Transportation in North America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transportation in North America is performed through a varied
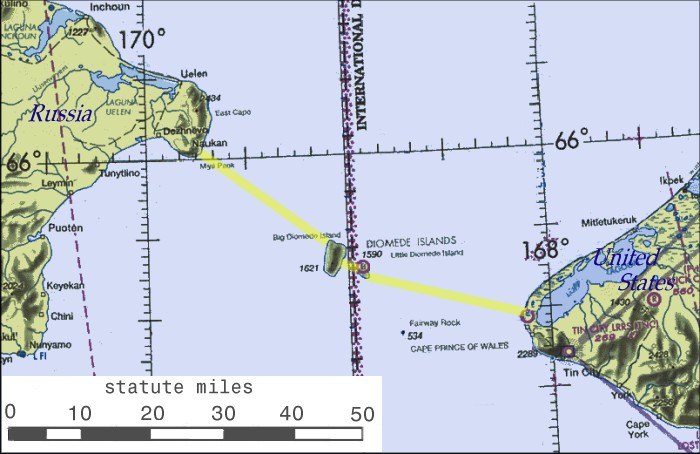 In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a rail tunnel under the Bering Strait between Chukotka and Alaska. The tunnel, as projected, would be long and would include oil and gas pipelines,
In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a rail tunnel under the Bering Strait between Chukotka and Alaska. The tunnel, as projected, would be long and would include oil and gas pipelines,
transportation
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, ...
system, whose quality ranges from being on par with a high-quality European motorway to an unpaved gravelled back road that can extend hundreds of miles. There is also an extensive transcontinental freight rail network, but passenger railway ridership is lower than in Europe and Asia.
Railways
Canada, the United States and Mexico
The railroad network of North America (using standard gauge) is extremely extensive, connecting nearly every major and most minor cities. The United States, Canada, and Mexico have an interconnected system withrailhead
In the UK, railheading refers to the practice of travelling further than necessary to reach a rail service, typically by car. The phenomenon is common among commuters seeking a more convenient journey. Reasons for railheading include, but are ...
s stretching from Hay River, Northwest Territories, Canada, to Tapachula
Tapachula de Córdova y Ordóñez, simply known as Tapachula, is a city and municipality located in the far southeast of the state of Chiapas in Mexico, near the Guatemalan border and the Pacific Ocean. It is one of the most important cities of ...
, Mexico, and on Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
. The state government of Alaska also operates the Alaska Railroad, which does not connect to the North American network. In Canada, rail lines from Labrador City, Newfoundland and Labrador
Labrador City is a town in western Labrador (part of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador), near the Quebec border. With a population of 7,412 as of 2021, it is the second-largest population centre in Labrador, behind Happy Valley- ...
, to Sept-Îles, Quebec
Sept-Îles ( Quebec French pronunciation : , French for "Seven Islands") is a city in the Côte-Nord region of eastern Quebec. It is among the northernmost locales with a paved connection to the rest of Quebec's road network. The population was ...
, also are not linked to the North American network.
Newfoundland and Labrador
There have been proposals to link the island of Newfoundland to the mainland of North America via a 17 km-long railtunnel
A tunnel is an underground passageway, dug through surrounding soil, earth or rock, and enclosed except for the entrance and exit, commonly at each end. A pipeline is not a tunnel, though some recent tunnels have used immersed tube cons ...
under the Strait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle (; french: Détroit de Belle Isle ) is a waterway in eastern Canada that separates the Labrador Peninsula from the island of Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is the northern o ...
, which would also carry automobile traffic on flatcar
A flatcar (US) (also flat car, or flatbed) is a piece of rolling stock that consists of an open, flat deck mounted on a pair of trucks (US) or bogies (UK), one at each end containing four or six wheels. Occasionally, flat cars designed to carry ...
s, similar to the Channel Tunnel between the United Kingdom and France. This has stalled due to the lack of a large road network and a lack of rail lines in Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, and the remoteness of the area on both sides of the strait in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
. Another issue to contend with is that Newfoundland had abandoned its Canadian National
The Canadian National Railway Company (french: Compagnie des chemins de fer nationaux du Canada) is a Canadian Class I freight railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec, which serves Canada and the Midwestern and Southern United States.
CN ...
/Newfoundland Railway
The Newfoundland Railway operated on the island of Newfoundland from 1898 to 1988. With a total track length of , it was the longest narrow-gauge railway system in North America.
Early construction
]
In 1880, a committee of the Newfoundland Leg ...
lines ( gauge until 1988–1990), turning it into the Newfoundland T'Railway
The Newfoundland T'Railway Provincial Park is a rail trail located in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Protected as a linear park under the provincial park system, the Newfoundland T'Railway consists of the railbed of the histor ...
, a rail trail spanning the entire island. An automobile tunnel would be most likely unfeasible due to the length needed to cross the strait, and the difficulties of removing automobile exhaust and bringing in fresh air via large circulation fans throughout the tunnel.
Alaska
Although Alaska is not connected to the North American rail network, there have been proposals to connect it viaBC Rail
BC Rail is a railway in the Canadian province of British Columbia.
Chartered as a private company in 1912 as the Pacific Great Eastern Railway (PGE), it was acquired by the provincial government in 1918. In 1972 it was renamed to the British ...
's incomplete but graded rail extension to Dease Lake
Dease Lake is a small community located in the Cassiar Country of the Northern Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located a few hours south of the Yukon border on Stewart–Cassiar Highway (Highway 37) at the south end of the lake ...
, where the rails have been laid to Jackson, British Columbia. The only way for rail-based equipment to enter or leave Alaska is via rail ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
from Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
, Washington. The only railway crossing the Alaska border is the White Pass and Yukon Route
The White Pass and Yukon Route (WP&Y, WP&YR) is a Canadian and U.S. Class III narrow-gauge railroad linking the port of Skagway, Alaska, with Whitehorse, the capital of Yukon. An isolated system, it has no direct connection to any other rai ...
, a narrow-gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
heritage railway linking Whitehorse, Yukon
Whitehorse () is the capital of Yukon, and the largest city in Northern Canada. It was incorporated in 1950 and is located at kilometre 1426 (Historic Mile 918) on the Alaska Highway in southern Yukon. Whitehorse's downtown and Riverdale areas ...
, with Skagway, Alaska
The Municipality and Borough of Skagway is a first-class borough in Alaska on the Alaska Panhandle. As of the 2020 census, the population was 1,240, up from 968 in 2010. The population doubles in the summer tourist season in order to deal with ...
.
Railheads of the network
The currentrailhead
In the UK, railheading refers to the practice of travelling further than necessary to reach a rail service, typically by car. The phenomenon is common among commuters seeking a more convenient journey. Reasons for railheading include, but are ...
s or endpoints of the rail network are, in the north, at Hay River, Northwest Territories (the northernmost part of the North American rail network, operated by CN), Jackson, British Columbia (formerly BC Rail
BC Rail is a railway in the Canadian province of British Columbia.
Chartered as a private company in 1912 as the Pacific Great Eastern Railway (PGE), it was acquired by the provincial government in 1918. In 1972 it was renamed to the British ...
), Lynn Lake
Lynn Lake is a town in the northwest region of Manitoba, Canada, approximately from Winnipeg. The town is the fourth-largest town in Manitoba in terms of land area. It is centred on the original urban community of Lynn Lake. The town was named ...
and Churchill, Manitoba ( Hudson Bay Railway), Moosonee ( Ontario Northland Railway), Chibougamau and Matagami
Matagami (, ) is a small town in Quebec, Canada. It is located north of Amos, on Matagami Lake, at the northern terminus of Route 109 and the start of the James Bay Road (French: ''Route de la Baie James''). It is enclaved within the local m ...
, Quebec (also CN). In the west, the railheads are at Vancouver, British Columbia, Prince Rupert, British Columbia
Prince Rupert is a port city in the province of British Columbia, Canada. Its location is on Kaien Island near the Alaskan panhandle. It is the land, air, and water transportation hub of British Columbia's North Coast, and has a population of 12 ...
(CN), with ferry service to Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
for the railways linking Nanaimo, Esquimalt
The Township of Esquimalt is a municipality at the southern tip of Vancouver Island, in British Columbia, Canada. It is bordered to the east by the provincial capital, Victoria, to the south by the Strait of Juan de Fuca, to the west by Esquim ...
, and Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
. In the east, the North American network extends to Halifax, and Sydney, Nova Scotia.
In the south, the rail lines terminate at Port of Chiapas
The Port Chiapas ( es, Puerto Chiapas) or Puerto Madero is a port in Puerto de San Benito in the Tapachula municipality of the Soconusco region in the southern portion of the Mexican state of Chiapas. The port entrance lies about northwest of the ...
, and Ciudad Hidalgo, with a short dual-gauge
In railway engineering, "gauge" is the transverse distance between the inner surfaces of the heads of two rails, which for the vast majority of railway lines is the number of rails in place. However, it is sometimes necessary for track to ca ...
spur line
A branch line is a phrase used in railway terminology to denote a secondary railway line which branches off a more important through route, usually a main line. A very short branch line may be called a spur line.
Industrial spur
An industr ...
to the border city of Ciudad Tecún Umán, Guatemala.
Proposed by Russia
 In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a rail tunnel under the Bering Strait between Chukotka and Alaska. The tunnel, as projected, would be long and would include oil and gas pipelines,
In April 2007 the Russian government announced that it was considering building a rail tunnel under the Bering Strait between Chukotka and Alaska. The tunnel, as projected, would be long and would include oil and gas pipelines, fiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre in Commonwealth English, is a flexible, transparent fiber made by drawing glass (silica) or plastic to a diameter slightly thicker than that of a human hair. Optical fibers are used most often as a means t ...
cables and power lines. The tunnel project was estimated to cost $65 billion and take 15–20 years to build. In addition to the Russian government, sponsors of the project apparently include Transneft
Joint Stock Company Transneft (russian: Транснефть) is a state-controlled pipeline transport company headquartered in Moscow, Russia. It is the largest oil pipeline company in the world. Transneft is operating over of trunk pipeline ...
and RAO United Energy Systems.
Central America
Mexico has a connection toCentral America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, but it is a break of gauge
With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge (the distance between the rails, or between the wheels of trains designed to run on those rails) meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally cannot ...
, since Mexico uses , while Guatemala and Central America use narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
. Aside from a short spur line linking border city
A border town is a town or city close to the boundary between two countries, states, or regions. Usually the term implies that the nearness to the border is one of the things the place is most famous for. With close proximities to a different cou ...
of Ciudad Tecún Umán, Guatemala, the entire nation is on gauge.
South of Guatemala, there are numerous breaks of gauge, such as (with Honduras), and El Salvador (which uses the same 914 mm gauge of rail, but is currently closed, with some sections abandoned and unusable). Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
has also closed its rail network in 1996, though the majority of it was gauge, with some lines along the Atlantic Coast. Costa Rica's railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
are of gauge, along with a private gauge railroad at 3.5 km in length. The railroads
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
of Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
are connected to Costa Rica. The country had two gauges: originally broad gauge , which was converted to standard gauge () in 2000, and narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
(914 mm). Like the situation with roads, the Darién Gap
The Darién Gap (, , es, Tapón del Darién , ) is a geographic region between the North and South American continents within Central America, consisting of a large watershed, forest, and mountains in Panama's Darién Province and the norther ...
is a formidable obstacle to railroads, and no railways cross it into South America.
Roadways
The continent's roads are of varying quality, withdivided highway
A dual carriageway ( BE) or divided highway ( AE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are ...
standards in some areas but poor-quality gravel or unpaved roads in others. The road network extends from Prudhoe Bay, Alaska
Prudhoe Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) located in North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population of the CDP was 2,174 people, up from just five residents in the 2000 census; however, at any give ...
, and Anchorage, Alaska, in the extreme northwest, to Sydney, Nova Scotia, Cartwright, Newfoundland and Labrador
Cartwright is a community located on the eastern side of the entrance to Sandwich Bay, along the southern coast of Labrador in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. It was incorporated in 1956. Cartwright is the largest settlement in ...
, Blanc Sablon and Natashquan, Quebec, in the extreme east, all the way to Yaviza, Panama, in the extreme south. It does not connect with the South American road network due to the Darién Gap
The Darién Gap (, , es, Tapón del Darién , ) is a geographic region between the North and South American continents within Central America, consisting of a large watershed, forest, and mountains in Panama's Darién Province and the norther ...
.
Some roads are seasonal, such as ice road
An ice road or ice bridge is a human-made structure that runs on a frozen water surface (a river, a lake or a sea water expanse).Masterson, D. and Løset, S., 2011, ISO 19906: Bearing capacity of ice and ice roads, Proceedings of the 21st Inte ...
s that cover frozen bodies of water, winter road
A winter road is a seasonal road only usable during the winter, i.e. it has to be re-built every year. This road typically runs over land and over frozen lakes, rivers, swamps, and sea ice.Proskin et al, 2011. Guidelines for the Construction an ...
s which cross otherwise impassable wetlands only in cold weather, and unpaved mountain roads that turn to mud in the spring. The road network does not reach all settlements, and some remote arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
and subarctic communities are only accessible by seasonal road, open land, sea, or air transport. Some North American islands are served only by ferries
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water tax ...
or private boat. Notable disconnected islands include the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
, Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
, Newfoundland (island), Martha's Vineyard, Nantucket, and the Canadian Arctic Archipelago
The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark).
Situated in the northern extremity of ...
. Some roads and some entire localities are intentionally car-free.
United States
The United States road network is the largest in the world, with 6.4 million km (4 million mi) of roadways. of those are Interstate Highways, and around another are U.S. Highways. The Interstate Highway system is almost completely composed of multi-lane,dual-carriageway
A dual carriageway ( BE) or divided highway ( AE) is a class of highway with carriageways for traffic travelling in opposite directions separated by a central reservation (BrE) or median (AmE). Roads with two or more carriageways which are ...
freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
s. The contiguous United States are also connected to its exclave, Alaska, via the Alaska Highway, which links the state to Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as ...
, British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, and the Lower 48 states
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
. The continental United States is disconnected from the state of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only state ...
and various insular area
In the law of the United States, an insular area is a U.S.-associated jurisdiction that is not part of the 50 states or the District of Columbia. This includes fourteen U.S. territories administered under U.S. sovereignty, as well as three so ...
s in the Caribbean and Oceania.
Many settlements in Alaska are disconnected from the continental road network except by ferry or boat, including the capital Juneau
The City and Borough of Juneau, more commonly known simply as Juneau ( ; tli, Dzánti K'ihéeni ), is the capital city of the state of Alaska. Located in the Gastineau Channel and the Alaskan panhandle, it is a unified municipality and the s ...
, Sitka
russian: Ситка
, native_name_lang = tli
, settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough
, image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg
, image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984
, image_size ...
, Kodiak, Bethel, Nome, and Utqiaġvik
Utqiagvik ( ik, Utqiaġvik; , , formerly known as Barrow ()) is the borough seat and largest city of the North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located north of the Arctic Circle, it is one of the northernmost cities and towns in the ...
.According to Google Maps directions, 25 March 2012. The Dalton Highway
The James W. Dalton Highway, usually referred to as the Dalton Highway (and signed as Alaska Route 11), is a road in Alaska. It begins at the Elliott Highway, north of Fairbanks, and ends at Deadhorse (an unincorporated community within the ...
connects the mainland via Fairbanks with the otherwise remote Prudhoe Bay, Alaska
Prudhoe Bay is a census-designated place (CDP) located in North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2010 census, the population of the CDP was 2,174 people, up from just five residents in the 2000 census; however, at any give ...
on the North Slope as a service road for the Trans-Alaska Pipeline
The Trans-Alaska Pipeline System (TAPS) is an oil transportation system spanning Alaska, including the trans-Alaska crude-oil pipeline, 11 pump stations, several hundred miles of feeder pipelines, and the Valdez Marine Terminal. TAPS is one o ...
.
Canada
TheTrans Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway ( French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the Atlantic Ocean o ...
spans the country along with its auxiliary branches. The Yellowhead Highway
The Yellowhead Highway (french: Route Yellowhead) is a major interprovincial highway in Western Canada that runs from Winnipeg to Graham Island off the coast of British Columbia via Saskatoon and Edmonton. It stretches across the four western ...
branches to the north, and the Crowsnest Highway
The Crowsnest Highway is an east-west highway in British Columbia and Alberta, Canada. It stretches across the southern portions of both provinces, from Hope, British Columbia to Medicine Hat, Alberta, providing the shortest highway connection b ...
, acts as a southern spur or shortcut to traveling from Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
to British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
across the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
. Canada's national highways are similar to the US Route network, as it is mostly two-lane without freeway sections, aside from in and near large population centres, such as Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
, Calgary, and Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
. Canada and the United States have also built the vital Alaska Highway, linking Anchorage, Alaska (and the rest of the state) to Canada and the rest of the United States.
Although Canada does not have a federal-level network of expressways, provinces from Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
to Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
are inter-linked by provincial-level freeways: Ontario's 400-series highways network, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
's Autoroute network, New Brunswick
New Brunswick (french: Nouveau-Brunswick, , locally ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. It is the only province with both English and ...
's upgrades to its portions of the Trans-Canada Highway, and Nova Scotia's 100-series highways. These expressways are the provincial equivalents to the United States' Interstate Highway system. The only gap in this inter-provincial expressway network (one can travel from Windsor to Halifax using expressways, but this involves crossing into the United States to use their Interstate Highway network, and back into Canada) between Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, on the south bank of the Detroit River directly across from Detroit, Michigan, United States. Geographically located within but administratively independent of Essex County, it is the southe ...
, and Halifax, Nova Scotia
Halifax is the capital and largest municipality of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Nova Scotia, and the largest municipality in Atlantic Canada. As of the 2021 Census, the municipal population was 439,819, with 348 ...
, is along Route 185/ Autoroute 85, which is being twinned and upgraded to become a fully divided expressway. This gap is quite busy and is expected to be upgraded by 2026.
Ontario is the only province to contain its own system of county road
A county highway (also county road or county route; usually abbreviated CH or CR) is a road in the United States and in the Canadian province of Ontario that is designated and/or maintained by the county highway department. Route numbering can ...
s, which are controlled and maintained by the counties, districts, and regions of Ontario.
Provinces from Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
west have their own networks of highways (the majority of which are not expressways or divided highways), with Winnipeg also having its own Winnipeg City Routes. Alberta has its own small but growing inter-connected network of divided highways and freeways, such as Alberta Highway 1
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 1, commonly referred to as Highway 1, is a major east–west highway in Southern Alberta that forms the southern mainline of the Trans-Canada Highway. It runs from the British Columbia border near Lake ...
, Highway 2, and Highway 16
Route 16, or Highway 16, can refer to:
International
* Asian Highway 16
* European route E16
* European route E016
Australia
- Thompsons Road (Victoria)
- South Australia
Canada
;Parts of the Trans-Canada Highway:
*Yellowhead Hi ...
. British Columbia also has a small network of freeways linking Vancouver to Kamloops, via Highway 1, and Highway 5
Route 5, or Highway 5, may refer to routes in the following countries:
International
* Asian Highway 5
* European route E05
* European route E005
Argentina
* National Route 5
Australia New South Wales
* M5 Motorway (Sydney)
* The De ...
, formerly a toll road
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or ''Toll (fee), toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically ...
.
Newfoundland and Labrador
In 2004 the provincial government studied the feasibility of a Newfoundland-Labrador fixed link joining the island of Newfoundland to the mainland of North America via a 17 km-long rail tunnel under theStrait of Belle Isle
The Strait of Belle Isle (; french: Détroit de Belle Isle ) is a waterway in eastern Canada that separates the Labrador Peninsula from the island of Newfoundland, in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Location
The strait is the northern o ...
, which would also carry automobile traffic on flat cars, similar to the Channel Tunnel between the United Kingdom and France. This has stalled due to the lack of a large road network and a lack of rail lines in Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, and the remoteness of the area on both sides of the strait in Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
. Another issue to contend with is that Newfoundland had abandoned its segments of its CN/Newfoundland Railway
The Newfoundland Railway operated on the island of Newfoundland from 1898 to 1988. With a total track length of , it was the longest narrow-gauge railway system in North America.
Early construction
]
In 1880, a committee of the Newfoundland Leg ...
lines ( narrow-gauge) in 1988–1990, turning it into the Newfoundland T'Railway
The Newfoundland T'Railway Provincial Park is a rail trail located in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Protected as a linear park under the provincial park system, the Newfoundland T'Railway consists of the railbed of the histor ...
, a rail trail spanning the entire island. An automobile tunnel would be most likely unfeasible due to the length needed to cross the strait, and the difficulties of removing automobile exhaust and bringing in fresh air via large circulation fans throughout the tunnel. Labrador is, however, connected to the continental road network via the Trans-Labrador Highway
The Trans-Labrador Highway (TLH) is a highway located in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. It is the primary public road in Labrador. Its total length is . The complete paving of the highway was completed in July 2022.
The ...
.
Mexico
Mexico also has a very large road network, 323,977 km worth of roads. Of these, 96,221 km are paved (this is including 6,335 km of expressways) The remainder (227,756 km worth) is unpaved. Since 1991, Mexico has been buildingtoll roads
A toll road, also known as a turnpike or tollway, is a public or private road (almost always a controlled-access highway in the present day) for which a fee (or '' toll'') is assessed for passage. It is a form of road pricing typically implemente ...
that link its major cities together. Currently, there are 6,335 km worth of toll freeways in the country, with the numbering scheme of ''n''-D (''n'' being the number of the road bypassed, such as 45, with toll freeway as 45-D, meaning 45 Diversion).
Central America
Central America's roadway network continues, linking every major city and capital, via thePan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway (french: (Auto)route panaméricaine/transaméricaine; pt, Rodovia/Auto-estrada Pan-americana; es, Autopista/Carretera/Ruta Panamericana) is a network of roads stretching across the Americas and measuring about in to ...
, which continues through Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, across the Panama Canal, to Yaviza, Panama. It is separated from South America by the large Darién Gap
The Darién Gap (, , es, Tapón del Darién , ) is a geographic region between the North and South American continents within Central America, consisting of a large watershed, forest, and mountains in Panama's Darién Province and the norther ...
.
Waterways
Waterways were the primary method of transportation of people and goods, and used by native aboriginal people indugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' ( ...
s and kayaks.
The waterways remained important since Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
arrived in 1492, right up until the First World War. Though their use has diminished somewhat with the arrival of rail transportation, the Interstate Highway/ 400 series highways networks of America and Canada, and with the debut of air travel, they are still widely used for transporting goods from the American Midwest to overseas markets.
The cities of Duluth, Minnesota
, settlement_type = City
, nicknames = Twin Ports (with Superior), Zenith City
, motto =
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top: urban Duluth skyline; Minnesota ...
and Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its population i ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
(to some extent, Chicago, Illinois
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
as well) are the most inland seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as H ...
s/deepwater port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ha ...
s in the world, being well over 2000 miles from the shores of the Atlantic Ocean, yet they still can cater to cargo ships, thanks to the St. Lawrence Seaway, Welland Canal
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway and Great Lakes Waterway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller in St. Catharines ...
and Soo Locks
The Soo Locks (sometimes spelled Sault Locks but pronounced "soo") are a set of parallel locks, operated and maintained by the United States Army Corps of Engineers, Detroit District, that enable ships to travel between Lake Superior and the low ...
, a joint-venture
A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties, generally characterized by shared ownership, shared returns and risks, and shared governance. Companies typically pursue joint ventures for one of four reasons: to acce ...
binational system of dam
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
s, lock
Lock(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lock ...
s, and canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
s built by Canada and the United States in 1959. The Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
/ Missouri River system also sees a large amount of oceanbound ship traffic from cities such as St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, Kansas City, and .
Churchill, Manitoba also serves as a minor port for grain and wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
loaded via railroad cars, and loaded onto ships bound for Europe at the intermodal facilities in that town.
The nation of Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
currently operates one of the world's busiest and most familiar waterways, the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
. This canal cuts through the Isthmus of Panama, connecting the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, shaving off more than for ships, instead of having them travel around the tip of Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
in South America. A ship travelling from New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
to San Francisco
San Francisco (; Spanish for " Saint Francis"), officially the City and County of San Francisco, is the commercial, financial, and cultural center of Northern California. The city proper is the fourth most populous in California and 17th ...
would be roughly in distance, while a trip around Cape Horn would be in length. The Canal functions similarly to the Suez Canal in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
.
Ferry services
Currently, car ferry andrail ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train ...
service between New York City, New York/, Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
/Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a coastal metropolis and the county seat of Miami-Dade County in South Florida, United States. With a population of 442,241 at ...
, Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, United States, and Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
is suspended, due to the ongoing embargo
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstances—they m ...
by the United States against Cuba. There is however, rail ferry service between Whittier, Alaska and Prince Rupert, British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
(the AquaTrain, operated by the Alaska Railroad) and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
state (Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest regio ...
), and a ferry to and from Mobile
Mobile may refer to:
Places
* Mobile, Alabama, a U.S. port city
* Mobile County, Alabama
* Mobile, Arizona, a small town near Phoenix, U.S.
* Mobile, Newfoundland and Labrador
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Mobile ( ...
, Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County
, LargestMetro = Greater Birmingham
, area_total_km2 = 135,765 ...
and the Port of Ponce Railroad in Ponce, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
. Regular ferry service also links Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is an island in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and part of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The island is in length, in width at its widest point, and in total area, while are of land. The island is the largest by ...
and isolated Sunshine Coast communities to the mainland and to Alaska. There is also automobile ferry service between Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and Newfoundland and Labrador
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic Canada, Atlantic region. The province comprises t ...
, from Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
to Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, and between Labrador and the island of Newfoundland.
Air travel
Air travel first entered as a viable alternative totranscontinental railroad
A transcontinental railroad or transcontinental railway is contiguous railroad trackage, that crosses a continental land mass and has terminals at different oceans or continental borders. Such networks can be via the tracks of either a single ...
s, and to the then-primitive (or non-existent) road networks that crossed the United States and Canada in the early 1930s, but truly increased in popularity after the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
.
Most of the continent's busiest airports are located in the United States. In fact the U.S. has 9 of North America's 10 busiest airports, including the world's busiest, Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport
Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport , also known as Atlanta Hartsfield–Jackson International Airport, Atlanta Airport, Hartsfield, Hartsfield–Jackson and, formerly, as the Atlanta Municipal Airport, is the primary internatio ...
in Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
. The busiest airport in North America outside the United States is Toronto Pearson International Airport
Lester B. Pearson International Airport , commonly known as Toronto Pearson International Airport, is an international airport located in Mississauga, Ontario, Canada. It is the main airport serving Toronto, its metropolitan area, and the surr ...
, located in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anch ...
, Canada.
See also
*Geography of North America
North America is the third largest continent, and is also a portion of the third largest supercontinent if North and South America are combined into the Americas and Africa, Europe, and Asia are considered to be part of one supercontinent called ...
* List of sovereign states
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty.
The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership withi ...
* Transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
* North American Transportation Statistics Interchange
The North American Transportation Statistics Interchange, established in 1991, is a trilateral forum of government officials from transportation and statistical agencies of the United States, Canada, and Mexico. The purpose of the NATS Interchange ...
* World economy#Transport
* List of countries by rail transport network size
This list of countries by rail transport network size based on International Union of Railways data ranks countries by length of rail lines worked at end of year updated with other reliable sources. These figures also include urban/suburban mass ...
* Transport in Europe
Transport in Europe provides for the movement needs of over 700 million people and associated freight.
Overview
The political geography of Europe divides the continent into over 50 sovereign states and territories. This fragmentation, along ...
* Bering Strait crossing
A Bering Strait crossing is a hypothetical bridge or tunnel that would span the relatively narrow and shallow Bering Strait between the Chukotka Peninsula in Russia and the Seward Peninsula in the U.S. state of Alaska. The crossing would prov ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Transportation In North America