Turan Melek Sultan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Turan ( ae, Tūiriiānəm, pal, Tūrān; fa, توران, Turân, , "The Land of Tur") is a
 In ancient Iranian mythology, Tūr or Turaj (''Tuzh'' in
In ancient Iranian mythology, Tūr or Turaj (''Tuzh'' in
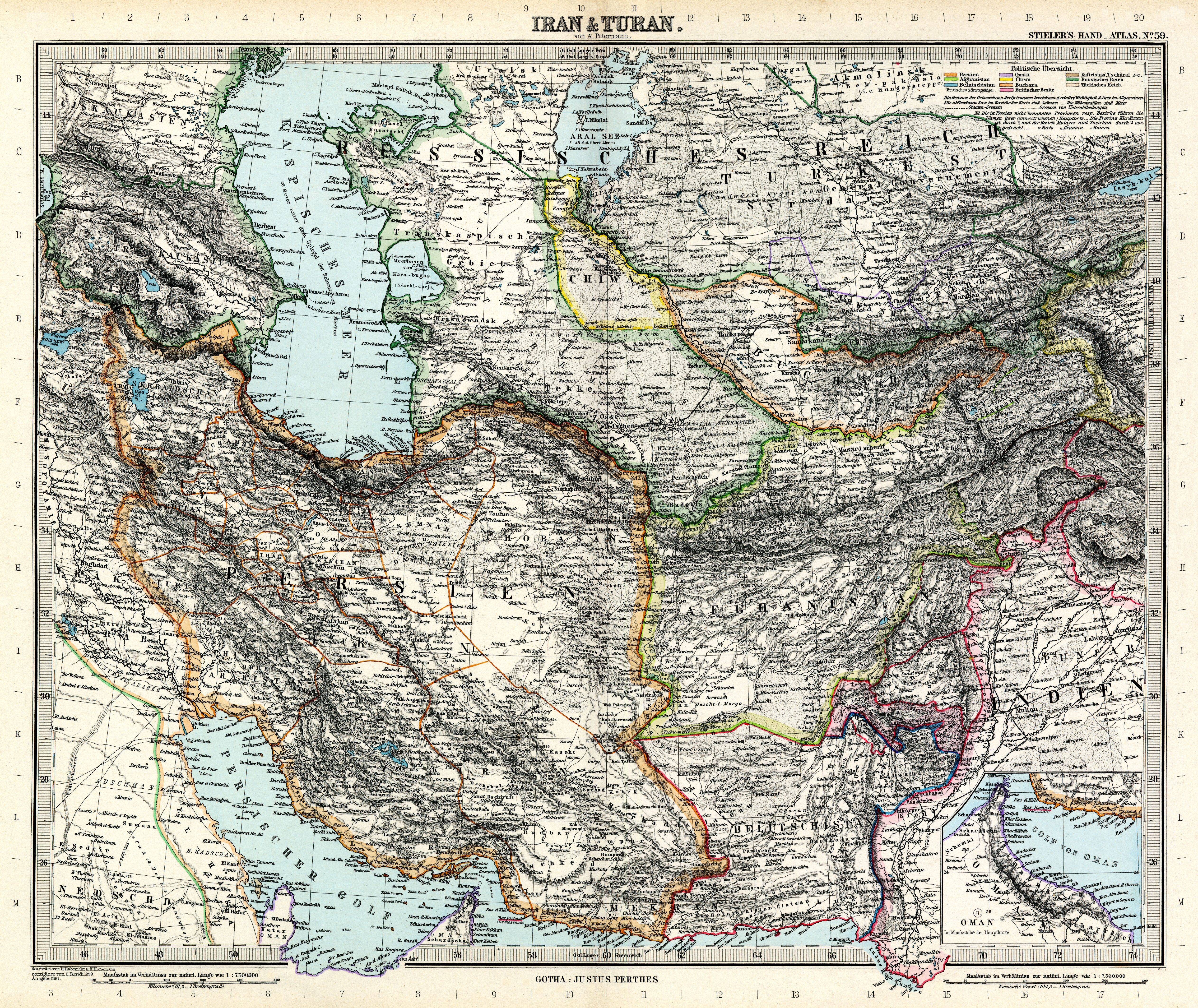 In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Western languages borrowed the word ''Turan'' as a general designation for modern
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Western languages borrowed the word ''Turan'' as a general designation for modern
 ''Turandot'' – or ''Turandokht'' – is a female name in Iran and it means ''"Turan's Daughter"'' in
''Turandot'' – or ''Turandokht'' – is a female name in Iran and it means ''"Turan's Daughter"'' in
Iranians and Turanians in the Avesta
{{Shahnameh Historical regions History of Central Asia Places in Shahnameh Locations in Persian mythology
historical region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing soc ...
in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. The term is of Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
origin and may refer to a particular prehistoric human settlement, a historic geographical region, or a culture. The original Turanians were an Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
tribe of the Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
n age.
Overview
 In ancient Iranian mythology, Tūr or Turaj (''Tuzh'' in
In ancient Iranian mythology, Tūr or Turaj (''Tuzh'' in Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle ...
) is the son of the emperor Fereydun
Fereydun ( ae, 𐬚𐬭𐬀𐬉𐬙𐬀𐬊𐬥𐬀, Θraētaona, pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭩𐭲𐭥𐭭, ; New Persian: , ''Fereydūn/Farīdūn'') is an Iranian mythical king and hero from the Pishdadian dynasty. He is known as an emblem of victory, just ...
. According to the account in the ''Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50 ...
'', the nomadic tribes who inhabited these lands were ruled by Tūr. In that sense, the Turanians could be members of two Iranian peoples both descending from Fereydun, but with different geographical domains and often at war with each other. Turan, therefore, comprised five areas: the Kopet Dag
The Köpet Dag, Kopet Dagh, or Koppeh Dagh ( tk, Köpetdag; fa, کپهداغ), also known as the Turkmen-Khorasan Mountain Range, is a mountain range on the border between Turkmenistan and Iran that extends about along the border southeast o ...
region, the Atrek
The Atrek ( fa, اترک, ku, Etrek, tk, Etrek derýasy), also known as the Attruck, Atrak, and Etrek, is a fast-moving river which begins in the mountains of north-eastern Iran (), and flows westward draining into the south-eastern corner of th ...
valley, parts of Bactria, Sogdia and Margiana
Margiana ( el, ''Margianḗ'', Old Persian: ''Marguš'', Middle Persian: ''Marv'') is a historical region centred on the oasis of Merv and was a minor satrapy within the Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, and a province within its successors, the Se ...
.
A later association of the original Turanians with Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging t ...
is based primarily on the subsequent Turkification
Turkification, Turkization, or Turkicization ( tr, Türkleştirme) describes a shift whereby populations or places received or adopted Turkic attributes such as culture, language, history, or ethnicity. However, often this term is more narrowly ...
of Central Asia, including the above areas. According to C. E. Bosworth, however, there was no cultural relationship between the ancient Turkic cultures and the Turanians of the Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50 ...
.
History
Ancient literature
Avesta
The oldest existing mention of Turan is in the Farvardin ''yasht
The Yashts are a collection of twenty-one hymns in the Younger Avestan language. Each of these hymns invokes a specific Zoroastrian divinity or concept. ''Yasht'' chapter and verse pointers are traditionally abbreviated as ''Yt.''
Overview
The wor ...
s'', which are in the Young Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
language and have been dated by linguists to about 2500 years ago. According to Gherardo Gnoli Gherardo Gnoli (6 December 1937 in Rome – 7 March 2012 in Cagli) was a historian of Italian religions and Iran expert.Carlo Cereti, “GNOLI, GHERARDO,” Encyclopædia Iranica, online edition, 2015, available at http://www.iranicaonline.org/artic ...
, the ''Avesta'' contains the names of various tribes who lived in proximity to each other: "the Airyas ryans Tuiryas uranians Sairimas armatians Sainus acaeand Dahis ahae
Yoo Byung-eun (Korean: 유병언; Hanja: 兪炳彥) was a South Korean businessman and inventor, who as a photographer was known under the art name Ahae.
Yoo became the focus of Park Geun-hye’s administration shortly after the Sinking of MV Sew ...
.G. Gnoli, ''Zoroaster's time and homeland'', Naples 1980 In the hymns of the ''Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
'', the adjective ''Tūrya'' is attached to various enemies of Zoroastrism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ...
like Fraŋrasyan (Shahnameh: Afrāsīāb). The word occurs only once in the '' Gathas'', but 20 times in the later parts of the ''Avesta''. The Tuiryas as they were called in Avesta play a more important role in the ''Avesta'' than the Sairimas, Sainus and Dahis. Zoroaster himself hailed from the Airya people but he also preached his message to other neighboring tribes.
According to Mary Boyce
Nora Elisabeth Mary Boyce (2 August 1920 – 4 April 2006) was a British scholar of Iranian languages, and an authority on Zoroastrianism. She was Professor of Iranian Studies at the School of Oriental and African Studies (SOAS) of the Un ...
, in the Farvardin Yasht, "In it (verses 143–144) are praised the fravashis of righteous men and women not only among the Aryas (as the "Avestan" people called themselves), but also among the Turiyas, Sairimas, Sainus and Dahis; and the personal names, like those of the people, all seem Iranian in character". Hostility between Tuirya and Airya is indicated also in the Farvardtn Yast (vv. 37-8), where the Fravashis of the Just are said to have provided support in battle against the Danus, who appear to be a clan of the Tura people. Thus in the ''Avesta'', some of the Tuiryas believed in the message of Zoroaster while others rejected the religion.
Similar to the ancient homeland of Zoroaster, the precise geography and location of Turan is unknown. In post-Avestan traditions they were thought to inhabit the region north of the Oxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
, the river separating them from the Iranians. Their presence accompanied by incessant wars with the Iranians, helped to define the latter as a distinct nation, proud of their land and ready to spill their blood in its defense.Ehsan Yarshater, "Iranian National History," in ''The Cambridge History of Iran'' 3(1)(1983), 408–409 The common names of Turanians in Avesta and ''Shahnameh
The ''Shahnameh'' or ''Shahnama'' ( fa, شاهنامه, Šāhnāme, lit=The Book of Kings, ) is a long epic poem written by the Persian poet Ferdowsi between c. 977 and 1010 CE and is the national epic of Greater Iran. Consisting of some 50 ...
'' include Frarasyan, Aghraethra, Biderafsh, Arjaspa Namkhwast. The names of Iranian tribes including those of the Turanians that appear in Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
have been studied by Manfred Mayrhofer
Manfred Mayrhofer (26 September 1926 – 31 October 2011) was an Austrian Indo-Europeanist who specialized in Indo-Iranian languages. Mayrhofer served as professor emeritus at the University of Vienna. He is noted for his etymological dictionar ...
in his comprehensive book on Avesta personal name etymologies.
Sassanian Empire
From the 5th century CE, the Sasanian Empire defined "Turan" in opposition to "Iran", as the land where lay its enemies to the northeast. The continuation of nomadic invasions on the north-eastern borders in historical times kept the memory of the Turanians alive. After the 6th century the Turks, who had been pushed westward by other tribes, became neighbours of Iran and were identified with the Turanians. The identification of the Turanians with the Turks was a late development, possibly made in the early 7th century; the Turks first came into contact with the Iranians only in the 6th century.Middle literature
Early Islamic era
According to Clifford E. Bosworth: The terms "Turk" and "Turanian" became used interchangeably during the Islamic era. ''The Shahnameh'', or the Book of Kings, the compilation of Iranian mythical heritage, uses the two terms equivalently. Other authors, including Tabari, Hakim Iranshah and many other texts follow like. A notable exception is the Abl-Hasan Ali ibn Masudi, an Arab historian who writes: "The birth of Afrasiyab was in the land of Turks and the error that historians and non-historians have made about him being a Turk is due to this reason". By the 10th century, the myth of Afrasiyab was adopted by the Qarakhanid dynasty. During the Safavid era, following the common geographical convention of the ''Shahnameh'', the term Turan was used to refer to the domain of the Uzbek empire in conflict with the Safavids. Some linguists derive the word from the Indo-Iranian root *''tura-'' "strong, quick, sword(Pashto)",Pashto
Pashto (,; , ) is an Eastern Iranian language in the Indo-European language family. It is known in historical Persian literature as Afghani ().
Spoken as a native language mostly by ethnic Pashtuns, it is one of the two official langua ...
''turan (thuran)'' "swordsman". Others link it to old Iranian *''tor'' "dark, black", related to the New Persian ''tār(ik)'', Pashto ''tor (thor)'', and possibly English ''dark''. In this case, it is a reference to the "dark civilization" of Central Asian nomads in contrast to the "illuminated" Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic ...
civilization of the settled Ārya.
Shahnameh
In the Persian epic ''Shahnameh'', the term ''Tūrān'' ("land of the Tūrya" like '' Ērān, Īrān'' = "land of the Ārya") refers to the inhabitants of the eastern-Iranian border and beyond theOxus
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
. According to the foundation myth given in the ''Shahnameh'', King Firēdūn (= Avestan Θraētaona) had three sons, Salm
Salm may refer to
People
* Constance de Salm (1767–1845), poet and miscellaneous writer; through her second marriage, she became Princess of Salm-Dyck
* Salm ibn Ziyad, an Umayyad governor of Khurasan and Sijistan
* House of Salm, a European ...
, Tūr and ''Iraj
Iraj ( fa, ایرج - ʾīraj; Pahlavi: ērič; from Avestan: 𐬀𐬌𐬭𐬌𐬌𐬀 airiia, literally "Aryan") is the seventh Shah of the Pishdadian dynasty, depicted in the ''Shahnameh''. Based on Iranian mythology, he is the youngest son of ...
'', among whom he divided the world: Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
was given to Salm, Turan to Tur and Iran to Īraj. The older brothers killed the younger, but he was avenged by his grandson, and the Iranians became the rulers of the world. However, the war continued for generations. In the ''Shahnameh'', the word Turan appears nearly 150 times and that of Iran nearly 750 times.
Some examples from the ''Shahnameh'':
Modern literature
Geography
 In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Western languages borrowed the word ''Turan'' as a general designation for modern
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, Western languages borrowed the word ''Turan'' as a general designation for modern Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
, although this expression has now fallen into disuse. Turan appears next to Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
on numerous maps of the 19th century to designate a region encompassing modern Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
and northern parts of Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
. This area roughly corresponds to what is called Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
today.
The phrase ''Turan Plain'' or ''Turan Depression
The Turan Depression, Turan Lowland or Turanian Basin is a low-lying desert basin region stretching from southern Turkmenistan through Uzbekistan to Kazakhstan.
Geography
The lowland region lies to the east of the Caspian Sea and southeast ...
'' became a geographical term referring to a part of Central Asia.
Linguistics
The term ''Turanian'', now obsolete, formerly occurred in the classifications used by European (especiallyGerman
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Hungarian, and Slovak) ethnologists
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology). ...
, linguists, and Romantics
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
to designate populations speaking non-Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
, non- Semitic, and non-Hamitic languages
Hamites is the name formerly used for some Northern and Horn of Africa peoples in the context of a now-outdated model of dividing humanity into different races which was developed originally by Europeans in support of colonialism and slavery. T ...
and specially speakers of Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are ...
, Dravidian, Uralic
The Uralic languages (; sometimes called Uralian languages ) form a language family of 38 languages spoken by approximately 25million people, predominantly in Northern Eurasia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian (w ...
, Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
and other languages.
Max Müller
Friedrich Max Müller (; 6 December 1823 – 28 October 1900) was a German-born philologist and Orientalist, who lived and studied in Britain for most of his life. He was one of the founders of the western academic disciplines of Indian ...
(1823–1900) identified different sub-branches within the Turanian language family:
* the Middle Altaic
Altaic (; also called Transeurasian) is a controversial proposed language family that would include the Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic language families and possibly also the Japonic and Koreanic languages. Speakers of these languages are ...
division branch, comprising Tungusic, Mongolic, Turkic.
* The Northern Ural
Ural may refer to:
*Ural (region), in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural Mountains, in Russia and Kazakhstan
*Ural (river), in Russia and Kazakhstan
* Ual (tool), a mortar tool used by the Bodo people of India
*Ural Federal District, in Russia
*Ural econ ...
Samoyedic, Ugriche and Finnic.
* the Southern branch consisted of Dravidian languages such as Tamil, Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam, and other Dravidian languages.
* the languages of the Caucasus
The Caucasian languages comprise a large and extremely varied array of languages spoken by more than ten million people in and around the Caucasus Mountains, which lie between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea.
Linguistic comparison allows t ...
which Müller classified as the ''scattered languages of the Turanian family''.
Müller also began to muse whether Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
belonged to the Northern branch or Southern branch.
The main relationships between Dravidian, Uralic, and Altaic languages were considered typological. According to Crystal & Robins, "Language families, as conceived in the historical study of languages, should not be confused with the quite separate classifications of languages by reference to their sharing certain predominant features of grammatical structure."
linguists classify languages according to the method of comparative linguistics rather than using their typological features. According to ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', Max's Müller's "efforts were most successful in the case of the Semites, whose affinities are easy to demonstrate, and probably least successful in the case of the Turanian peoples, whose early origins are hypothetical". the scholarly community no longer uses the word ''Turanian'' to denote a classification of language families. The relationship between Uralic and Altaic, whose speakers were also designated as Turanian people in 19th-century European literature, remains uncertain.
Ideology
In European discourse, the words ''Turan'' and ''Turanian'' can designate a certain mentality, i.e. thenomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic in contrast to the urbanized
''Urbanized'' is a documentary film directed by Gary Hustwit and released on 26 October 2011. It is considered the third of a three-part series on design known as the Design Trilogy; the first being ''Helvetica'', about the typeface, and the seco ...
agricultural civilizations. This usage probably matches the Zoroastrian concept of the ''Tūrya'', which is not primarily a linguistic or ethnic designation, but rather a name of the infidels that opposed the civilization based on the preaching of Zoroaster
Zoroaster,; fa, زرتشت, Zartosht, label= Modern Persian; ku, زەردەشت, Zerdeşt also known as Zarathustra,, . Also known as Zarathushtra Spitama, or Ashu Zarathushtra is regarded as the spiritual founder of Zoroastrianism. He is ...
.
Combined with physical anthropology, the concept of the Turanian mentality has a clear potential for cultural polemic. Thus in 1838 the scholar J.W. Jackson described the ''Turanid'' or ''Turanian'' race in the following words:"The Iran and Turan", ''Anthropological Review'' 6:22 (1868), p. 286
Polish philosopher Feliks Koneczny
Feliks Karol Koneczny (; 1 November 1862 – 10 February 1949) was a Polish historian, theatrical critic, librarian, journalist and social philosopher. He founded the original system of the comparative science of civilizations.
Biography
Ko ...
claimed the existence of a distinctive Turanian civilization, encompassing both Turkic and some Slavs, such as Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
. This alleged civilization's hallmark would be militarism, anti-intellectualism
Anti-intellectualism is hostility to and mistrust of intellect, intellectuals, and intellectualism, commonly expressed as deprecation of education and philosophy and the dismissal of art, literature, and science as impractical, politically ...
and an absolute obedience to the ruler. Koneczny saw this civilization as inherently inferior to Latin (Western European) civilization.
Politics
In the declining days of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, some Turkish nationalists adopted the word ''Turanian'' to express a pan-Turkic ideology, also called Turanism
Turanism, also known as pan-Turanianism, pan-Turanism, or simply Turan, is a pseudoscientific pan-nationalist cultural and political movement proclaiming the need for close cooperation or political unification between people who are claimed by ...
. Turanism forms an important aspect of the ideology of the Turkish Nationalist Movement Party
The Nationalist Movement Party (alternatively translated as Nationalist Action Party; tr, Milliyetçi Hareket Partisi, MHP) is a Turkish far-right and ultranationalist political party. The group is often described as neo-fascist, and has bee ...
(''MHP''), whose members are also known as Grey Wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
.
In recent times, the word ''Turanian'' has sometimes expressed a pan-Altaic nationalism (theoretically including Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
and Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
in addition to Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
), though no political organization seems to have adopted such an ambitious platform.
Names
 ''Turandot'' – or ''Turandokht'' – is a female name in Iran and it means ''"Turan's Daughter"'' in
''Turandot'' – or ''Turandokht'' – is a female name in Iran and it means ''"Turan's Daughter"'' in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
. (It is best known in the West through Puccini
Giacomo Puccini ( Lucca, 22 December 1858Bruxelles, 29 November 1924) was an Italian composer known primarily for his operas. Regarded as the greatest and most successful proponent of Italian opera after Verdi, he was descended from a long ...
's famous opera ''Turandot
''Turandot'' (; see below) is an opera in three acts by Giacomo Puccini, posthumously completed by Franco Alfano in 1926, and set to a libretto in Italian by Giuseppe Adami and Renato Simoni. ''Turandot'' best-known aria is " Nessun dorma", ...
'' (1921–24).)
Turan
Turan ( ae, Tūiriiānəm, pal, Tūrān; fa, توران, Turân, , "The Land of Tur") is a historical region in Central Asia. The term is of Iranian origin and may refer to a particular prehistoric human settlement, a historic geographical re ...
is also a common name in the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, and as family surnames in some countries including Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and an ...
, Iran, Bosnia and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
.
The Ayyubid ruler Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
had an older brother with the name Turan-Shah
Shams ad-Din Turanshah ibn Ayyub al-Malik al-Mu'azzam Shams ad-Dawla Fakhr ad-Din known simply as Turanshah ( ar, توران شاه بن أيوب) (died 27 June 1180) was the Ayyubid emir (prince) of Yemen (1174–1176), Damascus (1176–1179), ...
.
Turaj, whom ancient Iranian myths depict as the ancestor of the Turanians, is also a popular name and means ''Son of Darkness''. The name Turan according to Iranian myths derives from the homeland of Turaj. The Pahlavi pronunciation of Turaj is Tuzh, according to the Dehkhoda dictionary. Similarly, Iraj
Iraj ( fa, ایرج - ʾīraj; Pahlavi: ērič; from Avestan: 𐬀𐬌𐬭𐬌𐬌𐬀 airiia, literally "Aryan") is the seventh Shah of the Pishdadian dynasty, depicted in the ''Shahnameh''. Based on Iranian mythology, he is the youngest son of ...
, which is also a popular name, is the brother of Turaj in the ''Shahnameh''. An altered version of Turaj is ''Zaraj'', which means ''son of gold''.
See also
*Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
Hi ...
* Ariana
Ariana was a general geographical term used by some Greek and Roman authors of the ancient period for a district of wide extent between Central Asia and the Indus River, comprising the eastern provinces of the Achaemenid Empire that covered the ...
* Bactria
* Dahistan
* Khorasan
* Khwarazm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ea ...
* Margiana
Margiana ( el, ''Margianḗ'', Old Persian: ''Marguš'', Middle Persian: ''Marv'') is a historical region centred on the oasis of Merv and was a minor satrapy within the Achaemenid satrapy of Bactria, and a province within its successors, the Se ...
* Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
* Sogdia
* Tokharistan
Tokharistan (formed from "Tokhara" and the suffix ''-stan'' meaning "place of" in Persian) is an ancient Early Middle Ages name given to the area which was known as Bactria in Ancient Greek sources.
In the 7th and 8th century CE, Tokharistan c ...
* Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
* Turkestan
Turkestan, also spelled Turkistan ( fa, ترکستان, Torkestân, lit=Land of the Turks), is a historical region in Central Asia corresponding to the regions of Transoxiana and Xinjiang.
Overview
Known as Turan to the Persians, western Turk ...
References
Further reading
* * ''Archäologie in Iran und Turan'', Verlag Philipp von Zabern GmbH. Publisher – Verlag Marie Leidorf GmbH (Volume 1–3)External links
Iranians and Turanians in the Avesta
{{Shahnameh Historical regions History of Central Asia Places in Shahnameh Locations in Persian mythology