The Deluge (Polish history) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, lt, švedų tvanas) was a series of mid-17th-century military campaigns in the
 In July 1655 two Swedish armies, operating from Swedish Pomerania and the Province of Pomerania, entered
In July 1655 two Swedish armies, operating from Swedish Pomerania and the Province of Pomerania, entered
 On March 11, the Swedish army arrived at Jarosław, fighting its way across the San river. Charles Gustav sent some of his forces to capture
On March 11, the Swedish army arrived at Jarosław, fighting its way across the San river. Charles Gustav sent some of his forces to capture 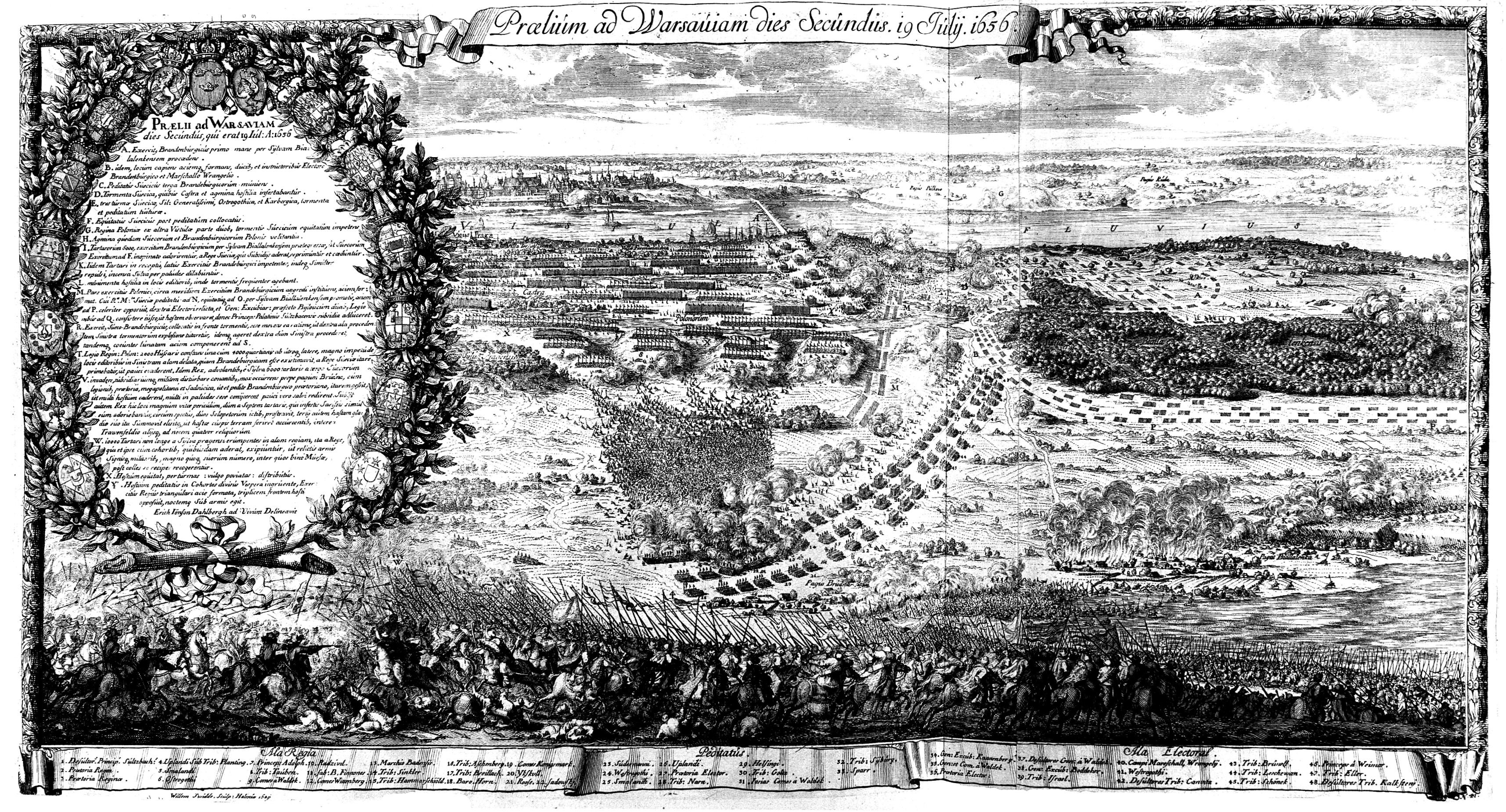 Already in late 1655, Charles Gustav realized that it would be impossible for him to control the Commonwealth. The Swedish king decided to find allies, who would help him to divide Poland-Lithuania. On June 29, 1656, he signed the Treaty of Marienburg, in which he offered
Already in late 1655, Charles Gustav realized that it would be impossible for him to control the Commonwealth. The Swedish king decided to find allies, who would help him to divide Poland-Lithuania. On June 29, 1656, he signed the Treaty of Marienburg, in which he offered
 In the spring of 1658, the Polish army, together with its Austrian allies under
In the spring of 1658, the Polish army, together with its Austrian allies under
 The Swedish invasion affected the richest provinces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (
The Swedish invasion affected the richest provinces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (
Map
of area occupied by
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: � ...
of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish theatres of the Russo-Polish and Second Northern War
The Second Northern War (1655–60), (also First or Little Northern War) was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1655–60), the Tsardom of Russia ( 1656–58), Brandenburg-Prussia (1657–60), the ...
s. In a stricter sense, the term refers to the Swedish invasion and occupation of the Commonwealth as a theatre of the Second Northern War (1655–1660) only; in Poland and Lithuania this period is called the Swedish Deluge ( pl, potop szwedzki, sv, Svenska syndafloden), or less commonly the Russo–Swedish Deluge ( pl, Potop szwedzko-rosyjski) due to the simultaneous Russo-Polish War. The term "deluge" (''potop'' in Polish) was popularized by Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, espe ...
in his novel '' The Deluge'' (1886).
During the wars the Commonwealth lost approximately one third of its population as well as its status as a great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power i ...
due to invasions by Sweden and Russia. According to Professor Andrzej Rottermund, manager of the Royal Castle in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, the destruction of Poland in the Deluge was more extensive than the destruction of the country in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
. Rottermund claims that Swedish invaders robbed the Commonwealth of its most important riches, and most of the stolen items never returned to Poland. Warsaw, the capital of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, was destroyed by the Swedes, and out of a pre-war population of 20,000, only 2,000 remained in the city after the war. According to the 2012 Polish estimates, the material damage caused by the Swedish army amounted to 4 billion złotys. 188 cities and towns, 186 villages, 136 churches, 89 palaces, and 81 castles were completely destroyed in Poland.
Historical background
In 1648,Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Zynovii Mykhailovych Khmelnytskyi ( Ruthenian: Ѕѣнові Богданъ Хмелнiцкiи; modern ua, Богдан Зиновій Михайлович Хмельницький; 6 August 1657) was a Ukrainian military commander and ...
led a popular uprising of Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
and Ukrainian peasants discontented with the rule of Polish and Lithuanian magnates. Although the initial phase of the rebellion ended (after much destruction) at the Battle of Berestechko (1651), it brought into focus the rivalry between Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
and the Commonwealth for hegemony over Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and over the eastern Slavic lands in general. Thus, in October 1653, the Russian Zemsky Sobor declared war on the Commonwealth, and in June 1654 the forces of Tsar Alexis of Russia invaded the eastern half of Poland-Lithuania, starting the Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667. In the summer of 1654, the Russians managed to capture most important cities and strongholds of today's Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. Smolensk was captured after a siege on October 3, 1654. The Swedish Empire, which technically already was at war with the Commonwealth (a ceasefire agreement existed from 1629 and was prolonged from 1635 to 1661), invaded in July 1655 and occupied the remaining half of the country.
Swedish invasion
Background
Following theThirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of batt ...
, the Swedish Empire emerged as one of the strongest nations on the continent. It had a large army but little money to pay its soldiers. The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, weakened by wars with the Cossacks and Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia or Tsardom of Rus' also externally referenced as the Tsardom of Muscovy, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of Tsar by Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter I ...
, seemed like easy prey, also because its best soldiers had been either killed in the 1652 Battle of Batih
The Battle of Batoh, also Battle of Batih, was a battle in 1652 in which Polish-Lithuanian forces under hetman Marcin Kalinowski were defeated by a united army of Crimean Tatars and Zaporozhian Cossacks in what is now Ukraine. A day after the ...
or massacred after it. Furthermore, Swedes remembered claims to their throne by Polish kings Sigismund III Vasa and his sons Władysław IV Vasa and John II Casimir
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
, who themselves belonged to the House of Vasa
The House of Vasa or Wasa Georg Starbäck in ''Berättelser ur Sweriges Medeltid, Tredje Bandet'' pp 264, 275, 278, 291–296 & 321 ( sv, Vasaätten, pl, Wazowie, lt, Vazos) was an early modern royal house founded in 1523 in Sweden. Its memb ...
. An earlier conflict, the Polish–Swedish War (1626–1629) had ended with the Treaty of Stuhmsdorf.
The Polish–Lithuanian King John II Casimir (reigned 1648–68) lacked support among the Commonwealth nobility () due to his sympathies with absolutist Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and his open contempt for the " Sarmatist" culture of the nobility. Earlier, in 1643, John Casimir had become a member of the Jesuits
, image = Ihs-logo.svg
, image_size = 175px
, caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits
, abbreviation = SJ
, nickname = Jesuits
, formation =
, founders = ...
and had received the title of Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**'' Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, t ...
. Nevertheless, in December 1646, he returned to Poland and, in October 1647, resigned his position as Cardinal to stand for election to the Polish throne, after the death of his brother Władysław IV Vasa. He became King in 1648. However, some of the nobility supported Charles Gustav (King of Sweden from 1654 to 1660 and John Casimir's cousin) for the Polish–Lithuanian throne. Many members of the Polish nobility regarded John Casimir as a weak king or a "Jesuit-King"; Grand Treasurer Bogusław Leszczyński, a Protestant, and Deputy Chancellor of the Crown
Chancellor of Poland ( pl, Kanclerz - , from la, cancellarius) was one of the highest officials in the historic Poland. This office functioned from the early Polish kingdom of the 12th century until the end of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwea ...
Hieronim Radziejowski, an old enemy of the Polish King who had been exiled to Sweden, encouraged Charles Gustav to claim the Polish crown. Two Lithuanian noble princes, Janusz Radziwiłł and Bogusław Radziwiłł, introduced dissension into the Commonwealth and began negotiations with the Swedish king Charles X Gustav of Sweden
Charles X Gustav, also Carl Gustav ( sv, Karl X Gustav; 8 November 1622 – 13 February 1660), was King of Sweden from 1654 until his death. He was the son of John Casimir, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken-Kleeburg and Catherine of Sweden. Afte ...
aimed at breaking up the Commonwealth and the Polish–Lithuanian union Polish–Lithuanian can refer to:
* Polish–Lithuanian union (1385–1569)
* Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795)
* Polish-Lithuanian identity as used to describe groups, families, or individuals with histories in the Polish–Lithuanian ...
. They signed the Treaty of Kėdainiai (1655), which envisaged the Radziwiłł princes ruling over two duchies carved out from the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
under Swedish protection.
1655
 In July 1655 two Swedish armies, operating from Swedish Pomerania and the Province of Pomerania, entered
In July 1655 two Swedish armies, operating from Swedish Pomerania and the Province of Pomerania, entered Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest cit ...
, one of the richest and most developed provinces of the Commonwealth, which had for centuries been unaffected by any military conflicts, and whose had not been used to fighting. Greater Poland's noble camp, located in the valley of the Noteć river, near the town of Ujście, looked more like a large party, as the , gathered there to face the Swedish Army, was more interested in drinking. To make matters worse, two powerful magnates, the Voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
of Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
Krzysztof Opaliński
Krzysztof Opaliński (21 January 1611 – 6 December 1655) was a Polish szlachta (nobleman), politician, writer, satirist, and Voivode (Governor) of Poznań. A notable figure during the Swedish Deluge, Opaliński was a skilled diplomat who o ...
, and the Voivode of Kalisz
(The oldest city of Poland)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = ''Top:'' Town Hall, Former "Calisia" Piano Factory''Middle:'' Courthouse, "Gołębnik" tenement''Bottom:'' Aerial view of the Kalisz Old Town
, image_flag = POL Kalisz flag.svg ...
, Andrzej Karol Grudziński, argued with each other whether to fight or to give up. Polish troops lacked gunpowder, cannons, and even food, which was stolen at local villages by hungry soldiers.
After an easy Swedish victory at the Battle of Ujście
The Battle of Ujście was fought on July 24–25, 1655 between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth commanded by Krzysztof Opaliński and Andrzej Grudziński on one side, and on the other Swedish forces commanded by Arvid Wittenber ...
, Krzysztof Opaliński
Krzysztof Opaliński (21 January 1611 – 6 December 1655) was a Polish szlachta (nobleman), politician, writer, satirist, and Voivode (Governor) of Poznań. A notable figure during the Swedish Deluge, Opaliński was a skilled diplomat who o ...
surrendered Greater Poland to Charles Gustav. On July 31, 1655, the army commanded by Arvid Wittenberg captured Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, and on August 20 near Konin, the armies of Wittenberg and Charles Gustav joined forces, and headed for Warsaw. On September 2, the Poles lost the Battle of Sobota
The Battle of Sobota was a battle that took place near Sobota, Poland, on 23 August 1655, between the armies of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth on the one hand and of Sweden on the other.
After Charles X Gustav
Charles X Gustav, a ...
, and on September 4, the Swedes captured Łowicz
Łowicz is a town in central Poland with 27,896 inhabitants (2020). It is situated in the Łódź Voivodeship (since 1999); previously, it was in Skierniewice Voivodeship (1975–1998). Together with a nearby station of Bednary, Łowicz is a m ...
. Four days later, the Swedish army entered the Polish capital, becoming the first foreign army in history to capture Warsaw. King Charles Gustav left a garrison in Warsaw, under Bengt Gabrielsson Oxenstierna
Count Bengt Gabrielsson Oxenstierna (1623–1702) was a Swedish soldier and statesman, who served as Foreign Minister from 1680 to 1697. During this period, he ensured Sweden remained neutral and moved away from its traditional French alliance ...
, and headed southwards, in pursuit of John Casimir. On September 16, the Swedes defeated Polish troops in the Battle of Żarnów, and the Polish forces gave up resistance and surrendered to the invaders. The Polish king headed towards Kraków on September 25, and then fled to the Głogówek castle near Prudnik in Upper Silesia. Kraków was left in the hands of Stefan Czarniecki; on October 3 Swedish forces once again defeated the Poles in the Battle of Wojnicz
The Battle of Wojnicz was fought around the medieval town of Wojnicz in Lesser Poland as part of the Second Northern War on October 3, 1655 between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth commanded by Field Crown Hetman Stanisław Lanckoro� ...
, which opened the road to Kraków. The ancient capital of Poland was captured after a siege, on October 13, 1655. With the three most populated and best developed Polish provinces in his hands (Greater Poland, Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
and Mazovia), Charles Gustav decided to head back northwards to Royal Prussia, which was defended by the Voivode of Malbork, Jakub Wejher. The Swedes, who were generally superior in training, discipline, and equipment, advanced rapidly.
Meanwhile, in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
, whose eastern part had been occupied by another Swedish army under Magnus Gabriel De la Gardie since August 1655, Janusz Radziwiłł and his cousin Bogusław Radziwiłł signed the Union of Kėdainiai (October 20, 1655), which ended Lithuania's union with Poland. The decision of the Radziwiłłs was the result of the 1654 Russian invasion, as Janusz Radziwiłł accused the Poles of not helping the Lithuanians with the defence of the Grand Duchy. The Russian capture of Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
(August 9, 1655) and the subsequent slaughter of its residents convinced the Lithuanian nobility that Swedish protection was the best solution. The situation of the Commonwealth was desperate, but hope appeared with the Truce of Vilna (November 3), in which Poland and the Tsardom of Russia formed an anti-Swedish alliance. With Russian forces attacking Sweden in Livonia
Livonia ( liv, Līvõmō, et, Liivimaa, fi, Liivinmaa, German and Scandinavian languages: ', archaic German: ''Liefland'', nl, Lijfland, Latvian and lt, Livonija, pl, Inflanty, archaic English: ''Livland'', ''Liwlandia''; russian: Ли ...
(see Russo-Swedish War (1656–1658)
The Russo-Swedish War of 1656–1658 was fought by Russia and Sweden as a theater of the Second Northern War. It took place during a pause in the contemporary Russo-Polish War (1654–1667) as a consequence of the Truce of Vilna. Despite ini ...
), Poland finally had time to recoup and gather fresh forces. On October 12, 1655, with permission from King John Casimir, Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, h ...
signed the Treaty of Rinsk
The treaty of Rinsk, concluded on 2 November ( O.S.) / 12 November ( N.S.) 1655, was a Ducal-Royal Prussian alliance during the Second Northern War.Frost (2000), p. 171 Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg and duke of Prussia, and the nob ...
, in which the Royal Prussian nobility agreed to allow Brandenburgian garrisons in their province to defend it against the Swedish invasion (the treaty did not include the cities of Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
, Elbląg
Elbląg (; german: Elbing, Old Prussian: ''Elbings'') is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 117,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg Count ...
and Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
). In November and December 1655 the Swedish army under Gustaf Otto Stenbock
Count Gustaf Otto Stenbock (7 September 1614 – 24 September 1685) was a Swedish soldier and politician.
He was son of Friherre Gustav Eriksson Stenbock (1575–1629) and Countess Beata Margareta Brahe (1583–1645), born in Torpa, Länghem ...
captured all the towns of Royal Prussia except for Gdańsk, Puck and Malbork
Malbork; ;
* la, Mariaeburgum, ''Mariae castrum'', ''Marianopolis'', ''Civitas Beatae Virginis''
* Kashubian: ''Malbórg''
* Old Prussian: ''Algemin'' is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has ...
.
To prevent John Casimir's return to Poland, Swedish units protected the border with Silesia. On November 18, 1655, the Swedes besieged the monastery at Jasna Góra Jasna may refer to:
Places
* Jasna, a village in Poland
* Jasná, a village and ski resort in Slovakia
Other uses
* Jasna (given name), a Slavic female given name
* JASNA, the Jane Austen Society of North America
See also
* Yasna
Yasna (;
, located in Lesser Poland, near the border. Led by the Grand Prior Augustyn Kordecki
Abbot Augustyn Kordecki (born Klemens Kordecki Ślepowron coat of arms; November 16, 1603 – March 20, 1673) was a prior of the Jasna Góra Monastery, Poland.
He was curate and provincial of the monastery. In 1655 during the Deluge
The Gene ...
, the garrison of this symbolic sanctuary-fortress of Poland held off its enemies in the Siege of Jasna Góra
The siege of Jasna Góra (also known less accurately as the ''Battle of Częstochowa'', pl , Oblężenie Jasnej Góry) took place in the winter of 1655 during the Second Northern War, or 'The Deluge' – as the Swedish invasion of ...
. The defense of Jasna Góra galvanized Polish resistance against the Swedes. The news of the siege spread across the nation, and in several areas guerrilla units were created, outraged at the Swedes' attempt to seize the monastery. On December 7, 1655, the unit of Colonel Gabriel Wojniłłowicz defeated the Swedes and their Polish collaborators near Krosno
Krosno (in full ''The Royal Free City of Krosno'', pl, Królewskie Wolne Miasto Krosno) is a historical town and county in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland. The estimated population of the town is 47,140 inhabitants as of 2 ...
. On December 13, Polish troops under Wojniłłowicz recaptured Nowy Sącz
Nowy Sącz (; hu, Újszandec; yi, Tzanz, צאַנז; sk, Nový Sonč; german: Neu-Sandez) is a city in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship of southern Poland. It is the district capital of Nowy Sącz County as a separate administrative unit. It has ...
, and soon afterwards Sweden lost Biała, Dukla
Dukla is a town and an eponymous municipality in southeastern Poland, in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 2,017. The total area of the commune is . Dukla belongs to Lesser Poland, and until the P ...
, Biecz, Wieliczka, and Oświęcim
Oświęcim (; german: Auschwitz ; yi, אָשפּיצין, Oshpitzin) is a city in the Lesser Poland ( pl, Małopolska) province of southern Poland, situated southeast of Katowice, near the confluence of the Vistula (''Wisła'') and Soła riv ...
. By late 1655, the situation in southern Lesser Poland had deteriorated to such an extent for the invaders that on December 27 they decided to lift the siege of Jasna Góra. On December 16, 1655, in Sokal
Sokal ( uk, Сокаль, romanized: ''Sokal'') is a city located on the Bug River in Chervonohrad Raion, Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Sokal urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. The population is appro ...
, Polish Crown hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
s urged the nation to fight the Swedish armies. Two days later, King John Casimir left the Głogówek in Silesia, and via Racibórz and Cieszyn, returned to Poland, arriving at Lubowla on December 27. Two days later, the Tyszowce Confederation was formed in support of the Polish king. John Casimir himself met with hetmans Stanisław Rewera Potocki Stanislav and variants may refer to:
People
*Stanislav (given name), a Slavic given name with many spelling variations (Stanislaus, Stanislas, Stanisław, etc.)
Places
* Stanislav, a coastal village in Kherson, Ukraine
* Stanislaus County, Ca ...
, Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski, Stanisław Lanckoroński and Stefan Czarniecki in Krosno, on December 31, 1655. The meeting was also attended by Primate Andrzej Leszczyński, and eight voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
s.
1656
While in Krosno, the Polish king found out about the end of the siege of Jasna Góra, and about the death of Janusz Radziwiłł. On January 12, 1656, John Casimir left Krosno, and after three days, arrived atŁańcut Castle
Łańcut Castle is a complex of historical buildings located in Łańcut, Poland. Historically the residence of the Pilecki, Lubomirski and Potocki families, the complex includes a number of buildings and is surrounded by a park.
The castle is ...
, which belonged to the Lubomirski family
The House of Lubomirski is a Polish princely family. The Lubomirski family's coat of arms is the Drużyna coat of arms, which is similar to the Szreniawa coat of arms but without a cross.
Origin and the coat of arms
The Lubomirski f ...
. On February 10, the king came to Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
, which, together with Gdańsk, was one of only two major cities of the Commonwealth not seized by any of Poland's enemies. Soon Polish Army units began to concentrate in the area of Lwów, including militias from Red Ruthenia, Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The ...
and Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, as well as forces under Potocki and Prince Lubomirski, together with the garrison of Kamieniec Podolski fortress. Charles Gustav, after finding out about the return of the Polish king, ordered his armies to concentrate in Łowicz. On February 8, 1656, the Swedes defeated Czarniecki in the Battle of Gołąb
The Battle of Gołąb was fought on either 18 or 19 February 1656, between forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth commanded by Stefan Czarniecki on one side, and on the other Swedish Empire's army commanded by Charles X Gustav. This bat ...
, and continued their march towards Lwów, reaching the Zamość Fortress
Zamość Fortress ( pl, Twierdza Zamość) is a set of fortifications constructed together with the city of Zamość (southeastern Poland). It was built between 1579 and 1618, and the construction was initiated by Chancellor and Hetman Jan Zamoys ...
on February 25. On March 1, realizing that without heavy guns it was impossible to capture the mighty stronghold, the Swedish army gave up the siege, and headed towards Bełżec. On March 3, Charles Gustav, whose units were harassed by Polish guerilla forces, decided to retreat. At the same time, guerilla warfare also broke out in Mazovia and Greater Poland, and Lithuanian units under the Grand Hetman of Lithuania Paweł Jan Sapieha
Paul John Sapieha ( lt, Povilas Jonas Sapiega) (1609–1665) was a Polish–Lithuanian nobleman (szlachcic).
Sapieha became a Hussar Rotmistrz in 1633, courtier in 1635, Obozny of Lithuania in 1638, Podstoli of Lithuania in 1645, voivode ...
began moving towards Red Ruthenia.
 On March 11, the Swedish army arrived at Jarosław, fighting its way across the San river. Charles Gustav sent some of his forces to capture
On March 11, the Swedish army arrived at Jarosław, fighting its way across the San river. Charles Gustav sent some of his forces to capture Przemyśl
Przemyśl (; yi, פשעמישל, Pshemishl; uk, Перемишль, Peremyshl; german: Premissel) is a city in southeastern Poland with 58,721 inhabitants, as of December 2021. In 1999, it became part of the Subcarpathian Voivodeship; it was p ...
, but on March 16 they returned to Jarosław without success. On March 22, the Swedish army set off northwards, along the San and Vistula rivers, back to Warsaw. They were followed by units of Stefan Czarniecki and Aleksander Koniecpolski, and during the retreat, Polish troops supporting the invaders changed sides, joining the forces of John Casimir. On March 30, the starving, cold and tired Swedish army of 5,000 stopped near Sandomierz, which was already in Polish hands. The Swedes camped among the forests of Sandomierz Forest
Sandomierz Forest ( pl, Puszcza Sandomierska) is one of the biggest forests in southern Poland; covering large parts of the Sandomierz Basin. Its name comes from the historical city of Sandomierz, and in the Middle Ages its eastern edge created ...
near Gorzyce, where they were quickly surrounded by approximately 23,000 Poles and Lithuanians. To help the besieged army, on March 27 Frederick VI left Warsaw with 2,500 reiters and dragoon
Dragoons were originally a class of mounted infantry, who used horses for mobility, but dismounted to fight on foot. From the early 17th century onward, dragoons were increasingly also employed as conventional cavalry and trained for combat w ...
s, so John Casimir ordered the mounted units of Czarnecki and Lubomirski to face the margrave. Frederick's army was defeated on April 7 in the Battle of Warka. At Gorzyce, however, second-quality Polish forces remained, and the Swedish king managed to break out (April 5), and on April 13, Charles Gustav reached Warsaw. Meanwhile, the Polish king made the Lwów Oath
The Lwów Oath ( pl, Śluby lwowskie) was an oath made on April 1, 1656 by Polish king John II Casimir in Latin cathedral in the city of Lwów (today Lviv, western Ukraine).
Background
During "the Deluge", when the Swedish armies invaded Polis ...
(April 1), in which he entrusted the Commonwealth to the Blessed Virgin Mary's protection, and declared her 'The Queen of the Polish Crown'.
After the Battle of Warka, Czarniecki and Lubomirski decided to head towards Greater Poland and Kujawy, to support guerrilla forces active there. By April 9, Polish troops reached Royal Prussia, capturing Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz ( , , ; german: Bromberg) is a city in northern Poland, straddling the meeting of the River Vistula with its left-bank tributary, the Brda. With a city population of 339,053 as of December 2021 and an urban agglomeration with mor ...
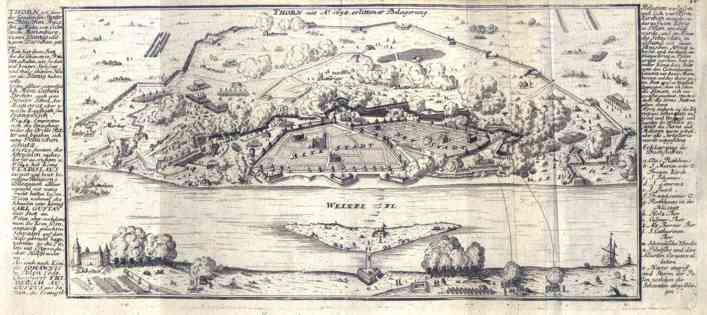
and Nakło (April 19). The Polish attempt to capture Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
, on April 17, was a failure. After a short rest, Stefan Czarniecki considered a raid of Swedish Pomerania, but other Polish leaders opposed this idea. Charles Gustav decided to prevent the Poles from taking control of the northern districts of the country, and departed Warsaw with an army of 10,000 (April 17). On April 21, the Lithuanians under Sapieha freed Lublin, and on April 23, the Lithuanian army reached Praga
Praga is a district of Warsaw, Poland. It is on the east bank of the river Vistula. First mentioned in 1432, until 1791 it formed a separate town with its own city charter.
History
The historical Praga was a small settlement located at ...
, which today is a right-bank district of Warsaw. The forces of Czarniecki and Lubomirski joined other troops near Piła, but on May 7 they were defeated in the Battle of Kłecko, despite their numerical superiority. After the battle, the surviving Polish units regrouped near Gniezno, and in late May, they headed for Warsaw, to help the Lithuanians in the siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
of the Polish capital (April 24 – July 1). Warsaw was being defended by Arvid Wittenberg with 2,000 soldiers, as the main Swedish army was busy besieging Gdańsk. Wittenberg capitulated on July 1, 1656.
 Already in late 1655, Charles Gustav realized that it would be impossible for him to control the Commonwealth. The Swedish king decided to find allies, who would help him to divide Poland-Lithuania. On June 29, 1656, he signed the Treaty of Marienburg, in which he offered
Already in late 1655, Charles Gustav realized that it would be impossible for him to control the Commonwealth. The Swedish king decided to find allies, who would help him to divide Poland-Lithuania. On June 29, 1656, he signed the Treaty of Marienburg, in which he offered Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, h ...
a reward for fighting on his side. Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohe ...
was promised sovereignty in four voivodeships – Poznań, Kalisz, Łęczyca, and Sieradz. On July 28, a reinforced Swedish–Brandenburgian army, under Charles Gustav, set out for Warsaw. Even though the allied army was smaller, it still managed to defeat the Poles and Lithuanians in the Battle of Warsaw (July 28–30), and to recapture Warsaw. This victory, however, achieved little, as the Poles retreated behind the Wieprz
The Wieprz (, ; ua, Вепр, Vepr) is a river in central-eastern Poland, a tributary of the Vistula. It is the country's ninth longest river, with a total length of 349 km and a catchment area of 10,497 km2, all within Poland. Its cour ...
, where they regrouped, and were soon ready to continue fighting. Finally, Charles Gustav decided to abandon Warsaw, and retreat to Royal Prussia. To punish Brandenburg-Prussia, Commonwealth forces decided to invade the Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
. In early October 1656, an army of 11,000 under Wincenty Korwin Gosiewski
Wincenty Aleksander Korwin Gosiewski '' de armis'' Ślepowron (c. 1620 – 29 November 1662) – was a Polish nobleman, general, Field-Commander of Lithuania from 1654, Grand Treasurer of Lithuania and Lithuanian Great-Quartermaster since 1652 ...
entered Prussia, supported by 2,000 Crimean Tatars. On October 8, Gosiewski's army won the Battle of Prostken (October 8), but after the Tatars decided to return to the Crimea, the Polish–Lithuanian army was defeated in the Battle of Filipów (October 22). In November 1656, Greater Poland's troops invaded the Brandenburger province of Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March ( pl, Nowa Marchia) or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945.
Call ...
, which resulted in withdrawal of Brandenburger forces from most of Greater Poland. Charles Gustav, knowing that he needed the support of the Elector, agreed to sign the Treaty of Labiau
The Treaty of Labiau was a treaty signed between Frederick William I, Elector of Brandenburg and Charles X Gustav of Sweden on 10 November ( O.S.) / 20 November ( N.S.) 1656 in Labiau (now Polessk). With several concessions, the most important be ...
(November 20), which granted full sovereignty to the Prussian ruler, in exchange for his complete military support of Sweden in the ongoing war. The Commonwealth, on the other hand, had already been negotiating with the House of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. On December 1, 1656, the first Treaty of Vienna was signed, which was followed by a second Treaty of Vienna, in which Emperor Leopold I promised to aid John Casimir with 12,000 troops against the Swedish-Brandenburgian alliance. By late 1656, Swedish troops had been pushed out of most of the Commonwealth. They only held the right-bank half of Royal Prussia, northern Mazovia, Łowicz, Kraków, and Tykocin.
1657
In 1653, the Transylvanian Hungarian ruler George II Rákóczi signed an alliance with Poland, and the relations between the Commonwealth and Transylvania were friendly. George had even been offered the Polish crown, on condition that he convert to Catholicism. Stunning Swedish successes, however, made Rákóczi change his mind. On May 18, 1656, Charles X Gustav, in a letter sent from Malbork, offered the Hungarian prince Red Ruthenia, in exchange for military support against the Commonwealth. Meanwhile, Rákóczi had already been negotiating with Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and on September 7, 1656, Transylvania and theZaporizhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich ( ua, Запорозька Січ, ; also uk, Вольностi Вiйська Запорозького Низового, ; Free lands of the Zaporozhian Host the Lower) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of C ...
signed a peace treaty, which obliged both sides to help each other in war. On December 8, 1656, the Treaty of Radnot was signed, which divided Poland-Lithuania among Charles X Gustav, Bogusław Radziwiłł, Elector Frederick William, Bohdan Khmelnytsky, and George II Rákóczi. In late January 1657, the Transylvanian army of 25,000 crossed the Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretche ...
, heading towards Medyka
Medyka (; uk, Медика, Medyka) is a village in Przemyśl County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland, on the border with Ukraine. It is the seat of the municipality (gmina) called Gmina Medyka. It lies approximately east of ...
, where 10,000 Cossack allies awaited them. To face the new invader, the army of hetman Stanisław Rewera Potocki rushed southwards. At the same time (January 2), in the Battle of Chojnice, the Swedes defeated the Poles. On February 26, Stefan Czarniecki and King John Casimir met in Kalisz
(The oldest city of Poland)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = ''Top:'' Town Hall, Former "Calisia" Piano Factory''Middle:'' Courthouse, "Gołębnik" tenement''Bottom:'' Aerial view of the Kalisz Old Town
, image_flag = POL Kalisz flag.svg ...
, where they decided to prevent the Swedish and Transylvanian armies from meeting.
After joining the Cossacks, Rákóczi decided not to attack Lwów, but set off towards Kraków, where the situation of the Swedish garrison under Wirtz was desperate. On March 21, Rákóczi captured Tarnów
Tarnów () is a city in southeastern Poland with 105,922 inhabitants and a metropolitan area population of 269,000 inhabitants. The city is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship since 1999. From 1975 to 1998, it was the capital of the Tarn� ...
, and on March 28, he reached Kraków. Along the way to the ancient Polish capital, the Transylvanian-Cossack army burned and looted towns and villages, murdering thousands. Since his army was too busy looting Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
, only 5,000 soldiers reached Kraków, which by the Treaty of Radnot, was to be ruled by Transylvania. After leaving 2,500 soldiers to help the Swedish garrison of Kraków, Rákóczi's army headed northwards, along the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
. On April 12, 1657, the Transylvanian-Cossack army met with Swedish forces under Charles X Gustav, at Ćmielów. The joined forces began to follow the Polish Crown army under Stanisław Potocki, and the Lithuanian army under Paweł Sapieha, to force a decisive battle. On April 29, the Polish and Lithuanian armies joined forces at Łosice
Łosice (; yi, לאָשיץ ''Loshitz'', russian: Лосице / Лoсічы ''Lositze'') is a town in eastern Poland, seat of the Łosice County and Gmina Łosice (commune) in the Masovian Voivodeship (since 1999). Previously it was located in ...
, and in early May 1657, the Poles decided to organize a revenge raid on Transylvania, under hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
Jerzy Sebastian Lubomirski. On May 13, Rákóczi and Charles X Gustav seized the fortress of Brześć Litewski, and on May 17, after a three-day siege, the Swedes, Cossacks, and Transylvanians captured Warsaw. Soon afterwards, however, the Dano-Swedish War began, and Charles X Gustav left Poland with most of his troops. The remaining Swedish army was commanded by Gustaf Otto Stenbock
Count Gustaf Otto Stenbock (7 September 1614 – 24 September 1685) was a Swedish soldier and politician.
He was son of Friherre Gustav Eriksson Stenbock (1575–1629) and Countess Beata Margareta Brahe (1583–1645), born in Torpa, Länghem ...
. The Swedish withdrawal made Rákóczi uneasy, as he was well aware of the poor quality of his soldiers. On July 7–8, 1656, at Łańcut Castle, King John Casimir and his hetmans agreed that Stefan Czarniecki would follow Rákóczi and the Cossacks, while Lubomirski's and Potocki's divisions together with Crimean Tatars.
The Ottomans were offended that George II Rakoczi, who was officially their vassal, did not ask their approval to attack Poland and did not want to open another war (in that time they tried to attack Venice through Dalmatia) but when he ignored them they ordered the Crimean Tatars to help the Polish troops and punish Rakoczi. They already replaced Rakoczi's vassal voivodes from Moldova and Wallachia.
On June 20, 1657, Stenbock was ordered by Charles X Gustav to abandon Rákóczi and head with his army to Stettin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
. To save his skin, the ruler of Transylvania began a quick retreat southwards, towards the Carpathians. On July 11, Stefan Czarniecki's division defeated Rákóczi at Magierów near Lwów, and on July 20, the Transylvanian-Cossack army was destroyed in the Battle of Czarny Ostrów in Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-centra ...
. Three days later, Rákóczi signed a peace treaty with the Commonwealth, in which he promised to break the alliance with Sweden, withdraw his troops from Kraków and Brześć Litewski, and pay for the damage inflicted by his army. On July 26, remnants of the Transylvanian army were surrounded by the Tatars near Skałat. Rákóczi himself managed to flee, and the army was temporarily commanded by John Kemény, who himself was captured by the Tatars. After six months of fighting in Poland, Rákóczi's army of 25,000 ceased to exist, with all survivors taken prisoner by the Tatars.
On August 30, the Swedish garrison left Kraków, and throughout August and September 1657, all Swedish troops in Poland moved northwards, to Royal Prussia. Altogether, by autumn of that year, only some 8,000 Swedish soldiers remained in Poland–Lithuania. The Swedes still kept some Prussian cities, as Malbork, Elbląg, Sztum, Brodnica, Grudziądz, and Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
. On September 11, an Austrian army of 11,000, allied with Poland, concentrated near Kraków and set off to Płock, where it spent the winter. Polish army commanders and King John Casimir, gathered in Poznań on November 26, decided to delay the attack on Swedish forces in Royal Prussia until spring 1658. On November 6, 1657, Poland and Brandenburg–Prussia signed the Treaty of Bromberg. Ducal Prussia, which had previously allied itself with Sweden and attacked Poland, changed sides and guaranteed military support of the Commonwealth, in return for sovereignty (it had been a fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
of Poland since 1466). This treaty is regarded as one of the worst mistakes in Polish history.
1658–1660
 In the spring of 1658, the Polish army, together with its Austrian allies under
In the spring of 1658, the Polish army, together with its Austrian allies under Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy.
Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier ...
, began a campaign in Royal Prussia, where several key towns and cities were still in Swedish hands. On July 1, the siege of Toruń began. The heavily fortified city was defended by 2400 soldiers under Barthod Hartwig von Bülow. The Polish troops included the divisions of Krzysztof Grodzicki
Krzysztof Grodzicki (died 1659) was a Polish artillery general, serving the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
Grodzicki underwent military education in the Dutch Republic. He served under Stanisław Koniecpolski in the Polish–Swedish War (1626� ...
, Jan Sapieha and Stefan Czarniecki. Furthermore, they were provided support by the Brandenburgian-Prussian army of Bogusław Radziwiłł, which after the Treaty of Bromberg changed sides. Altogether, almost 25,000 soldiers besieged Toruń. After a prolonged artillery bombardment, the main attack took place in the night of November 16–17, and on December 30 Toruń capitulated. Meanwhile, Stefan Czarniecki's division headed to Denmark–Norway
Denmark–Norway ( Danish and Norwegian: ) was an early modern multi-national and multi-lingual real unionFeldbæk 1998:11 consisting of the Kingdom of Denmark, the Kingdom of Norway (including the then Norwegian overseas possessions: the Faroe ...
, to help the Danes in the Dano-Swedish War. In October 1658, the Polish army of 4500 reached Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; nds, label=Hamburg German, Low Saxon, Hamborg ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg (german: Freie und Hansestadt Hamburg; nds, label=Low Saxon, Friee un Hansestadt Hamborg),. is the List of cities in Germany by popul ...
, and in December 1658, with the help of Polish troops, the fortress of Kolding was captured (see Battle of Kolding).
On July 1, 1658, the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
ordered the expulsion of the Polish Brethren, who were accused of collaborating with the Swedish invaders.
In 1659, the Swedish army still remaining in Poland under Lorens von der Linde
Baron Lorens von der Linde (July 30, 1610 – June 25, 1670) was a:
* Swedish Generalmajor since 1647
* Swedish General since 1655
* Swedish Field Marshal (after 1665).
He was commander of Swedish forces in Royal Prussia during Deluge (history)
...
was withdrawn to major Royal Prussian fortresses – Malbork, Głowa Gdańska, Grudziądz, Elbląg
Elbląg (; german: Elbing, Old Prussian: ''Elbings'') is a city in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Poland, located in the eastern edge of the Żuławy region with 117,390 inhabitants, as of December 2021. It is the capital of Elbląg Count ...
, and Brodnica. In August 1659, the Polish army captured Głowa and Grudziądz, and soon afterwards, the starving Swedish garrison at Brodnica surrendered. The siege of Malbork was continued, and Polish – Brandenburgian troops blocked Elbląg. In December 1659, the siege of Elbląg began. Meanwhile, in late 1658, the Polish–Russian truce ended when Russian forces under Ivan Andreyevich Khovansky (Tararui) and Jurij Aleksiejewicz Dołgorukow again attacked the Polish - Lithuanian units (see Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
The Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667, also called the Thirteen Years' War and the First Northern War, was a major conflict between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Between 1655 and 1660, the Swedish invasion was ...
). The Russians managed to capture large parts of the Commonwealth, but were later defeated in the Battle of Konotop and the Battle of Polonka
The Battle of Polonka (Połonka) took place near Połonka (modern Belarus) during the Polish-Russian War (1658-1667) on 29 June 1660 between Polish-Lithuanian and Russian forces. Polish-Lithuanian army under Stefan Czarniecki and Paweł Jan Sa ...
.
On May 3, 1660, the Treaty of Oliva was signed, which ended the Polish–Swedish War. After the conclusion of the conflict, Poland–Lithuania initiated a large offensive against the Russians, who were beaten in the Battle of Chudnov. In 1661, Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
was recaptured (December 2), and in 1663–64, Polish forces invaded Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine ( uk, Лівобережна Україна, translit=Livoberezhna Ukrayina; russian: Левобережная Украина, translit=Levoberezhnaya Ukraina; pl, Lewobrzeżna Ukraina) is a historic name of the part of Ukrain ...
. The war with Russia ended with the Truce of Andrusovo (January 30, 1667).
Other conflicts
The Deluge was the climax of a series of wars that took place in Poland–Lithuania in the mid-17th century. The Commonwealth was first affected by theKhmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: � ...
, which began in 1648, and affected southeastern provinces of the country. In the final stages of the uprising, the Russians invaded Poland–Lithuania in 1654, reaching as far west as the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river near Puławy. The Commonwealth also fought forces from Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
and Brandenburg-Prussia
Brandenburg-Prussia (german: Brandenburg-Preußen; ) is the historiographic denomination for the early modern realm of the Brandenburgian Hohenzollerns between 1618 and 1701. Based in the Electorate of Brandenburg, the main branch of the Hohe ...
, but the Duchy of Prussia
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia establish ...
gained formal Polish recognition of its independence outside of the Polish state ( Treaty of Wehlau, 1657). The Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
of the Crimean Khanate and the Nogai Horde conducted almost annual slave raids in the territories controlled by the Commonwealth. In all these other invasions, only the Russian invaders caused the most similar damages to the Swedes, due to Russian raids, destructions and rapid incursion which crippled Polish industries.
With the Treaty of Hadiach on September 16, 1658, the Polish Crown sought to elevate the in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
and Ruthenians
Ruthenian and Ruthene are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term Rutheni was used in medieval sou ...
to a position equal to that of Poland and Lithuania in the Polish–Lithuanian Union, and in fact transform the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth into a Polish–Lithuanian–Ruthenian Commonwealth (Polish: , "Commonwealth of Three Nations"). Supported by Cossack Hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
Ivan Vyhovsky and the , the treaty aimed to change the face of Eastern Europe. However, its terms never came into full operation: in addition to the unpopularity of continued integration with the Commonwealth with the majority of the Cossacks, Russia refused to recognize Hadiach, and maintained its claims to Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
. The Russo-Polish War (1654–1667) ended with the Treaty of Andrusovo of 13 January 1667. (Poland-Lithuania profited from Turkish participation in the Russo-Turkish War (1676–1681) due to Ottoman links with the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
.) The peace settlement gave Russia control over the so-called Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine ( uk, Лівобережна Україна, translit=Livoberezhna Ukrayina; russian: Левобережная Украина, translit=Levoberezhnaya Ukraina; pl, Lewobrzeżna Ukraina) is a historic name of the part of Ukrain ...
(left of the river Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
), with the Commonwealth retaining Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine ( uk , Правобережна Україна, ''Pravoberezhna Ukrayina''; russian: Правобережная Украина, ''Pravoberezhnaya Ukraina''; pl, Prawobrzeżna Ukraina, sk, Pravobrežná Ukrajina, hu, Jobb p ...
(right of the Dnieper). While initially the agreement stipulated that Russia would return Left-bank Ukraine to the Commonwealth in twenty years, the division became permanent with the Eternal Peace Treaty of 1686.
The Deluge brought to an end the era of Polish religious tolerance: mostly non-Catholic invaders antagonized the mostly Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
Poles. The expulsion of the Protestant Polish Brethren from Poland in 1658 exemplified the increasing intolerance. During the Deluge, many thousands of Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the l ...
also fell victim to violence carried out by the Zaporozhian Cossacks.
Destruction of the Commonwealth
 The Swedish invasion affected the richest provinces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (
The Swedish invasion affected the richest provinces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; german: Großpolen, sv, Storpolen, la, Polonia Maior), is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest cit ...
, Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name Małopolska ( la, Polonia Minor), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a ...
, Mazovia, Pomerelia, Kujawy, Podlasie
Podlachia, or Podlasie, ( pl, Podlasie, , be, Падляшша, translit=Padliašša, uk, Підляшшя, translit=Pidliashshia) is a historical region in the north-eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the c ...
), which for the most part had not been affected by major wars for 200 years. According to Professor Andrzej Rottermund, manager of the Royal Castle in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
, the Swedish army robbed Poland of her most precious goods – thousands of works of art, books and valuables. Most of these items have never been returned to Poland, and are kept both in private Swedish hands and in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
museums, such as the Swedish Army Museum
The Swedish Army Museum ( sv, Armémuseum) is a museum of military history located in the district of Östermalm in Stockholm. It reopened in 2002 after a long period of closure, and was awarded the title of the best museum of Stockholm in 2005. ...
, and Livrustkammaren. Almost all cities, towns, castles and churches in locations where Swedish troops were stationed were destroyed, and in guides to many Polish towns and cities one can find notes that read "object destroyed during Swedish invasion". From the Royal Castle in Warsaw the Swedes plundered approximately 200 paintings, a number of carpets and Turkish tents, musical instruments, furniture, Chinese porcelain, weapons, books, manuscripts, marbles, even dresses of maids and door frames pulled from walls. Meanwhile, the Russian invaders in the east had also destroyed and damaged much of the eastern part's infrastructure, partly due to heavy agricultural fertile developments there.
Hubert Kowalski of the University of Warsaw
The University of Warsaw ( pl, Uniwersytet Warszawski, la, Universitas Varsoviensis) is a public university in Warsaw, Poland. Established in 1816, it is the largest institution of higher learning in the country offering 37 different fields of ...
Institute of Archeology says that Swedes stole anything they could lay their hands on—windows, stairs, chimneys, sculptures, floors, doors and gates. Most goods were loaded on boats and transported along the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
to the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
and then to Sweden. In November 2011, archaeologists of the University of Warsaw found approximately 70 items (total weight five tons), which probably come from the Warsaw Royal Castle. They sank in the Vistula while being transported to Sweden. Even though Article 9 of the Treaty of Oliva stated that Sweden should return all stolen goods, all items are still kept in Stockholm and other Swedish locations. Several Polish kings (John II Casimir, John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobi ...
and Stanisław II Augustus) sent official missions to Sweden, but without success. In most situations, Swedish authorities claimed that they did not know where stolen goods were. In 1911, Kraków's Academy of Science sent its own mission, which was made up of renowned professors Eugeniusz Barwiński, Ludwik Birkenmajer and Jan Łoś. In Stockholm and Uppsala
Uppsala (, or all ending in , ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the county seat of Uppsala County and the fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inhabitants in 2019.
Located north of the ca ...
they found 205 manuscripts and 168 rare Polish books, describing their foundings in a report. In 2002, the Warsaw Royal Castle organized an exhibition, "Eagle and Three Crowns", which presented many items stolen from Poland, and kept in Swedish museums. After the Deluge, the Commonwealth became a "cultural desert". Poland and Lithuania lost 67 libraries and 17 archives. Of all major cities of the country, only Lwów
Lviv ( uk, Львів) is the largest city in Western Ukraine, western Ukraine, and the List of cities in Ukraine, seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is o ...
and Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
were not destroyed, and when Swedish soldiers were unable to steal an item, they would destroy or burn it. In ruins were castles, palaces, churches, abbeys, towns and villages. As a result of the Swedish invasion, few pre-Baroque buildings remained in Poland. An estimated 3 million died.
Among others, Swedish troops stole such items as:
* both Polish and Lithuanian state records (''Metrica Regni Poloniae''),
* the royal library from Warsaw,
* libraries from Ujazdów Castle, Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
, Bydgoszcz
Bydgoszcz ( , , ; german: Bromberg) is a city in northern Poland, straddling the meeting of the River Vistula with its left-bank tributary, the Brda. With a city population of 339,053 as of December 2021 and an urban agglomeration with mor ...
, Malbork
Malbork; ;
* la, Mariaeburgum, ''Mariae castrum'', ''Marianopolis'', ''Civitas Beatae Virginis''
* Kashubian: ''Malbórg''
* Old Prussian: ''Algemin'' is a town in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland. It is the seat of Malbork County and has ...
, Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint Joh ...
, Grudziądz, Gniezno, Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of ...
, Jarosław, Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
, Sandomierz, Radom, and Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula, Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland un ...
, also archives and libraries from most towns of Royal Prussia. Most of the stolen books are kept in the University Library at Uppsala, the Royal Library at Stockholm, and private libraries of the Bielke, Oxenstierna, Rosenhahne, Wrangel and Brahe families,
* all Warsaw palaces – completely robbed were the Kazanowski Palace, the Ossoliński Palace, the Daniłłowicz Palace, the Primate Palace, the Bishophoric Palace, the Royal Palace and the Royal Castle,
* castles and churches, which were robbed and destroyed, as were almost all Polish towns; the most notable examples are Golub-Dobrzyń
Golub-Dobrzyń () is a town in northern Poland, located on the Drwęca. Situated in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (since 1999), it was previously in the Torun Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital of Golub-Dobrzyń County and has a p ...
, Krzyżtopór
Krzyżtopór () is a castle located in the village of Ujazd, Iwaniska commune, Opatów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It was originally built by a Polish nobleman and Voivode of Sandomierz, Krzysztof Ossoliński (15 ...
, Wieluń, Krasnystaw
Krasnystaw ( uk, Красностав, Krasnostav) is a town in southeastern Poland with 18 630 inhabitants (31 december 2019). Situated in the Lublin Voivodeship (since 1999), previously in Chełm Voivodeship (1975–1998). It is the capital ...
, Wawel, Tęczyn, Lanckorona
Lanckorona is a village located south-west of Kraków in Lesser Poland. It lies on the Skawinka river, among the hills of the Beskids, above sea level. It is known for the Lanckorona Castle, today in ruins. Lanckorona is also known for the B ...
, Pieskowa Skała, Kielce
Kielce (, yi, קעלץ, Keltz) is a city in southern Poland, and the capital of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship. In 2021, it had 192,468 inhabitants. The city is in the middle of the Świętokrzyskie Mountains (Holy Cross Mountains), on the ban ...
, Sandomierz, Chęciny
Chęciny (Yiddish: חענטשין – Khantchin or Chentshin) is a town in Kielce County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, southern Poland, with 104,361 inhabitants as of December 2021. It was first mentioned in historical documents from 1275, and ...
Niepołomice, Ojców, Wiśnicz
Wiśnicz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Małogoszcz, within Jędrzejów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It lies approximately west of Małogoszcz, north-west of Jędrzejów, and west of t ...
, Łobzów, Kruszwica, Rabsztyn.
According to the estimates of Polish scholars I. Ihnatowicz, Z. Landau, A. Mączak and B. Zientara, the invasion by the Swedish army and its allies (Brandenburg-Prussia and Transilvania), resulted in the loss of 25% of the population in four core Polish provinces. Lesser Poland lost 23% of population, Mazovia 40% in villages and 70% in towns, Greater Poland 50% in villages and 60% in towns. Royal Prussia lost some 60% of its population. The Commonwealth's population losses are estimated at between 30% and 50% in 1648–1660.
In January 2013 Marek Poznański, a Palikot Movement member of the Polish parliament, announced his plan to send thousands of postcards to European politicians and journalists, in which he wanted to convince the recipients that Poland should get financial compensation from Sweden for the destruction of the country in the deluge. Poznański claims that in the 1660 Treaty of Oliwa, Sweden pledged to return all stolen goods, which never happened. The MP had previously intervened at the Polish Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Ministry of Culture; he also visited the Embassy of Sweden in Warsaw. A businessman from Warsaw, Sławian Krzywiński, joined Poznański, creating the Foundation of Reconstruction of Destruction Caused by the Swedish Invasion (Fundacja Odbudowy Zniszczeń Dokonanych w Czasie Potopu Szwedzkiego). According to Krzywiński, looted goods are still kept in Swedish museums and private collections. Among others, Poland lost the Braniewo Library, works of Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulat ...
, including the 1543 Nuremberg edition of ''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
''De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (English translation: ''On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres'') is the seminal work on the heliocentric theory of the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus (1473–1543) of the Polish Renaissance. The book, ...
'', and the oldest printed text of Bogurodzica
]
Bogurodzica (, calque of the Greek term ''Theotokos''), in English known as the Mother of God, is a medieval Roman Catholic hymn composed sometime between the 10th and 13th centuries in Poland. It is believed to be the oldest religious hymn or ...
. Krzywiński states that as an act of goodwill, the Swedish side should cover the cost of reconstruction of the Rawa Mazowiecka castle, which was destroyed by them in the 1650s.
Effect on the fate of the Commonwealth
One of the most notable effects of the devastating Deluge was the subsequent weakening of Poland's international standing. While Sweden destroyed more, Russia also took part and was second only to Sweden in the level of destruction. With the entire Polish nation crippled by the Swedes and Russians, Russia was able to rise, found theRussian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
in the early 18th century and play a major role in the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
in the latter half of the 18th century.
In popular culture
The Deluge had a major effect on Poland, and there are several books describing the war. In 1886Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, espe ...
described the Swedish invasion in his novel '. Based on the novel, Jerzy Hoffman directed the film ''The Deluge'' (') in 1974, a classic historical work. It starred Daniel Olbrychski as the character Andrzej Kmicic, a patriot who valiantly fought against the Swedish invasion. The film received a nomination for an Oscar in 1974, but lost to the Italian film ''Amarcord
''Amarcord'' () is a 1973 comedy-drama film directed by Federico Fellini, a semi- autobiographical tale about Titta, an adolescent boy growing up among an eccentric cast of characters in the village of Borgo San Giuliano (situated near the anci ...
''.
In 2000, Renata Ocieczek wrote the book (''The time of the Swedish deluge in Polish literature''), and in 2006 Jacek Płosiński wrote (''Swedish deluge in Podlasie
Podlachia, or Podlasie, ( pl, Podlasie, , be, Падляшша, translit=Padliašša, uk, Підляшшя, translit=Pidliashshia) is a historical region in the north-eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the c ...
''). Other books about this topic include: by Mirosław Nagielski, ("Bloody storm") by Augustyn Necel (describing the Deluge in the region of Kaszuby), (''The sign of the Jastrzębiec'') by Stanisław Maria Jankowski, and (''The memoir of the siege of Częstochowa''), by Father Augustyn Kordecki
Abbot Augustyn Kordecki (born Klemens Kordecki Ślepowron coat of arms; November 16, 1603 – March 20, 1673) was a prior of the Jasna Góra Monastery, Poland.
He was curate and provincial of the monastery. In 1655 during the Deluge
The Gene ...
. Furthermore, James Michener describes the Deluge in his novel ''Poland'' (1983). The Deluge has also found its way into video games. The video game '' Mount & Blade: With Fire & Sword'' (named after the first book of Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, especi ...
's trilogy) contains a quest called "The Deluge" that is based on the events of the actual Deluge.
See also
* '' Après nous le déluge'' (expression) * ''The Deluge'' (novel) * Kostka-Napierski Uprising * List of wars between Russia and Sweden *Northern Wars
"Northern Wars" is a term used for a series of wars fought in northern and northeastern Europe from the 16th to the 18th century. An internationally agreed-on nomenclature for these wars has not yet been devised. While the Great Northern War is g ...
* Polish–Swedish wars
* Tatar invasions
* Treaty of Hadiach
* Treaty of Oliva
References
External links
*Map
of area occupied by
Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
in 1657
{{DEFAULTSORT:Deluge (History)
Northern Wars
1650s in Europe
17th-century conflicts
Invasions
Wars involving Moldavia
Wars involving Poland
Wars involving Sweden
Wars involving Transylvania
Wars involving Wallachia
Wars involving Russia
Cossack uprisings
Guerrilla wars
Poland–Sweden relations
Warfare of the Early Modern period
Black Madonna of Częstochowa
1650s in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
Invasions by Sweden
Invasions by Russia
Polish-Swedish war