Trilobites on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are
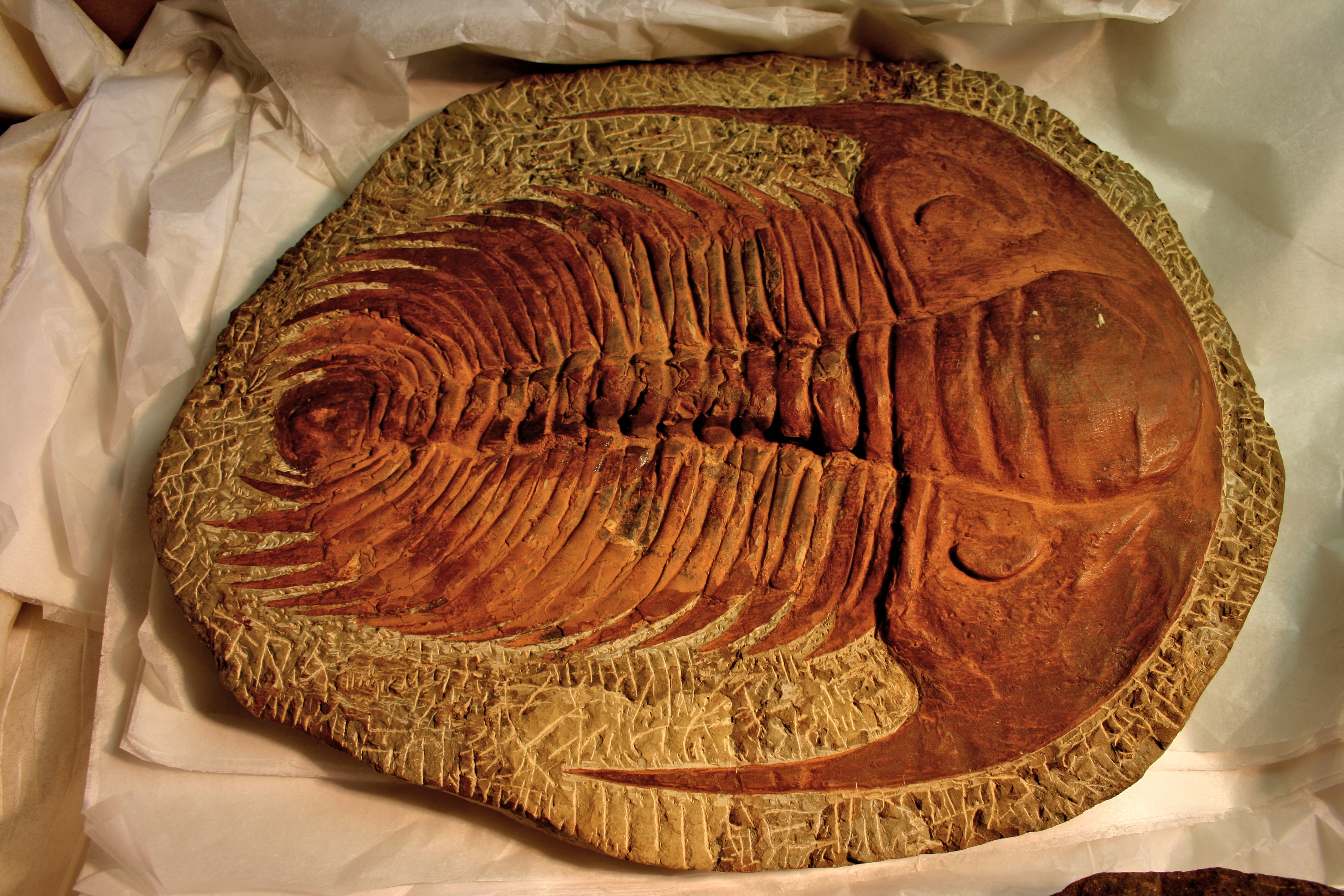


 The earliest trilobites known from the
The earliest trilobites known from the
 Trilobites saw incredible diversification over time. For such a long-lasting group of animals, it is no surprise that trilobite evolutionary history is marked by a number of extinction events where some groups perished and surviving groups diversified to fill ecological niches with comparable or unique adaptations. Generally, trilobites maintained high diversity levels throughout the
Trilobites saw incredible diversification over time. For such a long-lasting group of animals, it is no surprise that trilobite evolutionary history is marked by a number of extinction events where some groups perished and surviving groups diversified to fill ecological niches with comparable or unique adaptations. Generally, trilobites maintained high diversity levels throughout the

 The Early
The Early
 Most Early Silurian families constitute a subgroup of the Late Ordovician fauna. Few, if any, of the dominant Early Ordovician fauna survived to the end of the Ordovician, yet 74% of the dominant Late Ordovician trilobite fauna survived the Ordovician. Late Ordovician survivors account for all post-Ordovician trilobite groups except the
Most Early Silurian families constitute a subgroup of the Late Ordovician fauna. Few, if any, of the dominant Early Ordovician fauna survived to the end of the Ordovician, yet 74% of the dominant Late Ordovician trilobite fauna survived the Ordovician. Late Ordovician survivors account for all post-Ordovician trilobite groups except the
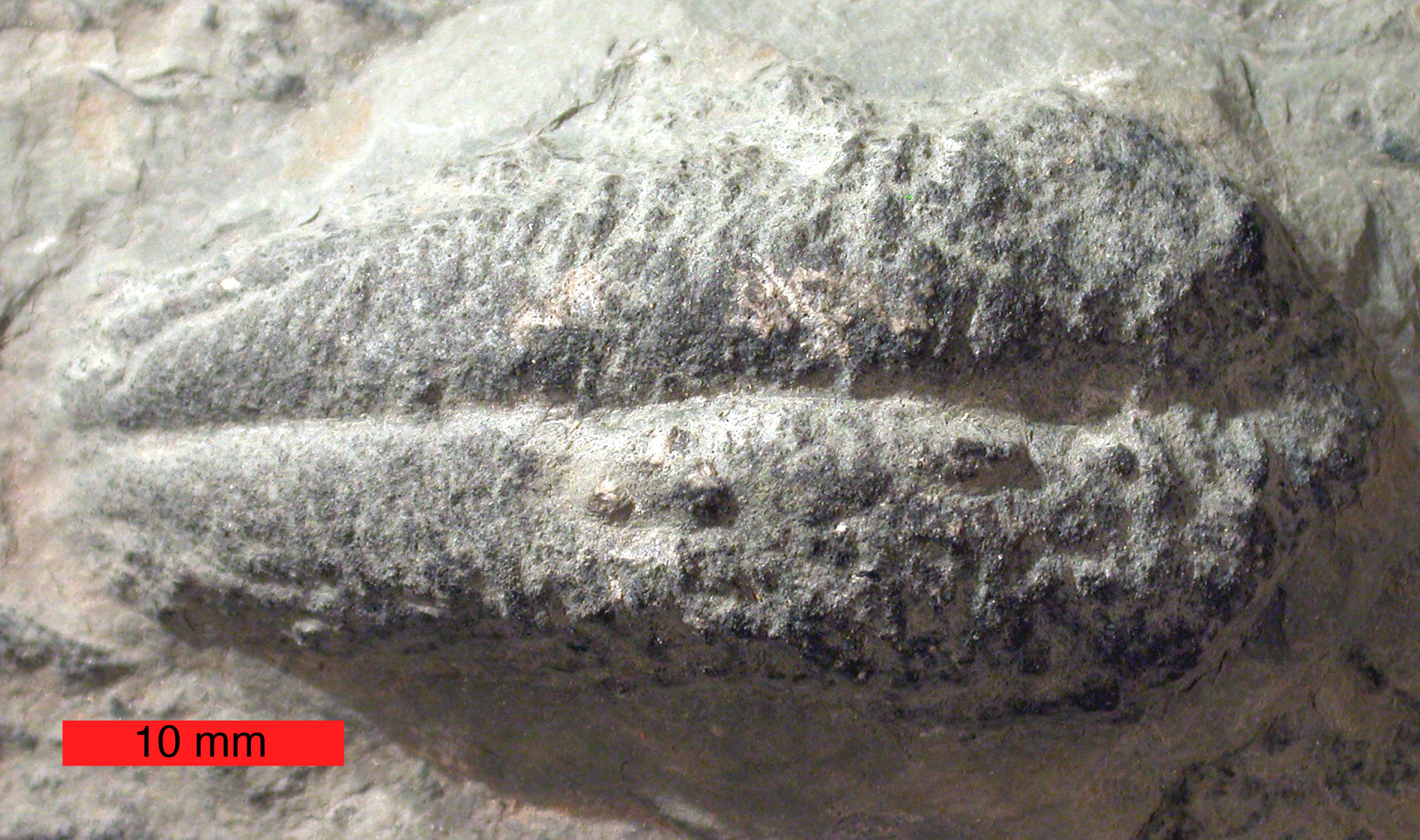



 Trilobites appear to have been primarily marine organisms, since the fossilized remains of trilobites are always found in rocks containing fossils of other salt-water animals such as brachiopods, crinoids, and corals. Some trackways suggest trilobites made at least temporary excursions unto land. Within the marine paleoenvironment, trilobites were found in a broad range from extremely shallow water to very deep water. Trilobites, like brachiopods, crinoids, and corals, are found on all modern continents, and occupied every ancient ocean from which Paleozoic fossils have been collected. The remnants of trilobites can range from the preserved body to pieces of the exoskeleton, which it shed in the process known as ecdysis. In addition, the tracks left behind by trilobites living on the sea floor are often preserved as
Trilobites appear to have been primarily marine organisms, since the fossilized remains of trilobites are always found in rocks containing fossils of other salt-water animals such as brachiopods, crinoids, and corals. Some trackways suggest trilobites made at least temporary excursions unto land. Within the marine paleoenvironment, trilobites were found in a broad range from extremely shallow water to very deep water. Trilobites, like brachiopods, crinoids, and corals, are found on all modern continents, and occupied every ancient ocean from which Paleozoic fossils have been collected. The remnants of trilobites can range from the preserved body to pieces of the exoskeleton, which it shed in the process known as ecdysis. In addition, the tracks left behind by trilobites living on the sea floor are often preserved as  In the United States, the best open-to-the-public collection of trilobites is located in
In the United States, the best open-to-the-public collection of trilobites is located in
 The
The
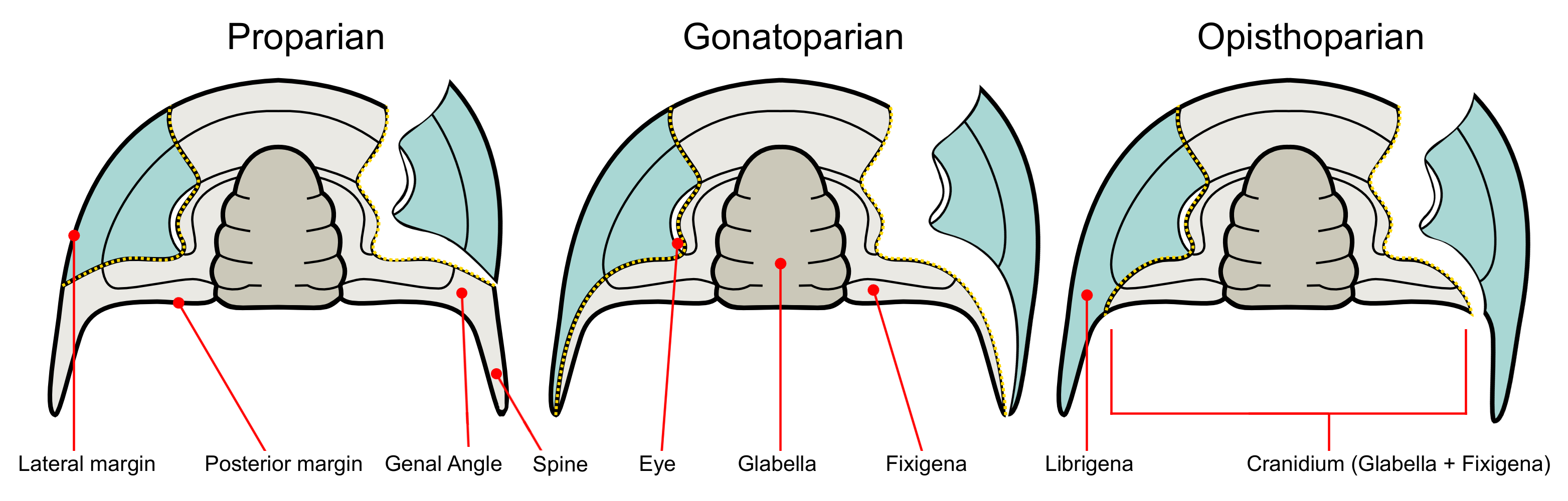 The primitive state of the dorsal sutures is proparian. Opisthoparian sutures have developed several times independently. There are no examples of proparian sutures developing in
The primitive state of the dorsal sutures is proparian. Opisthoparian sutures have developed several times independently. There are no examples of proparian sutures developing in
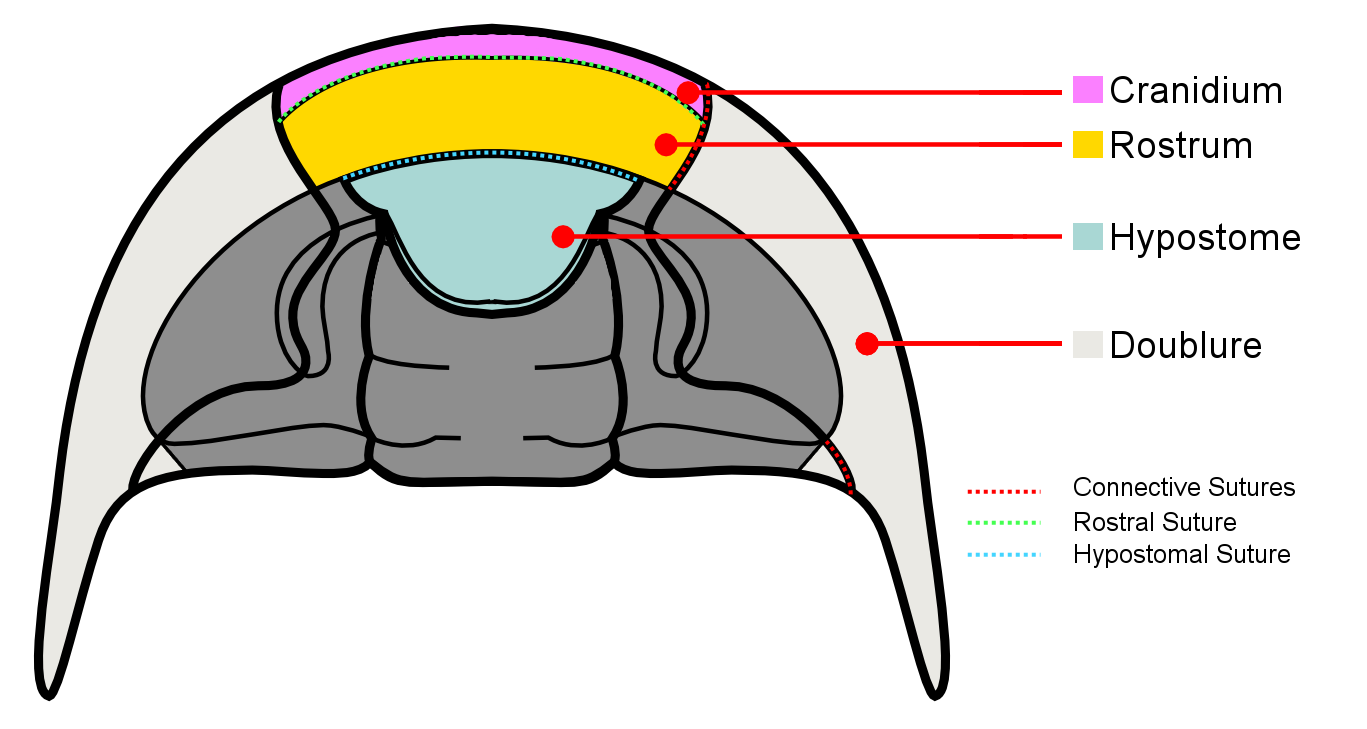 Dorsal facial sutures continue downward to the ventral side of the cephalon where they become the Connective sutures that divide the doublure. The following are the types of ventral sutures.
*Connective sutures – are the sutures that continue from the facial sutures past the front margin of the cephalon.
*Rostral suture – is only present when the trilobite possesses a rostrum (or rostral plate). It connects the rostrum to the front part of the dorsal cranidium.
*Hypostomal suture – separates the hypostome from the doublure when the hypostome is of the attached type. It is absent when the hypostome is free-floating (i.e. natant). it is also absent in some coterminant hypostomes where the hypostome is fused to the doublure.
*Median suture – exhibited by asaphid trilobites, they are formed when instead of becoming connective sutures, the two dorsal sutures converge at a point in front of the cephalon then divide straight down the center of the doublure.
Dorsal facial sutures continue downward to the ventral side of the cephalon where they become the Connective sutures that divide the doublure. The following are the types of ventral sutures.
*Connective sutures – are the sutures that continue from the facial sutures past the front margin of the cephalon.
*Rostral suture – is only present when the trilobite possesses a rostrum (or rostral plate). It connects the rostrum to the front part of the dorsal cranidium.
*Hypostomal suture – separates the hypostome from the doublure when the hypostome is of the attached type. It is absent when the hypostome is free-floating (i.e. natant). it is also absent in some coterminant hypostomes where the hypostome is fused to the doublure.
*Median suture – exhibited by asaphid trilobites, they are formed when instead of becoming connective sutures, the two dorsal sutures converge at a point in front of the cephalon then divide straight down the center of the doublure.
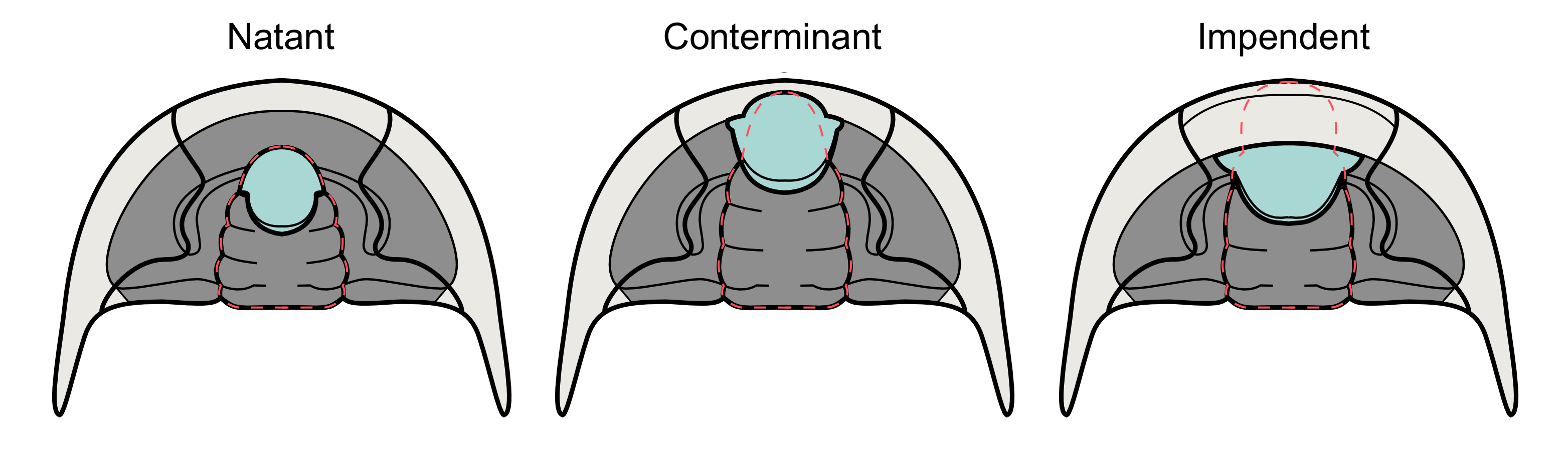 The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of the trilobite found on the ventral side of the cephalon typically below the glabella. The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella.
* Natant – Hypostome not attached to doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Conterminant – Hypostome attached to rostral plate of doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Impendent – Hypostome attached to rostral plate but not aligned to glabella.
The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of the trilobite found on the ventral side of the cephalon typically below the glabella. The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella.
* Natant – Hypostome not attached to doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Conterminant – Hypostome attached to rostral plate of doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Impendent – Hypostome attached to rostral plate but not aligned to glabella.
 Trilobite fossils are often found "enrolled" (curled up) like modern pill bugs for protection; evidence suggests enrollment ("
Trilobite fossils are often found "enrolled" (curled up) like modern pill bugs for protection; evidence suggests enrollment ("
 Trilobite exoskeletons show a variety of small-scale structures collectively called prosopon. Prosopon does not include large scale extensions of the cuticle (e.g. hollow pleural spines) but to finer scale features, such as ribbing, domes, pustules, pitting, ridging and perforations. The exact purpose of the prosopon is not resolved but suggestions include structural strengthening, sensory pits or hairs, preventing predator attacks and maintaining aeration while enrolled. In one example, alimentary ridge networks (easily visible in Cambrian trilobites) might have been either digestive or respiratory tubes in the cephalon and other regions.
Trilobite exoskeletons show a variety of small-scale structures collectively called prosopon. Prosopon does not include large scale extensions of the cuticle (e.g. hollow pleural spines) but to finer scale features, such as ribbing, domes, pustules, pitting, ridging and perforations. The exact purpose of the prosopon is not resolved but suggestions include structural strengthening, sensory pits or hairs, preventing predator attacks and maintaining aeration while enrolled. In one example, alimentary ridge networks (easily visible in Cambrian trilobites) might have been either digestive or respiratory tubes in the cephalon and other regions.
 Only 21 or so species are described from which soft body parts are preserved, so some features (e.g. the posterior antenniform cerci preserved only in '' Olenoides serratus'') remain difficult to assess in the wider picture.
Only 21 or so species are described from which soft body parts are preserved, so some features (e.g. the posterior antenniform cerci preserved only in '' Olenoides serratus'') remain difficult to assess in the wider picture.
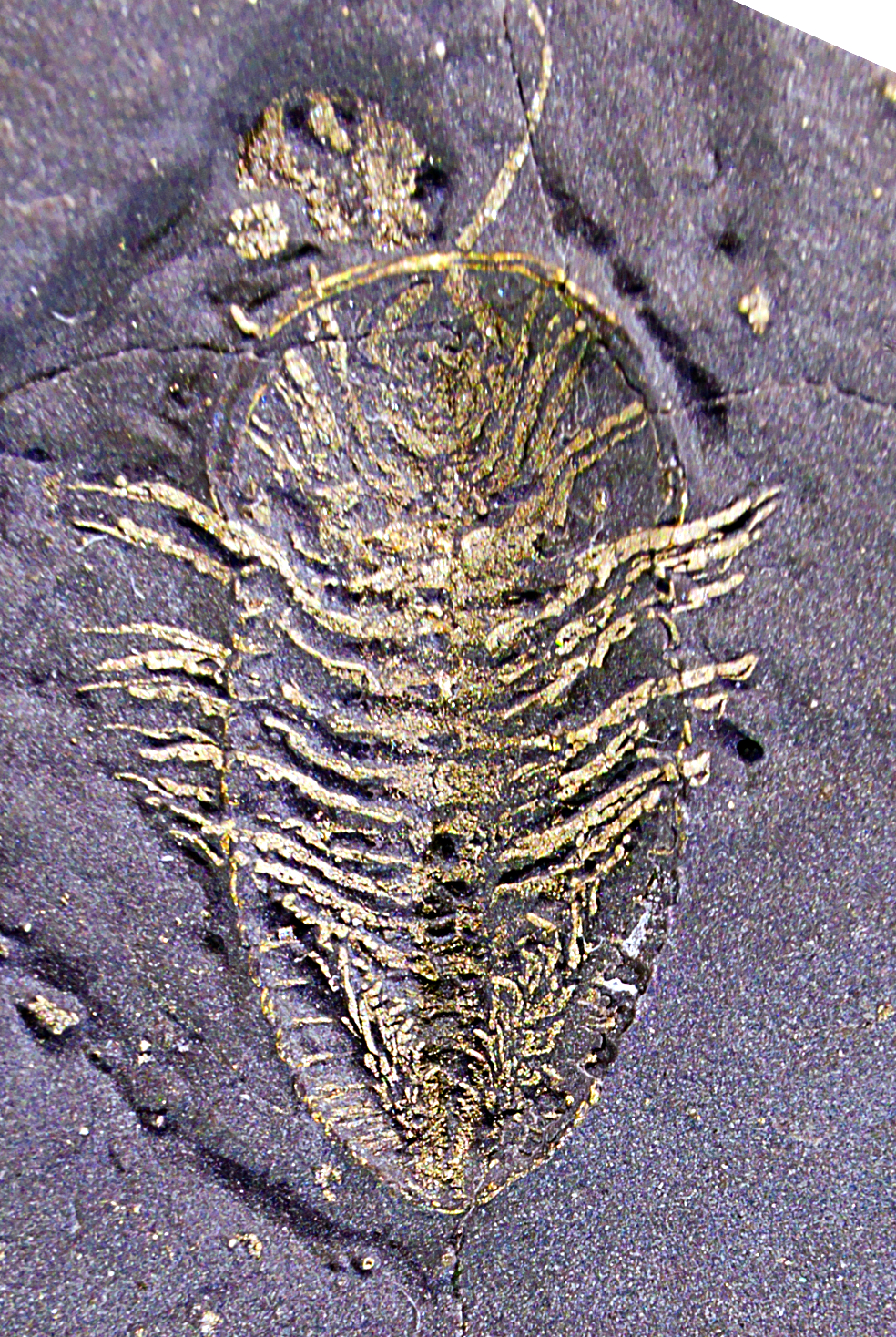
 Trilobites had a single pair of preoral antennae and otherwise undifferentiated
Trilobites had a single pair of preoral antennae and otherwise undifferentiated
 The pair of antennae suspected in most trilobites (and preserved in a few examples) were highly flexible to allow them to be retracted when the trilobite was enrolled. One species ('' Olenoides serratus'') preserves antenna-like cerci, which project from the rear of the trilobite.
The pair of antennae suspected in most trilobites (and preserved in a few examples) were highly flexible to allow them to be retracted when the trilobite was enrolled. One species ('' Olenoides serratus'') preserves antenna-like cerci, which project from the rear of the trilobite.
 Even the earliest trilobites had complex, compound eyes with lenses made of calcite (a characteristic of all trilobite eyes), confirming that the eyes of arthropods and probably other animals could have developed before the Cambrian. Improving eyesight of both predator and prey in marine environments has been suggested as one of the
Even the earliest trilobites had complex, compound eyes with lenses made of calcite (a characteristic of all trilobite eyes), confirming that the eyes of arthropods and probably other animals could have developed before the Cambrian. Improving eyesight of both predator and prey in marine environments has been suggested as one of the  * Schizochroal eyes typically had fewer (around 700), larger lenses than holochroal eyes and are found only in
* Schizochroal eyes typically had fewer (around 700), larger lenses than holochroal eyes and are found only in
 There are several types of prosopon that have been suggested as sensory apparatus collecting chemical or vibrational signals. The connection between large pitted fringes on the cephalon of
There are several types of prosopon that have been suggested as sensory apparatus collecting chemical or vibrational signals. The connection between large pitted fringes on the cephalon of
 Trilobites grew through successive
Trilobites grew through successive  Trilobite larvae are known from the Cambrian to the Carboniferous and from all sub-orders. As instars from closely related taxa are more similar than instars from distantly related taxa, trilobite larvae provide morphological information important in evaluating high-level phylogenetic relationships among trilobites.
Despite the absence of supporting fossil evidence, their similarity to living arthropods has led to the belief that trilobites multiplied sexually and produced eggs.
Some species may have kept eggs or larvae in a brood pouch forward of the glabella, particularly when the
Trilobite larvae are known from the Cambrian to the Carboniferous and from all sub-orders. As instars from closely related taxa are more similar than instars from distantly related taxa, trilobite larvae provide morphological information important in evaluating high-level phylogenetic relationships among trilobites.
Despite the absence of supporting fossil evidence, their similarity to living arthropods has led to the belief that trilobites multiplied sexually and produced eggs.
Some species may have kept eggs or larvae in a brood pouch forward of the glabella, particularly when the
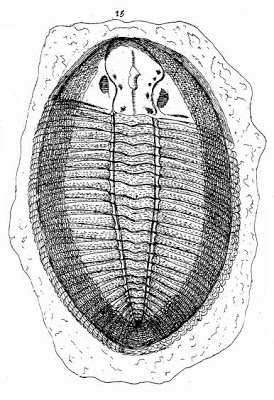 Rev. Edward Lhwyd published in 1698 in The ''
Rev. Edward Lhwyd published in 1698 in The ''
The Virtual Fossil Museum – Class Trilobita
– including extensive photographs organized by taxonomy and locality.
Western Trilobites Association
– a collection of photographs of trilobite fossils
The Paleontological Society
*
American Museum of Natural History Trilobite websiteA nice, copyrighted photo of a trilobite
{{Authority control Cambrian first appearances Lopingian extinctions Artiopoda
extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
marine arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s that form the class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differently ...
Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the Atdabanian
Cambrian Stage 3 is the still unnamed third stage of the Cambrian. It succeeds Cambrian Stage 2 and precedes Cambrian Stage 4, although neither its base nor top have been formally defined. The plan is for its lower boundary to correspond approxim ...
stage
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* Sta ...
of the Early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
() and they flourished throughout the lower Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ...
before slipping into a long decline, when, during the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
, all trilobite orders except the Proetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
died out. The last extant trilobites finally disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
about 252 million years ago. Trilobites were among the most successful of all early animals, existing in oceans for almost 270 million years, with over 22,000 species having been described.
By the time trilobites first appeared in the fossil record, they were already highly diversified and geographically dispersed. Because trilobites had wide diversity and an easily fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
ized exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
, they left an extensive fossil record. The study of their fossils has facilitated important contributions to biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of ...
, paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
, evolutionary biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life ...
, and plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label= Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of larg ...
. Trilobites are often placed within the arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
subphylum Schizoramia within the superclass Arachnomorpha
Arachnomorpha is a proposed subdivision or clade of Arthropoda, comprising the group formed by the trilobites and their close relatives (Artiopoda), Megacheira (which may be paraphyletic) and chelicerates. Under this proposed classification sch ...
(equivalent to the Arachnata), although several alternative taxonomies are found in the literature. More recently they have been placed within the Artiopoda
The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997 to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Tril ...
, which includes many organisms that are morphologically similar to trilobites, but are largely unmineralised.
Trilobites evolved into many ecological niches; some moved over the seabed as predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
s, scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feedin ...
s, or filter feeder
Filter feeders are a sub-group of suspension feeding animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water, typically by passing the water over a specialized filtering structure. Some animals that use this method of feedin ...
s, and some swam, feeding on plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cruc ...
. Some even crawled onto land. Most lifestyles expected of modern marine arthropods are seen in trilobites, with the possible exception of parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
(where scientific debate continues). Some trilobites (particularly the family Olenidae) are even thought to have evolved a symbiotic
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or para ...
relationship with sulfur-eating bacteria from which they derived food. The largest trilobites were more than long and may have weighed as much as .
Evolution
Trilobite relatives
Trilobites belong to theArtiopoda
The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997 to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Tril ...
, a group of extinct arthropods
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chitin, ...
generally morphologically similar to trilobites, but aside from trilobites lacking mineralised exoskeletons. Because of their lack of mineralised exoskeletons, non-trilobite artipodans are typically only found in exceptionally preserved deposits, mostly during the Cambrian period. The exact relationships of artiopods to other arthropods is uncertain. They have been considered closely related to chelicerates (which include horseshoe crabs
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to arac ...
and arachnids
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegar ...
) as part of a clade called Arachnomorpha
Arachnomorpha is a proposed subdivision or clade of Arthropoda, comprising the group formed by the trilobites and their close relatives (Artiopoda), Megacheira (which may be paraphyletic) and chelicerates. Under this proposed classification sch ...
, while others consider them to be more closely related to Mandibulata
Mandibulata, termed "mandibulates", is a clade of arthropods that comprises the extant subphyla Myriapoda (millipedes and others), Crustacea and Hexapoda (insects and others). Mandibulata is currently believed to be the sister group of the clade ...
(which contains insects
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs of j ...
, crustaceans
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean g ...
and myriapods
Myriapods () are the members of subphylum Myriapoda, containing arthropods such as millipedes and centipedes. The group contains about 13,000 species, all of them terrestrial.
The fossil record of myriapods reaches back into the late Silurian, ...
) as part of a clade called Antennulata.
Fossil record of early trilobites


 The earliest trilobites known from the
The earliest trilobites known from the fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
are redlichiids and ptychopariid bigotinids dated to around 520 million years ago. Contenders for the earliest trilobites include ''Profallotaspis jakutensis'' (Siberia), ''Fritzaspis'' spp. (western USA), ''Hupetina antiqua'' (Morocco) and ''Serrania gordaensis'' (Spain). All trilobites are thought to have originated in present-day Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
, with subsequent distribution and radiation from this location.
All Olenellina lack facial sutures (see below
Below may refer to:
*Earth
*Ground (disambiguation)
*Soil
*Floor
*Bottom (disambiguation)
*Less than
*Temperatures below freezing
*Hell or underworld
People with the surname
*Ernst von Below (1863–1955), German World War I general
*Fred Below ( ...
), and this is thought to represent the original state. The earliest sutured trilobite found so far ('' Lemdadella''), occurs almost at the same time as the earliest Olenellina, suggesting the trilobites origin lies before the start of the Atdabanian, but without leaving fossils. Other groups show secondary lost facial sutures, such as all Agnostina and some Phacopina
The Phacopina comprise a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida. Species belonging to the Phacopina lived from the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian) through the end of the Upper Devonian (Famennian).Moore, R.C. (ed.). Treatise on Invertebrate Pal ...
. Another common feature of the Olenellina also suggests this suborder to be the ancestral trilobite stock: early protaspid stages have not been found, supposedly because these were not calcified, and this also is supposed to represent the original state. Earlier trilobites may be found and could shed more light on the origin of trilobites.
Three specimens of a trilobite from Morocco, ''Megistaspis hammondi'', dated 478 million years old contain fossilized soft parts.
Divergence and extinction
 Trilobites saw incredible diversification over time. For such a long-lasting group of animals, it is no surprise that trilobite evolutionary history is marked by a number of extinction events where some groups perished and surviving groups diversified to fill ecological niches with comparable or unique adaptations. Generally, trilobites maintained high diversity levels throughout the
Trilobites saw incredible diversification over time. For such a long-lasting group of animals, it is no surprise that trilobite evolutionary history is marked by a number of extinction events where some groups perished and surviving groups diversified to fill ecological niches with comparable or unique adaptations. Generally, trilobites maintained high diversity levels throughout the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
and Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
periods before entering a drawn-out decline in the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
, culminating in the final extinction of the last few survivors at the end of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
period.
Evolutionary trends
Principal evolutionary trends from primitive morphologies, such as exemplified by ''Eoredlichia
''Eoredlichia'' is an extinct genus of trilobite of average to large size (up to long, or when including the spine on the ninth thorax segment pointing horizontally to the back, that itself equals the main body length). It lived during the ...
'', include the origin of new types of eyes, improvement of enrollment and articulation mechanisms, increased size of pygidium (micropygy to isopygy), and development of extreme spinosity in certain groups. Changes also included narrowing of the thorax and increasing or decreasing numbers of thoracic segments. Specific changes to the cephalon are also noted; variable glabella size and shape, position of eyes and facial sutures, and hypostome specialization. Several morphologies appeared independently within different major taxa (e.g. eye reduction or miniaturization).
Effacement, the loss of surface detail in the cephalon, pygidium, or the thoracic furrows, is also a common evolutionary trend. Notable examples of this were the order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
s Agnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
and Asaphida
Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies (Anomocaroidea, Asaphoidea, Cyclopygoidea, D ...
, and the suborder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
Illaenina of the Corynexochida
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
The middle region of the cephalon (the ...
. Effacement is believed to be an indication of either a burrowing lifestyle or a pelagic one. Effacement poses a problem for taxonomist
In biology, taxonomy () is the scientific study of naming, defining ( circumscribing) and classifying groups of biological organisms based on shared characteristics. Organisms are grouped into taxa (singular: taxon) and these groups are give ...
s since the loss of details (particularly of the glabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior t ...
) can make the determination of phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
relationships difficult.
Pre-Cambrian
Phylogenetic
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups ...
biogeographic
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
analysis of Early Cambrian Olenellidae and Redlichiidae suggests that a uniform trilobite fauna existed over Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
, Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
, and Siberia before the tectonic breakup of the supercontinent Pannotia
Pannotia (from Greek: '' pan-'', "all", '' -nótos'', "south"; meaning "all southern land"), also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontine ...
between 600 and . Tectonic breakup of Pannotia then allowed for the diversification and radiation expressed later in the Cambrian as the distinctive Olenellid province (Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
, Siberia, and Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, ...
) and the separate Redlichid province (Australia, Antarctica, and China).
Breakup of Pannotia significantly antedates the first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record, supporting a long and cryptic development of trilobites extending perhaps as far back as or possibly further back in time.
Cambrian
Very shortly after trilobite fossils appeared in the lower Cambrian, they rapidly diversified into the major orders that typified the Cambrian— Redlichiida,Ptychopariida
Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian ...
, Agnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
, and Corynexochida
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
The middle region of the cephalon (the ...
. The first major crisis in the trilobite fossil record occurred in the Middle Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
; surviving orders developed isopygius or macropygius bodies and developed thicker cuticles, allowing better defense against predators (see Thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the c ...
below). The end-Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
mass extinction event marked a major change in trilobite fauna; almost all Redlichiida (including the Olenelloidea) and most Late Cambrian stocks became extinct. A continuing decrease in Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
n continental shelf area is recorded at the same time as the extinctions, suggesting major environmental upheaval.
Notable trilobite genera appearing in the Cambrian include:
*'' Abadiella'' (Lower Cambrian)
*''Buenellus
''Buenellus higginsi'' is an average size (about ) trilobite, which lived during the Lower Cambrian period, in what is now North-West Greenland. It is a prominent member of the Sirius Passet fauna. ''Buenellus higginsi'' is the only known specie ...
'' (Lower Cambrian)
*'' Judomia'' (Lower Cambrian)
*''Olenellus
''Olenellus'' is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites, with species of average size (about long). It lived during the Botomian and Toyonian stages (''Olenellus''-zone), , in what is currently North-America, part of the palaeocontinent Lau ...
'' (Lower Cambrian)
*'' Ellipsocephalus'' (Middle Cambrian)
*''Elrathia
''Elrathia'' is a genus of trilobite belonging to Ptychopariacea known from the mid-Cambrian of Laurentia (North America). ''E. kingii'' is one of the most common trilobite fossils in the USA locally found in extremely high concentrations withi ...
'' (Middle Cambrian)
*''Paradoxides
''Paradoxides'' is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of ''Paradoxides davidis'', described by John William Salter in 1863, is . The cephalon was ...
'' (Middle Cambrian)
*''Peronopsis
''Peronopsis'' (meaning "broach-like" or possibly "boot-like") is a genus of trilobite restricted to the Middle Cambrian. Its remains have been found in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.
Etymology
The subgenus ''Svenax'' is a contra ...
'' (Middle Cambrian)
*'' Xiuqiella'' (Middle Cambrian)
*'' Yiliangella'' (Middle Cambrian)
*'' Yiliangellina'' (Middle Cambrian)
*''Olenus
In Greek mythology, Olenus (; Ancient Greek: Ὤλενος ''Olenos'') was the name of several individuals:
*Olenus, son of Hephaestus and father of Helike and Aex, two nurses of infant Zeus. A city in Aulis was named for him.
*Olenus, son of Ze ...
'' (Late Cambrian)
Ordovician

 The Early
The Early Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
is marked by vigorous radiations of articulate brachiopods, bryozoans, bivalves, echinoderms, and graptolites, with many groups appearing in the fossil record for the first time. Although intra-species trilobite diversity seems to have peaked during the Cambrian, trilobites were still active participants in the Ordovician radiation event, with a new fauna taking over from the old Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
one. Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
and Trinucleioidea are characteristic forms, highly differentiated and diverse, most with uncertain ancestors. The Phacopida and other "new" clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English ter ...
s almost certainly had Cambrian forebearers, but the fact that they have avoided detection is a strong indication that novel morphologies were developing very rapidly. Changes within the trilobite fauna during the Ordovician foreshadowed the mass extinction at the end of the Ordovician, allowing many families to continue into the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleoz ...
with little disturbance.
Ordovician trilobites were successful at exploiting new environments, notably reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes—deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock ...
s. The Ordovician mass extinction did not leave the trilobites unscathed; some distinctive and previously successful forms such as the Telephinidae
Telephinidae is a family of pelagic trilobites with large wide-angle eyes, occupying most of the free cheeks, downward directed facial spines and 9-10 thorax segments. The family is known during the entire Ordovician and occurred in deep water ar ...
and Agnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
became extinct. The Ordovician marks the last great diversification period amongst the trilobites: very few entirely new patterns of organisation arose post-Ordovician. Later evolution in trilobites was largely a matter of variations upon the Ordovician themes. By the Ordovician mass extinction, vigorous trilobite radiation has stopped and gradual decline is foreshadowed.
Some of the genera of Trilobites appearing in the Ordovician include:
*'' Cyclopyge'' (Early to Late Ordovician)
*'' Selenopeltis'' (Early to Late Ordovician)
*'' Parabolina'' (Early Ordovician)
*''Cheirurus
''Cheirurus'' (from Greek ''χείρ, cheir'' meaning "hand" and ''ουρά, oura'' meaning "tail") is a genus of phacopid trilobites that lived from the Ordovician to the Devonian. Its remains have been found in Africa, Asia, Australia, Euro ...
'' (Middle Ordovician)
*'' Eodalmanitina ''(Middle Ordovician)
*'' Trinucleus'' (Middle Ordovician)
*'' Triarthrus'' (Late Ordovician)
Silurian and Devonian
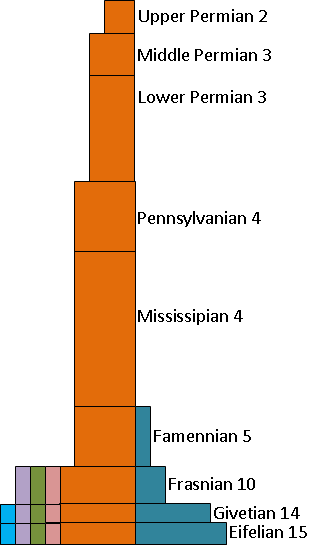
 Most Early Silurian families constitute a subgroup of the Late Ordovician fauna. Few, if any, of the dominant Early Ordovician fauna survived to the end of the Ordovician, yet 74% of the dominant Late Ordovician trilobite fauna survived the Ordovician. Late Ordovician survivors account for all post-Ordovician trilobite groups except the
Most Early Silurian families constitute a subgroup of the Late Ordovician fauna. Few, if any, of the dominant Early Ordovician fauna survived to the end of the Ordovician, yet 74% of the dominant Late Ordovician trilobite fauna survived the Ordovician. Late Ordovician survivors account for all post-Ordovician trilobite groups except the Harpetida
Harpetida is one of the eleven orders of the extinct arthropod class Trilobita. The first harpetid trilobites appear in the Upper Cambrian, and the last species die out at the end of the Devonian period.
Harpetid trilobites are characterized am ...
.
Silurian and Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
trilobite assemblages are superficially similar to Ordovician assemblages, dominated by Lichida
Lichida is an order of typically spiny trilobite that lived from the Furongian to the Devonian period. These trilobites usually have 8–13 thoracic segments. Their exoskeletons often have a grainy texture or have wart or spine-like tubercles. So ...
and Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
(including the well-known Calymenina
Calymenina is a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three relate ...
). A number of characteristic forms do not extend far into the Devonian and almost all the remainder were wiped out by a series of dramatic Middle and Late Devonian extinction
The Late Devonian extinction consisted of several extinction events in the Late Devonian Epoch, which collectively represent one of the five largest mass extinction events in the history of life on Earth. The term primarily refers to a major ex ...
s. Three orders and all but five families were exterminated by the combination of sea level changes and a break in the redox equilibrium (a meteorite impact has also been suggested as a cause). Only a single order, the Proetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
, survived into the Carboniferous.
Genera of trilobites during the Silurian and Devonian periods include:
*'' Dalmanites'' (Early to Late Silurian)
*'' Calymene'' (Silurian)
*''Encrinurus
''Encrinurus'' is a long-lived genus of phacopid trilobites that lived in what are now Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North America, and South America from the middle Ordovician to the early Devonian from 472 to 412.3 mya, existing for appr ...
'' (Silurian)
*'' Exallaspis'' (Middle to Late Silurian)
*''Paralejurus
''Paralejurus'' is a genus of trilobite from the Late Silurian to the Middle Devonian of Africa and Europe.
Features
These animals, up to nine centimeters long, had an oval outline and a strongly arched exoskeleton. The cephalon has a smooth, ...
'' (Early Devonian)
*'' Lioharpes'' (Middle Devonian)
*''Phacops
''Phacops'' is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, that lived in Europe, northwestern Africa, North and South America and China from the Late Ordovician until the very end of the Devonian, with a broader time range ...
'' (Middle to Late Devonian)
Carboniferous and Permian
TheProetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
survived for millions of years, continued through the Carboniferous period and lasted until the end of the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleo ...
(when the vast majority of species on Earth were wiped out). It is unknown why the order Proetida alone survived the Devonian. The Proetida maintained relatively diverse faunas in both deep and shallow water shelf environments throughout the Carboniferous. For many millions of years the Proetida existed untroubled in their ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
. An analogy would be today's crinoid
Crinoids are marine animals that make up the class Crinoidea. Crinoids that are attached to the sea bottom by a stalk in their adult form are commonly called sea lilies, while the unstalked forms are called feather stars or comatulids, which are ...
s, which mostly exist as deep water species; in the Paleozoic era, vast 'forests' of crinoids lived in shallow near-shore environments.
Some of the genera of trilobites during the Carboniferous and Permian periods include:
*'' Archegonus ''(Early to Middle Carboniferous)
*'' Hesslerides'' (Middle Carboniferous)
*''Endops
''Endops yanagisawai'' is a proetid trilobite belonging to the family Proetidae, endemic to Middle Permian-aged marine strata in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country i ...
'' (Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/ epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± ...
)
*'' Triproetus'' (Late Carboniferous to Early Permian)
*'' Ditomopyge ''(Late Carboniferous to Late Permian)
Final extinction
Exactly why the trilobites became extinct is not clear; with repeated extinction events (often followed by apparent recovery) throughout the trilobite fossil record, a combination of causes is likely. After the extinction event at the end of the Devonian period, what trilobite diversity remained was bottlenecked into the order Proetida. Decreasing diversity of genera limited to shallow-water shelf habitats coupled with a drastic lowering of sea level ( regression) meant that the final decline of trilobites happened shortly before the end of the Permian mass extinction event. With so many marine species involved in the Permian extinction, the end of nearly 300 million successful years for the trilobites would not have been unexpected at the time. Trilobites have no known direct descendants. Their closest living relatives would be the chelicerates due to both being arachnomorphs. Thoughhorseshoe crabs
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to arac ...
are often cited as their closest living relatives, they are no closer evolutionarily than other chelicerates.
Fossil distribution



 Trilobites appear to have been primarily marine organisms, since the fossilized remains of trilobites are always found in rocks containing fossils of other salt-water animals such as brachiopods, crinoids, and corals. Some trackways suggest trilobites made at least temporary excursions unto land. Within the marine paleoenvironment, trilobites were found in a broad range from extremely shallow water to very deep water. Trilobites, like brachiopods, crinoids, and corals, are found on all modern continents, and occupied every ancient ocean from which Paleozoic fossils have been collected. The remnants of trilobites can range from the preserved body to pieces of the exoskeleton, which it shed in the process known as ecdysis. In addition, the tracks left behind by trilobites living on the sea floor are often preserved as
Trilobites appear to have been primarily marine organisms, since the fossilized remains of trilobites are always found in rocks containing fossils of other salt-water animals such as brachiopods, crinoids, and corals. Some trackways suggest trilobites made at least temporary excursions unto land. Within the marine paleoenvironment, trilobites were found in a broad range from extremely shallow water to very deep water. Trilobites, like brachiopods, crinoids, and corals, are found on all modern continents, and occupied every ancient ocean from which Paleozoic fossils have been collected. The remnants of trilobites can range from the preserved body to pieces of the exoskeleton, which it shed in the process known as ecdysis. In addition, the tracks left behind by trilobites living on the sea floor are often preserved as trace fossil
A trace fossil, also known as an ichnofossil (; from el, ἴχνος ''ikhnos'' "trace, track"), is a fossil record of biological activity but not the preserved remains of the plant or animal itself. Trace fossils contrast with body fossils, ...
s.
There are three main forms of trace fossils associated with trilobites: ''Rusophycus'', ''Cruziana'' and ''Diplichnites''—such trace fossils represent the preserved life activity of trilobites active upon the sea floor. '' Rusophycus'', the resting trace, are trilobite excavations involving little or no forward movement and ethological interpretations suggest resting, protection and hunting. ''Cruziana
''Cruziana'' is a trace fossil consisting of elongate, bilobed, approximately bilaterally symmetrical burrows, usually preserved along bedding planes, with a sculpture of repeated striations that are mostly oblique to the long dimension. It is fo ...
'', the feeding trace, are furrows through the sediment, which are believed to represent the movement of trilobites while deposit feeding. Many of the '' Diplichnites'' fossils are believed to be traces made by trilobites walking on the sediment surface. Care must be taken as similar trace fossils are recorded in freshwater and post-Paleozoic deposits, representing non-trilobite origins.
Trilobite fossils are found worldwide, with thousands of known species. Because they appeared quickly in geological time, and moulted like other arthropods, trilobites serve as excellent index fossils
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Bio ...
, enabling geologists to date the age of the rocks in which they are found. They were among the first fossils to attract widespread attention, and new species are being discovered every year.
 In the United States, the best open-to-the-public collection of trilobites is located in
In the United States, the best open-to-the-public collection of trilobites is located in Hamburg, New York
Hamburg is a town in Erie County, New York, United States. As of the 2010 census, the town had a population of 56,936. It is named after the city of Hamburg, Germany. The town is on the western border of the county and is south of Buffalo. Ham ...
. The shale quarry, informally known as Penn Dixie, stopped mining in the 1960s. The large amounts of trilobites were discovered in the 1970s by Dan Cooper. As a well-known rock collector, he incited scientific and public interest in the location. The fossils are dated to the Givetian
The Givetian is one of two faunal stages in the Middle Devonian Period. It lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Eifelian Stage and followed by the Frasnian
The Frasnian is one of two faunal stages in the ...
(387.2 - 382.7 million years ago) when the Western New York Region was 30 degrees south of the equator and completely covered in water. The site was purchased from Vincent C. Bonerb by the Town of Hamburg with the cooperation of the Hamburg Natural History Society to protect the land from development. In 1994, the quarry became Penn Dixie Fossil Park & Nature Reserve when they received 501(c)3 status and was opened for visitation and collection of trilobite samples. The two most common found samples are ‘’Eldredgeops rana'' and ''Greenops''.
A famous location for trilobite fossils in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
is Wren's Nest
The Wren's Nest is a geological Site of Special Scientific Interest in the Dudley Metropolitan Borough, north west of the town centre of Dudley, in the West Midlands of England. It is one of the most important geological locations in Britai ...
, Dudley
Dudley is a large market town and administrative centre in the county of West Midlands, England, southeast of Wolverhampton and northwest of Birmingham. Historically an exclave of Worcestershire, the town is the administrative centre of the ...
, in the West Midlands, where '' Calymene blumenbachii'' is found in the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleoz ...
Wenlock Group. This trilobite is featured on the town's coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
and was named the ''Dudley Bug'' or ''Dudley Locust'' by quarrymen who once worked the now abandoned limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
quarries. Llandrindod Wells
Llandrindod Wells (, ; cy, Llandrindod, /ɬanˈdɾindɔd/ "Trinity Parish"), sometimes known colloquially as Llandod, is a town and community in Powys, within the historic boundaries of Radnorshire, Wales. It serves as the seat of Powy ...
, Powys
Powys (; ) is a county and preserved county in Wales. It is named after the Kingdom of Powys which was a Welsh successor state, petty kingdom and principality that emerged during the Middle Ages following the end of Roman rule in Britain.
Geog ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, is another famous trilobite location. The well-known '' Elrathia kingi'' trilobite is found in abundance in the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
Wheeler Shale
The Wheeler Shale (named by Charles Walcott) is a Cambrian ( 507 Ma) fossil locality world-famous
for prolific agnostid and '' Elrathia kingii'' trilobite remains (even though many areas are barren of fossils)
and represents a Konzen ...
of Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
.
Spectacularly preserved trilobite fossils, often showing soft body parts (legs, gills, antennae, etc.) have been found in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Canada (the Cambrian Burgess Shale
The Burgess Shale is a fossil-bearing deposit exposed in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia, Canada. It is famous for the exceptional preservation of the soft parts of its fossils. At old (middle Cambrian), it is one of the earliest fo ...
and similar localities); New York, U.S.A. (Ordovician Walcott–Rust quarry, near Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, and Beecher's Trilobite Bed
Beecher's Trilobite Bed is a Konservat-Lagerstätte of Late Ordovician (Caradoc) age located within the Frankfort Shale in Cleveland's Glen, Oneida County, New York, USA.Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
); China (Lower Cambrian Maotianshan Shales
The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their '' Konservat Lagerstätten'', deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales ...
near Chengjiang
Chengjiang (; earlier Tchinkiang) is a city located in Yuxi, Yunnan Province, China, just north of Fuxian Lake.
Administrative divisions
Chengjiang City has 2 subdistricts and 4 townships.
;2 subdistricts
* Fenglu ()
* Longjie ()
;4 towns
C ...
); Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
(the Devonian Hunsrück Slates near Bundenbach
Bundenbach is an '' Ortsgemeinde'' – a municipality belonging to a ''Verbandsgemeinde'', a kind of collective municipality – in the Birkenfeld district of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' Herrstein-Rhau ...
) and, much more rarely, in trilobite-bearing strata in Utah (Wheeler Shale and other formations), Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, and Manuels River, Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
.
Sites in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
also yield very well-preserved trilobites, many buried in mudslides alive and so perfectly preserved. An industry has developed around their recovery, leading to controversies about practices in restoral. The variety of eye and upper body forms and fragile protuberances is best known from these samples preserved similarly to bodies in Pompeii.
The French palaeontologist Joachim Barrande
Joachim Barrande (11 August 1799 – 5 October 1883) was a French geologist and palaeontologist.
Career
Barrande was born at Saugues, Haute Loire, and educated in the École Polytechnique and École Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées at Paris. A ...
(1799–1883) carried out his landmark study of trilobites in the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian of Bohemia, publishing the first volume of ''Système silurien du centre de la Bohême'' in 1852.
Importance
The study of Paleozoic trilobites in the Welsh-English borders byNiles Eldredge
Niles Eldredge (; born August 25, 1943) is an American biologist and paleontologist, who, along with Stephen Jay Gould, proposed the theory of punctuated equilibrium in 1972.
Education
Eldredge began his undergraduate studies in Latin at Columb ...
was fundamental in formulating and testing punctuated equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolutionary change for most of i ...
as a mechanism of evolution. Reprinted in
Identification of the 'Atlantic' and 'Pacific' trilobite faunas in North America and Europe implied the closure of the Iapetus Ocean (producing the Iapetus suture), thus providing important supporting evidence for the theory of continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pl ...
.
Trilobites have been important in estimating the rate of speciation during the period known as the Cambrian explosion because they are the most diverse group of metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in ...
known from the fossil record of the early Cambrian.
Trilobites are excellent stratigraphic markers of the Cambrian period: researchers who find trilobites with alimentary prosopon, and a micropygium, have found Early Cambrian strata. Most of the Cambrian stratigraphy is based on the use of trilobite marker fossils.
Trilobites are the state fossils of Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The sta ...
('' Isotelus''), Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
('' Calymene celebra'') and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
('' Phacops rana'').
Taxonomy
The 10 most commonly recognized trilobite orders areAgnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
, Redlichiida, Corynexochida
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
The middle region of the cephalon (the ...
, Lichida
Lichida is an order of typically spiny trilobite that lived from the Furongian to the Devonian period. These trilobites usually have 8–13 thoracic segments. Their exoskeletons often have a grainy texture or have wart or spine-like tubercles. So ...
, Odontopleurida, Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
, Proetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
, Asaphida
Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies (Anomocaroidea, Asaphoidea, Cyclopygoidea, D ...
, Harpetida
Harpetida is one of the eleven orders of the extinct arthropod class Trilobita. The first harpetid trilobites appear in the Upper Cambrian, and the last species die out at the end of the Devonian period.
Harpetid trilobites are characterized am ...
and Ptychopariida
Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian ...
. In 2020, an 11th order, Trinucleida, was proposed to be elevated out of the asaphid superfamily Trinucleioidea. Sometimes the Nektaspida
Nektaspida (also called Naraoiida, Nektaspia and Nectaspida) is an extinct order of non- mineralised artiopodan arthropods. They are known from the mid-Cambrian to the upper Silurian. Originally classified as trilobites, which they superficially ...
are considered trilobites, but these lack a calcified exoskeleton and eyes. Some scholars have proposed that the order Agnostida is polyphyletic, with the suborder Agnostina representing non-trilobite arthropods unrelated to the suborder Eodiscina
Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period (late Atdabanian) and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. ...
. Under this hypothesis, Eodiscina would be elevated to a new order, Eodiscida.
Over 20,000 species of trilobite have been described.
Despite their rich fossil record with thousands of described genera found throughout the world, the taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
and phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
of trilobites have many uncertainties. Except possibly for the members of the orders Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
and Lichida (which first appear during the early Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
), nine of the eleven trilobite order
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
s appear prior to the end of the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
. Most scientists believe that order Redlichiida, more specifically its suborder Redlichiina
Redlichiina is a suborder of the order Redlichiida of Trilobites. The suborder contains three superfamilies: Emuelloidea, Redlichioidea and Paradoxidoidea. These trilobites are some of the oldest trilobites known. They originated at the begin ...
, contains a common ancestor of all other orders, with the possible exception of the Agnostina. While many potential phylogenies are found in the literature, most have suborder Redlichiina giving rise to orders Corynexochida
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
The middle region of the cephalon (the ...
and Ptychopariida
Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian ...
during the Lower Cambrian, and the Lichida
Lichida is an order of typically spiny trilobite that lived from the Furongian to the Devonian period. These trilobites usually have 8–13 thoracic segments. Their exoskeletons often have a grainy texture or have wart or spine-like tubercles. So ...
descending from either the Redlichiida or Corynexochida in the Middle Cambrian. Order Ptychopariida
Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian ...
is the most problematic order for trilobite classification. In the 1959 Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology
The ''Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology'' (or ''TIP'') published by the Geological Society of America and the University of Kansas Press, is a definitive multi-authored work of some 50 volumes, written by more than 300 paleontologists, and co ...
, what are now members of orders Ptychopariida, Asaphida
Asaphida is a large, morphologically diverse order of trilobites found in marine strata dated from the Middle Cambrian until their extinction during the Silurian. Asaphida contains six superfamilies (Anomocaroidea, Asaphoidea, Cyclopygoidea, D ...
, Proetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
and Harpetida
Harpetida is one of the eleven orders of the extinct arthropod class Trilobita. The first harpetid trilobites appear in the Upper Cambrian, and the last species die out at the end of the Devonian period.
Harpetid trilobites are characterized am ...
were grouped together as order Ptychopariida; subclass Librostoma was erected in 1990 to encompass all of these orders, based on their shared ancestral character of a natant (unattached) hypostome. The most recently recognized of the nine trilobite orders, Harpetida, was erected in 2002. The progenitor of order Phacopida is unclear.
Relationship to other taxa
Once soft-part anatomy had been recovered, the trilobites were originally allied to the Crustacea. A relationship with the Chelicerata, in a clade termedArachnomorpha
Arachnomorpha is a proposed subdivision or clade of Arthropoda, comprising the group formed by the trilobites and their close relatives (Artiopoda), Megacheira (which may be paraphyletic) and chelicerates. Under this proposed classification sch ...
(Arachnata), was in vogue for some time, but, a more recent analysis of Panarthropoda suggests the trilobites are one of two major branches of Artiopoda
The Artiopoda is a grouping of extinct arthropods that includes trilobites and their close relatives. It was erected by Hou and Bergström in 1997 to encompass a wide diversity of arthropods that would traditionally have been assigned to the Tril ...
.
Morphology
When trilobites are found, only the exoskeleton is preserved (often in an incomplete state) in all but a handful of locations. A few locations (') preserve identifiable soft body parts (legs, gills, musculature & digestive tract) and enigmatic traces of other structures (e.g. fine details of eye structure) as well as the exoskeleton. Trilobites range in length from minute (less than ) to very large (over ), with an average size range of . Supposedly the smallest species is '' Acanthopleurella stipulae'' with a maximum of . The world's largest-known trilobite specimen, assigned to '' Isotelus rex'' is in length. It was found in 1998 by Canadian scientists in Ordovician rocks on the shores of Hudson Bay. However, a partial specimen of the Ordovician trilobite '' Hungioides bohemicus'' found in 2009 in Arouca, Portugal is estimated to have measured when complete in length.exoskeleton
An exoskeleton (from Greek ''éxō'' "outer" and ''skeletós'' "skeleton") is an external skeleton that supports and protects an animal's body, in contrast to an internal skeleton ( endoskeleton) in for example, a human. In usage, some of the ...
is composed of calcite and calcium phosphate minerals in a lattice of chitin that covers the upper surface (dorsal) of the trilobite and curled round the lower edge to produce a small fringe called the "doublure".Three distinctive '' tagmata'' (sections) are present: cephalon (head); thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
(body) and pygidium
The pygidium (plural pygidia) is the posterior body part or shield of crustaceans and some other arthropods, such as insects and the extinct trilobites. In groups other than insects, it contains the anus and, in females, the ovipositor. It is compo ...
(tail).
Terminology
As might be expected for a group of animals comprising genera, themorphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
and description of trilobites can be complex. Despite morphological complexity and an unclear position within higher classifications, there are a number of characteristics which distinguish the trilobites from other arthropods: a generally sub-elliptical, dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal c ...
, chitinous exoskeleton divided longitudinally into three distinct lobes (from which the group gets its name); having a distinct, relatively large head shield (cephalon) articulating axially with a thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
comprising articulated transverse segments, the hindmost of which are almost invariably fused to form a tail shield (pygidium
The pygidium (plural pygidia) is the posterior body part or shield of crustaceans and some other arthropods, such as insects and the extinct trilobites. In groups other than insects, it contains the anus and, in females, the ovipositor. It is compo ...
). When describing differences between trilobite taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
, the presence, size, and shape of the cephalic
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals m ...
features are often mentioned.
During moulting, the exoskeleton generally splits between the head and thorax, which is why so many trilobite fossils are missing one or the other. In most groups facial sutures on the cephalon helped facilitate moulting. Similar to lobsters and crabs, trilobites would have physically "grown" between the moult stage and the hardening of the new exoskeleton.
Cephalon
A trilobite's cephalon, or head section, is highly variable with a lot of morphological complexity. Theglabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to ...
forms a dome underneath which sat the "crop" or "stomach". Generally the exoskeleton has few distinguishing ventral features, but the cephalon often preserves muscle attachment scars and occasionally the hypostome, a small rigid plate comparable to the ventral plate in other arthropods. A toothless mouth and stomach sat upon the hypostome with the mouth facing backward at the rear edge of the hypostome.
Hypostome morphology is highly variable; sometimes supported by an un-mineralised membrane (natant), sometimes fused onto the anterior doublure with an outline very similar to the glabella above (conterminant) or fused to the anterior doublure with an outline significantly different from the glabella (impendent). Many variations in shape and placement of the hypostome have been described. The size of the glabella and the lateral fringe of the cephalon, together with hypostome variation, have been linked to different lifestyles, diets and specific ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
s.
The anterior and lateral fringe of the cephalon is greatly enlarged in the Harpetida
Harpetida is one of the eleven orders of the extinct arthropod class Trilobita. The first harpetid trilobites appear in the Upper Cambrian, and the last species die out at the end of the Devonian period.
Harpetid trilobites are characterized am ...
, in other species a bulge in the pre-glabellar area is preserved that suggests a brood pouch. Highly complex compound eyes are another obvious feature of the cephalon.
Facial sutures
Facial or cephalic sutures are the natural fracture lines in the cephalon of trilobites. Their function was to assist the trilobite in shedding its old exoskeleton during ecdysis (or molting). All species assigned to thesuborder
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and ...
Olenellina, that became extinct at the very end of the Early Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million years ago ...
(like '' Fallotaspis'', '' Nevadia'', '' Judomia'', and ''Olenellus
''Olenellus'' is an extinct genus of redlichiid trilobites, with species of average size (about long). It lived during the Botomian and Toyonian stages (''Olenellus''-zone), , in what is currently North-America, part of the palaeocontinent Lau ...
'') lacked facial sutures. They are believed to have never developed facial sutures, having pre-dated their evolution. Because of this (along with other primitive characteristics), they are thought to be the earliest ancestors of later trilobites.
Some other later trilobites also lost facial sutures secondarily. The type of sutures found in different species are used extensively in the taxonomy
Taxonomy is the practice and science of categorization or classification.
A taxonomy (or taxonomical classification) is a scheme of classification, especially a hierarchical classification, in which things are organized into groups or types. ...
and phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spe ...
of trilobites.
=Dorsal sutures
= The dorsal surface of the trilobite cephalon (the frontmost tagma, or the 'head') can be divided into two regions—thecranidium
''Cranidium''Westwood (1843) ''The Arcana Museum of Nature'' 2: 49. is an monotypic genus of stick insects
The Phasmatodea (also known as Phasmida, Phasmatoptera or Spectra) are an order of insects whose members are variously known as stic ...
and the librigena ("free cheeks"). The cranidium can be further divided into the glabella
The glabella, in humans, is the area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose. The term also refers to the underlying bone that is slightly depressed, and joins the two brow ridges. It is a cephalometric landmark that is just superior to ...
(the central lobe in the cephalon) and the fixigena ("fixed cheeks"). The facial sutures lie along the anterior edge, at the division between the cranidium and the librigena.
Trilobite facial sutures on the dorsal side can be roughly divided into five main types according to where the sutures end relative to the gena
Gena (Amharic: ገና) or qarsa (ቃርሳ) is a traditional field hockey game popular in the Ethiopian highlands. It is a game played in the space between villages but with no defined boundaries. It is played among two teams who attempt to throw ...
l angle (the edges where the side and rear margins of the cephalon converge).
*Absent – Facial sutures are lacking in the Olenellina. This is considered a primitive state, and is always combined with the presence of eyes.
*Proparian – The facial suture ends in front of the genal angle, along the lateral margin. Example genera showing this type of suture include '' Dalmanites'' of Phacopina
The Phacopina comprise a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida. Species belonging to the Phacopina lived from the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian) through the end of the Upper Devonian (Famennian).Moore, R.C. (ed.). Treatise on Invertebrate Pal ...
(Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
) and '' Ekwipagetia'' of Eodiscina
Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period (late Atdabanian) and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. ...
(Agnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
).
*Gonatoparian – The facial suture ends at the tip of the genal angle. Example genera showing this type of suture include '' Calymene'' and '' Trimerus'' of Calymenina
Calymenina is a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three relate ...
(Phacopida
Phacopida ("lens-face") is an order of trilobites that lived from the Late Cambrian to the Late Devonian. It is made up of a morphologically diverse assemblage of taxa in three related suborders.
Characteristics
Phacopida had 8 to 19 thoraci ...
).
*Opisthoparian – The facial suture ends at the posterior margin of the cephalon. Example genera showing this type of suture include ''Peltura
''Peltura'' is a genus of trilobites from the Upper Cambrian. The type specimen of ''Peltura scarabaeoides'', the type species of the genus, was discovered in the Alum Shale Formation of Sweden and described by the Swedish naturalist Göran Wah ...
'' of Olenina (Ptychopariida
Ptychopariida is a large, heterogeneous order of trilobite containing some of the most primitive species known. The earliest species occurred in the second half of the Lower Cambrian, and the last species did not survive the Ordovician–Silurian ...
) and '' Bumastus'' of Illaenina (Corynexochida
Corynexochida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Late Devonian. Like many of the other trilobite orders, Corynexochida contains many species with widespread characteristics.
The middle region of the cephalon (the ...
). This is the most common type of facial suture.
* Hypoparian or marginal – In some trilobites, dorsal sutures may be secondarily lost. Several exemplary time series of species show the "migration" of the dorsal suture until it coincides with the margins of the cephalon. As the visual surface of the eye is on the diminishing free cheek (or librigena), the number of lenses tends to go down, and eventually the eye disappears. The loss of dorsal sutures may arise from the proparian state, such as in some Eodiscina
Eodiscina is trilobite suborder. The Eodiscina first developed near the end of the Lower Cambrian period (late Atdabanian) and became extinct at the end of the Middle Cambrian. Species are tiny to small, and have a thorax of two or three segments. ...
like '' Weymouthia'', all Agnostina, and some Phacopina
The Phacopina comprise a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida. Species belonging to the Phacopina lived from the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian) through the end of the Upper Devonian (Famennian).Moore, R.C. (ed.). Treatise on Invertebrate Pal ...
such as '' Ductina''. The marginal sutures exhibited by the harpetids and trinucleioids, are derived from opisthoparian sutures. On the other hand, blindness is not always accompanied by the loss of facial sutures.
 The primitive state of the dorsal sutures is proparian. Opisthoparian sutures have developed several times independently. There are no examples of proparian sutures developing in
The primitive state of the dorsal sutures is proparian. Opisthoparian sutures have developed several times independently. There are no examples of proparian sutures developing in taxa
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular nam ...
with opisthoparian ancestry. Trilobites that exhibit opisthoparian sutures as adults commonly have proparian sutures as instars (known exceptions being '' Yunnanocephalus'' and '' Duyunaspis''). Hypoparian sutures have also arisen independently in several groups of trilobites.
The course of the facial sutures from the front of the visual surface varies at least as strongly as it does in the rear, but the lack of a clear reference point similar to the genal angle makes it difficult to categorize. One of the more pronounced states is that the front of the facial sutures do not cut the lateral or frontal border on its own, but coincide in front of the glabella, and cut the frontal border at the midline. This is, inter alia, the case in the Asaphida. Even more pronounced is the situation that the frontal branches of the facial sutures end in each other, resulting in yoked free cheeks. This is known in '' Triarthrus'', and in the Phacopidae, but in that family the facial sutures are not functional, as can be concluded from the fact that free cheeks are not found separated from the cranidium.
There are also two types of sutures in the dorsal surface connected to the compound eye
A compound eye is a visual organ found in arthropods such as insects and crustaceans. It may consist of thousands of ommatidia, which are tiny independent photoreception units that consist of a cornea, lens, and photoreceptor cells which disti ...
s of trilobites. They are:
*Ocular sutures – are sutures surrounding the edges of the compound eye. Trilobites with these sutures lose the entire surface of the eyes when molting. It is common among Cambrian trilobites.
*Palpebral sutures – are sutures which form part of the dorsal facial suture running along the top edges of the compound eye.
=Ventral sutures
= Dorsal facial sutures continue downward to the ventral side of the cephalon where they become the Connective sutures that divide the doublure. The following are the types of ventral sutures.
*Connective sutures – are the sutures that continue from the facial sutures past the front margin of the cephalon.
*Rostral suture – is only present when the trilobite possesses a rostrum (or rostral plate). It connects the rostrum to the front part of the dorsal cranidium.
*Hypostomal suture – separates the hypostome from the doublure when the hypostome is of the attached type. It is absent when the hypostome is free-floating (i.e. natant). it is also absent in some coterminant hypostomes where the hypostome is fused to the doublure.
*Median suture – exhibited by asaphid trilobites, they are formed when instead of becoming connective sutures, the two dorsal sutures converge at a point in front of the cephalon then divide straight down the center of the doublure.
Dorsal facial sutures continue downward to the ventral side of the cephalon where they become the Connective sutures that divide the doublure. The following are the types of ventral sutures.
*Connective sutures – are the sutures that continue from the facial sutures past the front margin of the cephalon.
*Rostral suture – is only present when the trilobite possesses a rostrum (or rostral plate). It connects the rostrum to the front part of the dorsal cranidium.
*Hypostomal suture – separates the hypostome from the doublure when the hypostome is of the attached type. It is absent when the hypostome is free-floating (i.e. natant). it is also absent in some coterminant hypostomes where the hypostome is fused to the doublure.
*Median suture – exhibited by asaphid trilobites, they are formed when instead of becoming connective sutures, the two dorsal sutures converge at a point in front of the cephalon then divide straight down the center of the doublure.
Rostrum
The rostrum (or the rostral plate) is a distinct part of the doublure located at the front of the cephalon. It is separated from the rest of the doublure by the rostral suture. During molting in trilobites like ''Paradoxides
''Paradoxides'' is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of ''Paradoxides davidis'', described by John William Salter in 1863, is . The cephalon was ...
'', the rostrum is used to anchor the front part of the trilobite as the cranidium separates from the librigena. The opening created by the arching of the body provides an exit for the molting trilobite.
It is absent in some trilobites like ''Lachnostoma
''Lachnostoma'' is an extinct genus from a well-known class of fossil marine arthropods, the trilobites. It lived during the early part of the Arenig stage of the Ordovician Period, a faunal stage
In chronostratigraphy, a stage is a successi ...
''.
Hypostome
 The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of the trilobite found on the ventral side of the cephalon typically below the glabella. The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella.
* Natant – Hypostome not attached to doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Conterminant – Hypostome attached to rostral plate of doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Impendent – Hypostome attached to rostral plate but not aligned to glabella.
The hypostome is the hard mouthpart of the trilobite found on the ventral side of the cephalon typically below the glabella. The hypostome can be classified into three types based on whether they are permanently attached to the rostrum or not and whether they are aligned to the anterior dorsal tip of the glabella.
* Natant – Hypostome not attached to doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Conterminant – Hypostome attached to rostral plate of doublure. Aligned with front edge of glabella.
* Impendent – Hypostome attached to rostral plate but not aligned to glabella.
Thorax
The thorax is a series of articulated segments that lie between the cephalon and pygidium. The number of segments varies between 2 and 103 with most species in the 2 to 16 range. Each segment consists of the central axial ring and the outer pleurae, which protected the limbs and gills. The pleurae are sometimes abbreviated or extended to form long spines. Apodemes are bulbous projections on the ventral surface of the exoskeleton to which most leg muscles attached, although some leg muscles attached directly to the exoskeleton. Determining a junction between thorax and pygidium can be difficult and many segment counts suffer from this problem.Volvation
volvation
Volvation (from Latin ''volvere'' "roll", and the suffix ''-(a)tion''; sometimes called enrollment or conglobation), is a defensive behavior in certain animals, in which the animal rolls its own body into a ball, presenting only the hardest parts ...
") helped protect against the inherent weakness of the arthropod cuticle
The cuticle forms the major part of the integument of the Arthropoda. It includes most of the material of the exoskeleton of the insects, Crustacea, Arachnida, and Myriapoda.
Morphology
In arthropods, the integument, the external "skin", or ...
that was exploited by anomalocarid predators.
Some trilobites achieved a fully closed capsule (e.g. ''Phacops
''Phacops'' is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, that lived in Europe, northwestern Africa, North and South America and China from the Late Ordovician until the very end of the Devonian, with a broader time range ...
''), while others with long pleural spines (e.g. '' Selenopeltis'') left a gap at the sides or those with a small pygidium (e.g. ''Paradoxides
''Paradoxides'' is a genus of large to very large trilobite found throughout the world during the Middle Cambrian period. One record-breaking specimen of ''Paradoxides davidis'', described by John William Salter in 1863, is . The cephalon was ...
'') left a gap between the cephalon and pygidium. In ''Phacops'', the pleurae overlap a smooth bevel (facet) allowing a close seal with the doublure. The doublure carries a Panderian notch or protuberance on each segment to prevent over rotation and achieve a good seal. Even in an agnostid, with only 2 articulating thoracic segments, the process of enrollment required a complex musculature to contract the exoskeleton and return to the flat condition.
Pygidium
The pygidium is formed from a number of segments and thetelson
The telson () is the posterior-most division of the body of an arthropod. Depending on the definition, the telson is either considered to be the final segment of the arthropod body, or an additional division that is not a true segment on accou ...
fused together. Segments in the pygidium are similar to the thoracic segments (bearing biramous limbs) but are not articulated. Trilobites can be described based on the pygidium being micropygous (pygidium smaller than cephalon), subisopygous (pygidium sub equal to cephalon), isopygous (pygidium equal in size to cephalon), or macropygous (pygidium larger than cephalon).
Prosopon (surface sculpture)
 Trilobite exoskeletons show a variety of small-scale structures collectively called prosopon. Prosopon does not include large scale extensions of the cuticle (e.g. hollow pleural spines) but to finer scale features, such as ribbing, domes, pustules, pitting, ridging and perforations. The exact purpose of the prosopon is not resolved but suggestions include structural strengthening, sensory pits or hairs, preventing predator attacks and maintaining aeration while enrolled. In one example, alimentary ridge networks (easily visible in Cambrian trilobites) might have been either digestive or respiratory tubes in the cephalon and other regions.
Trilobite exoskeletons show a variety of small-scale structures collectively called prosopon. Prosopon does not include large scale extensions of the cuticle (e.g. hollow pleural spines) but to finer scale features, such as ribbing, domes, pustules, pitting, ridging and perforations. The exact purpose of the prosopon is not resolved but suggestions include structural strengthening, sensory pits or hairs, preventing predator attacks and maintaining aeration while enrolled. In one example, alimentary ridge networks (easily visible in Cambrian trilobites) might have been either digestive or respiratory tubes in the cephalon and other regions.
Spines
Some trilobites such as those of the orderLichida
Lichida is an order of typically spiny trilobite that lived from the Furongian to the Devonian period. These trilobites usually have 8–13 thoracic segments. Their exoskeletons often have a grainy texture or have wart or spine-like tubercles. So ...
evolved elaborate spiny forms, from the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start of the Silurian Period Mya.
T ...
until the end of the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
period. Examples of these specimens have been found in the Hamar Laghdad Formation of Alnif in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
. There is a serious counterfeiting and fakery problem with much of the Moroccan material that is offered commercially. Spectacular spined trilobites have also been found in western Russia; Oklahoma, USA; and Ontario, Canada.
Some trilobites had horns on their heads similar to several modern beetles. Based on the size, location, and shape of the horns it has been suggested that these horns may have been used to combat for mates. Horns were widespread in the Raphiophoridae
Raphiophoridae is a family of small to average-sized trilobites that first occurred at the start of the Ordovician and became extinct at the end of the Middle Silurian.
Anatomy
All raphiophorids are blind, with headshields (or cephalons) tha ...
family (Asaphida).
Another function of these spines was protection from predators. When enrolled, trilobite spines offered additional protection.
This conclusion is likely to be applicable to other trilobites as well, such as in the Phacopid trilobite genus '' Walliserops,'' that developed spectacular tridents.
Soft body parts
 Only 21 or so species are described from which soft body parts are preserved, so some features (e.g. the posterior antenniform cerci preserved only in '' Olenoides serratus'') remain difficult to assess in the wider picture.
Only 21 or so species are described from which soft body parts are preserved, so some features (e.g. the posterior antenniform cerci preserved only in '' Olenoides serratus'') remain difficult to assess in the wider picture.
Appendages

 Trilobites had a single pair of preoral antennae and otherwise undifferentiated
Trilobites had a single pair of preoral antennae and otherwise undifferentiated biramous The arthropod leg is a form of jointed appendage of arthropods, usually used for walking. Many of the terms used for arthropod leg segments (called podomeres) are of Latin origin, and may be confused with terms for bones: ''coxa'' (meaning hip, plu ...
limbs (2, 3 or 4 cephalic pairs, followed by one pair per thoracic segment and some pygidium pairs). Each endopodite (walking leg) had 6 or 7 segments, homologous to other early arthropods. Endopodites are attached to the coxa, which also bore a feather-like exopodite, or gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
branch, which was used for respiration and, in some species, swimming. A 2021 study found that the upper limb branch of trilobites is a "well-developed gill" that oxygenates the hemolymph
Hemolymph, or haemolymph, is a fluid, analogous to the blood in vertebrates, that circulates in the interior of the arthropod (invertebrate) body, remaining in direct contact with the animal's tissues. It is composed of a fluid plasma in which ...
, comparable to the book gill in modern horseshoe crab ''Limulus
''Limulus'' is a genus of horseshoe crab, with one extant species, the Atlantic horseshoe crab (''Limulus polyphemus''). One fossil species is currently assigned to the genus though several other species have been named, which have since been as ...
''. In '' Olenoides'', the partially articulated junction with the body is distinct from the exopods of Chelicerata
The subphylum Chelicerata (from New Latin, , ) constitutes one of the major subdivisions of the phylum Arthropoda. It contains the sea spiders, horseshoe crabs, and arachnids (including harvestmen, scorpions, spiders, solifuges, ticks, and mi ...
or Crustacea. The inside of the coxa (or gnathobase) carries spines, probably to process prey items. The last exopodite segment usually had claws or spines. Many examples of hairs on the legs suggest adaptations for feeding (as for the gnathobases) or sensory organs to help with walking.
Digestive tract
The toothless mouth of trilobites was situated on the rear edge of the hypostome (facing backward), in front of the legs attached to the cephalon. The mouth is linked by a small esophagus to the stomach that lay forward of the mouth, below the glabella. The "intestine" led backward from there to the pygidium. The "feeding limbs" attached to the cephalon are thought to have fed food into the mouth, possibly "slicing" the food on the hypostome and/or gnathobases first. Alternative lifestyles are suggested, with the cephalic legs used to disturb the sediment to make food available. A large glabella, (implying a large stomach), coupled with an impendent hypostome has been used as evidence of more complex food sources, i.e. possibly a carnivorous lifestyle.Internal organs
While there is direct and implied evidence for the presence and location of the mouth, stomach and digestive tract (see above) the presence of heart, brain and liver are only implied (although "present" in many reconstructions) with little direct geological evidence.Musculature
Although rarely preserved, long lateral muscles extended from the cephalon to midway down the pygidium, attaching to the axial rings allowing enrollment while separate muscles on the legs tucked them out of the way.Sensory organs
Many trilobites had complex eyes; they also had a pair of antennae. Some trilobites were blind, probably living too deep in the sea for light to reach them. As such, they became secondarily blind in this branch of trilobite evolution. Other trilobites (e.g., '' Phacops rana'' and '' Erbenochile erbeni'') had large eyes that were for use in well lit, predator-filled waters.Antennae
 The pair of antennae suspected in most trilobites (and preserved in a few examples) were highly flexible to allow them to be retracted when the trilobite was enrolled. One species ('' Olenoides serratus'') preserves antenna-like cerci, which project from the rear of the trilobite.
The pair of antennae suspected in most trilobites (and preserved in a few examples) were highly flexible to allow them to be retracted when the trilobite was enrolled. One species ('' Olenoides serratus'') preserves antenna-like cerci, which project from the rear of the trilobite.
Eyes
 Even the earliest trilobites had complex, compound eyes with lenses made of calcite (a characteristic of all trilobite eyes), confirming that the eyes of arthropods and probably other animals could have developed before the Cambrian. Improving eyesight of both predator and prey in marine environments has been suggested as one of the
Even the earliest trilobites had complex, compound eyes with lenses made of calcite (a characteristic of all trilobite eyes), confirming that the eyes of arthropods and probably other animals could have developed before the Cambrian. Improving eyesight of both predator and prey in marine environments has been suggested as one of the evolutionary pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
s furthering an apparent rapid development of new life forms during what is known as the Cambrian explosion.
Trilobite eyes were typically compound
Compound may refer to:
Architecture and built environments
* Compound (enclosure), a cluster of buildings having a shared purpose, usually inside a fence or wall
** Compound (fortification), a version of the above fortified with defensive struc ...
, with each lens being an elongated prism. The number of lenses in such an eye varied: some trilobites had only one, while some had thousands of lenses in a single eye. In compound eyes, the lenses were typically arranged hexagonally. The fossil record of trilobite eyes is complete enough that their evolution can be studied through time, which compensates to some extent for the lack of preservation of soft internal parts.
Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
es of trilobites' eyes
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
were made of calcite ( calcium carbonate, CaCO3). Pure forms of calcite are transparent, and some trilobites used crystallographically oriented, clear calcite crystals to form each lens of each eye. Rigid calcite lenses would have been unable to accommodate to a change of focus like the soft lens in a human eye would; in some trilobites, the calcite formed an internal doublet structure, giving superb depth of field and minimal spherical aberration, according to optical principles discovered by French scientist René Descartes
René Descartes ( or ; ; Latinized: Renatus Cartesius; 31 March 1596 – 11 February 1650) was a French philosopher, scientist, and mathematician, widely considered a seminal figure in the emergence of modern philosophy and science. Ma ...
and Dutch physicist Christiaan Huygens in the 17th century. A living species with similar lenses is the brittle star
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomot ...
''Ophiocoma wendtii
''Ophiomastix wendtii'', also known by its common name, the red ophiocoma, and formerly as ''Ophiocoma wendtii'', is a species of brittle stars that inhabits coral reefs from Bermuda to Brazil, primarily in the Caribbean sea. club-like spines al ...
''.
In other trilobites, with a Huygens interface apparently missing, a gradient-index lens is invoked with the refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium.
The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or ...
of the lens changing toward the center.
Sublensar sensory structures have been found in the eyes of some phacopid trilobites. The structures consist of what appear to be several sensory cells surrounding a rhadomeric structure, resembling closely the sublensar structures found in the eyes of many modern arthropod apposition eye
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
s, especially ''Limulus
''Limulus'' is a genus of horseshoe crab, with one extant species, the Atlantic horseshoe crab (''Limulus polyphemus''). One fossil species is currently assigned to the genus though several other species have been named, which have since been as ...
'', a genus of horseshoe crabs.
*Holochroal eye
Holochroal eyes are compound eyes with many tiny lenses (sometimes more than 15,000, each 30-100μm, rarely larger). They are the oldest and most common type of trilobite eye, and found in all orders of trilobite from the Cambrian to the Permian ...
s had a great number (sometimes over 15,000) of small (30–100 μm, rarely larger) lenses. Lenses were hexagonally close packed, touching each other, with a single corneal membrane covering all lenses. Each lens was in direct contact with adjacent lenses. Holochroal eyes are the ancestral eye of trilobites, and are by far the most common, found in all orders except the Agnostida, and through the entirety of the Trilobites' existence. Little is known of the early history of holochroal eyes; Lower and Middle Cambrian trilobites rarely preserve the visual surface. The spatial resolving power of grated eyes (such as holochroal eyes) is dependent on light intensity, circular motion, receptor density, registered light angle, and the extent to which the signal of individual rhabdoms are neurally combined. This implies that lenses need to be larger under low light conditions (such as for '' Pricyclopyge'', when comparing it to '' Carolinites''), and for fast moving predators and prey. As the circular velocity caused by the forward speed of an animal itself is much higher for the ommatidia directed perpendicular to the movement, fast-moving trilobites (such as ''Carolinites'') have eyes flattened from the side and more curved were ommatia are directed to the front or back. Thus eye morphology can be used to make assumptions about the ecosystem of trilobites.Phacopina
The Phacopina comprise a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida. Species belonging to the Phacopina lived from the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian) through the end of the Upper Devonian (Famennian).Moore, R.C. (ed.). Treatise on Invertebrate Pal ...
. Each lens had a cornea, and adjacent lenses were separated by thick interlensar cuticle, known as sclera. Schizochroal eyes appear quite suddenly in the early Ordovician, and were presumably derived from a holochroal ancestor. Field of view (all-around vision), eye placement and coincidental development of more efficient enrollment mechanisms point to the eye as a more defensive "early warning" system than directly aiding in the hunt for food. Modern eyes that are functionally equivalent to the schizochroal eye were not thought to exist, but are found in the modern insect species '' Xenos peckii''.
*Abathochroal eyes are found only in Cambrian Eodiscina, and have around 70 small separate lenses that had individual cornea. The sclera was separate from the cornea, and was not as thick as the sclera in schizochroal eyes. Although well preserved examples are sparse in the early fossil record, abathochroal eyes have been recorded in the lower Cambrian, making them among the oldest known. Environmental conditions seem to have resulted in the later loss of visual organs in many Eodiscina.
Secondary blindness is not uncommon, particularly in long lived groups such as the Agnostida
Agnostida is an order of arthropod which have classically been seen as a group of highly modified trilobites, though some recent research has doubted this placement. Regardless, they appear to be close relatives as part of the Artiopoda. They ar ...
and Trinucleioidea. In Proetida
Proetida is an order of trilobite that lived from the Ordovician to the Permian. It was the last order of trilobite to go extinct, finally dying out in the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
Description
These typically small trilobites resem ...
and Phacopina
The Phacopina comprise a suborder of the trilobite order Phacopida. Species belonging to the Phacopina lived from the Lower Ordovician (Tremadocian) through the end of the Upper Devonian (Famennian).Moore, R.C. (ed.). Treatise on Invertebrate Pal ...
from western Europe and particularly Tropidocoryphinae from France (where there is good stratigraphic control), there are well studied trends showing progressive eye reduction between closely related species that eventually leads to blindness.
Several other structures on trilobites have been explained as photo-receptors. Of particular interest are "macula", the small areas of thinned cuticle on the underside of the hypostome. In some trilobites macula are suggested to function as simple "ventral eyes" that could have detected night and day or allowed a trilobite to navigate while swimming (or turned) upside down.
Sensory pits
Harpetida
Harpetida is one of the eleven orders of the extinct arthropod class Trilobita. The first harpetid trilobites appear in the Upper Cambrian, and the last species die out at the end of the Devonian period.
Harpetid trilobites are characterized am ...
and Trinucleoidea with corresponding small or absent eyes makes for an interesting possibility of the fringe as a "compound ear".
Development
 Trilobites grew through successive
Trilobites grew through successive moult
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
stages called instar
An instar (, from the Latin '' īnstar'', "form", "likeness") is a developmental stage of arthropods, such as insects, between each moult (''ecdysis''), until sexual maturity is reached. Arthropods must shed the exoskeleton in order to grow or ...
s, in which existing segments increased in size and new trunk segments appeared at a sub-terminal generative zone during the anamorphic phase of development. This was followed by the epimorphic developmental phase, in which the animal continued to grow and moult, but no new trunk segments were expressed in the exoskeleton. The combination of anamorphic and epimorphic growth constitutes the hemianamorphic developmental mode that is common among many living arthropods.
Trilobite development was unusual in the way in which articulations developed between segments, and changes in the development of articulation gave rise to the conventionally recognized developmental phases of the trilobite life cycle (divided into 3 stages), which are not readily compared with those of other arthropods. Actual growth and change in external form of the trilobite would have occurred when the trilobite was soft shelled, following moulting and before the next exoskeleton hardened.
 Trilobite larvae are known from the Cambrian to the Carboniferous and from all sub-orders. As instars from closely related taxa are more similar than instars from distantly related taxa, trilobite larvae provide morphological information important in evaluating high-level phylogenetic relationships among trilobites.
Despite the absence of supporting fossil evidence, their similarity to living arthropods has led to the belief that trilobites multiplied sexually and produced eggs.
Some species may have kept eggs or larvae in a brood pouch forward of the glabella, particularly when the
Trilobite larvae are known from the Cambrian to the Carboniferous and from all sub-orders. As instars from closely related taxa are more similar than instars from distantly related taxa, trilobite larvae provide morphological information important in evaluating high-level phylogenetic relationships among trilobites.
Despite the absence of supporting fossil evidence, their similarity to living arthropods has led to the belief that trilobites multiplied sexually and produced eggs.
Some species may have kept eggs or larvae in a brood pouch forward of the glabella, particularly when the ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
was challenging to larvae. Size and morphology of the first calcified stage are highly variable between (but not within) trilobite taxa, suggesting some trilobites passed through more growth within the egg than others. Early developmental stages prior to calcification of the exoskeleton are a possibility (suggested for fallotaspids), but so is calcification and hatching coinciding.
The earliest post-embryonic trilobite growth stage known with certainty are the "protaspid" stages (anamorphic phase). Starting with an indistinguishable proto-cephalon and proto-pygidium (anaprotaspid) a number of changes occur ending with a transverse furrow separating the proto-cephalon and proto-pygidium (metaprotaspid) that can continue to add segments. Segments are added at the posterior part of the pygidium, but all segments remain fused together.
The "meraspid" stages (anamorphic phase) are marked by the appearance of an articulation between the head and the fused trunk. Prior to the onset of the first meraspid stage the animal had a two-part structure—the head and the plate of fused trunk segments, the pygidium. During the meraspid stages, new segments appeared near the rear of the pygidium as well as additional articulations developing at the front of the pygidium, releasing freely articulating segments into the thorax. Segments are generally added one per moult (although two per moult and one every alternate moult are also recorded), with number of stages equal to the number of thoracic segments. A substantial amount of growth, from less than 25% up to 30%–40%, probably took place in the meraspid stages.
The "holaspid" stages (epimorphic phase) commence when a stable, mature number of segments has been released into the thorax. Moulting continued during the holaspid stages, with no changes in thoracic segment number. Some trilobites are suggested to have continued moulting and growing throughout the life of the individual, albeit at a slower rate on reaching maturity.
Some trilobites showed a marked transition in morphology at one particular instar, which has been called "trilobite metamorphosis". Radical change in morphology is linked to the loss or gain of distinctive features that mark a change in mode of life. A change in lifestyle during development has significance in terms of evolutionary pressure
Any cause that reduces or increases reproductive success in a portion of a population potentially exerts evolutionary pressure, selective pressure or selection pressure, driving natural selection. It is a quantitative description of the amount of ...
, as the trilobite could pass through several ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
s on the way to adult development and changes would strongly affect survivorship and dispersal of trilobite taxa. It is worth noting that trilobites with all protaspid stages solely planktonic and later meraspid stages benthic (e.g. asaphids) failed to last through the Ordovician extinctions, while trilobites that were planktonic for only the first protaspid stage before metamorphosing into benthic forms survived (e.g. lichids, phacopids). Pelagic larval life-style proved ill-adapted to the rapid onset of global climatic cooling and loss of tropical shelf habitats during the Ordovician.
History of usage and research
 Rev. Edward Lhwyd published in 1698 in The ''
Rev. Edward Lhwyd published in 1698 in The ''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society
''Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society'' is a scientific journal published by the Royal Society. In its earliest days, it was a private venture of the Royal Society's secretary. It was established in 1665, making it the first journa ...
'', the oldest scientific journal in the English language, part of his letter "Concerning Several Regularly Figured Stones Lately Found by Him", that was accompanied by a page of etchings of fossils. One of his etchings depicted a trilobite he found near Llandeilo
Llandeilo () is a town and community in Carmarthenshire, Wales, situated at the crossing of the River Towy by the A483 on a 19th-century stone bridge. Its population was 1,795 at the 2011 Census. It is adjacent to the westernmost point of the ...
, probably on the grounds of Lord Dynefor's castle, he described as "… the skeleton of some flat Fish …".
The discovery of '' Calymene blumenbachii'' (the Dudley locust) in 1749 by Charles Lyttleton, could be identified as the beginning of trilobite research. Lyttleton submitted a letter to the Royal Society of London in 1750 concerning a "petrified insect" he found in the "limestone pits at Dudley". In 1754, Manuel Mendez da Costa proclaimed that the Dudley locust was not an insect, but instead belonged to "the crustaceous tribe of animals." He proposed to call the Dudley specimens ''Pediculus marinus major trilobos'' (large trilobed marine louse), a name which lasted well into the 1800s. German naturalist Johann Walch, who executed the first inclusive study of this group, proposed the use of the name "trilobite". He considered it appropriate to derive the name from the unique three-lobed character of the central axis and a pleural zone to each side.
Written descriptions of trilobites date possibly from the third century BC and definitely from the fourth century AD. The Spanish geologists Eladio Liñán and Rodolfo Gozalo argue that some of the fossils described in Greek and Latin lapidaries as scorpion stone, beetle stone, and ant stone, refer to trilobite fossils. Less ambiguous references to trilobite fossils can be found in Chinese sources. Fossils from the Kushan formation of northeastern China were prized as inkstones and decorative pieces.
In the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
, American fossil hunters found plentiful deposits of ''Elrathia kingi'' in western Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
in the 1860s. Until the early 1900s, the Ute Native Americans of Utah wore these trilobites, which they called ''pachavee'' (little water bug), as amulets. A hole was bored in the head and the fossil was worn on a string. According to the Ute themselves, trilobite necklaces protect against bullets and diseases such as diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacterium '' Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild clinical course, but in some outbreaks more than 10% of those diagnosed with the disease may die. Signs and s ...
. In 1931, Frank Beckwith uncovered evidence of the Ute use of trilobites. Travelling through the badlands, he photographed two petroglyphs that most likely represent trilobites. On the same trip he examined a burial, of unknown age, with a drilled trilobite fossil lying in the chest cavity of the interred. Since then, trilobite amulets have been found all over the Great Basin, as well as in British Columbia and Australia.
In the 1880s, archaeologists discovered in the Grotte du Trilobite ( Caves of Arcy-sur-Cure, Yonne
Yonne () is a department in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in France. It is named after the river Yonne, which flows through it, in the country's north-central part. One of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté's eight constituent departments, it is l ...
, France) a much-handled trilobite fossil that had been drilled as if to be worn as a pendant. The occupation stratum in which the trilobite was found has been dated as 15,000 years old. Because the pendant was handled so much, the species of trilobite cannot be determined. This type of trilobite is not found around Yonne, so it may have been highly prized and traded from elsewhere.
See also
*Notostraca
The order Notostraca, containing the single family Triopsidae, is a group of crustaceans known as tadpole shrimp or shield shrimp. The two genera, ''Triops'' and '' Lepidurus'', are considered living fossils, with similar forms having existed sinc ...
* Horseshoe crab
Horseshoe crabs are marine and brackish water arthropods of the family Limulidae and the only living members of the order Xiphosura. Despite their name, they are not true crabs or crustaceans: they are chelicerates, most closely related to ar ...
* Isopoda
* List of trilobite genera
*History of life
The history of life on Earth traces the processes by which living and fossil organisms evolved, from the earliest emergence of life to present day. Earth formed about 4.5 billion years ago (abbreviated as ''Ga'', for ''gigaannum'') and evide ...
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
*. (A site with information covering trilobites from all angles. Includes many line drawings and photographs.)The Virtual Fossil Museum – Class Trilobita
– including extensive photographs organized by taxonomy and locality.
Western Trilobites Association
– a collection of photographs of trilobite fossils
The Paleontological Society
*
{{Authority control Cambrian first appearances Lopingian extinctions Artiopoda