Transglutamination on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transglutaminases are
 Nine transglutaminases have been characterised in humans, eight of which catalyse
Nine transglutaminases have been characterised in humans, eight of which catalyse
 In commercial food processing, transglutaminase is used to bond proteins together. Examples of foods made using transglutaminase include imitation crabmeat, and
In commercial food processing, transglutaminase is used to bond proteins together. Examples of foods made using transglutaminase include imitation crabmeat, and
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
s that in nature primarily catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
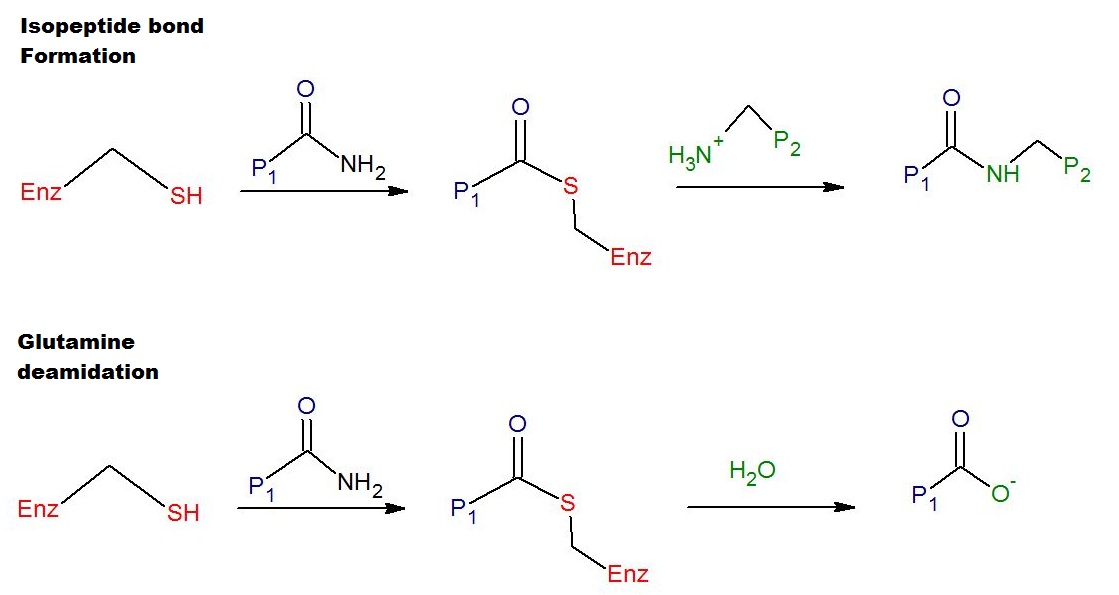
the formation of an isopeptide bond between γ- carboxamide groups ( -(C=O)NH2 ) of glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral ...
residue side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a ...
s and the ε-amino group
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
s ( -NH2 ) of lysine residue side chains with subsequent release of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
( NH3 ). Lysine and glutamine residues must be bound to a peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
...
or a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
so that this cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural ...
ing (between separate molecules) or intramolecular (within the same molecule) reaction can happen. Bonds formed by transglutaminase exhibit high resistance to proteolytic degradation ( proteolysis). The reaction is
: Gln-(C=O)NH2 + NH2-Lys → Gln-(C=O)NH-Lys + NH3
Transglutaminases can also join a primary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia (), wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such ...
( RNH2 ) to the side chain carboxyamide group of a protein/peptide bound glutamine residue thus forming an isopeptide bond
:Gln-(C=O)NH2 + RNH2 → Gln-(C=O)NHR + NH3
These enzymes can also deamidate glutamine residues to glutamic acid residues in the presence of water
:Gln-(C=O)NH2 + H2O → Gln-COOH + NH3
Transglutaminase isolated from '' Streptomyces mobaraensis'' -bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
for example, is a calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar t ...
-independent enzyme. Mammalian
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
transglutaminases among other transglutaminases require Ca2+ ions as a cofactor.
Transglutaminases were first described in 1959. The exact biochemical activity of transglutaminases was discovered in blood coagulation protein factor XIII
Factor XIII or fibrin stabilizing factor is a zymogen found in blood of humans and some other animals. It is activated by thrombin to factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa is an enzyme of the blood coagulation system that crosslinks fibrin. Deficiency of X ...
in 1968.
Examples
 Nine transglutaminases have been characterised in humans, eight of which catalyse
Nine transglutaminases have been characterised in humans, eight of which catalyse transamidation Transamidation is a chemical reaction in which an amide reacts with an amine to generate a new amide:
:RC(O)NR'2 + HNR"2 → RC(O)NR"2 + HNR'2
The reaction is typically very slow, but it can be accelerated with Lewis acid and organometallic ...
reactions. These TGases have a three or four-domain organization, with immunoglobulin-like domains surrounding the central catalytic domain. The core domain belongs to the papain-like protease
Papain-like proteases (or papain-like (cysteine) peptidases; abbreviated PLP or PLCP) are a large protein family of cysteine protease enzymes that share structural and enzymatic properties with the group's namesake member, papain. They are found ...
superfamily (CA clan) and uses a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad
A catalytic triad is a set of three coordinated amino acids that can be found in the active site of some enzymes. Catalytic triads are most commonly found in hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, li ...
. Protein 4.2 , also referred to as band 4.2, is a catalytically inactive member of the human transglutaminase family that has a Cys to Ala substitution at the catalytic triad.
Bacterial transglutaminases are single-domain proteins with a similarly-folded core. The transglutaminase found in some bacteria runs on a Cys-Asp diad.
Biological role
Transglutaminases form extensively cross-linked, generally insoluble protein polymers. These biological polymers are indispensable for an organism to create barriers and stable structures. Examples areblood clot
A thrombus (plural thrombi), colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of ...
s (coagulation factor XIII
Factor XIII or fibrin stabilizing factor is a zymogen found in blood of humans and some other animals. It is activated by thrombin to factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa is an enzyme of the blood coagulation system that crosslinks fibrin. Deficiency of X ...
), as well as skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different de ...
and hair. The catalytic reaction is generally viewed as being irreversible, and must be closely monitored through extensive control mechanisms.
Role in disease
Deficiency of factor XIII (a rare genetic condition) predisposes tohemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, v ...
; concentrated enzyme can be used to correct the abnormality and reduce bleeding risk.
Anti-transglutaminase antibodies are found in celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
and may play a role in the small bowel
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pa ...
damage in response to dietary gliadin
Gliadin (a type of prolamin) is a class of proteins present in wheat and several other cereals within the grass genus ''Triticum''. Gliadins, which are a component of gluten, are essential for giving bread the ability to rise properly during baki ...
that characterises this condition. In the related condition dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) is a chronic autoimmune blistering skin condition, characterised by intensely itchy blisters filled with a watery fluid. DH is a cutaneous manifestation of coeliac disease, although the exact causal mechanism is not k ...
, in which small bowel changes are often found and which responds to dietary exclusion of gliadin-containing wheat products, epidermal transglutaminase is the predominant autoantigen.
Recent research indicates that sufferers from neurological diseases like Huntington's and Parkinson's
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
may have unusually high levels of one type of transglutaminase, tissue transglutaminase
Tissue transglutaminase (abbreviated as tTG or TG2) is a 78-kDa, calcium-dependent enzyme () of the protein-glutamine γ-glutamyltransferases family (or simply transglutaminase family). Like other transglutaminases, it crosslinks proteins between ...
. It is hypothesized that tissue transglutaminase may be involved in the formation of the protein aggregates that causes Huntington's disease, although it is most likely not required.
Mutations in keratinocyte transglutaminase are implicated in lamellar ichthyosis
Lamellar ichthyosis, also known as ichthyosis lamellaris and nonbullous congenital ichthyosis, is a rare inherited skin disorder, affecting around 1 in 600,000 people.
Presentation
Affected babies are born in a collodion membrane, a shiny, waxy- ...
.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, 19structures
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
have been solved for this class of enzymes, with PDB accession codes , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , and .
Industrial and culinary applications
 In commercial food processing, transglutaminase is used to bond proteins together. Examples of foods made using transglutaminase include imitation crabmeat, and
In commercial food processing, transglutaminase is used to bond proteins together. Examples of foods made using transglutaminase include imitation crabmeat, and fish ball
Fish balls are rounded meat balls made from fish paste which are then boiled or deep fried. Similar in composition to fishcake, fish balls are often made from fish mince or surimi, salt, and a culinary binder such as tapioca flour, corn, or p ...
s. It is produced by '' Streptoverticillium mobaraense'' fermentation in commercial quantities () or extracted from animal blood, and is used in a variety of processes, including the production of processed meat and fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
products.
Transglutaminase can be used as a binding agent to improve the texture of protein-rich foods such as surimi or ham
Ham is pork from a leg cut that has been preserved by wet or dry curing, with or without smoking."Bacon: Bacon and Ham Curing" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 2, p. 39. As a processed meat, the term "ham ...
.
Thrombin
Thrombin (, ''fibrinogenase'', ''thrombase'', ''thrombofort'', ''topical'', ''thrombin-C'', ''tropostasin'', ''activated blood-coagulation factor II'', ''blood-coagulation factor IIa'', ''factor IIa'', ''E thrombin'', ''beta-thrombin'', ''gamma- ...
–fibrinogen
Fibrinogen (factor I) is a glycoprotein complex, produced in the liver, that circulates in the blood of all vertebrates. During tissue and vascular injury, it is converted enzymatically by thrombin to fibrin and then to a fibrin-based blood cl ...
" meat glue" from bovine and porcine sources was banned throughout the European Union as a food additive in 2010. Transglutaminase remains allowed and is not required to be declared, as it is considered a processing aid and not an additive which remains present in the final product.
Molecular gastronomy
Transglutaminase is also used inmolecular gastronomy
Molecular gastronomy is the scientific approach of nutrition from primarily the perspective of chemistry. The composition ( molecular structure), properties (mass, viscosity, etc) and transformations (chemical reactions, reactant products) o ...
to meld new textures with existing tastes. Besides these mainstream uses, transglutaminase has been used to create some unusual foods. British chef Heston Blumenthal
Heston Marc Blumenthal (; born 27 May 1966) is a British celebrity chef, TV personality and food writer. Blumenthal is regarded as a pioneer of multi-sensory cooking, food pairing and flavour encapsulation. He came to public attention with u ...
is credited with the introduction of transglutaminase into modern cooking.
Wylie Dufresne
Wylie Dufresne (born 1970) is the chef and owner of Du's Donuts and the former chef and owner of the wd~50 and Alder restaurants in Manhattan. Dufresne is a leading American proponent of molecular gastronomy, the movement to incorporate science ...
, chef of New York's avant-garde
The avant-garde (; In 'advance guard' or ' vanguard', literally 'fore-guard') is a person or work that is experimental, radical, or unorthodox with respect to art, culture, or society.John Picchione, The New Avant-garde in Italy: Theoretical ...
restaurant wd~50, was introduced to transglutaminase by Blumenthal, and invented a "pasta
Pasta (, ; ) is a type of food typically made from an unleavened dough of wheat flour mixed with water or eggs, and formed into sheets or other shapes, then cooked by boiling or baking. Rice flour, or legumes such as beans or lentils, ar ...
" made from over 95% shrimp thanks to transglutaminase.
Synonyms
* protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase (systematic) * fibrinoligase * glutaminylpeptide gamma-glutamyltransferase * protein-glutamine:amine gamma-glutamyltransferase * R-glutaminyl-peptide:amine gamma-glutamyl transferaseSee also
*Boneless Fish
Boneless Fish is a fish-based frozen food brand and grocery product, the process in the production of which was invented by Dairei Corporation (大冷株式会社) of Japan in 1998. It is essentially a fish that has been scaled, gutted and d ...
* Surimi
* Bromelain
Bromelain is an enzyme extract derived from the stems of pineapples, although it exists in all parts of the fresh pineapple. The extract has a history of folk medicine use. As an ingredient, it is used in cosmetics, as a topical medication, and as ...
* Papain
* Ficain
Ficain also known as ficin, debricin, or higueroxyl delabarre () is a proteolytic enzyme extracted from the latex sap from the stems, leaves, and unripe fruit of the American wild fig tree ''Ficus insipida''.
Ficain was originally called ficin, a ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * A transglutaminase catalyzing an acyl transfer reaction of a Γ-carboxyamide group of a glutamine residue in a peptide or protein chain in the absence of Ca2+ {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no * Food additives Autoantigens Calcium enzymes Enzymes of known structure