Traumatic brain injury on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an
 Systems also exist to classify TBI by its
Systems also exist to classify TBI by its
 Symptoms are dependent on the type of TBI (diffuse or focal) and the part of the brain that is affected. Unconsciousness tends to last longer for people with injuries on the left side of the brain than for those with injuries on the right. Symptoms are also dependent on the injury's severity. With mild TBI, the patient may remain conscious or may lose consciousness for a few seconds or minutes. Other symptoms of mild TBI include headache, vomiting, nausea, lack of
Symptoms are dependent on the type of TBI (diffuse or focal) and the part of the brain that is affected. Unconsciousness tends to last longer for people with injuries on the left side of the brain than for those with injuries on the right. Symptoms are also dependent on the injury's severity. With mild TBI, the patient may remain conscious or may lose consciousness for a few seconds or minutes. Other symptoms of mild TBI include headache, vomiting, nausea, lack of
 The type, direction, intensity, and duration of forces all contribute to the characteristics and severity TBI. Forces that may contribute to TBI include angular, rotational, shear, and translational forces.
Even in the absence of an impact, significant acceleration or deceleration of the head can cause TBI; however in most cases, a combination of impact and acceleration is probably to blame. Forces involving the head striking or being struck by something, termed ''contact'' or ''impact loading'', are the cause of most focal injuries, and movement of the brain within the skull, termed ''noncontact'' or ''inertial loading'', usually causes diffuse injuries. The violent shaking of an infant that causes shaken baby syndrome commonly manifests as diffuse injury. In impact loading, the force sends
The type, direction, intensity, and duration of forces all contribute to the characteristics and severity TBI. Forces that may contribute to TBI include angular, rotational, shear, and translational forces.
Even in the absence of an impact, significant acceleration or deceleration of the head can cause TBI; however in most cases, a combination of impact and acceleration is probably to blame. Forces involving the head striking or being struck by something, termed ''contact'' or ''impact loading'', are the cause of most focal injuries, and movement of the brain within the skull, termed ''noncontact'' or ''inertial loading'', usually causes diffuse injuries. The violent shaking of an infant that causes shaken baby syndrome commonly manifests as diffuse injury. In impact loading, the force sends
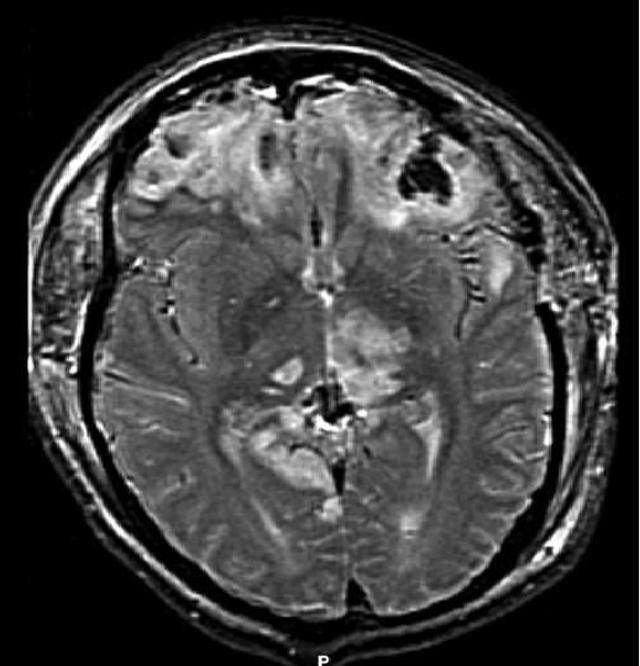 A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event; rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate. Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma. These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.
Secondary injury events include damage to the
A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event; rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate. Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma. These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.
Secondary injury events include damage to the
 Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score. Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give. DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available. Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.
Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score. Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give. DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available. Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.
 Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats and motorcycle helmets, and presence of roll bars and airbags. Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes. In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI. Due to the possibility that repeatedly "heading" a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed. Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk. Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as "spear tackling" in
Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats and motorcycle helmets, and presence of roll bars and airbags. Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes. In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI. Due to the possibility that repeatedly "heading" a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed. Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk. Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as "spear tackling" in
Accessed: May 1, 2009 People with moderate to severe injuries are likely to receive treatment in an
 Once medically stable, people may be transferred to a
Once medically stable, people may be transferred to a
 In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age. Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with
In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age. Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with
 To improve the gait pattern,
To improve the gait pattern,

 Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress. Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma,
Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress. Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma,
 TBI is a leading cause of death and disability around the globe and presents a major worldwide social, economic, and health problem. It is the number one cause of coma,. it plays the leading role in disability due to trauma, and is the leading cause of brain damage in children and young adults. In Europe it is responsible for more years of disability than any other cause. It also plays a significant role in half of trauma deaths.
Findings on the frequency of each level of severity vary based on the definitions and methods used in studies. A World Health Organization study estimated that between 70 and 90% of head injuries that receive treatment are mild, and a US study found that moderate and severe injuries each account for 10% of TBIs, with the rest mild.
The incidence of TBI varies by age, gender, region and other factors. Findings of incidence and prevalence in
TBI is a leading cause of death and disability around the globe and presents a major worldwide social, economic, and health problem. It is the number one cause of coma,. it plays the leading role in disability due to trauma, and is the leading cause of brain damage in children and young adults. In Europe it is responsible for more years of disability than any other cause. It also plays a significant role in half of trauma deaths.
Findings on the frequency of each level of severity vary based on the definitions and methods used in studies. A World Health Organization study estimated that between 70 and 90% of head injuries that receive treatment are mild, and a US study found that moderate and severe injuries each account for 10% of TBIs, with the rest mild.
The incidence of TBI varies by age, gender, region and other factors. Findings of incidence and prevalence in
 Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history. Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3 Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that
Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history. Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3 Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that  Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of
Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of
NINDS public domain pages on TBI
''
The Brain Injury Hub – information and practical advice to parents and family members of children with acquired brain injury
Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center – U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System center for traumatic brain injury
{{Good article Medical emergencies Intensive care medicine Neurotrauma Injuries of head Disorders causing seizures
injury
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, o ...
to the brain
A brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as Visual perception, vision. I ...
caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury
A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness (LOC); memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking, concentration, ...
TBI/concussionto severe traumatic brain injury), mechanism (closed
Closed may refer to:
Mathematics
* Closure (mathematics), a set, along with operations, for which applying those operations on members always results in a member of the set
* Closed set, a set which contains all its limit points
* Closed interval, ...
or penetrating head injury), or other features (e.g., occurring in a specific location or over a widespread area). Head injury is a broader category that may involve damage to other structures such as the scalp and skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
. TBI can result in physical, cognitive, social, emotional and behavioral symptoms, and outcomes can range from complete recovery to permanent disability
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, ...
or death.
Causes include falls, vehicle collisions and violence. Brain trauma occurs as a consequence of a sudden acceleration or deceleration within the cranium or by a complex combination of both movement and sudden impact. In addition to the damage caused at the moment of injury, a variety of events following the injury may result in further injury. These processes include alterations in cerebral blood flow
Cerebral circulation is the movement of blood through a network of cerebral arteries and veins supplying the brain. The rate of cerebral blood flow in an adult human is typically 750 milliliters per minute, or about 15% of cardiac output. A ...
and pressure within the skull. Some of the imaging techniques used for diagnosis include computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRIs).
Prevention measures include use of seat belts and helmets, not drinking and driving, fall prevention efforts in older adults and safety measures for children. Depending on the injury, treatment required may be minimal or may include interventions such as medications, emergency surgery or surgery years later. Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, pat ...
, speech therapy
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words (that is, all English words sound different from all French words, even if they are th ...
, recreation therapy, occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
and vision therapy may be employed for rehabilitation. Counseling
Counseling is the professional guidance of the individual by utilizing psychological methods especially in collecting case history data, using various techniques of the personal interview, and testing interests and aptitudes.
This is a list of co ...
, supported employment
Supported employment refers to service provisions wherein people with disabilities, including intellectual disabilities, mental health, and traumatic brain injury, among others, are assisted with obtaining and maintaining employment. Supported e ...
and community support services may also be useful.
TBI is a major cause of death and disability worldwide, especially in children and young adults. Males sustain traumatic brain injuries around twice as often as females. The 20th century saw developments in diagnosis and treatment that decreased death rates
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of ...
and improved outcomes.
Classification
Traumatic brain injury is defined as damage to the brain resulting from external mechanical force, such as rapid acceleration or deceleration, impact, blast waves, or penetration by a projectile. Brain function is temporarily or permanently impaired and structural damage may or may not be detectable with current technology. TBI is one of two subsets of acquired brain injury (brain damage that occur after birth); the other subset is non-traumatic brain injury, which does not involve external mechanicalforce
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a ...
(examples include stroke and infection). All traumatic brain injuries are head injuries, but the latter term may also refer to injury to other parts of the head. However, the terms ''head injury'' and ''brain injury'' are often used interchangeably. Similarly, brain injuries fall under the classification of central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
injuries LaPlaca et al. (2007). p. 16 and neurotrauma. In neuropsychology research literature, in general the term "traumatic brain injury" is used to refer to non-penetrating traumatic brain injuries.
TBI is usually classified based on severity, anatomical features of the injury, and the mechanism (the causative forces). Mechanism-related classification divides TBI into closed
Closed may refer to:
Mathematics
* Closure (mathematics), a set, along with operations, for which applying those operations on members always results in a member of the set
* Closed set, a set which contains all its limit points
* Closed interval, ...
and penetrating head injury. A closed (also called nonpenetrating, or blunt) injury occurs when the brain is not exposed. A penetrating, or open, head injury occurs when an object pierces the skull and breaches the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
, the outermost membrane surrounding the brain.
Severity
Brain injuries can be classified into mild, moderate, and severe categories. TheGlasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury.
The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These thr ...
(GCS), the most commonly used system for classifying TBI severity, grades a person's level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciou ...
on a scale of 3–15 based on verbal, motor, and eye-opening reactions to stimuli. Marion (1999). p. 4. In general, it is agreed that a TBI with a GCS of 13 or above is mild, 9–12 is moderate, and 8 or below is severe. Similar systems exist for young children. However, the GCS grading system has limited ability to predict outcomes. Because of this, other classification systems such as the one shown in the table are also used to help determine severity. A current model developed by the Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs uses all three criteria of GCS after resuscitation
Resuscitation is the process of correcting physiological disorders (such as lack of breathing or heartbeat) in an acutely ill patient. It is an important part of intensive care medicine, anesthesiology, trauma surgery and emergency medicine. ...
, duration of post-traumatic amnesia
Post-traumatic amnesia (PTA) is a state of confusion that occurs immediately following a traumatic brain injury (TBI) in which the injured person is disoriented and unable to remember events that occur after the injury.
The person may be unable ...
(PTA), and loss of consciousness
Loss may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''Loss'' (Bass Communion album) (2006)
* ''Loss'' (Mull Historical Society album) (2001)
*"Loss", a song by God Is an Astronaut from their self-titled album (2008)
* Losses "(Lil Tjay son ...
(LOC). It also has been proposed to use changes that are visible on neuroimaging
Neuroimaging is the use of quantitative (computational) techniques to study the structure and function of the central nervous system, developed as an objective way of scientifically studying the healthy human brain in a non-invasive manner. Incr ...
, such as swelling, focal lesions, or diffuse injury as method of classification. Grading scales also exist to classify the severity of mild TBI, commonly called concussion
A concussion, also known as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), is a head injury that temporarily affects brain functioning. Symptoms may include loss of consciousness (LOC); memory loss; headaches; difficulty with thinking, concentration ...
; these use duration of LOC, PTA, and other concussion symptoms.
Pathological features
 Systems also exist to classify TBI by its
Systems also exist to classify TBI by its pathological
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in th ...
features. Lesions can be extra-axial, (occurring within the skull but outside of the brain) or intra-axial (occurring within the brain tissue). Damage from TBI can be focal or diffuse, confined to specific areas or distributed in a more general manner, respectively. However, it is common for both types of injury to exist in a given case.
Diffuse injury manifests with little apparent damage in neuroimaging studies, but lesions can be seen with microscopy techniques post-mortem
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any d ...
, Granacher (2007). p. 32. and in the early 2000s, researchers discovered that diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), a way of processing MRI images that shows white matter tracts, was an effective tool for displaying the extent of diffuse axonal injury. Types of injuries considered diffuse include edema (swelling), concussion and diffuse axonal injury, which is widespread damage to axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
s including white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
tracts and projections to the cortex.
Focal injuries often produce symptoms related to the functions of the damaged area. Research shows that the most common areas to have focal lesions in non-penetrating traumatic brain injury are the orbitofrontal cortex (the lower surface of the frontal lobes) and the anterior temporal lobes
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain.
The temporal lobe is involved in pro ...
, areas that are involved in social behavior, emotion regulation, olfaction, and decision-making, hence the common social/emotional and judgment deficits following moderate-severe TBI. Symptoms such as hemiparesis
Hemiparesis, or unilateral paresis, is weakness of one entire side of the body ('' hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia is, in its most severe form, complete paralysis of half of the body. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia can be caused by different med ...
or aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in ...
can also occur when less commonly affected areas such as motor or language areas are, respectively, damaged.
One type of focal injury, cerebral laceration, occurs when the tissue is cut or torn. Such tearing is common in orbitofrontal cortex in particular, because of bony protrusions on the interior skull ridge above the eyes. In a similar injury, cerebral contusion (bruising of brain tissue), blood is mixed among tissue. In contrast, intracranial hemorrhage
Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is bleeding within the skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds (intraventricular bleeds and intraparenchymal bleeds), subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural blee ...
involves bleeding that is not mixed with tissue.
Hematomas, also focal lesions, are collections of blood in or around the brain that can result from hemorrhage. Intracerebral hemorrhage
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), also known as cerebral bleed, intraparenchymal bleed, and hemorrhagic stroke, or haemorrhagic stroke, is a sudden bleeding into the tissues of the brain, into its ventricles, or into both. It is one kind of bleed ...
, with bleeding in the brain tissue itself, is an intra-axial lesion. Extra-axial lesions include epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage
Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is bleeding into the subarachnoid space—the area between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater surrounding the brain. Symptoms may include a severe headache of rapid onset, vomiting, decreased level of cons ...
, and intraventricular hemorrhage. Epidural hematoma involves bleeding into the area between the skull and the dura mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. ...
, the outermost of the three membranes
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
surrounding the brain. In subdural hematoma, bleeding occurs between the dura and the arachnoid mater
The arachnoid mater (or simply arachnoid) is one of the three meninges, the protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. It is so named because of its resemblance to a spider web. The arachnoid mater is a derivative of the neura ...
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage involves bleeding into the space between the arachnoid membrane and the pia mater. Intraventricular hemorrhage occurs when there is bleeding in the ventricles.
Signs and symptoms
motor coordination Motor coordination is the orchestrated movement of multiple body parts as required to accomplish intended actions, like walking. This coordination is achieved by adjusting kinematic and kinetic parameters associated with each body part involved in ...
, dizziness, difficulty balancing, lightheadedness, blurred vision or tired eyes, ringing in the ears, bad taste in the mouth, fatigue or lethargy, and changes in sleep patterns. Cognitive and emotional symptoms include behavioral or mood changes, confusion, and trouble with memory, concentration, attention, or thinking. Mild TBI symptoms may also be present in moderate and severe injuries.
A person with a moderate or severe TBI may have a headache that does not go away, repeated vomiting or nausea, convulsions, an inability to awaken, dilation
Dilation (or dilatation) may refer to:
Physiology or medicine
* Cervical dilation, the widening of the cervix in childbirth, miscarriage etc.
* Coronary dilation, or coronary reflex
* Dilation and curettage, the opening of the cervix and surgi ...
of one or both pupils, slurred speech, aphasia
Aphasia is an inability to comprehend or formulate language because of damage to specific brain regions. The major causes are stroke and head trauma; prevalence is hard to determine but aphasia due to stroke is estimated to be 0.1–0.4% in ...
(word-finding difficulties), dysarthria
Dysarthria is a speech sound disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor–speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes. In other words, it is a condition in which problems effective ...
(muscle weakness that causes disordered speech), weakness or numbness in the limbs, loss of coordination, confusion, restlessness, or agitation. Common long-term symptoms of moderate to severe TBI are changes in appropriate social behavior, deficits in social judgment, and cognitive changes, especially problems with sustained attention, processing speed, and executive functioning. Alexithymia
Alexithymia is a personality trait characterized by the inability to identify and describe emotions experienced by oneself. The core characteristic of alexithymia is marked dysfunction in emotional awareness, social attachment, and interpersonal ...
, a deficiency in identifying, understanding, processing, and describing emotions occurs in 60.9% of individuals with TBI. Cognitive and social deficits have long-term consequences for the daily lives of people with moderate to severe TBI, but can be improved with appropriate rehabilitation.
When the pressure within the skull (intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adul ...
, abbreviated ICP) rises too high, it can be deadly. Signs of increased ICP include decreasing level of consciousness
An altered level of consciousness is any measure of arousal other than normal. Level of consciousness (LOC) is a measurement of a person's arousability and responsiveness to stimuli from the environment.
A mildly depressed level of consciou ...
, paralysis or weakness on one side of the body, and a blown pupil
Mydriasis is the dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, trauma, or the use of certain types of drugs.
Normally, ...
, one that fails to constrict in response to light or is slow to do so. Cushing's triad Cushing reflex (also referred to as the vasopressor response, the Cushing effect, the Cushing reaction, the Cushing phenomenon, the Cushing response, or Cushing's Law) is a physiological nervous system response to increased intracranial pressure (IC ...
, a slow heart rate with high blood pressure
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
and respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
is a classic manifestation of significantly raised ICP. Anisocoria
Anisocoria is a condition characterized by an unequal size of the eyes' pupils. Affecting up to 20% of the population, anisocoria is often entirely harmless, but can be a sign of more serious medical problems.
Causes
Anisocoria is a common condit ...
, unequal pupil size, is another sign of serious TBI. Abnormal posturing, a characteristic positioning of the limbs caused by severe diffuse injury or high ICP, is an ominous sign.
Small children with moderate to severe TBI may have some of these symptoms but have difficulty communicating them. Other signs seen in young children include persistent crying, inability to be consoled, listlessness, refusal to nurse or eat, and irritability.
Causes
The most common causes of TBI in the U.S. include violence, transportation accidents, construction site mishaps, and sports. Motor bikes are major causes, increasing in significance in developing countries as other causes reduce. The estimates that between 1.6 and 3.8 million traumatic brain injuries each year are a result of sports and recreation activities in the US. In children aged two to four, falls are the most common cause of TBI, while in older children traffic accidents compete with falls for this position. Granacher (2007). p. 16. TBI is the third most common injury to result fromchild abuse
Child abuse (also called child endangerment or child maltreatment) is physical, sexual, and/or psychological maltreatment or neglect of a child or children, especially by a parent or a caregiver. Child abuse may include any act or failure to a ...
. Abuse causes 19% of cases of pediatric brain trauma, and the death rate is higher among these cases. Although men are twice as likely to have a TBI. Domestic violence
Domestic violence (also known as domestic abuse or family violence) is violence or other abuse that occurs in a domestic setting, such as in a marriage or cohabitation. ''Domestic violence'' is often used as a synonym for '' intimate partn ...
is another cause of TBI, as are work-related and industrial accidents. Firearms and blast injuries from explosions are other causes of TBI, which is the leading cause of death and disability in war zones. According to Representative Bill Pascrell
William James Pascrell Jr. (born January 25, 1937) is an American politician who is the U.S. representative for , having served in this position since January 2013. A member of the Democratic Party and a native of Paterson, New Jersey, Pascrel ...
(Democrat, NJ), TBI is "the signature injury of the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan." There is a promising technology called activation database-guided EEG biofeedback, which has been documented to return a TBI's auditory memory ability to above the control group's performance
Mechanism
Physical forces
shock wave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
s through the skull and brain, resulting in tissue damage. Shock waves caused by penetrating injuries can also destroy tissue along the path of a projectile, compounding the damage caused by the missile itself.
Damage may occur directly under the site of impact, or it may occur on the side opposite the impact ( coup and contrecoup injury, respectively). When a moving object impacts the stationary head, coup injuries are typical, while contrecoup injuries are usually produced when the moving head strikes a stationary object.
Primary and secondary injury
 A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event; rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate. Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma. These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.
Secondary injury events include damage to the
A large percentage of the people killed by brain trauma do not die right away but rather days to weeks after the event; rather than improving after being hospitalized, some 40% of TBI patients deteriorate. Primary brain injury (the damage that occurs at the moment of trauma when tissues and blood vessels are stretched, compressed, and torn) is not adequate to explain this deterioration; rather, it is caused by secondary injury, a complex set of cellular processes and biochemical cascades that occur in the minutes to days following the trauma. These secondary processes can dramatically worsen the damage caused by primary injury and account for the greatest number of TBI deaths occurring in hospitals.
Secondary injury events include damage to the blood–brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable border of endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where ne ...
, release of factors that cause inflammation
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molec ...
, free radical overload, excessive release of the neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neu ...
glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
( excitotoxicity), influx of calcium and sodium ions into neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s, and dysfunction of mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
. Injured axons in the brain's white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distribu ...
may separate from their cell bodies as a result of secondary injury, potentially killing those neurons. Other factors in secondary injury are changes in the blood flow to the brain; ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
(insufficient blood flow); cerebral hypoxia (insufficient oxygen in the brain); cerebral edema (swelling of the brain); and raised intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adul ...
(the pressure within the skull). Intracranial pressure may rise due to swelling or a mass effect
''Mass Effect'' is a military science fiction media franchise created by Casey Hudson, Drew Karpyshyn and Preston Watamaniuk. The franchise depicts a distant future where humanity and several alien civilizations have colonized the known unive ...
from a lesion, such as a hemorrhage. As a result, cerebral perfusion pressure (the pressure of blood flow in the brain) is reduced; ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
results. When the pressure within the skull rises too high, it can cause brain death
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of brain function which may include cessation of involuntary activity necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some aut ...
or brain herniation
Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the t ...
, in which parts of the brain are squeezed by structures in the skull.
Diagnosis
 Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score. Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give. DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available. Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.
Diagnosis is suspected based on lesion circumstances and clinical evidence, most prominently a neurological examination, for example checking whether the pupils constrict normally in response to light and assigning a Glasgow Coma Score. Neuroimaging helps in determining the diagnosis and prognosis and in deciding what treatments to give. DSM-5 can be utilized to diagnose TBI and its psychiatric sequelae.
The preferred radiologic test in the emergency setting is computed tomography (CT): it is quick, accurate, and widely available. Follow-up CT scans may be performed later to determine whether the injury has progressed.
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) can show more detail than CT, and can add information about expected outcome in the long term. It is more useful than CT for detecting injury characteristics such as diffuse axonal injury in the longer term. However, MRI is not used in the emergency setting for reasons including its relative inefficacy in detecting bleeds and fractures, its lengthy acquisition of images, the inaccessibility of the patient in the machine, and its incompatibility with metal items used in emergency care. A variant of MRI since 2012 is High definition fiber tracking (HDFT).
Other techniques may be used to confirm a particular diagnosis. X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
s are still used for head trauma, but evidence suggests they are not useful; head injuries are either so mild that they do not need imaging or severe enough to merit the more accurate CT. Angiography
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is perfor ...
may be used to detect blood vessel pathology when risk factors such as penetrating head trauma are involved. Functional imaging
Functional imaging (or physiological imaging) is a medical imaging technique of detecting or measuring changes in metabolism, blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption.
As opposed to structural imaging, functional imaging center ...
can measure cerebral blood flow or metabolism, inferring neuronal activity in specific regions and potentially helping to predict outcome.
Neuropsychological assessment can be performed to evaluate the long-term cognitive sequelae and to aid in the planning of the rehabilitation
Rehabilitation or Rehab may refer to:
Health
* Rehabilitation (neuropsychology), therapy to regain or improve neurocognitive function that has been lost or diminished
* Rehabilitation (wildlife), treatment of injured wildlife so they can be retur ...
. Instruments range from short measures of general mental functioning to complete batteries formed of different domain-specific tests
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
.
Prevention
 Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats and motorcycle helmets, and presence of roll bars and airbags. Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes. In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI. Due to the possibility that repeatedly "heading" a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed. Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk. Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as "spear tackling" in
Since a major cause of TBI are vehicle accidents, their prevention or the amelioration of their consequences can both reduce the incidence and gravity of TBI. In accidents, damage can be reduced by use of seat belts, child safety seats and motorcycle helmets, and presence of roll bars and airbags. Education programs exist to lower the number of crashes. In addition, changes to public policy and safety laws can be made; these include speed limits, seat belt and helmet laws, and road engineering practices.
Changes to common practices in sports have also been discussed. An increase in use of helmets could reduce the incidence of TBI. Due to the possibility that repeatedly "heading" a ball practicing soccer could cause cumulative brain injury, the idea of introducing protective headgear for players has been proposed. Improved equipment design can enhance safety; softer baseballs reduce head injury risk. Rules against dangerous types of contact, such as "spear tackling" in American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
, when one player tackles another head first, may also reduce head injury rates.
Falls can be avoided by installing grab bars in bathrooms and handrails on stairways; removing tripping hazards such as throw rugs; or installing window guards and safety gates at the top and bottom of stairs around young children. Playgrounds with shock-absorbing surfaces such as mulch or sand also prevent head injuries. Child abuse prevention is another tactic; programs exist to prevent shaken baby syndrome by educating about the dangers of shaking children. Gun safety, including keeping guns unloaded and locked, is another preventative measure. Studies on the effect of laws that aim to control access to guns in the United States have been insufficient to determine their effectiveness preventing number of deaths or injuries.
Treatment
It is important to begin emergency treatment within the so-called " golden hour" following the injury.Kluger, Jeffrey. "Dealing with Brain Injuries. ''Time Magazine,'' April 6, 2009, p. 57. OnlineAccessed: May 1, 2009 People with moderate to severe injuries are likely to receive treatment in an
intensive care unit
220px, Intensive care unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensi ...
followed by a neurosurgical
Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty concerned with the surgical treatment of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord and ...
ward. Treatment depends on the recovery stage of the patient. In the acute stage, the primary aim is to stabilize the patient and focus on preventing further injury. This is done because the initial damage caused by trauma cannot be reversed. Rehabilitation is the main treatment for the subacute and chronic stages of recovery. International clinical guidelines have been proposed with the aim of guiding decisions in TBI treatment, as defined by an authoritative examination of current evidence
Evidence for a proposition is what supports this proposition. It is usually understood as an indication that the supported proposition is true. What role evidence plays and how it is conceived varies from field to field.
In epistemology, evidenc ...
.
Acute stage
Tranexamic acid
Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a medication used to treat or prevent excessive blood loss from major trauma, postpartum bleeding, surgery, tooth removal, nosebleeds, and heavy menstruation. It is also used for hereditary angioedema. It is taken ei ...
within three hours of a head injury decreases the risk of death. Certain facilities are equipped to handle TBI better than others; initial measures include transporting patients to an appropriate treatment center. Both during transport and in hospital the primary concerns are ensuring proper oxygen supply, maintaining adequate blood flow to the brain, and controlling raised intracranial pressure
Intracranial pressure (ICP) is the pressure exerted by fluids such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the skull and on the brain tissue. ICP is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) and at rest, is normally 7–15 mmHg for a supine adul ...
(ICP), since high ICP deprives the brain of badly needed blood flow and can cause deadly brain herniation
Brain herniation is a potentially deadly side effect of very high pressure within the skull that occurs when a part of the brain is squeezed across structures within the skull. The brain can shift across such structures as the falx cerebri, the t ...
. Other methods to prevent damage include management of other injuries and prevention of seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s. Some data supports the use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure ...
to improve outcomes. Further research is required to determine the effectiveness and clinical importance of positioning the head at different angles (degrees of head-of-bed elevation) while the person is being treated in intensive care.
Neuroimaging is helpful but not flawless in detecting raised ICP. A more accurate way to measure ICP is to place a catheter
In medicine, a catheter (/ˈkæθətər/) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgi ...
into a ventricle of the brain, which has the added benefit of allowing cerebrospinal fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless body fluid found within the tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates.
CSF is produced by specialised ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricles of the ...
to drain, releasing pressure in the skull. Treatment of raised ICP may be as simple as tilting the person's bed and straightening the head to promote blood flow through the veins of the neck. Sedative
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but ...
s, analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic (American English), analgaesic (British English), pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve relief from pain (that is, analgesia or pain management). It ...
s and paralytic agent
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
In cli ...
s are often used. Propofol and midazolam are equally effective as sedatives.
Hypertonic
In chemical biology, tonicity is a measure of the effective osmotic pressure gradient; the water potential of two solutions separated by a partially-permeable cell membrane. Tonicity depends on the relative concentration of selective membrane- ...
saline can improve ICP by reducing the amount of cerebral water (swelling), though it is used with caution to avoid electrolyte imbalances or heart failure. Mannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lo ...
, an osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region ...
diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
, appears to be as effective as hypertonic saline at reducing ICP. Some concerns, however, have been raised regarding some of the studies performed. Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics i ...
s, drugs that increase urine output to reduce excessive fluid in the system, may be used to treat high intracranial pressures, but may cause hypovolemia
Hypovolemia, also known as volume depletion or volume contraction, is a state of abnormally low extracellular fluid in the body. This may be due to either a loss of both salt and water or a decrease in blood volume. Hypovolemia refers to the los ...
(insufficient blood volume). Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation is irregular breathing that occurs when the rate or tidal volume of breathing eliminates more carbon dioxide than the body can produce. This leads to hypocapnia, a reduced concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in the bloo ...
(larger and/or faster breaths) reduces carbon dioxide levels and causes blood vessels to constrict; this decreases blood flow to the brain and reduces ICP, but it potentially causes ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems w ...
and is, therefore, used only in the short term.
Giving corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are inv ...
s is associated with an increased risk of death, and so their routine use is not recommended. There is no strong evidence that the following pharmaceutical interventions should be recommended to routinely treat TBI: magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
, monoaminergic
Monoaminergic means "working on monoamine neurotransmitters", which include serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and histamine.
A monoaminergic, or monoaminergic drug, is a chemical, which functions to directly modulate the ser ...
and dopamine agonists, progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
, aminosteroids, excitatory amino acid reuptake inhibitors, beta-2 antagonists (bronchodilators), haemostatic and antifibrinolytic Antifibrinolytics are a class of medication that are inhibitors of fibrinolysis. Examples include aminocaproic acid (ε-aminocaproic acid) and tranexamic acid. These lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to m ...
drugs.
Endotracheal intubation
Tracheal intubation, usually simply referred to as intubation, is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea (windpipe) to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs. It is frequentl ...
and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
may be used to ensure proper oxygen supply and provide a secure airway. Hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the di ...
(low blood pressure), which has a devastating outcome in TBI, can be prevented by giving intravenous fluids to maintain a normal blood pressure. Failing to maintain blood pressure can result in inadequate blood flow to the brain. Blood pressure may be kept at an artificially high level under controlled conditions by infusion of norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad ...
or similar drugs; this helps maintain cerebral perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is deliver ...
. Body temperature is carefully regulated because increased temperature raises the brain's metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
needs, potentially depriving it of nutrients. Seizures are common. While they can be treated with benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
s, these drugs are used carefully because they can depress breathing and lower blood pressure. Anti-convulsant medications have only been found to be useful for reducing the risk of an early seizure. Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The in ...
and leviteracetam appear to have similar levels of effectiveness for preventing early seizures. People with TBI are more susceptible to side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect, whether therapeutic or adverse, that is secondary to the one intended; although the term is predominantly employed to describe adverse effects, it can also apply to beneficial, but unintended, consequenc ...
and may react adversely to some medications. During treatment monitoring continues for signs of deterioration such as a decreasing level of consciousness.
Traumatic brain injury may cause a range of serious coincidental complications that include cardiac arrhythmias and neurogenic pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive liquid accumulation in the tissue and air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia and respiratory failure. It is due ...
. These conditions must be adequately treated and stabilised as part of the core care.
Surgery can be performed on mass lesion
In medicine, a mass effect is the effect of a growing mass that results in secondary pathological effects by pushing on or displacing surrounding tissue.
In oncology, the mass typically refers to a tumor.
For example, cancer of the thyroid glan ...
s or to eliminate objects that have penetrated the brain. Mass lesions such as contusions or hematomas causing a significant mass effect ( shift of intracranial structures) are considered emergencies and are removed surgically. For intracranial hematomas, the collected blood may be removed using suction
Suction is the colloquial term to describe the air pressure differential between areas.
Removing air from a space results in a pressure differential. Suction pressure is therefore limited by external air pressure. Even a perfect vacuum cannot ...
or forceps
Forceps (plural forceps or considered a plural noun without a singular, often a pair of forceps; the Latin plural ''forcipes'' is no longer recorded in most dictionaries) are a handheld, hinged instrument used for grasping and holding objects. Fo ...
or it may be floated off with water. Surgeons look for hemorrhaging blood vessels and seek to control bleeding. In penetrating brain injury, damaged tissue is surgically debrided, and craniotomy may be needed. Craniotomy, in which part of the skull is removed, may be needed to remove pieces of fractured skull or objects embedded in the brain. Decompressive craniectomy (DC) is performed routinely in the very short period following TBI during operations to treat hematomas; part of the skull is removed temporarily (primary DC). DC performed hours or days after TBI in order to control persistently high intracranial pressures (secondary DC), although can reduce intracranial pressure and length of stay in ICU, but have worse Glasgow Coma Scale
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a clinical scale used to reliably measure a person's level of consciousness after a brain injury.
The GCS assesses a person based on their ability to perform eye movements, speak, and move their body. These thr ...
(GCS) scores, and high chances of death, vegetative state, or severe disability when compared to those receiving standard medical therapies.
Chronic stage
subacute
In medicine, describing a disease as acute denotes that it is of short duration and, as a corollary of that, of recent onset. The quantification of how much time constitutes "short" and "recent" varies by disease and by context, but the core den ...
rehabilitation unit of the medical center or to an independent rehabilitation hospital Rehabilitation hospitals, also referred to as inpatient rehabilitation hospitals, are devoted to the rehabilitation of patients with various neurological, musculoskeletal, orthopedic, and other medical conditions following stabilization of their ac ...
. Rehabilitation aims to improve independent functioning at home and in society, and to help adapt to disabilities. Rehabilitation has demonstrated its general effectiveness when conducted by a team of health professionals who specialize in head trauma. As for any person with neurologic deficits, a multidisciplinary approach is key to optimizing outcome. Physiatrists or neurologists are likely to be the key medical staff involved, but depending on the person, doctors of other medical specialties may also be helpful. Allied health professions such as physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patie ...
, speech and language therapy, cognitive rehabilitation therapy
Cognitive rehabilitation refers to a wide range of evidence-based interventions designed to improve cognitive functioning in brain-injured or otherwise cognitively impaired individuals to restore normal functioning, or to compensate for cognitive ...
, and occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT) is a global healthcare profession. It involves the use of assessment and intervention to develop, recover, or maintain the meaningful activities, or ''occupations'', of individuals, groups, or communities. The field of ...
will be essential to assess function and design the rehabilitation activities for each person. Treatment of neuropsychiatric symptoms such as emotional distress and clinical depression may involve mental health
Mental health encompasses emotional, psychological, and social well-being, influencing cognition, perception, and behavior. It likewise determines how an individual handles Stress (biology), stress, interpersonal relationships, and decision-maki ...
professionals such as therapist
Therapist is a person who offers any kinds of therapy
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indi ...
s, psychologist
A psychologist is a professional who practices psychology and studies mental states, perceptual
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the pre ...
s, and psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry, the branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatrists are physicians and evaluate patients to determine whether their sy ...
s, while neuropsychologists can help to evaluate and manage cognitive deficit
Cognitive deficit is an inclusive term to describe any characteristic that acts as a barrier to the cognition process.
The term may describe
* deficits in overall intelligence (as with intellectual disabilities),
* specific and restricted defic ...
s. Social workers, rehabilitation support personnel, nutritionists, therapeutic recreationists, and pharmacists are also important members of the TBI rehabilitation team. After discharge from the inpatient rehabilitation treatment unit, care may be given on an outpatient
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other health care ...
basis. Community-based rehabilitation will be required for a high proportion of people, including vocational rehabilitation; this supportive employment matches job demands to the worker's abilities. People with TBI who cannot live independently or with family may require care in supported living facilities such as group homes. Respite care
__NOTOC__
Respite care is planned or emergency temporary care provided to caregivers of a child or adult.
Respite programs provide planned short-term and time-limited breaks for families and other unpaid caregivers of children with a developmenta ...
, including day centers and leisure facilities for disabled people, offers time off for caregivers, and activities for people with TBI.
Pharmacological treatment can help to manage psychiatric or behavioral problems. Medication is also used to control post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) is a form of acquired epilepsy that results from brain damage caused by physical trauma to the brain ( traumatic brain injury, abbreviated TBI). A person with PTE experiences repeated post-traumatic seizures (PTS, s ...
; however the preventive use of anti-epileptics is not recommended. In those cases where the person is bedridden due to a reduction of consciousness, has to remain in a wheelchair because of mobility problems, or has any other problem heavily impacting self-caring capacities, caregiving and nursing are critical.
The most effective research documented intervention approach is the activation database guided EEG biofeedback approach, which has shown significant improvements in memory abilities of the TBI subject that are far superior than traditional approaches (strategies, computers, medication intervention). Gains of 2.61 standard deviations have been documented. The TBI's auditory memory ability was superior to the control group after the treatment.
Effect on the gait pattern
 In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age. Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with
In patients who have developed paralysis of the legs in the form of spastic hemiplegia or diplegia as a result of the traumatic brain injury, various gait patterns can be observed, the exact extent of which can only be described with the help of complex gait analysis systems. In order to facilitate interdisciplinary communication in the interdisciplinary team between those affected, doctors, physiotherapists and orthotists, a simple description of the gait pattern is useful. J. Rodda and H. K. Graham already described in 2001 how gait patterns of CP patients can be more easily recognized and defined gait types which they compared in a classification. They also described that gait patterns can vary with age. Building on this, the Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed at the free university in Amsterdam, the VU medisch centrum. A special feature of this classification is that it makes different gait patterns very recognizable and can be used in patients in whom only one leg and both legs are affected. The Amsterdam Gait Classification was developed for viewing patients with cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
. However, it can be used just as well in patients with traumatic brain injuries. According to the Amsterdam Gait Classification, five gait types are described. To assess the gait pattern, the patient is viewed visually or via a video recording from the side of the leg to be assessed. At the point in time at which the leg to be viewed is in mid stance and the leg not to be viewed is in mid swing, the knee angle and the contact of the foot with the ground are assessed on the one hand.
Classification of the gait pattern according to the Amsterdam Gait Classification: In gait type 1, the knee angle is normal and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 2, the knee angle is hyperextended and the foot contact is complete. In gait type 3, the knee angle is hyperextended and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). In gait type 4, the knee angle is bent and foot contact is incomplete (only on the forefoot). With gait type 5, the knee angle is bent and the foot contact is complete.
Gait types 5 is also known as crouch gait.
Orthotics
 To improve the gait pattern,
To improve the gait pattern, orthotics
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functi ...
can be included in the therapy concept. An Orthosis
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functi ...
can support physiotherapeutic treatment in setting the right motor impulses in order to create new cerebral connections. The orthosis must meet the requirements of the medical prescription. In addition, the orthosis must be designed by the orthotist in such a way that it achieves the effectiveness of the necessary levers, matching the gait pattern, in order to support the proprioceptive approaches of physiotherapy. The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There may be problems with sens ...
. The characteristics of the stiffness of the orthosis shells and the adjustable dynamics in the ankle joint are important elements of the orthosis to be considered. The orthotic concepts of the treatment are based on the concepts for the patients with cerebral palsy. Due to these requirements, the development of orthoses has changed significantly in recent years, especially since around 2010. At about the same time, care concepts were developed that deal intensively with the orthotic treatment of the lower extremities in cerebral palsy. Modern materials and new functional elements enable the rigidity to be specifically adapted to the requirements that fits to the gait pattern of the patient. The adjustment of the stiffness has a decisive influence on the gait pattern and on the energy cost of walking. It is of great advantage if the stiffness of the orthosis can be adjusted separately from one another via resistances of the two functional elements in the two directions of movement, dorsiflexion and plantar flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ...
.
Prognosis
Prognosis worsens with the severity of injury. Most TBIs are mild and do not cause permanent or long-term disability; however, all severity levels of TBI have the potential to cause significant, long-lasting disability. Permanent disability is thought to occur in 10% of mild injuries, 66% of moderate injuries, and 100% of severe injuries. Most mild TBI is completely resolved within three weeks. Almost all people with mild TBI are able to live independently and return to the jobs they had before the injury, although a small portion have mild cognitive and social impairments. Over 90% of people with moderate TBI are able to live independently, although some require assistance in areas such as physical abilities, employment, and financial managing. Most people with severe closed head injury either die or recover enough to live independently; middle ground is less common. Coma, as it is closely related to severity, is a strong predictor of poor outcome. Prognosis differs depending on the severity and location of the lesion, and access to immediate, specialised acute management. Subarachnoid hemorrhage approximately doubles mortality. Subdural hematoma is associated with worse outcome and increased mortality, while people with epidural hematoma are expected to have a good outcome if they receive surgery quickly. Diffuse axonal injury may be associated with coma when severe, and poor outcome. Following the acute stage, prognosis is strongly influenced by the patient's involvement in activity that promote recovery, which for most patients requires access to a specialised, intensive rehabilitation service. TheFunctional Independence Measure
The Functional Independence Measure (FIM) is an assessment tool that aims to evaluate the functional status of patients throughout the rehabilitation process following a stroke, traumatic brain injury, spinal cord injury or cancer. Its area of use ...
is a way to track progress and degree of independence throughout rehabilitation.
Medical complications are associated with a bad prognosis. Examples of such complications include: hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the di ...
(low blood pressure), hypoxia (low blood oxygen saturation), lower cerebral perfusion pressures, and longer times spent with high intracranial pressures. Patient characteristics also influence prognosis. Examples of factors thought to worsen it include: abuse of substances such as illicit drugs and alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
and age over sixty or under two years (in children, younger age at time of injury may be associated with a slower recovery of some abilities). Other influences that may affect recovery include pre-injury intellectual ability, coping strategies, personality traits, family environment, social support systems and financial circumstances.
Life satisfaction has been known to decrease for individuals with TBI immediately following the trauma, but evidence has shown that life roles, age, and depressive symptoms influence the trajectory of life satisfaction as time passes. Many people with traumatic brain injuries have poor physical fitness following their acute injury and this may result with difficulties in day-to-day activities and increased levels of fatigue.
Complications
 Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress. Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma,
Improvement of neurological function usually occurs for two or more years after the trauma. For many years it was believed that recovery was fastest during the first six months, but there is no evidence to support this. It may be related to services commonly being withdrawn after this period, rather than any physiological limitation to further progress. Children recover better in the immediate time frame and improve for longer periods.
Complications are distinct medical problems that may arise as a result of the TBI. The results of traumatic brain injury vary widely in type and duration; they include physical, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral complications. TBI can cause prolonged or permanent effects on consciousness, such as coma, brain death
Brain death is the permanent, irreversible, and complete loss of brain function which may include cessation of involuntary activity necessary to sustain life. It differs from persistent vegetative state, in which the person is alive and some aut ...
, persistent vegetative state (in which patients are unable to achieve a state of alertness to interact with their surroundings), and minimally conscious state
A minimally conscious state (MCS) is a disorder of consciousness distinct from persistent vegetative state and locked-in syndrome. Unlike persistent vegetative state, patients with MCS have partial preservation of conscious awareness. MCS is a r ...
(in which patients show minimal signs of being aware of self or environment). Lying still for long periods can cause complications including pressure sores, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severit ...
or other infections, progressive multiple organ failure, and deep venous thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a type of venous thrombosis involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, most commonly in the legs or pelvis. A minority of DVTs occur in the arms. Symptoms can include pain, swelling, redness, and enla ...
, which can cause pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream ( embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathin ...
. Infections that can follow skull fractures and penetrating injuries include meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or ...
and abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
es. Complications involving the blood vessels include vasospasm, in which vessels constrict and restrict blood flow, the formation of aneurysm
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus ( ...
s, in which the side of a vessel weakens and balloons out, and stroke.
Movement disorders that may develop after TBI include tremor, ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
(uncoordinated muscle movements), spasticity
Spasticity () is a feature of altered skeletal muscle performance with a combination of paralysis, increased tendon reflex activity, and hypertonia. It is also colloquially referred to as an unusual "tightness", stiffness, or "pull" of muscles ...
(muscle contractions are overactive), myoclonus (shock-like contractions of muscles), and loss of movement range and control (in particular with a loss of movement repertoire). The risk of post-traumatic seizure
Post-traumatic seizures (PTS) are seizures that result from traumatic brain injury (TBI), brain damage caused by physical trauma. PTS may be a risk factor for post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE), but a person having a seizure or seizures due to traumati ...
s increases with severity of trauma (image at right) and is particularly elevated with certain types of brain trauma such as cerebral contusions or hematomas. People with early seizures, those occurring within a week of injury, have an increased risk of post-traumatic epilepsy
Post-traumatic epilepsy (PTE) is a form of acquired epilepsy that results from brain damage caused by physical trauma to the brain ( traumatic brain injury, abbreviated TBI). A person with PTE experiences repeated post-traumatic seizures (PTS, s ...
(recurrent seizures occurring more than a week after the initial trauma). People may lose or experience altered vision, hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is audit ...
, or smell.
Hormonal disturbances may occur secondary to hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is the decreased (''hypo'') secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. If there is decreased secretion of one specific pituitary hormone, the condition is know ...
, occurring immediately or years after injury in 10 to 15% of TBI patients. Development of diabetes insipidus
Diabetes insipidus (DI), recently renamed to Arginine Vasopressin Deficiency (AVP-D) and Arginine Vasopressin Resistance (AVP-R), is a condition characterized by large amounts of dilute urine and increased thirst. The amount of urine produced ...
or an electrolyte abnormality acutely after injury indicate need for endocrinologic work up. Signs and symptoms of hypopituitarism may develop and be screened for in adults with moderate TBI and in mild TBI with imaging abnormalities. Children with moderate to severe head injury may also develop hypopituitarism. Screening should take place 3 to 6 months, and 12 months after injury, but problems may occur more remotely.
Cognitive deficits that can follow TBI include impaired attention; disrupted insight, judgement, and thought; reduced processing speed; distractibility; and deficits in executive functions such as abstract reasoning, planning, problem-solving, and multitasking. Memory loss, the most common cognitive impairment among head-injured people, occurs in 20–79% of people with closed head trauma, depending on severity. People who have had TBI may also have difficulty with understanding or producing spoken or written language, or with more subtle aspects of communication such as body language. Post-concussion syndrome, a set of lasting symptoms experienced after mild TBI, can include physical, cognitive, emotional and behavioral problems such as headaches, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and depression. Multiple TBIs may have a cumulative effect. A young person who receives a second concussion before symptoms from another one have healed may be at risk for developing a very rare but deadly condition called second-impact syndrome
Second-impact syndrome (SIS) occurs when the brain swells rapidly, and catastrophically, after a person has a second concussion before symptoms from an earlier one have subsided. This second blow may occur minutes, days, or weeks after an initial ...
, in which the brain swells catastrophically after even a mild blow, with debilitating or deadly results. About one in five career boxers is affected by chronic traumatic brain injury (CTBI), which causes cognitive, behavioral, and physical impairments. Dementia pugilistica, the severe form of CTBI, affects primarily career boxers years after a boxing career. It commonly manifests as dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
, memory problems, and parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is a clinical syndrome characterized by tremor, bradykinesia (slowed movements), rigidity, and postural instability. These are the four motor symptoms found in Parkinson's disease (PD), after which it is named, dementia with Lew ...
(tremors and lack of coordination).
TBI may cause emotional, social, or behavioral problems and changes in personality. These may include emotional instability, depression, anxiety, hypomania
Hypomania (literally "under mania" or "less than mania") is a mental and behavioural disorder, characterised essentially by an apparently non-contextual elevation of mood (euphoria) that contributes to persistently disinhibited behaviour.
Th ...
, mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a mental and behavioral disorder defined as a state of abnormally elevated arousal, affect, and energy level, or "a state of heightened overall activation with enhanced affective expression together wi ...
, apathy, irritability, problems with social judgment, and impaired conversational skills. TBI appears to predispose survivors to psychiatric disorders including obsessive compulsive disorder
Obsession may refer to:
Psychology
* Celebrity worship syndrome, obsessive addictive disorder to a celebrity's personal and professional life
* Fixation (psychology), a persistent attachment to an object or idea
* Idée fixe (psychology), a pr ...
, substance abuse
Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods which are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, ...
, dysthymia
Dysthymia ( ), also known as persistent depressive disorder (PDD), is a mental and behavioral disorder, specifically a disorder primarily of mood, consisting of similar cognitive and physical problems as major depressive disorder, but with l ...
, clinical depression, bipolar disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of Depression (mood), depression and periods of abnormally elevated Mood (psychology), mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevat ...
, and anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phy ...
s. In patients who have depression after TBI, suicidal ideation is not uncommon; the suicide rate among these persons is increased 2- to 3-fold. Social and behavioral symptoms that can follow TBI include disinhibition, inability to control anger, impulsiveness, lack of initiative, inappropriate sexual activity, asociality
Asociality refers to the lack of motivation to engage in social interaction, or a preference for solitary activities. Asociality may be associated with avolition, but it can, moreover, be a manifestation of limited opportunities for social relat ...
and social withdrawal, and changes in personality.
TBI also has a substantial impact on the functioning of family systems Caregiving family members and TBI survivors often significantly alter their familial roles and responsibilities following injury, creating significant change and strain on a family system. Typical challenges identified by families recovering from TBI include: frustration and impatience with one another, loss of former lives and relationships, difficulty setting reasonable goals, inability to effectively solve problems as a family, increased level of stress and household tension, changes in emotional dynamics, and overwhelming desire to return to pre-injury status. In addition, families may exhibit less effective functioning in areas including coping, problem solving and communication. Psychoeducation and counseling models have been demonstrated to be effective in minimizing family disruption.
Epidemiology
epidemiological
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evid ...
studies vary based on such factors as which grades of severity are included, whether deaths are included, whether the study is restricted to hospitalized people, and the study's location. The annual incidence of mild TBI is difficult to determine but may be 100–600 people per 100,000.
Mortality
In the US, the case fatality rate is estimated to be 21% by 30 days after TBI. A study on Iraq War soldiers found that severe TBI carries a mortality of 30–50%. Deaths have declined due to improved treatments and systems for managing trauma in societies wealthy enough to provide modern emergency and neurosurgical services. The fraction of those who die after being hospitalized with TBI fell from almost half in the 1970s to about a quarter at the beginning of the 21st century. This decline in mortality has led to a concomitant increase in the number of people living with disabilities that result from TBI. Biological, clinical, and demographic factors contribute to the likelihood that an injury will be fatal. In addition, outcome depends heavily on the cause of head injury. In the US, patients with fall-related TBIs have an 89% survival rate, while only 9% of patients with firearm-related TBIs survive. In the US, firearms are the most common cause of fatal TBI, followed by vehicle accidents and then falls. Of deaths from firearms, 75% are considered to be suicides. The incidence of TBI is increasing globally, due largely to an increase in motor vehicle use in low- and middle-income countries. In developing countries, automobile use has increased faster than safety infrastructure could be introduced. In contrast, vehicle safety laws have decreased rates of TBI in high-income countries, which have seen decreases in traffic-related TBI since the 1970s. Each year in the United States, about two million people have a TBI, approximately 675,000 injuries are seen in the emergency department, and about 500,000 patients are hospitalized. The yearly incidence of TBI is estimated at 180–250 per 100,000 people in the US, 281 per 100,000 in France, 361 per 100,000 in South Africa, 322 per 100,000 in Australia, and 430 per 100,000 in England. In the European Union the yearly aggregate incidence of TBI hospitalizations and fatalities is estimated at 235 per 100,000.Demographics
TBI is present in 85% of traumatically injured children, either alone or with other injuries. The greatest number of TBIs occur in people aged 15–24. Because TBI is more common in young people, its costs to society are high due to the loss of productive years to death and disability. The age groups most at risk for TBI are children ages five to nine and adults over age 80, and the highest rates of death and hospitalization due to TBI are in people over age 65. The incidence of fall-related TBI in First-World countries is increasing as the population ages; thus themedian
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic f ...
age of people with head injuries has increased.
Regardless of age, TBI rates are higher in males. Men have twice as many TBIs as women do and have a fourfold risk of fatal head injury, and males account for two thirds of childhood and adolescent head trauma.
However, when matched for severity of injury, women appear to fare more poorly than men. Moppet07
Socioeconomic status
Socioeconomic status (SES) is an economic and sociological combined total measure of a person's work experience and of an individual's or family's economic access to resources and social position in relation to others. When analyzing a family's ...
also appears to affect TBI rates; people with lower levels of education and employment and lower socioeconomic status are at greater risk. Approximately half of those incarcerated in prisons and jails in the United States have had TBIs.
History
 Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history. Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3 Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that
Head injury is present in ancient myths that may date back before recorded history. Boake and Diller (2005). p. 3 Skulls found in battleground graves with holes drilled over fracture lines suggest that trepanation
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is dri ...
may have been used to treat TBI in ancient times. Granacher (2007). p. 1. Ancient Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
ns knew of head injury and some of its effects, including seizures, paralysis, and loss of sight, hearing or speech. The Edwin Smith Papyrus
The Edwin Smith Papyrus is an ancient Egyptian medical text, named after Edwin Smith who bought it in 1862, and the oldest known surgical treatise on trauma. From a cited quotation in another text, it may have been known to ancient surgeons as t ...
, written around 1650–1550 BC, describes various head injuries and symptoms and classifies them based on their presentation and tractability. Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic pe ...
physicians including Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history o ...
understood the brain to be the center of thought, probably due to their experience observing the effects of head trauma.
Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
surgeons continued the practice of trepanation for head injury. In the Middle Ages, physicians further described head injury symptoms and the term ''concussion'' became more widespread. Concussion symptoms were first described systematically in the 16th century by Berengario da Carpi
Jacopo Berengario da Carpi (also known as Jacobus Berengarius Carpensis, Jacopo Barigazzi, Giacomo Berengario da Carpi or simply Carpus; c. 1460 – c. 1530) was an Italian physician. His book "''Isagoge breves''" published in 1522 made him the mo ...
.
It was first suggested in the 18th century that intracranial pressure rather than skull damage was the cause of pathology after TBI. This hypothesis was confirmed around the end of the 19th century, and opening the skull to relieve pressure was then proposed as a treatment.
In the 19th century it was noted that TBI is related to the development of psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavi ...
. At that time a debate arose around whether post-concussion syndrome was due to a disturbance of the brain tissue or psychological factors. The debate continues today.
 Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of
Perhaps the first reported case of personality change after brain injury is that of Phineas Gage
Phineas P. Gage (18231860) was an American railroad construction foreman known for his improbable survival of an accident in which a large iron rod was driven completely through his head, destroying much of his brain's left frontal lobe, and ...
, who survived an accident in which a large iron rod was driven through his head, destroying one or both of his frontal lobes; numerous cases of personality change after brain injury have been reported since.
The 20th century saw the advancement of technologies that improved treatment and diagnosis such as the development of imaging tools including CT and MRI, and, in the 21st century, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). The introduction of intracranial pressure monitoring in the 1950s has been credited with beginning the "modern era" of head injury. Marion (1999). p. 3. Until the 20th century, the mortality rate of TBI was high and rehabilitation was uncommon; improvements in care made during World War I reduced the death rate and made rehabilitation possible. Facilities dedicated to TBI rehabilitation were probably first established during World War I. Explosives used in World War I caused many blast injuries; the large number of TBIs that resulted allowed researchers to learn about localization of brain functions. Blast-related injuries are now common problems in returning veterans from Iraq & Afghanistan; research shows that the symptoms of such TBIs are largely the same as those of TBIs involving a physical blow to the head.
In the 1970s, awareness of TBI as a public health problem grew, Boake and Diller (2005). p. 8 and a great deal of progress has been made since then in brain trauma research, such as the discovery of primary and secondary brain injury. The 1990s saw the development and dissemination of standardized guidelines for treatment of TBI, with protocols for a range of issues such as drugs and management of intracranial pressure. Research since the early 1990s has improved TBI survival; that decade was known as the "Decade of the Brain
The Decade of the Brain was a designation for 1990–1999 by U.S. president George H. W. Bush as part of a larger effort involving the Library of Congress and the National Institute of Mental Health of the National Institutes of Health "to enhance ...
" for advances made in brain research.
Research directions
Diagnosis
Quantitative EEG and EEG, which has no specific patterns in TBI is used in research settings to differentiate between mild TBI and no TBI.Medications
No medication is approved to halt the progression of the initial injury to secondary injury. The variety of pathological events presents opportunities to find treatments that interfere with the damage processes. Neuroprotection methods to decrease secondary injury, have been the subject of interest follows TBI. However, trials to test agents that could halt these cellular mechanisms have met largely with failure. For example, interest existed in cooling the injured brain; however, a 2020 Cochrane review did not find enough evidence to see if it was useful or not. Maintaining a normal temperature in the immediate period after a TBI appeared useful. One review found a lower than normal temperature was useful in adults but not children. While two other reviews found it did not appear to be useful. Further research is necessary to determine if the vasoconstrictor indomethacin (indometacin) can be used to treat increased pressure in the skull following a TBI. In addition, drugs such as NMDA receptor antagonists to halt neurochemical cascades such as excitotoxicity showed promise inanimal trial
In legal history, an animal trial was the criminal trial of a non-human animal. Such trials are recorded as having taken place in Europe from the thirteenth century until the eighteenth. In modern times, it is considered in most criminal just ...
s but failed in clinical trials. These failures could be due to factors including faults in the trials' design or in the insufficiency of a single agent to prevent the array of injury processes involved in secondary injury.
Other topics of research have included investigations into mannitol
Mannitol is a type of sugar alcohol used as a sweetener and medication. It is used as a low calorie sweetener as it is poorly absorbed by the intestines. As a medication, it is used to decrease pressure in the eyes, as in glaucoma, and to lo ...
, dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a glucocorticoid medication used to treat rheumatic problems, a number of skin diseases, severe allergies, asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, croup, brain swelling, eye pain following eye surgery, superior vena ...
, progesterone
Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the majo ...
, xenon
Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is a dense, colorless, odorless noble gas found in Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts. Although generally unreactive, it can undergo a few chemical reactions such as the ...
, barbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as we ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ...
(no strong evidence), calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s, PPAR-γ agonists, curcuminoids, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
, NMDA antagonists
NMDA receptor antagonists are a class of drugs that work to antagonize, or inhibit the action of, the ''N''-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor ( NMDAR). They are commonly used as anesthetics for animals and humans; the state of anesthesia they induc ...
, caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class. It is mainly recreational drug use, used recreationally as a Nootropic, cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional perfor ...
.
Procedures
In addition to traditional imaging modalities, there are several devices that help to monitor brain injury and facilitate research.Microdialysis
Microdialysis is a minimally-invasive sampling technique that is used for continuous measurement of free, unbound analyte concentrations in the extracellular fluid of virtually any tissue. Analytes may include endogenous molecules (e.g. neurotra ...
allows ongoing sampling of extracellular fluid for analysis of metabolites that might indicate ischemia or brain metabolism, such as glucose, glycerol, and glutamate. Intraparenchymal brain tissue oxygen monitoring systems (either Licox or Neurovent-PTO) are used routinely in neurointensive care in the US. A non invasive model called CerOx is in development.
Research is also planned to clarify factors correlated to outcome in TBI and to determine in which cases it is best to perform CT scans and surgical procedures.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
Hyperbaric medicine is medical treatment in which an ambient pressure greater than sea level atmospheric pressure is a necessary component. The treatment comprises hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT), the medical use of oxygen at an ambient pressure ...
(HBO) has been evaluated as an add on treatment following TBI. The findings of a 2012 Cochrane systematic review does not justify the routine use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat people recovering from a traumatic brain injury. This review also reported that only a small number of randomized controlled trials had been conducted at the time of the review, many of which had methodological problems and poor reporting. HBO for TBI is controversial with further evidence required to determine if it has a role.
Psychological
Further research is required to determine the effectiveness of non-pharmacological treatment approaches for treating depression in children/adolescents and adults with TBI. As of 2010, the use of predictive visual tracking measurement to identify mild traumatic brain injury was being studied. In visual tracking tests, a head-mounted display unit witheye-tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research ...
capability shows an object moving in a regular pattern. People without brain injury are able to track the moving object with smooth pursuit eye movements
In the scientific study of vision, smooth pursuit describes a type of eye movement in which the eyes remain fixated on a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movemen ...
and correct trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete tr ...
. The test requires both attention and working memory which are difficult functions for people with mild traumatic brain injury. The question being studied, is whether results for people with brain injury will show visual-tracking gaze
In critical theory, sociology, and psychoanalysis, the gaze (French ''le regard''), in the philosophical and figurative sense, is an individual's (or a group's) awareness and perception of other individuals, other groups, or oneself. The concept ...
errors relative to the moving target.
Monitoring pressure
Pressure reactivity index
Pressure reactivity index or PRx is tool for monitoring cerebral autoregulation in the intensive care setting for patients with severe traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid haemorrhage, in order to guide therapy to protect the brain from danger ...
is used to correlate intracranial pressure with arterial blood pressure to give information about the state of cerebral perfusion, thus guiding treatment and prevent excessively high or low blood flow to the brain. However, such method of monitoring intracranial pressure of equal or less than 20 mmHg is no better than imaging and clinical examination that monitor the neurological status of the brain in prolonging the survival, preserving the mental or functional status of the subject.
Sensory processing
In animal models of TBI, sensory processing has been widely studied to show systematic defects arise and are slowly but likely only partially recovered. It is especially characterised by an initial period of decreased activity in upper cortical layers. This period of decreased activity has also been characterised as by specific timing effects in the patterns of cortical activity in these upper layers in response to regular sensory stimuli.References
Cited texts
* * * * ''The original version of this article contained text from thNINDS public domain pages on TBI
''
External links
*The Brain Injury Hub – information and practical advice to parents and family members of children with acquired brain injury
Defense and Veterans Brain Injury Center – U.S. Department of Defense Military Health System center for traumatic brain injury
{{Good article Medical emergencies Intensive care medicine Neurotrauma Injuries of head Disorders causing seizures