Third Rome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the
The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the
 What modern historiography calls the "
What modern historiography calls the "
 On two occasions, the Eastern (Byzantine) Emperors reunited their church with its Western (Roman Catholic) counterpart, on political motivations and without durable effect. At the
On two occasions, the Eastern (Byzantine) Emperors reunited their church with its Western (Roman Catholic) counterpart, on political motivations and without durable effect. At the
 There is seamless continuity between the Roman and Byzantine Empires, to the extent that the date at which the former ends and the latter begins is essentially a matter of historiographical convention. The Byzantines consistently and near-exclusively called themselves Romans, before and after they adopted Greek as principal state language in the 7th century.
Traditional Western European historiography retains 395 as the date of beginning of the Byzantine Empire, when
There is seamless continuity between the Roman and Byzantine Empires, to the extent that the date at which the former ends and the latter begins is essentially a matter of historiographical convention. The Byzantines consistently and near-exclusively called themselves Romans, before and after they adopted Greek as principal state language in the 7th century.
Traditional Western European historiography retains 395 as the date of beginning of the Byzantine Empire, when
 The
The
 The
The

 After the
After the

 By the start of the 5th century, the Western Roman Empire remained close to its maximum territorial extent, notwithstanding the loss of the '' Agri Decumates'' during the crisis of the Third Century, but Roman rule had become fragile and many areas were depopulated. In the early years of the century, the Empire withdrew from Great Britain, leaving it open to Anglo-Saxon settlement. Mounting foreign incursions soon resulted in permanent settlement of Germanic and other ethnic groups into territories that became gradually autonomous, were sometimes acknowledged or even encouraged by treaty ('' foedus'') by the Western Empire, and often embarked on expansion by further conquest.
Thus, the
By the start of the 5th century, the Western Roman Empire remained close to its maximum territorial extent, notwithstanding the loss of the '' Agri Decumates'' during the crisis of the Third Century, but Roman rule had become fragile and many areas were depopulated. In the early years of the century, the Empire withdrew from Great Britain, leaving it open to Anglo-Saxon settlement. Mounting foreign incursions soon resulted in permanent settlement of Germanic and other ethnic groups into territories that became gradually autonomous, were sometimes acknowledged or even encouraged by treaty ('' foedus'') by the Western Empire, and often embarked on expansion by further conquest.
Thus, the  Political boundaries kept moving in the later 5th and 6th centuries.
Political boundaries kept moving in the later 5th and 6th centuries.
 The Popes needed to quickly reinvent their relationship to secular authority. Even though the neighboring Lombard kings were no longer heretical, they were often hostile. The more powerful and more distant Franks, which had by and large been allies of the Empire, were an alternative option as potential protectors. In 739, Gregory III sent a first embassy to
The Popes needed to quickly reinvent their relationship to secular authority. Even though the neighboring Lombard kings were no longer heretical, they were often hostile. The more powerful and more distant Franks, which had by and large been allies of the Empire, were an alternative option as potential protectors. In 739, Gregory III sent a first embassy to
 The coronation of
The coronation of 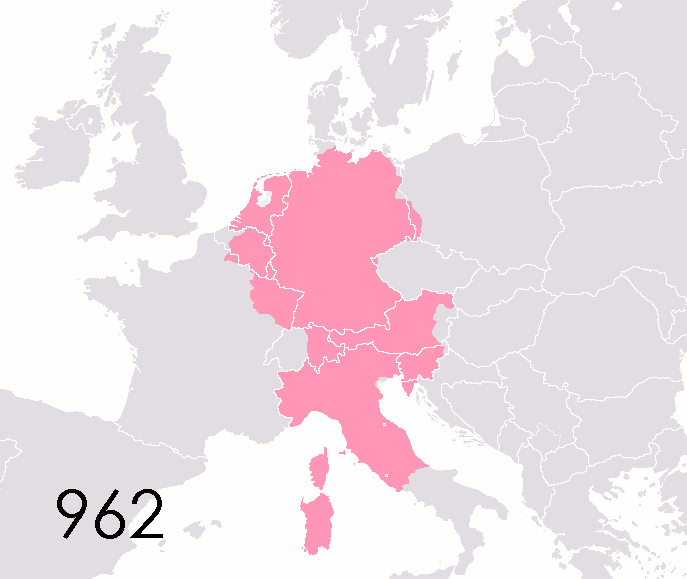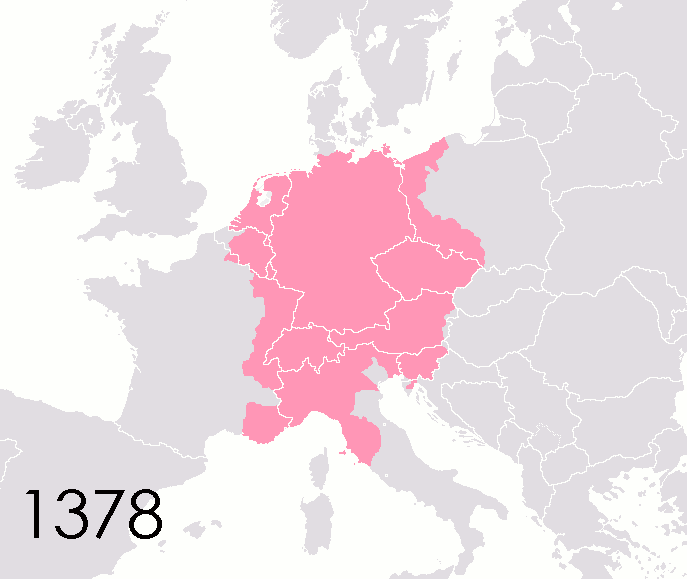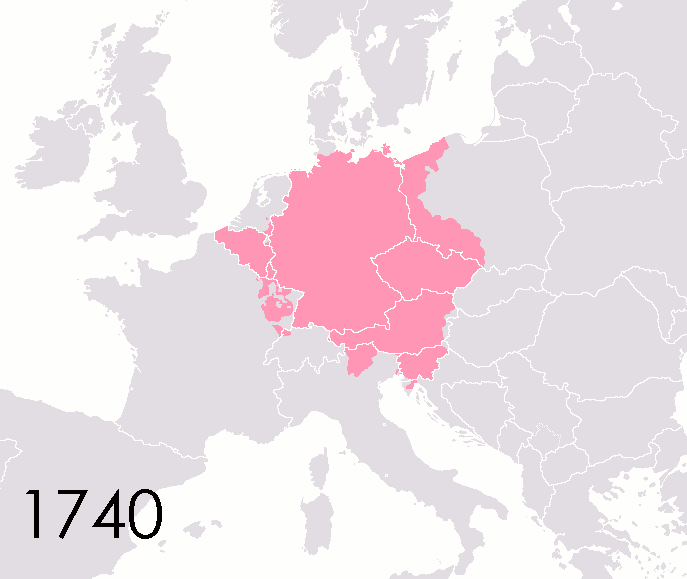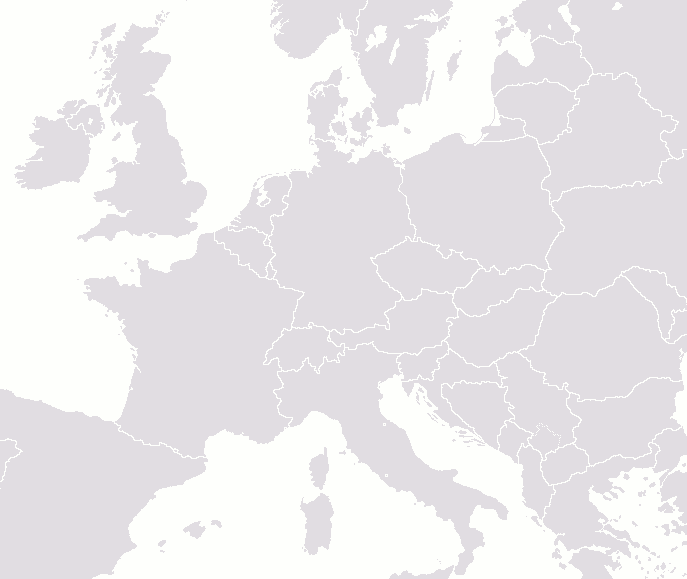

 Political authority fragmented within the Empire following Charlemagne's death. The eventual outcome was an association of the Imperial dignity with the easternmost ("German") lands of the Carolingian geography, but that was not self-evident at the start and took a long time to happen. From 843 to 875, the holders of the Imperial title only ruled over Northern Italy and, at the start, the "middle kingdom" of Lotharingia. On Christmas Day 875, exactly 75 years after Charlemagne,
Political authority fragmented within the Empire following Charlemagne's death. The eventual outcome was an association of the Imperial dignity with the easternmost ("German") lands of the Carolingian geography, but that was not self-evident at the start and took a long time to happen. From 843 to 875, the holders of the Imperial title only ruled over Northern Italy and, at the start, the "middle kingdom" of Lotharingia. On Christmas Day 875, exactly 75 years after Charlemagne,
 According to his biographer
According to his biographer

 Early in the Empire's history,
Early in the Empire's history,
 Ivan III of Russia in 1472 married Sophia (Zoé) Palaiologina, a niece of the last Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI, and styled himself
Ivan III of Russia in 1472 married Sophia (Zoé) Palaiologina, a niece of the last Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI, and styled himself
Moscow is the Third Rome (МОСКВА – ТРЕТІЙ РИМ)
Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia.''
 Several political regimes in the 19th and early 20th centuries defined themselves with reference to continuators of the Roman Empire, but not to the (Classical) Roman Empire itself. They all assumed nationalist reinterpretations of those continuators, and underplayed the extent to which the latter had portrayed themselves as Roman.
*
Several political regimes in the 19th and early 20th centuries defined themselves with reference to continuators of the Roman Empire, but not to the (Classical) Roman Empire itself. They all assumed nationalist reinterpretations of those continuators, and underplayed the extent to which the latter had portrayed themselves as Roman.
*
Encyclopædia Britannica Online This nationalist aspiration drove Greek foreign relations and, to a significant extent, domestic politics for much of the first century after independence. The expression was new in 1844 but the concept had roots in the Greek popular psyche - the "Greece of Two Continents and Five Seas" (Europe and Asia, the Ionian, Aegean, Marmara, Black and Libyan seas, respectively). The effort to realize the idea after the World War I defeat of the Ottoman Empire, however, ended in disaster with the
 Memories of the Roman Empire have accompanied the
Memories of the Roman Empire have accompanied the
 The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the
The continuation, succession and revival of the Roman Empire is a running theme of the history of Europe and the Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and wa ...
. It reflects the lasting memories of power and prestige associated with the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
itself.
Several polities have claimed immediate continuity with the Roman Empire, using its name or a variation thereof as their own exclusive or non-exclusive self-description. As centuries went by and more political ruptures occurred, the idea of institutional continuity became increasingly debatable. The most enduring and significant claimants of continuation of the Roman Empire have been, in the East, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
which both claimed succession of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
after 1453; and in the West, the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
from 800 to 1806.
Separately from claims of continuation, the view that the Empire had ended has led to various attempts to revive it or appropriate its legacy, notably in the case of Orthodox Russia. The vocabulary of a "Third Rome", the "First Rome" being Rome in Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and the "Second Rome" being Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in the Byzantine Empire, is often used to convey such assertions of legitimate succession.
Historiography and nomenclature
In Western Europe, the view of theDeposition of Romulus Augustulus
Odoacer's deposition of Romulus Augustus, occurring in 476 AD, was a coup that marked the end of the reign of the Western Roman Emperor last approved by the Western Roman Senate and the creation of the Kingdom of Italy, although Julius Nepos e ...
in 476 CE as a historic watershed, marking the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its va ...
and thus the beginning of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, was introduced by Leonardo Bruni in the early 15th century, strengthened by Christoph Cellarius
Christoph (Keller) Cellarius (22 November 1638 – 4 June 1707) was a German classical scholar from Schmalkalden who held positions in Weimar and Halle. Although the Ancient-Medieval-Modern division of history was used earlier by Italian Re ...
in the late 17th century, and cemented by Edward Gibbon
Edward Gibbon (; 8 May 173716 January 1794) was an English historian, writer, and member of parliament. His most important work, '' The History of the Decline and Fall of the Roman Empire'', published in six volumes between 1776 and 1788, i ...
in the late 18th century. It is, however, little more than a historiographic convention, since the Imperial idea long survived the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
in most of Western Europe, and indeed reached territories that had never been under Roman rule during classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
.
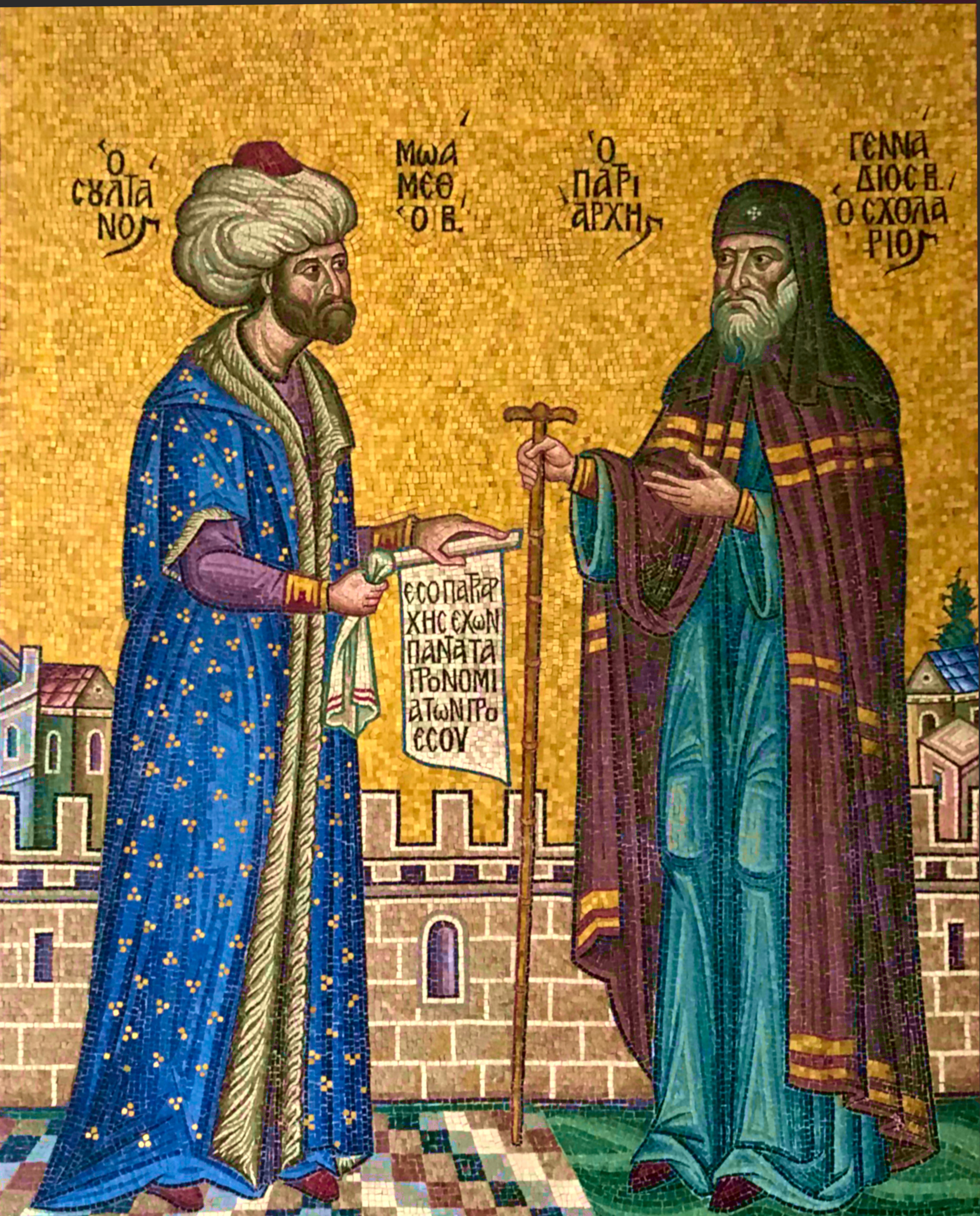
The fall of Constantinople in 1453 is historically and broadly accepted as the end of the Eastern Roman/Byzantine Empire and the end of the Middle Ages. However, two notable claims to succession of the Eastern Roman Empire arose in the centuries after the fall of Constantinople: the Ottoman Empire and the Russian Empire; notably, Mehmed II, the Ottoman sultan who captured Constantinople, justified his assumption of the title of Emperor of the Romans (''Kayser-i Rum'') by right of conquest, which was consistent with Byzantine imperial ideology which believed that control of Constantinople constituted the key legitimizing factor for an emperor and also was supported by contemporary historiographer George of Trebizond. Mehmed II's claim was also recognized by Gennadius Scholarius
Gennadius II ( Greek Γεννάδιος Βʹ; lay name Γεώργιος Κουρτέσιος Σχολάριος, ''Georgios Kourtesios Scholarios''; c. 1400 – c. 1473) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher and theologian, and Ecumenical Patriarc ...
after Mehmed II installed him as ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople ( Istanbul), New Rome and '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of ...
in 1454, the year after the fall of Constantinople. Mehmed II's claims were not accepted by the Roman Catholic Church or the Christian states of Europe at the time, and though Mehmed II intended to follow through on his claims by launching a conquest of Italy, his death in 1481 signaled the last time the Ottoman state attempted to conquer Italy or Rome itself; rather subsequent Ottoman emperors instead fought rival claimants to the Roman title (the Holy Roman Empire and the Russian Empire). As the Ottoman Empire continued its break with Greco-Roman legitimacy in favor of strengthening its Islamic legitimacy, Ottoman claims to the Roman Empire faded; the last official use of the title ''Kayser-i Rum'' was in the 18th century.
Names
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
" never used that expression, and kept calling itself the ''Roman Empire'', ''Empire of the Romans'', or ''Romania'' until the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
. Following the establishment of the Holy Roman Empire in 800, Christian Western Europeans were reluctant to apply the "Roman" epithet to the Eastern Empire and frequently called it "Empire of the Greeks" or "Greek Empire", even though they also used ''Romania'' – the latter also for the Latin Empire
The Latin Empire, also referred to as the Latin Empire of Constantinople, was a feudal Crusader state founded by the leaders of the Fourth Crusade on lands captured from the Byzantine Empire. The Latin Empire was intended to replace the Byza ...
of the 13th century. By contrast, Muslims in the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and farther east typically referred to the people of the Eastern Empire as "Romans" (''Rum''), and to Western Europeans, including those from the Holy Roman Empire, as "Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
" ('' Farang'').
The name Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
refers to the ancient city on the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
, now Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, which Constantine renamed Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 330. It was not used thereafter, except in rare historical or poetic contexts, until it first took its new meaning in 1557 – when the German scholar Hieronymus Wolf published his ''Corpus Historiæ Byzantinæ'', a collection of historical sources about the Eastern Empire. Then from 1648 onwards, Philippe Labbe and fellow French Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
published the 24-volume ''De Byzantinæ historiæ scriptoribus'', and in 1680 Du Cange
Charles du Fresne, sieur du Cange (; December 18, 1610 in Amiens – October 23, 1688 in Paris, aged 77), also known simply as Charles Dufresne, was a distinguished French philologist and historian of the Middle Ages and Byzantium.
Life
Educat ...
produced his own ''Historia Byzantina''. These endeavors further entrenched the use of the "Byzantine" label among French authors, including Montesquieu
Charles Louis de Secondat, Baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu (; ; 18 January 168910 February 1755), generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French judge, man of letters, historian, and political philosopher.
He is the princi ...
in the 18th century. Outside France in the Western world, it only came into general use around the mid-19th century, after Barthold Georg Niebuhr and his continuators published the 50-volume '' Corpus Scriptorum Historiae Byzantinae''.
Similarly, what historians call the "Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
" and "Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
" – in French and Spanish, "Holy Roman Germanic Empire" (''Saint Empire romain germanique'', ''Sacro Imperio Romano Germánico'') was the ''Roman Empire'', ''Empire of the Romans'' or simply ''Empire'' to their own subjects and rulers, with "Frankish" or "of the Franks" sometimes added depending on context. Only in 1157 did the twists and turns of the Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, also called Investiture Contest (German: ''Investiturstreit''; ), was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops ( investiture) and abbots of mona ...
lead to the practice of calling the Empire, though not the Emperor himself, "holy" (''sacrum''). The reference to Germany (''Heiliges Römisches Reich Deutscher Nation'', ''Sacrum Imperium Romanum Nationis Germanicæ''), which first appeared in the late 15th century, was never much used in official Imperial documents, and even then was a misnomer since the Empire's jurisdiction in Italy had not entirely disappeared. Other colloquial designations in the early Modern era included "German Empire" () or "Roman-German Empire" ().
In 1773, a few decades before the Holy Roman Empire's demise, Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet (; 21 November 169430 May 1778) was a French Enlightenment writer, historian, and philosopher. Known by his '' nom de plume'' M. de Voltaire (; also ; ), he was famous for his wit, and his criticism of Christianity—e ...
made the famous quip that it "was in no way holy, nor Roman, nor an empire."
Roman imperial legitimacy
In the early decades of the Roman Empire, legitimacy was largely defined by the institutions inherited from theRoman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
, initially together with a form of hereditary succession within the Julio-Claudian dynasty
, native_name_lang=Latin, coat of arms=Great_Cameo_of_France-removebg.png, image_size=260px, caption= The Great Cameo of France depicting emperors Augustus, Tiberius, Claudius and Nero, type= Ancient Roman dynasty, country= Roman Empire, estates=* ...
. As the old Republican institutions gradually lost relevance, many later Emperors derived their legitimacy from acclamation by the army, and during the Nerva–Antonine dynasty
The Nerva–Antonine dynasty comprised 7 Roman emperors who ruled from 96 to 192 AD: Nerva (96–98), Trajan (98–117), Hadrian (117–138), Antoninus Pius (138–161), Marcus Aurelius (161–180), Lucius Verus (161–169), and Commodus (18 ...
, adoption by their predecessor. The Roman Empire itself was long defined by its eponymous capital, but this equation became blurred after the crisis of the Third Century as the administrative center was moved to Mediolanum (Milan), then further fragmented into various locations (e.g. Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
, Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyria ...
, Augusta Treverorum, Serdica
Serdika or Serdica ( Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria.
Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandov ...
) before being reconsolidated by Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
in Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
, renamed and dedicated as Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 330 - while Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
replaced Milan as Western political capital in 402. Meanwhile, the Empire was Christianized
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
in the course of the 4th century, which partly redefined the authority of the Emperor as he became the protector of the new state religion.
Thus, the Imperial identity, and therefore the question of which polity could rightfully claim to be the Roman Empire, rested not on a single criterion but on a variety of factors: dominant territorial power and the related attributes of peace and order; rule over Rome and/or Constantinople; protection of justice and of the Christian faith (against paganism, heresy, and later Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
); as well as, albeit only intermittently, considerations of dynastic succession or of ethnic nationalism.
Conflicting claims
The multidimensionality of the imperial claim, together with the unique prestige of the imperial title, explains the recurrence of often intractable conflicts about which polities and rulers could rightfully assume them. These conflicts lost their potency in the course of the Early modern period, however, as improved communications and literacy increasingly undermined any claim of universal supremacy. A letter of Carolingian Emperor Louis II to Byzantine Emperor Basil I, probably drafted in Roman circles close to the Papacy in response to a lost original and surviving in 13th-century copy kept at theVatican Library
The Vatican Apostolic Library ( la, Bibliotheca Apostolica Vaticana, it, Biblioteca Apostolica Vaticana), more commonly known as the Vatican Library or informally as the Vat, is the library of the Holy See, located in Vatican City. Formally es ...
, articulates how the debate was framed in its time (ca. 871). The following quotes are from a full translation by scholar Charles West.
Territorial rule over Constantinople is not the exclusive criterion for a rightful Imperial claim:
While the Empire as an idea is unitary, there is no established doctrine that there should be only one Emperor at any time, especially if the two Emperors are on friendly terms. Whether on purpose or not, Louis's description of two Emperors of a single Empire matches the doctrine underlying the Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
or the division between Eastern and Western Empire between 395 and 476:
Louis's claim is ancient enough to be justified by tradition since it has already held for several generations:
Louis defends the Carolingian principle of dynastic succession as validated by tradition. Furthermore, Louis thinks that there should be no exclusive ethnic criterion for the Imperial dignity. Here Louis apparently refers to a claim by Basil that the Emperor should be a Roman and not from a non-Roman ethnicity (''gens''):
Using a modern vocabulary, Louis thought that those populations (gens) he cited (e.g. Spaniards, Isaurian etc.) were not Romans and that only the inhabitants of the city of Rome were Romans, not recognizing that those populations would have been seen as Romans, being citizens of the empire. While for Basil, the population (gens) of the Franks would not make good emperors because they were not citizens of the empire.
Empire and Christianity
Since the 4th century and particularly since the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, the defense and promotion of Christianity has been a key driver of Imperial identity. After that date, however, the territorial scope of the Empire or any of its continuating entities has never exactly coincided with that of Christendom, and the discrepancies led to enduring conflicts of legitimacy. The most consequential of these was theEast-West Schism
East West (or East and West) may refer to:
* East–West dichotomy, the contrast between Eastern and Western society or culture
Arts and entertainment
Books, journals and magazines
*''East, West'', an anthology of short stories written by Salm ...
, which crystallized in 1054 as a consequence of longstanding fights over governance and jurisdiction (known as ecclesiastical differences) and over doctrine ( theological differences), and can be fairly viewed as a delayed effect of the problem of two emperors arising from the creation of the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
in 800.
Earlier examples include the preference of several "Barbarian" kingdoms during the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
for Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
after the competing Nicene Creed
The original Nicene Creed (; grc-gre, Σύμβολον τῆς Νικαίας; la, Symbolum Nicaenum) was first adopted at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. In 381, it was amended at the First Council of Constantinople. The amended form is ...
had regained dominance in Constantinople: the Burgundians
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and ...
until 516, Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
until 534, Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
until 553, Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
until the 560s, Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
until 587, and Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
intermittently until 652. The adoption of Arianism protected these kingdoms' rulers from the religious disputes and policy initiatives of Constantinople, while being more acceptable to their majority-Catholic subjects than paganism.
 On two occasions, the Eastern (Byzantine) Emperors reunited their church with its Western (Roman Catholic) counterpart, on political motivations and without durable effect. At the
On two occasions, the Eastern (Byzantine) Emperors reunited their church with its Western (Roman Catholic) counterpart, on political motivations and without durable effect. At the Second Council of Lyon
:''The First Council of Lyon, the Thirteenth Ecumenical Council, took place in 1245.''
The Second Council of Lyon was the fourteenth ecumenical council of the Roman Catholic Church, convoked on 31 March 1272 and convened in Lyon, Kingdom of Arl ...
in 1274, Emperor Michael VIII aimed to appease the Papacy to keep his "Frankish" adversaries in check, particularly Charles I of Anjou
Charles I (early 1226/12277 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–85) and Forcalquier (1246–48, 1256–85) i ...
's plans to (re-)invade the Empire; the union was never widely accepted in Constantinople, and was reversed at the Council of Blachernae in 1285 after both Michael and Charles had died. At the Council of Ferrara/Florence in 1438–39, Emperor John VIII negotiated under the threat of Ottoman conquest, but the union agreement was again resisted in Constantinople and only proclaimed by Isidore of Kiev in December 1452, four years after John's death and too late to prevent the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
a few months later.
Conversely, the Ottoman Sultans' policies as self-proclaimed Emperors of the Romans (i.e. in the language of the time, of the Eastern Orthodox Christians) supported the independence of the Orthodox Church from Rome and occasionally favored reforms to keep religiously inspired separatism in check, e.g. the revival of the Serbian Patriarchate of Peć in 1557. The initial instrument of that policy, Gennadius Scholarius
Gennadius II ( Greek Γεννάδιος Βʹ; lay name Γεώργιος Κουρτέσιος Σχολάριος, ''Georgios Kourtesios Scholarios''; c. 1400 – c. 1473) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher and theologian, and Ecumenical Patriarc ...
, had been a prominent opponent of the union of the Eastern and Western churches in the 1440s and early 1450s.
The link between Empire and Christianity has a durable legacy: to this day, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
remains the seat of the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
, and Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
(Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
) that of the Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
with a widely recognized status of ''primus inter pares
''Primus inter pares'' is a Latin phrase meaning first among equals. It is typically used as an honorary title for someone who is formally equal to other members of their group but is accorded unofficial respect, traditionally owing to their se ...
'' within the Eastern Orthodox Church
The Eastern Orthodox Church, also called the Orthodox Church, is the second-largest Christian church, with approximately 220 million baptized members. It operates as a communion of autocephalous churches, each governed by its bishops via ...
. (In 2018, the negotiations over autocephaly
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Or ...
of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine
The Orthodox Church of Ukraine ( uk, Православна церква України, Pravoslavna tserkva Ukrainy; OCU) is an autocephalous Eastern Orthodox church whose canonical territory is Ukraine.
The church was united at the uni ...
led to a schism between Moscow and Constantinople as the Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
unilaterally severed full communion
Full communion is a communion or relationship of full agreement among different Christian denominations that share certain essential principles of Christian theology. Views vary among denominations on exactly what constitutes full communion, but ...
with the Ecumenical Patriarchate. A similar schism had occurred in 1996 over the Estonian Apostolic Orthodox Church, but unlike in 2018 it was resolved after a few months.)
The Imperial connection extends, through the legacy of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
as well. Istanbul was also until 1923 the seat of the only widely recognized Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
of the last half-millennium, and keeps most of the surviving Relics of Muhammad as the Sacred Trust in Topkapı Palace
The Topkapı Palace ( tr, Topkapı Sarayı; ota, طوپقپو سرايى, ṭopḳapu sarāyı, lit=cannon gate palace), or the Seraglio, is a large museum in the east of the Fatih district of Istanbul in Turkey. From the 1460s to the compl ...
, close to the location of the former Roman Imperial palace.
Continuation in the East
Roman/Byzantine Empire until 1204
 There is seamless continuity between the Roman and Byzantine Empires, to the extent that the date at which the former ends and the latter begins is essentially a matter of historiographical convention. The Byzantines consistently and near-exclusively called themselves Romans, before and after they adopted Greek as principal state language in the 7th century.
Traditional Western European historiography retains 395 as the date of beginning of the Byzantine Empire, when
There is seamless continuity between the Roman and Byzantine Empires, to the extent that the date at which the former ends and the latter begins is essentially a matter of historiographical convention. The Byzantines consistently and near-exclusively called themselves Romans, before and after they adopted Greek as principal state language in the 7th century.
Traditional Western European historiography retains 395 as the date of beginning of the Byzantine Empire, when Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
was succeeded by Arcadius in the East and Honorius in the West. Alternative conventions date the transition from Rome to Byzantium at the translation of the imperial capital from Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
to Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 330, or at the reign of Heraclius marking the end of late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English h ...
.
Even though the Byzantine Empire went through numerous political upheavals, and faced periods of dramatic contraction in the 7th and late 11th centuries, it exhibited unquestionable institutional continuity until 1204, not least because its central and defining seat of power, Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, was never conquered during this period.
Conversely, in the Eastern Mediterranean territories that ceased being part of the Empire during that period, there emerged almost no competing claim of Imperial legitimacy. In their different ways, the Avars and Slavs in the Balkans, and the Sasanians and Muslims in the Levant and Northern Africa, had different models of governance and no appetite for posing as Romans. This may also be linked to their inability to conquer the Imperial capital despite numerous attempts, as is suggested by the counter-example of the Ottoman Sultans claiming the Imperial title after 1453.
Bulgarian Empire
In the period before 1204, the only significant competing Imperial claim in the East appeared in 913, when Simeon I the Great, ruler ofBulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, was crowned "Emperor and Autocrat of all Bulgarians and Romans" (''Car i samodǎržec na vsički bǎlgari i gǎrci'' in the modern vernacular) by the Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of th ...
and imperial regent Nicholas Mystikos outside of the Byzantine capital. The decade 914–927 was then spent in a destructive Byzantine–Bulgarian war over the Imperial claim and other matters of conflict. The Bulgarian monarch was eventually recognized as "Emperor of the Bulgarians" (''basileus tōn Boulgarōn'') by the Byzantine Emperor Romanos I Lakapenos in 924, following the convention also adopted with the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
that ''basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean " monarch", referring to either a " king" or an "emperor" and ...
'' (a Greek word that can translate as "king" or "emperor" depending on context) was not an equal title to that of the Emperor as long as it did not explicitly confer authority over the "Romans". Constantinople's recognition of the ''basileus'' dignity of the Bulgarian monarch and the patriarchal dignity of the Bulgarian patriarch was again confirmed at the conclusion of permanent peace and a Bulgarian–Byzantine dynastic marriage in 927. The Bulgarian title "tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
" ('' Caesar'') was adopted by all Bulgarian monarchs up to the fall of Bulgaria under Ottoman rule.
During the Second Bulgarian Empire
The Second Bulgarian Empire (; ) was a medieval Bulgarian state that existed between 1185 and 1396. A successor to the First Bulgarian Empire, it reached the peak of its power under Tsars Kaloyan and Ivan Asen II before gradually being conque ...
, 14th-century literary compositions portrayed the then capital of Tarnovo, now Veliko Tarnovo
Veliko Tarnovo ( bg, Велико Търново, Veliko Tărnovo, ; "Great Tarnovo") is a town in north central Bulgaria and the administrative centre of Veliko Tarnovo Province.
Often referred as the "''City of the Tsars''", Veliko Tarnovo ...
, as successor of both Rome and Constantinople. Bulgarian contemporaries called the city "Tsarevgrad Tarnov", the ''Imperial city of Tarnovo'', echoing the Bulgarian name then used for Constantinople, Tsarigrad
''Tsargrad'' is a Slavic name for the city or land of Constantinople (present-day Istanbul in Turkey), the capital of the Byzantine Empire. It is rendered in several ways depending on the language, for instance Old Church Slavonic Цѣсарь� ...
.
Fourth Crusade and its aftermath
 The
The Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and sack of Constantinople
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusader armies captured, looted, and destroyed parts of Constantinople, then the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the ...
in 1204 marked a major rupture in the history of the Eastern Roman/Byzantine Empire, and opened a period of fragmentation and competing claims of Imperial legitimacy. The crusading ("Latin") invaders divided most of the Empire among themselves by a formal treaty of partition, under which the Latin Empire of Constantinople's direct rule did not extend greatly further than the city itself. It included the Straits and their immediate hinterland, e.g. Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian border ...
and Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocle ...
, but neither Salonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
nor Nicaea
Nicaea, also known as Nicea or Nikaia (; ; grc-gre, Νίκαια, ) was an ancient Greek city in Bithynia, where located in northwestern Anatolia and is primarily known as the site of the First and Second Councils of Nicaea (the first and s ...
. Other territories of the former Empire were not conquered by the Latin crusaders, and remained held by various holdovers of the former ("Greek") Empire.
Several of the polities emerging from that fragmentation claimed to be the rightful successor of the prior Empire, on various motives: the Latin Empire held the Imperial capital; the rulers of the Empire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through ...
stemmed from the formerly Imperial Komnenos family; those of the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It clai ...
(briefly the Empire of Thessalonica) were from the Angelos family, even though they renounced the imperial claim by accepting Nicaean overlordship in 1248; the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhous ...
successfully claimed the patriarchate in 1206, and eventually prevailed through skillful management of alliances and its recapture of Constantinople in 1261.
Latin Empire of Constantinople
The Latin Empire had its own line of Imperial succession, initially dominated by theHouse of Flanders
The House of Flanders—also called the Baldwins ( la, Balduini, french: Baudouinides)—was a medieval ruling family that was founded by Baldwin Iron Arm, son-in-law of Charles the Bald.
From 1051, the House of Flanders also reigned ove ...
then by the French House of Courtenay. It was embattled almost from the start, however, as the city was never able to recover from the trauma of 1204. Despite its theoretical suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
, the Latin Empire was not even politically dominant among the crusader states, which were referred to as Latin or Frankish by Easterners.
After being expelled from Constantinople in 1261, its titular Emperors occasionally held territorial power in parts of modern Greece. Jacques des Baux was Prince of Achaea
The Prince of Achaea was the ruler of the Principality of Achaea, one of the crusader states founded in Greece in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade (1202–1204). Though more or less autonomous, the principality was never a fully independent sta ...
in 1381–83, and the last recorded claimant to the Latin Imperial title.
Late Byzantine era
Palaiologos dynasty
The House of Palaiologos ( Palaiologoi; grc-gre, Παλαιολόγος, pl. , female version Palaiologina; grc-gre, Παλαιολογίνα), also found in English-language literature as Palaeologus or Palaeologue, was a Byzantine Greek f ...
prolonged the Roman Imperial experience from its recovery of Constantinople in 1261 until the Ottoman conquest in 1453. The Empire shrunk considerably during that period, however, and at the end it was only the imperial city itself without any hinterland, plus most of the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge which ...
(then referred to as Morea) typically under the direct rule of one of the Emperor's sons with the title of Despot. This line of Imperial succession ceased in 1453: even though the Despotate of the Morea lingered on a few more years, until the Ottomans conquered it in 1460, its rulers at the time did not claim Imperial authority.
Serbian Empire
In 1345, theSerbian King
This is an archontological list of Serbian monarchs, containing monarchs of the medieval principalities, to heads of state of modern Serbia.
The Serbian monarchy dates back to the Early Middle Ages. The Serbian royal titles used include Knyaz ...
Stefan Dušan proclaimed himself Emperor (Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
) and was crowned as such at Skopje
Skopje ( , , ; mk, Скопје ; sq, Shkup) is the capital and largest city of North Macedonia. It is the country's political, cultural, economic, and academic centre.
The territory of Skopje has been inhabited since at least 4000 BC; r ...
on Easter
Easter,Traditional names for the feast in English are "Easter Day", as in the '' Book of Common Prayer''; "Easter Sunday", used by James Ussher''The Whole Works of the Most Rev. James Ussher, Volume 4'') and Samuel Pepys''The Diary of Samue ...
1346 by the newly created Serbian Patriarch, as well as by the Patriarch of All Bulgaria
The Patriarch of All Bulgaria is the patriarch of the Bulgarian Orthodox Church. The patriarch is officially styled as ''Patriarch of All Bulgaria and Metropolitan of Sofia''. Patriarch Neophyte acceded to this position on 24 February 2013.
Hi ...
and the Archbishop of Ohrid. His imperial title was recognized by, among others, the Bulgarian Empire, much diminished following the Battle of Velbazhd in 1330, albeit not by the Byzantine Empire. In Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia ( Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hu ...
, the title of " Emperor of Serbs and Romans" (in its final simplified form; ''цар Срба и Римљана'' / ''car Srba i Rimljana'' in modern Serbian) was only employed thereafter by Stefan Dušan's son Stefan Uroš V until his death in 1371. A half-brother of Dušan, Simeon Uroš, and then his son Jovan Uroš, used the same title until the latter's abdication in 1373, while ruling as dynasts in Thessaly
Thessaly ( el, Θεσσαλία, translit=Thessalía, ; ancient Thessalian: , ) is a traditional geographic and modern administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thes ...
.
Empire of Trebizond
TheEmpire of Trebizond
The Empire of Trebizond, or Trapezuntine Empire, was a monarchy and one of three successor rump states of the Byzantine Empire, along with the Despotate of the Morea and the Principality of Theodoro, that flourished during the 13th through ...
, one of the entities that had emerged from the fragmentation of the early 13th century, survived until Ottoman conquest in 1461. Its Komnenos rulers claimed the Imperial title for themselves in competition to the ones in Constantinople, even though they did not receive any meaningful international recognition.
A separate polity on the Crimean coast of the Black Sea, the Principality of Theodoro
The Principality of Theodoro ( el, Αὐθεντία πόλεως Θεοδωροῦς καὶ παραθαλασσίας), also known as Gothia ( el, Γοτθία) or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern p ...
, only fell to the Ottomans in 1475. There is no indication that its rulers made any claim of being Roman Emperors.
Andreas Palaiologos's cessions
Andreas Palaiologos, a nephew of the last Byzantine EmperorConstantine XI Palaiologos
Constantine XI Dragases Palaiologos or Dragaš Palaeologus ( el, Κωνσταντῖνος Δραγάσης Παλαιολόγος, ''Kōnstantînos Dragásēs Palaiológos''; 8 February 1405 – 29 May 1453) was the last Roman (Byzantine) e ...
and the head of what remained of the Palaiologos family, started calling himself Emperor of Constantinople in 1483 and, possibly childless, sold what he viewed as his imperial title to Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable (french: l'Affable; 30 June 1470 – 7 April 1498), was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. He succeeded his father Louis XI at the age of 13.Paul Murray Kendall, ''Louis XI: The Universal Spider'' (Ne ...
in 1494. The following Kings of France kept the claim until Charles IX in 1566, when it went into disuse. Charles IX wrote that the imperial Byzantine title "is not more eminent than that of king, which sounds better and sweeter."
In his last will in 1502, Andreas Palaiologos again ceded his self-awarded imperial title, this time to Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia fro ...
and Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I ( es, Isabel I; 22 April 1451 – 26 November 1504), also called Isabella the Catholic (Spanish: ''la Católica''), was Queen of Castile from 1474 until her death in 1504, as well as Queen consort of Aragon from 1479 until 1504 b ...
. Other pretenders to the Byzantine throne have appeared following his death that year, with increasingly dubious claims as centuries went by. Charles I Gonzaga, Duke of Mantua
Charles Gonzaga ( it, Carlo I Gonzaga) (6 May 1580 – 22 September 1637) was Duke of Mantua and Duke of Montferrat from 1627 until his death. He was also Charles III Duke of Nevers and Rethel, as well as Prince of Arche and Charleville.
Biogra ...
, who also claimed descent from the Palaiologos family, declared in 1612 his intent to reclaim Constantinople but only succeeded in provoking an uprising in the Mani Peninsula
The Mani Peninsula ( el, Μάνη, Mánē), also long known by its medieval name Maina or Maïna (Μαΐνη), is a geographical and cultural region in Southern Greece that is home to the Maniots (Mανιάτες, ''Maniátes'' in Greek), who cl ...
, which lasted until 1619.
Ottoman Empire after 1453

 After the
After the fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
in 1453, Mehmed II
Mehmed II ( ota, محمد ثانى, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ānī; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, ابو الفتح, Ebū'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
declared himself Roman Emperor: ''Kayser-i Rum'', literally " Caesar of the Romans", the standard title for earlier Byzantine Emperors in Arab, Persian and Turkish lands. In 1454, he ceremonially established Gennadius Scholarius
Gennadius II ( Greek Γεννάδιος Βʹ; lay name Γεώργιος Κουρτέσιος Σχολάριος, ''Georgios Kourtesios Scholarios''; c. 1400 – c. 1473) was a Byzantine Greek philosopher and theologian, and Ecumenical Patriarc ...
, a staunch antagonist of Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and of the Sultan's European enemies, as Ecumenical Patriarch of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople ( Istanbul), New Rome and '' primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of ...
and ethnarch (''milletbashi'') of the Rum Millet
Rūm millet (millet-i Rûm), or "''Roman nation''", was the name of the Eastern Orthodox Christian community in the Ottoman Empire. Despite being subordinated within the Ottoman political system, the community maintained a certain internal auto ...
, namely Greek Orthodox Christians
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
within the Empire. In turn, Gennadius endorsed Mehmed's claim of Imperial succession.
Mehmed's claim rested principally with the idea that Constantinople was the rightful seat of the Roman Empire, as it had indeed been for more than a millennium even if the 1204-1261 period is subtracted. Contemporary scholar George of Trebizond wrote that "the seat of the Roman Empire is Constantinople (...) and he who is and remains Emperor of the Romans is also the Emperor of the whole world". An additional though questionable claim of legitimacy referred to the past alliances between the Ottoman dynasty and Byzantine Imperial families. Byzantine Princess Theodora Kantakouzene had been one of the wives of Orhan I, and an unsupported but widespread story portrayed Mehmed as a descendant of John Tzelepes Komnenos
John Komnenos ( gr, Ἰωάννης Κομνηνός, Iōannēs Komnēnos), later surnamed Tzelepes (Τζελέπης, ''Tzelepēs''), was the son of the ''sebastokrator'' Isaac Komnenos and grandson of the Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos. A ...
.
George of Trebizond addressed Mehmed in a poem:
Mehmed's imperial plans went further and aimed at conquering Rome itself, thus reuniting the Empire in a way it hadn't been for nearly eight centuries. His Italian campaign started in 1480 with the invasion of Otranto, but was cut short by Mehmed's sudden death on 3 May 1481. None of his successors renewed that endeavor. Instead, they repeatedly (albeit never successfully) attempted to conquer the capital of the rival contenders to the Imperial Roman title, with a first siege of Vienna in 1529 and a second one in 1683.
Being the rightful heir of the Roman/Byzantine Empire became part of the identity of the Sultanate, along with its Turkish and Muslim heritage, even though that dimension was played down by Western observers. According to Turkish scholar F. Asli Ergul:
Additionally, over the centuries, many Greeks abandoned Orthodoxy and embraced the Islam, to the point that today, in part because of the intermingling of ethnic Greeks with Turks in the Ottoman Empire, genetic studies have found that modern Turks are closer, genetically, to Mediterranean and Middle Eastern people than to Central Asians.
In diplomatic exchanges with the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
, the Ottomans initially refused to acknowledge the latter's Imperial claim, because they saw themselves as the only rightful successors of Rome. In the Treaty of Constantinople (1533), the Austrian negotiators agreed not to make any mention of the holy Roman Empire, only referring to Ferdinand I as King of Germany and Charles V as King of Spain. The Ottomans, however, abandoned that requirement in the Treaty of Sitvatorok in 1606, and similarly to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
in the Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca in 1774.
Chinese usage during the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
referred to the Ottomans as Lumi (魯迷), derived from Rûm
Rūm ( ar, روم , collective; singulative: Rūmī ; plural: Arwām ; fa, روم Rum or Rumiyān, singular Rumi; tr, Rûm or , singular ), also romanized as ''Roum'', is a derivative of the Aramaic (''rhπmÈ'') and Parthian (''frwm'') ...
i, literally "Roman". Presumably thought that it was still Byzantine empire of the Greeks.
Continuation in the West
Political fragmentation and imperial overlordship
 By the start of the 5th century, the Western Roman Empire remained close to its maximum territorial extent, notwithstanding the loss of the '' Agri Decumates'' during the crisis of the Third Century, but Roman rule had become fragile and many areas were depopulated. In the early years of the century, the Empire withdrew from Great Britain, leaving it open to Anglo-Saxon settlement. Mounting foreign incursions soon resulted in permanent settlement of Germanic and other ethnic groups into territories that became gradually autonomous, were sometimes acknowledged or even encouraged by treaty ('' foedus'') by the Western Empire, and often embarked on expansion by further conquest.
Thus, the
By the start of the 5th century, the Western Roman Empire remained close to its maximum territorial extent, notwithstanding the loss of the '' Agri Decumates'' during the crisis of the Third Century, but Roman rule had become fragile and many areas were depopulated. In the early years of the century, the Empire withdrew from Great Britain, leaving it open to Anglo-Saxon settlement. Mounting foreign incursions soon resulted in permanent settlement of Germanic and other ethnic groups into territories that became gradually autonomous, were sometimes acknowledged or even encouraged by treaty ('' foedus'') by the Western Empire, and often embarked on expansion by further conquest.
Thus, the Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic peoples, Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal Kingdom, Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The ...
crossed the Rhine in 406, the Pyrenees in 409, the Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar ( ar, مضيق جبل طارق, Maḍīq Jabal Ṭāriq; es, Estrecho de Gibraltar, Archaic: Pillars of Hercules), also known as the Straits of Gibraltar, is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Medi ...
in 428, and established the Vandal Kingdom in Northern Africa and the Western Mediterranean islands by the mid-5th century; the Suebi
The Suebi (or Suebians, also spelled Suevi, Suavi) were a large group of Germanic peoples originally from the Elbe river region in what is now Germany and the Czech Republic. In the early Roman era they included many peoples with their own name ...
, initially moving alongside the Vandals, established their Western Iberian kingdom in 409; the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
was initially established by treaty in 418 in the Garonne Valley, and soon expanded into the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
; the Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes
*
*
*
on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into pres ...
expanded into Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
and beyond, from their initial base in the '' Agri Decumates''; in the 440s, the Kingdom of the Burgundians was established around the Rhone; an autonomous Kingdom of Soissons was carved out from 457 by Roman military commanders between the Seine
)
, mouth_location = Le Havre/ Honfleur
, mouth_coordinates =
, mouth_elevation =
, progression =
, river_system = Seine basin
, basin_size =
, tributaries_left = Yonne, Loing, Eure, Risle
, tributa ...
and Somme __NOTOC__
Somme or The Somme may refer to: Places
*Somme (department), a department of France
*Somme, Queensland, Australia
*Canal de la Somme, a canal in France
*Somme (river), a river in France
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Somme'' (book), a ...
rivers; last but not least, the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
, which had been established north of the Rhine in 358 by treaty with Emperor Julian, expanded into what is now Belgium and Northern France. As a consequence, when the last Western Emperor Romulus Augustulus was deposed by military commander Odoacer
Odoacer ( ; – 15 March 493 AD), also spelled Odovacer or Odovacar, was a soldier and statesman of barbarian background, who deposed the child emperor Romulus Augustulus and became Rex/Dux (476–493). Odoacer's overthrow of Romulus August ...
in 476, his direct rule did not extend much beyond the current Northern borders of Italy. Another military leader, Julius Nepos, briefly Romulus Augustulus's predecessor, held territory in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
and kept the Imperial title until his assassination in 480.
In a symbolic act that would fascinate later historians, Odoacer sent back the Imperial '' regalia'' or accessories of Romulus Augustulus to the Eastern Emperor Zeno in Constantinople. Far from signaling the end of imperial rule in Italy, however, this meant that Odoacer acknowledged Zeno's overlordship and did not claim full sovereignty. Like previous ''foederati'' leaders, he adopted the title of King (''Rex'') and ruled in the name of the remaining Emperors, namely Zeno and also Julius Nepos while the latter was still alive. This arrangement was kept by Theodoric the Great
Theodoric (or Theoderic) the Great (454 – 30 August 526), also called Theodoric the Amal ( got, , *Þiudareiks; Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ), was king of the Ostrogoths (471–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy ...
, who vanquished and killed Odoacer in 493 and replaced him as King of Italy
King of Italy ( it, links=no, Re d'Italia; la, links=no, Rex Italiae) was the title given to the ruler of the Kingdom of Italy after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. The first to take the title was Odoacer, a barbarian military leader ...
.
 Political boundaries kept moving in the later 5th and 6th centuries.
Political boundaries kept moving in the later 5th and 6th centuries. Clovis I
Clovis ( la, Chlodovechus; reconstructed Frankish: ; – 27 November 511) was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single ki ...
, king of the Franks (d. 511), conquered Alemannia, the Kingdom of Soissons and most of the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
north of the Pyrenees, and his sons conquered the Kingdom of the Burgundians in 534, thus creating a vast kingdom of Francia, which was however periodically divided between various members of the Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
. Meanwhile, Eastern Emperor Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
reestablished direct Imperial rule in Southern Spain, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and especially Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, reconquered during the hard-fought Gothic War (535–554)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the l ...
. Later in the 6th century, Emperor Maurice
Maurice ( la, Mauricius or ''Mauritius''; ; 539 – 27 November 602) was Eastern Roman emperor from 582 to 602 and the last member of the Justinian dynasty. A successful general, Maurice was chosen as heir and son-in-law by his predecessor Tib ...
sponsored Gundoald, a member of Clovis's Merovingian dynasty
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
, in his claim to the Frankish kingdom, which however ended unsuccessfully in 585 at Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges
Saint-Bertrand-de-Comminges (, literally ''Saint-Bertrand of Comminges''; Gascon: ''Sent Bertran de Comenge'') is a commune (municipality) and former episcopal see in the Haute-Garonne department in southwestern France. It is a member of the ' ...
.
Even though it was out of the Empire's direct military reach, Francia
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
kept acknowledging the overlordship of Constantinople throughout the 6th century. At a ceremony in early 508 in Tours
Tours ( , ) is one of the largest cities in the region of Centre-Val de Loire, France. It is the prefecture of the department of Indre-et-Loire. The commune of Tours had 136,463 inhabitants as of 2018 while the population of the whole metro ...
, Clovis received the ''insignia
An insignia () is a sign or mark distinguishing a group, grade, rank, or function. It can be a symbol of personal power or that of an official group or governing body.
On its own, an insignia is a sign of a specific or general authority and is ...
'' sent by Emperor Anastasius I
Anastasius I Dicorus ( grc-gre, Ἀναστάσιος, Anastásios; – 9 July 518) was Eastern Roman emperor from 491 to 518. A career civil servant, he came to the throne at the age of 61 after being chosen by the wife of his predecessor, ...
which established his service to the Empire as Consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
. Similarly, in the early 6th century, King Gundobad of the still-independent Burgundians
The Burgundians ( la, Burgundes, Burgundiōnes, Burgundī; on, Burgundar; ang, Burgendas; grc-gre, Βούργουνδοι) were an early Germanic tribe or group of tribes. They appeared in the middle Rhine region, near the Roman Empire, and ...
, despite being an Arian
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
, was ''Magister militum
(Latin for "master of soldiers", plural ) was a top-level military command used in the later Roman Empire, dating from the reign of Constantine the Great. The term referred to the senior military officer (equivalent to a war theatre commander, ...
'' in the name of the Emperor. The ''Gesta pontificum Autissiodorensium'', a compendium of information about the Bishops of Auxerre first compiled in the late 9th century, keeps referring to the reigning Roman Emperor up to Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Des ...
(d. 621), listed as bishop "in the reigns of Phocas
Phocas ( la, Focas; grc-gre, Φωκάς, Phōkás; 5475 October 610) was Eastern Roman emperor from 602 to 610. Initially, a middle-ranking officer in the Eastern Roman army, Phocas rose to prominence as a spokesman for dissatisfied soldie ...
and Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the exarch of Africa, led a revol ...
" (''imperantibus Foca, atque Heraclio''). No such deference appears to have existed in the Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of the Goths ( la, Regnum Gothorum), was a kingdom that occupied what is now southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to the 8th centuries. One of the Germanic successor states to ...
at the same time, however. Chris Wickham portrays the Visigothic king Euric (466-484) as "the first major ruler of a 'barbarian' polity in Gaul - the second in the Empire after Geiseric - to have a fully autonomous political practice, uninfluenced by any residual Roman loyalties." A century and a half later, in the 620s Isidore of Seville
Isidore of Seville ( la, Isidorus Hispalensis; c. 560 – 4 April 636) was a Spanish scholar, theologian, and archbishop of Seville. He is widely regarded, in the words of 19th-century historian Montalembert, as "the last scholar of ...
articulated for the Visigothic Kingdom, by then a Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
monarchy following the conversion of Reccared I
Reccared I (or Recared; la, Flavius Reccaredus; es, Flavio Recaredo; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianis ...
in 587, a vision of Christian monarchy on an equal status with the Eastern Roman Empire that would have seminal influence on later Western European political thinking.
Imperial rule in the West eroded further from the late 6th century. In Britain, to the extent discernible from scarce documentation, Roman rule was at best a distant memory. In Francia, references to Imperial overlordship disappear at the time of Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gaul ...
renewal in the early 7th century under Chlothar II and Dagobert I. In the Iberian Peninsula, the Visigothic
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is ...
King Suintila expelled the last Imperial forces from Southern Spain in 625. In Italy, the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the ''History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
invaded in 568, and the resulting Kingdom of the Lombards
The Kingdom of the Lombards ( la, Regnum Langobardorum; it, Regno dei Longobardi; lmo, Regn di Lombard) also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy ( la, Regnum totius Italiae), was an early medieval state established ...
was hostile to the Empire whose territorial footprint shrunk gradually.
Papal pivot
The Roman Papacy was to become the instrument of the Imperial idea's revival in the West. Rome was increasingly isolated from Constantinople following the devastations ofGothic War (535–554)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the l ...
, subsequent imperial choices to favor Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
over Rome, and the Lombard invasion of Italy starting in 568, which limited its communications with the main imperial outposts in Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the c ...
and Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
. The Column of Phocas on the Roman Forum
The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum ( it, Foro Romano), is a rectangular forum ( plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancie ...
, dedicated in 608, counts among the last monumental expressions of (eastern) imperial power in Rome. In 649, in breach of tradition, Pope Martin I was elected and consecrated without waiting for imperial confirmation. Constans II
Constans II ( grc-gre, Κώνστας, Kōnstas; 7 November 630 – 15 July 668), nicknamed "the Bearded" ( la, Pogonatus; grc-gre, ὁ Πωγωνᾶτος, ho Pōgōnãtos), was the Eastern Roman emperor from 641 to 668. Constans was the last ...
was the last (eastern) emperor to visit Rome for centuries, in 663, and plundered several of the remaining monuments to adorn Constantinople. Meanwhile and for various reasons, Catholicism finally triumphed over Arianism
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God ...
in the Western kingdoms: in the Visigothic Iberian Peninsula with the conversion of Reccared I
Reccared I (or Recared; la, Flavius Reccaredus; es, Flavio Recaredo; 559 – December 601; reigned 586–601) was Visigothic King of Hispania and Septimania. His reign marked a climactic shift in history, with the king's renunciation of Arianis ...
in 587, and in Lombard-held Italy, after some back-and-forth, following the death of King Rothari in 652. Pope Gregory I
Pope Gregory I ( la, Gregorius I; – 12 March 604), commonly known as Saint Gregory the Great, was the bishop of Rome from 3 September 590 to his death. He is known for instigating the first recorded large-scale mission from Rome, the Gregoria ...
(590-604) established the foundations for the papacy's incipient role as leader of Christianity in the West, even though at the time there was no conception of an alternative imperial authority to be established there in competition with Constantinople.
The promotion of iconoclasm
Iconoclasm (from Greek: grc, εἰκών, lit=figure, icon, translit=eikṓn, label=none + grc, κλάω, lit=to break, translit=kláō, label=none)From grc, εἰκών + κλάω, lit=image-breaking. ''Iconoclasm'' may also be consid ...
by Emperor Leo III the Isaurian
Leo III the Isaurian ( gr, Λέων ὁ Ἴσαυρος, Leōn ho Isauros; la, Leo Isaurus; 685 – 18 June 741), also known as the Syrian, was Byzantine Emperor from 717 until his death in 741 and founder of the Isaurian dynasty. He put an e ...
from 726 led to a deepening rupture between the Eastern Empire and the Papacy. Pope Gregory II saw iconoclasm as the latest in a series of imperial heresies. In 731, his successor Pope Gregory III organized a synod
A synod () is a council of a Christian denomination, usually convened to decide an issue of doctrine, administration or application. The word '' synod'' comes from the meaning "assembly" or "meeting" and is analogous with the Latin word mean ...
in Rome which declared iconoclasm punishable by excommunication
Excommunication is an institutional act of religious censure used to end or at least regulate the communion of a member of a congregation with other members of the religious institution who are in normal communion with each other. The purpose ...
. Leo III responded in 732/33 by confiscating all papal patrimonies in south Italy and Sicily, and further removed the bishoprics of Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, Corinth
Corinth ( ; el, Κόρινθος, Kórinthos, ) is the successor to an ancient city, and is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform, it has been part ...
, Syracuse
Syracuse may refer to:
Places Italy
* Syracuse, Sicily, or spelled as ''Siracusa''
* Province of Syracuse
United States
*Syracuse, New York
**East Syracuse, New York
** North Syracuse, New York
* Syracuse, Indiana
*Syracuse, Kansas
*Syracuse, M ...
, Reggio, Nicopolis, Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
, and Patras
)
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 =
, demographics1_info2 =
, timezone1 = EET
, utc_offset1 = +2
...
from papal jurisdiction, instead subjecting them to the Patriarch of Constantinople. This was in effect an act of triage: it strengthened the imperial grip in Southern Italy, but all but guaranteed the eventual destruction of the exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
, which soon occurred at Lombard hands. In effect, the papacy had been "cast out of the empire". Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary ( la, Zacharias; 679 – March 752) was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of sla ...
, in 741, was the last pope to announce his election to a Byzantine ruler or seek their approval.
 The Popes needed to quickly reinvent their relationship to secular authority. Even though the neighboring Lombard kings were no longer heretical, they were often hostile. The more powerful and more distant Franks, which had by and large been allies of the Empire, were an alternative option as potential protectors. In 739, Gregory III sent a first embassy to
The Popes needed to quickly reinvent their relationship to secular authority. Even though the neighboring Lombard kings were no longer heretical, they were often hostile. The more powerful and more distant Franks, which had by and large been allies of the Empire, were an alternative option as potential protectors. In 739, Gregory III sent a first embassy to Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
seeking protection against Liutprand, King of the Lombards
Liutprand was the king of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his multiple phases of law-giving, in fifteen separate sessions from 713 to 735 inclusive, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mos ...
, but the Frankish strongman had been Liutbrand's ally in the past and had asked him in 737 to ceremonially adopt his son. The Papacy had more luck with the latter, Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
, who succeeded Charles in October 741 together with his elder brother Carloman (who withdrew from public life and became a monk in 747). Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary ( la, Zacharias; 679 – March 752) was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of sla ...
was pressed into action by the final Lombard campaign against the exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
, whose fall in mid-751 sealed the end of Byzantine rule in Central Italy. He was in contact with the Frankish ruling elites through the venerable Boniface, Archbishop of Mainz
The Elector of Mainz was one of the seven Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire. As both the Archbishop of Mainz and the ruling prince of the Electorate of Mainz, the Elector of Mainz held a powerful position during the Middle Ages. The Archb ...
, and other clerics such as Burchard of Würzburg
Burchard of Würzburg (in German Burkard or Burkhard) was an Anglo-Saxon missionary who became the first Bishop of Würzburg (741–751).
Life
He was an Anglo-Saxon Benedictine monk possibly of noble birth, and educated at Malmesbury Abbey. He l ...
and Fulrad. In March 751 he moved to depose Childeric III, the last Merovingian King, following which Pepin was dedicated as King of France in Soissons
Soissons () is a commune in the northern French department of Aisne, in the region of Hauts-de-France. Located on the river Aisne, about northeast of Paris, it is one of the most ancient towns of France, and is probably the ancient capital o ...
. In 754, Zachary's successor Pope Stephen II
Pope Stephen II ( la, Stephanus II; 714 – 26 April 757) was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzan ...
undertook the first-ever papal visit north of the Alps, met Pepin in Ponthion
Ponthion () is a commune in the Marne department in north-eastern France.
It is located southeast of Châlons-en-Champagne.
History
Ponthion was a royal pfalz (crown estate) under both the Merovingian (mainly Neustrian branch) and the Caroling ...
and anointed him as king at Saint-Denis on July 28, setting the template for later rites of coronation of French Kings. Stephen further legitimized the Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pi ...
by also anointing Pepin's sons Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was " ...
and Carloman, by prohibiting the election of any non-descendant of Pepin as king, and by proclaiming that "the Frankish nation is above all nations". This in return prompted the Donation of Pepin
The Donation of Pepin in 756 provided a legal basis for the creation of the Papal States, thus extending the temporal rule of the popes beyond the duchy of Rome.
Background
In 751, Aistulf, king of the Lombards, conquered what remained of the ...
in 756, cementing the Popes' rule over the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
over the next eleven centuries. Subsequently, in 773–774, Pepin's son and successor Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
conquered the Lombard Kingdom of Italy.
Holy Roman Empire
 The coronation of
The coronation of Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
by Pope Leo III
Pope Leo III (died 12 June 816) was bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 26 December 795 to his death. Protected by Charlemagne from the supporters of his predecessor, Adrian I, Leo subsequently strengthened Charlemagne's position ...
, in Rome on Christmas Day 800, was explicitly intended as establishing continuity with the Roman Empire that still existed in the East. In Constantinople, Irene of Athens
Irene of Athens ( el, Εἰρήνη, ; 750/756 – 9 August 803), surname Sarantapechaina (), was Byzantine empress consort to Emperor Leo IV from 775 to 780, regent during the childhood of their son Constantine VI from 780 until 790, co-ruler ...
had blinded and deposed her son Emperor Constantine VI a few years earlier. With no precedent of a woman being sole holder of the imperial title, her critics in the West (e.g. Alcuin) viewed the imperial throne as vacant rather than recognizing her as Empress. Thus, as Peter H. Wilson
Peter Hamish Wilson (born 1963) is a British historian. Since 2015, he has held the Chichele Professor of the History of War chair at All Souls College, University of Oxford.
Biography
Wilson studied at the University of Liverpool (BA (Hons)) and ...
put it, "it is highly likely Charlemagne believed he was being made Roman Emperor" at the time of his coronation. Charlemagne's imperial title, however, rested on a different base from any of the Roman emperors until him, as it was structurally reliant on the partnership with the Papacy, embodied in the act of his coronation by the Pope.
If we accept that Charlemagne was indeed made Roman Emperor, we would have to go with the line of Holy Roman Emperors. This would make Karl von Hapsburg the heir to the Roman Empire. Of course, this assumes that the Holy Roman Empire was the successor to the Roman Empire and not the Byzantine or Ottoman Empires.
Meanwhile, the accession to the Byzantine throne of Nikephoros I
Nikephoros I or Nicephorus I ( gr, Νικηφόρος; 750 – 26 July 811) was Byzantine emperor from 802 to 811. Having served Empress Irene as '' genikos logothetēs'', he subsequently ousted her from power and took the throne himself. In r ...
in 802 confirmed the conflict of legitimacy between the Frankish and Byzantine incarnations of the Roman Empire, known in historiography as the problem of two emperors (in German, ''Zweikaiserproblem''). According to Theophanes the Confessor
Theophanes the Confessor ( el, Θεοφάνης Ὁμολογητής; c. 758/760 – 12 March 817/818) was a member of the Byzantine aristocracy who became a monk and chronicler. He served in the court of Emperor Leo IV the Khazar before taking ...
, Charlemagne had attempted to prevent that conflict with a project to marry Irene, but this was not completed. The territorial conflicts were addressed in the following years through a series of negotiations known as the ''Pax Nicephori
''Pax Nicephori'', Latin for the "Peace of Nicephorus", is a term used to refer to both a peace treaty of 803, tentatively concluded between emperors Charlemagne, of the Frankish empire, and Nikephoros I, of the Byzantine empire, and the outcom ...
'', but the broader conflict with Constantinople about Imperial legitimacy proved extremely durable.

 Political authority fragmented within the Empire following Charlemagne's death. The eventual outcome was an association of the Imperial dignity with the easternmost ("German") lands of the Carolingian geography, but that was not self-evident at the start and took a long time to happen. From 843 to 875, the holders of the Imperial title only ruled over Northern Italy and, at the start, the "middle kingdom" of Lotharingia. On Christmas Day 875, exactly 75 years after Charlemagne,
Political authority fragmented within the Empire following Charlemagne's death. The eventual outcome was an association of the Imperial dignity with the easternmost ("German") lands of the Carolingian geography, but that was not self-evident at the start and took a long time to happen. From 843 to 875, the holders of the Imperial title only ruled over Northern Italy and, at the start, the "middle kingdom" of Lotharingia. On Christmas Day 875, exactly 75 years after Charlemagne, Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a se ...
of West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from ab ...
was crowned Emperor in Rome by Pope John VIII, adopting the motto ''renovatio imperii Romani et Francorum'', which raised the prospect of an Empire centered on what is today France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. But Charles died soon afterwards in 877. His successor Charles the Fat only briefly managed to reunite all the Carolingian domains, and after his death in 888 the Western part of Francia
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
was dominated by the non-Carolingian Robertians, later the Capetian dynasty
The Capetian dynasty (; french: Capétiens), also known as the House of France, is a dynasty of Frankish origin, and a branch of the Robertians. It is among the largest and oldest royal houses in Europe and the world, and consists of Hug ...
. For over seven decades the Emperors' authority was then mostly confined to Northern Italy, until Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
revived the Imperial idea and was crowned by Pope John XII
Pope John XII ( la, Ioannes XII; c. 930/93714 May 964), born Octavian, was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 16 December 955 to his death in 964. He was related to the counts of Tusculum, a powerful Roman family which had do ...
in Rome in 962. From then on, all Emperors had dynastic roots in the Germanic-speaking lands (even though Frederick II was born in Italy, Henry VII in Valenciennes
Valenciennes (, also , , ; nl, label=also Dutch, Valencijn; pcd, Valincyinnes or ; la, Valentianae) is a commune in the Nord department, Hauts-de-France, France.
It lies on the Scheldt () river. Although the city and region experienced a ...
, Charles IV in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
, Charles V in Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded i ...
, Ferdinand I in Spain, Charles VII in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
, Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
in Nancy, and Francis II in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
).
During the millennium of the Holy Roman Empire, several specific attempts were made to recall the Empire's classical heritage. Emperor Otto III reigned from Rome from 998 to his death in 1002, and made a short-lived attempt to revive ancient Roman institutions and traditions in partnership with Pope Sylvester II, who chose his papal name as an echo of the time of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
. Frederick II took a keen interest in Roman antiquity, sponsored archaeological excavations, organized a Roman-style triumph in Cremona
Cremona (, also ; ; lmo, label= Cremunés, Cremùna; egl, Carmona) is a city and ''comune'' in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po river in the middle of the ''Pianura Padana'' ( Po Valley). It is the capital of the ...
in 1238 to celebrate his victory at the battle of Cortenuova, and had himself depicted in classical imagery. Similarly, Maximilian I was highly mindful of classical references in his "memorial" projects of the 1510s that included the three monumental woodblock prints
Woodblock printing or block printing is a technique for printing text, images or patterns used widely throughout East Asia and originating in China in antiquity as a method of printing on textiles and later paper. Each page or image is crea ...
of the ''Triumphal Arch
A triumphal arch is a free-standing monumental structure in the shape of an archway with one or more arched passageways, often designed to span a road. In its simplest form a triumphal arch consists of two massive piers connected by an arch, cr ...
'', '' Triumphal Procession'' and ''Large Triumphal Carriage
The ''Large Triumphal Carriage'' or ''Great Triumphal Car'' (in German, ''Triumphwagen'') is a large 16th-century woodcut print by Albrecht Dürer, commissioned by the Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I. The work was originally intended to be the ...
''.
Papacy and the imperial title
Einhard
Einhard (also Eginhard or Einhart; la, E(g)inhardus; 775 – 14 March 840) was a Frankish scholar and courtier. Einhard was a dedicated servant of Charlemagne and his son Louis the Pious; his main work is a biography of Charlemagne, the ''Vita ...
, Charlemagne was unhappy about his coronation, a fact that later historians have interpreted as displeasure about the Pope's assumption of the key role in the legitimation of Imperial rule. Instead of the traditional recognition by popular acclamation, Leo III had crowned Charlemagne at the outset of the ceremony, just before the crowd acclaimed him. In September 813, Charlemagne tried to override that precedent by himself crowning his son Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
in Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th ...
, but the principle of Papal coronation survived and was renewed in 962 when Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
restored the Empire and its rituals after decades of turmoil and received the Imperial Crown from Pope John XII
Pope John XII ( la, Ioannes XII; c. 930/93714 May 964), born Octavian, was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 16 December 955 to his death in 964. He was related to the counts of Tusculum, a powerful Roman family which had do ...
.
The interdependence between Pope and Emperor led to conflict after the Papacy started asserting its position with the Gregorian Reform
The Gregorian Reforms were a series of reforms initiated by Pope Gregory VII and the circle he formed in the papal curia, c. 1050–80, which dealt with the moral integrity and independence of the clergy. The reforms are considered to be na ...
of the mid-11th century. The Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy, also called Investiture Contest (German: ''Investiturstreit''; ), was a conflict between the Church and the state in medieval Europe over the ability to choose and install bishops ( investiture) and abbots of mona ...
(1076-1122) included episodes of dramatic confrontation, in which the pope attempted to deprive the emperor of his imperial dignity. The ''Dictatus papae
''Dictatus papae'' is a compilation of 27 statements of authority claimed by the pope that was included in Pope Gregory VII's register under the year 1075.
Principles
The principles expressed in ''Dictatus Papae'' are mostly those expressed ...
'', a papal document issued in 1075 shortly after the election of Gregory VII, states that the pope "alone may use the Imperial Insignia", that "All princes shall kiss the feet of the Pope alone", and that "It may be permitted to him to depose emperors". Following Emperor Henry IV
Henry IV (german: Heinrich IV; 11 November 1050 – 7 August 1106) was Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 to 1105, King of Germany from 1054 to 1105, King of Italy and Burgundy from 1056 to 1105, and Duke of Bavaria from 1052 to 1054. He was the son ...
's walk to Canossa in January 1077, Gregory VII pronounced his absolution but referred to him as ''rex Teutonicorum'' ("king of the Germans"), thus omitting the imperial title and the fact that Henry was king (''rex'') of several realms, including Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
. Wars of Guelphs and Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines (, , ; it, guelfi e ghibellini ) were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy.
During the 12th and 13th centuries, r ...
, the respective partisans of the Pope and the Emperor, lasted until the 15th century. In 1527, the Pope's involvement in the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
led to the traumatic sack of Rome by Charles V's imperial troops, after which the Papacy's influence in international politics was significantly reduced.
Kingdoms and the imperial title
 Early in the Empire's history,
Early in the Empire's history, Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
formally established the supremacy of the Empire over Catholic kingdoms through the document issued in 817 and later known as ''Ordinatio Imperii
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aquita ...
''. The view at the time was that the Empire covered all Western Christendom under one authority. (The British Isles, Brittany, and the Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias ( la, Asturum Regnum; ast, Reinu d'Asturies) was a kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula founded by the Visigothic nobleman Pelagius. It was the first Christian political entity established after the Umayyad conquest of ...
were omitted in this vision.) Under Louis's arrangement, only his elder son Lothair would hold the title of Emperor, and Lothair's younger brothers Pepin and Louis should obey him even though they were kings, respectively, of Aquitaine and Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
. That document was controversial from the start, however, not least as it did not conform to Frankish succession law and practices. Following Louis the Pious's death in June 840, the Battle of Fontenoy (841)
The three-year Carolingian Civil War culminated in the decisive Battle of Fontenoy, also called the Battle of Fontenoy-en-Puisaye, fought at Fontenoy, near Auxerre, on 25 June 841. The war was fought to decide the territorial inheritances of ...
, Oaths of Strasbourg
The Oaths of Strasbourg were a military pact made on 14 February 842 by Charles the Bald and Louis the German against their older brother Lothair I, the designated heir of Louis the Pious, the successor of Charlemagne. One year later the T ...
(842) and Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
(843) established a different reality, in which the Imperial title remained undivided but its holder competed with kings for territory, even though at the time all were still bound by the family links of the Carolingian dynasty
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pi ...
and the bounds of Catholic Christianity.
Following the gradual demise of the Carolingian dynasty in the late 9th and 10th centuries, the rivalry between the Empire and individual kingdoms developed on these early precedents. The Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
, developing from Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald (french: Charles le Chauve; 13 June 823 – 6 October 877), also known as Charles II, was a 9th-century king of West Francia (843–877), king of Italy (875–877) and emperor of the Carolingian Empire (875–877). After a se ...
's West Francia
In medieval history, West Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the West Franks () refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from ab ...
, was continually reluctant to acknowledge the Emperor's senior status among European monarchs. As Latin Christendom expanded in the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, new kingdoms appeared outside of the Empire and would similarly bid for territory and supremacy. France itself was instrumental in the developments that led to the Empire's political decline from the 16th to the early 19th centuries.
Modern-era nationalist revivals
A number of political regimes have claimed various forms of successorship of the Roman Empire, even though they acknowledged a significant time lag between what they viewed as the Empire's extinction and their own efforts to revive it. These attempts have increasingly been framed in nationalist terms, in line with the times. Despite its name, Europeanimperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic powe ...
has typically not invoked the memories of the Roman Empire, with the only exception of Italy for a few decades in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Thus, European colonial empires are not mentioned in this section.
Imperial Russia
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
(''Царь'', "Caesar") or ''imperator
The Latin word ''imperator'' derives from the stem of the verb la, imperare, label=none, meaning 'to order, to command'. It was originally employed as a title roughly equivalent to ''commander'' under the Roman Republic. Later it became a part o ...
''. In 1547, Ivan IV
Ivan IV Vasilyevich (russian: Ива́н Васи́льевич; 25 August 1530 – ), commonly known in English as Ivan the Terrible, was the grand prince of Moscow from 1533 to 1547 and the first Tsar of all Russia from 1547 to 1584.
Iva ...
cemented the title as "Tsar of All Rus" (''Царь Всея Руси''). In 1589, the Metropolitanate
A metropolis religious jurisdiction, or a metropolitan archdiocese, is an episcopal see whose bishop is the metropolitan bishop or archbishop of an ecclesiastical province. Metropolises, historically, have been important cities in their provinces.
...
of Moscow was granted autocephaly
Autocephaly (; from el, αὐτοκεφαλία, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Or ...
by the Patriarchate of Constantinople and thus became the Patriarchate of Moscow, thanks to the efforts of Boris Godunov
Borís Fyodorovich Godunóv (; russian: Борис Фёдорович Годунов; 1552 ) ruled the Tsardom of Russia as ''de facto'' regent from c. 1585 to 1598 and then as the first non-Rurikid tsar from 1598 to 1605. After the end of his ...
. This sequence of events supported the narrative, encouraged by successive rulers, that Muscovy was the rightful successor of Byzantium as the "Third Rome", based on a mix of religious ( Orthodox), ethno-linguistic ( East Slavic) and political ideas (the autocracy of the Tsar). Supporters of that view also asserted that the topography of the seven hills of Moscow offered parallels to the seven hills of Rome and the seven hills of Constantinople.
In 1492 Zosimus, Metropolitan of Moscow, in a foreword to his ''Presentation of the Paschalion'', referred to Ivan III as "the new Tsar Constantine of the new city of Constantine
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
— Moscow." In a panegyric
A panegyric ( or ) is a formal public speech or written verse, delivered in high praise of a person or thing. The original panegyrics were speeches delivered at public events in ancient Athens.
Etymology
The word originated as a compound of gr ...
letter to Grand Duke Vasili III composed in 1510, Russian monk Philotheus (Filofey) of Pskov proclaimed, "Two Romes have fallen. The third stands. And there will be no fourth. No one shall replace your Christian Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East and South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the ter ...
dom!"Mashkov, A.D. Moscow is the Third Rome (МОСКВА – ТРЕТІЙ РИМ)
Ukrainian Soviet Encyclopedia.''
Risorgimento and Fascist Italy
Italy's nationalist visionary Giuseppe Mazzini promoted the notion of the "Third Rome" during the Risorgimento: "After the Rome of the emperors, after the Rome of the Popes, there will come the Rome of the people", addressingItalian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
and the establishment of Rome as the capital. After the Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
into the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
, the state was referred to as the Third Rome by some Italian figures. After unification, Rome was chosen as capital despite its relative backwardness as it evoked the prestige of the former Empire. Mazzini spoke of the need of Italy as a Third Rome to have imperial aspirations, to be realized in the Italian Empire
The Italian colonial empire ( it, Impero coloniale italiano), known as the Italian Empire (''Impero Italiano'') between 1936 and 1943, began in Africa in the 19th century and comprised the colonies, protectorates, concessions and dependenci ...
.Silvana Patriarca, Lucy Riall. The Risorgimento Revisited: Nationalism and Culture in Nineteenth-Century Italy. p. 248. Mazzini said that Italy should "invade and colonize Tunisian lands" as it was the "key to the Central Mediterranean", and he viewed Italy as having the right to dominate the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
as ancient Rome had done.
In his speeches, Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini (; 29 July 188328 April 1945) was an Italian politician and journalist who founded and led the National Fascist Party. He was Prime Minister of Italy from the March on Rome in 1922 until his deposition in ...
echoed the rhetoric of the ''Risorgimento'' and referred to his regime as a "Third Rome" or as a New Roman Empire. ''Terza Roma'' (Third Rome) was also a name for Mussolini's plan to expand Rome towards Ostia and the sea. The EUR neighbourhood was the first step in that direction.
Non-Roman reinterpretations
 Several political regimes in the 19th and early 20th centuries defined themselves with reference to continuators of the Roman Empire, but not to the (Classical) Roman Empire itself. They all assumed nationalist reinterpretations of those continuators, and underplayed the extent to which the latter had portrayed themselves as Roman.
*
Several political regimes in the 19th and early 20th centuries defined themselves with reference to continuators of the Roman Empire, but not to the (Classical) Roman Empire itself. They all assumed nationalist reinterpretations of those continuators, and underplayed the extent to which the latter had portrayed themselves as Roman.
* Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
claimed the heritage of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks dur ...
, both the Merovingians
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
, conveniently forgetting the fact that they acknowledged Constantinople's overlordship, and Carolingians
The Carolingian dynasty (; known variously as the Carlovingians, Carolingus, Carolings, Karolinger or Karlings) was a Frankish noble family named after Charlemagne, grandson of mayor Charles Martel and a descendant of the Arnulfing and Pippi ...
, whose legacy was easy to appropriate since he had conquered their heartlands in what are now Belgium and Western Germany. Thus, from his imperial coronation as Emperor of the French
Emperor of the French (French: ''Empereur des Français'') was the title of the monarch and supreme ruler of the First and the Second French Empires.
Details
A title and office used by the House of Bonaparte starting when Napoleon was procla ...
on 2 December 1804, he used both the symbolism of the bees from the burial of Childeric I
Childeric I (; french: Childéric; la, Childericus; reconstructed Frankish: ''*Hildirīk''; – 481 AD) was a Frankish leader in the northern part of imperial Roman Gaul and a member of the Merovingian dynasty, described as a king (Latin ''r ...
(which had been unearthed in 1653 in Tournai
Tournai or Tournay ( ; ; nl, Doornik ; pcd, Tornai; wa, Tornè ; la, Tornacum) is a city and municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It lies southwest of Brussels on the river Scheldt. Tournai is part of Eurome ...
) and a mock-Carolingian style for his coronation crown
A coronation crown is a crown used by a monarch when being crowned. In some monarchies, monarchs have or had a number of crowns for different occasions, such as a coronation crown for the moment of coronation and a ''state crown'' for general u ...
, which he dubbed the Crown of Charlemagne. Even after his first defeat, Napoleon again borrowed the Merovingian-inspired bees to compose the Flag of Elba.
* The Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
, and after it the Austrian Republic, borrowed from the imagery and symbolism of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
following its demise in 1806. To this day, the Imperial eagle is a symbol of the Austrian government, as is also the case in Germany.
* In Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders wi ...
, the '' Megali Idea'' ("Great Idea") developed shortly after the War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List of ...
of recreating the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, understood as an ethnic-Greek polity with capital in Constantinople. The idea first appeared during the debates of Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
Ioannis Kolettis with King Otto that preceded the promulgation of the 1844 constitution.''History of Greece''Encyclopædia Britannica Online This nationalist aspiration drove Greek foreign relations and, to a significant extent, domestic politics for much of the first century after independence. The expression was new in 1844 but the concept had roots in the Greek popular psyche - the "Greece of Two Continents and Five Seas" (Europe and Asia, the Ionian, Aegean, Marmara, Black and Libyan seas, respectively). The effort to realize the idea after the World War I defeat of the Ottoman Empire, however, ended in disaster with the
Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922)
The Greco-Turkish War of 1919–1922, ota, گرب جابهاسی, Garb Cebhesi) in Turkey, and the Asia Minor Campaign ( el, Μικρασιατική Εκστρατεία, Mikrasiatikí Ekstrateía) or the Asia Minor Catastrophe ( el, Μικ ...
.
* The German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871 claimed lineage from the Holy Roman Empire, reinterpreted as a national (German) rather than universalist endeavor - thus the lingering historiographical question on whether it started with the coronation of Charlemagne in 800, or (according to the nationalist version) in 962 with the coronation of the more unambiguously German Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
. The narrative of continuity from the Ottonians to the Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenb ...
was expressed in countless occasions, e.g. the creative restoration of the Imperial Palace of Goslar
The Imperial Palace of Goslar (german: link=no, Kaiserpfalz Goslar) is a historical building complex at the foot of the Rammelsberg hill in the south of the town of Goslar north of the Harz mountains, central Germany. It covers an area of about ...
in the 1870s.Warwick Ball. ''Rome in the East: The Transformation of an Empire''. London, England, UK: Routledge, 2000. p. 449.Craig M. White. ''The Great German Nation: Origins and Destiny''. AuthorHouse, 2007. p. 169. Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
subsequently called itself the Third Reich (''Drittes Reich''), succeeding both the Holy Roman Empire and the German Empire. The Holy Roman Empire reference was awkward, however, as it did not fit well with Nazi ideology. In 1939, a circular not intended for publication prohibited further use of the expression "Third Reich".Reinhard Bollmus: ''Das Amt Rosenberg und seine Gegner. Studien zum Machtkampf im nationalsozialistischen Herrschaftssystem.'' Stuttgart 1970, S. 236.
Supranationalism and the Roman imperial idea
In the 20th century, several political thinkers and politicians have associated the multi-level governance andmultilingualism
Multilingualism is the use of more than one language, either by an individual speaker or by a group of speakers. It is believed that multilingual speakers outnumber monolingual speakers in the world's population. More than half of all ...
of the Roman Empire in its various successive incarnations with the modern legal concepts of federalism
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments ( provincial, state, cantonal, territorial, or other sub-unit governments) in a single ...
and supranationalism.
League of Nations
French historian Louis Eisenmann, in a 1926 article titled ''The Imperial Idea in the History of Europe'', portrayed the newly createdLeague of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
as the modern expression of an "imperial idea" that had been degraded by the nationalistic drift of the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
, Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
and Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
. He argued that the three empires' final demise and the League's establishment represent a renewal of the Pax Romana
The Pax Romana (Latin for 'Roman peace') is a roughly 200-year-long timespan of Roman history which is identified as a period and as a golden age of increased as well as sustained Roman imperialism, relative peace and order, prosperous stabilit ...
imperial idea.
European Union
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
since its inception with the 1950 Schuman Plan
The Schuman Declaration, or Schuman Plan, was a proposal to place French and West German production of coal and steel under a single authority that later became the European Coal and Steel Community, made by the French foreign minister, Robert ...
.
The Roman Empire has provided the European Union, like many countries, with Roman legal concepts and their language, Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
. As such Latin has been used in some circumstances as one non-official ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' in the European Union, for example by EU Institutions using Latin concepts in texts and titles.
The comparison of the European Union with the Holy Roman Empire, in a negative or positive light, is a common trope of political commentary.
The European Union has been viewed as a reincarnation of a foreign and overbearing Roman Empire in some European countries, particularly the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
. The 2020 withdrawal of the UK from the Union, or Brexit
Brexit (; a portmanteau of "British exit") was the Withdrawal from the European Union, withdrawal of the United Kingdom (UK) from the European Union (EU) at 23:00 Greenwich Mean Time, GMT on 31 January 2020 (00:00 1 February 2020 Central Eur ...
, has been variously compared with the Boudica Rebellion or with end of Roman rule in Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew t ...
.
A different negative view of the European Union as new Roman Empire has been regularly formulated in Christian fundamentalist circles, principally in the United States. According to that view, the EU, like other supranational endeavors such as the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
and World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
, by attempting to revive the Roman Empire, signals the approaching end time, rapture
The rapture is an Christian eschatology, eschatological position held by some Christians, particularly those of American evangelicalism, consisting of an Eschatology, end-time event when all Christian believers who are alive, along with resurre ...
or Second Coming
The Second Coming (sometimes called the Second Advent or the Parousia) is a Christian (as well as Islamic and Baha'i) belief that Jesus will return again after his ascension to heaven about two thousand years ago. The idea is based on messia ...
. Occasionally, the European Union is portrayed as a "Fourth Reich", further emphasizing its demonic nature. This critique is often portrayed as fringe despite its widespread following among American Evangelicals for several decades.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *References
{{Authority control Former empires in Europe Former empires in Asia History of Rome Roman Empire History of the Roman Empire Legacy of the Roman Empire Fall of the Western Roman Empire Christian states Byzantine Empire History of Eastern Orthodoxy Constantinople Carolingian Empire Holy Roman Empire East–West Schism Latin Empire Christian messianism German nationalism 16th century in the Grand Duchy of Moscow Politics of the Russian Empire Russian nationalism Italian unification Italian Fascism Historiography