Wheel of the Year on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of
The Wheel of the Year is an annual cycle of
 By the late 1950s the Bricket Wood coven led by
By the late 1950s the Bricket Wood coven led by
About Naming Ostara, Litha, and Mabon
Including Paganism. ''Patheos''. Accessed 8 May 2019. Popularization of these names happened gradually; in her 1978 book ''Witchcraft For Tomorrow'' influential Wiccan author
Enough With the Mabon Hate!
Under the Ancient Oaks. ''Patheos''. 11 Sep 2018. Valiente identified the four "Greater Sabbats", or fire festivals, by the names Candlemas, May Eve, Lammas, and Hallowe'en, though she also identified their Irish counterparts as Imbolc, Beltane, Lughnassadh, and Samhain.Valiente, Doreen. 1978. ''Witchcraft For Tomorrow''. London: Robert Hale Limited. Due to early Wicca's influence on modern paganism and the
 In many traditions of modern pagan
In many traditions of modern pagan
 Derived from a reconstruction produced by linguist Jacob Grimm of an Old High German form of the Old English goddess name '' Ēostre'', Ostara marks the vernal equinox in some modern Pagan traditions.
Known as Alban Eilir to modern Druid traditions, this holiday is the second of three spring celebrations (the midpoint between Imbolc and Beltane), during which light and darkness are again in balance, with light on the rise. It is a time of new beginnings and of life emerging further from the grips of winter.
Derived from a reconstruction produced by linguist Jacob Grimm of an Old High German form of the Old English goddess name '' Ēostre'', Ostara marks the vernal equinox in some modern Pagan traditions.
Known as Alban Eilir to modern Druid traditions, this holiday is the second of three spring celebrations (the midpoint between Imbolc and Beltane), during which light and darkness are again in balance, with light on the rise. It is a time of new beginnings and of life emerging further from the grips of winter.
 Samhain () is one of the four ''Greater Sabbats'' among Wiccans. Samhain is typically considered as a time to celebrate the lives of those who have passed on, and it often involves paying respect to ancestors, family members, elders of the faith, friends, pets, and other loved ones who have died. Aligned with the contemporary observance of Halloween and
Samhain () is one of the four ''Greater Sabbats'' among Wiccans. Samhain is typically considered as a time to celebrate the lives of those who have passed on, and it often involves paying respect to ancestors, family members, elders of the faith, friends, pets, and other loved ones who have died. Aligned with the contemporary observance of Halloween and
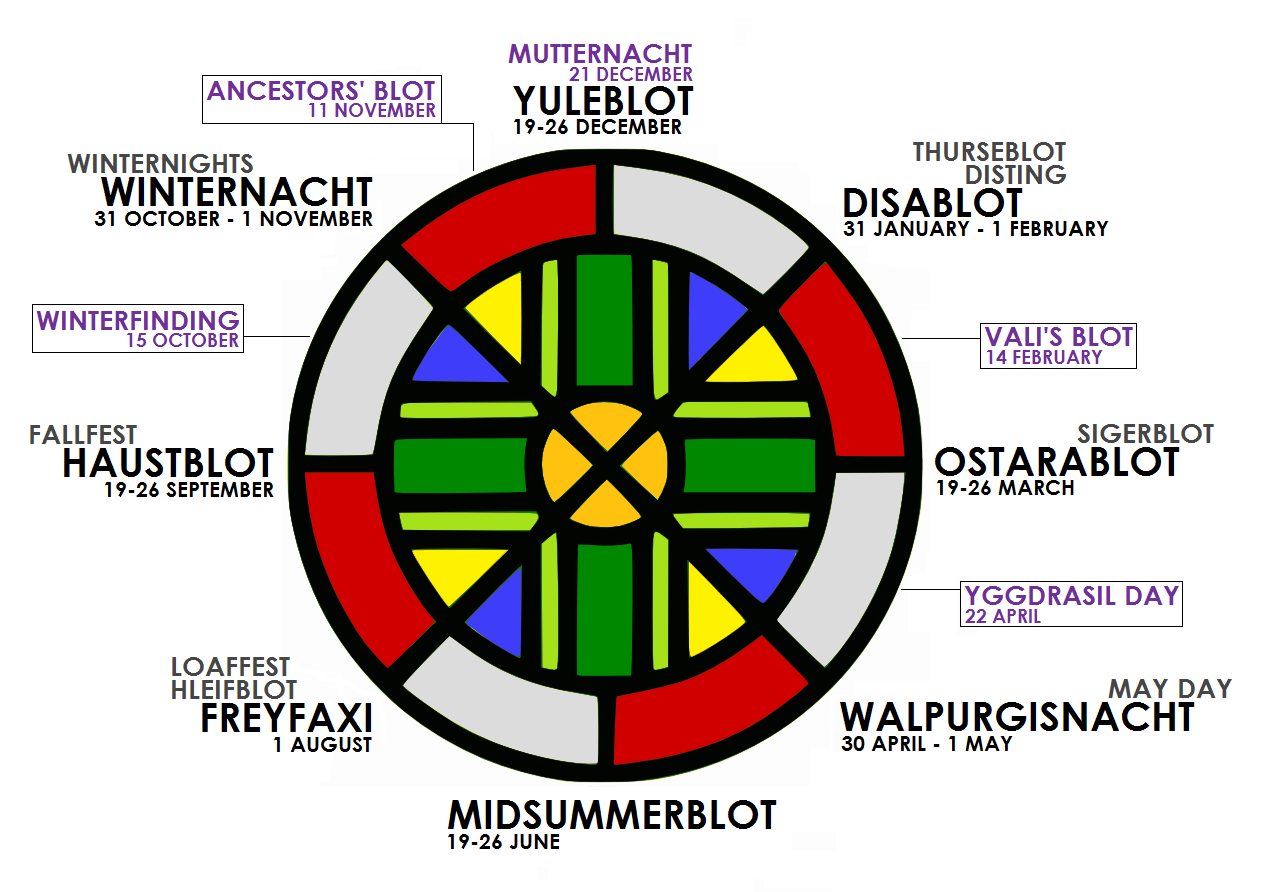 Some of the holidays listed in the “Runic Era Calendar” of the Ásatrú Alliance:
;Vali's Blot (14 February)
:Celebration dedicated to the god
Some of the holidays listed in the “Runic Era Calendar” of the Ásatrú Alliance:
;Vali's Blot (14 February)
:Celebration dedicated to the god
 Offerings of food, drink, various objects, etc. have been central in
Offerings of food, drink, various objects, etc. have been central in
 Slavic mythology tells of a persisting conflict involving
Slavic mythology tells of a persisting conflict involving
 In
In
Astronomical cusps and pagan holidays
Celebrating the Seasons at Circle Sanctuary
Atheopagan Sabbaths
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wheel Of The Year Modern pagan holidays Time in religion Wicca Neo-druidism 1950s in modern paganism cs:Sabat (wicca)
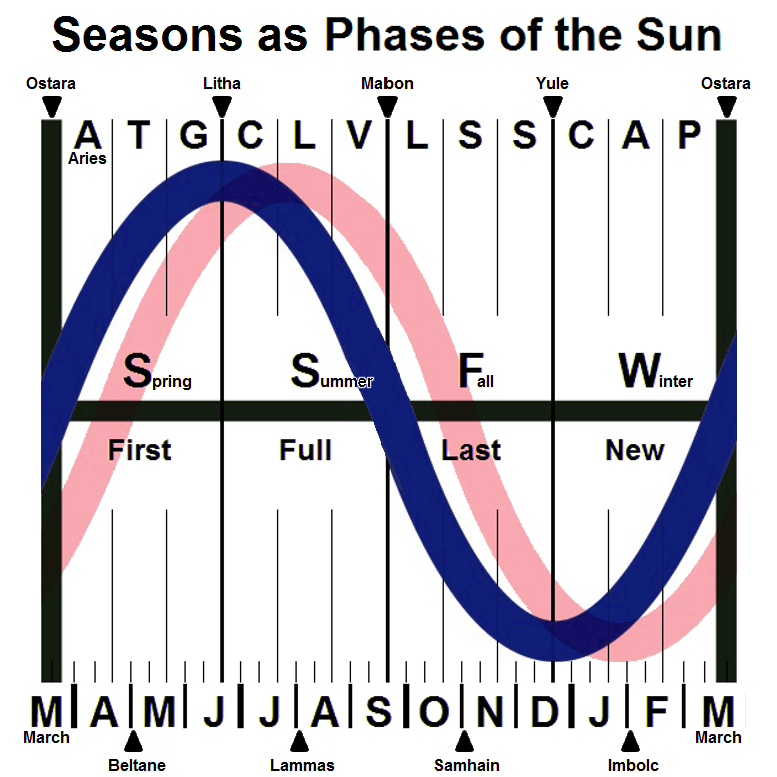
seasonal
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and po ...
festival
A festival is an event ordinarily celebrated by a community and centering on some characteristic aspect or aspects of that community and its religion or cultures. It is often marked as a local or national holiday, mela, or eid. A festival ...
s, observed by many modern pagans, consisting of the year
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hou ...
's chief solar events (solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
s and equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and se ...
es) and the midpoints between them. While names for each festival vary among diverse pagan traditions, syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
treatments often refer to the four solar events as " quarter days", with the four midpoint events as "cross-quarter days". Differing sects of modern paganism also vary regarding the precise timing of each celebration, based on distinctions such as lunar phase and geographic hemisphere.
Observing the cycle of the seasons has been important to many people, both ancient and modern. Contemporary Pagan festivals that rely on the Wheel are based to varying degrees on folk tradition
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging fro ...
s, regardless of actual historical pagan practices. Among Wiccans, each festival is also referred to as a sabbat (), based on Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, as well as an author and an amateur anthropology, anthropologist and archaeology, archaeologist. He was instrumental in bri ...
's view that the term was passed down from the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, when the terminology for Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
Shabbat was commingled with that of other heretical
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
celebrations. Contemporary conceptions of the Wheel of the Year calendar were largely influenced by mid-20th century British paganism.
Origins
Illustration of a Witches'_Sabbath,_"Darstellung_des_Hexensabbats"_from_the_Wickiana,_''circa''_1570..html" ;"title="Wickiana.html" ;"title="Witches' Sabbath, "Darstellung des Hexensabbats" from the Wickiana">Witches' Sabbath, "Darstellung des Hexensabbats" from the Wickiana, ''circa'' 1570.">Wickiana.html" ;"title="Witches' Sabbath, "Darstellung des Hexensabbats" from the Wickiana">Witches' Sabbath, "Darstellung des Hexensabbats" from the Wickiana, ''circa'' 1570. Historical and archaeological evidence suggests ancient pagan and polytheist peoples varied in their cultural observations; Anglo-Saxons celebrated the solstices and equinoxes, whileCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
celebrated the seasonal divisions with various fire festivals. In the tenth century Cormac Mac Cárthaigh wrote about "four great fires...lighted up on the four great festivals of the Druids...in February, May, August, and November."Murray, Margaret. 1931. ''The God of the Witches''.
The contemporary Neopagan festival cycle, prior to being known as the Wheel of the Year, was influenced by works such as '' The Golden Bough'' by James George Frazer (1890) and ''The Witch-Cult in Western Europe
''The Witch-Cult in Western Europe'' is a 1921 anthropological book by Margaret Murray, published at the height of the success of Frazer's '' Golden Bough.'' Certain university circles subsequently celebrated Margaret Murray as the expert on west ...
'' (1921) by Margaret Murray
Margaret Alice Murray (13 July 1863 – 13 November 1963) was an Anglo-Indian Egyptologist, archaeologist, anthropologist, historian, and folklorist. The first woman to be appointed as a lecturer in archaeology in the United Kingdom, she work ...
. Frazer claimed that Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
(the beginning of summer) and Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year ...
(the beginning of winter) were the most important of the four Gaelic festivals mentioned by Cormac. Murray used records from early modern witch trials
Witch trials in the early modern period saw that between 1400 to 1782, around 40,000 to 60,000 were killed due to suspicion that they were practicing witchcraft. Some sources estimate that a total of 100,000 trials occurred at its maximum for a s ...
, as well as the folklore surrounding European witchcraft, in an attempt to identify the festivals celebrated by a supposedly widespread underground pagan religion that had survived into the early modern period. Murray reports a 1661 trial record from Forfar
Forfar ( sco, Farfar, gd, Baile Fharfair) is the county town of Angus, Scotland and the administrative centre for Angus Council, with a new multi-million pound office complex located on the outskirts of the town. As of 2021, the town has a pop ...
, Scotland, where the accused witch (Issobell Smyth) is connected with meetings held "every quarter at Candlemas, Rud−day, Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference ...
, and Hallomas." In '' The White Goddess'' (1948) Robert Graves claimed that, despite Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
, the importance of agricultural and social cycles had preserved the "continuity of the ancient British festal system" consisting of eight holidays: "English social life was based on agriculture, grazing, and hunting" implicit in "the popular celebration of the festivals now known as Candlemas, Lady Day
In the Western liturgical year, Lady Day is the traditional name in some English-speaking countries of the Feast of the Annunciation, which is celebrated on 25 March, and commemorates the visit of the archangel Gabriel to the Virgin Mary, durin ...
, May Day
May Day is a European festival of ancient origins marking the beginning of summer, usually celebrated on 1 May, around halfway between the spring equinox and summer solstice. Festivities may also be held the night before, known as May Eve. Tr ...
, Midsummer Day
Midsummer is a celebration of the season of summer usually held at a date around the summer solstice. It has pagan pre-Christian roots in Europe.
The undivided Christian Church designated June 24 as the feast day of the early Christian martyr S ...
, Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference ...
, Michaelmas
Michaelmas ( ; also known as the Feast of Saints Michael, Gabriel, and Raphael, the Feast of the Archangels, or the Feast of Saint Michael and All Angels) is a Christian festival observed in some Western liturgical calendars on 29 September, ...
, All-Hallowe'en, and Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
; it was also secretly preserved as religious doctrine in the covens of the anti-Christian witch-cult."
Gerald Gardner
Gerald Brosseau Gardner (13 June 1884 – 12 February 1964), also known by the craft name Scire, was an English Wiccan, as well as an author and an amateur anthropology, anthropologist and archaeology, archaeologist. He was instrumental in bri ...
and the Order of Bards, Ovates and Druids
The Order of Bards, Ovates & Druids or OBOD is a Neo-Druidic organisation based in England, but based in part on the Welsh Gorsedd of Bards. It has grown to become a dynamic druid organisation, with members in all parts of the world.
The conc ...
led by Ross Nichols
Philip Peter Ross Nichols (28 June 1902 – 30 April 1975) was a Cambridge academic and published poet, artist and historian, who founded the Order of Bards, Ovates and Druids in 1964. He wrote prolifically on the subjects of Druidism and Celt ...
had both adopted eight-fold ritual calendars, in order to hold more frequent celebrations. Popular legend holds that Gardner and Nichols developed the calendar during a naturist
Naturism is a lifestyle of practising non-sexual social nudity in private and in public; the word also refers to the cultural movement which advocates and defends that lifestyle. Both may alternatively be called nudism. Though the two terms a ...
retreat, where Gardner advocated for celebrating the solstices and equinoxes while Nichols preferred celebrating the four Celtic fire festivals; ultimately they combined the two approaches into a single festival cycle. Though this coordination eventually had the benefit of more closely aligning celebrations between the two early Neopagan groups, Gardner's first published writings omit any mention of the solstices and equinoxes, focusing exclusively on the fire festivals. Gardner initially referred to these as "May eve, August eve, November eve (Hallowe'en), and February eve." Gardner further identified these modern witch festivals with the Gaelic fire festivals Beltene, Lugnasadh, Samhuin, and Brigid (Imbolc). By the mid-1960s, the phrase ''Wheel of the Year'' had been coined to describe the yearly cycle of witches' holidays.
Aidan Kelly
Aidan A. Kelly (born October 22, 1940) is an American academic, poet and influential figure in the Neopagan religion of Wicca. Having developed his own branch of the faith, the New Reformed Orthodox Order of the Golden Dawn, during the 1960s, he wa ...
gave names to the summer solstice (Litha) and equinox holidays (Ostara and Mabon) of Wicca in 1974, which were subsequently promulgated by Timothy Zell through his '' Green Egg'' magazine.Kelly, AidanAbout Naming Ostara, Litha, and Mabon
Including Paganism. ''Patheos''. Accessed 8 May 2019. Popularization of these names happened gradually; in her 1978 book ''Witchcraft For Tomorrow'' influential Wiccan author
Doreen Valiente
Doreen Edith Dominy Valiente (4 January 1922 – 1 September 1999) was an English Wiccan who was responsible for writing much of the early religious liturgy within the tradition of Gardnerian Wicca. An author and poet, she also published five b ...
did not use Kelly's holiday names, instead simply identifying the solstices and equinoxes ("Lesser Sabbats") by their seasons.Beckett, JohnEnough With the Mabon Hate!
Under the Ancient Oaks. ''Patheos''. 11 Sep 2018. Valiente identified the four "Greater Sabbats", or fire festivals, by the names Candlemas, May Eve, Lammas, and Hallowe'en, though she also identified their Irish counterparts as Imbolc, Beltane, Lughnassadh, and Samhain.Valiente, Doreen. 1978. ''Witchcraft For Tomorrow''. London: Robert Hale Limited. Due to early Wicca's influence on modern paganism and the
syncretic
Syncretism () is the practice of combining different beliefs and various schools of thought. Syncretism involves the merging or assimilation of several originally discrete traditions, especially in the theology and mythology of religion, thu ...
adoption of Anglo-Saxon and Celtic motifs, the most commonly used English festival names for the Wheel of the Year tend to be the Celtic ones introduced by Gardner and the mostly Germanic-derived names introduced by Kelly, even when the celebrations are not based on those cultures. The American Ásatrú movement has adopted, over time, a calendar in which the Heathen major holidays figure alongside many ''Days of Remembrance'' which celebrate heroes of the Edda
"Edda" (; Old Norse ''Edda'', plural ''Eddur'') is an Old Norse term that has been attributed by modern scholars to the collective of two Medieval Icelandic literary works: what is now known as the ''Prose Edda'' and an older collection of poems ...
and the Sagas, figures of Germanic history, and the Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
Leif Ericson
Leif Erikson, Leiv Eiriksson, or Leif Ericson, ; Modern Icelandic: ; Norwegian: ''Leiv Eiriksson'' also known as Leif the Lucky (), was a Norse explorer who is thought to have been the first European to have set foot on continental Nort ...
, who explored and settled Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John ...
(North America). These festivals are not, however, as evenly distributed throughout the year as in Wicca and other Heathen denominations.
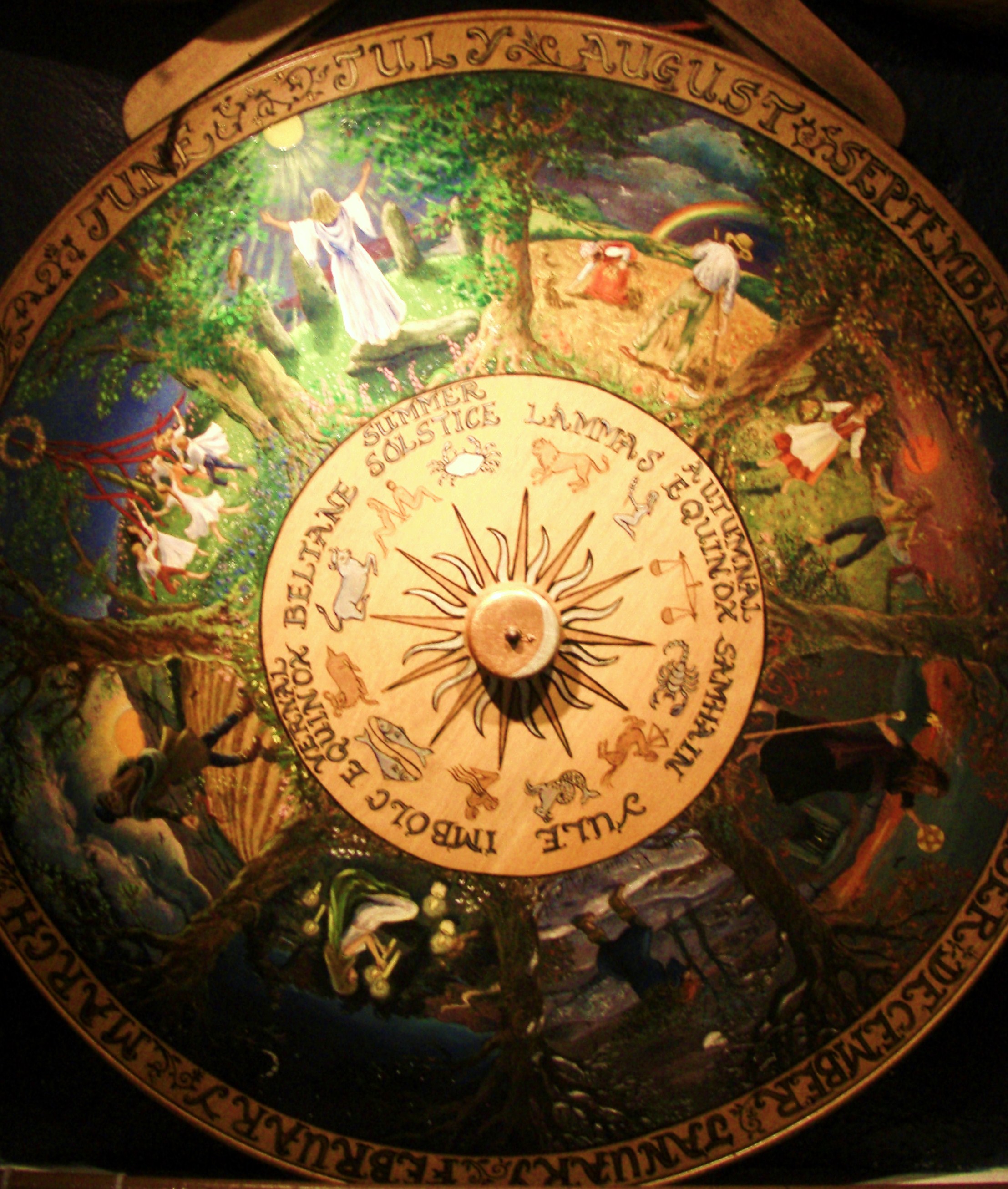
Festivals
cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', and in 1731 taken up in Latin by German philosopher ...
, all things are considered to be cyclical, with time as a perpetual cycle of growth and retreat tied to the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
's annual death and rebirth. This cycle is also viewed as a micro- and macrocosm of other life cycles in an immeasurable series
Series may refer to:
People with the name
* Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series
* George Series (1920–1995), English physicist
Arts, entertainment, and media
Music
* Series, the ordered sets used in ...
of cycles composing the Universe. The days that fall on the landmarks of the yearly cycle traditionally mark the beginnings and middles of the four season
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and ...
s. They are regarded with significance and host to major communal festivals. These eight festivals are the most common times for community celebrations.
While the "major" festivals are usually the quarter and cross-quarter days, other festivals are also celebrated throughout the year, especially among the non- Wiccan traditions such as those of polytheistic reconstructionism and other ethnic
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
traditions.
In Wiccan and Wicca-influenced traditions, the festivals, being tied to solar movements, have generally been steeped in solar mythology
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narra ...
and symbolism, centered on the life cycles of the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. Similarly, the Wiccan esbats An esbat is a coven meeting or ritual at a time other than one of the Sabbats within Wicca and other Wiccan-influenced forms of contemporary Paganism.
Esbats can span a wide range of purposes from coven business meetings and initiation ceremonies ...
are traditionally tied to the lunar cycles. Together, they represent the most common celebrations in Wiccan-influenced forms of Neopaganism, especially in contemporary Witchcraft
Witchcraft traditionally means the use of magic or supernatural powers to harm others. A practitioner is a witch. In medieval and early modern Europe, where the term originated, accused witches were usually women who were believed to have ...
groups.
Winter Solstice (Yule)
Midwinter, known commonly as Yule or within modern Druid traditions as Alban Arthan, has been recognised as a significant turning point in the yearly cycle since the late Stone Age. The ancientmegalith
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The ...
ic sites of Newgrange
Newgrange ( ga, Sí an Bhrú) is a prehistoric monument in County Meath in Ireland, located on a rise overlooking the River Boyne, west of Drogheda. It is an exceptionally grand passage tomb built during the Neolithic Period, around 3200 B ...
and Stonehenge, carefully aligned with the solstice sunrise and sunset, exemplify this. The reversal of the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
's ebbing presence in the sky symbolizes the rebirth of the solar god and presages the return of fertile seasons. From Germanic to Roman tradition, this is the most important time of celebration.
Practices vary, but sacrifice offerings, feasting, and gift giving are common elements of Midwinter festivities. Bringing sprigs and wreaths of evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. This also pertains to plants that retain their foliage only in warm climates, and contrasts with deciduous plants, whic ...
ery (such as holly
''Ilex'' (), or holly, is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen o ...
, ivy, mistletoe, yew, and pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
) into the home and tree decorating are also common during this time.
In Roman traditions additional festivities take place during the six days leading up to Midwinter.
Imbolc (Candlemas)
The cross-quarter day following Midwinter falls on the first of February and traditionally marks the first stirrings of spring. It aligns with the contemporary observance of Groundhog Day. It is time for purification and spring cleaning in anticipation of the year's new life. In Rome, it was historically a shepherd's holiday, while theCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
associated it with the onset of ewes' lactation, prior to birthing the spring lambs.
For Celtic pagans, the festival is dedicated to the goddess Brigid
Brigid ( , ; meaning 'exalted one' from Old Irish),Campbell, MikBehind the Name.See also Xavier Delamarre, ''brigantion / brigant-'', in ''Dictionnaire de la langue gauloise'' (Éditions Errance, 2003) pp. 87–88: "Le nom de la sainte irlandais ...
, daughter of The Dagda
The Dagda (Old Irish: ''In Dagda,'' ga, An Daghdha, ) is an important god in Irish mythology. One of the Tuatha Dé Danann, the Dagda is portrayed as a father-figure, king, and druid.Koch, John T. ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia ...
and one of the Tuatha Dé Danann
The Tuath(a) Dé Danann (, meaning "the folk of the goddess Danu"), also known by the earlier name Tuath Dé ("tribe of the gods"), are a supernatural race in Irish mythology. Many of them are thought to represent deities of pre-Christian Gae ...
.
Among Reclaiming tradition
Reclaiming is a modern witchcraft tradition, aiming to combine the Goddess movement with feminism and political activism (in the peace and anti-nuclear movements). Reclaiming was founded in 1979, in the context of the ''Reclaiming Collective'' ...
Witches, this is the traditional time for pledges and rededications for the coming year and for initiation among Dianic Wicca
Dianic Wicca, also known as Dianic Witchcraft, and, to some also as "Dianism," "Dianic Feminist Witchcraft," or simply "Feminist Witchcraft"' is a modern pagan, goddess tradition, focused on female experience and empowerment. Leadership is by w ...
ns.
Spring Equinox (Ostara)
 Derived from a reconstruction produced by linguist Jacob Grimm of an Old High German form of the Old English goddess name '' Ēostre'', Ostara marks the vernal equinox in some modern Pagan traditions.
Known as Alban Eilir to modern Druid traditions, this holiday is the second of three spring celebrations (the midpoint between Imbolc and Beltane), during which light and darkness are again in balance, with light on the rise. It is a time of new beginnings and of life emerging further from the grips of winter.
Derived from a reconstruction produced by linguist Jacob Grimm of an Old High German form of the Old English goddess name '' Ēostre'', Ostara marks the vernal equinox in some modern Pagan traditions.
Known as Alban Eilir to modern Druid traditions, this holiday is the second of three spring celebrations (the midpoint between Imbolc and Beltane), during which light and darkness are again in balance, with light on the rise. It is a time of new beginnings and of life emerging further from the grips of winter.
Beltane (May Eve)
Traditionally the first day of summer in Ireland, in Rome the earliest celebrations appeared in pre-Christian times with the festival ofFlora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' ...
, the Roman goddess of flowers, and the Walpurgisnacht celebrations of the Germanic countries.
Since the Christianisation
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of Europe, a more secular version of the festival has continued in Europe and America, commonly referred to as May Day. In this form, it is well known for maypole dancing and the crowning of the Queen of the May
In the British Isles and parts of the Commonwealth, the May Queen or Queen of May is a personification of the May Day holiday, and of springtime and also summer. The May Queen is a girl who rides or walks at the front of a parade for May Day cel ...
.
Celebrated by many pagan traditions, among modern Druids this festival recognizes the power of life in its fullness, the greening of the world, youthfulness and flourishing.
Summer Solstice (Litha)
Midsummer is one of the four solar holidays and is considered the turning point at which summer reaches its height and the sun shines longest. Among the Wiccan sabbats, Midsummer is preceded byBeltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
, and followed by Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference ...
or Lughnasadh
Lughnasadh or Lughnasa ( , ) is a Gaelic festival marking the beginning of the harvest season. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. In Modern Irish it is called , in gd, Lùnastal, and in gv, ...
.
Some Wiccan traditions call the festival ''Litha'', a name occurring in Bede's ''The Reckoning of Time
''The Reckoning of Time'' ( la, De temporum ratione) is an Anglo-Saxon era treatise written in Medieval Latin by the Northumbrian monk Bede in 725. The treatise includes an introduction to the traditional ancient and medieval view of the cosm ...
'' (', eighth century), which preserves a list of the (then-obsolete) Anglo-Saxon names for the twelve months. ' (''first'' or ''preceding'' ') roughly corresponds to June in the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years dif ...
, and ' (''following'' ') to July. Bede writes that "Litha means ''gentle'' or ''navigable'', because in both these months the calm breezes are gentle and they were wont to sail upon the smooth sea".
Modern Druids celebrate this festival as Alban Hefin. The sun in its greatest strength is greeted and celebrated on this holiday. While it is the time of greatest strength of the solar current, it also marks a turning point, for the sun also begins its time of decline as the wheel of the year turns. Arguably the most important festival of the Druid traditions, due to the great focus on the sun and its light as a symbol of divine inspiration. Druid groups frequently celebrate this event at Stonehenge.
Lughnasadh (Lammas)
Lammas or Lughnasadh () is the first of the three Wiccan harvest festivals, the other two being the autumnal equinox (or Mabon) andSamhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year ...
. Wiccans mark the holiday by baking a figure of the god in bread and eating it, to symbolise the sanctity and importance of the harvest. Celebrations vary, as not all Pagans are Wiccans. The Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
name Lughnasadh
Lughnasadh or Lughnasa ( , ) is a Gaelic festival marking the beginning of the harvest season. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. In Modern Irish it is called , in gd, Lùnastal, and in gv, ...
Starhawk (1979, 1989) ''The Spiral Dance: A Rebirth of the Ancient Religion of the Great Goddess''. New York, Harper and Row pp.191-2 (revised edition) is used in some traditions to designate this holiday. Wiccan celebrations of this holiday are neither generally based on Celtic culture nor centered on the Celtic deity Lugh
Lugh or Lug (; ga, label= Modern Irish, Lú ) is a figure in Irish mythology. A member of the Tuatha Dé Danann, a group of supernatural beings, Lugh is portrayed as a warrior, a king, a master craftsman and a savior.Olmsted, Garrett. ''The Go ...
. This name seems to have been a late adoption among Wiccans. In early versions of Wiccan literature the festival is referred to as ''August Eve''.
The name ''Lammas'' (contraction of ''loaf mass'') implies it is an agrarian-based festival and feast of thanksgiving for grain and bread, which symbolises the first fruits of the harvest. Christian festivals may incorporate elements from the Pagan Ritual.
Autumn Equinox (Mabon)
The holiday of the autumnal equinox, ''Harvest Home'', ''Mabon'', the ''Feast of the Ingathering'', ', ', or ' (in Neo-Druid traditions), is a modern Pagan ritual of thanksgiving for the fruits of the earth and a recognition of the need to share them to secure the blessings of the Goddess and the Gods during the coming winter months. The name ''Mabon'' was coined byAidan Kelly
Aidan A. Kelly (born October 22, 1940) is an American academic, poet and influential figure in the Neopagan religion of Wicca. Having developed his own branch of the faith, the New Reformed Orthodox Order of the Golden Dawn, during the 1960s, he wa ...
around 1970 as a reference to , a character from Welsh mythology. Among the sabbats, it is the second of the three Pagan harvest festivals, preceded by Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference ...
/ Lughnasadh
Lughnasadh or Lughnasa ( , ) is a Gaelic festival marking the beginning of the harvest season. Historically, it was widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. In Modern Irish it is called , in gd, Lùnastal, and in gv, ...
and followed by Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year ...
.
Samhain
 Samhain () is one of the four ''Greater Sabbats'' among Wiccans. Samhain is typically considered as a time to celebrate the lives of those who have passed on, and it often involves paying respect to ancestors, family members, elders of the faith, friends, pets, and other loved ones who have died. Aligned with the contemporary observance of Halloween and
Samhain () is one of the four ''Greater Sabbats'' among Wiccans. Samhain is typically considered as a time to celebrate the lives of those who have passed on, and it often involves paying respect to ancestors, family members, elders of the faith, friends, pets, and other loved ones who have died. Aligned with the contemporary observance of Halloween and Day of the Dead
The Day of the Dead ( es, Día de Muertos or ''Día de los Muertos'') is a holiday traditionally celebrated on November 1 and 2, though other days, such as October 31 or November 6, may be included depending on the locality. It is widely obser ...
, in some traditions the spirits of the departed are invited to attend the festivities. It is seen as a festival of darkness, which is balanced at the opposite point of the Wheel by the festival of Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
, which is celebrated as a festival of light and fertility.Starhawk (1979, 1989) ''The Spiral Dance: A Rebirth of the Ancient Religion of the Great Goddess''. New York, Harper and Row pp.193-6 (revised edition)
Many Neopagans believe that the veil between this world and the afterlife is at its thinnest point of the year at Samhain, making it easier to communicate with those who have departed.
Some authorities claim the Christian festival of All Hallows Day (All Saints Day) and the preceding evening are appropriations of Samhain by early Christian missionaries to the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
.
Minor festivals
In addition to the eight major holidays common to most modern pagans, there are a number of minor holidays during the year to commemorate various events.Germanic
 Some of the holidays listed in the “Runic Era Calendar” of the Ásatrú Alliance:
;Vali's Blot (14 February)
:Celebration dedicated to the god
Some of the holidays listed in the “Runic Era Calendar” of the Ásatrú Alliance:
;Vali's Blot (14 February)
:Celebration dedicated to the god Váli
In Norse mythology, Váli (Old Norse: ) is a God and the son of the god Odin and the giantess Rindr. Váli has numerous brothers including Thor, Baldr, and Víðarr. He was born for the sole purpose of avenging Baldr, and does this by killing ...
and to love
;Feast of the Einherjar
In Norse mythology, the einherjar (singular einheri) literally "army of one", "those who fight alone"Simek, Rudolf. 1993. Dictionary of Northern Mythology. Translated by Angela Hall. p. 71Orchard (1997:36) and Lindow (2001:104).) are those who h ...
(11 November)
:Celebration to honor kin who died in battle
;Ancestors’ Blot (11 November)
:Celebration of one’s own ancestry or the common ancestors of a Germanic ethnicity
;Yggdrasil Day (22 April)
:Celebration of the world tree Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil (from Old Norse ), in Norse cosmology, is an immense and central sacred tree. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional ...
, of the reality world it represents, of tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
s and nature
;Winterfinding (mid-October)
:Celebration which marks the beginning of winter, held on a date between Haustblot and Winternights
;Summerfinding (mid-April)
:Celebration which marks the beginning of summer, held on a date between Ostara and Walpurgis Night
Walpurgis Night (), an abbreviation of Saint Walpurgis Night (from the German ), also known as Saint Walpurga's Eve (alternatively spelled Saint Walburga's Eve), is the eve of the Christian feast day of Saint Walpurga, an 8th-century abbess ...
Practice
Celebration commonly takes place outdoors in the form of a communal gathering.Dates of celebration
The precise dates on which festivals are celebrated are often flexible. Dates may be on the days of the quarter and cross-quarter days proper, the nearestfull moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180°). This means ...
, the nearest new moon, or the nearest weekend for secular convenience. The festivals were originally celebrated by peoples in the middle latitudes
The middle latitudes (also called the mid-latitudes, sometimes midlatitudes, or moderate latitudes) are a spatial region on Earth located between the Tropic of Cancer ( latitudes 23°26'22") to the Arctic Circle (66°33'39"), and Tropic of Cap ...
of the Northern Hemisphere. Consequently, the traditional times for seasonal celebrations do not agree with the seasons in the Southern Hemisphere or near the equator. Pagans in the Southern Hemisphere often advance these dates by six months to coincide with their own seasons.
Offerings
ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized ...
propitiation
Propitiation is the act of appeasing or making well-disposed a deity, thus incurring divine favor or avoiding divine retribution. While some use the term interchangeably with expiation, others draw a sharp distinction between the two. The discus ...
and veneration
Veneration ( la, veneratio; el, τιμάω ), or veneration of saints, is the act of honoring a saint, a person who has been identified as having a high degree of sanctity or holiness. Angels are shown similar veneration in many religions. Ety ...
for millennia. Modern pagan practice strongly avoids sacrificing animals in favour of grains, herbs, milk, wines, incense, baked goods, minerals, etc. The exception being with ritual feasts including meat, where the inedible parts of the animal are often burned as offerings while the community eats the rest.
Sacrifices are typically offered to gods and ancestors by burning them. Burying and leaving offerings in the open are also common in certain circumstances. The purpose of offering is to benefit the venerated, show gratitude, and give something back, strengthening the bonds between humans and divine and between members of a community.
Narratives
Celtic
It is a misconception in some quarters of the Neopagan community, influenced by the writings of Robert Graves, that historicalCelts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
had an overarching narrative for the entire cycle of the year. While the various Celtic calendar
The Celtic calendar is a compilation of pre-Christian Celtic systems of timekeeping, including the Gaulish Coligny calendar, used by Celtic countries to define the beginning and length of the day, the week, the month, the seasons, quarter days, ...
s include ''some'' cyclical patterns, and a belief in the balance of light and dark, these beliefs vary between the different Celtic cultures. Modern preservationists and revivalists usually observe the four 'fire festivals' of the Gaelic Calendar, and some also observe local festivals that are held on dates of significance in the different Celtic nations
The Celtic nations are a cultural area and collection of geographical regions in Northwestern Europe where the Celtic languages and cultural traits have survived. The term ''nation'' is used in its original sense to mean a people who shar ...
.
Slavic
 Slavic mythology tells of a persisting conflict involving
Slavic mythology tells of a persisting conflict involving Perun
In Slavic mythology, Perun (Cyrillic: Перýн) is the highest god of the pantheon and the god of sky, thunder, lightning, storms, rain, law, war, fertility and oak trees. His other attributes were fire, mountains, wind, iris, eagle, f ...
, god of thunder and lightning, and Veles, the ''black god'' and ''horned god'' of the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwor ...
. Enmity between the two is initiated by Veles' annual ascent up the world tree in the form of a huge serpent and his ultimate theft of Perun's divine cattle from the heavenly domain. Perun retaliates to this challenge of the divine order by pursuing Veles, attacking with his lightning bolts from the sky. Veles taunts Perun and flees, transforming himself into various animals and hiding behind trees, houses, even people. (Lightning bolts striking down trees or homes were explained as results of this.) In the end Perun overcomes and defeats Veles, returning him to his place in the realm of the dead. Thus the order of the world is maintained.
The idea that storms and thunder are actually divine battle is pivotal to the changing of the seasons. Dry periods are identified as chaotic results of Veles' thievery. This duality and conflict represents an opposition of the natural principles of earth, water, substance, and chaos (Veles) and of heaven, fire, spirit, order (Perun), not a clash of good and evil. The cosmic battle between the two also echoes the ancient Indo-European narrative of a fight between the sky-borne storm god and chthonic dragon.
On the ''great night'' (New Year
New Year is the time or day currently at which a new calendar year begins and the calendar's year count increments by one. Many cultures celebrate the event in some manner. In the Gregorian calendar, the most widely used calendar system to ...
), two children of Perun are born, Jarilo, god of fertility and vegetation and son of the Moon, and Morana Morana may refer to:
* Moraña, a municipality in Galicia, Spain
* Morana Dam, an earthfill dam on Morana river near Patan, Satara district in the state of Maharashtra in India
* Marzanna
Marzanna (in Polish), Morė (in Lithuanian), Marena (in ...
, goddess of nature and death and daughter of the Sun. On the same night, the infant Jarilo is snatched and taken to the underworld, where Veles raises him as his own. At the time of the spring equinox, Jarilo returns across the sea from the world of the dead, bringing with him fertility and spring from the evergreen underworld into the realm of the living. He meets his sister Morana and courts her. With the beginning of summer, the two are married bringing fertility and abundance to Earth, ensuring a bountiful harvest. The union of Perun's kin and Veles' stepson brings peace between two great gods, staving off storms which could damage the harvest. After the harvest, however, Jarilo is unfaithful to his wife and she vengefully slays him, returning him to the underworld and renewing enmity between Perun and Veles. Without her husband, god of fertility and vegetation, Morana – and all of nature with her – withers and freezes in the ensuing winter. She grows into the old and dangerous goddess of darkness and frost, eventually dying by the year's end only to be reborn again with her brother in the new year.
Wicca and Druidry
Wicca
Wicca () is a modern Pagan religion. Scholars of religion categorise it as both a new religious movement and as part of the occultist stream of Western esotericism. It was developed in England during the first half of the 20th century and w ...
, the narrative of the Wheel of the Year traditionally centers on the sacred marriage of the God and the Goddess and the god
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
/ goddess duality. In this cycle, the God is perpetually born from the Goddess at Yule, grows in power at the vernal equinox (as does the Goddess, now in her ''maiden aspect''), courts and impregnates the Goddess at Beltane
Beltane () is the Gaelic May Day festival. Commonly observed on the first of May, the festival falls midway between the spring equinox and summer solstice in the northern hemisphere. The festival name is synonymous with the month marking the ...
, reaches his peak at the summer solstice, wanes in power at Lammas
Lammas Day (Anglo-Saxon ''hlaf-mas'', "loaf-mass"), also known as Loaf Mass Day, is a Christian holiday celebrated in some English-speaking countries in the Northern Hemisphere on 1 August. The name originates from the word "loaf" in reference ...
, passes into the underworld at Samhain
Samhain ( , , , ; gv, Sauin ) is a Gaelic festival on 1 NovemberÓ hÓgáin, Dáithí. ''Myth Legend and Romance: An Encyclopaedia of the Irish Folk Tradition''. Prentice Hall Press, 1991. p. 402. Quote: "The basic Irish division of the year ...
(taking with him the fertility of the Goddess/Earth, who is now in her ''crone aspect'') until he is once again born from Her mother/crone aspect at Yule. The Goddess, in turn, ages and rejuvenates endlessly with the seasons, being courted by and giving birth to the Horned God
The Horned God is one of the two primary deities found in Wicca and some related forms of Neopaganism.
The term ''Horned God'' itself predates Wicca, and is an early 20th-century syncretic term for a horned or antlered anthropomorphic god partl ...
.
Many Wiccan, Neo-Druid, and eclectic Neopagans incorporate a narrative of the Holly King and Oak King as rulers of the waning year and the waxing year respectively. These two figures battle endlessly with the turning of the seasons. At the summer solstice, the Holly King defeats the Oak King and commences his reign. After the Autumn equinox Autumnal equinox or variations, may refer to:
* September equinox, the autumnal equinox in the Northern Hemisphere
* March equinox, the autumnal equinox in the Southern Hemisphere
Other uses
* Autumnal Equinox Day (Japanese: 秋分の日, ''Shūbu ...
the Oak King slowly begins to regain his power as the sun begins to wane. Come the winter solstice
The winter solstice, also called the hibernal solstice, occurs when either of Earth's poles reaches its maximum tilt away from the Sun. This happens twice yearly, once in each hemisphere (Northern and Southern). For that hemisphere, the winter ...
the Oak King in turn vanquishes the Holly King.After the spring equinox the sun begins to wax again and the Holly King slowly regains his strength until he once again defeats the Oak King at the summer solstice. The two are ultimately seen as essential parts of a whole, light and dark aspects of the male God, and would not exist without each other.
The Holly King is often portrayed as a woodsy figure, similar to the modern Santa Claus, dressed in red with sprigs of holly in his hair and the Oak King as a fertility god
A fertility deity is a god or goddess associated with fertility, sex, pregnancy, childbirth, and crops. In some cases these deities are directly associated with these experiences; in others they are more abstract symbols. Fertility rites may acc ...
.
See also
* Ember days, quarterly periods (usually three days) ofprayer
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deified ...
and fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
in the liturgical calendar
The liturgical year, also called the church year, Christian year or kalendar, consists of the cycle of liturgical seasons in Christian churches that determines when feast days, including celebrations of saints, are to be observed, and whi ...
of Western Christian
Western Christianity is one of two sub-divisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic ...
churches.
* List of neo-pagan festivals and events
Events organized for, or largely attended by, members of Neopagan spiritual paths: often planned around the Wheel of the Year or coinciding with adjacent phases of the Moon.
Festivals
* Council of Magickal Arts
* Faerieworlds
* Free Spirit Gathe ...
* Medicine wheel
To some indigenous peoples of North America, the medicine wheel is a metaphor for a variety of spiritual concepts. A medicine wheel may also be a stone monument that illustrates this metaphor.
Historically, most medicine wheels follow the basic ...
, metaphor for a variety of Native American spiritual concepts
* Solar term
A solar term is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisola ...
s, year's divisions in China and East Asia
Calendars
*Celtic calendar
The Celtic calendar is a compilation of pre-Christian Celtic systems of timekeeping, including the Gaulish Coligny calendar, used by Celtic countries to define the beginning and length of the day, the week, the month, the seasons, quarter days, ...
** Gaelic calendar
** Welsh seasonal festivals
Various traditions are practiced on certain days of the year in Wales both currently and historically, including festivities originating in Welsh, Celtic, English and Christian cultures.
History
As recorded in the Laws of Hywel Dda, the three ma ...
* Germanic calendar
The early Germanic calendars were the regional calendars used among the early Germanic peoples before they adopted the Julian calendar in the Early Middle Ages. The calendars were an element of early Germanic culture.
The Germanic peoples had nam ...
** Runic calendar
A Runic calendar (also Rune staff or Runic Almanac) is a perpetual calendar, variants of which were used in Northern Europe until the 19th century. A typical runic calendar consisted of several horizontal lines of symbols, one above the o ...
* Hellenic calendars
** Attic calendar
The Attic calendar or Athenian calendar is the lunisolar calendar beginning in midsummer with the lunar month of Hekatombaion, in use in ancient Attica, the ancestral territory of the Athenian polis. It is sometimes called the Greek calendar be ...
** Macedonian calendar
* Roman calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the dictator Julius Caesar and emperor Augustus in the late 1stcenturyBC and sometim ...
** Roman festivals
Festivals in ancient Rome were a very important part in Roman religious life during both the Republican and Imperial eras, and one of the primary features of the Roman calendar. ''Feriae'' ("holidays" in the sense of "holy days"; singula ...
References
External links
Astronomical cusps and pagan holidays
Celebrating the Seasons at Circle Sanctuary
Atheopagan Sabbaths
{{DEFAULTSORT:Wheel Of The Year Modern pagan holidays Time in religion Wicca Neo-druidism 1950s in modern paganism cs:Sabat (wicca)