U.S. policy to only collect import duties at its ports; there could be no serious injury to the South to justify the armed revolution during his administration. His speech closed with a plea for restoration of the bonds of union, famously calling on "the mystic chords of memory" binding the two regions.
The Davis government of the new Confederacy sent three delegates to Washington to negotiate a peace treaty with the United States of America. Lincoln rejected any negotiations with Confederate agents because he claimed the Confederacy was not a legitimate government, and that making any treaty with it would be tantamount to recognition of it as a sovereign government. Lincoln instead attempted to negotiate directly with the governors of individual seceded states, whose administrations he continued to recognize.
Complicating Lincoln's attempts to defuse the crisis were the actions of the new Secretary of State,
William Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
. Seward had been Lincoln's main rival for the Republican presidential nomination. Shocked and deeply embittered by this defeat, Seward agreed to support Lincoln's candidacy only after he was guaranteed the executive office that was considered at that time to be by far the most powerful and important after the presidency itself. Even in the early stages of Lincoln's presidency Seward still held little regard for the new chief executive due to his perceived inexperience, and therefore viewed himself as the ''
de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' head of government or "
prime minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
" behind the throne of Lincoln. In this role, Seward attempted to engage in unauthorized and indirect negotiations that failed. However, President Lincoln was determined to hold all remaining Union-occupied forts in the Confederacy:
Fort Monroe
Fort Monroe, managed by partnership between the Fort Monroe Authority for the Commonwealth of Virginia, the National Park Service as the Fort Monroe National Monument, and the City of Hampton, is a former military installation in Hampton, Virgi ...
in Virginia,
Fort Pickens
Fort Pickens is a pentagonal historic United States military fort on Santa Rosa Island in the Pensacola, Florida, area. It is named after American Revolutionary War hero Andrew Pickens. The fort was completed in 1834 and was one of the few ...
,
Fort Jefferson and
Fort Taylor
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
in Florida, and
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battle ...
in South Carolina.
Battle of Fort Sumter
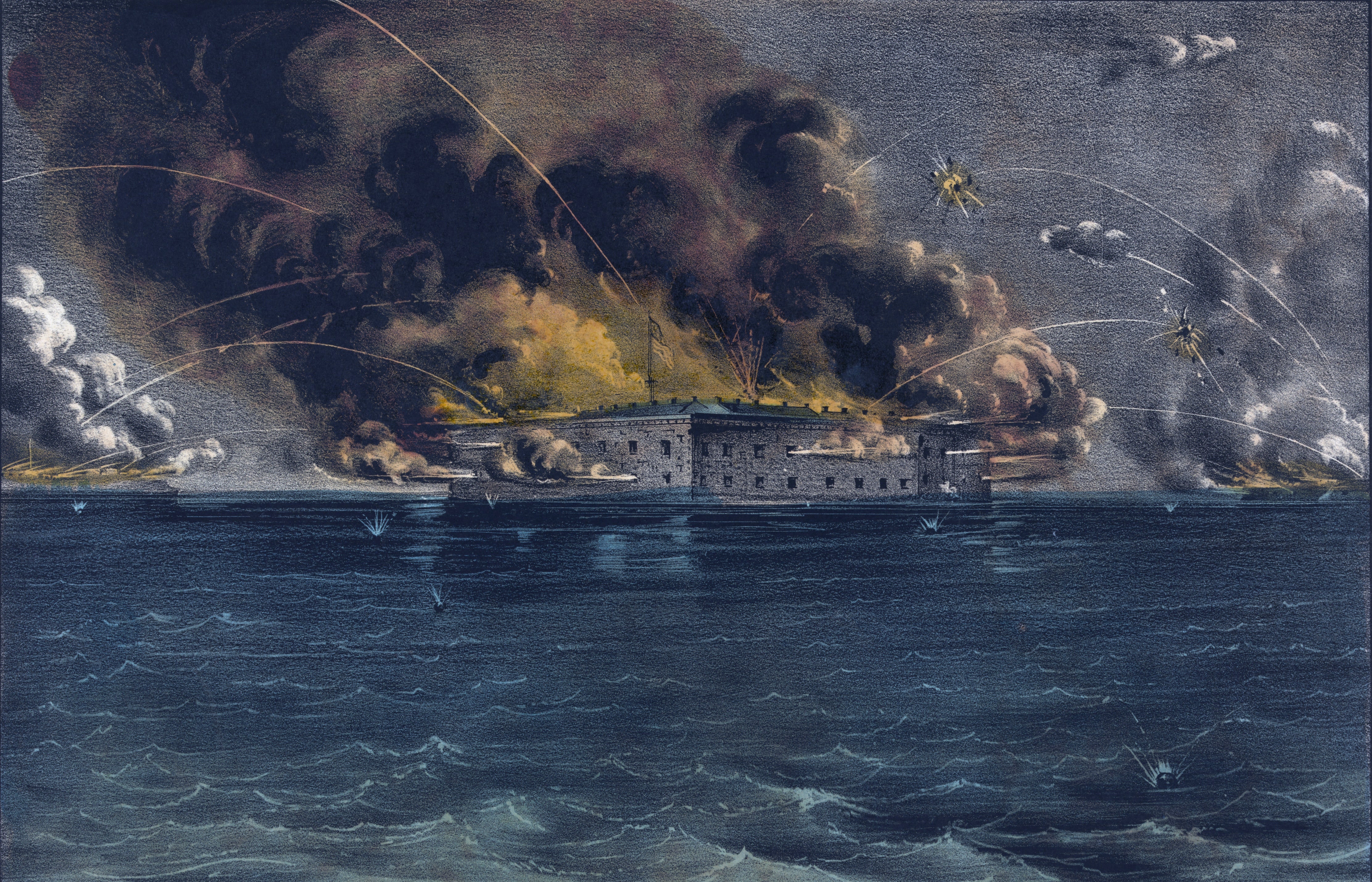

The American Civil War began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces opened fire on the Union-held
Fort Sumter
Fort Sumter is a sea fort built on an artificial island protecting Charleston, South Carolina from naval invasion. Its origin dates to the War of 1812 when the British invaded Washington by sea. It was still incomplete in 1861 when the Battle ...
. Fort Sumter is located in the middle of the harbor of
Charleston, South Carolina. Its status had been contentious for months. Outgoing President Buchanan had dithered in reinforcing the Union garrison in the harbor, which was under command of Major
Robert Anderson. Anderson took matters into his own hands and on December 26, 1860, under the cover of darkness, sailed the garrison from the poorly placed
Fort Moultrie
Fort Moultrie is a series of fortifications on Sullivan's Island, South Carolina, built to protect the city of Charleston, South Carolina. The first fort, formerly named Fort Sullivan, built of palmetto logs, inspired the flag and n ...
to the stalwart island Fort Sumter. Anderson's actions catapulted him to hero status in the North. An attempt to resupply the fort on January 9, 1861, failed and nearly started the war then and there. But an informal truce held. On March 5, the newly sworn in Lincoln was informed that the Fort was running low on supplies.
Fort Sumter proved to be one of the main challenges of the new Lincoln administration. Back-channel dealing by Secretary of State Seward with the Confederates undermined Lincoln's decision-making; Seward wanted to pull out of the fort. But a firm hand by Lincoln tamed Seward, and Seward became one of Lincoln's staunchest allies. Lincoln ultimately decided that holding the fort, which would require reinforcing it, was the only workable option. Thus, on April 6, Lincoln informed the Governor of South Carolina that a ship with food but no ammunition would attempt to supply the Fort. Historian McPherson describes this win-win approach as "the first sign of the mastery that would mark Lincoln's presidency"; the Union would win if it could resupply and hold onto the Fort, and the South would be the aggressor if it opened fire on an unarmed ship supplying starving men. An April 9 Confederate cabinet meeting resulted in President Davis's ordering General
P. G. T. Beauregard to take the Fort before supplies could reach it.
At 4:30 am on April 12, Confederate forces fired the first of 4,000 shells at the Fort; it fell the next day. The loss of Fort Sumter lit a patriotic fire under the North. On April 15, Lincoln called on the states to field
75,000 volunteer troops for 90 days; impassioned Union states met the quotas quickly. On May 3, 1861, Lincoln called for an additional 42,000 volunteers for a period of three years.
Shortly after this,
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
,
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
,
Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the O ...
, and
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
seceded and joined the Confederacy. To reward Virginia, the Confederate capital was moved to
Richmond.
Attitude of the border states

Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
,
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
,
Missouri
Missouri is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking 21st in land area, it is bordered by eight states (tied for the most with Tennessee): Iowa to the north, Illinois, Kentucky and Tennessee to the east, Arkansas t ...
, and
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
were slave states whose people had divided loyalties to Northern and Southern businesses and family members. Some men enlisted in the Union Army and others in the Confederate Army.
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
separated from
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
and was admitted to the
Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
on June 20, 1863.
Maryland's territory surrounded the United States' capital of
Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, and could cut it off from the North. It had numerous anti-Lincoln officials who tolerated anti-army
rioting in Baltimore and the burning of bridges, both aimed at hindering the passage of troops to the South. Maryland's legislature voted overwhelmingly (53–13) to stay in the Union, but also rejected hostilities with its southern neighbors, voting to close Maryland's rail lines to prevent them from being used for war.
Lincoln responded by establishing
martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
and unilaterally suspending
habeas corpus
''Habeas corpus'' (; from Medieval Latin, ) is a recourse in law through which a person can report an unlawful detention or imprisonment to a court and request that the court order the custodian of the person, usually a prison official, t ...
in Maryland, along with sending in militia units from the North. Lincoln rapidly took control of Maryland and the District of Columbia by seizing many prominent figures, including arresting 1/3 of the members of the
Maryland General Assembly
The Maryland General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland that convenes within the State House in Annapolis. It is a bicameral body: the upper chamber, the Maryland Senate, has 47 representatives and the lower chamber ...
on the day it reconvened.
All were held without trial, with Lincoln ignoring a ruling on June 1, 1861, by U.S. Supreme Court Chief Justice
Roger Taney, not speaking for the Court, that only Congress (and not the president) could suspend habeas corpus (''
Ex parte Merryman
''Ex parte Merryman'', 17 F. Cas. 144 (C.C.D. Md. 1861) (No. 9487), is a well-known and controversial U.S. federal court case that arose out of the American Civil War. It was a test of the authority of the President to suspend "t ...
''). Federal troops imprisoned a prominent Baltimore newspaper editor,
Frank Key Howard
Frank Key Howard (October 25, 1826 – May 29, 1872) (also cited as Francis Key Howard) was the grandson of Francis Scott Key and Revolutionary War colonel John Eager Howard. Howard was the editor of the ''The Daily Exchange, Daily Exchange' ...
, Francis Scott Key's grandson, after he criticized Lincoln in an editorial for ignoring Taney's ruling.
In Missouri, an
elected convention on secession voted decisively to remain within the Union. When pro-Confederate Governor
Claiborne F. Jackson called out the state militia, it was attacked by federal forces under General
Nathaniel Lyon
Nathaniel Lyon (July 14, 1818 – August 10, 1861) was the first Union general to be killed in the American Civil War. He is noted for his actions in Missouri in 1861, at the beginning of the conflict, to forestall secret secessionist plans of th ...
, who chased the governor and the rest of the State Guard to the southwestern corner of the state (''see also'':
Missouri secession
During the American Civil War, the secession of Missouri from the Union was controversial because of the state's disputed status. Missouri was claimed by both the Union and the Confederacy, had two rival state governments, and sent representativ ...
). In the resulting vacuum, the convention on secession reconvened and took power as the Unionist provisional government of Missouri.
Kentucky did not secede; for a time, it declared itself neutral. When Confederate forces entered the state in September 1861, neutrality ended and the state reaffirmed its Union status while maintaining slavery. During a brief invasion by Confederate forces in 1861, Confederate sympathizers organized a secession convention, formed the shadow
Confederate Government of Kentucky
The Confederate government of Kentucky was a shadow government established for the Commonwealth of Kentucky by a self-constituted group of Confederate sympathizers during the American Civil War. The shadow government never replaced the elect ...
, inaugurated a governor, and gained recognition from the Confederacy. Its jurisdiction extended only as far as Confederate battle lines in the Commonwealth, and it went into exile after October 1862.
After Virginia's secession, a
Unionist government in
Wheeling asked 48 counties to vote on an ordinance to create a new state on October 24, 1861. A voter turnout of 34 percent approved the statehood bill (96 percent approving).
Twenty-four secessionist counties were included in the new state,
and the ensuing guerrilla war engaged about 40,000 federal troops for much of the war. Congress admitted
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
to the Union on June 20, 1863. West Virginia provided about 20,000–22,000 soldiers to both the Confederacy and the Union.
A Unionist secession attempt occurred in
East Tennessee, but was suppressed by the Confederacy, which arrested over 3,000 men suspected of being loyal to the Union. They were held without trial.
War
The Civil War was a contest marked by the ferocity and frequency of battle. Over four years, 237 named battles were fought, as were many more minor actions and skirmishes, which were often characterized by their bitter intensity and high casualties. In his book ''The American Civil War'', British historian
John Keegan
Sir John Desmond Patrick Keegan (15 May 1934 – 2 August 2012) was an English military historian, lecturer, author and journalist. He wrote many published works on the nature of combat between prehistory and the 21st century, covering land, ...
writes that "The American Civil War was to prove one of the most ferocious wars ever fought". In many cases, without geographic objectives, the only target for each side was the enemy's soldier.
Mobilization
As the first seven states began organizing a Confederacy in Montgomery, the entire U.S. army numbered 16,000. However, Northern governors had begun to mobilize their militias. The Confederate Congress authorized the new nation up to 100,000 troops sent by governors as early as February. By May, Jefferson Davis was pushing for 100,000 soldiers for one year or the duration, and that was answered in kind by the U.S. Congress.
In the first year of the war, both sides had far more volunteers than they could effectively train and equip. After the initial enthusiasm faded, reliance on the cohort of young men who came of age every year and wanted to join was not enough. Both sides used a draft law—
conscription—as a device to encourage or force volunteering; relatively few were drafted and served. The Confederacy passed a draft law in April 1862 for young men aged 18 to 35; overseers of slaves, government officials, and clergymen were exempt.
The U.S. Congress followed in July, authorizing a militia draft within a state when it could not meet its quota with volunteers. European
immigrants joined the
Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
in large numbers, including 177,000 born in Germany and 144,000 born in Ireland.

When the
Emancipation Proclamation went into effect in January 1863, ex-slaves were energetically recruited by the states and used to meet the state quotas. States and local communities offered higher and higher cash bonuses for white volunteers. Congress tightened the law in March 1863. Men selected in the draft could provide substitutes or, until mid-1864, pay commutation money. Many eligibles pooled their money to cover the cost of anyone drafted. Families used the substitute provision to select which man should go into the army and which should stay home. There was much evasion and overt resistance to the draft, especially in Catholic areas. The
draft riot in New York City in July 1863 involved Irish immigrants who had been signed up as citizens to swell the vote of the
city's Democratic political machine, not realizing it made them liable for the draft.
Of the 168,649 men procured for the Union through the draft, 117,986 were substitutes, leaving only 50,663 who had their services conscripted.
In both the North and South, the draft laws were highly unpopular. In the North, some 120,000 men evaded conscription, many of them fleeing to Canada, and another 280,000 soldiers deserted during the war. At least 100,000 Southerners deserted, or about 10 percent; Southern desertion was high because, according to one historian writing in 1991, the highly localized Southern identity meant that many Southern men had little investment in the outcome of the war, with individual soldiers caring more about the fate of their local area than any grand ideal. In the North, "
bounty jumpers" enlisted to get the generous bonus, deserted, then went back to a second recruiting station under a different name to sign up again for a second bonus; 141 were caught and executed.
From a tiny frontier force in 1860, the Union and Confederate armies had grown into the "largest and most efficient armies in the world" within a few years. Some European observers at the time dismissed them as amateur and unprofessional, but historian John Keegan concluded that each outmatched the French, Prussian, and Russian armies of the time, and without the Atlantic, would have threatened any of them with defeat.
Prisoners
At the start of the Civil War, a system of paroles operated. Captives agreed not to fight until they were officially exchanged. Meanwhile, they were held in camps run by their army. They were paid, but they were not allowed to perform any military duties. The system of exchanges collapsed in 1863 when the Confederacy refused to exchange black prisoners. After that, about 56,000 of the 409,000 POWs died in prisons during the war, accounting for nearly 10 percent of the conflict's fatalities.
Women
Historian
Elizabeth D. Leonard writes that, according to various estimates, between five hundred and one thousand women enlisted as soldiers on both sides of the war, disguised as men.
Women also served as spies, resistance activists, nurses, and hospital personnel. Women served on the Union hospital ship
''Red Rover'' and nursed Union and Confederate troops at field hospitals.
, the only woman ever to receive the
Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valo ...
, served in the Union Army and was given the medal for her efforts to treat the wounded during the war. Her name was deleted from the Army Medal of Honor Roll in 1917 (along with over 900 other Medal of Honor recipients); however, it was restored in 1977.
Naval tactics

The small
U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage o ...
of 1861 was rapidly enlarged to 6,000 officers and 45,000 sailors in 1865, with 671 vessels, having a tonnage of 510,396. Its mission was to blockade Confederate ports, take control of the river system, defend against Confederate raiders on the high seas, and be ready for a possible war with the British
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
. Meanwhile, the main riverine war was fought in the West, where a series of major rivers gave access to the Confederate heartland. The U.S. Navy eventually gained control of the Red, Tennessee, Cumberland, Mississippi, and Ohio rivers. In the East, the Navy shelled Confederate forts and provided support for coastal army operations.
The Civil War occurred during the early stages of the industrial revolution. Many naval innovations emerged during this time, most notably the advent of the
ironclad warship. It began when the Confederacy, knowing they had to meet or match the Union's naval superiority, responded to the Union blockade by building or converting more than 130 vessels, including twenty-six ironclads and floating batteries. Only half of these saw active service. Many were equipped with ram bows, creating "ram fever" among Union squadrons wherever they threatened. But in the face of overwhelming Union superiority and the Union's ironclad warships, they were unsuccessful.
In addition to ocean-going warships coming up the Mississippi, the Union Navy used timberclads, tinclads, and armored gunboats. Shipyards at Cairo, Illinois, and St. Louis built new boats or modified steamboats for action.
The Confederacy experimented with the
submarine , which did not work satisfactorily, and with building an ironclad ship, , which was based on rebuilding a sunken Union ship, . On its first foray, on March 8, 1862, ''Virginia'' inflicted significant damage to the Union's wooden fleet, but the next day the first Union ironclad, , arrived to challenge it in the
Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the Eastern Shore of Maryland / ...
. The resulting three-hour
Battle of Hampton Roads was a draw, but it proved that ironclads were effective warships. Not long after the battle, the Confederacy was forced to scuttle the ''Virginia'' to prevent its capture, while the Union built many copies of the ''Monitor''. Lacking the technology and infrastructure to build effective warships, the Confederacy attempted to obtain warships from
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It i ...
. However, this failed, because Great Britain had no interest in selling warships to a nation that was at war with a stronger enemy, and doing so could sour relations with the
U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Union blockade

By early 1861, General
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early s ...
had devised the
Anaconda Plan
The Anaconda Plan is the name applied to a strategy outlined by the Union Army for suppressing the Confederacy at the beginning of the American Civil War. Proposed by Union General-in-Chief Winfield Scott, the plan emphasized a Union blockade ...
to win the war with as little bloodshed as possible, which called for blockading the Confederacy and slowly suffocating the South to surrender. Lincoln adopted parts of the plan, but chose to prosecute a more active vision of war. In April 1861, Lincoln announced the Union blockade of all Southern ports; commercial ships could not get insurance and regular traffic ended. The South blundered in embargoing cotton exports in 1861 before the blockade was effective; by the time they realized the mistake, it was too late. "
King Cotton
"King Cotton" is a slogan that summarized the strategy used before the American Civil War (of 1861–1865) by secessionists in the southern states (the future Confederate States of America) to claim the feasibility of secession and to prove ther ...
" was dead, as the South could export less than 10 percent of its cotton. The blockade shut down the ten Confederate seaports with railheads that moved almost all the cotton, especially New Orleans, Mobile, and Charleston. By June 1861, warships were stationed off the principal Southern ports, and a year later nearly 300 ships were in service.
Blockade runners

The Confederates began the war short on military supplies and in desperate need of large quantities of arms which the agrarian South could not provide. Arms manufactures in the industrial North were restricted by an arms embargo, keeping shipments of arms from going to the South, and ending all existing and future contracts. The Confederacy subsequently looked to foreign sources for their enormous military needs and sought out financiers and companies like
S. Isaac, Campbell & Company and the
London Armoury Company
The London Armoury Company was a London arms manufactory that existed from 1856 until 1866. It was the major arms supplier to the Confederacy during the U.S. Civil War. The same company name was used during World War I to import arms from Amer ...
in Britain, who acted as purchasing agents for the Confederacy, connecting them with Britain's many arms manufactures, and ultimately becoming the Confederacy's main source of arms.
To get the arms safely to the Confederacy, British investors built small, fast, steam-driven
blockade runners that traded arms and supplies brought in from Britain through Bermuda, Cuba, and the Bahamas in return for high-priced cotton. Many of the ships were lightweight and designed for speed and could only carry a relatively small amount of cotton back to England. When the Union Navy seized a blockade runner, the ship and cargo were condemned as a
prize of war
A prize of war is a piece of enemy property or land seized by a belligerent party during or after a war or battle, typically at sea. This term was used nearly exclusively in terms of captured ships during the 18th and 19th centuries. Basis in inte ...
and sold, with the proceeds given to the Navy sailors; the captured crewmen were mostly British, and they were released.
Economic impact
The Southern economy nearly collapsed during the war. There were multiple reasons for this: the severe deterioration of food supplies, especially in cities, the failure of Southern railroads, the loss of control of the main rivers, foraging by Northern armies, and the seizure of animals and crops by Confederate armies.
Most historians agree that the blockade was a major factor in ruining the Confederate economy; however, Wise argues that the blockade runners provided just enough of a lifeline to allow Lee to continue fighting for additional months, thanks to fresh supplies of 400,000 rifles, lead, blankets, and boots that the homefront economy could no longer supply.
[Stephen R. Wise, ''Lifeline of the Confederacy: Blockade Running during the Civil War'' (1991).]
Surdam argues that the blockade was a powerful weapon that eventually ruined the Southern economy, at the cost of few lives in combat. Practically, the entire Confederate cotton crop was useless (although it was sold to Union traders), costing the Confederacy its main source of income. Critical imports were scarce and the coastal trade was largely ended as well. The measure of the blockade's success was not the few ships that slipped through, but the thousands that never tried it. Merchant ships owned in Europe could not get insurance and were too slow to evade the blockade, so they stopped calling at Confederate ports.
To fight an offensive war, the Confederacy purchased ships in Britain, converted them to warships, and raided American merchant ships in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans. Insurance rates skyrocketed and the American flag virtually disappeared from international waters. However, the same ships were reflagged with European flags and continued unmolested. After the war ended, the U.S. government demanded that Britain compensate them for the damage done by the raiders outfitted in British ports. Britain acquiesced to their demand, paying the U.S. $15 million in 1871.
Dinçaslan argues that another outcome of the blockade was oil's rise to prominence as a widely used and traded commodity. The already declining whale oil industry took a blow as many old whaling ships were used in blockade efforts such as the
Stone Fleet
The Stone Fleet consisted of a fleet of aging ships (mostly whaleships) purchased in New Bedford and other New England ports, loaded with stone, and sailed south during the American Civil War by the Union Navy for use as blockships. They were to ...
, and Confederate raiders harassing Union whalers aggravated the situation. Oil products that had been treated mostly as lubricants, especially kerosene, started to replace whale oil used in lamps and essentially became a fuel commodity. This increased the importance of oil as a commodity, long before its eventual use as fuel for combustion engines.
[M. Bahadırhan Dinçaslan, ''Amerikan İç Savaşı El Kitabı'' (2022), p. 73.]
Diplomacy
Although the Confederacy hoped that Britain and France would join them against the Union, this was never likely, and so they instead tried to bring the British and French governments in as mediators. The Union, under Lincoln and Secretary of State
William H. Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
, worked to block this and threatened war if any country officially recognized the existence of the Confederate States of America. In 1861, Southerners voluntarily embargoed cotton shipments, hoping to start an economic depression in Europe that would force Britain to enter the war to get cotton, but this did not work. Worse, Europe turned to Egypt and India for cotton, which they found superior, hindering the South's recovery after the war.
proved a failure as Europe had a surplus of cotton, while the 1860–62 crop failures in Europe made the North's grain exports of critical importance. It also helped to turn European opinion further away from the Confederacy. It was said that "King Corn was more powerful than King Cotton", as U.S. grain went from a quarter of the British import trade to almost half. Meanwhile, the war created employment for arms makers, ironworkers, and ships to transport weapons.
Lincoln's administration initially failed to appeal to European public opinion. At first, diplomats explained that the United States was not committed to the ending of slavery, and instead repeated legalistic arguments about the unconstitutionality of secession. Confederate representatives, on the other hand, started off much more successful, by ignoring slavery and instead focusing on their struggle for liberty, their commitment to free trade, and the essential role of cotton in the European economy.
The European aristocracy was "absolutely gleeful in pronouncing the American debacle as proof that the entire experiment in popular government had failed. European government leaders welcomed the fragmentation of the ascendant American Republic."
[Don H. Doyle, ''The Cause of All Nations: An International History of the American Civil War'', New York: Basic Books (2015), pp. 8 (quote), 69–70, 70–74.] However, there was still a European public with liberal sensibilities, that the U.S. sought to appeal to by building connections with the international press. As early as 1861, many Union diplomats such as
Carl Schurz realized emphasizing the war against slavery was the Union's most effective moral asset in the struggle for public opinion in Europe. Seward was concerned that an overly radical case for reunification would distress the European merchants with cotton interests; even so, Seward supported a widespread campaign of public diplomacy.
U.S.
minister to Britain
Charles Francis Adams proved particularly adept and convinced Britain not to openly challenge the Union blockade. The Confederacy purchased several warships from commercial shipbuilders in Britain (, , , , , and some others). The most famous, the , did considerable damage and led to serious
postwar disputes. However, public opinion against slavery in Britain created a political liability for British politicians, where the
anti-slavery movement
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
was powerful.
War loomed in late 1861 between the U.S. and Britain over the
''Trent'' affair, which began when U.S. Navy personnel boarded the British ship and seized two Confederate diplomats. However, London and Washington were able to smooth over the problem after Lincoln released the two men.
had left his deathbed to
issue diplomatic instructions to
Lord Lyons
Richard Bickerton Pemell Lyons, 1st Earl Lyons (26 April 1817 – 5 December 1887) was a British diplomat, who was the favourite diplomat of Queen Victoria, during the four great crises of the second half of the 19th century: Italian unificat ...
during the
Trent affair
The ''Trent'' Affair was a diplomatic incident in 1861 during the American Civil War that threatened a war between the United States and Great Britain. The U.S. Navy captured two Confederate envoys from a British Royal Mail steamer; the Brit ...
. His request was honored, and, as a result, the British response to the United States was toned down and helped avert the British becoming involved in the war. In 1862, the British government considered mediating between the Union and Confederacy, though even such an offer would have risked war with the United States. British Prime Minister
Lord Palmerston
Henry John Temple, 3rd Viscount Palmerston, (20 October 1784 – 18 October 1865) was a British statesman who was twice Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in the mid-19th century. Palmerston dominated British foreign policy during the period ...
reportedly read ''
Uncle Tom's Cabin
''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' is an anti-slavery novel by American author Harriet Beecher Stowe. Published in two volumes in 1852, the novel had a profound effect on attitudes toward African Americans and slavery in the U ...
'' three times when deciding on what his decision would be.
The Union victory in the
Battle of Antietam caused the British to delay this decision. The
Emancipation Proclamation over time would reinforce the political liability of supporting the Confederacy. Realizing that Washington could not intervene in
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
as long as the Confederacy controlled Texas,
France invaded Mexico in 1861. Washington repeatedly protested France's violation of the
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile act ...
. Despite sympathy for the Confederacy, France's seizure of Mexico ultimately deterred it from war with the Union. Confederate offers late in the war to end slavery in return for diplomatic recognition were not seriously considered by London or Paris. After 1863, the
Polish revolt against Russia further distracted the European powers and ensured that they would remain neutral.
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
supported the Union, largely because it believed that the U.S. served as a counterbalance to its geopolitical rival, the United Kingdom. In 1863, the
Russian Navy's Baltic and Pacific fleets wintered in the American ports of New York and San Francisco, respectively.
Eastern theater

The Eastern theater refers to the military operations east of the
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, including the states of
Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
,
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
,
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, and
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
, the
District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, and the coastal fortifications and seaports of
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
.
Background
; Army of the Potomac
Maj. Gen.
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan (December 3, 1826 – October 29, 1885) was an American soldier, Civil War Union general, civil engineer, railroad executive, and politician who served as the 24th governor of New Jersey. A graduate of West Point, McCl ...
took command of the Union
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confede ...
on July 26, 1861 (he was briefly general-in-chief of all the Union armies, but was subsequently relieved of that post in favor of Maj. Gen.
Henry W. Halleck
Henry Wager Halleck (January 16, 1815 – January 9, 1872) was a senior United States Army officer, scholar, and lawyer. A noted expert in military studies, he was known by a nickname that became derogatory: "Old Brains". He was an important par ...
), and the war began in earnest in 1862. The 1862 Union strategy called for simultaneous advances along four axes:
# McClellan would lead the main thrust in Virginia towards Richmond.
# Ohio forces would advance through Kentucky into Tennessee.
# The Missouri Department would drive south along the Mississippi River.
# The westernmost attack would originate from Kansas.
; Army of Northern Virginia

The primary Confederate force in the Eastern theater was the
Army of Northern Virginia
The Army of Northern Virginia was the primary military force of the Confederate States of America in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was also the primary command structure of the Department of Northern Virginia. It was most oft ...
. The Army originated as the
(Confederate) Army of the Potomac, which was organized on June 20, 1861, from all operational forces in Northern Virginia. On July 20 and 21, the
Army of the Shenandoah and forces from the District of Harpers Ferry were added. Units from the
Army of the Northwest were merged into the Army of the Potomac between March 14 and May 17, 1862. The Army of the Potomac was renamed ''Army of Northern Virginia'' on March 14. The
Army of the Peninsula
The Army of the Peninsula or Magruder's Army Boatner, Mark Mayo, III. ''The Civil War Dictionary.'' page 501 was a Confederate army early in the American Civil War.
In May 1861, Colonel John B. Magruder was assigned to command operations on th ...
was merged into it on April 12, 1862.
When Virginia declared its secession in April 1861,
Robert E. Lee chose to follow his home state, despite his desire for the country to remain intact and an offer of a senior Union command.
Lee's biographer,
Douglas S. Freeman, asserts that the army received its final name from Lee when he issued orders assuming command on June 1, 1862. However, Freeman does admit that Lee corresponded with Brigadier General
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston (February 3, 1807 – March 21, 1891) was an American career army officer, serving with distinction in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and the Seminole Wars. After Virginia secede ...
, his predecessor in army command, before that date and referred to Johnston's command as the Army of Northern Virginia. Part of the confusion results from the fact that Johnston commanded the Department of Northern Virginia (as of October 22, 1861) and the name Army of Northern Virginia can be seen as an informal consequence of its parent department's name. Jefferson Davis and Johnston did not adopt the name, but it is clear that the organization of units as of March 14 was the same organization that Lee received on June 1, and thus it is generally referred to today as the Army of Northern Virginia, even if that is correct only in retrospect.
On July 4 at Harper's Ferry, Colonel
Thomas J. Jackson assigned
Jeb Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a United States Army officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials o ...
to command all the cavalry companies of the Army of the Shenandoah. He eventually commanded the Army of Northern Virginia's cavalry.
Battles

In one of the first highly visible battles, in July 1861, a march by Union troops under the command of
Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Irvin McDowell
Irvin McDowell (October 15, 1818 – May 4, 1885) was a career American army officer. He is best known for his defeat in the First Battle of Bull Run, the first large-scale battle of the American Civil War. In 1862, he was given command ...
on the Confederate forces led by Gen.
P. G. T. Beauregard near Washington was repulsed at the
First Battle of Bull Run
The First Battle of Bull Run (the name used by Union forces), also known as the Battle of First Manassas (also known as First Manassas).
The Union had the upper hand at first, nearly pushing confederate forces holding a defensive position into a rout, but Confederate reinforcements under Joseph E. Johnston arrived from the
Shenandoah Valley by railroad, and the course of the battle quickly changed. A
brigade of Virginians under the relatively unknown brigadier general from the
Virginia Military Institute,
Thomas J. Jackson, stood its ground, which resulted in Jackson receiving his famous nickname, "Stonewall".
Upon the strong urging of President Lincoln to begin offensive operations, McClellan attacked Virginia in the spring of 1862 by way of the
peninsula between the
York River and
James River, southeast of Richmond. McClellan's army reached the gates of Richmond in the
Peninsula Campaign.
Also in the spring of 1862, in the Shenandoah Valley, Stonewall Jackson led his
Valley Campaign. Employing audacity and rapid, unpredictable movements on interior lines, Jackson's 17,000 troops marched 646 miles (1,040 km) in 48 days and won several minor battles as they successfully engaged three Union armies (52,000 men), including those of
Nathaniel P. Banks
Nathaniel Prentice (or Prentiss) Banks (January 30, 1816 – September 1, 1894) was an American politician from Massachusetts and a Union general during the Civil War. A millworker by background, Banks was prominent in local debating societies, ...
and
John C. Fremont, preventing them from reinforcing the Union offensive against Richmond. The swiftness of Jackson's men earned them the nickname of "
foot cavalry".
Johnston halted McClellan's advance at the
Battle of Seven Pines
The Battle of Seven Pines, also known as the Battle of Fair Oaks or Fair Oaks Station, took place on May 31 and June 1, 1862, in Henrico County, Virginia, nearby Sandston, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was th ...
, but he was wounded in the battle, and Robert E. Lee assumed his position of command. General Lee and top subordinates
James Longstreet and Stonewall Jackson defeated McClellan in the
Seven Days Battles
The Seven Days Battles were a series of seven battles over seven days from June 25 to July 1, 1862, near Richmond, Virginia, during the American Civil War. Confederate General Robert E. Lee drove the invading Union Army of the Potomac, comman ...
and forced his retreat.
The
Northern Virginia Campaign, which included the
Second Battle of Bull Run, ended in yet another victory for the South. McClellan resisted General-in-Chief Halleck's orders to send reinforcements to
John Pope's Union
Army of Virginia
The Army of Virginia was organized as a major unit of the Union Army and operated briefly and unsuccessfully in 1862 in the American Civil War. It should not be confused with its principal opponent, the Confederate Army of ''Northern'' Virginia ...
, which made it easier for Lee's Confederates to defeat twice the number of combined enemy troops.

Emboldened by Second Bull Run, the Confederacy made its first invasion of the North with the
Maryland Campaign. General Lee led 45,000 troops of the Army of Northern Virginia across the
Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augu ...
into Maryland on September 5. Lincoln then restored Pope's troops to McClellan. McClellan and Lee fought at the
Battle of Antietam near
Sharpsburg, Maryland, on September 17, 1862, the bloodiest single day in United States military history. Lee's army checked at last, returned to Virginia before McClellan could destroy it. Antietam is considered a Union victory because it halted Lee's invasion of the North and provided an opportunity for Lincoln to announce his Emancipation Proclamation.
When the cautious McClellan failed to follow up on Antietam, he was replaced by Maj. Gen.
Ambrose Burnside
Ambrose Everett Burnside (May 23, 1824 – September 13, 1881) was an American army officer and politician who became a senior Union general in the Civil War and three times Governor of Rhode Island, as well as being a successful inventor ...
. Burnside was soon defeated at the
Battle of Fredericksburg on December 13, 1862, when more than 12,000 Union soldiers were killed or wounded during repeated futile frontal assaults against Marye's Heights. After the battle, Burnside was replaced by Maj. Gen.
Joseph Hooker
Joseph Hooker (November 13, 1814 – October 31, 1879) was an American Civil War general for the Union, chiefly remembered for his decisive defeat by Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Chancellorsville in 1863.
Hooker had serv ...
.

Hooker, too, proved unable to defeat Lee's army; despite outnumbering the Confederates by more than two to one, his Chancellorsville Campaign proved ineffective and he was humiliated in the
Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville, April 30 – May 6, 1863, was a major battle of the American Civil War (1861–1865), and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville campaign.
Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because h ...
in May 1863. Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because his risky decision to divide his army in the presence of a much larger enemy force resulted in a significant Confederate victory. Gen. Stonewall Jackson was shot in the arm by accidental friendly fire during the battle and subsequently died of complications. Lee famously said: "He has lost his left arm, but I have lost my right arm."
The fiercest fighting of the battle—and the second bloodiest day of the Civil War—occurred on May 3 as Lee launched multiple attacks against the Union position at Chancellorsville. That same day,
John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick (September 13, 1813 – May 9, 1864) was a military officer and Union Army general during the American Civil War.
He was wounded three times at the Battle of Antietam while leading his division in an unsuccessful assault against Co ...
advanced across the
Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the entir ...
, defeated the small Confederate force at Marye's Heights in the
Second Battle of Fredericksburg
The Second Battle of Fredericksburg, also known as the Second Battle of Marye's Heights, took place on May 3, 1863, in Fredericksburg, Virginia, as part of the Chancellorsville Campaign of the American Civil War.
Background
Confederate Gen. Rob ...
, and then moved to the west. The Confederates fought a successful delaying action at the
Battle of Salem Church
The Battle of Salem Church, also known as the Battle of Banks' Ford, took place on May 3 and 4, 1863, in Spotsylvania County, Virginia, as part of the Chancellorsville Campaign of the American Civil War.
Background
After occupying Marye's Hei ...
.

Gen. Hooker was replaced by Maj. Gen.
George Meade
George Gordon Meade (December 31, 1815 – November 6, 1872) was a United States Army officer and civil engineer best known for decisively defeating Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. H ...
during Lee's
second invasion of the North, in June. Meade defeated Lee at the
Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
(July 1 to 3, 1863). This was the bloodiest battle of the war and has been called the war's
turning point
A turning point, or climax, is the point of highest tension in a narrative work.
Turning Point or Turning Points may refer to:
Film
* ''The Turning Point'', a 1914 silent film starring Caroline Cooke
* ''The Turning Point'' (1920 film), an Ame ...
.
Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge (July 3, 1863), also known as the Pickett–Pettigrew–Trimble Charge, was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on the last day of the ...
on July 3 is often considered the
high-water mark of the Confederacy
The high-water mark of the Confederacy or high tide of the Confederacy refers to an area on Cemetery Ridge near Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, marking the farthest point reached by Confederate forces during Pickett's Charge on July 3, 1863. Similar ...
because it signaled the collapse of serious Confederate threats of victory. Lee's army suffered 28,000 casualties (versus Meade's 23,000).
Western theater
The Western theater refers to military operations between the Appalachian Mountains and the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
, including the states of
Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
,
Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
,
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
,
Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
,
North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and ...
,
Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia ...
,
South Carolina
)'' Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
and
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, as well as parts of
Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
.
Background
; Army of the Tennessee and Army of the Cumberland
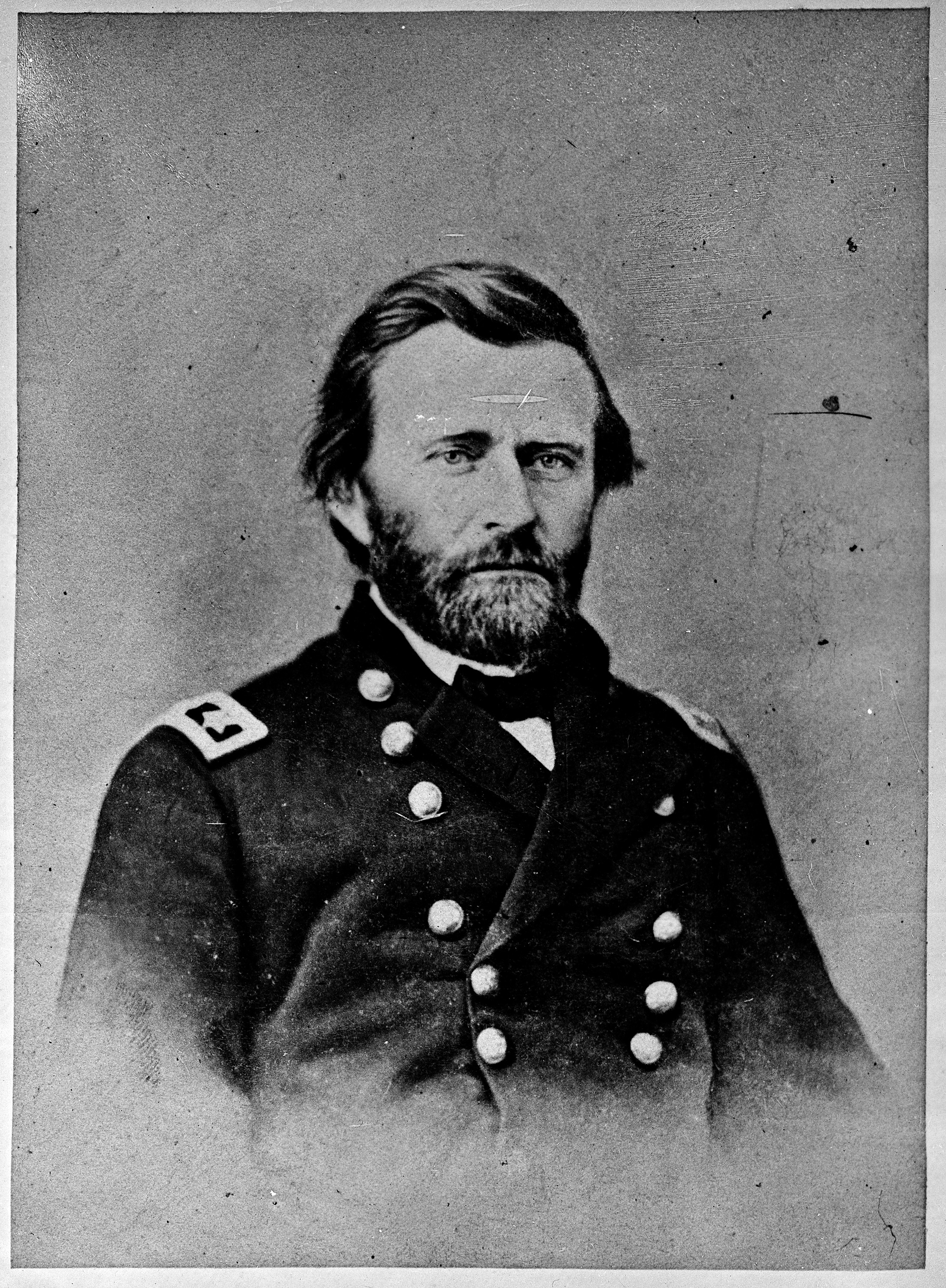

The primary Union forces in the Western theater were the
Army of the Tennessee
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
and the
Army of the Cumberland
The Army of the Cumberland was one of the principal Union armies in the Western Theater during the American Civil War. It was originally known as the Army of the Ohio.
History
The origin of the Army of the Cumberland dates back to the creation ...
, named for the two rivers, the
Tennessee River
The Tennessee River is the largest tributary of the Ohio River. It is approximately long and is located in the southeastern United States in the Tennessee Valley. The river was once popularly known as the Cherokee River, among other name ...
and
Cumberland River. After Meade's inconclusive fall campaign, Lincoln turned to the Western Theater for new leadership. At the same time, the Confederate stronghold of Vicksburg surrendered, giving the Union control of the Mississippi River, permanently isolating the western Confederacy, and producing the new leader Lincoln needed,
Ulysses S. Grant.
; Army of Tennessee
The primary Confederate force in the Western theater was the
Army of Tennessee
The Army of Tennessee was the principal Confederate army operating between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River during the American Civil War. It was formed in late 1862 and fought until the end of the war in 1865, participating in ...
. The army was formed on November 20, 1862, when General
Braxton Bragg renamed the former
Army of Mississippi
There were three formations known as the Army of Mississippi in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. This name is contrasted against Army of ''the'' Mississippi, which was a Union Army named for the Mississippi River, not ...
. While the Confederate forces had numerous successes in the Eastern Theater, they were defeated many times in the West.
Battles
The Union's key strategist and tactician in the West was Ulysses S. Grant, who won victories at Forts
Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
(February 6, 1862) and
Donelson (February 11 to 16, 1862), earning him the nickname of "Unconditional Surrender" Grant, by which the Union seized control of the Tennessee and Cumberland Rivers.
Nathan Bedford Forrest rallied nearly 4,000 Confederate troops and led them to escape across the Cumberland.
Nashville and central
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
thus fell to the Union, leading to attrition of local food supplies and livestock and a breakdown in social organization.
Leonidas Polk
Lieutenant-General Leonidas Polk (April 10, 1806 – June 14, 1864) was a bishop of the Episcopal Diocese of Louisiana and founder of the Protestant Episcopal Church in the Confederate States of America, which separated from the Episcopal Ch ...
's invasion of
Columbus ended Kentucky's policy of neutrality and turned it against the Confederacy. Grant used river transport and
Andrew Foote's gunboats of the Western Flotilla to threaten the Confederacy's "Gibraltar of the West" at Columbus, Kentucky. Although rebuffed at Belmont, Grant cut off Columbus. The Confederates, lacking their gunboats, were forced to retreat and the Union took control of western Kentucky and opened Tennessee in March 1862.
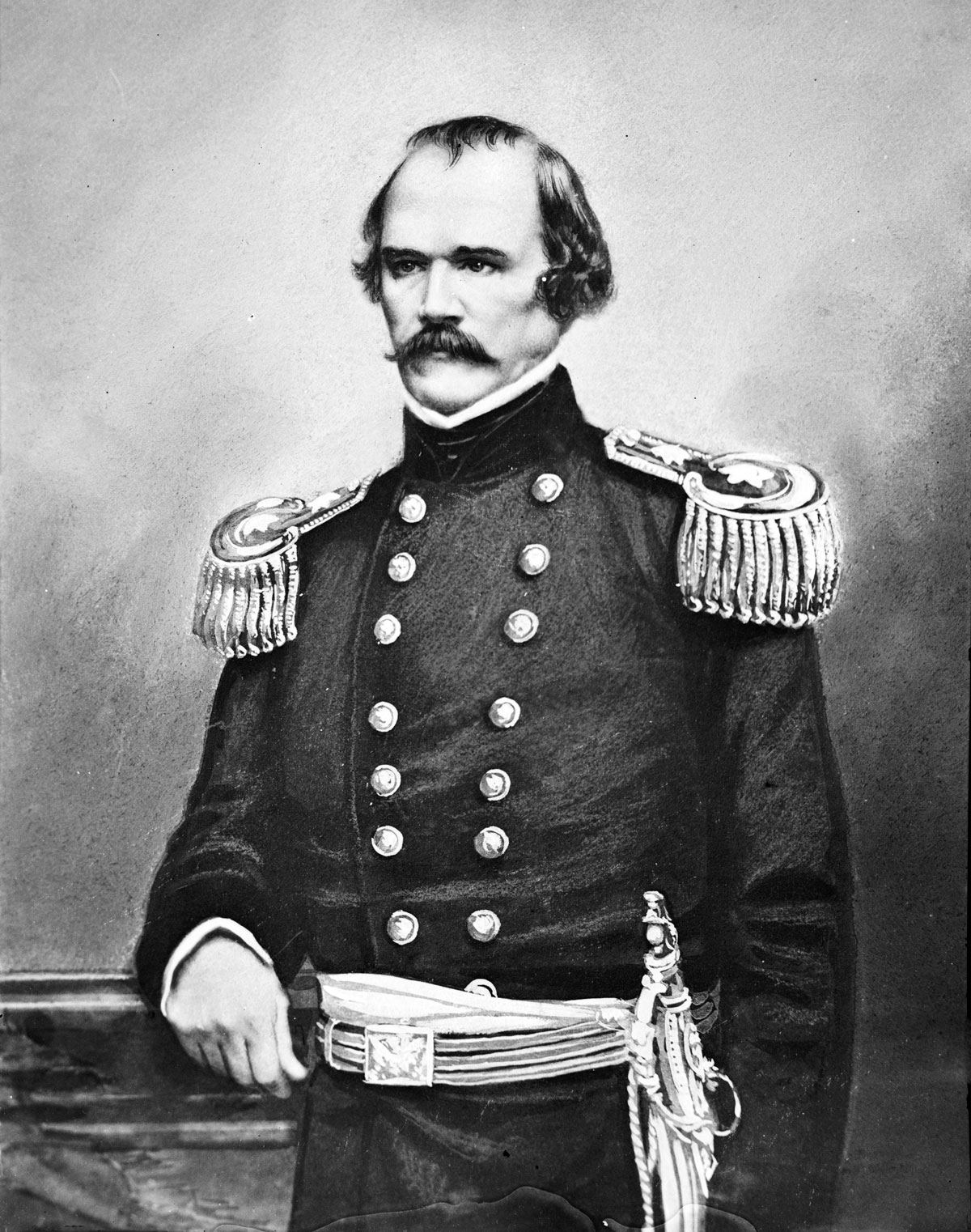

At the
Battle of Shiloh, in Shiloh, Tennessee in April 1862, the Confederates made a surprise attack that pushed Union forces against the river as night fell. Overnight, the Navy landed additional reinforcements, and Grant counter-attacked. Grant and the Union won a decisive victory—the first battle with the high casualty rates that would repeat over and over. The Confederates lost Albert Sidney Johnston, considered their finest general before the emergence of Lee.
One of the early Union objectives in the war was the capture of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
, to cut the Confederacy in half. The Mississippi River was opened to Union traffic to the southern border of Tennessee with the taking of Battle of Island Number Ten, Island No. 10 and New Madrid, Missouri, New Madrid, Missouri, and then Memphis, Tennessee.
In April 1862, the Union Navy Capture of New Orleans, captured New Orleans. "The key to the river was New Orleans, the South's largest port
ndgreatest industrial center." U.S. Naval forces under David Farragut, Farragut ran past Confederate defenses south of New Orleans. Confederate forces abandoned the city, giving the Union a critical anchor in the deep South. which allowed Union forces to begin moving up the Mississippi. Battle of Memphis, Memphis fell to Union forces on June 6, 1862, and became a key base for further advances south along the Mississippi River. Only the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, Vicksburg, Mississippi, prevented Union control of the entire river.
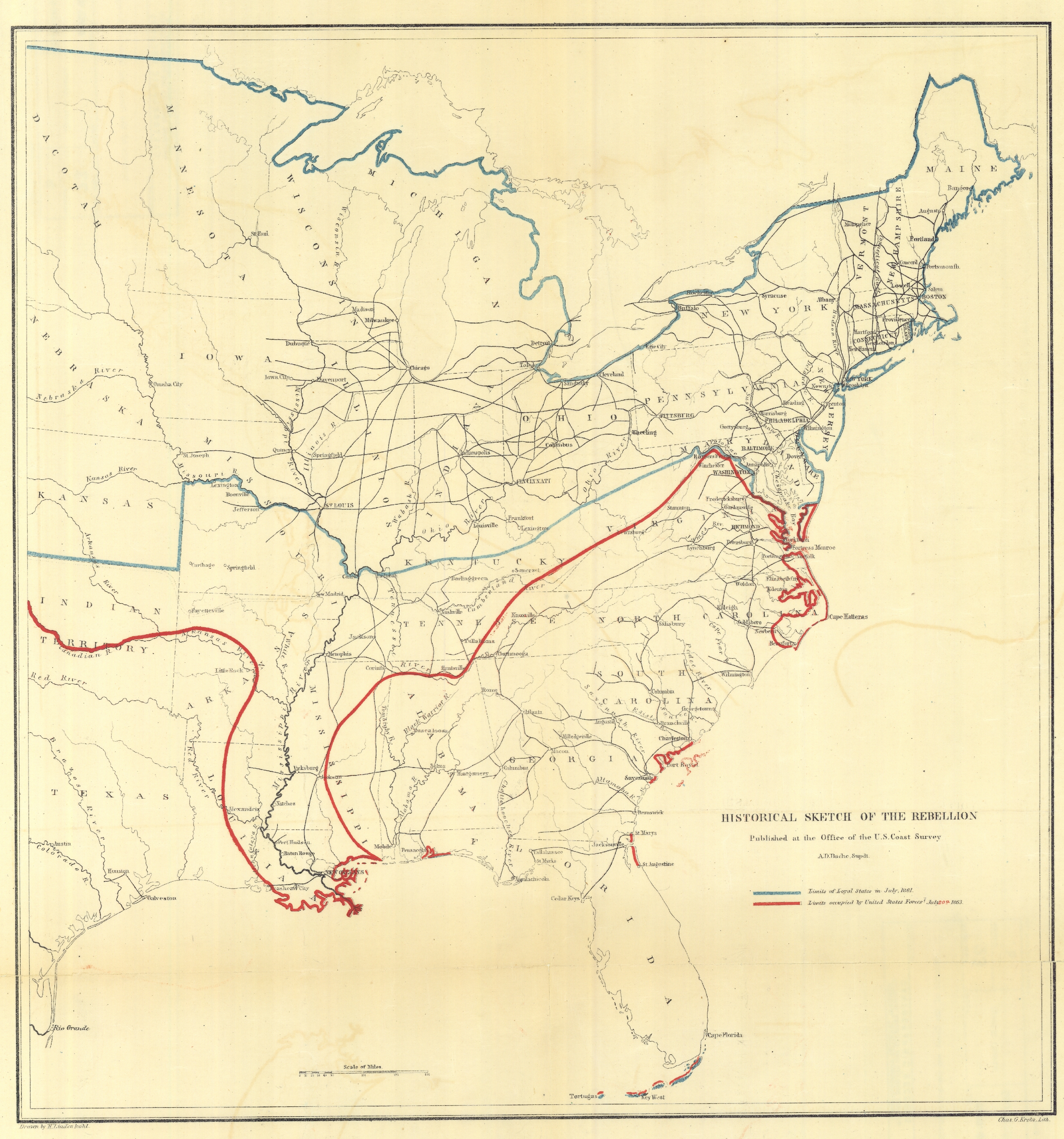
Bragg's second invasion of Kentucky in the Confederate Heartland Offensive included initial successes such as Edmund Kirby Smith, Kirby Smith's triumph at the Battle of Richmond and the capture of the Kentucky capital of Frankfort on September 3, 1862. However, the campaign ended with a meaningless victory over Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell at the Battle of Perryville. Bragg was forced to end his attempt at invading Kentucky and retreat due to lack of logistical support and lack of infantry recruits for the Confederacy in that state.
Bragg was narrowly defeated by Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans at the Battle of Stones River in
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to th ...
, the culmination of the Stones River Campaign.
Naval forces assisted Grant in the long, complex Vicksburg Campaign that resulted in the Confederates surrendering at the Siege of Vicksburg, Battle of Vicksburg in July 1863, which cemented Union control of the Mississippi River and is considered one of the Turning point of the American Civil War, turning points of the war.

The one clear Confederate victory in the West was the Battle of Chickamauga. After Rosecrans' successful Tullahoma Campaign, Bragg, reinforced by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet's corps (from Lee's army in the east), defeated Rosecrans, despite the heroic defensive stand of Maj. Gen. George Henry Thomas.
Rosecrans retreated to Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga, which Bragg then besieged in the Chattanooga Campaign. Grant marched to the relief of Rosecrans and defeated Bragg at the Chattanooga Campaign, Third Battle of Chattanooga, eventually causing Longstreet to abandon his Knoxville Campaign and driving Confederate forces out of Tennessee and opening a route to Atlanta and the heart of the Confederacy.
Trans-Mississippi theater
Background
The Trans-Mississippi theater refers to military operations west of the Mississippi River, encompassing most of Missouri, Arkansas, most of Louisiana, and Indian Territory (now Oklahoma). The Trans-Mississippi District was formed by the Confederate Army to better coordinate Ben McCulloch's command of troops in Arkansas and Louisiana, Sterling Price's Missouri State Guard, as well as the portion of Earl Van Dorn's command that included the Indian Territory and excluded the Army of the West. The Union's command was the Trans-Mississippi Division, or the Military Division of West Mississippi.
Battles

The first battle of the Trans-Mississippi theater was the Battle of Wilson's Creek (August 1861). The Confederates were driven from Missouri early in the war as a result of the Battle of Pea Ridge.
Extensive guerrilla warfare characterized the trans-Mississippi region, as the Confederacy lacked the troops and the logistics to support regular armies that could challenge Union control. Roving Confederate bands such as Quantrill's Raiders terrorized the countryside, striking both military installations and civilian settlements. The "Sons of Liberty" and "Order of the American Knights" attacked pro-Union people, elected officeholders, and unarmed uniformed soldiers. These partisans could not be entirely driven out of the state of Missouri until an entire regular Union infantry division was engaged. By 1864, these violent activities harmed the nationwide anti-war movement organizing against the re-election of Lincoln. Missouri not only stayed in the Union but Lincoln took 70 percent of the vote for re-election.
Numerous small-scale military actions south and west of Missouri sought to control Indian Territory in the American Civil War, Indian Territory and New Mexico Territory in the American Civil War, New Mexico Territory for the Union. The Battle of Glorieta Pass was the decisive battle of the New Mexico Campaign. The Union repulsed Confederate incursions into New Mexico in 1862, and the exiled Arizona government withdrew into Texas. In the Indian Territory, civil war broke out within tribes. About 12,000 Indian warriors fought for the Confederacy and smaller numbers for the Union. The most prominent Cherokee was Brigadier General Stand Watie, the last Confederate general to surrender.
After the fall of Siege of Vicksburg, Vicksburg in July 1863, General Kirby Smith in Texas was informed by Jefferson Davis that he could expect no further help from east of the Mississippi River. Although he lacked resources to beat Union armies, he built up a formidable arsenal at Tyler, along with his own Kirby Smithdom economy, a virtual "independent fiefdom" in Texas, including railroad construction and international smuggling. The Union, in turn, did not directly engage him. Its 1864 Red River Campaign to take Shreveport, Louisiana, was a failure and Texas remained in Confederate hands throughout the war.
Lower Seaboard theater
Background
The Lower Seaboard theater refers to military and naval operations that occurred near the coastal areas of the Southeast (Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, and Texas) as well as the southern part of the Mississippi River (Port Hudson and south). Union Naval activities were dictated by the Anaconda Plan.
Battles
One of the earliest battles of the war was fought at Battle of Port Royal, Port Royal Sound (November 1861), south of Charleston. Much of the war along the South Carolina coast concentrated on capturing Charleston, South Carolina, Charleston. In attempting to capture Charleston, the Union military tried two approaches: by land over James or Morris Islands or through the harbor. However, the Confederates were able to drive back each Union attack. One of the most famous of the land attacks was the Second Battle of Fort Wagner, in which the 54th Massachusetts Volunteer Infantry, 54th Massachusetts Infantry took part. The Union suffered a serious defeat in this battle, losing 1,515 soldiers while the Confederates lost only 174. However, the 54th was hailed for its valor in that battle, which encouraged the general acceptance of the recruitment of African American soldiers into the Union Army, which reinforced the Union's numerical advantage.
Fort Pulaski on the Georgia coast was an early target for the Union navy. Following the capture of Port Royal, an expedition was organized with engineer troops under the command of Captain Quincy Adams Gillmore, Quincy A. Gillmore, forcing a Confederate surrender. The Union army occupied the fort for the rest of the war after repairing it.

In April 1862, a Union naval task force commanded by Commander David Dixon Porter, David D. Porter attacked Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip, Forts Jackson and St. Philip, which guarded the river approach to
from the south. While part of the fleet bombarded the forts, other vessels forced a break in the obstructions in the river and enabled the rest of the fleet to steam upriver to the city. A Union army force commanded by Major General Benjamin Butler (politician), Benjamin Butler landed near the forts and forced their surrender. Butler's controversial command of New Orleans earned him the nickname "Beast".
The following year, the Union Army of the Gulf commanded by Major General Nathaniel P. Banks laid Siege of Port Hudson, siege to Port Hudson for nearly eight weeks, the longest siege in US military history. The Confederates attempted to defend with the Bayou Teche Campaign but surrendered after Vicksburg. These two surrenders gave the Union control over the entire Mississippi.
Several small skirmishes were fought in Florida, but no major battles. The biggest was the Battle of Olustee in early 1864.
Pacific Coast theater
The Pacific Coast theater refers to military operations on the Pacific Ocean and in the states and Territories west of the Continental Divide.
Conquest of Virginia

At the beginning of 1864, Lincoln made Grant commander of all Union armies. Grant made his headquarters with the Army of the Potomac and put Maj. Gen.
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
in command of most of the western armies. Grant understood the concept of total war and believed, along with Lincoln and Sherman, that only the utter defeat of Confederate forces and their economic base would end the war.
This was total war not in killing civilians but rather in taking provisions and forage and destroying homes, farms, and railroads, that Grant said "would otherwise have gone to the support of secession and rebellion. This policy I believe exercised a material influence in hastening the end." Grant devised a coordinated strategy that would strike at the entire Confederacy from multiple directions. Generals
George Meade
George Gordon Meade (December 31, 1815 – November 6, 1872) was a United States Army officer and civil engineer best known for decisively defeating Confederate General Robert E. Lee at the Battle of Gettysburg in the American Civil War. H ...
and Benjamin Butler were ordered to move against Lee near Richmond, General Franz Sigel (and later Philip Sheridan) were to Valley Campaigns of 1864, attack the Shenandoah Valley, General Sherman was to capture Atlanta and march to the sea (the Atlantic Ocean), Generals George Crook and William W. Averell were to operate against railroad supply lines in
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the B ...
, and Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks was to capture Mobile, Alabama, Mobile, Alabama.
Grant's Overland Campaign

Grant's army set out on the Overland Campaign intending to draw Lee into a defense of Richmond, where they would attempt to pin down and destroy the Confederate army. The Union army first attempted to maneuver past Lee and fought several battles, notably at the Battle of the Wilderness, Wilderness, Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, Spotsylvania, and Battle of Cold Harbor, Cold Harbor. These battles resulted in heavy losses on both sides and forced Lee's Confederates to fall back repeatedly. At the Battle of Yellow Tavern, the Confederates lost
Jeb Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a United States Army officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials o ...
.
An attempt to outflank Lee from the south failed under Butler, who was trapped inside the Bermuda Hundred Campaign, Bermuda Hundred river bend. Each battle resulted in setbacks for the Union that mirrored what they had suffered under prior generals, though, unlike those prior generals, Grant fought on rather than retreat. Grant was tenacious and kept pressing Lee's Army of Northern Virginia back to Richmond. While Lee was preparing for an attack on Richmond, Grant unexpectedly turned south to cross the
James River and began the protracted
Siege of Petersburg
The Richmond–Petersburg campaign was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War. Although it is more popularly known as the Siege of Petersburg, it was not a cla ...
, where the two armies engaged in trench warfare for over nine months.
Sheridan's Valley Campaign

Grant finally found a commander, General Philip Sheridan, aggressive enough to prevail in the Valley Campaigns of 1864. Sheridan was initially repelled at the Battle of New Market by former U.S. vice president and Confederate Gen. John C. Breckinridge. The Battle of New Market was the Confederacy's last major victory of the war and included a charge by teenage VMI cadets. After redoubling his efforts, Sheridan defeated Maj. Gen. Jubal Early, Jubal A. Early in a series of battles, including a final decisive defeat at the Battle of Cedar Creek. Sheridan then proceeded to destroy the agricultural base of the
Shenandoah Valley, a strategy similar to the tactics Sherman later employed in Georgia.
Sherman's March to the Sea
Image:The Peacemakers 1868.jpg, left, ''The Peacemakers'' by George Peter Alexander Healy portrays William Tecumseh Sherman, Sherman, Ulysses S. Grant, Grant, Abraham Lincoln, Lincoln, and David Dixon Porter, Porter discussing plans for the last weeks of the Civil War aboard the steamer ''River Queen (steamboat), River Queen'' in March 1865. ''(Clickable image—use cursor to identify.)'', alt=Painting of four men conferring in a ship's cabin, entitled "The Peacemakers".
poly 486 710 579 672 663 739 687 863 649 936 579 965 739 1133 782 1037 800 956 910 905 905 1025 855 1305 576 1223 513 1371 620 1388 687 1467 846 1510 1010 2035 1160 2140 869 2135 718 1682 663 1685 634 2000 725 2030 489 2095 504 1800 362 1775 263 1710 225 1516 252 1226 269 1046 324 948 434 913 481 866 446 782 William Tecumseh Sherman, William Sherman
poly 1092 794 1182 823 1188 892 1162 970 1220 1023 1330 1179 1429 1153 1478 1223 1388 1498 1440 1548 1397 1568 1397 1788 1429 1826 1385 1867 1301 1838 1275 1571 1243 1533 1243 1478 1095 1492 985 1588 924 1133 970 1028 1046 991 1028 907 1034 837 Ulysses S. Grant, Ulysses Grant
poly 1634 802 1715 770 1794 825 1800 950 1933 962 2194 1072 2188 1185 2116 1347 2029 1396 2032 1547 1669 1544 1740 1947 1527 1945 1579 1875 1620 1852 1599 1730 1565 1883 1394 1930 1408 1872 1454 1817 1559 1333 1568 1260 1599 1182 1672 980 1620 886 Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
poly 2620 780 2740 775 2754 889 2745 991 2855 1064 2864 1316 2800 1420 2766 1516 2806 1600 2772 1942 2664 1919 2577 1791 2508 1780 2496 1719 2455 1745 2496 2052 2348 2145 2308 2128 2345 2038 2293 1759 2229 2081 1977 2076 1997 2035 2058 2009 2093 1965 2174 1537 2461 1429 2453 1290 2357 1382 2287 1336 2290 1287 2354 1203 2412 1179 2499 1133 2540 1072 2560 988 2595 837 David Dixon Porter, David Porter
Meanwhile, Sherman maneuvered from Chattanooga to Atlanta, defeating Confederate Generals
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston (February 3, 1807 – March 21, 1891) was an American career army officer, serving with distinction in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and the Seminole Wars. After Virginia secede ...
and John Bell Hood along the way. The Battle of Atlanta, fall of Atlanta on September 2, 1864, guaranteed the reelection of Lincoln as president. Hood left the Atlanta area to swing around and menace Sherman's supply lines and invade Tennessee in the Franklin–Nashville Campaign. Union Maj. Gen. John Schofield defeated Hood at the Battle of Franklin (1864), Battle of Franklin, and George Henry Thomas, George H. Thomas dealt Hood a massive defeat at the Battle of Nashville, effectively destroying Hood's army.
Leaving Atlanta, and his base of supplies, Sherman's army marched with an unknown destination, laying waste to about 20 percent of the farms in Georgia in his "Sherman's March to the Sea, March to the Sea". He reached the Atlantic Ocean at Savannah, Georgia, Savannah, Georgia, in December 1864. Sherman's army was followed by thousands of freed slaves; there were no major battles along the March. Sherman turned north through South Carolina and North Carolina to approach the Confederate Virginia lines from the south, increasing the pressure on Lee's army.
The Waterloo of the Confederacy
Lee's army, thinned by desertion and casualties, was now much smaller than Grant's. One last Confederate attempt to break the Union hold on Petersburg failed at the decisive Battle of Five Forks (sometimes called "the Waterloo of the Confederacy") on April 1. This meant that the Union now controlled the entire perimeter surrounding Richmond-Petersburg, completely cutting it off from the Confederacy. Realizing that the capital was now lost, Lee decided to evacuate his army. The Confederate capital fell to the XXV Corps (Union Army), Union XXV Corps, composed of black troops. The remaining Confederate units fled west after a defeat at Battle of Sayler's Creek, Sayler's Creek.
End of the War
Initially, Lee did not intend to surrender but planned to regroup at Appomattox Station, where supplies were to be waiting and then continue the war. Grant chased Lee and got in front of him so that when Lee's army reached the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park, village of Appomattox Court House, they were surrounded. After Battle of Appomattox Court House, an initial battle, Lee decided that the fight was now hopeless, and surrendered his Army of Northern Virginia on April 9, 1865, at "Wilmer McLean's farmhouse, located less than 100 yards west of the county courthouse", now known as the McLean House (Appomattox, Virginia), McLean House.
In an untraditional gesture and as a sign of Grant's respect and anticipation of peacefully restoring Confederate states to the Union, Lee was permitted to keep his sword and his horse, Traveller (horse), Traveller. His men were paroled, and a chain of Confederate surrenders began.
On April 14, 1865, President Lincoln Assassination of Abraham Lincoln, was shot by John Wilkes Booth, a Confederate sympathizer. Lincoln died early the next morning. Lincoln's vice president, Andrew Johnson, was unharmed, because his would-be assassin, George Atzerodt, lost his nerve, so Johnson was immediately sworn in as president. Meanwhile, Confederate forces across the South surrendered as news of Lee's surrender reached them.
On April 26, 1865, the same day Boston Corbett killed Booth at a tobacco barn, General
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston (February 3, 1807 – March 21, 1891) was an American career army officer, serving with distinction in the United States Army during the Mexican–American War (1846–1848) and the Seminole Wars. After Virginia secede ...
surrendered nearly 90,000 troops of the
Army of Tennessee
The Army of Tennessee was the principal Confederate army operating between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River during the American Civil War. It was formed in late 1862 and fought until the end of the war in 1865, participating in ...
to Major General
William Tecumseh Sherman
William Tecumseh Sherman ( ; February 8, 1820February 14, 1891) was an American soldier, businessman, educator, and author. He served as a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War (1861–1865), achieving recognition for his com ...
at Bennett Place near present-day Durham, North Carolina. It proved to be the largest surrender of Confederate forces. On May 4, all remaining Confederate forces in Alabama, Louisiana east of the Mississippi River, and Mississippi under Lieutenant General Richard Taylor (Confederate general), Richard Taylor surrendered.
The Confederate president,
Jefferson Davis, was captured at Irwinsville, Georgia on May 10, 1865.
On May 13, 1865, the last land battle of the war was fought at the Battle of Palmito Ranch in Texas.
On May 26, 1865, Confederate Lt. Gen. Simon Bolivar Buckner, Simon B. Buckner, acting for General Edmund Kirby Smith, signed a military convention surrendering the Confederate trans-Mississippi Department forces. This date is often cited by contemporaries and historians as the end date of the American Civil War.
[ On June 2, 1865, with most of his troops having already gone home, technically deserted, a reluctant Kirby Smith had little choice but to sign the official surrender document. On June 23, 1865, Cherokee leader and Confederate Brig. Gen. Stand Watie became the last Confederate general to surrender his forces.
On June 19, 1865, Union Maj. Gen. Gordon Granger announced General Order No. 3, bringing the Emancipation Proclamation into effect in Texas and freeing the last slaves of the Confederacy. The anniversary of this date is now celebrated as Juneteenth.]William Seward
William Henry Seward (May 16, 1801 – October 10, 1872) was an American politician who served as United States Secretary of State from 1861 to 1869, and earlier served as governor of New York and as a United States Senator. A determined oppon ...
welcomed the withdrawal of concessions to the Confederates but objected to the exceptions. Finally, on October 18, 1865, Russell advised the Admiralty that the time specified in his June 2, 1865 message had elapsed and "all measures of a restrictive nature on vessels of war of the United States in British ports, harbors, and waters, are now to be considered as at an end". Nonetheless, the final Confederate surrender was in Liverpool, England where James Iredell Waddell, the captain of the ''CSS Shenandoah'', surrendered the cruiser to British authorities on November 6, 1865.[Heidler, pp. 703–06.]
Legally, the war did not end until August 20, 1866, when President Andrew Johnson issued a proclamation that declared "that the said insurrection is at an end and that peace, order, tranquillity, and civil authority now exist in and throughout the whole of the United States of America".
Union victory and aftermath
Explaining the Union victory
 The Origins of the American Civil War, causes of the war, the reasons for its outcome, and even Naming the American Civil War, the name of the war itself are subjects of lingering contention today. The North and West grew rich while the once-rich South became poor for a century. The national political power of the slaveowners and rich Southerners ended. Historians are less sure about the results of the postwar Reconstruction, especially regarding the second-class citizenship of the freedmen and their poverty.
Historians have debated whether the Confederacy could have won the war. Most scholars, including James M. McPherson, argue that Confederate victory was at least possible. McPherson argues that the North's advantage in population and resources made Northern victory likely but not guaranteed. He also argues that if the Confederacy had fought using unconventional tactics, it would have more easily been able to hold out long enough to exhaust the Union.
The Origins of the American Civil War, causes of the war, the reasons for its outcome, and even Naming the American Civil War, the name of the war itself are subjects of lingering contention today. The North and West grew rich while the once-rich South became poor for a century. The national political power of the slaveowners and rich Southerners ended. Historians are less sure about the results of the postwar Reconstruction, especially regarding the second-class citizenship of the freedmen and their poverty.
Historians have debated whether the Confederacy could have won the war. Most scholars, including James M. McPherson, argue that Confederate victory was at least possible. McPherson argues that the North's advantage in population and resources made Northern victory likely but not guaranteed. He also argues that if the Confederacy had fought using unconventional tactics, it would have more easily been able to hold out long enough to exhaust the Union.
Casualties
The war resulted in at least 1,030,000 casualties (3 percent of the population), including about 620,000 soldier deaths—two-thirds by disease—and 50,000 civilians.[Herbert Aptheker, "Negro Casualties in the Civil War", ''The Journal of Negro History'', Vol. 32, No. 1. (January 1947).]
The United States National Park Service uses the following figures in its official tally of war losses: While the figures of 360,000 army deaths for the Union and 260,000 for the Confederacy remained commonly cited, they are incomplete. In addition to many Confederate records being missing, partly as a result of Confederate widows not reporting deaths due to being ineligible for benefits, both armies only counted troops who died during their service and not the tens of thousands who died of wounds or diseases after being discharged. This often happened only a few days or weeks later. Francis Amasa Walker, superintendent of the 1870 census, used census and surgeon general data to estimate a minimum of 500,000 Union military deaths and 350,000 Confederate military deaths, for a total death toll of 850,000 soldiers. While Walker's estimates were originally dismissed because of the 1870 census's undercounting, it was later found that the census was only off by 6.5% and that the data Walker used would be roughly accurate.
While the figures of 360,000 army deaths for the Union and 260,000 for the Confederacy remained commonly cited, they are incomplete. In addition to many Confederate records being missing, partly as a result of Confederate widows not reporting deaths due to being ineligible for benefits, both armies only counted troops who died during their service and not the tens of thousands who died of wounds or diseases after being discharged. This often happened only a few days or weeks later. Francis Amasa Walker, superintendent of the 1870 census, used census and surgeon general data to estimate a minimum of 500,000 Union military deaths and 350,000 Confederate military deaths, for a total death toll of 850,000 soldiers. While Walker's estimates were originally dismissed because of the 1870 census's undercounting, it was later found that the census was only off by 6.5% and that the data Walker used would be roughly accurate.
Emancipation
 Abolishing slavery was not a Union war goal from the outset, but it quickly became one. Lincoln's initial claims were that preserving the Union was the central goal of the war. In contrast, the South saw itself as fighting to preserve slavery. While not all Southerners saw themselves as fighting for slavery, most of the officers and over a third of the rank and file in Robert E. Lee, Lee's army had close family ties to slavery. To Northerners, in contrast, the motivation was primarily to preserve the
Abolishing slavery was not a Union war goal from the outset, but it quickly became one. Lincoln's initial claims were that preserving the Union was the central goal of the war. In contrast, the South saw itself as fighting to preserve slavery. While not all Southerners saw themselves as fighting for slavery, most of the officers and over a third of the rank and file in Robert E. Lee, Lee's army had close family ties to slavery. To Northerners, in contrast, the motivation was primarily to preserve the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
, not to abolish slavery. However, as the war dragged on, and it became clear that slavery was central to the conflict, and that emancipation was (to quote from the Emancipation Proclamation) "a fit and necessary war measure for suppressing [the] rebellion," Lincoln and his cabinet made ending slavery a war goal, culminating in the Emancipation Proclamation.[McPherson, pp. 506–8.] By warning that free blacks would flood the North, Democrats made gains in the 1862 congressional elections, 1862 elections, but they did not gain control of Congress. The Republicans' counterargument that slavery was the mainstay of the enemy steadily gained support, with the Democrats losing decisively in the 1863 elections in the Northern state of Ohio when they tried to resurrect anti-black sentiment.
Emancipation Proclamation
Slavery for the Confederacy's 3.5 million blacks effectively ended in each area when Union armies arrived; they were nearly all freed by the Emancipation Proclamation. The last Confederate slaves were freed on June 19, 1865, celebrated as the modern holiday of Juneteenth. Slaves in the border states and those located in some former Confederate territory occupied before the Emancipation Proclamation were freed by state action or (on December 6, 1865) by the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, Thirteenth Amendment. The Emancipation Proclamation enabled African Americans, both free blacks and escaped slaves, to join the Union Army. About 190,000 volunteered, further enhancing the numerical advantage the Union armies enjoyed over the Confederates, who did not dare emulate the equivalent manpower source for fear of fundamentally undermining the legitimacy of slavery.
During the Civil War, sentiment concerning slaves, enslavement and emancipation in the United States was divided. Lincoln's fears of making slavery a war issue were based on a harsh reality: abolition did not enjoy wide support in the west, the territories, and the border states.[Lincoln's letter to O. H. Browning, September 22, 1861. Sentiment among German Americans was largely antislavery especially among Forty-Eighters, resulting in hundreds of thousands of German Americans volunteering to fight for the Union."" Christian B. Keller, "Flying Dutchmen and Drunken Irishmen: The Myths and Realities of Ethnic Civil War Soldiers," ''Journal of Military History'', Vol. 73, No. 1, January 2009, pp. 117–45; for primary sources, see Walter D. Kamphoefner and Wolfgang Helbich, eds., ''Germans in the Civil War: The Letters They Wrote Home'' (2006). "On the other hand, many of the recent immigrants in the North viewed freed slaves as competition for scarce jobs, and as the reason why the Civil War was being fought." Baker, Kevin (March 2003)]
"Violent City"
''American Heritage (magazine), American Heritage''. Retrieved July 29, 2010. "Due in large part to this fierce competition with free blacks for labor opportunities, the poor and working class Irish American, Irish Catholics generally opposed emancipation. When the draft began in the summer of 1863, they launched New York Draft Riots, a major riot in New York City that was suppressed by the military, as well as much smaller protests in other cities." Barnet Schecter, ''The Devil's Own Work: The Civil War Draft Riots and the Fight to Reconstruct America'' (2007), ch. 6. Many Catholics in the North had volunteered to fight in 1861, sending thousands of soldiers to the front and suffering high casualties, especially at Battle of Fredericksburg, Fredericksburg; their volunteering fell off after 1862. Copperheads (politics), Copperheads and some War Democrats opposed emancipation, although the latter eventually accepted it as part of the total war needed to save the Union.
At first, Lincoln reversed attempts at emancipation by Secretary of War Simon Cameron and Generals John C. Frémont (in Missouri) and David Hunter (in South Carolina, Georgia and Florida) to keep the loyalty of the border states and the War Democrats. Lincoln warned the border states that a more radical type of emancipation would happen if his plan of gradual compensated emancipation and back-to-Africa movement, voluntary colonization was rejected. But District of Columbia Compensated Emancipation Act, compensated emancipation occurred only in the District of Columbia, where Congress had the power to enact it. When Lincoln told his cabinet about his proposed emancipation proclamation, which would apply to the states still in rebellion on January 1, 1863, Seward advised Lincoln to wait for a victory before issuing it, as to do otherwise would seem like "our last shriek on the retreat". Lincoln laid the groundwork for public support in an open letter published in response to Horace Greeley's "The Prayer of Twenty Millions". He also laid the groundwork at a meeting at the White House with five African American representatives on August 14, 1862. Arranging for a reporter to be present, he urged his visitors to agree to the voluntary colonization of black people, apparently to make his forthcoming preliminary Emancipation Proclamation more palatable to racist white people. A Union victory in the Battle of Antietam on September 17, 1862, provided Lincoln with an opportunity to issue the preliminary Emancipation Proclamation, and the subsequent War Governors' Conference added support for the proclamation.
Lincoln issued his preliminary Emancipation Proclamation on September 22, 1862. It stated that the slaves in all states in rebellion on January 1, 1863, would be free. He issued his final Emancipation Proclamation on January 1, 1863, keeping his promise. In his letter to Albert G. Hodges, Lincoln explained his belief that "If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong .... And yet I have never understood that the Presidency conferred upon me an unrestricted right to act officially upon this judgment and feeling .... I claim not to have controlled events, but confess plainly that events have controlled me."
Lincoln's moderate approach succeeded in inducing the border states to remain in the Union and War Democrats to support the Union. The border states (Kentucky, Missouri, Maryland, Delaware) and Union-controlled regions around New Orleans, Norfolk, and elsewhere, were not covered by the Emancipation Proclamation. Nor was Tennessee, which had come under Union control. Missouri and Maryland abolished slavery on their own; Kentucky and Delaware did not. Still, the proclamation did not enjoy universal support. It caused much unrest in what were then considered western states, where racist sentiments led to a great fear of abolition. There was some concern that the proclamation would lead to the secession of western states, and its issuance prompted the stationing of Union troops in Illinois in case of rebellion.
Since the Emancipation Proclamation was based on the President's war powers, it applied only in territory held by Confederates at the time. However, the Proclamation became a symbol of the Union's growing commitment to add emancipation to the Union's definition of liberty. The Emancipation Proclamation greatly reduced the Confederacy's hope of being recognized or otherwise aided by Britain or France. By late 1864, Lincoln was playing a leading role in getting the House of Representatives to vote for the Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution, which mandated the ending of chattel slavery.
Reconstruction

 The war had utterly devastated the South and posed serious questions of how the South would be re-integrated to the Union. The war destroyed much of the wealth that had existed in the South. All accumulated investment in Confederate bonds was forfeited; most banks and railroads were bankrupt. The income per person in the South dropped to less than 40 percent of that of the North, a condition that lasted until well into the 20th century. Southern influence in the federal government, previously considerable, was greatly diminished until the latter half of the 20th century.
The war had utterly devastated the South and posed serious questions of how the South would be re-integrated to the Union. The war destroyed much of the wealth that had existed in the South. All accumulated investment in Confederate bonds was forfeited; most banks and railroads were bankrupt. The income per person in the South dropped to less than 40 percent of that of the North, a condition that lasted until well into the 20th century. Southern influence in the federal government, previously considerable, was greatly diminished until the latter half of the 20th century.
Memory and historiography
The Civil War is one of the central events in American collective memory. There are innumerable statues, commemorations, books, and archival collections. The memory includes the home front, military affairs, the treatment of soldiers, both living and dead, in the war's aftermath, depictions of the war in literature and art, evaluations of heroes and villains, and considerations of the moral and political lessons of the war.
Lost Cause
The memory of the war in the white South crystallized in the myth of the Lost Cause of the Confederacy, "Lost Cause": that the Confederate cause was just and heroic. The myth shaped regional identity and race relations for generations.
Battlefield preservation
 The first efforts at Civil War battlefield preservation and memorialization came during the war itself with the establishment of National Cemeteries at Gettysburg, Mill Springs and Chattanooga. Soldiers began erecting markers on battlefields beginning with the
The first efforts at Civil War battlefield preservation and memorialization came during the war itself with the establishment of National Cemeteries at Gettysburg, Mill Springs and Chattanooga. Soldiers began erecting markers on battlefields beginning with the First Battle of Bull Run
The First Battle of Bull Run (the name used by Union forces), also known as the Battle of First Manassas in July 1861, but the oldest surviving monument is the Hazen Brigade Monument near Murfreesboro, Tennessee, built in the summer of 1863 by soldiers in Union Col. William Babcock Hazen, William B. Hazen's brigade to mark the spot where they buried their dead following the Battle of Stones River. In the 1890s, the United States government established five Civil War battlefield parks under the jurisdiction of the War Department, beginning with the creation of the Chickamauga and Chattanooga National Military Park in Tennessee and the Antietam National Battlefield in Maryland in 1890. The Shiloh National Military Park was established in 1894, followed by the Gettysburg National Military Park in 1895 and Vicksburg National Military Park in 1899. In 1933, these five parks and other national monuments were transferred to the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. Chief among modern efforts to preserve Civil War sites has been the American Battlefield Trust, with more than 130 battlefields in 24 states. The five major Civil War battlefield parks operated by the National Park Service (Gettysburg, Antietam, Shiloh, Chickamauga/Chattanooga and Vicksburg) had a combined 3.1 million visitors in 2018, down 70% from 10.2 million in 1970.
Civil War commemoration
The American Civil War has been commemorated in many capacities, ranging from the reenactment of battles to statues and memorial halls erected, to films being produced, to stamps and coins with Civil War themes being issued, all of which helped to shape public memory. These commemorations occurred in greater numbers on the 100th and 150th anniversaries of the war.
Technological significance
Numerous technological innovations during the Civil War had a great impact on 19th-century science. The Civil War was one of the earliest examples of an "Industrial warfare, industrial war", in which technological might is used to achieve military supremacy in a war. New inventions, such as the Military railways, train and Telegraphy, telegraph, delivered soldiers, supplies and messages at a time when horses were considered to be the fastest way to travel. It was also in this war that aerial warfare, in the form of reconnaissance History of aerial warfare#American Civil War, balloons, was first used. It saw the first action involving steam-powered ironclad warships in naval warfare history. Repeating rifle, Repeating firearms such as the Henry rifle, Spencer rifle, Colt revolving rifle, Triplett & Scott carbine and others, first appeared during the Civil War; they were a revolutionary invention that would soon replace Muzzleloader, muzzle-loading and single-shot firearms in warfare. The war also saw the first appearances of rapid-firing weapons and machine guns such as the Agar gun and the Gatling gun.
In works of culture and art
The Civil War is one of the most studied events in American history, and the collection of cultural works around it is enormous.
Literature
* ''When Lilacs Last in the Dooryard Bloom'd'' and ''O Captain! My Captain!'' (1865) by Walt Whitman, famous eulogies to Lincoln
* ''Battle-Pieces and Aspects of the War'' (1866) poetry by Herman Melville
* ''The Rise and Fall of the Confederate Government'' (1881) by Jefferson Davis
* ''The Private History of a Campaign That Failed'' (1885) by Mark Twain
* ''Texar's Revenge, or, North Against South'' (1887) by Jules Verne
* ''An Occurrence at Owl Creek Bridge'' (1890) by Ambrose Bierce
* ''The Red Badge of Courage'' (1895) by Stephen Crane
* ''Gone with the Wind (novel), Gone with the Wind'' (1936) by Margaret Mitchell
* ''North and South (trilogy), North and South'' (1982) by John Jakes
* ''The March (novel), The March: A Novel'' (2005) by E. L. Doctorow, fictionalized account of Sherman's March to the Sea
Film
* ''The Birth of a Nation'' (1915, US)
* ''The General (1926 film), The General'' (1926, US)
* ''Operator 13'' (1934, US)
* ''Gone with the Wind (film), Gone with the Wind'' (1939, US)
* ''The Red Badge of Courage (1951 film), The Red Badge of Courage'' (1951, US)
* ''The Horse Soldiers'' (1959, US)
* ''Shenandoah (film), Shenandoah'' (1965, US)
* ''The Good, the Bad and the Ugly'' (1966, Italy-Spain-FRG)
* ''The Beguiled (1971 film), The Beguiled'' (1971, US)
* ''The Outlaw Josey Wales'' (1976, US)
* ''Glory (1989 film), Glory'' (1989, US)
* ''The Civil War (miniseries), The Civil War'' (1990, US)
* ''Gettysburg (1993 film), Gettysburg'' (1993, US)
* ''The Last Outlaw (1993 film), The Last Outlaw'' (1993, US)
* ''Cold Mountain (film), Cold Mountain'' (2003, US)
* ''Gods and Generals (film), Gods and Generals'' (2003, US)
* ''North and South (miniseries), North and South'' (miniseries)
* ''Lincoln (film), Lincoln'' (2012, US)
* ''Free State of Jones (film), Free State of Jones'' (2016, US)
Music
* Dixie (song), Dixie
* Battle Cry of Freedom
* Battle Hymn of the Republic
* The Bonnie Blue Flag
* John Brown's Body
* When Johnny Comes Marching Home
* Marching Through Georgia
* The Night They Drove Old Dixie Down
Video games
* ''North & South (video game), North & South'' (1989, FR)
* ''Sid Meier's Gettysburg!'' (1997, US)
* ''Sid Meier's Antietam!'' (1999, US)
* ''American Conquest#American Conquest: Divided Nation, American Conqest: Divided Nation'' (2006, US)
* ''Forge of Freedom: The American Civil War'' (2006, US)
* ''The History Channel: Civil War – A Nation Divided'' (2006, US)
* ''Ageod's American Civil War'' (2007, US/FR)
* ''History Civil War: Secret Missions'' (2008, US)
* ''Call of Juarez: Bound in Blood'' (2009, US)
* ''Darkest of Days'' (2009, US)
* ''Victoria II: A House Divided'' (2011, US)
* ''Ageod's American Civil War II'' (2013, US/FR)
* ''Ultimate General#Ultimate General: Gettysburg, Ultimate General: Gettysburg'' (2014, UKR)
* ''Ultimate General#Ultimate General: Civil War, Ultimate General: Civil War'' (2016, UKR)
* ''War of Rights'' (2018, US)
See also
General reference
* American Civil War Corps Badges
* List of American Civil War battles
** List of costliest American Civil War land battles
* List of weapons in the American Civil War
* Second American Civil War
Union
* Presidency of Abraham Lincoln
* Uniform of the Union Army
Confederacy
* Central Confederacy
* Uniforms of the Confederate States Armed Forces
Ethnic articles
* Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War, African Americans in the American Civil War
* German Americans in the American Civil War
* Irish Americans in the American Civil War
* Italian Americans in the Civil War, Italian Americans in the American Civil War
* Native Americans in the American Civil War (disambiguation), Native Americans in the American Civil War
Topical articles
* Commemoration of the American Civil War
* Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps
* Dorothea Dix
* Education of freed people during the Civil War
*
** American Civil War spies, Spies in the American Civil War
* Gender issues in the American Civil War
* Infantry in the American Civil War
* List of ships captured in the 19th century#American Civil War
* Slavery during the American Civil War
National articles
* Canada in the American Civil War
* Foreign enlistment in the American Civil War
* Prussia and the American Civil War, Prussia in the American Civil War
* United Kingdom and the American Civil War, United Kingdom in the American Civil War
State articles
* :American Civil War by state
Memorials
* List of Confederate monuments and memorials
* List of memorials and monuments at Arlington National Cemetery
* List of memorials to Jefferson Davis
* List of memorials to Robert E. Lee
* List of memorials to Stonewall Jackson
* List of monuments erected by the United Daughters of the Confederacy
* List of monuments of the Gettysburg Battlefield
* List of Union Civil War monuments and memorials
* Memorials to Abraham Lincoln
* Removal of Confederate monuments and memorials
Other modern civil wars in the world
* Boxer Rebellion
* Chinese Civil War
* Finnish Civil War
* Mexican Revolution
* Russian Civil War
* Spanish Civil War
* Taiping Rebellion
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
*
*
*
* Beringer, Richard E., Archer Jones, and Herman Hattaway (1986). ''Why the South Lost the Civil War'', influential analysis of factors; an abridged version is ''The Elements of Confederate Defeat: Nationalism, War Aims, and Religion'' (1988)
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Gary W. Gallagher, Gallagher, Gary W. (2011). ''The Union War''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. .
* Gara, Larry (1964). "The Fugitive Slave Law: A Double Paradox," in Irwin Unger, Unger, Irwin, ''Essays on the Civil War and Reconstruction'', New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1970 (originally published in ''Civil War History'', Vol. 10, No. 3, September 1964, pp. 229–240).
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Allan Nevins, Nevins, Allan. ''Ordeal of the Union'', an 8-volume set (1947–1971). the most detailed political, economic and military narrative; by Pulitzer Prize-winner
** 1
''Fruits of Manifest Destiny, 1847–1852'' online
2. ''A House Dividing, 1852–1857''; 3. ''Douglas, Buchanan, and Party Chaos, 1857–1859''; 4. ''Prologue to Civil War, 1859–1861''; vols 5–8 have the series title ''War for the Union''; 5. ''The Improvised War, 1861–1862''; 6
online
''War Becomes Revolution, 1862–1863''; 7. ''The Organized War, 1863–1864''; 8. ''The Organized War to Victory, 1864–1865''
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Sheehan-Dean, Aaron
A Companion to the U.S. Civil War
2 vol. (April 2014) Wiley-Blackwell, New York . 1232pp; 64 Topical chapters by scholars and experts; emphasis on historiography.
*
*
* Stoker, Donald. ''The Grand Design: Strategy and the U.S. Civil War'' (2010
excerpt
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* Borrow book at
archive.org
*
Further reading
* Bibliography of the American Civil War
* Bibliography of early American naval history#American Civil War, Bibliography of American Civil War naval history
*
External links
West Point Atlas of Civil War Battles
at the National Archives and Records Administration, National Archives
View images
from th
Civil War Photographs Collection
at the Library of Congress
American Battlefield Trust
– A non-profit land preservation and educational organization with two divisions, the Civil War Trust and the Revolutionary War Trust, dedicated to preserving America's battlefields through land acquisitions.
– This collection contains digital images of political cartoons, personal papers, pamphlets, maps, paintings and photographs from the Civil War Era held in Special Collections at Gettysburg College.
Civil War 150
– ''Washington Post'' interactive website on the 150th Anniversary of the American Civil War.
Civil War in the American South
– An Association of Southeastern Research Libraries (ASERL) portal with links to almost 9,000 digitized Civil War-era items—books, pamphlets, broadsides, letters, maps, personal papers, and manuscripts—held at ASERL member libraries
The Civil War
– site with 7,000 pages, including the complete run of Harper's Weekly newspapers from the Civil War
*
"American Civil World" maps at the Persuasive Cartography, The PJ Mode Collection
Cornell University Library
Civil War Manuscripts
at Shapell Manuscript Foundation
Statements of each state as to why they were seceding
battlefields.org
{{Authority control
American Civil War,
Rebellions against the United States
Conflicts in 1861
Conflicts in 1862
Conflicts in 1863
Conflicts in 1864
Conflicts in 1865
19th-century conflicts
Wars involving the United States, Civil War
1860s in the United States
Wars of independence
Internal wars of the United States
1860s conflicts
 The abolitionists—those advocating the end of slavery—were active in the decades leading up to the Civil War. They traced their philosophical roots back to the
The abolitionists—those advocating the end of slavery—were active in the decades leading up to the Civil War. They traced their philosophical roots back to the  In the decades leading up to the Civil War, abolitionists, such as Theodore Parker,
In the decades leading up to the Civil War, abolitionists, such as Theodore Parker,  Nationalism was a powerful force in the early 19th century, with famous spokesmen such as
Nationalism was a powerful force in the early 19th century, with famous spokesmen such as  Among the ordinances of secession passed by the individual states, those of three—Texas, Alabama, and Virginia—specifically mentioned the plight of the "slaveholding states" at the hands of Northern abolitionists. The rest make no mention of the slavery issue and are often brief announcements of the dissolution of ties by the legislatures. However, at least four states—South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, and TexasThe text o
Among the ordinances of secession passed by the individual states, those of three—Texas, Alabama, and Virginia—specifically mentioned the plight of the "slaveholding states" at the hands of Northern abolitionists. The rest make no mention of the slavery issue and are often brief announcements of the dissolution of ties by the legislatures. However, at least four states—South Carolina, Mississippi, Georgia, and TexasThe text o On March 4, 1861, Abraham Lincoln was sworn in as president. In his
On March 4, 1861, Abraham Lincoln was sworn in as president. In his  The American Civil War began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces opened fire on the Union-held
The American Civil War began on April 12, 1861, when Confederate forces opened fire on the Union-held 
 When the Emancipation Proclamation went into effect in January 1863, ex-slaves were energetically recruited by the states and used to meet the state quotas. States and local communities offered higher and higher cash bonuses for white volunteers. Congress tightened the law in March 1863. Men selected in the draft could provide substitutes or, until mid-1864, pay commutation money. Many eligibles pooled their money to cover the cost of anyone drafted. Families used the substitute provision to select which man should go into the army and which should stay home. There was much evasion and overt resistance to the draft, especially in Catholic areas. The draft riot in New York City in July 1863 involved Irish immigrants who had been signed up as citizens to swell the vote of the city's Democratic political machine, not realizing it made them liable for the draft. Of the 168,649 men procured for the Union through the draft, 117,986 were substitutes, leaving only 50,663 who had their services conscripted.
In both the North and South, the draft laws were highly unpopular. In the North, some 120,000 men evaded conscription, many of them fleeing to Canada, and another 280,000 soldiers deserted during the war. At least 100,000 Southerners deserted, or about 10 percent; Southern desertion was high because, according to one historian writing in 1991, the highly localized Southern identity meant that many Southern men had little investment in the outcome of the war, with individual soldiers caring more about the fate of their local area than any grand ideal. In the North, " bounty jumpers" enlisted to get the generous bonus, deserted, then went back to a second recruiting station under a different name to sign up again for a second bonus; 141 were caught and executed.
From a tiny frontier force in 1860, the Union and Confederate armies had grown into the "largest and most efficient armies in the world" within a few years. Some European observers at the time dismissed them as amateur and unprofessional, but historian John Keegan concluded that each outmatched the French, Prussian, and Russian armies of the time, and without the Atlantic, would have threatened any of them with defeat.
When the Emancipation Proclamation went into effect in January 1863, ex-slaves were energetically recruited by the states and used to meet the state quotas. States and local communities offered higher and higher cash bonuses for white volunteers. Congress tightened the law in March 1863. Men selected in the draft could provide substitutes or, until mid-1864, pay commutation money. Many eligibles pooled their money to cover the cost of anyone drafted. Families used the substitute provision to select which man should go into the army and which should stay home. There was much evasion and overt resistance to the draft, especially in Catholic areas. The draft riot in New York City in July 1863 involved Irish immigrants who had been signed up as citizens to swell the vote of the city's Democratic political machine, not realizing it made them liable for the draft. Of the 168,649 men procured for the Union through the draft, 117,986 were substitutes, leaving only 50,663 who had their services conscripted.
In both the North and South, the draft laws were highly unpopular. In the North, some 120,000 men evaded conscription, many of them fleeing to Canada, and another 280,000 soldiers deserted during the war. At least 100,000 Southerners deserted, or about 10 percent; Southern desertion was high because, according to one historian writing in 1991, the highly localized Southern identity meant that many Southern men had little investment in the outcome of the war, with individual soldiers caring more about the fate of their local area than any grand ideal. In the North, " bounty jumpers" enlisted to get the generous bonus, deserted, then went back to a second recruiting station under a different name to sign up again for a second bonus; 141 were caught and executed.
From a tiny frontier force in 1860, the Union and Confederate armies had grown into the "largest and most efficient armies in the world" within a few years. Some European observers at the time dismissed them as amateur and unprofessional, but historian John Keegan concluded that each outmatched the French, Prussian, and Russian armies of the time, and without the Atlantic, would have threatened any of them with defeat.
 The small
The small  By early 1861, General
By early 1861, General  The Confederates began the war short on military supplies and in desperate need of large quantities of arms which the agrarian South could not provide. Arms manufactures in the industrial North were restricted by an arms embargo, keeping shipments of arms from going to the South, and ending all existing and future contracts. The Confederacy subsequently looked to foreign sources for their enormous military needs and sought out financiers and companies like S. Isaac, Campbell & Company and the
The Confederates began the war short on military supplies and in desperate need of large quantities of arms which the agrarian South could not provide. Arms manufactures in the industrial North were restricted by an arms embargo, keeping shipments of arms from going to the South, and ending all existing and future contracts. The Confederacy subsequently looked to foreign sources for their enormous military needs and sought out financiers and companies like S. Isaac, Campbell & Company and the  The Eastern theater refers to the military operations east of the
The Eastern theater refers to the military operations east of the  The primary Confederate force in the Eastern theater was the
The primary Confederate force in the Eastern theater was the  In one of the first highly visible battles, in July 1861, a march by Union troops under the command of
In one of the first highly visible battles, in July 1861, a march by Union troops under the command of  Emboldened by Second Bull Run, the Confederacy made its first invasion of the North with the Maryland Campaign. General Lee led 45,000 troops of the Army of Northern Virginia across the
Emboldened by Second Bull Run, the Confederacy made its first invasion of the North with the Maryland Campaign. General Lee led 45,000 troops of the Army of Northern Virginia across the  Hooker, too, proved unable to defeat Lee's army; despite outnumbering the Confederates by more than two to one, his Chancellorsville Campaign proved ineffective and he was humiliated in the
Hooker, too, proved unable to defeat Lee's army; despite outnumbering the Confederates by more than two to one, his Chancellorsville Campaign proved ineffective and he was humiliated in the  Gen. Hooker was replaced by Maj. Gen.
Gen. Hooker was replaced by Maj. Gen.  The primary Union forces in the Western theater were the
The primary Union forces in the Western theater were the  At the Battle of Shiloh, in Shiloh, Tennessee in April 1862, the Confederates made a surprise attack that pushed Union forces against the river as night fell. Overnight, the Navy landed additional reinforcements, and Grant counter-attacked. Grant and the Union won a decisive victory—the first battle with the high casualty rates that would repeat over and over. The Confederates lost Albert Sidney Johnston, considered their finest general before the emergence of Lee.
One of the early Union objectives in the war was the capture of the
At the Battle of Shiloh, in Shiloh, Tennessee in April 1862, the Confederates made a surprise attack that pushed Union forces against the river as night fell. Overnight, the Navy landed additional reinforcements, and Grant counter-attacked. Grant and the Union won a decisive victory—the first battle with the high casualty rates that would repeat over and over. The Confederates lost Albert Sidney Johnston, considered their finest general before the emergence of Lee.
One of the early Union objectives in the war was the capture of the  Bragg's second invasion of Kentucky in the Confederate Heartland Offensive included initial successes such as Edmund Kirby Smith, Kirby Smith's triumph at the Battle of Richmond and the capture of the Kentucky capital of Frankfort on September 3, 1862. However, the campaign ended with a meaningless victory over Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell at the Battle of Perryville. Bragg was forced to end his attempt at invading Kentucky and retreat due to lack of logistical support and lack of infantry recruits for the Confederacy in that state.
Bragg was narrowly defeated by Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans at the Battle of Stones River in
Bragg's second invasion of Kentucky in the Confederate Heartland Offensive included initial successes such as Edmund Kirby Smith, Kirby Smith's triumph at the Battle of Richmond and the capture of the Kentucky capital of Frankfort on September 3, 1862. However, the campaign ended with a meaningless victory over Maj. Gen. Don Carlos Buell at the Battle of Perryville. Bragg was forced to end his attempt at invading Kentucky and retreat due to lack of logistical support and lack of infantry recruits for the Confederacy in that state.
Bragg was narrowly defeated by Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans at the Battle of Stones River in  The one clear Confederate victory in the West was the Battle of Chickamauga. After Rosecrans' successful Tullahoma Campaign, Bragg, reinforced by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet's corps (from Lee's army in the east), defeated Rosecrans, despite the heroic defensive stand of Maj. Gen. George Henry Thomas.
Rosecrans retreated to Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga, which Bragg then besieged in the Chattanooga Campaign. Grant marched to the relief of Rosecrans and defeated Bragg at the Chattanooga Campaign, Third Battle of Chattanooga, eventually causing Longstreet to abandon his Knoxville Campaign and driving Confederate forces out of Tennessee and opening a route to Atlanta and the heart of the Confederacy.
The one clear Confederate victory in the West was the Battle of Chickamauga. After Rosecrans' successful Tullahoma Campaign, Bragg, reinforced by Lt. Gen. James Longstreet's corps (from Lee's army in the east), defeated Rosecrans, despite the heroic defensive stand of Maj. Gen. George Henry Thomas.
Rosecrans retreated to Chattanooga, Tennessee, Chattanooga, which Bragg then besieged in the Chattanooga Campaign. Grant marched to the relief of Rosecrans and defeated Bragg at the Chattanooga Campaign, Third Battle of Chattanooga, eventually causing Longstreet to abandon his Knoxville Campaign and driving Confederate forces out of Tennessee and opening a route to Atlanta and the heart of the Confederacy.
 The first battle of the Trans-Mississippi theater was the Battle of Wilson's Creek (August 1861). The Confederates were driven from Missouri early in the war as a result of the Battle of Pea Ridge.
Extensive guerrilla warfare characterized the trans-Mississippi region, as the Confederacy lacked the troops and the logistics to support regular armies that could challenge Union control. Roving Confederate bands such as Quantrill's Raiders terrorized the countryside, striking both military installations and civilian settlements. The "Sons of Liberty" and "Order of the American Knights" attacked pro-Union people, elected officeholders, and unarmed uniformed soldiers. These partisans could not be entirely driven out of the state of Missouri until an entire regular Union infantry division was engaged. By 1864, these violent activities harmed the nationwide anti-war movement organizing against the re-election of Lincoln. Missouri not only stayed in the Union but Lincoln took 70 percent of the vote for re-election.
Numerous small-scale military actions south and west of Missouri sought to control Indian Territory in the American Civil War, Indian Territory and New Mexico Territory in the American Civil War, New Mexico Territory for the Union. The Battle of Glorieta Pass was the decisive battle of the New Mexico Campaign. The Union repulsed Confederate incursions into New Mexico in 1862, and the exiled Arizona government withdrew into Texas. In the Indian Territory, civil war broke out within tribes. About 12,000 Indian warriors fought for the Confederacy and smaller numbers for the Union. The most prominent Cherokee was Brigadier General Stand Watie, the last Confederate general to surrender.
After the fall of Siege of Vicksburg, Vicksburg in July 1863, General Kirby Smith in Texas was informed by Jefferson Davis that he could expect no further help from east of the Mississippi River. Although he lacked resources to beat Union armies, he built up a formidable arsenal at Tyler, along with his own Kirby Smithdom economy, a virtual "independent fiefdom" in Texas, including railroad construction and international smuggling. The Union, in turn, did not directly engage him. Its 1864 Red River Campaign to take Shreveport, Louisiana, was a failure and Texas remained in Confederate hands throughout the war.
The first battle of the Trans-Mississippi theater was the Battle of Wilson's Creek (August 1861). The Confederates were driven from Missouri early in the war as a result of the Battle of Pea Ridge.
Extensive guerrilla warfare characterized the trans-Mississippi region, as the Confederacy lacked the troops and the logistics to support regular armies that could challenge Union control. Roving Confederate bands such as Quantrill's Raiders terrorized the countryside, striking both military installations and civilian settlements. The "Sons of Liberty" and "Order of the American Knights" attacked pro-Union people, elected officeholders, and unarmed uniformed soldiers. These partisans could not be entirely driven out of the state of Missouri until an entire regular Union infantry division was engaged. By 1864, these violent activities harmed the nationwide anti-war movement organizing against the re-election of Lincoln. Missouri not only stayed in the Union but Lincoln took 70 percent of the vote for re-election.
Numerous small-scale military actions south and west of Missouri sought to control Indian Territory in the American Civil War, Indian Territory and New Mexico Territory in the American Civil War, New Mexico Territory for the Union. The Battle of Glorieta Pass was the decisive battle of the New Mexico Campaign. The Union repulsed Confederate incursions into New Mexico in 1862, and the exiled Arizona government withdrew into Texas. In the Indian Territory, civil war broke out within tribes. About 12,000 Indian warriors fought for the Confederacy and smaller numbers for the Union. The most prominent Cherokee was Brigadier General Stand Watie, the last Confederate general to surrender.
After the fall of Siege of Vicksburg, Vicksburg in July 1863, General Kirby Smith in Texas was informed by Jefferson Davis that he could expect no further help from east of the Mississippi River. Although he lacked resources to beat Union armies, he built up a formidable arsenal at Tyler, along with his own Kirby Smithdom economy, a virtual "independent fiefdom" in Texas, including railroad construction and international smuggling. The Union, in turn, did not directly engage him. Its 1864 Red River Campaign to take Shreveport, Louisiana, was a failure and Texas remained in Confederate hands throughout the war.
 In April 1862, a Union naval task force commanded by Commander David Dixon Porter, David D. Porter attacked Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip, Forts Jackson and St. Philip, which guarded the river approach to from the south. While part of the fleet bombarded the forts, other vessels forced a break in the obstructions in the river and enabled the rest of the fleet to steam upriver to the city. A Union army force commanded by Major General Benjamin Butler (politician), Benjamin Butler landed near the forts and forced their surrender. Butler's controversial command of New Orleans earned him the nickname "Beast".
The following year, the Union Army of the Gulf commanded by Major General Nathaniel P. Banks laid Siege of Port Hudson, siege to Port Hudson for nearly eight weeks, the longest siege in US military history. The Confederates attempted to defend with the Bayou Teche Campaign but surrendered after Vicksburg. These two surrenders gave the Union control over the entire Mississippi.
Several small skirmishes were fought in Florida, but no major battles. The biggest was the Battle of Olustee in early 1864.
In April 1862, a Union naval task force commanded by Commander David Dixon Porter, David D. Porter attacked Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip, Forts Jackson and St. Philip, which guarded the river approach to from the south. While part of the fleet bombarded the forts, other vessels forced a break in the obstructions in the river and enabled the rest of the fleet to steam upriver to the city. A Union army force commanded by Major General Benjamin Butler (politician), Benjamin Butler landed near the forts and forced their surrender. Butler's controversial command of New Orleans earned him the nickname "Beast".
The following year, the Union Army of the Gulf commanded by Major General Nathaniel P. Banks laid Siege of Port Hudson, siege to Port Hudson for nearly eight weeks, the longest siege in US military history. The Confederates attempted to defend with the Bayou Teche Campaign but surrendered after Vicksburg. These two surrenders gave the Union control over the entire Mississippi.
Several small skirmishes were fought in Florida, but no major battles. The biggest was the Battle of Olustee in early 1864.
 At the beginning of 1864, Lincoln made Grant commander of all Union armies. Grant made his headquarters with the Army of the Potomac and put Maj. Gen.
At the beginning of 1864, Lincoln made Grant commander of all Union armies. Grant made his headquarters with the Army of the Potomac and put Maj. Gen.  Grant's army set out on the Overland Campaign intending to draw Lee into a defense of Richmond, where they would attempt to pin down and destroy the Confederate army. The Union army first attempted to maneuver past Lee and fought several battles, notably at the Battle of the Wilderness, Wilderness, Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, Spotsylvania, and Battle of Cold Harbor, Cold Harbor. These battles resulted in heavy losses on both sides and forced Lee's Confederates to fall back repeatedly. At the Battle of Yellow Tavern, the Confederates lost
Grant's army set out on the Overland Campaign intending to draw Lee into a defense of Richmond, where they would attempt to pin down and destroy the Confederate army. The Union army first attempted to maneuver past Lee and fought several battles, notably at the Battle of the Wilderness, Wilderness, Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, Spotsylvania, and Battle of Cold Harbor, Cold Harbor. These battles resulted in heavy losses on both sides and forced Lee's Confederates to fall back repeatedly. At the Battle of Yellow Tavern, the Confederates lost  Grant finally found a commander, General Philip Sheridan, aggressive enough to prevail in the Valley Campaigns of 1864. Sheridan was initially repelled at the Battle of New Market by former U.S. vice president and Confederate Gen. John C. Breckinridge. The Battle of New Market was the Confederacy's last major victory of the war and included a charge by teenage VMI cadets. After redoubling his efforts, Sheridan defeated Maj. Gen. Jubal Early, Jubal A. Early in a series of battles, including a final decisive defeat at the Battle of Cedar Creek. Sheridan then proceeded to destroy the agricultural base of the Shenandoah Valley, a strategy similar to the tactics Sherman later employed in Georgia.
Grant finally found a commander, General Philip Sheridan, aggressive enough to prevail in the Valley Campaigns of 1864. Sheridan was initially repelled at the Battle of New Market by former U.S. vice president and Confederate Gen. John C. Breckinridge. The Battle of New Market was the Confederacy's last major victory of the war and included a charge by teenage VMI cadets. After redoubling his efforts, Sheridan defeated Maj. Gen. Jubal Early, Jubal A. Early in a series of battles, including a final decisive defeat at the Battle of Cedar Creek. Sheridan then proceeded to destroy the agricultural base of the Shenandoah Valley, a strategy similar to the tactics Sherman later employed in Georgia.
 The Origins of the American Civil War, causes of the war, the reasons for its outcome, and even Naming the American Civil War, the name of the war itself are subjects of lingering contention today. The North and West grew rich while the once-rich South became poor for a century. The national political power of the slaveowners and rich Southerners ended. Historians are less sure about the results of the postwar Reconstruction, especially regarding the second-class citizenship of the freedmen and their poverty.
Historians have debated whether the Confederacy could have won the war. Most scholars, including James M. McPherson, argue that Confederate victory was at least possible. McPherson argues that the North's advantage in population and resources made Northern victory likely but not guaranteed. He also argues that if the Confederacy had fought using unconventional tactics, it would have more easily been able to hold out long enough to exhaust the Union.
Confederates did not need to invade and hold enemy territory to win but only needed to fight a defensive war to convince the North that the cost of winning was too high. The North needed to conquer and hold vast stretches of enemy territory and defeat Confederate armies to win. Lincoln was not a military dictator and could continue to fight the war only as long as the American public supported a continuation of the war. The Confederacy sought to win independence by outlasting Lincoln; however, after Atlanta fell and Lincoln defeated McClellan in the election of 1864, all hope for a political victory for the South ended. At that point, Lincoln had secured the support of the Republicans, War Democrats, the border states, emancipated slaves, and the neutrality of Britain and France. By defeating the Democrats and McClellan, he also defeated the Copperheads (politics), Copperheads, who had wanted a negotiated peace with the Confederate States of America.
Some scholars argue that the Union held an insurmountable long-term advantage over the Confederacy in industrial strength and population. Confederate actions, they argue, only delayed defeat. Civil War historian Shelby Foote expressed this view succinctly: "I think that the North fought that war with one hand behind its back .... If there had been more Southern victories, and a lot more, the North simply would have brought that other hand out from behind its back. I don't think the South ever had a chance to win that War."
A minority view among historians is that the Confederacy lost because, as E. Merton Coulter put it, "people did not will hard enough and long enough to win." However, most historians reject the argument. McPherson, after reading thousands of letters written by Confederate soldiers, found strong patriotism that continued to the end; they truly believed they were fighting for freedom and liberty. Even as the Confederacy was visibly collapsing in 1864–65, he says most Confederate soldiers were fighting hard. Historian Gary Gallagher cites General Sherman, who in early 1864 commented, "The devils seem to have a determination that cannot but be admired." Despite their loss of slaves and wealth, with starvation looming, Sherman continued, "yet I see no sign of let-up—some few deserters—plenty tired of war, but the masses determined to fight it out."
Also important were Lincoln's eloquence in rationalizing the national purpose and his skill in keeping the border states committed to the Union cause. The Emancipation Proclamation was an effective use of the President's war powers. The Confederate government failed in its attempt to get Europe involved in the war militarily, particularly Great Britain and France. Southern leaders needed to get European powers to help break up the blockade the Union had created around the Southern ports and cities. Lincoln's naval blockade was 95% effective at stopping trade goods; as a result, imports and exports to the South declined significantly. The abundance of European cotton and Britain's hostility to the institution of slavery, along with Lincoln's Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico naval blockades, severely decreased any chance that either Britain or France would enter the war.
Historian Don Doyle has argued that the Union victory had a major impact on the course of world history. The Union victory energized popular democratic forces. A Confederate victory, on the other hand, would have meant a new birth of slavery, not freedom. Historian Fergus Bordewich, following Doyle, argues that:
Scholars have debated what the effects of the war were on political and economic power in the South. The prevailing view is that the southern planter elite retained its powerful position in the South. However, a 2017 study challenges this, noting that while some Southern elites retained their economic status, the turmoil of the 1860s created greater opportunities for economic mobility in the South than in the North.
The Origins of the American Civil War, causes of the war, the reasons for its outcome, and even Naming the American Civil War, the name of the war itself are subjects of lingering contention today. The North and West grew rich while the once-rich South became poor for a century. The national political power of the slaveowners and rich Southerners ended. Historians are less sure about the results of the postwar Reconstruction, especially regarding the second-class citizenship of the freedmen and their poverty.
Historians have debated whether the Confederacy could have won the war. Most scholars, including James M. McPherson, argue that Confederate victory was at least possible. McPherson argues that the North's advantage in population and resources made Northern victory likely but not guaranteed. He also argues that if the Confederacy had fought using unconventional tactics, it would have more easily been able to hold out long enough to exhaust the Union.
Confederates did not need to invade and hold enemy territory to win but only needed to fight a defensive war to convince the North that the cost of winning was too high. The North needed to conquer and hold vast stretches of enemy territory and defeat Confederate armies to win. Lincoln was not a military dictator and could continue to fight the war only as long as the American public supported a continuation of the war. The Confederacy sought to win independence by outlasting Lincoln; however, after Atlanta fell and Lincoln defeated McClellan in the election of 1864, all hope for a political victory for the South ended. At that point, Lincoln had secured the support of the Republicans, War Democrats, the border states, emancipated slaves, and the neutrality of Britain and France. By defeating the Democrats and McClellan, he also defeated the Copperheads (politics), Copperheads, who had wanted a negotiated peace with the Confederate States of America.
Some scholars argue that the Union held an insurmountable long-term advantage over the Confederacy in industrial strength and population. Confederate actions, they argue, only delayed defeat. Civil War historian Shelby Foote expressed this view succinctly: "I think that the North fought that war with one hand behind its back .... If there had been more Southern victories, and a lot more, the North simply would have brought that other hand out from behind its back. I don't think the South ever had a chance to win that War."
A minority view among historians is that the Confederacy lost because, as E. Merton Coulter put it, "people did not will hard enough and long enough to win." However, most historians reject the argument. McPherson, after reading thousands of letters written by Confederate soldiers, found strong patriotism that continued to the end; they truly believed they were fighting for freedom and liberty. Even as the Confederacy was visibly collapsing in 1864–65, he says most Confederate soldiers were fighting hard. Historian Gary Gallagher cites General Sherman, who in early 1864 commented, "The devils seem to have a determination that cannot but be admired." Despite their loss of slaves and wealth, with starvation looming, Sherman continued, "yet I see no sign of let-up—some few deserters—plenty tired of war, but the masses determined to fight it out."
Also important were Lincoln's eloquence in rationalizing the national purpose and his skill in keeping the border states committed to the Union cause. The Emancipation Proclamation was an effective use of the President's war powers. The Confederate government failed in its attempt to get Europe involved in the war militarily, particularly Great Britain and France. Southern leaders needed to get European powers to help break up the blockade the Union had created around the Southern ports and cities. Lincoln's naval blockade was 95% effective at stopping trade goods; as a result, imports and exports to the South declined significantly. The abundance of European cotton and Britain's hostility to the institution of slavery, along with Lincoln's Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico naval blockades, severely decreased any chance that either Britain or France would enter the war.
Historian Don Doyle has argued that the Union victory had a major impact on the course of world history. The Union victory energized popular democratic forces. A Confederate victory, on the other hand, would have meant a new birth of slavery, not freedom. Historian Fergus Bordewich, following Doyle, argues that:
Scholars have debated what the effects of the war were on political and economic power in the South. The prevailing view is that the southern planter elite retained its powerful position in the South. However, a 2017 study challenges this, noting that while some Southern elites retained their economic status, the turmoil of the 1860s created greater opportunities for economic mobility in the South than in the North.
 While the figures of 360,000 army deaths for the Union and 260,000 for the Confederacy remained commonly cited, they are incomplete. In addition to many Confederate records being missing, partly as a result of Confederate widows not reporting deaths due to being ineligible for benefits, both armies only counted troops who died during their service and not the tens of thousands who died of wounds or diseases after being discharged. This often happened only a few days or weeks later. Francis Amasa Walker, superintendent of the 1870 census, used census and surgeon general data to estimate a minimum of 500,000 Union military deaths and 350,000 Confederate military deaths, for a total death toll of 850,000 soldiers. While Walker's estimates were originally dismissed because of the 1870 census's undercounting, it was later found that the census was only off by 6.5% and that the data Walker used would be roughly accurate.
Analyzing the number of dead by using census data to calculate the deviation of the death rate of men of fighting age from the norm suggests that at least 627,000 and at most 888,000, but most likely 761,000 soldiers, died in the war. This would break down to approximately 350,000 Confederate and 411,000 Union military deaths, going by the proportion of Union to Confederate battle losses.
Deaths among former slaves has proven much harder to estimate, due to the lack of reliable census data at the time, though they were known to be considerable, as former slaves were set free or escaped in massive numbers in an area where the Union army did not have sufficient shelter, doctors, or food for them. University of Connecticut Professor James Downs states that tens to hundreds of thousands of slaves died during the war from disease, starvation, or exposure and that if these deaths are counted in the war's total, the death toll would exceed 1 million.
Losses were far higher than during the recent Mexican–American War, defeat of Mexico, which saw roughly thirteen thousand American deaths, including fewer than two thousand killed in battle, between 1846 and 1848. One reason for the high number of battle deaths during the war was the continued use of tactics similar to those of the Napoleonic Wars at the turn of the century, such as charge (warfare), charging. With the advent of more accurate rifled barrels, Minié balls, and (near the end of the war for the Union army) repeating firearms such as the Spencer repeating rifle, Spencer Repeating Rifle and the Henry rifle, Henry Repeating Rifle, soldiers were mowed down when standing in lines in the open. This led to the adoption of trench warfare, a style of fighting that defined much of World War I.
While the figures of 360,000 army deaths for the Union and 260,000 for the Confederacy remained commonly cited, they are incomplete. In addition to many Confederate records being missing, partly as a result of Confederate widows not reporting deaths due to being ineligible for benefits, both armies only counted troops who died during their service and not the tens of thousands who died of wounds or diseases after being discharged. This often happened only a few days or weeks later. Francis Amasa Walker, superintendent of the 1870 census, used census and surgeon general data to estimate a minimum of 500,000 Union military deaths and 350,000 Confederate military deaths, for a total death toll of 850,000 soldiers. While Walker's estimates were originally dismissed because of the 1870 census's undercounting, it was later found that the census was only off by 6.5% and that the data Walker used would be roughly accurate.
Analyzing the number of dead by using census data to calculate the deviation of the death rate of men of fighting age from the norm suggests that at least 627,000 and at most 888,000, but most likely 761,000 soldiers, died in the war. This would break down to approximately 350,000 Confederate and 411,000 Union military deaths, going by the proportion of Union to Confederate battle losses.
Deaths among former slaves has proven much harder to estimate, due to the lack of reliable census data at the time, though they were known to be considerable, as former slaves were set free or escaped in massive numbers in an area where the Union army did not have sufficient shelter, doctors, or food for them. University of Connecticut Professor James Downs states that tens to hundreds of thousands of slaves died during the war from disease, starvation, or exposure and that if these deaths are counted in the war's total, the death toll would exceed 1 million.
Losses were far higher than during the recent Mexican–American War, defeat of Mexico, which saw roughly thirteen thousand American deaths, including fewer than two thousand killed in battle, between 1846 and 1848. One reason for the high number of battle deaths during the war was the continued use of tactics similar to those of the Napoleonic Wars at the turn of the century, such as charge (warfare), charging. With the advent of more accurate rifled barrels, Minié balls, and (near the end of the war for the Union army) repeating firearms such as the Spencer repeating rifle, Spencer Repeating Rifle and the Henry rifle, Henry Repeating Rifle, soldiers were mowed down when standing in lines in the open. This led to the adoption of trench warfare, a style of fighting that defined much of World War I.

 The war had utterly devastated the South and posed serious questions of how the South would be re-integrated to the Union. The war destroyed much of the wealth that had existed in the South. All accumulated investment in Confederate bonds was forfeited; most banks and railroads were bankrupt. The income per person in the South dropped to less than 40 percent of that of the North, a condition that lasted until well into the 20th century. Southern influence in the federal government, previously considerable, was greatly diminished until the latter half of the 20th century. Reconstruction began during the war, with the Emancipation Proclamation of January 1, 1863, and it continued until 1877. It comprised multiple complex methods to resolve the outstanding issues of the war's aftermath, the most important of which were the three "Reconstruction Amendments" to the Constitution: the 13th outlawing slavery (1865), the 14th guaranteeing citizenship to slaves (1868), and the 15th ensuring voting rights to slaves (1870). From the Union perspective, the goals of Reconstruction were to consolidate the Union victory on the battlefield by reuniting the Union, to guarantee a "Republicanism in the United States, republican form of government" for the ex-Confederate states, and to permanently end slavery—and prevent semi-slavery status.
President Johnson took a lenient approach and saw the achievement of the main war goals as realized in 1865 when each ex-rebel state repudiated secession and ratified the Thirteenth Amendment. Radical Republicans demanded proof that Confederate nationalism was dead and that the slaves were truly free. They Freedmen's Bureau bills, overrode Johnson's vetoes of Civil Rights Act of 1866, civil rights legislation, and the House Impeachment of Andrew Johnson, impeached him, although the Senate did not convict him. In 1868 and 1872, the Republican candidate Ulysses S. Grant won the presidency. In 1872, the Liberal Republican Party (United States), "Liberal Republicans" argued that the war goals had been achieved and that Reconstruction should end. They chose Horace Greeley 1872 presidential campaign, Horace Greeley to head a presidential ticket in 1872 but were decisively defeated. In 1874, Democrats, primarily Southern, took control of Congress and opposed further reconstruction. The Compromise of 1877 closed with a national consensus, except perhaps on the part of former slaves, that the Civil War had finally ended. With the withdrawal of federal troops, however, whites retook control of every Southern legislature, and the Jim Crow era of Disfranchisement after the Reconstruction era, disenfranchisement and legal segregation was ushered in.
The Civil War would have a huge impact on American politics in the years to come. Many veterans on both sides were subsequently elected to political office, including five U.S. Presidents: General Ulysses Grant, Rutherford B. Hayes, James Garfield, Benjamin Harrison, and William McKinley.
The war had utterly devastated the South and posed serious questions of how the South would be re-integrated to the Union. The war destroyed much of the wealth that had existed in the South. All accumulated investment in Confederate bonds was forfeited; most banks and railroads were bankrupt. The income per person in the South dropped to less than 40 percent of that of the North, a condition that lasted until well into the 20th century. Southern influence in the federal government, previously considerable, was greatly diminished until the latter half of the 20th century. Reconstruction began during the war, with the Emancipation Proclamation of January 1, 1863, and it continued until 1877. It comprised multiple complex methods to resolve the outstanding issues of the war's aftermath, the most important of which were the three "Reconstruction Amendments" to the Constitution: the 13th outlawing slavery (1865), the 14th guaranteeing citizenship to slaves (1868), and the 15th ensuring voting rights to slaves (1870). From the Union perspective, the goals of Reconstruction were to consolidate the Union victory on the battlefield by reuniting the Union, to guarantee a "Republicanism in the United States, republican form of government" for the ex-Confederate states, and to permanently end slavery—and prevent semi-slavery status.
President Johnson took a lenient approach and saw the achievement of the main war goals as realized in 1865 when each ex-rebel state repudiated secession and ratified the Thirteenth Amendment. Radical Republicans demanded proof that Confederate nationalism was dead and that the slaves were truly free. They Freedmen's Bureau bills, overrode Johnson's vetoes of Civil Rights Act of 1866, civil rights legislation, and the House Impeachment of Andrew Johnson, impeached him, although the Senate did not convict him. In 1868 and 1872, the Republican candidate Ulysses S. Grant won the presidency. In 1872, the Liberal Republican Party (United States), "Liberal Republicans" argued that the war goals had been achieved and that Reconstruction should end. They chose Horace Greeley 1872 presidential campaign, Horace Greeley to head a presidential ticket in 1872 but were decisively defeated. In 1874, Democrats, primarily Southern, took control of Congress and opposed further reconstruction. The Compromise of 1877 closed with a national consensus, except perhaps on the part of former slaves, that the Civil War had finally ended. With the withdrawal of federal troops, however, whites retook control of every Southern legislature, and the Jim Crow era of Disfranchisement after the Reconstruction era, disenfranchisement and legal segregation was ushered in.
The Civil War would have a huge impact on American politics in the years to come. Many veterans on both sides were subsequently elected to political office, including five U.S. Presidents: General Ulysses Grant, Rutherford B. Hayes, James Garfield, Benjamin Harrison, and William McKinley.
 The first efforts at Civil War battlefield preservation and memorialization came during the war itself with the establishment of National Cemeteries at Gettysburg, Mill Springs and Chattanooga. Soldiers began erecting markers on battlefields beginning with the
The first efforts at Civil War battlefield preservation and memorialization came during the war itself with the establishment of National Cemeteries at Gettysburg, Mill Springs and Chattanooga. Soldiers began erecting markers on battlefields beginning with the