Thumb Wrestling Federation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The thumb is the first digit of the hand, next to the
 *
*
 There is a variation of the human thumb where the angle between the first and second (proximal and distal) Distal phalanges, phalanges varies between 0° and almost 90° when the thumb is in a Thumbs Up, thumbs-up gesture.
It has been suggested that the variation is an autosomal recessive trait, called a hitchhiker's thumb, with homozygous carriers having an angle close to 90°. However this theory has been disputed, since the variation in thumb angle is known to fall on a continuum and shows little evidence of the Bimodal distribution, bi-modality seen in other recessive genetic traits.
Other variations of the thumb include Brachydactyly type D, brachydactyly type D (which is a thumb with a congenitally short distal phalanx), a triphalangeal thumb (which is a thumb which has 3 phalanges instead of the usual two), and polysyndactyly (which is a combination of radial polydactyly and syndactyly).
There is a variation of the human thumb where the angle between the first and second (proximal and distal) Distal phalanges, phalanges varies between 0° and almost 90° when the thumb is in a Thumbs Up, thumbs-up gesture.
It has been suggested that the variation is an autosomal recessive trait, called a hitchhiker's thumb, with homozygous carriers having an angle close to 90°. However this theory has been disputed, since the variation in thumb angle is known to fall on a continuum and shows little evidence of the Bimodal distribution, bi-modality seen in other recessive genetic traits.
Other variations of the thumb include Brachydactyly type D, brachydactyly type D (which is a thumb with a congenitally short distal phalanx), a triphalangeal thumb (which is a thumb which has 3 phalanges instead of the usual two), and polysyndactyly (which is a combination of radial polydactyly and syndactyly).
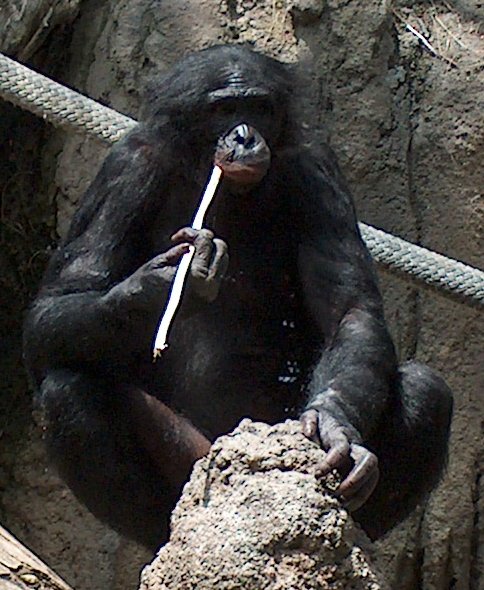
 Opposability of the thumb should not be confused with a precision grip as some animals possess semi-opposable thumbs yet are known to have extensive precision grips (Cebus apella, Tufted Capuchins for example). Nevertheless, precision grips are usually only found in higher apes, and only in degrees significantly more restricted than in humans.
The pad-to-pad pinch between the thumb and index finger is made possible because of the human ability to passively hyperextend the Distal phalanges, distal phalanx of the index finger. Most non-human primates have to flex their long fingers in order for the small thumb to reach them.
In humans, the distal pads are wider than in other primates because the soft tissues of the finger tip are attached to a horseshoe-shaped edge on the underlying bone, and, in the grasping hand, the distal pads can therefore conform to uneven surfaces while pressure is distributed more evenly in the finger tips. The distal pad of the human thumb is divided into a proximal and a distal compartment, the former more deformable than the latter, which allows the thumb pad to mold around an object.
In robotics, almost all robotic hands have a long and strong opposable thumb. Like human hands, the thumb of a robotic hand also plays a key role in gripping an object. One inspiring approach of robotic grip planning is to mimic human thumb placement.
In a sense, human thumb placement indicates which surface or part of the object is good for grip. Then the robot places its thumb to the same location and plans the other fingers based on the thumb placement.
The function of the thumb declines physiologically with aging. This can be demonstrated by assessing the motor sequencing of the thumb.
Opposability of the thumb should not be confused with a precision grip as some animals possess semi-opposable thumbs yet are known to have extensive precision grips (Cebus apella, Tufted Capuchins for example). Nevertheless, precision grips are usually only found in higher apes, and only in degrees significantly more restricted than in humans.
The pad-to-pad pinch between the thumb and index finger is made possible because of the human ability to passively hyperextend the Distal phalanges, distal phalanx of the index finger. Most non-human primates have to flex their long fingers in order for the small thumb to reach them.
In humans, the distal pads are wider than in other primates because the soft tissues of the finger tip are attached to a horseshoe-shaped edge on the underlying bone, and, in the grasping hand, the distal pads can therefore conform to uneven surfaces while pressure is distributed more evenly in the finger tips. The distal pad of the human thumb is divided into a proximal and a distal compartment, the former more deformable than the latter, which allows the thumb pad to mold around an object.
In robotics, almost all robotic hands have a long and strong opposable thumb. Like human hands, the thumb of a robotic hand also plays a key role in gripping an object. One inspiring approach of robotic grip planning is to mimic human thumb placement.
In a sense, human thumb placement indicates which surface or part of the object is good for grip. Then the robot places its thumb to the same location and plans the other fingers based on the thumb placement.
The function of the thumb declines physiologically with aging. This can be demonstrated by assessing the motor sequencing of the thumb.
index finger
The index finger (also referred to as forefinger, first finger, second finger, pointer finger, trigger finger, digitus secundus, digitus II, and many other terms) is the second digit of a human hand. It is located between the thumb and the mid ...
. When a person is standing in the medical anatomical position (where the palm is facing to the front), the thumb is the outermost digit. The Medical Latin English noun for thumb is ''pollex'' (compare ''hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
'' for big toe), and the corresponding adjective for thumb is ''pollical''.
Definition
Thumb and fingers
The English word ''finger'' has two senses, even in the context of appendages of a single typical human hand: # Any of the five terminal members of the hand. # Any of the four terminal members of the hand, other than the thumb Linguistically, it appears that the original sense was the first of these two: (also rendered as ) was, in the inferredProto-Indo-European language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
, a suffixed form of (or ), which has given rise to many Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
-family words (tens of them defined in English dictionaries) that involve, or stem from, concepts of fiveness.
The thumb shares the following with each of the other four fingers:
* Having a skeleton of phalanges, joined by hinge-like joints that provide flexion toward the palm of the hand
* Having a dorsal surface that features hair and a nail, and a hairless palmar aspect with fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfac ...
ridges
The thumb contrasts with each of the other four fingers by being the only one that:
* Is opposable to the other four fingers
* Has two phalanges rather than three
* Has greater breadth in the distal phalanx than in the proximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
phalanx
* Is attached to such a mobile metacarpus (which produces most of the opposability)
*Curls horizontally instead of vertically
and hence the etymology of the word: is Proto-Indo-European for 'swelling' (cf 'tumour' and 'thigh') since the thumb is the stoutest of the fingers.
Opposition and apposition
Humans
Anatomists and other researchers focused on human anatomy have hundreds of definitions of ''opposition''. Some anatomists restrict ''opposition'' to when the thumb is approximated to the fifth finger (little finger) and refer to other approximations between the thumb and other fingers as ''apposition''. To anatomists, this makes sense as two intrinsic hand muscles are named for this specific movement (theopponens pollicis
The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.
Structure
The op ...
and opponens digiti minimi
The opponens digiti minimi (opponens digiti quinti in older texts) is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of t ...
respectively).
Other researchers use another definition, referring to opposition-apposition as the transition between flexion-abduction and extension-adduction; the ''side'' of the distal thumb phalanx thus approximated to the palm or the hand's radial side (side of index finger) during ''apposition'' and the ''pulp'' or "palmar" side of the distal thumb phalanx approximated to either the palm or other fingers during ''opposition''.
Moving a limb back to its neutral position is called reposition and a rotary movement is referred to as circumduction.
Primatologists and hand research pioneers John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and Prudence Napier defined opposition as: "A movement by which the pulp surface of the thumb is placed squarely in contact with or diametrically opposite to the terminal pads of one or all of the remaining fingers." For this ''true'', pulp-to-pulp opposition to be possible, the thumb must rotate about its long axis (at the carpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
). Arguably, this definition was chosen to underline what is unique to the human thumb.
Other primates
 *
* Primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
s fall into one of six groups:
** Thumbless: spider monkey
Spider monkeys are New World monkeys belonging to the genus ''Ateles'', part of the subfamily Atelinae, family Atelidae. Like other atelines, they are found in tropical forests of Central and South America, from southern Mexico to Brazil. The ...
and colobus
Black-and-white colobuses (or colobi) are Old World monkeys of the genus ''Colobus'', native to Africa. They are closely related to the red colobus monkeys of genus '' Piliocolobus''. There are five species of this monkey, and at least eight subs ...
** Nonopposable thumbs: tarsiers (which are found in the islands of Southeast Asia), marmoset
The marmosets (), also known as zaris or sagoin, are 22 New World monkey species of the genera '' Callithrix'', '' Cebuella'', '' Callibella'', and ''Mico''. All four genera are part of the biological family Callitrichidae. The term "marmoset" ...
s (which are New World monkeys
New World monkeys are the five families of primates that are found in the tropical regions of Mexico, Central and South America: Callitrichidae, Cebidae, Aotidae, Pitheciidae, and Atelidae. The five families are ranked together as the Ceboidea ...
)
** Pseudo-opposable thumbs: all strepsirrhine
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini (; ) is a suborder of primates that includes the lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Africa, and the lorises from India and southeast Asia. Colle ...
s (lemurs, pottos and lorises) and Cebidae (capuchin and squirrel monkeys, which are New World monkeys
New World monkeys are the five families of primates that are found in the tropical regions of Mexico, Central and South America: Callitrichidae, Cebidae, Aotidae, Pitheciidae, and Atelidae. The five families are ranked together as the Ceboidea ...
)
** Opposable thumbs: Old World monkey
Old World monkey is the common English name for a family of primates known taxonomically as the Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons ...
s (Circopithecidae) except colobus, and all great apes
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); ''Gorilla'' (the ...
** Opposable with comparatively long thumbs: gibbons (or lesser apes)
** Yet to be classified: other New World monkeys
New World monkeys are the five families of primates that are found in the tropical regions of Mexico, Central and South America: Callitrichidae, Cebidae, Aotidae, Pitheciidae, and Atelidae. The five families are ranked together as the Ceboidea ...
(tamarin
The tamarins are squirrel-sized New World monkeys from the family Callitrichidae in the genus ''Saguinus''. They are the first offshoot in the Callitrichidae tree, and therefore are the sister group of a clade formed by the lion tamarins, Goe ...
s, Aotidae: night or owl monkeys, Pitheciidae: titis, sakis and uakaris, Atelidae: howler and woolly monkeys)
The spider monkey compensates for being virtually thumbless by using the hairless part of its long, prehensile tail for grabbing objects. In ape
Apes (collectively Hominoidea ) are a clade of Old World simians native to sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia (though they were more widespread in Africa, most of Asia, and as well as Europe in prehistory), which together with its sister g ...
s and Old World monkeys, the thumb can be rotated around its axis, but the extensive area of contact between the pulps of the thumb and index finger is a human characteristic.
''Darwinius, Darwinius masillae'', an Eocene primate transitional fossil between prosimian and simian, had hands and feet with highly flexible digits featuring opposable thumbs and halluces.
Other placental mammals
* Giant pandas — five clawed fingers plus an extra-long Sesamoid bone#Panda anatomy, sesamoid bone beside the true first finger that, though not a true finger, works like an opposable thumb. * In some ''Muridae'' the hallux is clawless and fully opposable, including arboreal species such as ''Hapalomys'', ''Chiropodomys'', ''Vandeleuria'', and ''Chiromyscus''; and saltatorial, bipedal species such as ''Notomys'' and possibly some Gerbillinae. * The East African maned rat (''Lophiomys imhausi''), an arboreal, porcupine-like rodent, has four fingers on its hands and feet and a partially opposable thumb. * Most rodents have a partly opposable toe on each front paw, letting them grasp. Additionally, in many polydactyl cats, both the innermost toe and outermost toe (Little finger, pinky) may become opposable, allowing the cat to perform more complex tasks.Marsupials
* In most phalangerid marsupials (a family of Phalangeriformes, possums) except species ''Trichosurus'' and ''Wyulda'' the first and second toes of the forefoot are opposable to the other three. In the hind foot, the first toe is clawless but opposable and provides firm grip on branches. The second and third toes are partly Dactyly, syndactylous, united by skin at the top joint while the two separate nails serve as hair combs. The fourth and fifth toes are the largest of the hind foot. * Similar to though in a different family, koalas have five toes on their fore and hind feet with sharp curved claws except for the first toe of the hind foot. The first and second toes of the forefeet are opposable to the other three, which enables the koala to grip smaller branches and search for fresh leaves in the outer canopy. Similar to the phalangerids, the second and third toes of the hind foot are fused but have separate claws. * Opossums are New World marsupials with opposable thumbs in the hind feet giving these animals their characteristic grasping capability (with the exception of the water opossum, the webbed feet of which restrict opposability). * The mouse-like Microbiotheria, microbiotheres were a group of South American marsupials most closely related to Australian marsupials. The only extant member, ''Monito del Monte, Dromiciops gliroides'', is not closely related to opossums but has paws similar to these animals, each having opposable toes adapted for gripping.Reptiles
* The front feet of chameleons are organized into a medial bundle of toes 1, 2 and 3, and a lateral bundle of toes 4 and 5, and the hind feet are organized into a medial bundle of toes 1 and 2, and a lateral bundle of toes 3, 4 and 5.Dinosaurs
* Dinosaurs belong to the family of bird-like dinosaur Troodontidae had a partially opposable finger. It is possible that this adaptation was used to better manipulate ground objects or moving undergrowth branches when searching for prey. * The small predatory dinosaur ''Bambiraptor'' may have had mutually opposable first and third fingers and a forelimb manoeuvrability that would allow the hand to reach its mouth. Its forelimb morphology and range of motion enabled two-handed prehension, one-handed clutching of objects to the chest, and use of the hand as a hook. * ''Nqwebasaurus'' — a coelurosaur with a long, three-fingered hand which included a partially opposable thumb (a "killer claw"). In addition to these, some other dinosaurs may have had partially or completely opposed toes in order to manipulate food and/or grasp prey.Birds
* Most birds have at least one opposable toe on the foot, in Dactyly#In birds, various configurations, though these are seldom called "thumbs". They are more often known simply ashallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being '' digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being '' pl ...
es.
Pterosaurs
* The Wukongopteridae, wukongopterid pterosaur ''Kunpengopterus'' bore an opposable first toe on each wing. The presence of opposable thumbs in this taxon is thought to be an arboreal adaptation.Amphibians
* ''Phyllomedusa'', a genus of frogs native to South America.Human anatomy
Skeleton
The skeleton of the thumb consists of the first metacarpal bone which articulatesproximal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
ly with the Carpal bones, carpus at the Articulatio carpometacarpea pollicis, carpometacarpal joint and distally with the proximal phalanges, proximal phalanx at the metacarpophalangeal joint. This latter bone articulates with the Distal phalanges, distal phalanx at the interphalangeal articulations of hand, interphalangeal joint. Additionally, there are two sesamoid bones at the metacarpophalangeal joint.
Muscles
The muscles of the thumb can be compared to guy-wires supporting a flagpole; tension from these muscular guy-wires must be provided in all directions to maintain stability in the articulated column formed by the bones of the thumb. Because this stability is actively maintained by muscles rather than by articular constraints, most muscles attached to the thumb tend to be active during most thumb motions. The muscles acting on the thumb can be divided into two groups: The extrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the forearm, and the intrinsic hand muscles, with their muscle bellies located in the hand proper.Extrinsic
A ventral forearm muscle, the Flexor pollicis longus muscle, flexor pollicis longus (FPL) originates on the anterior side of the Radius (bone), radius distal to the radial tuberosity and from the Interosseous membrane of forearm, interosseous membrane. It passes through the carpal tunnel in a separate tendon sheath, after which it lies between the heads of the flexor pollicis brevis. It finally attaches onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. It is innervated by the Anterior interosseous nerve, anterior interosseus branch of the median nerve (C7-C8) It is a persistence of one of the former contrahentes muscles that pulled the fingers or toes together. Three dorsal forearm muscles act on the thumb: The Abductor pollicis longus muscle, abductor pollicis longus (APL) originates on the dorsal sides of both the ulna and the radius, and from the interosseous membrane. Passing through the first tendon compartment, it inserts to the base of the first Metacarpus, metacarpal bone. A part of the tendon reaches the trapezium, while another fuses with the tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and the abductor pollicis brevis. Except for abducting the hand, it flexes the hand towards the palm and abducts it radially. It is innervated by the deep branch of the radial nerve (C7-C8). The Extensor pollicis longus muscle, extensor pollicis longus (EPL) originates on the dorsal side of the ulna and the interosseous membrane. Passing through the third tendon compartment, it is inserted onto the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb. It uses the dorsal tubercle on the lower extremity of the radius as a Lever, fulcrum to extend the thumb and also dorsiflexes and abducts the hand at the wrist. It is innervated by the deep branch of the radial nerve (C7-C8). The Extensor pollicis brevis muscle, extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) originates on the ulna distal to the abductor pollicis longus, from the interosseus membrane, and from the dorsal side of the radius. Passing through the first tendon compartment together with the abductor pollicis longus, it is attached to the base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb. It extends the thumb and, because of its close relationship to the long abductor, also abducts the thumb. It is innervated by the deep branch of the radial nerve (C7-T1). The tendons of the extensor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis form what is known as the anatomical snuff box (an indentation on the lateral aspect of the thumb at its base) The radial artery can be palpated anteriorly at the wrist (not in the snuffbox).Intrinsic
There are three Thenar eminence, thenar muscles: The Abductor pollicis brevis muscle, abductor pollicis brevis (APB) originates on the Scaphoid bone, scaphoid tubercle and the Flexor retinaculum of the hand, flexor retinaculum. It inserts to the radial sesamoid bone and the proximal phalanx of the thumb. It is innervated by the median nerve (C8-T1). The Flexor pollicis brevis muscle, flexor pollicis brevis (FPB) has two heads. The superficial head arises on the flexor retinaculum, while the deep head originates on three carpal bones: the Trapezium (bone), trapezium, Trapezoid bone, trapezoid, and Capitate bone, capitate. The muscle is inserted onto the radial sesamoid bone of the metacarpophalangeal joint. It acts to flex, adduct, and abduct the thumb, and is therefore also able to oppose the thumb. The superficial head is innervated by the median nerve, while the deep head is innervated by the ulnar nerve (C8-T1). Theopponens pollicis
The opponens pollicis is a small, triangular muscle in the hand, which functions to oppose the thumb. It is one of the three thenar muscles. It lies deep to the abductor pollicis brevis and lateral to the flexor pollicis brevis.
Structure
The op ...
originates on the tubercle of the trapezium and the flexor retinaculum. It is inserted onto the radial side of the first metacarpal. It opposes the thumb and assists in adduction. It is innervated by the median nerve.
Other muscles involved are:
The Adductor pollicis muscle, adductor pollicis also has two heads. The transversal head originates along the entire third metacarpal bone, while the oblique head originates on the carpal bones proximal to the third metacarpal. The muscle is inserted onto the ulnar sesamoid bone of the metacarpophalangeal joint. It adducts the thumb, and assists in opposition and flexion. It is innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve (C8-T1).
The first Dorsal interossei of the hand, dorsal interosseous, one of the central muscles of the hand, extends from the base of the thumb metacarpal to the radial side of the proximal phalanx of the index finger.
Variations
 There is a variation of the human thumb where the angle between the first and second (proximal and distal) Distal phalanges, phalanges varies between 0° and almost 90° when the thumb is in a Thumbs Up, thumbs-up gesture.
It has been suggested that the variation is an autosomal recessive trait, called a hitchhiker's thumb, with homozygous carriers having an angle close to 90°. However this theory has been disputed, since the variation in thumb angle is known to fall on a continuum and shows little evidence of the Bimodal distribution, bi-modality seen in other recessive genetic traits.
Other variations of the thumb include Brachydactyly type D, brachydactyly type D (which is a thumb with a congenitally short distal phalanx), a triphalangeal thumb (which is a thumb which has 3 phalanges instead of the usual two), and polysyndactyly (which is a combination of radial polydactyly and syndactyly).
There is a variation of the human thumb where the angle between the first and second (proximal and distal) Distal phalanges, phalanges varies between 0° and almost 90° when the thumb is in a Thumbs Up, thumbs-up gesture.
It has been suggested that the variation is an autosomal recessive trait, called a hitchhiker's thumb, with homozygous carriers having an angle close to 90°. However this theory has been disputed, since the variation in thumb angle is known to fall on a continuum and shows little evidence of the Bimodal distribution, bi-modality seen in other recessive genetic traits.
Other variations of the thumb include Brachydactyly type D, brachydactyly type D (which is a thumb with a congenitally short distal phalanx), a triphalangeal thumb (which is a thumb which has 3 phalanges instead of the usual two), and polysyndactyly (which is a combination of radial polydactyly and syndactyly).
Grips
One of the earlier significant contributors to the study of hand grips was orthopedic primatologist and paleoanthropologist John Napier (primatologist), John Napier, who proposed organizing the movements of the hand by their anatomical basis as opposed to work done earlier that had only used arbitrary classification. Most of this early work on hand grips had a pragmatic basis as it was intended to narrowly define compensable injuries to the hand, which required an understanding of the anatomical basis of hand movement. Napier proposed two primary prehensile grips: the ''precision grip'' and the ''power grip''. The precision and power grip are defined by the position of the thumb and fingers where: * The power grip is when the fingers (and sometimes palm) clamp down on an object with the thumb making counter pressure. Examples of the power grip are gripping a hammer, opening a jar using ''both your palm and fingers'', and during pullups. * The precision grip is when the intermediate and distal phalanges ("fingertips") and the thumb press against each other. Examples of a precision grip are writing with a pencil, opening a jar ''with the fingertips alone'', and gripping a ball (only if the ball is not tight against the palm). Opposability of the thumb should not be confused with a precision grip as some animals possess semi-opposable thumbs yet are known to have extensive precision grips (Cebus apella, Tufted Capuchins for example). Nevertheless, precision grips are usually only found in higher apes, and only in degrees significantly more restricted than in humans.
The pad-to-pad pinch between the thumb and index finger is made possible because of the human ability to passively hyperextend the Distal phalanges, distal phalanx of the index finger. Most non-human primates have to flex their long fingers in order for the small thumb to reach them.
In humans, the distal pads are wider than in other primates because the soft tissues of the finger tip are attached to a horseshoe-shaped edge on the underlying bone, and, in the grasping hand, the distal pads can therefore conform to uneven surfaces while pressure is distributed more evenly in the finger tips. The distal pad of the human thumb is divided into a proximal and a distal compartment, the former more deformable than the latter, which allows the thumb pad to mold around an object.
In robotics, almost all robotic hands have a long and strong opposable thumb. Like human hands, the thumb of a robotic hand also plays a key role in gripping an object. One inspiring approach of robotic grip planning is to mimic human thumb placement.
In a sense, human thumb placement indicates which surface or part of the object is good for grip. Then the robot places its thumb to the same location and plans the other fingers based on the thumb placement.
The function of the thumb declines physiologically with aging. This can be demonstrated by assessing the motor sequencing of the thumb.
Opposability of the thumb should not be confused with a precision grip as some animals possess semi-opposable thumbs yet are known to have extensive precision grips (Cebus apella, Tufted Capuchins for example). Nevertheless, precision grips are usually only found in higher apes, and only in degrees significantly more restricted than in humans.
The pad-to-pad pinch between the thumb and index finger is made possible because of the human ability to passively hyperextend the Distal phalanges, distal phalanx of the index finger. Most non-human primates have to flex their long fingers in order for the small thumb to reach them.
In humans, the distal pads are wider than in other primates because the soft tissues of the finger tip are attached to a horseshoe-shaped edge on the underlying bone, and, in the grasping hand, the distal pads can therefore conform to uneven surfaces while pressure is distributed more evenly in the finger tips. The distal pad of the human thumb is divided into a proximal and a distal compartment, the former more deformable than the latter, which allows the thumb pad to mold around an object.
In robotics, almost all robotic hands have a long and strong opposable thumb. Like human hands, the thumb of a robotic hand also plays a key role in gripping an object. One inspiring approach of robotic grip planning is to mimic human thumb placement.
In a sense, human thumb placement indicates which surface or part of the object is good for grip. Then the robot places its thumb to the same location and plans the other fingers based on the thumb placement.
The function of the thumb declines physiologically with aging. This can be demonstrated by assessing the motor sequencing of the thumb.
Human evolution
A primitive autonomization of the firstcarpometacarpal joint
The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five joints in the wrist that articulate the distal row of carpal bones and the proximal bases of the five metacarpal bones.
The CMC joint of the thumb or the first CMC joint, also known as the trapeziometaca ...
(CMC) may have occurred in dinosaurs. A real differentiation appeared an estimated 70 mya in early primates, while the shape of the human thumb CMC finally appears about 5 mya. The result of this evolutionary process is a human CMC joint positioned at 80° of pronation, 40 of abduction, and 50° of flexion in relation to an axis passing through the second and third CMC joints.
Opposable thumbs are shared by some primates, including most Catarrhini, catarrhines. The climbing and suspensory behaviour in Orthograde posture, orthograde apes, such as Common chimpanzee, chimpanzees, has resulted in elongated hands while the thumb has remained short. As a result, these primates are unable to perform the pad-to-pad grip associated with opposability. However, in pronograde monkeys such as baboons, an adaptation to a terrestrial lifestyle has led to reduced finger length and thus hand proportions similar to those of humans. Consequently, these primates have dexterous hands and are able to grasp objects using a pad-to-pad grip. It can thus be difficult to identify hand adaptations to manipulation-related tasks based solely on thumb proportions.
The evolution of the fully opposable thumb is usually associated with ''Homo habilis'', a forerunner of ''Homo sapiens''. This, however, is the suggested result of evolution from ''Homo erectus'' (around 1 mya (unit), mya) via a series of intermediate simian, anthropoid stages, and is therefore a much more complicated link.
Modern humans are unique in the musculature of their forearm and hand. Yet, they remain autapomorphic, meaning each muscle is found in one or more non-human primates. The extensor pollicis brevis and flexor pollicis longus allow modern humans to have great manipulative skills and strong flexion in the thumb.
However, a more likely scenario may be that the specialized precision gripping hand (equipped with opposable thumb) of ''Homo habilis'' preceded walking, with the specialized adaptation of the spine, pelvis, and lower extremities preceding a more advanced hand. And, it is logical that a conservative, highly functional adaptation be followed by a series of more complex ones that complement it. With ''Homo habilis'', an advanced grasping-capable hand was accompanied by facultative bipedalism, possibly implying, assuming a co-opted evolutionary relationship exists, that the latter resulted from the former as obligate bipedalism was yet to follow. Walking may have been a by-product of busy hands and not vice versa.
HACNS1 (also known as Human accelerated regions, Human Accelerated Region 2) is a Enhancer (genetics), gene enhancer "that may have contributed to the evolution of the uniquely opposable human thumb, and possibly also modifications in the ankle or foot that allow humans to walk on two legs". Evidence to date shows that of the 110,000 gene enhancer sequences identified in the human genome, HACNS1 has undergone the most change during the human evolution since the chimpanzee-human last common ancestor.
See also
* Prehensility * Thumb signal * Thumb twiddling * Thumb war * PollicizationNotes
References
* * * * (National Center for Biotechnology Information, NCBI) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * {{Authority control Fingers