Truro on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 *
*
 * Nick Nieland (born 1972), javelin gold medallist at the 2006 Commonwealth Games
* Matthew Etherington (born 1981), former professional footballer with 426 club caps, he played for West Ham and Stoke City.
* David Paynter (born 1981), former first-class cricketer
* Tom Voyce (born 1981) former rugby union footballer with London Wasps and England
* Annabel Vernon (born 1982), retired rower, team silver medallist at the 2008 Summer Olympics
* Chris Harris (born 1982), international speedway rider
* Gemma Prescott (born 1983), Paralympic track and field athlete
* Darren Dawidiuk (born 1987), rugby union footballer
* Craig Alcock (born 1987), professional footballer with 300 club caps
* Matthew Whorwood (born 1989), Paralympic swimmer, bronze medallist in two Paralympic Games
*
* Nick Nieland (born 1972), javelin gold medallist at the 2006 Commonwealth Games
* Matthew Etherington (born 1981), former professional footballer with 426 club caps, he played for West Ham and Stoke City.
* David Paynter (born 1981), former first-class cricketer
* Tom Voyce (born 1981) former rugby union footballer with London Wasps and England
* Annabel Vernon (born 1982), retired rower, team silver medallist at the 2008 Summer Olympics
* Chris Harris (born 1982), international speedway rider
* Gemma Prescott (born 1983), Paralympic track and field athlete
* Darren Dawidiuk (born 1987), rugby union footballer
* Craig Alcock (born 1987), professional footballer with 300 club caps
* Matthew Whorwood (born 1989), Paralympic swimmer, bronze medallist in two Paralympic Games
*
Truro City Council websiteCornwall Record Office Online Catalogue for TruroEnjoy Truro – official guide to the city, including latest news and events
(provided b
Totally Truro
the local not-for-profit Business Improvement District) {{Authority control Cornish capitals Cities in South West England Towns in Cornwall Civil parishes in Cornwall County towns in England Populated places established in the 12th century Ports and harbours of Cornwall Cornish Killas
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a
 Truro prospered in the 18th and 19th centuries through improved mining methods and higher prices for tin, and its consequent attraction to wealthy mine-owners. Elegant Georgian and Victorian
Truro prospered in the 18th and 19th centuries through improved mining methods and higher prices for tin, and its consequent attraction to wealthy mine-owners. Elegant Georgian and Victorian  Through those prosperous times Truro remained a social centre. Among the many notables were Richard Lander, the first European explorer to reach the mouth of the
Through those prosperous times Truro remained a social centre. Among the many notables were Richard Lander, the first European explorer to reach the mouth of the
 Truro lies in the centre of western Cornwall, about from the south coast, at the confluence of the rivers Kenwyn and Allen, which combine as the Truro River – one of a series of waterways and drowned valleys leading into the
Truro lies in the centre of western Cornwall, about from the south coast, at the confluence of the rivers Kenwyn and Allen, which combine as the Truro River – one of a series of waterways and drowned valleys leading into the
 The Truro urban area, including parts of surrounding parishes, had a 2001 census population of 20,920. By 2011 the population, including Threemilestone, was 23,040. Its status as the county's prime destination for retail and leisure and administration is unusual in that it is only its fourth most populous settlement. Indeed population growth at 10.5 per cent between 1971 and 1998 was slow compared with other Cornish towns and Cornwall.
Major employers include the Royal Cornwall Hospital,
The Truro urban area, including parts of surrounding parishes, had a 2001 census population of 20,920. By 2011 the population, including Threemilestone, was 23,040. Its status as the county's prime destination for retail and leisure and administration is unusual in that it is only its fourth most populous settlement. Indeed population growth at 10.5 per cent between 1971 and 1998 was slow compared with other Cornish towns and Cornwall.
Major employers include the Royal Cornwall Hospital,
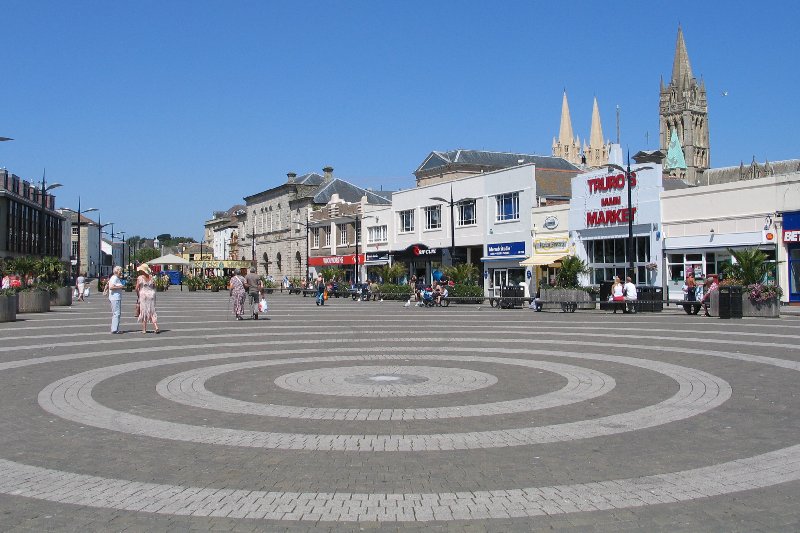

 Lemon Quay is the year-round centre of most festivities in Truro.
In April, Truro prepares to partake in the
Lemon Quay is the year-round centre of most festivities in Truro.
In April, Truro prepares to partake in the  Truro's Christmas includes a Winter Festival with a "City of Lights"
Truro's Christmas includes a Winter Festival with a "City of Lights"
 Truro is the centre of Cornwall's local media. The county weeklies, the '' Cornish Guardian'' and ''
Truro is the centre of Cornwall's local media. The county weeklies, the '' Cornish Guardian'' and ''

 Truro City Council forms its basic level of government, as one of 213 parish bodies in the county. Centred upstairs at the Municipal Buildings in Boscawen Street, it covers Truro's public library, parks and gardens,
Truro City Council forms its basic level of government, as one of 213 parish bodies in the county. Centred upstairs at the Municipal Buildings in Boscawen Street, it covers Truro's public library, parks and gardens,
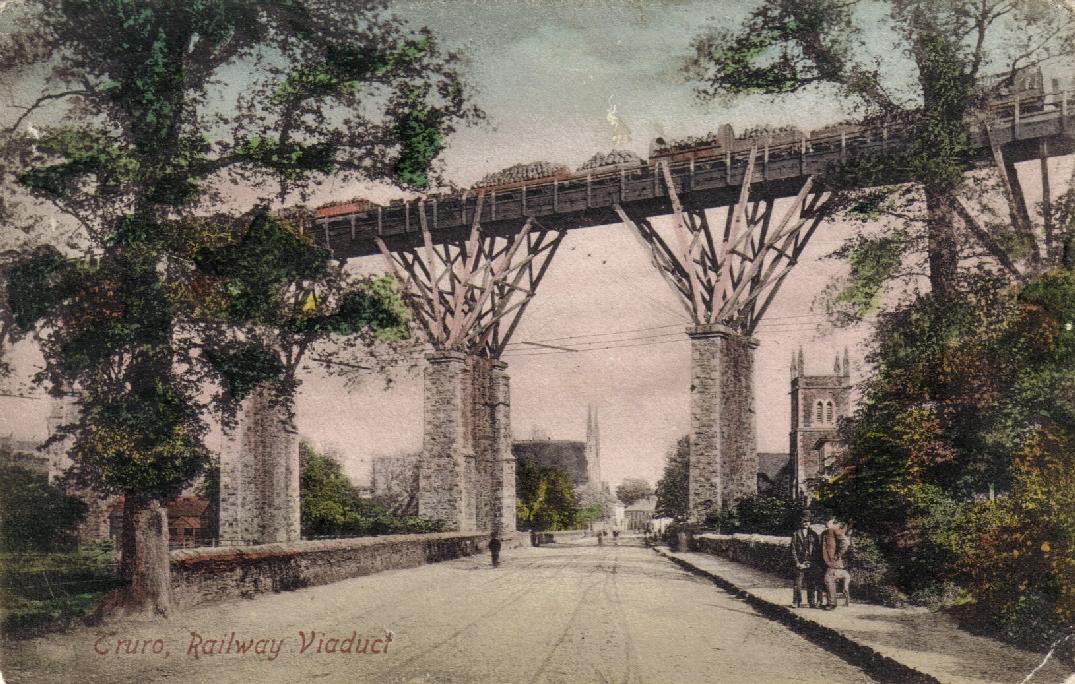 Truro railway station, about from the city centre, is on the
Truro railway station, about from the city centre, is on the  Truro's first railway station, at Highertown, was opened in 1852 by the West Cornwall Railway for trains to Redruth and Penzance, and was known as Truro Road Station. It was extended to the Truro River at Newham in 1855, but closed, so that Newham served as the terminus. When the
Truro's first railway station, at Highertown, was opened in 1852 by the West Cornwall Railway for trains to Redruth and Penzance, and was known as Truro Road Station. It was extended to the Truro River at Newham in 1855, but closed, so that Newham served as the terminus. When the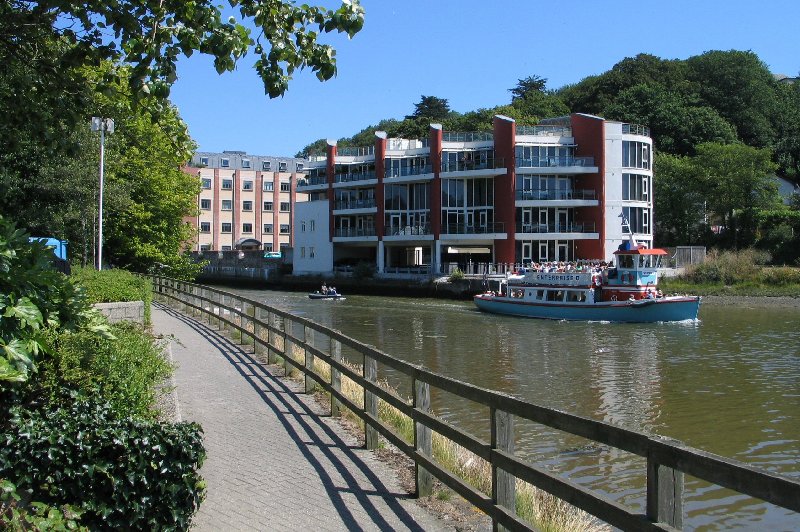 
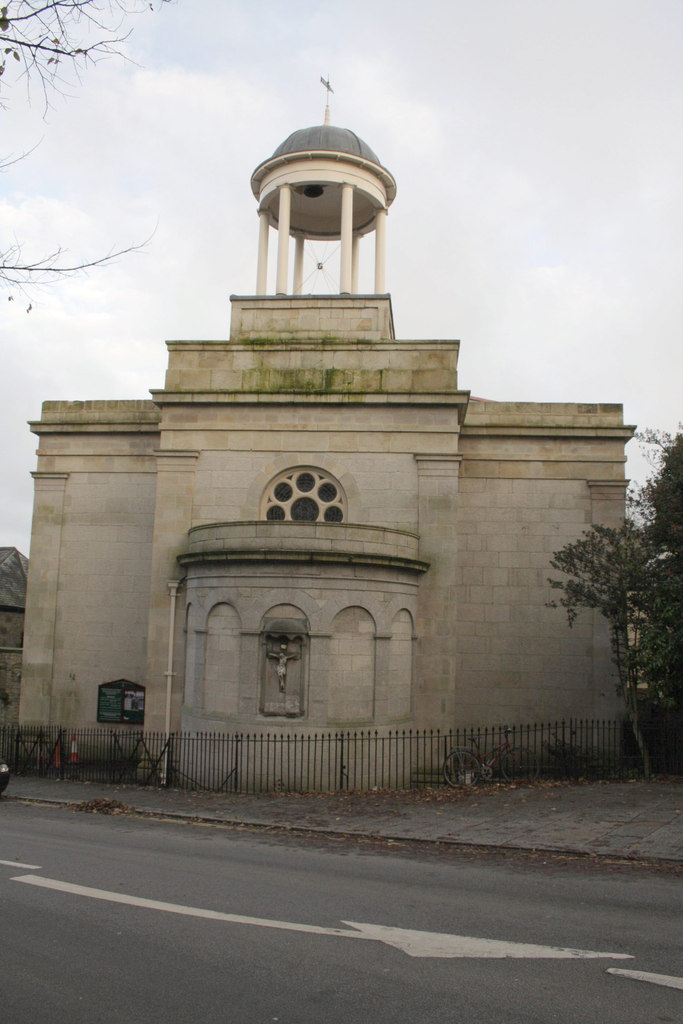
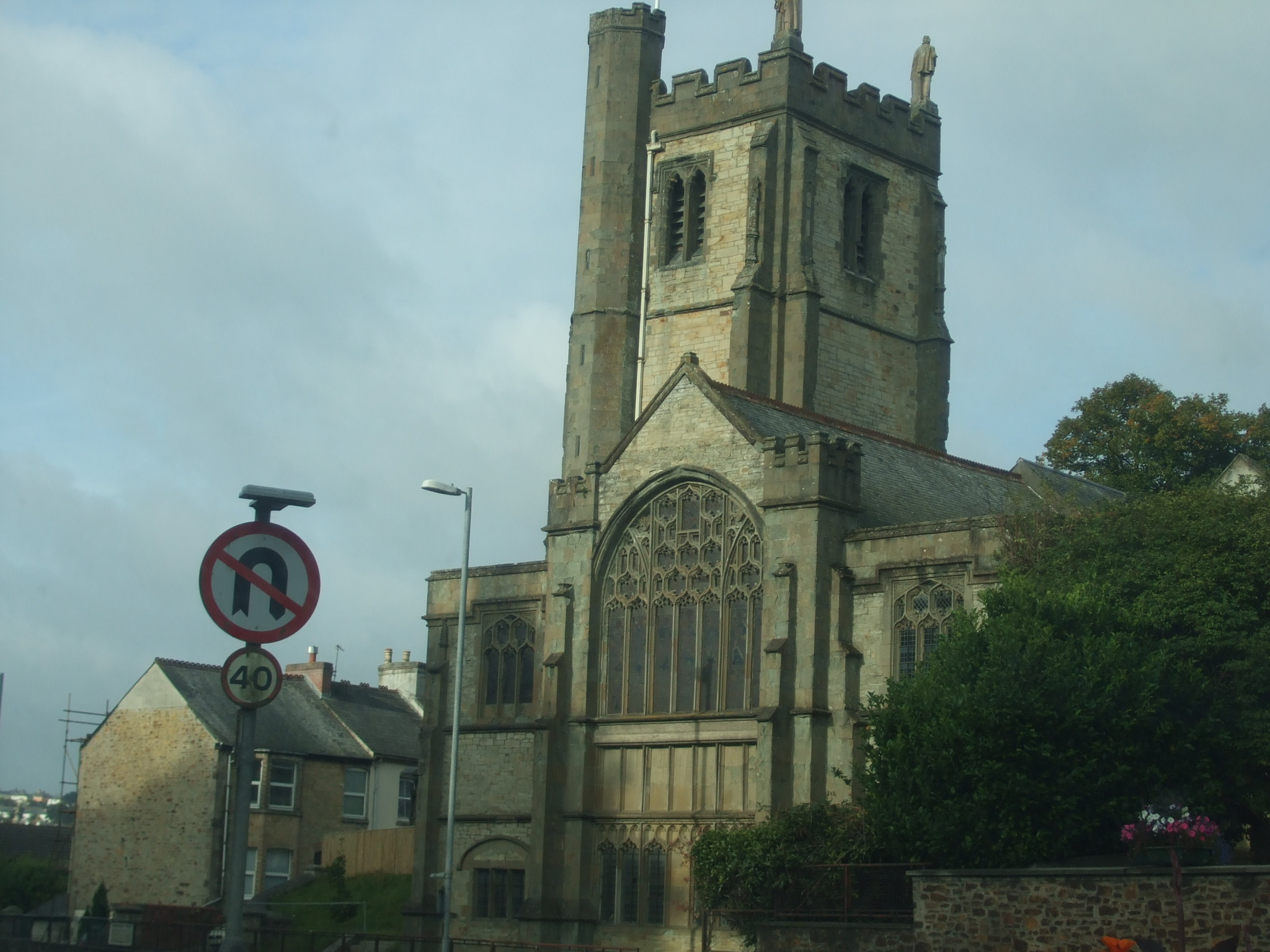


 The old parish church of Truro was St Mary's, which was incorporated into the cathedral in the later 19th century. The building dates from 1518, with a later tower and spire dating from 1769.
Parts of the town were in the parishes of Kenwyn and St Clement ( Moresk) until the mid 19th century, when other parishes were created. The lofty St George's church in Truro, designed by Rev. William Haslam, vicar of
The old parish church of Truro was St Mary's, which was incorporated into the cathedral in the later 19th century. The building dates from 1518, with a later tower and spire dating from 1769.
Parts of the town were in the parishes of Kenwyn and St Clement ( Moresk) until the mid 19th century, when other parishes were created. The lofty St George's church in Truro, designed by Rev. William Haslam, vicar of
 Truro has many proposed urban development schemes, most of which are intended to counter the main problems, notably traffic congestion and lack of housing.
Major proposals include construction of a distributor road to carry traffic away from the busy Threemilestone-Treliske-Highertown corridor, reconnecting at either Green Lane or Morlaix Avenue. This will also serve the new housing planned for that area.
Changes proposed for the city centre include pedestrianisation of main shopping streets and
Truro has many proposed urban development schemes, most of which are intended to counter the main problems, notably traffic congestion and lack of housing.
Major proposals include construction of a distributor road to carry traffic away from the busy Threemilestone-Treliske-Highertown corridor, reconnecting at either Green Lane or Morlaix Avenue. This will also serve the new housing planned for that area.
Changes proposed for the city centre include pedestrianisation of main shopping streets and
correspondent
* NneNne Iwuji-Eme (born c. 1978), British diplomat, UK High Commissioner to Mozambique
* Staff Sergeant Olaf Schmid, (1979–2009), a British Army bomb-disposal expert
cathedral city
Cathedral city is a city status in the United Kingdom.
Cathedral city may also refer to:
* Cathedral City, California, a city in Southern California, United States
* Cathedral City Cheddar, a brand of Cheddar cheese
* Cathedral City High Scho ...
and civil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of administrative parish used for local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below districts and counties, or their combined form, the unitary authorit ...
in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro can be called Truronians. It grew as a trade centre through its port and as a stannary town
A stannary was an administrative division established under stannary law in the English counties of Cornwall and Devon to manage the collection of tin coinage, which was the duty payable on the metal tin smelted from the ore cassiterite mined ...
for tin mining. It became mainland Britain's southernmost city in 1876, with the founding of the Diocese of Truro. Sights include the Royal Cornwall Museum
The Royal Cornwall Museum in Truro holds an extensive mineral collection rooted in Cornwall's mining and engineering heritage (including much of the mineral collection of Philip Rashleigh (1729-1811), Philip Rashleigh). The county's artistic her ...
, Truro Cathedral (completed 1910), the Hall for Cornwall
Hall for Cornwall, known as Truro City Hall until 1997, is an events venue in Boscawen Street in Truro, Cornwall, England. The building, which was previously the headquarters of Truro City Council, is a Grade II* listed building.
History
The f ...
and Cornwall's Courts of Justice.
Toponymy
Truro's name may derive from the Cornish ''tri-veru'' meaning "three rivers", but authorities such as the ''Oxford Dictionary of English Place Names'' have doubts about the "tru" meaning "three". An expert on Cornish place-names,Oliver Padel
Oliver James Padel (born 31 October 1948 in St Pancras, London, England) is an English medievalist and toponymist specializing in Welsh and Cornish studies. He is currently Honorary Research Fellow in the Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse, an ...
, in ''A Popular Dictionary of Cornish Place-names'', called the "three rivers" meaning "possible". Alternatively the name may come from '' tre-uro'' or similar, i. e. settlement on the river ''Uro''.
History
A castle was built in the 12th century byRichard de Luci
Richard de Luci (or Lucy; 1089 – 14 July 1179) was first noted as High Sheriff of Essex, after which he was made Chief Justiciar of England.
Biography
His mother was Aveline, the niece and heiress of William Goth. In the charter for Sées Ca ...
, Chief Justice of England in the reign of Henry II, who for court services was granted land in Cornwall, including the area round the confluence of the two rivers. The town grew below the castle and gained borough status from further economic activity. The castle has long disappeared.
Richard de Lucy fought in Cornwall under Count Alan of Brittany after leaving Falaise late in 1138. The small adulterine castle
Adulterine castles were fortifications built in England during the 12th century without royal approval, particularly during the civil war of the Anarchy between 1139 and 1154.
Details
During the civil war of the Anarchy, fought between the facti ...
at Truro, Cornwall, originally the parish of Kenwyn, later known as "Castellum de Guelon", was probably built by him in 1139–1140. He styled himself "Richard de Lucy, de Trivereu". The castle passed to Reginald FitzRoy, an illegitimate son of Henry I, when he was invested by King Stephen as the first Earl of Cornwall. Reginald married Mabel FitzRichard, daughter of William FitzRichard, a major landholder in Cornwall. The -diameter castle was in ruins by 1270 and the motte was levelled in 1840. Today Truro Crown Court
Truro Crown Court is a judicial complex in Truro, Cornwall, England. It is a Grade II* listed building.
History
The courthouse was commissioned to replace the old Shire Hall in Bodmin. The site selected had previously been occupied by a former ...
stands on the site. In a charter of about 1170, Reginald FitzRoy confirmed to Truro's burgesses the privileges granted by Richard de Lucy. Richard held ten knights' fees in Cornwall before 1135. At his death the county still accounted for a third of his considerable total holding.
By the early 14th century Truro was a major port, due to an inland location away from invaders, to prosperity from the fishing industry, and to a role as a stannary town
A stannary was an administrative division established under stannary law in the English counties of Cornwall and Devon to manage the collection of tin coinage, which was the duty payable on the metal tin smelted from the ore cassiterite mined ...
for assaying and stamping tin and copper from Cornish mines. The Black Death brought a trade recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various ...
and an exodus that left the town in a very neglected state. Trade and prosperity gradually returned in the Tudor period. Local government came in 1589 with a new charter of Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
giving it an elected mayor and control over the port of Falmouth.
During the Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
in the 17th century, Truro raised a sizeable force to fight for the king and a royalist mint was set up. Defeat by Parliamentary troops came after the Battle of Naseby
The Battle of Naseby took place on 14 June 1645 during the First English Civil War, near the village of Naseby in Northamptonshire. The Parliamentarian New Model Army, commanded by Sir Thomas Fairfax and Oliver Cromwell, destroyed the main ...
in 1646, when the victorious General Fairfax led his army south-west to relieve Taunton and capture the Royalist-held West Country. The Royalist forces surrendered at Truro while leading Royalist commanders, including Lord Hopton, the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the rulers ...
, Sir Edward Hyde, and Lord Capell, fled to Jersey from Falmouth.
Later in the century, Falmouth gained its own charter, giving rights to its harbour and starting a long rivalry with Truro. The dispute was settled in 1709 with control of the River Fal
The River Fal ( kw, Dowr Fala) flows through Cornwall, England, rising at Pentevale on Goss Moor (between St. Columb and Roche) and reaching the English Channel at Falmouth. On or near the banks of the Fal are the castles of Pendennis and ...
divided between them. The arms of Truro city are "Gules the base wavy of six Argent and Azure, thereon an ancient ship of three masts under sail, on each topmast a banner of St George, on the waves in base two fishes of the second."
 Truro prospered in the 18th and 19th centuries through improved mining methods and higher prices for tin, and its consequent attraction to wealthy mine-owners. Elegant Georgian and Victorian
Truro prospered in the 18th and 19th centuries through improved mining methods and higher prices for tin, and its consequent attraction to wealthy mine-owners. Elegant Georgian and Victorian townhouses
A townhouse, townhome, town house, or town home, is a type of terraced housing. A modern townhouse is often one with a small footprint on multiple floors. In a different British usage, the term originally referred to any type of city residence ...
of the period can be seen today in Lemon Street, named after the mining magnate and local Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
Sir William Lemon. Truro became the centre for county society, even dubbed "the London of Cornwall".
 Through those prosperous times Truro remained a social centre. Among the many notables were Richard Lander, the first European explorer to reach the mouth of the
Through those prosperous times Truro remained a social centre. Among the many notables were Richard Lander, the first European explorer to reach the mouth of the River Niger
The Niger River ( ; ) is the main river of West Africa, extending about . Its drainage basin is in area. Its source is in the Guinea Highlands in south-eastern Guinea near the Sierra Leone border. It runs in a crescent shape through Mali, ...
in Africa and was awarded the first gold medal of the Royal Geographical Society, and Henry Martyn
Henry Martyn (18 February 1781 – 16 October 1812) was an Anglican priest and missionary to the peoples of India and Persia. Born in Truro, Cornwall, he was educated at Truro Grammar School and St John's College, Cambridge. A chance encount ...
, who read mathematics at Cambridge, was ordained and became a missionary, translating the New Testament into Urdu and Persian. Others include Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
, educated in Truro and the inventor of the miner's safety lamp, and Samuel Foote, an actor and playwright from Boscawen Street.
Truro's importance increased later in the 19th century with an iron-smelting works, potteries, and tanneries. From the 1860s, the Great Western Railway provided a direct link to London Paddington. The Bishopric of Truro Act 1876 gave the town a bishop and later a cathedral. In 1877 it gained city status. The New Bridge Street drill hall was completed in the late 19th century.
Geography
 Truro lies in the centre of western Cornwall, about from the south coast, at the confluence of the rivers Kenwyn and Allen, which combine as the Truro River – one of a series of waterways and drowned valleys leading into the
Truro lies in the centre of western Cornwall, about from the south coast, at the confluence of the rivers Kenwyn and Allen, which combine as the Truro River – one of a series of waterways and drowned valleys leading into the River Fal
The River Fal ( kw, Dowr Fala) flows through Cornwall, England, rising at Pentevale on Goss Moor (between St. Columb and Roche) and reaching the English Channel at Falmouth. On or near the banks of the Fal are the castles of Pendennis and ...
and then the large natural harbour of Carrick Roads
Carrick Roads ( kw, Dowr Carrek, meaning "rock anchorage") is the estuary of the River Fal on the south coast of Cornwall in England. It joins the English Channel at its southern end near Falmouth.
Geography
It is a large flooded valley, or ...
. The valleys form a steep bowl surrounding the city on the north, east and west, open to the Truro River in the south. This shape, along with high precipitation that swells the rivers and a spring tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ca ...
in the River Fal, were major factors in the 1988 floods that seriously damaged the city centre. Since then, flood defences have been constructed, including an emergency dam at New Mill on the River Kenwyn and a tidal barrier on the Truro River.
The city is amidst several protected natural areas such as the historic parklands at Pencalenick and areas of ornamental landscape such as Trelissick Garden and Tregothnan
Tregothnan is a country house and estate near the village of St Michael Penkivel, southeast of Truro, Cornwall, England, which has for many centuries been a possession of the Boscawens.
Geography Location
Tregothnan is located on a hill overl ...
down the Truro River. An area south-east of the city, including Calenick Creek, has been included in the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
The Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty covers in Cornwall, England, UK; that is, about 27% of the total area of the county. It comprises 12 separate areas, designated under the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949 for ...
. Other protected zones include an Area of Great Landscape Value comprising farmland and wooded valleys to the north east, and Daubuz Moors, a local nature reserve by the River Allen, close to the city centre.
Truro has mainly grown and developed round the historic city centre in a nuclear fashion along the slopes of the bowl valley, except for fast linear development along the A390 to the west, towards Threemilestone. As Truro grew, it encompassed other settlements as suburbs or districts, including Kenwyn and Moresk to the north, Trelander to the east, Newham to the south, and Highertown, Treliske and Gloweth to the west.
Climate
The Truro area, like the rest of Cornwall, has an oceanic climate. This means fewer extremes in temperature than elsewhere in England, marked by high rainfall, cool summers and mild winters with infrequent frosts.Demography and economy
 The Truro urban area, including parts of surrounding parishes, had a 2001 census population of 20,920. By 2011 the population, including Threemilestone, was 23,040. Its status as the county's prime destination for retail and leisure and administration is unusual in that it is only its fourth most populous settlement. Indeed population growth at 10.5 per cent between 1971 and 1998 was slow compared with other Cornish towns and Cornwall.
Major employers include the Royal Cornwall Hospital,
The Truro urban area, including parts of surrounding parishes, had a 2001 census population of 20,920. By 2011 the population, including Threemilestone, was 23,040. Its status as the county's prime destination for retail and leisure and administration is unusual in that it is only its fourth most populous settlement. Indeed population growth at 10.5 per cent between 1971 and 1998 was slow compared with other Cornish towns and Cornwall.
Major employers include the Royal Cornwall Hospital, Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
and Truro College. There are about 22,000 jobs available in Truro, but only 9,500 economically active people living there, which make commuting a major factor in its traffic congestion. Average earnings are higher than elsewhere in Cornwall.
Housing prices in Truro in the 2000s were 8 or more per cent higher than in the rest of Cornwall. Truro was named in 2006 as the top small city in the United Kingdom for rising house prices, at 262 per cent since 1996.
Culture


Attractions
Truro's dominant feature is theGothic-revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
Truro Cathedral, designed by architect John Loughborough Pearson, rising above the city at its highest spire. It was built in 1880–1910 on the site of St Mary's Church, consecrated over 600 years earlier. Georgian architecture is well represented, with terraces and townhouses along Walsingham Place and Lemon Street often said to be "the finest examples of Georgian architecture west of the city of Bath".
The main attraction to the region is a wide variety of shopping facilities. Truro has various chain stores
A chain store or retail chain is a retail outlet in which several locations share a brand, central management and standardized business practices. They have come to dominate the retail and dining markets and many service categories, in many pa ...
, speciality shops and markets that reflect its history as a market town
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
. The indoor Pannier Market is open all year with many stalls and small businesses. The city is also popular for catering and night life, with bars, clubs and restaurants. It houses the Hall for Cornwall
Hall for Cornwall, known as Truro City Hall until 1997, is an events venue in Boscawen Street in Truro, Cornwall, England. The building, which was previously the headquarters of Truro City Council, is a Grade II* listed building.
History
The f ...
, a performing arts and entertainment venue.
The Royal Cornwall Museum is the oldest and premier museum of Cornish history and culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
. Its collections cover fields such as archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsca ...
, art and geology. Among the exhibits is the so-called Arthur's inscribed stone. Its parks and open spaces include Victoria Gardens, Boscawen Park and Daubuz Moors
Daubuz Moors is a nature reserve near the centre of Truro, in Cornwall, England.
The land was given to the citizens of Truro in 1977 by the Rev. C. Enys of the Enys Estate to celebrate the Queen's Silver Jubilee and the centenary of the city of ...
.
Events
 Lemon Quay is the year-round centre of most festivities in Truro.
In April, Truro prepares to partake in the
Lemon Quay is the year-round centre of most festivities in Truro.
In April, Truro prepares to partake in the Britain in Bloom
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
competition, with floral displays and hanging baskets dotted around the city throughout the summer. A "continental market" comes to Truro in the holiday-making season, featuring food and craft stalls from France, Spain, Italy, Germany, Belgium, the Netherlands, Greece and elsewhere.
Cornwall Pride, a Pride event to mark diversity and the LGBT community, takes place on the last Saturday of August. The Truro City Carnival, held every September over a weekend, includes various arts and music performances, children's activities, a fireworks
Fireworks are a class of low explosive pyrotechnic devices used for aesthetic and entertainment purposes. They are most commonly used in fireworks displays (also called a fireworks show or pyrotechnics), combining a large number of devices ...
display, food and drinks fairs, a circus
A circus is a company of performers who put on diverse entertainment shows that may include clowns, acrobats, trained animals, trapeze acts, musicians, dancers, hoopers, tightrope walkers, jugglers, magicians, ventriloquists, and unicyclis ...
, and a parade. A half-marathon organised by Truro Running Club also occurs in September, running from the city centre into the country towards Kea, returning to finish at Lemon Quay.
paper lantern
A paper lantern is a lantern made of thin, brightly colored paper. Paper lanterns come in various shapes and sizes, as well as various methods of construction. In their simplest form, they are simply a paper bag with a candle placed inside, a ...
parade. Local schools, colleges, and community and youth groups join in.
Sports
Truro temporarily held theCornish Pirates
The Cornish Pirates ( kw, An Vorladron Gernewek) are a professional rugby union team who play in the Championship, the second level of the English rugby union pyramid, and are the premier Cornish rugby club. Formerly known as Penzance & Newlyn ...
rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
club in the 2005–2006 season, but it moved again for 2006–2007 to share the ground of Camborne RFC. In April 2018, the construction of a Stadium for Cornwall was discussed with Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
, which had pledged £3 million for the £14.3 million project. It is planned for a site in Threemilestone. The town's remaining rugby union side, Truro RFC, founded in 1885. It belongs to Tribute Western Counties West and plays home games at St Clements Hill. It has hosted the CRFU Cornwall Cup several times.
Truro City F.C., a football team in the National League South, is the only Cornish club ever to reach this tier of the English football league system. It achieved national recognition by winning the FA Vase in 2007 against A.F.C. Totton in only the second final at the new Wembley Stadium
Wembley Stadium (branded as Wembley Stadium connected by EE for sponsorship reasons) is a football stadium in Wembley, London. It opened in 2007 on the site of the original Wembley Stadium, which was demolished from 2002 to 2003. The stadium ...
, becoming the first Cornish side ever to win that award. Its home ground is Treyew Road. Cornwall County Cricket Club plays some home fixtures at Boscawen Park, also the home ground of Truro Cricket Club.
Truro Fencing Club is a national flagship, having won numerous national championships and supplied three fencers for Team GB at the London 2012 Olympics.
Other sports amenities include a leisure centre, golf course and tennis courts.
Media
 Truro is the centre of Cornwall's local media. The county weeklies, the '' Cornish Guardian'' and ''
Truro is the centre of Cornwall's local media. The county weeklies, the '' Cornish Guardian'' and ''The West Briton
''The West Briton'' is a local weekly newspaper published every Thursday. It serves various areas of Cornwall in the United Kingdom: there are four separate editions – Truro and mid-Cornwall; Falmouth and Penryn; Redruth, Camborne and Hayle; ...
'', are based there, the latter providing a Truro and Mid-Cornwall edition. The city also holds the studios of BBC Radio Cornwall, and those of the West district of ITV Westcountry, whose main studio is now in Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
after a merger with ITV West. This closed the studio in Plymouth – the Westcountry Live
''Westcountry Live'' was the flagship regional news programme of ITV Westcountry, serving South West England.
History
The programme was first broadcast on Monday 4 January 1993 - four days after Westcountry Television took over the ITV regional ...
programme was replaced by The West Country Tonight
''ITV News West Country'' is a British television news service broadcast and produced by ITV West Country.
Overview
''ITV News West Country''
is broadcast from studios in Brislington, Bristol, with district reporters and camera crews based in ...
.
Customs
Amummers play
Mummers' plays are folk plays performed by troupes of amateur actors, traditionally all male, known as mummers or guisers (also by local names such as ''rhymers'', ''pace-eggers'', ''soulers'', ''tipteerers'', ''wrenboys'', and ''galoshins''). ...
text ascribed until recently to Mylor, Cornwall
Mylor is a civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated approximately five miles north of Falmouth.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 204 ''Truro & Falmouth''
The church town of the ecclesiastical parish is Mylor Chur ...
(quoted in studies of folk plays such as ''The Mummers Play'' by R. J. E. Tiddy – published posthumously in 1923 – and ''The English Folk-Play'' (1933) by E. K. Chambers), has now been shown by genealogical and other research to have originated in Truro about 1780.
The traditional Nine Lessons and Carols
Nine Lessons and Carols, also known as the Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols and Service of Nine Lessons and Carols, is a service of Christian worship traditionally celebrated on or near Christmas Eve. The story of the fall of humanity, the ...
at Christmas originated in Truro in 1880, when its bishop, Edward White Benson, began to provide chances for evening singing of carols before Christmas Day, often on Christmas Eve.
Administration
 Truro City Council forms its basic level of government, as one of 213 parish bodies in the county. Centred upstairs at the Municipal Buildings in Boscawen Street, it covers Truro's public library, parks and gardens,
Truro City Council forms its basic level of government, as one of 213 parish bodies in the county. Centred upstairs at the Municipal Buildings in Boscawen Street, it covers Truro's public library, parks and gardens, tourist information centre
A visitor center or centre (see American and British English spelling differences), visitor information center, tourist information center, is a physical location that provides tourist information to visitors.
Types of visitor center
A visi ...
, allotments and cemeteries. It also views planning issues and was involved in creating the Truro and Kenwyn Neighbourhood Plan in association with Cornwall Council. The City Council has four wards – Boscawen, Moresk, Tregolls and Trehaverne – with 24 councillors elected for four-year terms. It is affiliated to Truro Chamber of Commerce and other civic bodies.
The City Council comes under the unitary Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
, which is directly under central government. Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
, a unitary authority, is based at Lys Kernow, formerly County Hall, west of the city centre. It covers planning, infrastructure, development and environmental issues. Truro seats four members on it, one from each of its wards: Truro Tregolls, Truro Boscawen, Truro Redannick and Truro Trehaverne. Threemilestone and Gloweth, conurbations of the city, also elect a member.
Truro's borough court, first granted in 1153, became a free borough in 1589, and a city in 1877, receiving letters patent after the Anglican diocese was placed there in 1876. However, it forms the eighth smallest UK city in population, city council area and urban area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities ...
.
Twinning
Truro is twinned with * Boppard, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany *Morlaix
Morlaix (; br, Montroulez) is a commune in the Finistère department of Brittany in northwestern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department.
Leisure and tourism
The old quarter of the town has winding streets of cobbled stones and overha ...
, Brittany, France
Namesakes
Several towns outside Britain have taken Truro as their name: *Truro, Nova Scotia
Truro (Mi'kmaq: ''Wagobagitik''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Truru'') is a town in central Nova Scotia, Canada. Truro is the shire town of Colchester County and is located on the south side of the Salmon River floodplain, close to the river's mouth at ...
, Canada
*Truro, Massachusetts
Truro is a town in Barnstable County, Massachusetts, United States, comprising two villages: Truro and North Truro. Located slightly more than 100 miles (160 km) by road from Boston, it is a summer vacation community just south of the no ...
, United States
*Truro, Iowa
Truro is a city in southeast Madison County, Iowa, United States. The population was 509 at the time of the 2020 census. Truro is part of the Des Moines–West Des Moines Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
Truro was laid out and platted ...
, United States
*Truro, South Australia
Truro (postcode 5356, altitude 311m) is a town in South Australia, 80 km northeast of Adelaide. It is situated in an agricultural and pastoral district on the Sturt Highway, east of the Barossa Valley, where the highway crosses somewhat lof ...
, Australia
Transport
Roads and bus services
Truro is from the A30 trunk road, to which it is linked by the A39 from Falmouth and Penryn. Also passing through is the A390 between Redruth to the west andLiskeard
Liskeard ( ; kw, Lyskerrys) is a small ancient stannary and market town in south-east Cornwall, South West England. It is situated approximately 20 miles (32 km) west of Plymouth, west of the Devon border, and 12 miles (20 km) eas ...
to the east, where it joins the A38 for Plymouth, Exeter and the M5 motorway
The M5 is a motorway in England linking the Midlands with the South West England, South West. It runs from junction 8 of the M6 motorway, M6 at West Bromwich near Birmingham to Exeter in Devon. Heading south-west, the M5 runs east of West Brom ...
. Truro as the southernmost city in the United Kingdom is just under west-south-west of Charing Cross, London.
The city and surroundings have extensive bus services, mainly from First Kernow and Transport for Cornwall. Most routes terminate at Truro bus station near Lemon Quay. A permanent Park and Ride
A park and ride, also known as incentive parking or a commuter lot, is a parking lot with public transport connections that allows commuters and other people heading to city centres to leave their vehicles and transfer to a bus, rail system ( ...
scheme, known as Park for Truro, opened in August 2008. Buses based at Langarth Park in Threemilestone carry commuters into the city via Truro College, the Royal Cornwall Hospital Treliske, County Hall, Truro railway station
Truro railway station serves the city of Truro, Cornwall, England. The station is from via . It is situated on the Cornish Main Line and is the junction for the Maritime Line to Falmouth Docks.
The station is managed by Great Western Railway ...
, the Royal Cornwall Museum and Victoria Square, through to a second car park on the east side of Truro. Truro also has long-distance coach services run by National Express
National Express Group is a British multinational public transport company headquartered in Birmingham, England. It operates bus, coach, train and tram services in the United Kingdom, Ireland (National Express operates Eurolines in conjunction ...
.
Railways
 Truro railway station, about from the city centre, is on the
Truro railway station, about from the city centre, is on the Cornish Main Line
The Cornish Main Line ( kw, Penn-hyns-horn Kernow) is a railway line in Cornwall and Devon in the United Kingdom. It runs from Penzance to Plymouth, crossing from Cornwall into Devon over the famous Royal Albert Bridge at Saltash.
It directly ...
with direct links to London Paddington and to the Midlands, North and Scotland. North-east of the station is a stone viaduct with views over the city, cathedral and Truro River in the distance. The longest viaduct on the line, it replaced Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "on ...
's wooden Carvedras Viaduct in 1904. Connecting to the main line at Truro is the Maritime Line to Falmouth in the south.
 Truro's first railway station, at Highertown, was opened in 1852 by the West Cornwall Railway for trains to Redruth and Penzance, and was known as Truro Road Station. It was extended to the Truro River at Newham in 1855, but closed, so that Newham served as the terminus. When the
Truro's first railway station, at Highertown, was opened in 1852 by the West Cornwall Railway for trains to Redruth and Penzance, and was known as Truro Road Station. It was extended to the Truro River at Newham in 1855, but closed, so that Newham served as the terminus. When the Cornwall Railway
The Cornwall Railway was a broad gauge railway from Plymouth in Devon to Falmouth in Cornwall, England, built in the second half of the nineteenth century. It was constantly beset with shortage of capital for the construction, and was eventu ...
connected the line to Plymouth, its trains ran to the present station above the city centre. The West Cornwall Railway (WCR) diverted most passenger trains to the new station, leaving Newham mainly as a goods station until it closed in 1971. The WCR became part of the Great Western Railway. The route from Highertown to Newham is now a cycle path on a countryside loop through the south side of the city. The steam locomotive '' City of Truro'' was built in 1903 and still runs on UK mainline and preserved railways.

Air and river transport
Newquay, Cornwall's main airport, is north of Truro. It was thought in 2017 to be the "fastest growing airport" in the UK. It has regular flights to London Heathrow and other airports, and to the Isles of Scilly,Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of the Wicklow Mountains range. At the 2016 c ...
and Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian language, Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second- ...
, Germany.
There is a boat link to Falmouth along the Truro and Fal four times a day, tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
permitting. The fleet run by Enterprise Boats as part of the Fal River Links calls on the way at Malpas, Trelissick, Tolverne and St Mawes.
Churches



 The old parish church of Truro was St Mary's, which was incorporated into the cathedral in the later 19th century. The building dates from 1518, with a later tower and spire dating from 1769.
Parts of the town were in the parishes of Kenwyn and St Clement ( Moresk) until the mid 19th century, when other parishes were created. The lofty St George's church in Truro, designed by Rev. William Haslam, vicar of
The old parish church of Truro was St Mary's, which was incorporated into the cathedral in the later 19th century. The building dates from 1518, with a later tower and spire dating from 1769.
Parts of the town were in the parishes of Kenwyn and St Clement ( Moresk) until the mid 19th century, when other parishes were created. The lofty St George's church in Truro, designed by Rev. William Haslam, vicar of Baldhu
Baldhu (; kw, Bal Du, meaning ''black mine'') is a village and parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in the civil parish of Kea.
The parish church of Saint Michael and All Angels, designed by William White, is the burial place of ...
, was built of Cornish granite in 1855. The parish of St George's Truro was formed from part of Kenwyn in 1846. In 1865 two more parishes were created: St John's from part of Kenwyn and St Paul's from part of St Clement. St George's contains a large wall painting behind the high altar, the work of Stephany Cooper in the 1920s. Her father, Canon Cooper, had been a missionary in Zanzibar
Zanzibar (; ; ) is an insular semi-autonomous province which united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania. It is an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of many small islan ...
and elsewhere. The theme of the mural is "Three Heavens": the first heaven has views of Zanzibar and its cathedral (a happy period in the life of the artist), the second views of the city of Truro including the cathedral, the railway viaduct and St George's Church (another happy period), and the third, above the others, separated from them by the River of Life (Christ is seen bridging the river and 17 saints including St Piran
Saint Piran or Pyran ( kw, Peran; la, Piranus), died c. 480,Patrons - The Orthodox Church of Archangel Michael and Holy Piran'' Oecumenical Patriarchate, Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain. Laity Moor, Nr Ponsanooth, Cornwall. TR3 7 ...
and St Kenwyn are depicted).
Charles William Hempel was organist of St Mary's Church for 40 years from 1804 and also taught music. In 1805 he composed and printed ''Psalms from the New Version for the use of the Congregation of St. Mary's'', and in 1812 ''Sacred Melodies'' for the same congregation. These melodies gained popularity.
The oldest church in Truro is at Kenwyn, on the northern side. It dates from the 14th and 15th centuries, but was almost wholly rebuilt in 1820, having deteriorated to the point where it was deemed unsafe.
St John's Church (dedicated to St John the Evangelist) was built in 1828 (architect P. Sambell) in the Classical style on a rectangular plan and with a gallery. Alterations were carried out in the 1890s.
St Paul's Church was built in 1848. The chancel was replaced in 1882–1884, the new chancel being the work of J. D. Sedding. The tower is "broad and strong" (Pevsner) and the exterior of the aisles are ornamented in Sedding's version of the Perpendicular style.N. Pevsner, 1970. ''Cornwall''; 2nd ed. Penguin Books; pp. 234–235. In the parish of St Paul is the former Convent of the Epiphany (Anglican) at Alverton House, Tregolls Road, an early 19th-century house extended for the convent of the Community of the Epiphany and the chapel was built in 1910 by Edmund H. Sedding. The sisterhood was founded by the Bishop of Truro, George Howard Wilkinson in 1883 and closed in 2001 when two surviving nuns moved into care homes. The sisters had been involved in pastoral and educational work and care of the cathedral and St Paul's Church. St Paul's Church, built with a tower on a river bed with poor foundations, has fallen into disrepair and is no longer used. Services are now held at the churches of St Clement, St George, and St John. St Paul and St Clement form a united benefice, as do St George and St John.
Other denominations
One Methodist place of worship remains in use, in Union Place – Truro Methodist Church – which has a broad granite front (1830, but since enlarged). There is a Quaker Meeting House in granite (c. 1830) and numerous other churches, some meeting in their own modern buildings, e. g. St Piran's Roman Catholic church and All Saints, Highertown, and some in schools or halls. St Piran's, dedicated to Our Lady of the Portal and St Piran, was built on the site of a medieval chapel by Margaret Steuart Pollard in 1973, for which she received the Benemerenti Medal from the Pope. The Baptist church building occupies the site of the former Lake's pottery, one of the oldest in Cornwall.Education
A freegrammar school
A grammar school is one of several different types of school in the history of education in the United Kingdom and other English-speaking countries, originally a school teaching Latin, but more recently an academically oriented secondary school ...
associated with St Mary's Church was endowed in the 16th century. Its distinguished pupils have included the scientist Sir Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
, General Sir Hussey Vivian and the clergyman, Henry Martyn
Henry Martyn (18 February 1781 – 16 October 1812) was an Anglican priest and missionary to the peoples of India and Persia. Born in Truro, Cornwall, he was educated at Truro Grammar School and St John's College, Cambridge. A chance encount ...
.
The former Truro Girls Grammar School was converted into a Sainsbury's
J Sainsbury plc, trading as Sainsbury's, is the second largest chain of supermarkets in the United Kingdom, with a 14.6% share of UK supermarket sales.
Founded in 1869 by John James Sainsbury with a shop in Drury Lane, London, the company ...
supermarket.
Educational institutions in Truro today include:
*Archbishop Benson – A Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
voluntary aided primary school
*Polwhele House Preparatory School
Polwhele House School is a day and boarding prep school at Polwhele House, near Truro, Cornwall.
It follows the thirteen-plus Common Entrance Examination syllabus.
In 2020, the school announced plans to provide senior school education, slo ...
— since the closure of Truro Cathedral School educating also the 18 boy choristers of Truro Cathedral
*Truro School
Truro School is a coeducational independent day and boarding school located in the city of Truro, Cornwall, England. It is the largest coeducational independent school in Cornwall with over 1050 pupils from pre-prep to sixth form. It is a membe ...
— a public school founded in 1880
* Truro High School for Girls — a public school for ages 13–18
* Penair School — a state co-educational science college for ages 11–16
* Richard Lander School — a state co-educational technology college for ages 11–16
* Truro and Penwith College — A further
Further or Furthur may refer to:
* ''Furthur'' (bus), the Merry Pranksters' psychedelic bus
* Further (band), a 1990s American indie rock band
* Furthur (band), a band formed in 2009 by Bob Weir and Phil Lesh
* ''Further'' (The Chemical Brothers a ...
and higher education college attached to the Combined Universities in Cornwall
The Combined Universities in Cornwall (CUC) ( kw, Pennskolyow Kesunys yn Kernow) is a project to provide higher education in Cornwall, England, which is one of the poorest areas of the United Kingdom in terms of GVA per capita.
History
Develop ...
*University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
Medical School
Development
 Truro has many proposed urban development schemes, most of which are intended to counter the main problems, notably traffic congestion and lack of housing.
Major proposals include construction of a distributor road to carry traffic away from the busy Threemilestone-Treliske-Highertown corridor, reconnecting at either Green Lane or Morlaix Avenue. This will also serve the new housing planned for that area.
Changes proposed for the city centre include pedestrianisation of main shopping streets and
Truro has many proposed urban development schemes, most of which are intended to counter the main problems, notably traffic congestion and lack of housing.
Major proposals include construction of a distributor road to carry traffic away from the busy Threemilestone-Treliske-Highertown corridor, reconnecting at either Green Lane or Morlaix Avenue. This will also serve the new housing planned for that area.
Changes proposed for the city centre include pedestrianisation of main shopping streets and beautification
Beautification is the process of making visual improvements to a town, city, or urban area. This most often involves planting trees, shrubbery, and other greenery, but frequently also includes adding decorative or historic-style street lights and ...
of uncharacteristic storefronts built in the 1960s. New retail developments on the current Carrick District Council site and Garras Wharf waterfront site will provide more space for shops, open spaces and public amenities. Along with redevelopment of the waterfront, a tidal barrier is planned to dam water into the Truro River, which is currently blighted by mud banks that appear at low tide.
Controversial plans include the construction of a new stadium for Truro City F.C. and the Cornish Pirates
The Cornish Pirates ( kw, An Vorladron Gernewek) are a professional rugby union team who play in the Championship, the second level of the English rugby union pyramid, and are the premier Cornish rugby club. Formerly known as Penzance & Newlyn ...
, and relocation of the city's golf course
A golf course is the grounds on which the sport of golf is played. It consists of a series of holes, each consisting of a tee box, a fairway, the rough and other hazards, and a green with a cylindrical hole in the ground, known as a "cup". ...
to make way for more housing. A smaller project is the addition of two large sculptures in the Piazza.
Notable residents
Public thinking, public service
* Sir Henry Killigrew (c. 1528–1603), Cornish diplomat and an ambassador * Owen Fitzpen (1552–1636), philanthropist and merchant seaman, led a successful slave revolt in 1627 to free captives of Barbary pirates, memorialised on a plaque in St Mary's Church. * John Robartes, 1st Earl of Radnor (1606–1685) a politician who fought for the Parliamentary cause * William Gwavas (1676–1741), barrister and writer in the Cornish language *Edward Boscawen
Admiral of the Blue Edward Boscawen, PC (19 August 171110 January 1761) was a British admiral in the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament for the borough of Truro, Cornwall, England. He is known principally for his various naval commands during ...
(1711–1761), Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
admiral, eponym of a cobbled street at the centre of Truro and a park
* Samuel Walker (1714–1761), evangelical clergyman, curate of Truro from 1746
*Richard Polwhele
Richard Polwhele (6 January 1760 – 12 March 1838) was a Cornish clergyman, poet and historian of Cornwall and Devon.
Biography
Richard Polwhele's ancestors long held the manor of Treworgan, 4 3/4 miles south-east of Truro in Cornwall, whi ...
(1760–1838) a clergyman, poet and historian of Cornwall and Devon
*Charles Sandoe Gilbert
Charles Sandoe Gilbert (1760–1831) was a Cornish druggist and historian of Cornwall.
Life
The son of Thomas Gilbert, Charles was born in the parish of Kenwyn, near Truro, in 1760. In conjunction with a Mr. Powell he became an itinerant vendor o ...
(1760–1831), druggist
A pharmacist, also known as a chemist (Commonwealth English) or a druggist (North American and, archaically, Commonwealth English), is a healthcare professional who prepares, controls and distributes medicines and provides advice and instructi ...
and historian of Cornwall
* Hussey Vivian, 1st Baron Vivian (1775–1842) a senior British cavalry officer
*Henry Martyn
Henry Martyn (18 February 1781 – 16 October 1812) was an Anglican priest and missionary to the peoples of India and Persia. Born in Truro, Cornwall, he was educated at Truro Grammar School and St John's College, Cambridge. A chance encount ...
(1781–1812), Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a College town, university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cam ...
mathematician and missionary in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, who translated the Bible into local languages
*Thomas Wilde, 1st Baron Truro
Thomas Wilde, 1st Baron Truro, (7 July 178211 November 1855) was a British lawyer, judge, and politician. He was Lord High Chancellor of Great Britain between 1850 and 1852.
Background and education
Born in London, Truro was the second son of ...
(1782–1855) Lord High Chancellor, 1850 to 1852.
* Admiral Sir Barrington Reynolds (1786–1861) senior Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against ...
officer
* FitzRoy Somerset, 1st Baron Raglan (1788–1855) a senior Army officer and MP for Truro in 1818 & 1826.
* Richard Spurr (1800–1855), cabinet maker and lay preacher imprisoned for Chartism. A large allotment in the town was dedicated to him in 2011.
* Major-General Sir Henry James (1803–1877), a Royal Engineers officer and DG of the Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
1854–1875
*Richard Lemon Lander
Richard Lemon Lander (8 February 1804 – 6 February 1834) was a British explorer of western Africa. He and his brother John were the first Europeans to follow the course of the River Niger, and discover that it led to the Atlantic.
Biograp ...
(1804–1834), explorer in West Africa. A local secondary school is named in his honour and a monument to his memory stands at the top of Lemon Street.
* John Lander (1806–1839), printer and explorer with his brother Richard Lemon Lander
Richard Lemon Lander (8 February 1804 – 6 February 1834) was a British explorer of western Africa. He and his brother John were the first Europeans to follow the course of the River Niger, and discover that it led to the Atlantic.
Biograp ...
* Charles Chorley (c. 1810–1874), journalist and man of letters
* William Bennett Bond (1815–1906), Canadian priest and second primate of the Anglican Church of Canada
*Alexander Mackennal
Alexander Mackennal (14 January 183523 June 1904) was a British Nonconformist minister.
Life
He was born at Truro in Cornwall, the son of Patrick Mackennal, a Scot, who had settled there. In 1848 the family removed to London, and at sixteen he w ...
(1835–1904), nonconformist minister
* Silvanus Trevail (1851–1903) local architect and mayor of Truro
* Joseph Hunkin (1887–1950), Bishop of Truro from 1935 to 1950
* James Henry Fynn (Finn, 1893–1917), recipient of the Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously ...
* Barbara Joyce West (1911–2007), second-to-last survivor of the
* Alison Adburgham (1912–1997), social historian and fashion journalist, died in the town.
* Hugh Clegg (1920–1995), academic, founded the National Board for Prices and Incomes (1965–1971)
*David Penhaligon
David Charles Penhaligon (6 June 1944 – 22 December 1986) was a British politician from Cornwall who was Liberal Member of Parliament for the constituency of Truro from 1974–86. He was a popular figure in all parties and had potential to ...
(1944–1986), politician, Liberal MP for Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro ...
1974–1986
* Paul Myners, Baron Myners, (1948-2022), businessman and politician
* Mark Laity (born c. 1962), NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
spokesman and former BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Arts

 *
*Giles Farnaby
Giles Farnaby (c. 1563 – November 1640) was an English composer and virginalist whose music spans the Transition from Renaissance to Baroque in instrumental music, transition from the Renaissance to the Baroque period.
Life
Giles Farnaby was ...
(c. 1563–1640), composer and virginalist
* Samuel Foote (1720–1777), actor and playwright
* Henry Bone (1755–1834), porcelain, jewellery and enamel painter
* Joseph Antonio Emidy (1775–1835), former slave from Guinea turned violinist
* Charles William Hempel (1777–1855), organist of St Mary's Church, Truro, and poet
* Nicholas Michell (1807–1880) a Cornish writer, best known for his poetry
* Charles Frederick Hempel (1811–1867), organist and composer
* Walter Hawken Tregellas (1831–1894) professional draughtsman and historical and biographical writer
*Francis Charles Hingeston-Randolph
Francis Charles Hingeston-Randolph, known until 1860 as Francis Hingston (1833–1910) was an English cleric, antiquary and author.
Life
Francis Hingston was born at Truro on 31 March 1833, the son of Francis Hingston (1796–1841), controller ...
(1833–1910), cleric, antiquary and author
*Henry Dawson Lowry
Henry Dawson Lowry (22 February 1869 – 21 October 1906) was an English journalist, short story writer, novelist and poet.
Early life
Lowry was born at Truro, as the eldest son of Thomas Shaw Lowry, bank clerk at Truro, afterwards bank manager ...
(1869–1906), journalist, short story writer, novelist and poet
*Hugh Walpole
Sir Hugh Seymour Walpole, Commander of the Order of the British Empire, CBE (13 March 18841 June 1941) was an English novelist. He was the son of an Anglican clergyman, intended for a career in the church but drawn instead to writing. Among th ...
(1884–1941) novelist, who attended a preparatory school in Truro
*Maria Kuncewiczowa
Maria Kuncewiczowa (Samara, Russia, Samara, Russian Empire, 30 October 1895 - 15 July 1989, Lublin, Poland) was a Polish writer and novelist. Kuncewiczowa's works span from short stories to novels to radio novels to literary diaries.
Early life
...
(1895–1989), Polish writer living in Truro after WWII. Her novel ''Tristan 1946'' was set here.
* Margaret Steuart Pollard (1904–1996), poet and translator lived in Truro from 1930s
* William Golding (1911–1993), novelist, playwright and poet, gained the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1983. Born in St Columb Minor, he returned to live near Truro in 1985.
* Alison Adburgham (1912–1997), author, social historian and fashion editor of The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
* Irene Newton (1915–1992), artist
* Catherine Grubb, artist (born 1945), lives in Truro.
* Roger Taylor (born 1949), drummer from the rock band Queen
Queen or QUEEN may refer to:
Monarchy
* Queen regnant, a female monarch of a Kingdom
** List of queens regnant
* Queen consort, the wife of a reigning king
* Queen dowager, the widow of a king
* Queen mother, a queen dowager who is the mother ...
* Robert Goddard (born 1954), novelist, lives in Truro.
* James Marsh (born 1963), film director and Academy Award winner
* Ben Salfield (born 1971), guitarist, lutenist, composer and teacher, has lived in Truro since age of nine.
* Paul Kerensa (born 1979), comedy writer and stand-up comedian
* Brett Harvey (born c. 1980), film writer and director based in Cornwall
*Calvin Dean
Calvin Ainsley Dean (born 21 May 1985) is an English actor, best known for portraying Darren Mullet in the 2009 film '' Tormented'' and for his appearance in Doctor Who.
Background
Dean was born in Truro, Cornwall. He grew up in Polruan, Cornw ...
(born 1985), award-winning actor

Science and business
* John Vivian (1750–1826) industrialist in Swansea, descendant of the Vivian family * Elizabeth Andrew Warren (1786–1864) a Cornish botanist and marine algologist * Charles Foster Barham (1804–1884), physician and writer on public health * Edwin Dunkin (1821–1898) an astronomer and the president of the Royal Astronomical Society * Henry Charlton Bastian (1837–1915), physiologist andneurologist
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
* Edward Arnold (1857–1942), a publisher, founded Edward Arnold Publishers Ltd in 1890.
* Elsie Wilkins Sexton (1868–1959) a zoologist and biological illustrator
* H. Lou Gibson (1906–1992), expert in medical uses of infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
to detect breast cancer
Sport
 * Nick Nieland (born 1972), javelin gold medallist at the 2006 Commonwealth Games
* Matthew Etherington (born 1981), former professional footballer with 426 club caps, he played for West Ham and Stoke City.
* David Paynter (born 1981), former first-class cricketer
* Tom Voyce (born 1981) former rugby union footballer with London Wasps and England
* Annabel Vernon (born 1982), retired rower, team silver medallist at the 2008 Summer Olympics
* Chris Harris (born 1982), international speedway rider
* Gemma Prescott (born 1983), Paralympic track and field athlete
* Darren Dawidiuk (born 1987), rugby union footballer
* Craig Alcock (born 1987), professional footballer with 300 club caps
* Matthew Whorwood (born 1989), Paralympic swimmer, bronze medallist in two Paralympic Games
*
* Nick Nieland (born 1972), javelin gold medallist at the 2006 Commonwealth Games
* Matthew Etherington (born 1981), former professional footballer with 426 club caps, he played for West Ham and Stoke City.
* David Paynter (born 1981), former first-class cricketer
* Tom Voyce (born 1981) former rugby union footballer with London Wasps and England
* Annabel Vernon (born 1982), retired rower, team silver medallist at the 2008 Summer Olympics
* Chris Harris (born 1982), international speedway rider
* Gemma Prescott (born 1983), Paralympic track and field athlete
* Darren Dawidiuk (born 1987), rugby union footballer
* Craig Alcock (born 1987), professional footballer with 300 club caps
* Matthew Whorwood (born 1989), Paralympic swimmer, bronze medallist in two Paralympic Games
*Matthew Shepherd
Matthew Joseph Shepherd (born February 21, 1976) is an attorney from his native El Dorado, Arkansas, who is a Republican member of the Arkansas House of Representatives for District 6, which includes western Union County. He was elected in the ...
(born 1990), rugby union player
* Alex Quinn (born 2000), racing driver
See also
* Diocese of Truro *List of topics related to Cornwall
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Cornwall:
Cornwall – ceremonial county and unitary authority area of England within the United Kingdom. Cornwall is a peninsula bordered to the north and wes ...
References
External links
* *Truro City Council website
(provided b
Totally Truro
the local not-for-profit Business Improvement District) {{Authority control Cornish capitals Cities in South West England Towns in Cornwall Civil parishes in Cornwall County towns in England Populated places established in the 12th century Ports and harbours of Cornwall Cornish Killas