Timbre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from
 The richness of a sound or note a musical instrument produces is sometimes described in terms of a sum of a number of distinct
The richness of a sound or note a musical instrument produces is sometimes described in terms of a sum of a number of distinct
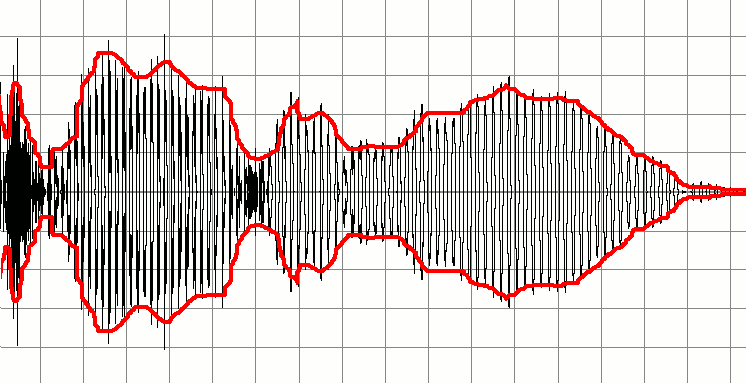 The timbre of a sound is also greatly affected by the following aspects of its ''envelope'': attack time and characteristics, decay, sustain, release (
The timbre of a sound is also greatly affected by the following aspects of its ''envelope'': attack time and characteristics, decay, sustain, release (
 In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from
In music, timbre ( ), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics
Psychoacoustics is the branch of psychophysics involving the scientific study of sound perception and audiology—how humans perceive various sounds. More specifically, it is the branch of science studying the psychological responses associated wi ...
), is the perceived sound quality of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes different types of sound production, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish different instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe
The oboe ( ) is a type of double reed woodwind instrument. Oboes are usually made of wood, but may also be made of synthetic materials, such as plastic, resin, or hybrid composites. The most common oboe plays in the treble or soprano range.
...
and a clarinet
The clarinet is a musical instrument in the woodwind family. The instrument has a nearly cylindrical bore and a flared bell, and uses a single reed to produce sound.
Clarinets comprise a family of instruments of differing sizes and pitch ...
, both woodwind instruments
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and re ...
).
In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctively with its own unique tone color. Experienced musicians are able to distinguish between different instruments of the same type based on their varied timbres, even if those instruments are playing notes at the same fundamental pitch and loudness.
The physical characteristics of sound that determine the perception of timbre include frequency spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors ...
and envelope
An envelope is a common packaging item, usually made of thin, flat material. It is designed to contain a flat object, such as a letter or card.
Traditional envelopes are made from sheets of paper cut to one of three shapes: a rhombus, a ...
. Singers and instrumental musicians can change the timbre of the music they are singing/playing by using different singing or playing techniques. For example, a violinist can use different bowing styles or play on different parts of the string to obtain different timbres (e.g., playing sul tasto produces a light, airy timbre, whereas playing sul ponticello produces a harsh, even and aggressive tone). On electric guitar and electric piano, performers can change the timbre using effects unit
An effects unit or effects pedal is an electronic device that alters the sound of a musical instrument or other audio source through audio signal processing.
Common effects include distortion/overdrive, often used with electric guitar in ...
s and graphic equalizers.
Synonyms
''Tone quality'' and ''tone color'' are synonyms for ''timbre'', as well as the "''texture'' attributed to a single instrument". However, the word texture can also refer to the type of music, such as multiple, interweaving melody lines versus a singable melody accompanied by subordinate chords.Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Associat ...
used the German ''Klangfarbe'' (''tone color''), and John Tyndall
John Tyndall FRS (; 2 August 1820 – 4 December 1893) was a prominent 19th-century Irish physicist. His scientific fame arose in the 1850s from his study of diamagnetism. Later he made discoveries in the realms of infrared radiation and the ...
proposed an English translation, ''clangtint'', but both terms were disapproved of by Alexander Ellis, who also discredits ''register'' and ''color'' for their pre-existing English meanings. Determined by its frequency composition, the sound of a musical instrument may be described with words such as ''bright'', ''dark'', ''warm'', ''harsh'', and other terms. There are also colors of noise
In audio engineering, electronics, physics, and many other fields, the color of noise or noise spectrum refers to the power spectrum of a noise signal (a signal produced by a stochastic process). Different colors of noise have significantly ...
, such as pink
Pink is the color of a namesake flower that is a pale tint of red. It was first used as a color name in the late 17th century. According to surveys in Europe and the United States, pink is the color most often associated with charm, politeness, ...
and white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White ...
. In visual representations of sound, timbre corresponds to the shape of the image, while loudness corresponds to brightness; pitch corresponds to the y-shift of the spectrogram.
ASA definition
TheAcoustical Society of America
The Acoustical Society of America (ASA) is an international scientific society founded in 1929 dedicated to generating, disseminating and promoting the knowledge of acoustics and its practical applications. The Society is primarily a voluntary org ...
(ASA) Acoustical Terminology definition 12.09 of timbre describes it as "that attribute of auditory sensation which enables a listener to judge that two nonidentical sounds, similarly presented and having the same loudness and pitch, are dissimilar", adding, "Timbre depends primarily upon the frequency spectrum, although it also depends upon the sound pressure and the temporal characteristics of the sound".
Attributes
Many commentators have attempted to decompose timbre into component attributes. For example, J. F. Schouten (1968, 42) describes the "elusive attributes of timbre" as "determined by at least five major acoustic parameters", which Robert Erickson finds, "scaled to the concerns of much contemporary music": # Range between tonal and noiselike character # Spectral envelope # Time envelope in terms of rise, duration, and decay (ADSR, which stands for "attack, decay, sustain, release") # Changes both of spectral envelope (formant-glide) andfundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'', is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. I ...
( micro-intonation)
# Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particul ...
, or onset
Onset may refer to:
* Onset (audio), the beginning of a musical note or sound
* Onset, Massachusetts, village in the United States
**Onset Island (Massachusetts), a small island located at the western end of the Cape Cod Canal
* Interonset interva ...
of a sound, quite dissimilar to the ensuing lasting vibration
An example of a tonal sound is a musical sound that has a definite pitch, such as pressing a key on a piano; a sound with a noiselike character would be white noise
In signal processing, white noise is a random signal having equal intensity at different frequencies, giving it a constant power spectral density. The term is used, with this or similar meanings, in many scientific and technical disciplines ...
, the sound similar to that produced when a radio is not tuned to a station.
Erickson gives a table of subjective experiences and related physical phenomena based on Schouten's five attributes:
See also Psychoacoustic evidence below.
Harmonics
 The richness of a sound or note a musical instrument produces is sometimes described in terms of a sum of a number of distinct
The richness of a sound or note a musical instrument produces is sometimes described in terms of a sum of a number of distinct frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is e ...
. The lowest frequency is called the ''fundamental frequency
The fundamental frequency, often referred to simply as the ''fundamental'', is defined as the lowest frequency of a periodic waveform. In music, the fundamental is the musical pitch of a note that is perceived as the lowest partial present. I ...
'', and the pitch it produces is used to name the note, but the fundamental frequency is not always the dominant frequency. The dominant frequency is the frequency that is most heard, and it is always a multiple of the fundamental frequency. For example, the dominant frequency for the transverse flute
A transverse flute or side-blown flute is a flute which is held horizontally when played. The player blows across the embouchure hole, in a direction perpendicular to the flute's body length.
Transverse flutes include the Western concert f ...
is double the fundamental frequency. Other significant frequencies are called overtone
An overtone is any resonant frequency above the fundamental frequency of a sound. (An overtone may or may not be a harmonic) In other words, overtones are all pitches higher than the lowest pitch within an individual sound; the fundamental i ...
s of the fundamental frequency, which may include harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', t ...
s and partials. Harmonics are whole number multiples of the fundamental frequency, such as ×2, ×3, ×4, etc. Partials are other overtones. There are also sometimes subharmonic
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of notes that results from inverting the intervals of the overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones mus ...
s at whole number ''divisions'' of the fundamental frequency. Most instruments produce harmonic sounds, but many instruments produce partials and inharmonic tones, such as cymbals and other indefinite-pitched instruments.
When the tuning note in an orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
or concert band
A concert band, also called a wind band, wind ensemble, wind symphony, wind orchestra, symphonic band, the symphonic winds, or symphonic wind ensemble, is a performing ensemble consisting of members of the woodwind, brass, and percussion fami ...
is played, the sound is a combination of 440 Hz, 880 Hz, 1320 Hz, 1760 Hz and so on. Each instrument in the orchestra or concert band produces a different combination of these frequencies, as well as harmonics and overtones. The sound waves of the different frequencies overlap and combine, and the balance of these amplitudes is a major factor in the characteristic sound of each instrument.
William Sethares wrote that just intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is the tuning of musical intervals as whole number ratios (such as 3:2 or 4:3) of frequencies. An interval tuned in this way is said to be pure, and is called a just interval. Just intervals (and ...
and the western equal tempered scale are related to the harmonic spectra/timbre of many western instruments in an analogous way that the inharmonic timbre of the Thai renat (a xylophone-like instrument) is related to the seven-tone near-equal tempered pelog scale in which they are tuned. Similarly, the inharmonic spectra of Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and ...
nese metallophones combined with harmonic instruments such as the stringed rebab
The ''rebab'' ( ar, ربابة, ''rabāba'', variously spelled ''rebap'', ''rubob'', ''rebeb'', ''rababa'', ''rabeba'', ''robab'', ''rubab'', ''rebob'', etc) is the name of several related string instruments that independently spread via I ...
or the voice, are related to the five-note near-equal tempered slendro scale commonly found in Indonesian gamelan
Gamelan () ( jv, ꦒꦩꦼꦭꦤ꧀, su, ᮌᮙᮨᮜᮔ᮪, ban, ᬕᬫᭂᬮᬦ᭄) is the traditional ensemble music of the Javanese, Sundanese, and Balinese peoples of Indonesia, made up predominantly of percussive instruments. T ...
music.
Envelope
 The timbre of a sound is also greatly affected by the following aspects of its ''envelope'': attack time and characteristics, decay, sustain, release (
The timbre of a sound is also greatly affected by the following aspects of its ''envelope'': attack time and characteristics, decay, sustain, release (ADSR envelope ADSR may refer to:
* ADSR envelope (attack decay sustain release), a common type of music envelope
* Accelerator-driven sub-critical reactor, a nuclear reactor using a particle accelerator to generate a fission reaction in a sub-critical assembly ...
) and transient
ECHELON, originally a secret government code name, is a surveillance program (signals intelligence/SIGINT collection and analysis network) operated by the five signatory states to the UKUSA Security Agreement:Given the 5 dialects that us ...
s. Thus these are all common controls on professional synthesizer
A synthesizer (also spelled synthesiser) is an electronic musical instrument that generates audio signals. Synthesizers typically create sounds by generating waveforms through methods including subtractive synthesis, additive synthesis a ...
s. For instance, if one takes away the attack from the sound of a piano or trumpet, it becomes more difficult to identify the sound correctly, since the sound of the hammer hitting the strings or the first blast of the player's lips on the trumpet mouthpiece are highly characteristic of those instruments. The envelope is the overall amplitude structure of a sound.
In music history
Instrumental timbre played an increasing role in the practice oforchestration
Orchestration is the study or practice of writing music for an orchestra (or, more loosely, for any musical ensemble, such as a concert band) or of adapting music composed for another medium for an orchestra. Also called "instrumentation", orch ...
during the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Berlioz and Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
made significant contributions to its development during the nineteenth century. For example, Wagner's "Sleep motif" from Act 3 of his opera '' Die Walküre'', features a descending chromatic scale
The chromatic scale (or twelve-tone scale) is a set of twelve pitches (more completely, pitch classes) used in tonal music, with notes separated by the interval of a semitone. Chromatic instruments, such as the piano, are made to produce th ...
that passes through a gamut of orchestral timbres. First the woodwind (flute, followed by oboe), then the massed sound of strings with the violins carrying the melody, and finally the brass (French horns).Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 – 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionism in music, Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most infl ...
, who composed during the last decades of the nineteenth and the first decades of the twentieth centuries, has been credited with elevating further the role of timbre: "To a marked degree the music of Debussy elevates timbre to an unprecedented structural status; already in '' Prélude à l'après-midi d'un faune'' the ''color'' of flute
The flute is a family of classical music instrument in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, meaning they make sound by vibrating a column of air. However, unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is a reedles ...
and harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
functions referentially". Mahler’s approach to orchestration
Orchestration is the study or practice of writing music for an orchestra (or, more loosely, for any musical ensemble, such as a concert band) or of adapting music composed for another medium for an orchestra. Also called "instrumentation", orch ...
illustrates the increasing role of differentiated timbres in music of the early twentieth century. Norman Del Mar describes the following passage from the Scherzo movement of his Sixth Symphony, as "a seven-bar link to the trio consisting of an extension in diminuendo of the repeated As… though now rising in a succession of piled octaves which moreover leap-frog with Cs added to the As. The lower octaves then drop away and only the Cs remain so as to dovetail with the first oboe phrase of the trio." During these bars, Mahler passes the repeated notes through a gamut of instrumental colors, mixed and single: starting with horns and pizzicato strings, progressing through trumpet, clarinet, flute, piccolo and finally, oboe: See also Klangfarbenmelodie.
In rock music
Rock music is a broad genre of popular music that originated as " rock and roll" in the United States in the late 1940s and early 1950s, developing into a range of different styles in the mid-1960s and later, particularly in the United States a ...
from the late 1960s to the 2000s, the timbre of specific sounds is important to a song. For example, in heavy metal music
Heavy metal (or simply metal) is a genre of rock music that developed in the late 1960s and early 1970s, largely in the United Kingdom and United States. With roots in blues rock, psychedelic rock and acid rock, heavy metal bands develope ...
, the sonic impact of the heavily amplified, heavily distorted power chord played on electric guitar through very loud guitar amplifiers and rows of speaker cabinet
A loudspeaker enclosure or loudspeaker cabinet is an enclosure (often rectangular box-shaped) in which speaker drivers (e.g., loudspeakers and tweeters) and associated electronic hardware, such as crossover circuits and, in some cases, power ...
s is an essential part of the style's musical identity.
Psychoacoustic evidence
Often, listeners can identify an instrument, even at different pitches and loudness, in different environments, and with different players. In the case of theclarinet
The clarinet is a musical instrument in the woodwind family. The instrument has a nearly cylindrical bore and a flared bell, and uses a single reed to produce sound.
Clarinets comprise a family of instruments of differing sizes and pitch ...
, acoustic analysis shows waveforms irregular enough to suggest three instruments rather than one. David Luce suggests that this implies that " rtain strong regularities in the acoustic waveform of the above instruments must exist which are invariant with respect to the above variables". However, Robert Erickson argues that there are few regularities and they do not explain our "...powers of recognition and identification." He suggests borrowing the concept of subjective constancy from studies of vision and visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to interpret the surrounding environment through photopic vision (daytime vision), color vision, scotopic vision (night vision), and mesopic vision (twilight vision), using light in the visible spectrum ref ...
.
Psychoacoustic experiments from the 1960s onwards tried to elucidate the nature of timbre. One method involves playing pairs of sounds to listeners, then using a multidimensional scaling algorithm to aggregate their dissimilarity judgments into a timbre space. The most consistent outcomes from such experiments are that brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, ...
or spectral energy distribution, and the ''bite'', or rate and synchronicity and rise time, of the attack are important factors.
Tristimulus timbre model
The concept of tristimulus originates in the world of color, describing the way three primary colors can be mixed together to create a given color. By analogy, the musical tristimulus measures the mixture ofharmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', t ...
s in a given sound, grouped into three sections. It is basically a proposal of reducing a huge number of sound partials, that can amount to dozens or hundreds in some cases, down to only three values. The first tristimulus measures the relative weight of the first harmonic; the second tristimulus measures the relative weight of the second, third, and fourth harmonics taken together; and the third tristimulus measures the relative weight of all the remaining harmonics.
:
However, more evidence, studies and applications would be needed regarding this type of representation, in order to validate it.
Brightness
The term "brightness" is also used in discussions of sound timbres, in a rough analogy with visual brightness. Timbre researchers consider brightness to be one of the perceptually strongest distinctions between sounds, and formalize it acoustically as an indication of the amount of high-frequency content in a sound, using a measure such as the spectral centroid.See also
*Formant
In speech science and phonetics, a formant is the broad spectral maximum that results from an acoustic resonance of the human vocal tract. In acoustics, a formant is usually defined as a broad peak, or local maximum, in the spectrum. For harmoni ...
Footnotes
References
* * * * * * {{Authority control Opera terminology Sound Acoustics