Tropical climate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the

 Tropical climates normally have only two seasons, a wet season and a dry season. Depending on the location of the region, the wet and dry seasons can have varying duration. Annual temperature changes in the tropics are small. Due to the high temperatures and abundant rainfall, much of the plant life grows throughout the year. High temperature and humidity is the most suitable environment for epiphytes to grow. In many tropical climates, vegetation grow in layers:
Tropical climates normally have only two seasons, a wet season and a dry season. Depending on the location of the region, the wet and dry seasons can have varying duration. Annual temperature changes in the tropics are small. Due to the high temperatures and abundant rainfall, much of the plant life grows throughout the year. High temperature and humidity is the most suitable environment for epiphytes to grow. In many tropical climates, vegetation grow in layers:
 Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the coolest month, and feature hot temperatures all year-round. Annual precipitation is often abundant in tropical climates, and shows a seasonal rhythm but may have seasonal dryness to varying degrees. There are normally only two seasons in tropical climates, a wet (rainy / monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
) season and a dry season. The annual temperature range in tropical climates is normally very small. Sunlight is intense in these climates.
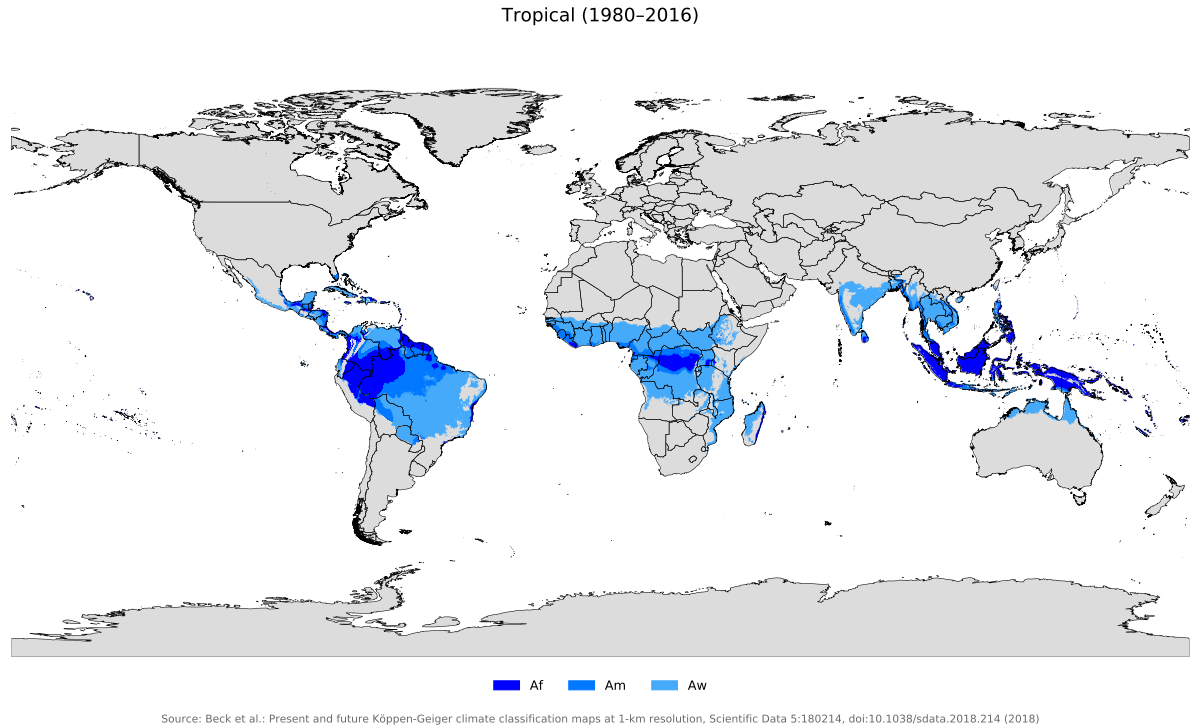
There are three basic types of tropical climates within the tropical climate group: tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southe ...
(Af), tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
(Am) and tropical wet and dry climate or tropical savannah (Aw for dry winters, and As for dry summers), which are classified and distinguished by the precipitation and the precipitation levels of the driest month in those regions.
Köppen climate classification
TheKöppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It defines a tropical climate as a region where the mean temperature of the coldest month is greater than or equal to 18 °C (64.4 °F) and doesn't fit into the criteria for B-group climates, classifying them as an A-group (tropical climate group). A-group regions are usually found in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also refer ...
, below 23.5 latitude in both the southern and northern hemisphere; they include areas around the Equator, Central America, North-central portions of South America, central Africa, southern portions of Asia and parts of North Australia and the Pacific Ocean islands.
In Group A, there are three types of this climate: the tropical rainforest climate (Af), tropical monsoon climate (Am) and tropical wet and dry or savanna climate (Aw or As). All of the three climates are classified by their Pdry (short for precipitation of the driest month). Tropical rainforest climate's Pdry should be greater than or equal 60 mm (2.4 inches). Tropical monsoon climate's Pdry should be in the range from to 60 mm. Tropical wet and dry or savanna climate's Pdry should be less than .
Tropical climate biome
 Tropical climates normally have only two seasons, a wet season and a dry season. Depending on the location of the region, the wet and dry seasons can have varying duration. Annual temperature changes in the tropics are small. Due to the high temperatures and abundant rainfall, much of the plant life grows throughout the year. High temperature and humidity is the most suitable environment for epiphytes to grow. In many tropical climates, vegetation grow in layers:
Tropical climates normally have only two seasons, a wet season and a dry season. Depending on the location of the region, the wet and dry seasons can have varying duration. Annual temperature changes in the tropics are small. Due to the high temperatures and abundant rainfall, much of the plant life grows throughout the year. High temperature and humidity is the most suitable environment for epiphytes to grow. In many tropical climates, vegetation grow in layers: shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from tree ...
s under tall trees, bushes under shrubs and grasses
Poaceae () or Gramineae () is a large and nearly ubiquitous family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos and the grasses of natural grassland and species cultivated in lawns ...
under bushes. Tropical plants are rich in resources, including coffee, cocoa and oil palm. Listed below are the types of vegetation unique to each of the three climates that make up the tropical climate biome.
Natural vegetation
Tropical rainforest vegetation including: Bengal bamboo,bougainvillea
''Bougainvillea'' ( , ) is a genus of thorny ornamental vines, bushes, and trees belonging to the four o' clock family, Nyctaginaceae. It is native to eastern South America, found from Brazil, west to Peru, and south to southern Argentina. ...
, curare, coconut tree
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family ( Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the ...
, durian and banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus ''Musa''. In some countries, bananas used for cooking may be called "plantains", disting ...
.
Tropical monsoon vegetation including: teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters ( pan ...
, deodar, rosewood, sandalwood
Sandalwood is a class of woods from trees in the genus '' Santalum''. The woods are heavy, yellow, and fine-grained, and, unlike many other aromatic woods, they retain their fragrance for decades. Sandalwood oil is extracted from the woods for ...
and bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
.
Tropical wet and dry or savanna vegetation including: acacia senegal
''Senegalia senegal'' (also known as ''Acacia senegal'') is a small thorny deciduous tree from the genus ''Senegalia'', which is known by several common names, including gum acacia, gum arabic tree, Sudan gum and Sudan gum arabic. In parts of In ...
, elephant grass The term Elephant grass may refer to the following grass species:
* The Asian '' Miscanthus giganteus'', also known as giant miscanthus, commonly used as a biomass crop
* The African ''Cenchrus purpureus'', also known as Napier grass, Uganda grass ...
, jarrah tree, gum tree eucalyptus and whistling thorn.
Tropical rainforest climate
The Köppen classification identifies tropical rainforest climates (Zone Af: f = "feucht", German for moist) as usually having north and south latitudinal ranges of just 5-10 degrees from the equator. Tropical rainforest climates have high temperatures: the yearly average temperature is normally between 21 °C to 30 °C ( 70 °F to 85 °F ). The precipitation can reach over 100 inches a year. The seasons are evenly distributed throughout the year, and there is almost no drought period here. Regions that contain tropical rainforest climate mainly include the upper Amazon basin of South America, the Northern Zaire (Congo) basin of Africa, and the islands of the East Indies. The tropical rainforest climate differs from other subtypes of tropical climates as it has more kinds of trees due to itsprecipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
. The large number of trees contribute back to the humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
of the climate because of the transpiration, which is the process of water evaporated from the surface of living plants to the atmosphere. The warmth and abundant precipitation heavily contributes to the diversity and characteristics of vegetations under the tropical rainforest climate. The vegetations develop a vertical stratification and various growth forms to receive enough sunlight, which is unusual under other types of climate.
Tropical monsoon climate
The Köppen classification tool identifies tropical monsoon climate as having small annual temperature ranges, high temperatures, and plentiful precipitation. This climate also has a short dry season which almost always occurs in the winter. The tropical monsoon climate is often found within countries in the south and southeast Asia region between the latitude of 10 degrees north and the Tropic of Cancer. It can also be found in West Africa and South America. The annual temperature of regions under tropical monsoon climate is also stable. Thetropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
has the following main characteristic. The average annual temperature is around and has an average annual temperature range of about 3.6 °C (2 °F). Distinction between wet and drought seasons, the tropical monsoon climate is different from other tropical climates because of its uneven precipitation throughout the year. The precipitation is heavy in the summer, and a short-drought season occurs in the winter. This climate has an annual total precipitation of on average 3409.2mm, and a 3115.9mm summer precipitation and 293.3mm winter precipitation.
There are three main seasons of tropical monsoon climate: the cool dry season is from fall to late winter, the hot dry season is in the spring and the rainy or monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
season is near or during the summer months.
The tropical monsoon forest mainly consists of three layered structures. The first layer is the surface layer which is a very dense layer of shrubs and grasses. The second layer is the understory layer with trees about 15 meters tall. The top layer is called the canopy tree layer which has trees from 25 to 40 meters tall and those trees grow closely while above is the emergent layer with sporadic trees taller than 35 meters.
Tropical wet and dry or forest climate
Tropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories ''Aw'' (for a dry winter) and ''As'' (for a dry summer). The driest month has less than of ...
s are mainly located between the 10° and 25° north-south latitudes, and often occur at the outer margins of the tropics. Typical regions include central Africa, parts of South America, as well as northern and eastern Australia. The temperature range of savanna climate is between 20 °C to 30 °C (68 °F - 86 °F). In summer, the temperature is between 25 °C - 30 °C, while in winter the temperature is between 20 °C - 30 °C, but still stays above an 18 °C mean. The annual precipitation is between 700 to 1000 mm. The driest months are generally in the winter and they have less than 60 mm of rainfall (often much less).
Regions under the savanna climate usually have lands covered with flat grassland vegetation with areas of woodlands. Those grassland biomes cover almost 20% of the Earth's surface. The grassland vegetation types include Rhodes grass, red oats grass, star grass and lemongrass.
See also
*Tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also refer ...
* Subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° nort ...
* Humid subtropical
* Megathermal
* Tropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, humid tropical climate or equatorial climate is a tropical climate sub-type usually found within 10 to 15 degrees latitude of the equator. There are some other areas at higher latitudes, such as the coast of southe ...
* Tropical monsoon climate
An area of tropical monsoon climate (occasionally known as a sub-equatorial, tropical wet climate or a tropical monsoon and trade-wind littoral climate) is a tropical climate sub-type that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification category ...
* Tropical savannah climate
* Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
References
{{Authority control Climate