The Art of Painting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''The Art of Painting'' (Dutch: ''Allegorie op de schilderkunst''), also known as ''The Allegory of Painting'', or ''Painter in his Studio'', is a 17th-century oil on canvas painting by
 This canvas depicts an artist painting a woman dressed in blue posing as a model in his studio. The subject is standing by a window and a large map of the
This canvas depicts an artist painting a woman dressed in blue posing as a model in his studio. The subject is standing by a window and a large map of the
 The painting has only two figures, the painter and his subject, a woman with downcast eyes. The painter was thought to be a self-portrait of the artist; Jean-Louis Vaudoyer suggested the young woman could be his daughter. The painter sits in front of the painting on the easel, where you can see the sketch of the crown. He is dressed in an elegant black garment with cuts on the sleeves and on the back that offers a glimpse of the shirt underneath. He has short puffy breeches and orange stockings, an expensive and fashionable garment that is also found in other works of the time, as in a well-known self-portrait by Rubens.
The tapestry and the chair, both repoussoirs, lead the viewer into the painting. As in ''
The painting has only two figures, the painter and his subject, a woman with downcast eyes. The painter was thought to be a self-portrait of the artist; Jean-Louis Vaudoyer suggested the young woman could be his daughter. The painter sits in front of the painting on the easel, where you can see the sketch of the crown. He is dressed in an elegant black garment with cuts on the sleeves and on the back that offers a glimpse of the shirt underneath. He has short puffy breeches and orange stockings, an expensive and fashionable garment that is also found in other works of the time, as in a well-known self-portrait by Rubens.
The tapestry and the chair, both repoussoirs, lead the viewer into the painting. As in '' The map, remarkable for the representation of light on it, shows the
The map, remarkable for the representation of light on it, shows the
 Vermeer had a theoretical interest for painting. The subject is presumed to be Fama, Pictura, or
Vermeer had a theoretical interest for painting. The subject is presumed to be Fama, Pictura, or 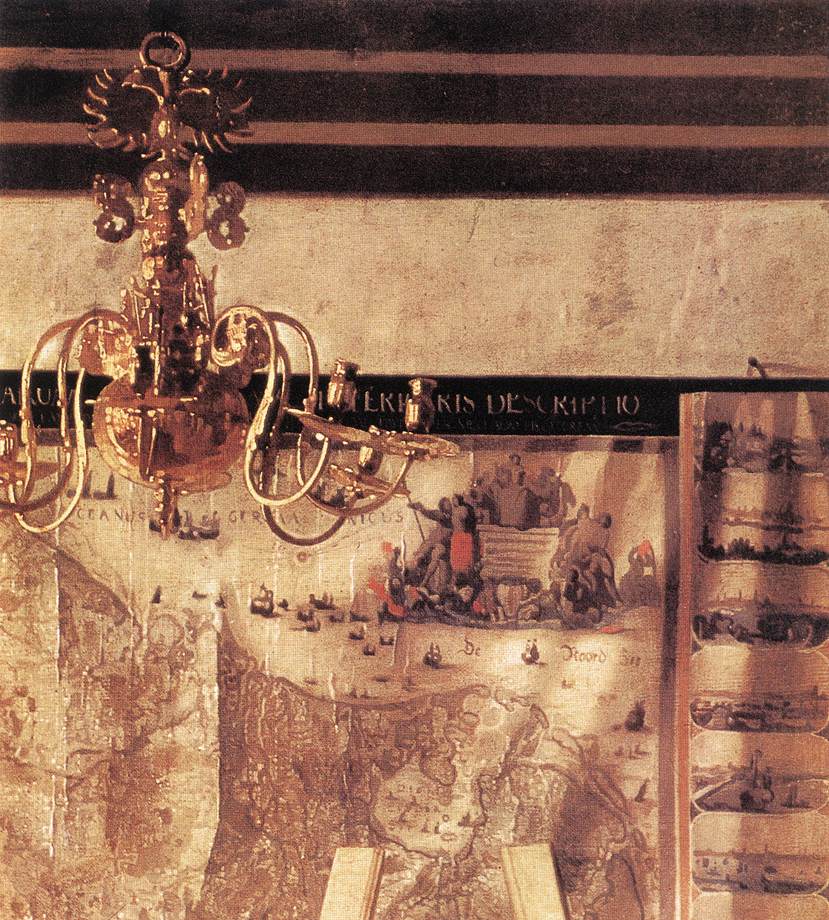 The
The
 In 1935, Count Jaromir Czernin had tried to sell the painting to
In 1935, Count Jaromir Czernin had tried to sell the painting to
Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
painter Johannes Vermeer
Johannes Vermeer ( , , see below; also known as Jan Vermeer; October 1632 – 15 December 1675) was a Dutch Baroque Period painter who specialized in domestic interior scenes of middle-class life. During his lifetime, he was a moderately succe ...
. It is owned by the Austrian Republic
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ci ...
and is on display in the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
.
Many art historians think that it is an allegory of painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
, hence the alternative title of the painting. Its composition and iconography make it the most complex Vermeer work of all. After Vermeer's ''Christ in the House of Martha and Mary
Jesus at the home of Martha and Mary (also referred to as Christ in the House of Martha and by other variant names) refers to a Biblical episode in the life of Jesus in the New Testament which appears only in Luke's Gospel (), immediately after th ...
'' and ''The Procuress'' it is his largest work.
This illusionistic painting is one of Vermeer's most famous. In 1868 Thoré-Bürger, known today for his rediscovery of the work of painter Johannes Vermeer, regarded this painting as his most interesting. Svetlana Alpers
Svetlana Leontief Alpers (born February 10, 1936) is an American art historian, also a professor, writer and critic. Her specialty is Dutch Golden Age painting, a field she revolutionized with her 1984 book ''The Art of Describing''. She has also ...
describes it as unique and ambitious; Walter Liedtke
Walter Arthur Liedtke, Jr. (August 28, 1945 – February 3, 2015) was an American art historian, writer and Curator of Dutch and Flemish Paintings at the Metropolitan Museum of Art. He was known as one of the world's leading scholars of Dutch a ...
"as a virtuoso display of the artist's power of invention and execution, staged in an imaginary version of his studio ..." According to Albert Blankert "No other painting so flawlessly integrates naturalistic technique, brightly illuminated space, and a complexly integrated composition."
Description
 This canvas depicts an artist painting a woman dressed in blue posing as a model in his studio. The subject is standing by a window and a large map of the
This canvas depicts an artist painting a woman dressed in blue posing as a model in his studio. The subject is standing by a window and a large map of the Low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
hangs on the wall behind. It is signed to the right of the girl "I annesVer. Meer", but not dated. Most experts assume it was executed sometime between 1665/1668, but some suggest the work could have been created as late as 1670–1675.
In 1663 Vermeer had been visited by Balthasar de Monconys, but had no painting to show, so it was possibly done "in order to have an outstanding specimen of his art in his studio." Vermeer obviously liked the painting; he never sold it during his lifetime. According to Alpers "it stands as a kind of summary and assessment of what has been done."
Elements
 The painting has only two figures, the painter and his subject, a woman with downcast eyes. The painter was thought to be a self-portrait of the artist; Jean-Louis Vaudoyer suggested the young woman could be his daughter. The painter sits in front of the painting on the easel, where you can see the sketch of the crown. He is dressed in an elegant black garment with cuts on the sleeves and on the back that offers a glimpse of the shirt underneath. He has short puffy breeches and orange stockings, an expensive and fashionable garment that is also found in other works of the time, as in a well-known self-portrait by Rubens.
The tapestry and the chair, both repoussoirs, lead the viewer into the painting. As in ''
The painting has only two figures, the painter and his subject, a woman with downcast eyes. The painter was thought to be a self-portrait of the artist; Jean-Louis Vaudoyer suggested the young woman could be his daughter. The painter sits in front of the painting on the easel, where you can see the sketch of the crown. He is dressed in an elegant black garment with cuts on the sleeves and on the back that offers a glimpse of the shirt underneath. He has short puffy breeches and orange stockings, an expensive and fashionable garment that is also found in other works of the time, as in a well-known self-portrait by Rubens.
The tapestry and the chair, both repoussoirs, lead the viewer into the painting. As in ''The Allegory of Faith
''The Allegory of Faith'', also known as ''Allegory of the Catholic Faith'', is a Dutch Golden Age painting by Johannes Vermeer from about 1670–1672. It has been in the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York since 1931.
This and '' Art of Pain ...
'', the ceiling can be seen.
Experts attribute symbols to various aspects of the painting. A number of the items, a plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "re ...
mask
A mask is an object normally worn on the face, typically for protection, disguise, performance, or entertainment and often they have been employed for rituals and rights. Masks have been used since antiquity for both ceremonial and pra ...
, perhaps representing the debate on paragone
Paragone ( it, paragone, meaning ''comparison''), was a debate during the Italian Renaissance in which painting and sculpture (and to a degree, architecture) were each championed as forms of art superior and distinct to each other. While other ar ...
, the presence of a piece of cloth, a folio
The term "folio" (), has three interconnected but distinct meanings in the world of books and printing: first, it is a term for a common method of arranging sheets of paper into book form, folding the sheet only once, and a term for a book ma ...
, and some leather on the table have been linked to the symbols of Liberal Arts
Liberal arts education (from Latin "free" and "art or principled practice") is the traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term '' art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically th ...
. The representation of the marble tiled floor and the splendid golden chandelier are examples of Vermeer's craftsmanship and show his knowledge of perspective. Each object reflects or absorbs light differently, getting the most accurate rendering of material effects.
 The map, remarkable for the representation of light on it, shows the
The map, remarkable for the representation of light on it, shows the Seventeen Provinces
The Seventeen Provinces were the Imperial states of the Habsburg Netherlands in the 16th century. They roughly covered the Low Countries, i.e., what is now the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of the French departments of Nord (Fre ...
of the Netherlands, flanked by 20 views of prominent Dutch cities. It was published by Claes Janszoon Visscher in 1636. This map, but without the city views on the left and right can be seen on paintings by Jacob Ochtervelt and Nicolaes Maes. Similar maps were found in the Bibliothèque Nationale
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vi ...
in Paris and in the Swedish Skokloster. In the top left of the map two women can be seen; one bearing a cross-staff
The term Jacob's staff is used to refer to several things, also known as cross-staff, a ballastella, a fore-staff, a ballestilla, or a balestilha. In its most basic form, a Jacob's staff is a stick or pole with length markings; most staffs ar ...
and compasses, while the other has a palette, brush, and a city view in the hand.
Symbolism and allegory
 Vermeer had a theoretical interest for painting. The subject is presumed to be Fama, Pictura, or
Vermeer had a theoretical interest for painting. The subject is presumed to be Fama, Pictura, or Clio
In Greek mythology, Clio ( , ; el, Κλειώ), also spelled Kleio, is the muse of history, or in a few mythological accounts, the muse of lyre playing.
Etymology
Clio's name is etymologically derived from the Greek root κλέω/κλεί ...
, the Muse
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai, el, Μούσες, Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the ...
of History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, evidenced by her wearing a laurel wreath
A laurel wreath is a round wreath made of connected branches and leaves of the bay laurel (), an aromatic broadleaf evergreen, or later from spineless butcher's broom (''Ruscus hypoglossum'') or cherry laurel (''Prunus laurocerasus''). It is a s ...
, holding a trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitched one octave below the standard ...
, possibly carrying a book by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
or Thucydides
Thucydides (; grc, , }; BC) was an Athenian historian and general. His '' History of the Peloponnesian War'' recounts the fifth-century BC war between Sparta and Athens until the year 411 BC. Thucydides has been dubbed the father of " scienti ...
, which matches the description in Cesare Ripa
Cesare Ripa (c. 1555, Perugia – Rome) was an Italian iconographer who worked for Cardinal Anton Maria Salviati as a cook and butler.
Life
Little is known about his life. He was born of humble origin in Perugia about 1555. The exact date o ...
's 16th century book on emblem
An emblem is an abstract or representational pictorial image that represents a concept, like a moral truth, or an allegory, or a person, like a king or saint.
Emblems vs. symbols
Although the words ''emblem'' and '' symbol'' are often us ...
s and personifications entitled '' Iconologia''. However, according to Ripa History should look back and not down as in this painting. Following Vermeer's contemporary Gerard de Lairesse
Gerard or Gérard (de) Lairesse (11 September 1641 – June 1711) was a Dutch Golden Age painter and art theorist. His broad range of skills included music, poetry, and theatre. De Lairesse was influenced by the Perugian Cesare Ripa and Fr ...
, interested in French Classicism and Ripa, there is another explanation; he mentions history and poetry as the main resources of a painter. The woman in blue could be representing poetry, pointing to Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for hi ...
who observed that "Simonides
Simonides of Ceos (; grc-gre, Σιμωνίδης ὁ Κεῖος; c. 556–468 BC) was a Greek lyric poet, born in Ioulis on Ceos. The scholars of Hellenistic Alexandria included him in the canonical list of the nine lyric poets esteemed ...
calls painting silent poetry and poetry painting that speaks", later paraphrased by the Latin poet Horace as ut pictura poesis. If so, the map is representing history.
 The
The double-headed eagle
In heraldry and vexillology, the double-headed eagle (or double-eagle) is a charge associated with the concept of Empire. Most modern uses of the symbol are directly or indirectly associated with its use by the late Byzantine Empire, origina ...
, symbol of the Habsburg Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, which possibly adorns the central golden chandelier, may represent the former rulers of the Low Countries.
The large map on the back wall has a prominent crease
Crease may refer to:
* A line (geometry) or mark made by folding or doubling any pliable substance
* Crease (band), American hard rock band that formed in Ft. Lauderdale, Florida in 1994
* Crease pattern, origami diagram type that consists of all ...
that divides the Seventeen Provinces into the north and south. (West is at the top of the map.) The crease may symbolize the division between the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
to the north and southern provinces
The Southern Provinces ( ar, الأقاليم الجنوبية, Al-Aqalim al-Janubiyah, french: Provinces du Sud) or Moroccan Sahara ( ar, الصحراء المغربية, Assahra al-Maghribiya, french: Sahara marocain) are the terms used by th ...
under Habsburg rule. The map shows the earlier political division between the Union of Utrecht
The Union of Utrecht ( nl, Unie van Utrecht) was a treaty signed on 23 January 1579 in Utrecht, Netherlands, unifying the northern provinces of the Netherlands, until then under the control of Habsburg Spain.
History
The Union of Utrecht is r ...
to the north, and the loyal provinces to the south. This interpretation might have appealed to Hitler who owned the painting during the war. According to Liedtke a political interpretation of the map and the Habsburg eagle is unconvincing; they overlook other motives.
The map could suggest though that painting has brought fame to the Netherlands; ships sailing over the folds suggest that.
Provenance
The painting is considered a work with significance for Vermeer because he did not part with it or sell it, even when he was in debt. On 24 February 1676, his widow Catharina bequeathed it to her mother,Maria Thins
Maria Thins (c. 1593 – 27 December 1680) was the mother-in-law of Johannes Vermeer and a member of the Gouda Thins family.
Life
Maria was born in Gouda. In 1622 she married Reynier Bolnes, a prominent and prosperous brickmaker. In 1635 the ma ...
, in an attempt to avoid the sale of the painting to satisfy creditors. The executor of Vermeer's estate, the famous Delft microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek, determined that the transferral of the work to the late painter's mother-in-law was illegal and, according to John Michael Montias
John Michael Montias (3 October 1928 – 26 July 2005) was a French-born American economist and art historian, known for his contributions to cultural economics, particularly related to Dutch Golden Age painting. Montias was part of the Annales ...
, at least a curious transaction. On 15 March 1677 most of his paintings were sold in an auction at the Guild in Delft. It is not known who bought the Art of Painting; perhaps it was Jacob Dissius
Jacob Abrahamsz. Dissius (1653 - 1695) was a Dutch typographer and printer. He is most notable as an art collector and for his links to Johannes Vermeer - his collection included 21 Vermeer works (including '' The Milkmaid'', '' Portrait of a Young ...
. It can not be determined with certainty whether the painting is quoted in the auction Dissius of 1696 as "Portrait of Vermeer in a room with various accessories." The painting was owned by Gerard van Swieten
Gerard van Swieten (7 May 1700 – 18 June 1772) was a Dutch physician who from 1745 was the personal physician of the Holy Roman Empress Maria Theresa and transformed the Austrian health service and medical university education. He was the fat ...
, and passed into the hands of Gottfried van Swieten
Gottfried Freiherr van Swieten (29 October 1733 – 29 March 1803) was a Dutch-born Austrian diplomat, librarian, and government official who served the Holy Roman Empire during the 18th century. He was an enthusiastic amateur musician and is be ...
. In 1813, it was purchased for 50 florins by the Bohemian-Austrian Count Rudolf Czernin. It was placed on public display in the Czernin Museum in Vienna.
Until 1860, the painting was considered to have been painted by Vermeer's contemporary, Pieter de Hooch
Pieter de Hooch (, also spelled "Hoogh" or "Hooghe"; 20 December 1629 (baptized) – 24 March 1684 (buried)) was a Dutch Golden Age painter famous for his genre works of quiet domestic scenes with an open doorway. He was a contemporary of ...
; Vermeer was little-known until the late 19th century. Hooch's signature was even forged on the painting. It was at the intervention of the German art historian Gustav Friedrich Waagen that it was recognised as a Vermeer original.
Nazi interest
 In 1935, Count Jaromir Czernin had tried to sell the painting to
In 1935, Count Jaromir Czernin had tried to sell the painting to Andrew W. Mellon
Andrew William Mellon (; March 24, 1855 – August 26, 1937), sometimes A. W. Mellon, was an American banker, businessman, industrialist, philanthropist, art collector, and politician. From the wealthy Mellon family of Pittsburgh, Pennsylv ...
, but the Austrian government prohibited the export of the painting. After the annexation of Austria
The (, or , ), also known as the (, en, Annexation of Austria), was the annexation of the Federal State of Austria into the German Reich on 13 March 1938.
The idea of an (a united Austria and Germany that would form a " Greater Germany ...
, Philipp Reemtsma
Reemtsma Cigarettenfabriken GmbH is one of the biggest tobacco and cigarette manufacturing companies in Europe and a subsidiary of Imperial Brands. The company's headquarters is in Hamburg, Germany.
History
Reemtsma was created in 1910 in Erf ...
with the help of Reichsmarschall Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring (or Goering; ; 12 January 1893 – 15 October 1946) was a German politician, military leader and convicted war criminal. He was one of the most powerful figures in the Nazi Party, which ruled Germany from 1933 to 1 ...
attempted to acquire the painting. The transaction to a private person was refused being cultural heritage. It was finally acquired by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
for the collection of the Linzer Museum at a price of 1.82 million Reichsmark
The (; sign: ℛℳ; abbreviation: RM) was the currency of Germany from 1924 until 20 June 1948 in West Germany, where it was replaced with the , and until 23 June 1948 in East Germany, where it was replaced by the East German mark. The Reich ...
through his agent, Hans Posse on 20 November 1940. The painting was rescued from a salt mine
Salt mining extracts natural salt deposits from underground. The mined salt is usually in the form of halite (commonly known as rock salt), and extracted from evaporite formations.
History
Before the advent of the modern internal combustio ...
near Altaussee
Altaussee (Central Bavarian: ''Oid Aussee'') is a municipality and spa town in the district of Liezen in Styria, Austria. The small village is nestled on the shores of the Lake Altaussee, beneath the Loser Plateau. Occupying an area of 92 ...
at the end of World War II in 1945, where it was preserved from Allied bombing raids, with other works of art. The painting was escorted to Vienna from Munich by Andrew Ritchie, chief of the Monuments, Fine Arts, and Archives program (MFA&A) for Austria, who transported it by locking himself and the painting in a train compartment.
The Americans presented the painting to the Austrian Government in late 1945 since the Czernin family were deemed to have sold it voluntarily, without undue force from Hitler. The Czernin family made several attempts to claim restitution, each time being rejected, although this played a role in securing an official certification of Hitler's death in 1956. In 1958, Vermeer's ''The Art of Painting'' was finally moved from temporary status into the permanent collection of the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna. A 1998 restitution law, which pertains to public institutions, bolstered the family's legal position, but the case was rejected again by the Austrian government in 2011.
See also
*100 Great Paintings
''100 Great Paintings'' is a British television series broadcast in 1980 on BBC 2, devised by Edwin Mullins.http://ftvdb.bfi.org.uk/sift/series/11652 13 January 2007 He chose 20 thematic groups, such as war, th ...
* Salvador Dalí
Salvador Domingo Felipe Jacinto Dalí i Domènech, Marquess of Dalí of Púbol (; ; ; 11 May 190423 January 1989) was a Spanish surrealist artist renowned for his technical skill, precise draftsmanship, and the striking and bizarre images in ...
refers to ''The Art of Painting'' in his own surrealistic
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to ...
painting ''The Ghost of Vermeer of Delft Which Can Be Used As a Table
''The Ghost of Vermeer of Delft Which Can Be Used As a Table'' is a small Surrealist oil painting by Salvador Dalí. Its full title is ''The Ghost of Vermeer of Delft Which Can Be Used as a Table (Phenomenologic Theory of Furniture-Nutrition)''. ...
'' (1934). In Dalí's painting the image of Vermeer from ''The Art of Painting'', although not true to the representation regarding Vermeer's clothes, is viewed from behind, re-created as a strange kind of table.
* In 1968, British artist Malcolm Morley painted an acrylic copy of ''The Art of Painting'' in his signature "super-realistic" style, using a gridding technique to scale it up to 105 x 87 inches (266.7 x 220.98 cm) raising questions of appropriation that influenced mid- to late-20th century art discourse.
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Art of Painting, The History paintings by Johannes Vermeer Paintings in the collection of the Kunsthistorisches Museum category:17th-century allegorical paintings category:Allegorical paintings by Dutch artists 1660s paintings Paintings about painting Musical instruments in art Books in art Maps in art Cartography in the Dutch Republic Early modern Netherlandish cartography