). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.).
, coordinates =
, largest_city =
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, official_languages =
, englishmotto = "One for all, all for one"
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, religion =
, demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra
, government_type =
Federal assembly-independent directorial republic with elements of a
direct democracy
, leader_title1 =
Federal Council
, leader_name1 =
, leader_title2 =
, leader_name2 =
Walter Thurnherr
Walter Thurnherr (born 11 July 1963) is a Swiss government official who has served as Chancellor of Switzerland since 2016. Although he holds a traditionally nonpartisan office, he was elected as a member of the Christian Democratic People's P ...
, legislature =
Federal Assembly
, upper_house =
Council of States
, lower_house =
National Council
, sovereignty_type =
History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
, established_event1 =
Founded
, established_date1 = 1 August 1291
, established_event2 = Sovereignty recognised (
Peace of Westphalia)
, established_date2 = 24 October 1648
, established_event3 =
Federal Treaty
The Federal Treaty (German: ''Bundesvertrag'', French: ''Pacte fédéral'', Italian: ''Patto federale'') was the legal foundation for the new Swiss Confederacy of 1815. It came about after interventions by the great powers of the Sixth Coalition ...
, established_date3 = 7 August 1815
, established_event4 =
Federal state
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-gover ...
, established_date4 = 12 September 1848
, area_km2 = 41,285
, area_rank = 132nd
, area_sq_mi = 15,940
, percent_water = 4.34 (2015)
, population_estimate =
, population_census = 8,327,126
, population_estimate_year = 2020
, population_estimate_rank = 99th
, population_census_year = 2015
, population_density_km2 =
, population_density_rank = 48th
, GDP_PPP = $739.49 billion
, GDP_PPP_year = 2022
, GDP_PPP_rank = 35th
, GDP_PPP_per_capita = $84,658
, GDP_PPP_per_capita_rank = 5th
, GDP_nominal = $841.69 billion
, GDP_nominal_year = 2022
, GDP_nominal_rank = 20th
, GDP_nominal_per_capita = $92,434
, GDP_nominal_per_capita_rank = 7th
, Gini = 29.7
, Gini_year = 2018
, Gini_change = decrease
, Gini_ref =
, HDI = 0.962
, HDI_year = 2021
, HDI_change = increase
, HDI_ref =
, HDI_rank = 1st
, currency =
Swiss franc
, currency_code = CHF
, time_zone =
CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast En ...
, utc_offset = +1
, utc_offset_DST = +2
, time_zone_DST =
CEST
, date_format = dd.mm.yyyy (
AD)
, drives_on = right
, calling_code =
+41
, patron_saint =
St Nicholas of Flüe
, iso3166code = CH
, cctld =
.ch
.ch is the country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Switzerland in the Domain Name System of the Internet. Made available in 1987, only two years after .com, it is administered by SWITCH Information Technology Services.
The domain ''ch'', as ...
,
.swiss
.swiss is a top-level domain (TLD) for Switzerland. It was approved by ICANN
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN ) is an American multistakeholder group and nonprofit organization responsible for coordinati ...
, today =
, ethnic_groups =
, ethnic_groups_ref =
, ethnic_groups_year = 2020
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a
landlocked country
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
located at the confluence of
Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
,
Central and
Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Alba ...
. It is bordered by
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
to the south,
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
to the west,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
to the north and
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
to the east.
Switzerland is geographically divided among the
Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
, the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
and the
Jura; the Alps occupy the greater part of the territory, whereas the
Swiss population of approximately 8.7 million is concentrated mostly on the plateau, where the largest cities and economic centres are located, including
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
,
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
and
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
.
Switzerland originates from the
Old Swiss Confederacy established in the
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
following a series of military successes against
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and
Burgundy. The
Federal Charter of 1291
The Federal Charter or Letter of Alliance (german: Bundesbrief) is one of the earliest constitutional documents of Switzerland. A treaty of alliance from 1291 between the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, the Charter is one of a series ...
is considered the country's founding document. Since the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
of the 16th century, Switzerland has maintained a policy of
armed neutrality
A neutral country is a state that is neutral towards belligerents in a specific war or holds itself as permanently neutral in all future conflicts (including avoiding entering into military alliances such as NATO, CSTO or the SCO). As a type of ...
. Swiss independence from the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
was formally recognised in the
Peace of Westphalia in 1648. Switzerland has not fought an international war since 1815. It joined the United Nations only in 2002, though it pursues an active foreign policy, including participation in frequent peace-building processes worldwide. Switzerland is the birthplace of the
Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and ...
, one of the world's oldest and best-known humanitarian organisations, and hosts the headquarters or offices of most major
international institutions
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
, including the
WTO, the
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
, the
ILO,
FIFA, and the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
. It is a founding member of the
European Free Trade Association (EFTA), but not part of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
(EU), the
European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
, or the
Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro ( €) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU polici ...
; however, it participates in the
European single market and the
Schengen Area through bilateral treaties.
Switzerland is a
federal republic composed of
26 cantons, with federal authorities based in
Bern.
It has four main linguistic and cultural regions: German, French, Italian and
Romansh. Although most Swiss are German-speaking, national identity is rooted in a common historical background, shared values such as
federalism and
direct democracy, and
Alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National Pa ...
symbolism.
This identity transcends language, ethnicity, and religion, leading to Switzerland being described as a ("nation of volition") rather than a
nation state
A nation state is a political unit where the state and nation are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may i ...
.
Due to its linguistic diversity, Switzerland is known by multiple native names: (
German); (
French); (
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
); and (
Romansh). On
coins
A coin is a small, flat (usually depending on the country or value), round piece of metal or plastic used primarily as a medium of exchange or legal tender. They are standardized in weight, and produced in large quantities at a mint in order t ...
and
stamps
Stamp or Stamps or Stamping may refer to:
Official documents and related impressions
* Postage stamp, used to indicate prepayment of fees for public mail
* Ration stamp, indicating the right to rationed goods
* Revenue stamp, used on documents to ...
, the Latin name, — frequently shortened to "
Helvetia
Helvetia () is the female national personification of Switzerland, officially ''Confoederatio Helvetica,'' the Swiss Confederation.
The allegory is typically pictured in a flowing gown, with a spear and a shield emblazoned with the Swiss fl ...
" — is used instead of the spoken languages.
Switzerland is one of the world's most developed countries. It has the highest nominal
wealth per adult of any country and the
eighth-highest gross domestic product per capita. Switzerland ranks first in the
Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, wh ...
since 2021 and performs highly also on several international metrics, including
economic competitiveness and
democratic governance. Cities such as Zürich, Geneva and Basel rank among the highest in terms of quality of life, albeit with some of the highest
costs of living
Cost of living is the cost of maintaining a certain standard of living. Changes in the cost of living over time can be operationalized in a cost-of-living index. Cost of living calculations are also used to compare the cost of maintaining a cer ...
.
Etymology
The English name ''Switzerland'' is a portmanteau of ''Switzer'', an obsolete term for a
Swiss person which was in use during the 16th to 19th centuries, and ''land''. The English adjective ''Swiss'' is a
loanword
A loanword (also loan word or loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language. This is in contrast to cognates, which are words in two or more languages that are similar because t ...
from French ', also in use since the 16th century. The name ''Switzer'' is from the
Alemannic ', in origin an inhabitant of ''
Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
'' and its
associated territory, one of the cantons which formed the nucleus of the
Old Swiss Confederacy. The Swiss began to adopt the name for themselves after the
Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
of 1499, used alongside the term for "Confederates", (literally: ''comrades by oath''), used since the 14th century. The
data code for Switzerland, CH, is derived from
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
( en, Helvetic Confederation).
The toponym ''Schwyz'' itself was first attested in 972, as
Old High German
Old High German (OHG; german: Althochdeutsch (Ahd.)) is the earliest stage of the German language, conventionally covering the period from around 750 to 1050.
There is no standardised or supra-regional form of German at this period, and Old High ...
', perhaps related to ' ‘to burn’ (cf.
Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlemen ...
‘to singe, burn’), referring to the area of forest that was burned and cleared to build. The name was extended to the area dominated by the canton, and after the Swabian War of 1499 gradually came to be used for the entire Confederation. The
Swiss German name of the country, ', is homophonous to that of the canton and the settlement, but distinguished by the use of the definite article (' for the Confederation, but simply ' for the canton and the town). The long
ːof Swiss German is historically and still often today spelled rather than , preserving the original identity of the two names even in writing.
The Latin name was
neologised and introduced gradually after the
formation of the federal state in 1848, harking back to the Napoleonic
Helvetic Republic. It appeared on coins from 1879, inscribed on the
Federal Palace in 1902 and after 1948 used in the official seal (e.g., the
ISO banking code "CHF" for the
Swiss franc, and the country top-level domain ".ch", are both taken from the state's Latin name). is derived from the ''
Helvetii'', a
Gaulish tribe living on the
Swiss Plateau
The Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau (german: Schweizer Mittelland; french: plateau suisse; it, altopiano svizzero) is one of the three major landscapes in Switzerland, lying between the Jura Mountains and the Swiss Alps. It covers about 30% of ...
before the
Roman era
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC ...
.
''
Helvetia
Helvetia () is the female national personification of Switzerland, officially ''Confoederatio Helvetica,'' the Swiss Confederation.
The allegory is typically pictured in a flowing gown, with a spear and a shield emblazoned with the Swiss fl ...
'' appeared as a
national personification of the Swiss confederacy in the 17th century in a 1672 play by Johann Caspar Weissenbach.
History
The state of Switzerland took its present form with the adoption of the
Swiss Federal Constitution in 1848. Switzerland's precursors established a defensive alliance in 1291, forming a loose confederation that persisted for centuries.
Beginnings
The oldest traces of hominid existence in Switzerland date to about 150,000 years ago.
The oldest known farming settlements in Switzerland, which were found at
Gächlingen
Gächlingen is a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland.
History
An area near Gächlingen was the site of the first settlement in Switzerland. This Linear Band Ceramic settlement dates to about 6000BC and is the first long-t ...
, date to around 5300 BC.

The earliest known tribes formed the
Hallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
and
La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
s, named after the archaeological site of La Tène on the north side of
Lake Neuchâtel
Lake Neuchâtel (french: Lac de Neuchâtel ; frp, Lèc de Nôchâtél; german: Neuenburgersee) is a lake primarily in Romandy, in the French-speaking part of Switzerland. The lake lies mainly in the canton of Neuchâtel, but is also shared by t ...
. La Tène culture developed and flourished during the late
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
from around 450 BC,
possibly influenced by
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and
Etruscan civilisations. One of the most important tribal groups was the
Helvetii. Steadily harassed by
Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
, in 58 BC, the Helvetii decided to abandon the Swiss Plateau and migrate to western
Gallia
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Rep ...
.
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
's armies pursued and defeated them at the
Battle of Bibracte
The Battle of Bibracte was fought between the Helvetii and six Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. It was the second major battle of the Gallic Wars.
Prelude
The Helvetii, a confederation of Gallic tribes, had begun a total ...
, in today's eastern France, forcing the tribe to move back to its homeland.
In 15 BC,
Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
(later the second Roman emperor) and his brother
Drusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
conquered the Alps, integrating them into the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
. The area occupied by the Helvetii first became part of Rome's
Gallia Belgica
Gallia Belgica ("Belgic Gaul") was a province of the Roman Empire located in the north-eastern part of Roman Gaul, in what is today primarily northern France, Belgium, and Luxembourg, along with parts of the Netherlands and Germany.
In 50 BC, a ...
province and then of its
Germania Superior province. The eastern portion of modern Switzerland was integrated into the
Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
of
Raetia
Raetia ( ; ; also spelled Rhaetia) was a province of the Roman Empire, named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west ...
. Sometime around the start of the
Common Era
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the o ...
, the Romans maintained a large camp called
Vindonissa
Vindonissa (from a Gaulish toponym in *''windo-'' "white") was a Roman legion camp, vicus and later a bishop's seat at modern Windisch, Switzerland. The remains of the camp are listed as a heritage site of national significance. The city of B ...
, now a ruin at the confluence of the
Aare
The Aare () or Aar () is a tributary of the High Rhine and the longest river that both rises and ends entirely within Switzerland.
Its total length from its source to its junction with the Rhine comprises about , during which distance it descen ...
and
Reuss rivers, near the town of
Windisch.
The first and second century AD was an age of prosperity on the Swiss Plateau. Towns such as
Aventicum
Aventicum was the largest town and capital of Roman Switzerland (Helvetia or Civitas Helvetiorum). Its remains are beside the modern town of Avenches.
The city was probably created ''ex nihilo'' in the early 1st century AD, as the capital of ...
,
Iulia Equestris
Noviodunum or Colonia Iulia Equestris was a Roman era settlement in what is now Nyon in the Canton of Vaud in Switzerland.
Origin of the name
Noviodunum is a name of Celtic origin, meaning "new fort": It comes from '' nowyo'', Celtic for "new", a ...
and
Augusta Raurica
Augusta Raurica is a Roman archaeological site and an open-air museum in Switzerland located on the south bank of the Rhine river about 20 km east of Basel near the villages of Augst and Kaiseraugst. It is the site of the oldest known ...
, reached a remarkable size, while hundreds of agricultural estates (
Villae rusticae) were established in the countryside.
Around 260 AD, the fall of the
Agri Decumates
The ''Agri Decumates'' or ''Decumates Agri'' ("Decumatian Fields") were a region of the Roman Empire's provinces of Germania Superior and Raetia, covering the Black Forest, Swabian Jura, and Franconian Jura areas between the Rhine, Main, and Da ...
territory north of the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
transformed today's Switzerland into a frontier land of the Empire. Repeated raids by the
Alamanni tribes provoked the ruin of the Roman towns and economy, forcing the population to shelter near Roman fortresses, like the
Castrum Rauracense
Kaiseraugst (Swiss German: ''Chäiseraugscht'') is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality within the district of Rheinfelden (district), Rheinfelden in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is named after the Anc ...
near Augusta Raurica. The Empire built another line of defence at the north border (the so-called Donau-Iller-Rhine-Limes). At the end of the fourth century, the increased Germanic pressure forced the Romans to abandon the linear defence concept. The Swiss Plateau was finally open to
Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
.
In the
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, from the end of the fourth century, the western extent of modern-day Switzerland was part of the territory of the
Kings of the Burgundians. The
Alemanni settled the Swiss Plateau in the fifth century and the
valleys of the Alps
The main valleys of the Alps, orographically by drainage basin.
Rhine basin (North Sea)
High Rhine
*Aare
**Limmat
***Linth (Glarus)
**** Lake Walen
***** Seeztal
**** Klöntal
**** Sernftal
**Reuss
***Lake Lucerne
**** Sarner Aa ( Brünig Pas ...
in the eighth century, forming
Alemannia. Modern-day Switzerland was then divided between the kingdoms of Alemannia and
Burgundy.
The entire region became part of the expanding
Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
in the sixth century, following
Clovis I's victory over the Alemanni at
Tolbiac in 504 AD, and later Frankish domination of the Burgundians.
Throughout the rest of the sixth, seventh and eighth centuries, Swiss regions continued under Frankish hegemony (
Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from the middle of the 5th century until 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the Franks and northern Gauli ...
and
Carolingian dynasties) but after its extension under
Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, the
Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
was divided by the
Treaty of Verdun
The Treaty of Verdun (), agreed in , divided the Frankish Empire into three kingdoms among the surviving sons of the emperor Louis I, the son and successor of Charlemagne. The treaty was concluded following almost three years of civil war and ...
in 843.
The territories of present-day Switzerland became divided into
Middle Francia
Middle Francia ( la, Francia media) was a short-lived Frankish kingdom which was created in 843 by the Treaty of Verdun after an intermittent civil war between the grandsons of Charlemagne resulted in division of the united empire. Middle Franc ...
and
East Francia until they were reunified under the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
around 1000 AD.
By 1200, the Swiss Plateau comprised the dominions of the houses of
Savoy,
Zähringer,
Habsburg, and
Kyburg.
Some regions (
Uri,
Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
,
Unterwalden
Unterwalden, translated from the Latin ''inter silvas''(''between the forests''), is the old name of a forest-canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy in central Switzerland, south of Lake Lucerne, consisting of two valleys or '' Talschaften'', no ...
, later known as ) were accorded the
Imperial immediacy
Imperial immediacy (german: Reichsfreiheit or ') was a privileged constitutional and political status rooted in German feudal law under which the Imperial estates of the Holy Roman Empire such as Imperial cities, prince-bishoprics and secular pri ...
to grant the empire direct control over the mountain passes. With the extinction of its male line in 1263, the Kyburg dynasty fell in AD 1264. The Habsburgs under
King Rudolph I (Holy Roman Emperor in 1273) laid claim to the Kyburg lands and annexed them, extending their territory to the eastern Swiss Plateau.
Old Swiss Confederacy
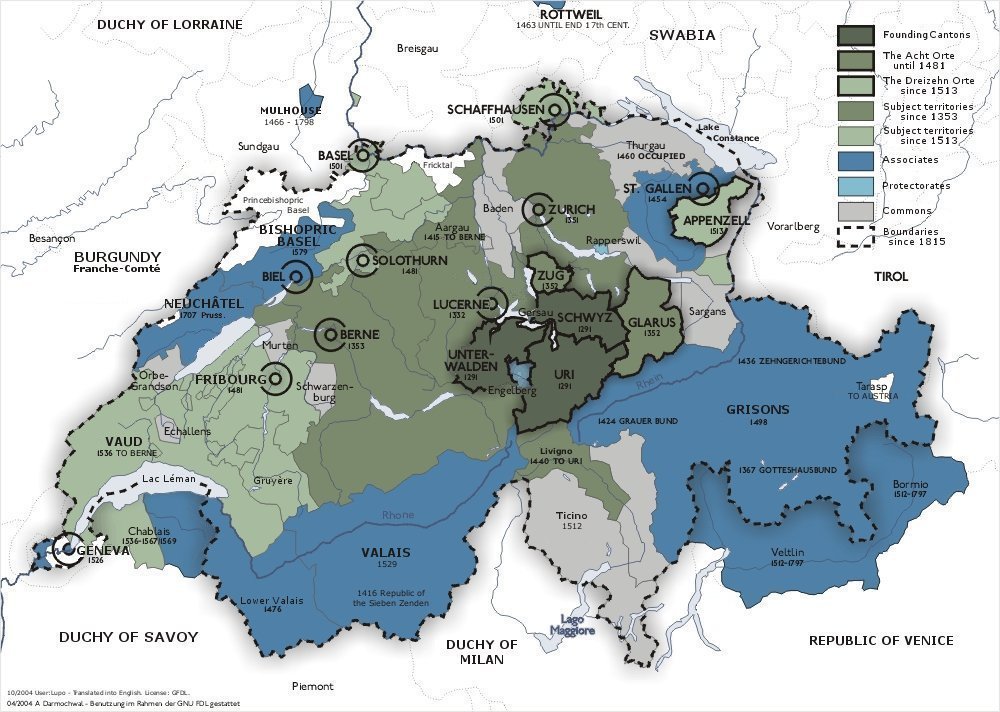
The Old Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of the central Alps. The Confederacy was governed by
nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteri ...
and
patricians
The patricians (from la, patricius, Greek: πατρίκιος) were originally a group of ruling class families in ancient Rome. The distinction was highly significant in the Roman Kingdom, and the early Republic, but its relevance waned after ...
of various cantons who facilitated management of common interests and ensured peace on mountain trade routes. The
Federal Charter of 1291
The Federal Charter or Letter of Alliance (german: Bundesbrief) is one of the earliest constitutional documents of Switzerland. A treaty of alliance from 1291 between the cantons of Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden, the Charter is one of a series ...
is considered the confederacy's founding document, even though similar alliances likely existed decades earlier. The document was agreed among the
rural communes of
Uri,
Schwyz
The town of Schwyz (; french: Schwytz; it, Svitto) is the capital of the canton of Schwyz in Switzerland.
The Federal Charter of 1291 or ''Bundesbrief'', the charter that eventually led to the foundation of Switzerland, can be seen at the ' ...
, and
Unterwalden
Unterwalden, translated from the Latin ''inter silvas''(''between the forests''), is the old name of a forest-canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy in central Switzerland, south of Lake Lucerne, consisting of two valleys or '' Talschaften'', no ...
.
By 1353, the three original
cantons had joined with the cantons of
Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
and
Zug and the
Lucerne,
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
and
Bern city-states to form the "Old Confederacy" of eight states that obtained through the end of the 15th century.
The expansion led to increased power and wealth for the confederation. By 1460, the confederates controlled most of the territory south and west of the Rhine to the Alps and the
Jura mountains, and the
University of Basel
The University of Basel (Latin: ''Universitas Basiliensis'', German: ''Universität Basel'') is a university in Basel, Switzerland. Founded on 4 April 1460, it is Switzerland's oldest university and among the world's oldest surviving universit ...
was founded (with a faculty of medicine) establishing a tradition of chemical and medical research. This increased after victories against the Habsburgs (
Battle of Sempach,
Battle of Näfels), over
Charles the Bold
Charles I (Charles Martin; german: Karl Martin; nl, Karel Maarten; 10 November 1433 – 5 January 1477), nicknamed the Bold (German: ''der Kühne''; Dutch: ''de Stoute''; french: le Téméraire), was Duke of Burgundy from 1467 to 1477. ...
of
Burgundy during the 1470s, and the success of the
Swiss mercenaries
The Swiss mercenaries (german: Reisläufer) were a powerful infantry force constituted by professional soldiers originating from the cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. They were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially among t ...
. The Swiss victory in the
Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( gsw, Schwoobechrieg (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin") in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of ...
against the
Swabian League
The Swabian League (''Schwäbischer Bund'') was a mutual defence and peace keeping association of Imperial Estates – free Imperial cities, prelates, principalities and knights – principally in the territory of the early medieval stem duchy o ...
of
Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
Maximilian I in 1499 amounted to ''de facto'' independence within the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
.
In 1501, Basel and Schaffhausen joined the Old Swiss Confederacy.
The Confederacy acquired a reputation of invincibility during these earlier wars, but
expansion of the confederation suffered a setback in 1515 with the Swiss defeat in the
Battle of Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was the last major engagement of the War of the League of Cambrai and took place on 13–14 September 1515, near the town now called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan. It pitted the French army, composed of the b ...
. This ended the so-called "heroic" epoch of Swiss history.
The success of
Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the Univ ...
's
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in some cantons led to inter-cantonal religious conflicts in 1529 and 1531 (
Wars of Kappel). It was not until more than one hundred years after these internal wars that, in 1648, under the
Peace of Westphalia, European countries recognised Switzerland's independence from the Holy Roman Empire and its
neutrality.
During the
Early Modern period of Swiss history, the growing
authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
of the patriciate families combined with a financial crisis in the wake of the
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
led to the
Swiss peasant war of 1653
The Swiss peasant war of 1653 () was a popular revolt in the Old Swiss Confederacy at the time of the Ancien Régime. A devaluation of Bernese money caused a tax revolt that spread from the Entlebuch valley in the Canton of Lucerne to the Emmen ...
. In the background to this struggle, the conflict between
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
cantons persisted, erupting in further violence at the
First War of Villmergen
The First War of Villmergen Encarta-encyclopedie Winkler Prins (1993–2002) s.v. "Zwitserland. §5.2 Reformatie". Microsoft Corporation/Het Spectrum. was a Swiss religious war which lasted from 5 January until 7 March 1656, at the time of the Ol ...
, in 1656, and the
Toggenburg War
The Toggenburg War, also known as the Second War of Villmergen or the Swiss Civil War of 1712, was a Swiss civil war during the Old Swiss Confederacy from 12 April to 11 August 1712. The Catholic "inner cantons" and the Imperial Abbey of Saint ...
(or Second War of Villmergen), in 1712.
Napoleonic era

In 1798, the
revolutionary French government invaded Switzerland and imposed a new unified constitution.
This centralised the government of the country, effectively abolishing the cantons: moreover,
Mülhausen left Switzerland and the
Valtellina
Valtellina or the Valtelline (occasionally spelled as two words in English: Val Telline; rm, Vuclina (); lmo, Valtelina or ; german: Veltlin; it, Valtellina) is a valley in the Lombardy region of northern Italy, bordering Switzerland. Toda ...
valley became part of the
Cisalpine Republic
The Cisalpine Republic ( it, Repubblica Cisalpina) was a sister republic of France in Northern Italy that existed from 1797 to 1799, with a second version until 1802.
Creation
After the Battle of Lodi in May 1796, Napoleon Bonaparte organiz ...
. The new regime, known as the Helvetic Republic, was highly unpopular. An invading foreign army had imposed and destroyed centuries of tradition, making Switzerland nothing more than a French
satellite state
A satellite state or dependent state is a country that is formally independent in the world, but under heavy political, economic, and military influence or control from another country. The term was coined by analogy to planetary objects orbitin ...
. The fierce French suppression of the
Nidwalden Revolt in September 1798 was an example of the oppressive presence of the
French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed Force ...
and the local population's resistance to the occupation.
When war broke out between France and its rivals, Russian and
Austrian forces invaded Switzerland. The Swiss refused to fight alongside the French in the name of the Helvetic Republic. In 1803
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
organised a meeting of the leading Swiss politicians from both sides in Paris. The
Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
was the result, which largely restored Swiss autonomy and introduced a Confederation of 19 cantons.
Henceforth, much of Swiss politics would concern balancing the cantons' tradition of self-rule with the need for a central government.
In 1815 the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
fully re-established Swiss independence, and the European powers recognised permanent Swiss neutrality.
Swiss troops served foreign governments until 1860 when they fought in the
siege of Gaeta. The treaty allowed Switzerland to increase its territory, with the admission of the cantons of
Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
,
Neuchâtel and
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
. Switzerland's borders saw only minor adjustments thereafter.
Federal state

The restoration of power to the patriciate was only temporary. After a period of unrest with repeated violent clashes, such as the
Züriputsch
The Züriputsch of 6 September 1839 was a putsch of the rural conservative population against the liberal rule of the city of Zürich on the eve of the formation of the Swiss federal state. The reason for the putsch was the appointment of th ...
of 1839, civil war (the ''
Sonderbundskrieg'') broke out in 1847 when some Catholic cantons tried to set up a separate alliance (the ''Sonderbund'').
The war lasted less than a month, causing fewer than 100 casualties, most of which were through
friendly fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy/hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while en ...
. The Sonderbundskrieg had a significant impact on the psychology and society of Switzerland.
The war convinced most Swiss of the need for unity and strength. Swiss from all strata of society, whether Catholic or Protestant, from the liberal or conservative current, realised that the cantons would profit more from merging their economic and religious interests.
Thus, while the rest of Europe saw
revolutionary uprisings, the Swiss drew up a constitution that provided for a
federal layout, much of it inspired by the
American example. This constitution provided central authority while leaving the cantons the right to self-government on local issues. Giving credit to those who favoured the power of the cantons (the Sonderbund Kantone), the national assembly was divided between an
upper house
An upper house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house.''Bicameralism'' (1997) by George Tsebelis The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restric ...
(the
Council of States, two representatives per canton) and a
lower house (the
National Council, with representatives elected from across the country).
Referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
s were made mandatory for any amendments.
This new constitution ended the legal power of
nobility in Switzerland.

A single system of weights and measures was introduced, and in 1850 the
Swiss franc became the Swiss
single currency
A currency union (also known as monetary union) is an intergovernmental agreement that involves two or more states sharing the same currency. These states may not necessarily have any further integration (such as an economic and monetary union, ...
, complemented by the WIR franc in 1934. Article 11 of the constitution forbade sending troops to serve abroad, marking the end of foreign service. It came with the expectation of serving the
Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
, and the Swiss were still obliged to serve
Francis II of the Two Sicilies
, image = Francesco II of the Two Sicilies.JPG
, caption = King Francis II
, succession = King of the Two Sicilies
, reign = 22 May 1859 – 20 March 1861
, predecessor = Ferdinand II
, successor = ''Ki ...
with Swiss Guards present at the
siege of Gaeta in 1860.
An important clause of the constitution was that it could be entirely rewritten if necessary, thus enabling it to evolve as a whole rather than being modified one amendment at a time.
This need soon proved itself when the rise in population and the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
that followed led to calls to modify the constitution accordingly. The population rejected an early draft in 1872, but modifications led to its acceptance in 1874.
It introduced the
facultative referendum for laws at the federal level. It also established federal responsibility for defence, trade, and legal matters.
In 1891, the constitution was revised with unusually strong elements of
direct democracy, which remain unique today.
Modern history

Switzerland was not invaded during either of the world wars. During
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Switzerland was home to the revolutionary and founder of the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
Vladimir Illych Ulyanov (
Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 1 ...
) who remained there until 1917. Swiss neutrality was seriously questioned by the short-lived
Grimm–Hoffmann affair in 1917. In 1920, Switzerland joined the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
, which was based in
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
, after it was exempted from military requirements.
During
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
,
detailed invasion plans were drawn up by the Germans, but Switzerland was never attacked.
Switzerland was able to remain independent through a combination of military deterrence, concessions to Germany, and good fortune, as larger events during the war intervened.
General
Henri Guisan, appointed the
commander-in-chief for the duration of the war ordered a general mobilisation of the armed forces. The Swiss military strategy changed from static defence at the borders to organised long-term attrition and withdrawal to strong, well-stockpiled positions high in the Alps, known as the
Reduit
A reduit is a fortified structure such as a citadel or a keep into which the defending troops can retreat when the outer defences are breached. The term is also used to describe an area of a country, which, through a ring of heavy fortifications ...
. Switzerland was an important base for espionage by both sides and often mediated communications between the
Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
and
Allied powers.
Switzerland's trade was blockaded by both the Allies and the Axis. Economic cooperation and extension of credit to
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
varied according to the perceived likelihood of invasion and the availability of other trading partners. Concessions reached a peak after a crucial rail link through
Vichy France
Vichy France (french: Régime de Vichy; 10 July 1940 – 9 August 1944), officially the French State ('), was the fascist French state headed by Marshal Philippe Pétain during World War II. Officially independent, but with half of its te ...
was severed in 1942, leaving Switzerland (together with
Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
) entirely isolated from the wider world by Axis-controlled territory. Over the course of the war, Switzerland interned over 300,000 refugees
aided by the
International Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signato ...
, based in Geneva. Strict immigration and
asylum
Asylum may refer to:
Types of asylum
* Asylum (antiquity), places of refuge in ancient Greece and Rome
* Benevolent Asylum, a 19th-century Australian institution for housing the destitute
* Cities of Refuge, places of refuge in ancient Judea
...
policies and the financial relationships with Nazi Germany raised controversy, only at the end of the 20th century.
During the war, the Swiss Air Force engaged aircraft of both sides, shooting down 11 intruding
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...
planes in May and June 1940, then forcing down other intruders after a change of policy following threats from Germany. Over 100 Allied bombers and their crews were interned. Between 1940 and 1945,
Switzerland was bombed by the Allies, causing fatalities and property damage.
Among the cities and towns bombed were
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
,
Brusio
Brusio (Lombardy, Lombard: ''Brüs'', Romansh language, Romansh ''Brüsch'') is a municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Bernina Region in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Grisons in Switzerland.
History
Brusio is first mentioned ...
,
Chiasso
Chiasso (; lmo, Ciass ) is a municipality in the district of Mendrisio in the canton of Ticino in Switzerland.
As the southernmost of Switzerland's municipalities, Chiasso is on the border with Italy, in front of Ponte Chiasso (a frazione of Co ...
,
Cornol, Geneva,
Koblenz,
Niederweningen
Niederweningen is a municipality in the district of Dielsdorf in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Niederweningen is first mentioned between 1096 and 1111 as ''Waningen''. In 1269 it was mentioned as ''Nidirunweningin''.
The railway ...
,
Rafz
Rafz is a municipality in the district of Bülach in the northwest of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
Rafz was first mentioned in 1413 as ''Rafsa''.
Geography
Rafz has an area of . Of this area, 52% is used for agricultural purposes, whi ...
,
Renens
Renens ( ) is a municipality in the canton of Vaud, Switzerland. It is located in the district of Ouest Lausannois, and is a suburb of the city of Lausanne. It is the fourth largest city in the canton. It is considered a very multiethnic town, a ...
,
Samedan
Samedan (, ) is a town and municipality in the Maloja Region in the Swiss canton of Grisons. It is served by Samedan railway station on the Rhaetian Railway network and by the Samedan Airport.
History
Samedan is first mentioned in 1139 as '' ...
,
Schaffhausen
Schaffhausen (; gsw, Schafuuse; french: Schaffhouse; it, Sciaffusa; rm, Schaffusa; en, Shaffhouse) is a town with historic roots, a municipality in northern Switzerland, and the capital of the canton of the same name; it has an estimate ...
,
Stein am Rhein
Stein am Rhein (abbreviated as Stein a. R.) is a historic town and a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland.
The town's medieval centre retains the ancient street plan. The site of the city wall, and the city gates are preserve ...
,
Tägerwilen
Tägerwilen is a municipality in the district of Kreuzlingen in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland.
Geography
Tägerwilen has an area, , of . Of this area, or 47.5% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 37.4% is forested. Of the res ...
,
Thayngen
Thayngen () is a village and a municipality in the canton of Schaffhausen in Switzerland. On 1 January 2009 Altdorf, Bibern, Hofen, Opfertshofen merged into Thayngen.[Vals Vals is the word for waltz in many European languages.
Vals or VALS may also refer to:
* Peruvian waltz
* Venezuelan waltz
* Vals (dance), a dance related to Argentine tango
* VALS, "Values And Lifestyles," a psychographic segmentation tool
Place ...]
, and Zürich. Allied forces maintained that the bombings, which violated the 96th
Article of War, resulted from navigation errors, equipment failure, weather conditions, and pilot errors. The Swiss expressed fear and concern that the bombings were intended to put pressure on Switzerland to end economic cooperation and neutrality with Nazi Germany.
Court-martial proceedings took place in England. The U.S. paid SFR 62,176,433.06 for reparations.
Switzerland's attitude towards
refugees was complicated and controversial; over the course of the war, it admitted as many as 300,000 refugees
while refusing tens of thousands more, including Jews persecuted by the Nazis.
After the war, the Swiss government exported credits through the charitable fund known as the Schweizerspende and donated to the
Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred over $13 billion (equivalent of about $ in ) in economic re ...
to help Europe's recovery, efforts that ultimately benefited the
Swiss economy.
During the
Cold War, Swiss authorities
considered the construction of a Swiss
nuclear bomb. Leading nuclear physicists at the
Federal Institute of Technology Zürich such as
Paul Scherrer
Paul Hermann Scherrer (3 February 1890 – 25 September 1969) was a Swiss physicist. Born in St. Gallen, Switzerland, he studied at Göttingen, Germany, before becoming a lecturer there. Later, Scherrer became head of the Department of Physics ...
made this a realistic possibility. In 1988, the
Paul Scherrer Institute
The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is a multi-disciplinary research institute for natural and engineering sciences in Switzerland. It is located in the Canton of Aargau in the municipalities Villigen and Würenlingen on either side of the River ...
was founded in his name to explore the therapeutic uses of
neutron scattering
Neutron scattering, the irregular dispersal of free neutrons by matter, can refer to either the naturally occurring physical process itself or to the man-made experimental techniques that use the natural process for investigating materials. Th ...
technologies. Financial problems with the defence budget and ethical considerations prevented the substantial funds from being allocated, and the
Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty
The Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, commonly known as the Non-Proliferation Treaty or NPT, is an international treaty whose objective is to prevent the spread of nuclear weapons and weapons technology, to promote cooperation ...
of 1968 was seen as a valid alternative. Plans for building nuclear weapons were dropped by 1988. Switzerland joined the
Council of Europe in 1963.

Switzerland was the last Western republic (the
Principality of Liechtenstein followed in 1984) to grant women the
right to vote
Suffrage, political franchise, or simply franchise, is the right to vote in public, political elections and referendums (although the term is sometimes used for any right to vote). In some languages, and occasionally in English, the right to v ...
. Some Swiss cantons approved this in 1959, while at the federal level, it was achieved in 1971
and, after resistance, in the last canton
Appenzell Innerrhoden (one of only two remaining ''
Landsgemeinde
The ''Landsgemeinde'' ("cantonal assembly"; , plural ''Landsgemeinden'') is a public, non-secret ballot voting system operating by majority rule, which constitutes one of the oldest forms of direct democracy. Still at use – in a few places � ...
'', along with
Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
) in 1990. After obtaining suffrage at the federal level, women quickly rose in political significance. The first woman on the seven-member
Federal Council executive was
Elisabeth Kopp
Elisabeth Kopp (born 16 December 1936, in Zürich) is a Swiss politician and the first woman elected to the Swiss Federal Council (1984–1989).
Biography
Elisabeth Kopp grew up in Bern. After finishing her law studies in 1960, she married H ...
, who served from 1984 to 1989,
and the first female president was
Ruth Dreifuss
Ruth Dreifuss (born 9 January 1940 in St. Gallen) is a Swiss politician affiliated with the Social Democratic Party. She was a member of the Swiss Federal Council from 1993 to 2002, representing the Canton of Geneva.
She was elected to the Swis ...
in 1999.
In 1979 areas from the canton of
Bern attained independence from the Bernese, forming the new
canton of Jura
The Republic and Canton of Jura (french: République et canton du Jura), less formally the Canton of Jura or Canton Jura ( , ), is the newest (founded in 1979) of the 26 Swiss cantons, located in the northwestern part of Switzerland. The capital ...
. On 18 April 1999, the Swiss population and the cantons voted in favour of a completely revised
federal constitution.
In 2002 Switzerland became a full member of the United Nations, leaving
Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
as the last widely recognised state without full UN membership. Switzerland is a founding member of the
EFTA
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European U ...
but not the
European Economic Area
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the ''Agreement on the European Economic Area'', an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade As ...
(EEA). An application for membership in the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
was sent in May 1992, but did not advance since rejecting the EEA in December 1992
when Switzerland conducted a referendum on the EEA. Several referendums on the EU issue ensued; due to opposition from the citizens, the membership application was withdrawn. Nonetheless, Swiss law is gradually changing to conform with that of the EU, and the government signed
bilateral agreements with the European Union. Switzerland, together with Liechtenstein, has been surrounded by the EU since Austria's entry in 1995. On 5 June 2005, Swiss voters agreed by a 55% majority to join the
Schengen treaty
The Schengen Agreement ( , ) is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the t ...
, a result that EU commentators regarded as a sign of support.
In September 2020, a referendum calling for a vote to end the pact that allowed a free movement of people from the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
was introduced by the
Swiss People's Party (SPP). However, voters rejected the attempt to retake control of
immigration
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, a ...
, defeating the motion by a roughly 63%–37% margin.
On 9 February 2014, 50.3% of Swiss voters approved a ballot
initiative
In political science, an initiative (also known as a popular initiative or citizens' initiative) is a means by which a petition signed by a certain number of registered voters can force a government to choose either to enact a law or hold a ...
launched by the
Swiss People's Party (SVP/UDC) to
restrict immigration. This initiative was mostly backed by rural (57.6% approval) and suburban groups (51.2% approval), and isolated towns (51.3% approval) as well as by a strong majority (69.2% approval) in Ticino, while metropolitan centres (58.5% rejection) and the French-speaking part (58.5% rejection) rejected it. In December 2016, a political compromise with the EU was attained that eliminated quotas on EU citizens, but still allowed favourable treatment of Swiss-based job applicants.
On 27 September 2020, 62% of Swiss voters rejected the anti-free movement referendum by SVP.
Geography

Extending across the north and south side of the
Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Swi ...
in
west
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
-
central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, Switzerland encompasses diverse landscapes and climates across its .
Switzerland lies between latitudes
45° and
48° N, and longitudes
5° and
11° E. It contains three basic topographical areas: the
Swiss Alps to the south, the Swiss Plateau or Central Plateau, and the
Jura mountains on the west. The Alps are a mountain range running across the central and south of the country, constituting about 60% of the country's area. The majority of the population live on the Swiss Plateau. The Swiss Alps host many glaciers, covering . From these originate the headwaters of several major rivers, such as the
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
,
Inn
Inns are generally establishments or buildings where travelers can seek lodging, and usually, food and drink. Inns are typically located in the country or along a highway; before the advent of motorized transportation they also provided accommo ...
,
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
and
Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
, which flow in the four cardinal directions, spreading across Europe. The hydrographic network includes several of the largest bodies of fresh water in Central and Western Europe, among which are
Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
(Lac Léman in French),
Lake Constance (Bodensee in German) and
Lake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; it, Lago Maggiore ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh Maggior; pms, Lagh Magior; literally 'Greater Lake') or Verbano (; la, Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest l ...
. Switzerland has more than 1500 lakes and contains 6% of Europe's freshwater stock. Lakes and glaciers cover about 6% of the national territory. Lake Geneva is the largest lake and is shared with France. The Rhône is both the main source and outflow of Lake Geneva. Lake Constance is the second largest and, like Lake Geneva, an intermediate step by the Rhine at the border with Austria and Germany. While the Rhône flows into the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
at the French
Camargue
Camargue (, also , , ; oc, label= Provençal, Camarga) is a region of France located south of Arles, between the Mediterranean Sea and the two arms of the Rhône delta. The eastern arm is called the ''Grand Rhône''; the western one is the '' ...
region and the Rhine flows into the
North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea, epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the ...
at
Rotterdam
Rotterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Rotte'') is the second largest city and municipality in the Netherlands. It is in the province of South Holland, part of the North Sea mouth of the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta, via the ''"Ne ...
, about apart, both springs are only about apart in the Swiss Alps.
Forty-eight mountains are or higher in height.
At ,
Monte Rosa
:
, other_name = Monte Rosa massif
, translation = Mount Rose
, photo = Dufourspitze (Monte Rosa) and Monte Rosa Glacier as seen from Gornergrat, Wallis, Switzerland, 2012 August.jpg
, photo_caption = Central Mon ...
is the highest, although the
Matterhorn
The (, ; it, Cervino, ; french: Cervin, ; rm, Matterhorn) is a mountain of the Alps, straddling the main watershed and border between Switzerland and Italy. It is a large, near-symmetric pyramidal peak in the extended Monte Rosa area of the ...
() is the best known. Both are located within the
Pennine Alps
The Pennine Alps (german: Walliser Alpen, french: Alpes valaisannes, it, Alpi Pennine, la, Alpes Poeninae), also known as the Valais Alps, are a mountain range in the western part of the Alps. They are located in Switzerland (Valais) and Italy ...
in the canton of
Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, on the border with Italy. The section of the
Bernese Alps
, topo_map= Swiss Federal Office of Topography swisstopo
, photo=BerneseAlps.jpg
, photo_caption=The Eiger, Mönch, and Jungfrau
, country= Switzerland
, subdivision1_type= Cantons
, subdivision1=
, parent= Western Alps
, borders_on=
, ...
above the deep glacial
Lauterbrunnen
, neighboring_municipalities= Aeschi bei Spiez, Blatten (Lötschen) (VS), Fieschertal (VS), Grindelwald, Gündlischwand, Kandersteg, Lütschental, Reichenbach im Kandertal, Saxeten, Wilderswil
, twintowns =
}
Lauterbrunnen is a village ...
valley, containing 72 waterfalls, is well known for the
Jungfrau
The Jungfrau ( "maiden, virgin"), at is one of the main summits of the Bernese Alps, located between the northern canton of Bern and the southern canton of Valais, halfway between Interlaken and Fiesch. Together with the Eiger and Mönch, the Ju ...
()
Eiger and
Mönch
The Mönch (, German: "monk") at is a mountain in the Bernese Alps, in Switzerland. Together with the Eiger and the Jungfrau, it forms a highly recognisable group of mountains, visible from far away.
The Mönch lies on the border between the c ...
peaks, and its many picturesque valleys. In the southeast the long
Engadin
The Engadin or Engadine ( rm, ;This is the name in the two Romansh idioms that are spoken in the Engadin, Vallader and Puter, as well as in Sursilvan and Rumantsch Grischun. In Surmiran, the name is ''Nagiadegna'', and in Sutsilvan, it is ...
Valley, encompassing
St. Moritz, is also well known; the highest peak in the neighbouring
Bernina Alps
The Bernina Range is a mountain range in the Alps of eastern Switzerland and northern Italy. It is considered to be part of the Rhaetian Alps within the Central Eastern Alps. It is one of the highest ranges of the Alps, covered with many glaciers. ...
is
Piz Bernina
Piz Bernina ( Romansh, it, Pizzo Bernina, ) is the highest mountain in the Eastern Alps, the highest point of the Bernina Range, and the highest peak in the Rhaetian Alps. It rises and is located south of Pontresina and near the major Alpine ...
().
The Swiss Plateau has greater open and hilly landscapes, partly forested, partly open pastures, usually with grazing herds or vegetable and fruit fields, but it is still hilly. Large lakes and the biggest Swiss cities are found there.
Switzerland contains two small
enclaves:
Büsingen belongs to Germany, while
Campione d'Italia
Campione d'Italia ( Comasco: , ) is a ''comune'' of the Province of Como in the Lombardy region of Italy and an enclave surrounded by the Swiss canton of Ticino (it is also an exclave). At its closest, the enclave is less than from the rest ...
belongs to Italy. Switzerland has no exclaves.
Climate

The Swiss climate is generally
temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
, but can vary greatly across localities,
from glacial conditions on the mountaintops to the near-
Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
at Switzerland's southern tip. Some valley areas in the southern part of Switzerland offer cold-hardy palm trees. Summers tend to be warm and humid at times with periodic rainfall, ideal for pastures/grazing. The less humid winters in the mountains may see weeks-long intervals of stable conditions. At the same time, the lower lands tend to suffer from
inversion during such periods, hiding the sun.
A weather phenomenon known as the
föhn (with an identical effect to the
chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
) can occur any time and is characterised by an unexpectedly warm wind, bringing low relative humidity air to the north of the Alps during rainfall periods on the south-facing slopes. This works both ways across the alps but is more efficient if blowing from the south due to the steeper step for oncoming wind. Valleys running south to north trigger the best effect. The driest conditions persist in all inner alpine valleys that receive less rain because arriving clouds lose a lot of their moisture content while crossing the mountains before reaching these areas. Large alpine areas such as
Graubünden remain drier than pre-alpine areas, and as in the main valley of the
Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, wine grapes are grown there.
The wettest conditions persist in the high Alps and in the
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
canton, which has much sun yet heavy bursts of rain from time to time.
Precipitation tends to be spread moderately throughout the year, with a peak in summer. Autumn is the driest season, winter receives less precipitation than summer, yet the weather patterns in Switzerland are not in a stable climate system. They can vary from year to year with no strict and predictable periods.
Environment
Switzerland contains two terrestrial ecoregions:
Western European broadleaf forests
The Western European broadleaf forests is an ecoregion in Western Europe, and parts of the Alps. It comprises temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, that cover large areas of France, Germany and the Czech Republic and more moderately sized parts ...
and
Alps conifer and mixed forests.
Switzerland's many small valleys separated by high mountains often host unique ecologies. The mountainous regions themselves offer a rich range of plants not found at other altitudes. The climatic, geological and topographical conditions of the alpine region make for a fragile ecosystem that is particularly sensitive to
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
.
According to the
2014 Environmental Performance Index, Switzerland ranks first among 132 nations in safeguarding the environment, due to its high scores on environmental public health, its heavy reliance on renewable sources of energy (
hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
and
geothermal energy), and its level of
greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and ...
. In 2020 it was ranked third out of 180 countries. The country pledged to cut
GHG emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and larg ...
by 50% by 2030 compared to the level of 1990 and plans to reach zero emissions by 2050.
However, access to
biocapacity
The biocapacity or biological capacity of an ecosystem is an estimate of its production of certain biological materials such as natural resources, and its absorption and filtering of other materials such as carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Bio ...
in Switzerland is far lower than the world average. In 2016, Switzerland had 1.0 hectares
of biocapacity per person within its territory, 40 percent less than world average of 1.6. In contrast, in 2016, Swiss consumption required 4.6 hectares of biocapacity – their
ecological footprint, 4.6 times as much as Swiss territory can support. The remainder comes from other countries and the shared resources (such as the atmosphere impacted by greenhouse gas emissions).
Switzerland had a 2019
Forest Landscape Integrity Index
The Forest Landscape Integrity Index (FLII) is an annual global index of forest condition measured by degree of anthropogenic modification. Created by a team of 48 scientists, the FLII, in its measurement of 300m pixels of forest across the globe ...
mean score of 3.53/10, ranking it 150th globally out of 172 countries.
Urbanisation

Between two-thirds and three-quarters of the population live in urban areas.
[Städte und Agglomerationen unter der Lupe](_blank)
admin.ch. Retrieved on 26 June 2009 Switzerland went from a largely rural country to an urban one from 1930 to 2000. After 1935 urban development claimed as much of the Swiss landscape as it did during the prior 2,000 years.
Urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
affects the plateau, the Jura and the Alpine foothills, raising concerns about land use. During the 21st century, population growth in urban areas is higher than in the countryside.
Switzerland has a dense network of complementary large, medium and small towns.
The plateau is densely populated with about 450 people per km
2 and the landscape shows uninterrupted signs of human presence. The weight of the largest metropolitan areas –
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
,
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
–
Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
,
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
and
Bern – tend to increase.
The importance of these urban areas is greater than their population suggests.
These urban centers are recognised for their high quality of life.
The average
population density
Population density (in agriculture: Stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical ...
in 2019 was .
[ ''Note: page number refers to report pagination; PDF viewer displays pages two numbers higher.''] In the largest canton by area,
Graubünden, lying entirely in the Alps, population density falls to .
In the
canton of Zürich, with its large urban capital, the density is .
Government and politics

The
Federal Constitution adopted in 1848 is the legal foundation of Switzerland's federal state.
A new Swiss Constitution was adopted in 1999 that did not introduce notable changes to the federal structure. It outlines rights of individuals and citizen participation in public affairs, divides the powers between the Confederation and the cantons and defines federal jurisdiction and authority. Three main bodies govern on the federal level:
the
bicameral parliament (legislative), the
Federal Council (executive) and the
Federal Court (judicial).
Parliament
The
Swiss Parliament
The Federal Assembly (german: Bundesversammlung, french: Assemblée fédérale, it, Assemblea federale, rm, Assamblea federala), also known as the Swiss parliament (''Parlament'', ''Parlement'', ''Parlamento''), is Switzerland's federal legi ...
consists of two houses: the
Council of States which has 46 representatives (two from each canton and one from each
half-canton) who are elected under a system determined by each canton, and the
National Council, which consists of 200 members who are elected under a system of
proportional representation
Proportional representation (PR) refers to a type of electoral system under which subgroups of an electorate are reflected proportionately in the elected body. The concept applies mainly to geographical (e.g. states, regions) and political divis ...
, reflecting each canton's population. Members serve part-time for 4 years (a ''Milizsystem'' or
citizen legislature
A citizen legislature is a legislative chamber made up primarily of citizens who have a full-time occupation besides being a legislator. Such citizen legislatures can be found on the state level, as in some U.S. states, or on the national level as ...
).
When both houses are in joint session, they are known collectively as the
Federal Assembly. Through
referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
s, citizens may challenge any law passed by parliament and, through
initiative
In political science, an initiative (also known as a popular initiative or citizens' initiative) is a means by which a petition signed by a certain number of registered voters can force a government to choose either to enact a law or hold a ...
s, introduce amendments to the federal constitution, thus making Switzerland a
direct democracy.
Federal Council

The Federal Council directs the federal government, the
federal administration, and serves as a collective
Head of State
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state Foakes, pp. 110–11 " he head of statebeing an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and l ...
. It is a collegial body of seven members, elected for a four-year term by the Federal Assembly, which also oversees the council. The
President of the Confederation is elected by the Assembly from among the seven members, traditionally in rotation and for a one-year term; the President chairs the government and executes representative functions. The president is a ''
primus inter pares'' with no additional powers and remains the head of a department within the administration.
The government has been a coalition of the four major political parties since 1959, each party having a number of seats that roughly reflects its share of the electorate and representation in the federal parliament. The classic distribution of 2 CVP/PDC, 2 SPS/PSS, 2 FDP/PRD and 1 SVP/UDC as it stood from 1959 to 2003 was known as the "
magic formula". Following the
2015 Federal Council elections, the seven seats in the Federal Council were distributed as follows:
* 1 seat for the
Christian Democratic People's Party (CVP/PDC),
* 2 seats for the
Free Democratic Party (FDP/PRD),
* 2 seats for the
Social Democratic Party (SPS/PSS),
* 2 seats for the
Swiss People's Party (SVP/UDC).
Supreme Court
The function of the Federal Supreme Court is to hear appeals against rulings of cantonal or federal courts. The judges are elected by the Federal Assembly for six-year terms.
Direct democracy
 Direct democracy
Direct democracy and
federalism are hallmarks of the Swiss political system.
Swiss citizens are subject to three legal jurisdictions: the municipality, canton and federal levels. The 1848 and 1999 Swiss Constitutions define a system of direct democracy (sometimes called half-direct or representative direct democracy because it includes institutions of a
representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of represe ...
). The instruments of this system at the federal level, known as popular rights (german: Volksrechte, french: droits populaires, it, diritti popolari),
include the right to submit a federal initiative and a referendum, both of which may overturn parliamentary decisions.
By calling a federal referendum, a group of citizens may challenge a law passed by parliament by gathering 50,000 signatures against the law within 100 days. If so, a national vote is scheduled where voters decide by a
simple majority whether to accept or reject the law. Any eight cantons can also call a constitutional referendum on federal law.
Similarly, the federal ''constitutional initiative'' allows citizens to put a
constitutional amendment to a national vote, if 100,000 voters sign the proposed amendment within 18 months. The Federal Council and the Federal Assembly can supplement the proposed amendment with a counterproposal. Then, voters must indicate a preference on the ballot if both proposals are accepted. Constitutional amendments, whether introduced by initiative or in parliament, must be accepted by a
double majority
A double majority is a voting system which requires a majority of votes according to two separate criteria. The mechanism is usually used to require strong support for any measure considered to be of great importance. Typically in legislative b ...
of the national popular vote and the popular cantonal votes.
Cantons
The Swiss Confederation consists of 26 cantons:
The cantons are
federated state
A federated state (which may also be referred to as a state, a province, a region, a canton, a land, a governorate, an oblast, an emirate or a country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states d ...
s. They have a permanent constitutional status and, in comparison with other countries, a high degree of independence. Under the Federal Constitution, all 26 cantons are equal in status, except that 6 (referred to often as the
half-cantons) are represented by one councillor instead of two in the
Council of States and have only half a cantonal vote with respect to the required cantonal majority in
referendums on constitutional amendments. Each canton has its own constitution and its own parliament, government, police and courts.
However, considerable differences define the individual cantons, particularly in terms of population and geographical area. Their populations vary between 16,003 (Appenzell Innerrhoden) and 1,487,969 (Zürich), and their area between (Basel-Stadt) and (
Grisons).
Municipalities
As of 2018 the cantons comprised 2,222 municipalities.
Federal City
Until 1848, the loosely coupled Confederation did not have a central political organisation. Issues thought to affect the whole Confederation were the subject of periodic meetings in various locations.

In 1848, the federal constitution provided that details concerning federal institutions, such as their locations, should be addressed by the
Federal Assembly (BV 1848 Art. 108). Thus on 28 November 1848, the Federal Assembly voted in the majority to locate the seat of government in Bern and, as a prototypical federal compromise, to assign other federal institutions, such as the
Federal Polytechnical School (1854, the later ETH) to Zürich, and other institutions to Lucerne, such as the later
SUVA (1912) and the Federal Insurance Court (1917).
Other federal institutions were subsequently attributed to
Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
(
Federal Supreme Court in 1872, and
EPFL in 1969),
Bellinzona
Bellinzona ( , , Ticinese ; french: Bellinzone ; german: Bellenz ; rm, Blizuna )is a municipality, a historic Swiss town, and the capital of the canton of Ticino in Switzerland. The town is famous for its three castles (Castelgrande, Montebell ...
(
Federal Criminal Court, 2004), and
St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
(
Federal Administrative Court and
Federal Patent Court, 2012).
The 1999 Constitution does not mention a Federal City and the Federal Council has yet to address the matter. Thus as of 2022, no city in Switzerland has the official status either of capital or of Federal City. Nevertheless, Bern is commonly referred to as "Federal City" (german: Bundesstadt, french: ville fédérale, it, città federale).
Foreign relations and international institutions

Traditionally, Switzerland avoids alliances that might entail military, political, or direct economic action and has been neutral since the end of its
expansion in 1515. Its
policy of neutrality
A neutral country is a state that is neutral towards belligerents in a specific war or holds itself as permanently neutral in all future conflicts (including avoiding entering into military alliances such as NATO, CSTO or the SCO). As a type of ...
was internationally recognised at the
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
in 1815.
Swiss neutrality
Swiss neutrality is one of the main principles of Switzerland's foreign policy which dictates that Switzerland is not to be involved in armed or political conflicts between other states. This policy is self-imposed and designed to ensure external ...
has been questioned at times. In 2002 Switzerland became a full member of the
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
.
It was the first state to join it by
referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
. Switzerland maintains diplomatic relations with almost all countries and historically has served as an intermediary between other states.
Switzerland is not a member of the
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
; the Swiss people have consistently rejected membership since the early 1990s.
However, Switzerland does participate in the
Schengen Area.

Many international institutions have headquarters in Switzerland, in part because of its policy of neutrality.
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
is the birthplace of the
Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, the
Geneva Conventions
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conve ...
and, since 2006, hosts the
United Nations Human Rights Council
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), CDH is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. ...
. Even though Switzerland is one of the most recent countries to join the United Nations, the
Palace of Nations
The Palace of Nations (french: Palais des Nations, ) is the home of the United Nations Office at Geneva, located in Geneva, Switzerland. It was built between 1929 and 1938 to serve as the headquarters of the League of Nations. It has served ...
in Geneva is the second biggest centre for the United Nations after New York. Switzerland was a founding member and hosted the
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
.
Apart from the United Nations headquarters, the Swiss Confederation is host to many UN agencies, including the World Health Organization (
WHO
Who or WHO may refer to:
* Who (pronoun), an interrogative or relative pronoun
* Who?, one of the Five Ws in journalism
* World Health Organization
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Who, a creature in the Dr. Seuss book '' Horton He ...
), the International Labour Organization (
ILO), the International Telecommunication Union (
ITU), the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (
UNHCR
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrat ...
) and about 200 other international organisations, including the
World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
and the
World Intellectual Property Organization
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO; french: link=no, Organisation mondiale de la propriété intellectuelle (OMPI)) is one of the 15 specialized agencies of the United Nations (UN). Pursuant to the 1967 Convention Establishi ...
.
The annual meetings of the
World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental and lobbying organisation based in Cologny, canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German engineer and economist Klaus Schwab. The foundation, ...
in
Davos bring together business and political leaders from Switzerland and foreign countries to discuss important issues. The headquarters of the
Bank for International Settlements
The Bank for International Settlements (BIS) is an international financial institution owned by central banks that "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks".
The BIS carries out its work thr ...
(BIS) moved to
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
in 1930.
Many sports federations and organisations are located in the country, including the
International Handball Federation
The International Handball Federation (IHF) is the administrative and controlling body for handball and beach handball. IHF is responsible for the organisation of handball's major international tournaments, notably the IHF World Men's Handball ...
in Basel, the
International Basketball Federation
The International Basketball Federation (FIBA ; French: ) is an association of national organizations which governs the sport of basketball worldwide. Originally known as the (hence FIBA), in 1989 it dropped the word ''amateur'' from its nam ...
in Geneva, the Union of European Football Associations (
UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
) in
Nyon
Nyon (; outdated German: or ; outdated Italian: , ) is a municipality in Nyon District in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland. It is located some 25 kilometers north east of Geneva's city centre, and since the 1970s it has become part of the Ge ...
, the International Federation of Association Football (
FIFA) and the
International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
both in
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, the
International Cycling Union
The ''Union Cycliste Internationale'' (UCI; ; en, International Cycling Union) is the world governing body for sports cycling and oversees international competitive cycling events. The UCI is based in Aigle, Switzerland.
The UCI issues racing ...
in
Aigle
, neighboring_municipalities= Vaud: Yvorne, Leysin, Ormont-Dessous, Ollon; Valais: Vouvry, Collombey-Muraz
, twintowns = L'Aigle (France), Tübingen (Germany), Bassersdorf (Switzerland)
}
Aigle ( French for "eagle", ; frp, Âgllo) is ...
, and the
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
in
Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
.
Switzerland is scheduled to become a member of the
United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
for the 2023–2024 period.
Switzerland and the European Union
Although not a member, Switzerland maintains relationships with the EU and European countries through bilateral agreements. The Swiss have brought their economic practices largely into conformity with those of the EU, in an effort to compete internationally.
EU membership faces considerable negative popular sentiment. It is opposed by the conservative
SVP party, the largest party in the National Council, and not advocated by several other political parties. The membership application was formally withdrawn in 2016. The western French-speaking areas and the urban regions of the rest of the country tend to be more pro-EU, but do not form a significant share of the population.

An Integration Office operates under the
Department of Foreign Affairs and the
Department of Economic Affairs. Seven bilateral agreements liberalised trade ties, taking effect in 2001. This first series of bilateral agreements included the free movement of persons. A second series of agreements covering nine areas was signed in 2004, including the
Schengen Treaty
The Schengen Agreement ( , ) is a treaty which led to the creation of Europe's Schengen Area, in which internal border checks have largely been abolished. It was signed on 14 June 1985, near the town of Schengen, Luxembourg, by five of the t ...
and the
Dublin Convention.
In 2006, a referendum approved 1 billion francs of supportive investment in Southern and Central European countries in support of positive ties to the EU as a whole. A further referendum will be needed to approve 300 million francs to support Romania and Bulgaria and their recent admission.
The Swiss have faced EU and international pressure to reduce
banking secrecy
Banking secrecy, alternately known as financial privacy, banking discretion, or bank safety,Guex (2000), p. 240 is a conditional agreement between a bank and its clients that all foregoing activities remain secure, confidential, and private. Mos ...
and raise tax rates to parity with the EU. Preparatory discussions involve four areas: the electricity market, participation in project
Galileo, cooperating with the
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control
The European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) is an agency of the European Union (EU) whose mission is to strengthen Europe's defences against infectious diseases. It covers a wide spectrum of activities, such as: surveillance, ...
and certificates of origin for food products.
Switzerland is a member of the Schengen passport-free zone. Land
border checkpoint
A border checkpoint is a location on an international border where travelers or goods are inspected and allowed (or denied) passage through. Authorization often is required to enter a country through its borders. Access-controlled borders ofte ...
s apply on to goods movements, but not people.
Military

The
Swiss Armed Forces
The Swiss Armed Forces (german: Schweizer Armee, french: Armée suisse, it, Esercito svizzero, rm, Armada svizra; ) operates on land and in the air, serving as the primary armed forces of Switzerland. Under the country's militia system, re ...
, including the
Land Forces
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islan ...
and the
Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
, are
composed mostly of conscripts, male citizens aged from 20 to 34 (in exceptional cases up to 50) years. Being a
landlocked country, Switzerland has no navy; however, on lakes bordering neighbouring countries, armed boats patrol. Swiss citizens are prohibited from serving in foreign armies, except for the
Swiss Guards of the
Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
, or if they are
dual citizen
Dual or Duals may refer to:
Paired/two things
* Dual (mathematics), a notion of paired concepts that mirror one another
** Dual (category theory), a formalization of mathematical duality
*** see more cases in :Duality theories
* Dual (grammatical ...
s of a foreign country and reside there.
The Swiss militia system stipulates that soldiers keep their army-issued equipment, including personal weapons, at home. Some organisations and political parties find this practice controversial. Women can serve voluntarily. Men usually receive military conscription orders for training at the age of 18. About two-thirds of young Swiss are found suitable for service; for the others, various forms of alternative service are available. Annually, approximately 20,000 persons are trained in recruit centres for 18 to 21 weeks. The reform "Army XXI" was adopted by popular vote in 2003, replacing "Army 95", reducing the rolls from 400,000 to about 200,000. Of those, 120,000 are active in periodic Army training, and 80,000 are non-training reserves.
The newest reform of the military, WEA/DEVA/USEs, started in 2019 and was expected to reduce the number of army personnel to 100,000 by the end of 2022.

Overall, three general mobilisations have been declared to ensure the integrity and neutrality of Switzerland. The first one was held in response to the
Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71. The second was in response to the
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
outbreak in August 1914. The third mobilisation took place in September 1939 in response to the
German attack on Poland.
Because of its neutrality policy, the Swiss army does not take part in armed conflicts in other countries, but joins some peacekeeping missions. Since 2000 the armed force department has maintained the
Onyx
Onyx primarily refers to the parallel banded variety of chalcedony, a silicate mineral. Agate and onyx are both varieties of layered chalcedony that differ only in the form of the bands: agate has curved bands and onyx has parallel bands. The ...
intelligence gathering system to monitor satellite communications.
Gun politics in Switzerland
Firearms regulation in Switzerland allows the acquisition of semi-automatic, and – with a may-issue permit – fully automatic firearms, by Swiss citizens and foreigners with or without permanent residence.The law of 1997 (SR 514.54) made ...
are unique in Europe in that 2–3.5 million guns are in the hands of civilians, giving the nation an estimate of 28–41 guns per 100 people.
It is worth noting that as per the Small Arms Survey, only 324,484 guns are owned by the military. Only 143,372 are in the hands of soldiers. However, ammunition is no longer issued.
Economy and labour law



Switzerland has a stable, prosperous and high-tech economy. It is the world's wealthiest country per capita in multiple rankings. The country ranks as one of the
least corrupt countries in the world, while
its banking sector is rated as "
one of the most corrupt in the world". It has the world's
twentieth largest economy by nominal
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
and the
thirty-eighth largest by
purchasing power parity. It is the
seventeenth largest exporter. Zürich and Geneva are regarded as
global cities, ranked as
Alpha and Beta respectively. Basel is the capital of Switzerland's pharmaceutical industry, hosting
Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
,
Roche
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche, is a Swiss multinational healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on the SIX ...
, and many other players. It is one of the world's most important centres for the life sciences industry.
Switzerland had the highest European rating in the
Index of Economic Freedom 2010, while also providing significant public services. On a per capita basis, nominal GDP is higher than those of the larger Western and Central European economies and Japan,
while
adjusted for purchasing power, Switzerland ranked 11th in 2017, fifth in 2018 and ninth in 2020.
The 2016 World Economic Forum's
Global Competitiveness Report
The ''Global Competitiveness Report'' (GCR) is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. Since 2004, the ''Global Competitiveness Report'' ranks countries based on the Global Competitiveness Index, developed by Xavier Sala-i-Martin an ...
ranked Switzerland's economy as the world's most competitive; as of 2019, it ranks fifth globally. The
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
labeled it Europe's most innovative country and the most innovative country in the
Global Innovation Index
The Global Innovation Index is an annual ranking of countries by their capacity for, and success in, innovation, published by the World Intellectual Property Organization. It was started in 2007 by INSEAD and ''World Business'', a British ma ...
in 2022, as it had done in 2021, 2020 and 2019.
It ranked 20th of 189 countries in the
Ease of Doing Business Index
The ease of doing business index was an index created jointly by Simeon Djankov, Michael Klein, and Caralee McLiesh, three leading economists at the World Bank Group. The academic research for the report was done jointly with professors Edward ...
. Switzerland's slow growth in the 1990s and the early 2000s increased support for economic reforms and harmonisation with the European Union.
In 2020,
IMD placed Switzerland first in attracting skilled workers.
For much of the 20th century, Switzerland was the wealthiest country in Europe by a considerable margin (per capita GDP).
Switzerland has one of the world's largest
account balances as a percentage of GDP. In 2018, the canton of Basel-City had the highest GDP per capita, ahead of Zug and Geneva. According to
Credit Suisse, only about 37% of residents own their own homes, one of the lowest rates of
home ownership
Owner-occupancy or home-ownership is a form of housing tenure in which a person, called the owner-occupier, owner-occupant, or home owner, owns the home in which they live. The home can be a house, such as a single-family house, an apartment, c ...
in Europe. Housing and food price levels were 171% and 145% of the
EU-25
The largest expansion of the European Union (EU), in terms of territory, number of states, and population took place on 1 May 2004.
The simultaneous accessions concerned the following countries (sometimes referred to as the "A10" countries): C ...
index in 2007, compared to 113% and 104% in Germany.
[Swiss Statistical Yearbook 2008 by ]Swiss Federal Statistical Office
The Federal Statistical Office (FSO) is a Federal agency of the Swiss Confederation. It is the statistics office of Switzerland, situated in Neuchâtel and attached to the Federal Department of Home Affairs.
The Federal Statistical Office ...
Switzerland is home to several large multinational corporations. The largest by revenue are
Glencore,
Gunvor
Gunvor Group Ltd is a Cypriot-domiciled multinational commodity trading company registered in Cyprus, with its main trading office in Geneva, Switzerland. Gunvor also has trading offices in Singapore, the Bahamas, and Dubai, with a network of re ...
,
Nestlé
Nestlé S.A. (; ; ) is a Swiss multinational food and drink processing conglomerate corporation headquartered in Vevey, Vaud, Switzerland. It is the largest publicly held food company in the world, measured by revenue and other metrics, since ...
,
Mediterranean Shipping Company
Mediterranean Shipping Company S.A. (MSC) is an international shipping line founded by Gianluigi Aponte in Italy in 1970, with headquarters in Switzerland since 1978. The privately held company is owned by the Aponte family. It has been the lar ...
,
Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
,
Hoffmann-La Roche,
ABB
ABB Ltd. is a Swedish- Swiss multinational corporation headquartered in Zürich, Switzerland. The company was formed in 1988 when Sweden's Allmänna Svenska Elektriska Aktiebolaget (ASEA) and Switzerland's Brown, Boveri & Cie merged to crea ...
,
Mercuria Energy Group and
Adecco
The Adecco Group, is a Swiss-French company based in Zurich, Switzerland, and is the world's second largest Human Resources provider and temporary staffing firm, and a Fortune Global 500 company.
They directly employ 700,000 people a day ...
. Also, notable are
UBS AG
UBS Group AG is a multinational investment bank and financial services company founded and based in Switzerland. Co-headquartered in the cities of Zürich and Basel, it maintains a presence in all major financial centres as the largest Swis ...
,
Zurich Financial Services
Zurich Insurance Group Ltd is a Swiss insurance company, headquartered in Zürich, and the country's largest insurer. As of 2021, the group is the world's 112th largest public company according to ''Forbes'' Global 2000s list, and in 2011 it ran ...
,
Richemont
Compagnie Financière Richemont S.A., commonly known as Richemont, is a Switzerland-based luxury goods holding company founded in 1988 by South African businessman Johann Rupert. Through its various subsidiaries, Richemont produces and sells j ...
,
Credit Suisse,
Barry Callebaut
Barry Callebaut is a Belgian-Swiss cocoa processor and chocolate manufacturer, with an average annual production of 2.3 million tonnes of cocoa & chocolate (fiscal year 2021/2022).
It was created in 1996 through the merging of the Belgian ...
,
Swiss Re
Swiss Reinsurance Company Ltd,
Swiss Re. Retrieved on 18 January 2011. "Swiss Reinsurance Company Ltd ("Swiss Re") ...
,
Rolex
Rolex SA () is a British-founded Swiss watch designer and manufacturer based in Geneva, Switzerland. Founded in 1905 as ''Wilsdorf and Davis'' by Hans Wilsdorf and Alfred Davis in London, the company registered ''Rolex'' as the brand name of ...
,
Tetra Pak
Tetra Pak is a Swedish–Swiss multinational food packaging and processing company with head offices in Lund, Sweden, and Pully, Switzerland. The company offers packaging, filling machines and processing for dairy, beverages, cheese, ice crea ...
,
The Swatch Group
The Swatch Group Ltd is a Swiss manufacturer of watches and jewellery. The company was founded in 1983 by the merger of ASUAG and SSIH to move to manufacturing quartz-crystal watches to resolve the quartz crisis threatening the traditional Swi ...
and
Swiss International Air Lines
Swiss International Air Lines AG, colloquially known as SWISS, is the flag carrier of Switzerland, operating scheduled services in Europe and to North America, South America, Africa and Asia. Zurich Airport serves as its sole hub and Geneva ...
.
Switzerland's most important economic sector is manufacturing. Manufactured products include specialty
chemicals
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wit ...
,
health and pharmaceutical goods, scientific and precision
measuring instrument
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Est ...
s and
musical instruments. The largest exported goods are chemicals (34% of exported goods), machines/electronics (20.9%), and precision instruments/watches (16.9%).
The service sector – especially
banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Becau ...
and
insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge ...
,
commodities trading
A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products, such as cocoa, fruit and sugar. Hard commodities are mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing ...
,
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
, and
international organisations
An international organization or international organisation (see spelling differences), also known as an intergovernmental organization or an international institution, is a stable set of norms and rules meant to govern the behavior of states an ...
– is another important industry for Switzerland. Exported services amount to a third of exports.
Agricultural protectionism—a rare exception to Switzerland's free trade policies—contributes to high
food prices
Food prices refer to the average price level for food across countries, regions and on a global scale. Food prices have an impact on producers and consumers of food.
Price levels depend on the food production process, including food marketing ...
. Product market liberalisation is lagging behind many
EU countries according to the
OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
.
Apart from agriculture, economic and trade barriers between the European Union and Switzerland are minimal, and Switzerland has free trade agreements with many countries. Switzerland is a member of the
European Free Trade Association (EFTA).
Taxation and government spending
Switzerland is a
tax haven
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or n ...
.
The private sector economy dominates. It features low tax rates;
tax revenue to GDP ratio is one of the smallest of
developed countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
. The
Swiss Federal budget reached 62.8 billion Swiss francs in 2010, 11.35% of GDP; however, canton and municipality budgets are not counted as part of the federal budget. Total
government spending is closer to 33.8% of GDP. The main sources of income for the federal government are the
value-added tax
A value-added tax (VAT), known in some countries as a goods and services tax (GST), is a type of tax that is assessed incrementally. It is levied on the price of a product or service at each stage of production, distribution, or sale to the en ...
(33% of tax revenue) and the direct federal tax (29%). The main areas of expenditure are in social welfare and finance/taxes. The expenditures of the Swiss Confederation have been growing from 7% of GDP in 1960 to 9.7% in 1990 and 10.7% in 2010. While the social welfare and finance sectors and tax grew from 35% in 1990 to 48.2% in 2010, a significant reduction of expenditures has been occurring in agriculture and national defence; from 26.5% to 12.4% (estimation for the year 2015).
Labour force
Slightly more than 5 million people work in Switzerland; about 25% of employees belonged to a trade union in 2004. Switzerland has a more flexible
labor market than neighbouring countries and the
unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the refere ...
rate is consistently low. The unemployment rate increased from 1.7% in June 2000 to 4.4% in December 2009. It then decreased to 3.2% in 2014 and held steady for several years, before further dropping to 2.5% in 2018 and 2.3% in 2019. Population growth (from net immigration) reached 0.52% of population in 2004, increased in the following years before falling to 0.54% again in 2017.
The
foreign citizen population was 28.9% in 2015, about the same as in Australia.
In 2016, the median monthly gross income in Switzerland was 6,502 francs per month (equivalent to US$6,597 per month).
After rent, taxes and pension contributions, plus spending on goods and services, the average household has about 15% of its gross income left for savings. Though 61% of the population made less than the mean income, income inequality is relatively low with a
Gini coefficient of 29.7, placing Switzerland among the top 20 countries. In 2015, the richest 1% owned 35% of the wealth. Wealth inequality increased through 2019.
About 8.2% of the population live below
the national poverty line, defined in Switzerland as earning less than CHF3,990 per month for a household of two adults and two children, and a further 15% are at risk of poverty. Single-parent families, those with no post-compulsory education and those out of work are among the most likely to live below the poverty line. Although work is considered a way out of poverty, some 4.3% are considered working poor. One in ten jobs in Switzerland is considered low-paid; roughly 12% of Swiss workers hold such jobs, many of them women and foreigners.
Education and science


Education in Switzerland is diverse, because the
constitution of Switzerland delegates the operation for the school system to the
cantons.
Public and private schools are available, including many private international schools.
Primary education
The minimum age for primary school is about six years, but most cantons provide a free "children's school" starting at age four or five.
Primary school continues until grade four, five or six, depending on the school. Traditionally, the first foreign language in school was one of the other Swiss languages, although, in 2000, English was elevated in a few cantons.
At the end of primary school or at the beginning of secondary school, pupils are assigned according to their capacities into one of several sections (often three). The fastest learners are taught advanced classes to prepare for further studies and the
matura
or its translated terms (''Mature'', ''Matur'', , , , , , ) is a Latin name for the secondary school exit exam or "maturity diploma" in various European countries, including Albania, Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, C ...
,
while other students receive an education adapted to their needs.
Tertiary education
Switzerland hosts
12 universities, ten of which are maintained at
cantonal
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Con ...
level and usually offer non-technical subjects. It ranked 87th on the 2019
Academic Ranking of World Universities. The largest is the
University of Zurich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 f ...
with nearly 25,000 students. The
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich
(colloquially)
, former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule
, image = ETHZ.JPG
, image_size =
, established =
, type = Public
, budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021)
, rector = Günther Dissertori
, president = Joël Mesot
, a ...
(ETHZ) and the
University of Zurich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 f ...
are listed 20th and 54th respectively, on the 2015
Academic Ranking of World Universities.
The federal government sponsors two institutes: the
Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich
(colloquially)
, former_name = eidgenössische polytechnische Schule
, image = ETHZ.JPG
, image_size =
, established =
, type = Public
, budget = CHF 1.896 billion (2021)
, rector = Günther Dissertori
, president = Joël Mesot
, a ...
(ETHZ) in
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
, founded in 1855 and the
École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
École may refer to:
* an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée)
* École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France
* École, Savoi ...
(EPFL) in
Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
, founded in 1969, formerly associated with the
University of Lausanne
The University of Lausanne (UNIL; french: links=no, Université de Lausanne) in Lausanne, Switzerland was founded in 1537 as a school of Protestant theology, before being made a university in 1890. The university is the second oldest in Switzer ...
.
Eight of the world's ten best
hotel school
Hospitality Management and Tourism is the study of the hospitality industry. A degree in the subject may be awarded either by a university college dedicated to the studies of hospitality management or a business school with a relevant departme ...
s are located in Switzerland. In addition, various
Universities of Applied Sciences are available. In business and management studies, the
University of St. Gallen, (HSG) is ranked 329th in the world according to
QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
and the
International Institute for Management Development
International Institute for Management Development (IMD) is a private business school in Lausanne, Switzerland specializes in executive education offering open enrollment programs for senior executives, as well as longer-term educational engageme ...
(IMD), was ranked first in open programmes worldwide''.''
[Financial Times Executive Education Rankings – Open Programs – 2015](_blank)
Retrieved 8 July 2015 Switzerland has the second highest rate (almost 18% in 2003) of foreign students in tertiary education, after Australia (slightly over 18%).
The
Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies
The Graduate Institute of International and Development Studies, or the Geneva Graduate Institute (french: Institut de hautes études internationales et du développement), abbreviated IHEID, is a government-accredited postgraduate institution ...
, located in
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
, is continental Europe's oldest graduate school of international and development studies. It is widely held to be one of its most prestigious.
Science
Switzerland has birthed many
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
laureates. They include
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein ( ; ; 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist, widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest and most influential physicists of all time. Einstein is best known for developing the theory ...
, who developed his
special relativity
In physics, the special theory of relativity, or special relativity for short, is a scientific theory regarding the relationship between space and time. In Albert Einstein's original treatment, the theory is based on two postulates:
# The laws ...
in Bern. Later,
Vladimir Prelog
Vladimir Prelog (23 July 1906 – 7 January 1998) was a Croatian-Swiss organic chemist who received the 1975 Nobel Prize in chemistry for his research into the stereochemistry of organic molecules and reactions. Prelog was born and grew up in ...
,
Heinrich Rohrer,
Richard Ernst,
Edmond Fischer,
Rolf Zinkernagel,
Kurt Wüthrich
Kurt Wüthrich (born 4 October 1938 in Aarberg, Canton of Bern) is a Swiss chemist/biophysicist and Nobel Chemistry laureate, known for developing nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) methods for studying biological macromolecules.
Education and ...
and
Jacques Dubochet
Jacques Dubochet (born 8 June 1942) is a retired Swiss biophysicist. He is a former researcher at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory in Heidelberg, Germany, and an honorary professor of biophysics at the University of Lausanne in Switzer ...
received Nobel science prizes. In total, 114 laureates across all fields have a relationship to Switzerland. The
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
has been awarded nine times to organisations headquartered in Switzerland.

Geneva and the nearby French department of
Ain
Ain (, ; frp, En) is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Named after the Ain river, it is bordered by the Saône and Rhône rivers. Ain is located on the country's eastern edge, on the Swiss border, where ...
co-host the world's largest
laboratory
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physic ...
,
CERN, dedicated to
particle physics
Particle physics or high energy physics is the study of fundamental particles and forces that constitute matter and radiation. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) an ...
research. Another important research centre is the
Paul Scherrer Institute
The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI) is a multi-disciplinary research institute for natural and engineering sciences in Switzerland. It is located in the Canton of Aargau in the municipalities Villigen and Würenlingen on either side of the River ...
.
Notable inventions include
lysergic acid diethylamide
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), also known colloquially as acid, is a potent psychedelic drug. Effects typically include intensified thoughts, emotions, and sensory perception. At sufficiently high dosages LSD manifests primarily mental, vi ...
(LSD),
diazepam
Diazepam, first marketed as Valium, is a medicine of the benzodiazepine family that acts as an anxiolytic. It is commonly used to treat a range of conditions, including anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal syndrome, muscle spasms, insomnia, ...
(Valium), the
scanning tunnelling microscope (Nobel prize) and
Velcro
Velcro, officially known as Velcro IP Holdings LLC and trading as Velcro Companies, is a British privately held company, founded by Swiss electrical engineer George de Mestral in the 1950s. It is the original manufacturer of hook-and-loop fast ...
. Some technologies enabled the exploration of new worlds such as the pressurised balloon of
Auguste Piccard and the
Bathyscaphe which permitted
Jacques Piccard
Jacques Piccard (28 July 19221 November 2008) was a Swiss oceanographer and engineer, known for having developed underwater submarines for studying ocean currents. In the Challenger Deep, he and Lt. Don Walsh of the United States Navy were the f ...
to reach the deepest point of the world's oceans.
The
Swiss Space Office
The Swiss Space Office (SSO) is the federal government's competence centre for national and international space matters. In its role it cooperates closely with other federal offices and is responsible for the preparation and implementation of the ...
has been involved in various space technologies and programmes. It was one of the 10 founders of
the European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
in 1975 and is the seventh largest contributor to the ESA budget. In the private sector, several companies participate in the space industry, such as
Oerlikon Space
RUAG Holding (originally Rüstungs Unternehmen Aktiengesellschaft; Joint Stock Defence Company) is a Swiss company specialising in aerospace engineering and the defence industry. Its headquarters are located in Bern, while it also has numerous pr ...
or Maxon Motors.
Energy

Electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
generated in Switzerland is 56% from
hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
and 39% from
nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
, producing negible CO
2. On 18 May 2003, two
anti-nuclear
The anti-nuclear movement is a social movement that opposes various nuclear technologies. Some direct action groups, environmental movements, and professional organisations have identified themselves with the movement at the local, nationa ...
referendums were defeated: ''Moratorium Plus'', aimed at forbidding the building of new
nuclear power plants (41.6% supported), and Electricity Without Nuclear (33.7% supported) after a moratorium expired in 2000. After the
Fukushima nuclear disaster
The was a nuclear accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Ōkuma, Fukushima, Japan. The proximate cause of the disaster was the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami, which occurred on the afternoon of 11 March 2011 ...
, in 2011 the government announced plans to end the use of nuclear energy in the following 2 or 3 decades. In November 2016, Swiss voters rejected a
Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation f ...
referendum to accelerate the phaseout of nuclear power (45.8% supported). The Swiss Federal Office of Energy (SFOE) is responsible for energy supply and energy use within the
Federal Department of Environment, Transport, Energy and Communications
The Federal Department of Environment, Transport, Energy and Communications (DETEC, german: Eidgenössisches Departement für Umwelt, Verkehr, Energie und Kommunikation, french: Département fédéral de l'environnement, des transports, de l'én ...
(DETEC). The agency supports the
2000-watt society initiative to cut the nation's energy use by more than half by 2050.
Transport

The densest rail network in Europe
spans and carries over 596 million passengers annually as of 2015.
In 2015, each Swiss resident travelled on average by rail, more than any other European country.
Virtually 100% of the network is electrified. 60% of the network is operated by the
Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS). Besides the second largest
standard gauge railway company,
BLS AG, two railways companies operate on
narrow gauge
A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge narrower than standard . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and .
Since narrow-gauge railways are usually built with tighter curves, smaller structu ...
networks: the
Rhaetian Railway
The Rhaetian Railway (german: Rhätische Bahn; it, Ferrovia retica; rm, Viafier retica), abbreviated RhB, is a Swiss transport company that owns the largest network of all private railway operators in Switzerland. Headquartered in Chur, the Rh ...
(RhB) in Graubünden, which includes some World Heritage lines, and the
Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn
The Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn is a narrow gauge railway line and a railway company (Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn AG, MGB) in Switzerland. The track width is . It was created in 2003 through an amalgamation of Furka Oberalp Bahn (FO) and BVZ Zermatt- ...
(MGB), which co-operates with RhB the
Glacier Express
The Glacier Express (GEX) is a direct train connecting railway stations of the two major mountain resorts of Zermatt and St. Moritz via Andermatt in the central Swiss Alps. The train is not an "express" in the sense of being a high-speed train ...
between
Zermatt
Zermatt () is a municipality in the district of Visp in the German-speaking section of the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It has a year-round population of about 5,800 and is classified as a town by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office (FSO) ...
and
St. Moritz/
Davos. Switzerland operates the
world's longest and deepest railway tunnel and the first flat, low-level route through the Alps, the
Gotthard Base Tunnel
, rm, Tunnel da basa dal Sogn Gottard
, image = 20141120 gotthard-basistunnel02-wikipedia-hannes-ortlieb.jpg
, image_size = 250
, caption = Turnout at Faido multifunction station
, line = Gotthard Line
, location = Switzerland ( Uri, Grisons and ...
, the largest part of the
New Railway Link through the Alps (NRLA) project.
Switzerland has a publicly managed, toll-free road network financed by highway permits as well as vehicle and
gasoline taxes. The Swiss autobahn/autoroute system requires the annual purchase of a
vignette
Vignette may refer to:
* Vignette (entertainment), a sketch in a sketch comedy
* Vignette (graphic design), decorative designs in books (originally in the form of leaves and vines) to separate sections or chapters
* Vignette (literature), short, i ...
(toll sticker)—for 40
Swiss francs—to use its roadways, including passenger cars and trucks. The Swiss autobahn/autoroute network stretches for and has one of the highest
motorway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
densities in the world.
Zurich Airport
Zürich Airport (), french: Aéroport de Zurich, it, Aeroporto di Zurigo, rm, Eroport da Turitg is the largest international airport of Switzerland and the principal hub of Swiss International Air Lines. It serves Zürich, Switzerland's la ...
is Switzerland's largest international flight gateway; it handled 22.8 million passengers in 2012. The other international airports are
Geneva Airport
Geneva Airport ,, german: Flughafen Genf, it, Aeroporto di Ginevra, rm, Eroport de Genevra formerly and still unofficially known as Cointrin Airport, is the international airport of Geneva, the second most populous city in Switzerland. It i ...
(13.9 million passengers in 2012),
EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg
EuroAirport Basel Mulhouse Freiburg IATA airport 3-letter codes for the French area, the Swiss area, and the metropolitan area, french: Aéroport de Bâle-Mulhouse-Fribourg, it, Aeroporto di Basilea-Mulhouse-Friburgo, rm, Eroport da Basilea-Mu ...
(located in France),
Bern Airport
The Regional Aerodrome Bern-Belp , marketed as ''Bern Airport'',, french: Aéroport de Berne, it, Aeroporto di Berna, rm, Eroport da Berna officially referred to as in German, is a regional aerodrome serving Bern, the de facto capital of Switz ...
,
Lugano Airport
Lugano Airport , german: Flughafen Lugano-Agno, french: Aéroport de Lugano, rm, Eroport da Lugano is a regional airport located west of the Swiss city of Lugano, approximately north of Milan, in the municipalities of Agno, Bioggio and Muzz ...
,
St. Gallen-Altenrhein Airport and
Sion Airport.
Swiss International Air Lines
Swiss International Air Lines AG, colloquially known as SWISS, is the flag carrier of Switzerland, operating scheduled services in Europe and to North America, South America, Africa and Asia. Zurich Airport serves as its sole hub and Geneva ...
is the flag carrier. Its main hub is Zürich, but it is legally domiciled in Basel.
Environment
Switzerland has one of the best environmental records among developed nations. It is a signatory to the
Kyoto Protocol. With Mexico and South Korea it forms the
Environmental Integrity Group (EIG).
The country is active in recycling and anti-littering programs and is one of the world's top recyclers, recovering 66% to 96% of recyclable materials, varying across the country. The 2014 Global Green Economy Index placed Switzerland among the top 10 green economies.
Switzerland has an economic system for garbage disposal, which is based mostly on recycling and energy-producing
incinerators. As in other European countries, the illegal disposal of garbage is heavily fined. In almost all Swiss municipalities, mandatory stickers or dedicated garbage bags allow the identification of disposable garbage.
Demographics

In common with other developed countries, the Swiss population increased rapidly during the industrial era, quadrupling between 1800 and 1990 and has continued to grow.
The population is about 8.7 million (2020 est.). Population growth was projected into 2035, due mostly to immigration. Like most of Europe, Switzerland faces an
ageing population
Population ageing is an increasing median age in a population because of declining fertility rates and rising life expectancy. Most countries have rising life expectancy and an ageing population, trends that emerged first in developed countries ...
, with a fertility rate close to
replacement level. Switzerland has one of the world's oldest populations, with an average age of 42.5 years.
Fourteen percent of men and 6.5% of women between 20 and 24 reported
consuming cannabis in the past 30 days, and 5 Swiss cities were listed among the top 10 European cities for
cocaine use as measured in wastewater.
Immigration
, resident foreigners made up 25.7%. Most of these (83%) were from European countries. Italy provided the largest single group of foreigners, providing 14.7% of total foreign population, followed closely by Germany (14.0%), Portugal (11.7%), France (6.6%), Kosovo (5.1%), Spain (3.9%), Turkey (3.1%),
North Macedonia
North Macedonia, ; sq, Maqedonia e Veriut, (Macedonia before February 2019), officially the Republic of North Macedonia,, is a country in Southeast Europe. It gained independence in 1991 as one of the successor states of Yugoslavia. It ...
(3.1%), Serbia (2.8%), Austria (2.0%), United Kingdom (1.9%), Bosnia and Herzegovina (1.3%) and Croatia (1.3%). Immigrants from
Sri Lanka (1.3%), most of them former
Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
* Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils
**Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia
* Tamil language, nativ ...
refugees, were the largest group of Asian origin (7.9%).
2021 figures show that 39.5% (compared to 34.7% in 2012) of the permanent resident population aged 15 or over (around 2.89 million), had an immigrant background. 38% of the population with an immigrant background (1.1 million) held Swiss citizenship.
In the 2000s, domestic and international institutions expressed concern about what was perceived as an increase in
xenophobia
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
. In reply to one critical report, the Federal Council noted that "racism unfortunately is present in Switzerland", but stated that the high proportion of foreign citizens in the country, as well as the generally successful integration of foreigners, underlined Switzerland's openness. A follow-up study conducted in 2018 reported that 59% considered
racism a serious problem in Switzerland. The proportion of the population that claimed to have been targeted by racial discrimination increased from 10% in 2014 to almost 17% in 2018, according to the Federal Statistical Office.
Largest cities
Languages

Switzerland has four
national language
A national language is a language (or language variant, e.g. dialect) that has some connection—de facto or de jure—with a nation. There is little consistency in the use of this term. One or more languages spoken as first languages in the te ...
s: mainly
German (spoken natively by 62.8% of the population in 2016);
French (22.9%) in the west; and
Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
(8.2%) in the south.
The fourth national language,
Romansh (0.5%), is a
Romance language
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language f ...
spoken locally in the southeastern trilingual
canton of Grisons
The Grisons () or Graubünden,Names include:
*german: (Kanton) Graubünden ;
* Romansh:
** rm, label=Sursilvan, (Cantun) Grischun
** rm, label= Vallader, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label= Puter, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label= Surmiran, (Can ...
, and is designated by Article 4 of the Federal Constitution as a national language along with German, French, and Italian. In Article 70 it is mentioned as an official language if the authorities communicate with persons who speak Romansh. However, federal laws and other official acts do not need to be decreed in Romansh.
In 2016, the languages most spoken at home among permanent residents aged 15 and older were
Swiss German (59.4%), French (23.5%),
Standard German (10.6%), and Italian (8.5%). Other languages spoken at home included
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(5.0%),
Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
(3.8%),
Albanian (3.0%),
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
(2.6%) and
Serbian and Croatian
Serbo-Croatian () – also called Serbo-Croat (), Serbo-Croat-Bosnian (SCB), Bosnian-Croatian-Serbian (BCS), and Bosnian-Croatian-Montenegrin-Serbian (BCMS) – is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language and the primary language of Ser ...
(2.5%). 6.9% reported speaking another language at home. In 2014 almost two-thirds (64.4%) of the permanent resident population indicated speaking more than one language regularly.
The federal government is obliged to communicate in the official languages, and in the federal parliament simultaneous translation is provided from and into German, French and Italian.
Aside from the official forms of their respective languages, the four linguistic regions of Switzerland also have local dialectal forms. The role played by dialects in each linguistic region varies dramatically: in German-speaking regions,
Swiss German dialects have become more prevalent since the second half of the 20th century, especially in the media, and are used as an everyday language for many, while the
Swiss variety of Standard German is almost always used instead of dialect for written communication (c.f.
diglossic usage of a language).
Conversely, in the French-speaking regions, local
Franco-Provençal
Franco-Provençal (also Francoprovençal, Patois or Arpitan) is a language within Gallo-Romance originally spoken in east-central France, western Switzerland and northwestern Italy.
Franco-Provençal has several distinct dialects and is separ ...
dialects have almost disappeared (only 6.3% of the population of Valais, 3.9% of Fribourg, and 3.1% of Jura still spoke dialects at the end of the 20th century), while in the Italian-speaking regions, the use of
Lombard dialects is mostly limited to family settings and casual conversation.
The principal official languages have terms not used outside of Switzerland, known as
Helvetism
Helvetisms (New Latin ''Helvetia'' "Switzerland" and ''-ism'') are features distinctive of Swiss Standard German, that distinguish it from Standard German. The most frequent Helvetisms are in vocabulary and pronunciation, but there are also some d ...
s. German Helvetisms are, roughly speaking, a large group of words typical of
Swiss Standard German that do not appear in
Standard German, nor in other German dialects. These include terms from Switzerland's surrounding language cultures (German ''Billett''
from French), from similar terms in another language (Italian ''azione'' used not only as ''act'' but also as ''discount'' from German ''Aktion'').
Swiss French
Swiss French (french: français de Suisse or ') is the variety of French spoken in the French-speaking area of Switzerland known as Romandy. French is one of the four official languages of Switzerland, the others being German, Italian, and ...
, while generally close to the French of France, also contains some Helvetisms. The most frequent characteristics of Helvetisms are in vocabulary, phrases, and pronunciation, although certain Helvetisms denote themselves as special in syntax and
orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
.
Duden
The Duden () is a dictionary of the Standard High German language, first published by Konrad Duden in 1880, and later by Bibliographisches Institut GmbH. The Duden is updated regularly with new editions appearing every four or five years. , ...
, the comprehensive German dictionary, contains about 3000 Helvetisms.
Current French dictionaries, such as the
Petit Larousse, include several hundred Helvetisms; notably, Swiss French uses different terms than that of France for the numbers 70 (''septante'') and 90 (''nonante'') and often 80 (''huitante'') as well.
Learning one of the other national languages is compulsory for all Swiss pupils, so many Swiss are supposed to be at least
bilingual, especially those belonging to linguistic minority groups. Because the largest part of Switzerland is German-speaking, many French, Italian, and Romansh speakers migrating to the rest of Switzerland and the children of those non-German-speaking Swiss born within the rest of Switzerland speak German. While learning one of the other national languages at school is important, most Swiss learn English to communicate to Swiss speakers other languages, as it is perceived as a neutral means of communication. English often functions as a
lingua franca.
Health
Swiss residents are required to buy
health insurance from private insurance companies, which in turn are required to accept every applicant. While the cost of the system is among the highest, its health outcomes compare well with other European countries; patients have been reported as in general, highly satisfied with it. In 2012, life expectancy at birth was 80.4 years for men and 84.7 years for women
– the world's highest.
However, spending on health at 11.4% of
GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
(2010) is on par with Germany and France (11.6%) and other European countries, but notably less than the US (17.6%).
From 1990, costs steadily increased.
It is estimated that one out of six Swiss persons suffers from
mental illness.
Culture

Swiss culture is characterised by diversity, which is reflected in diverse traditional customs. A region may be in some ways culturally connected to the neighbouring country that shares its language, all rooted in western
European culture
The culture of Europe is rooted in its art, architecture, film, different types of music, economics, literature, and philosophy. European culture is largely rooted in what is often referred to as its "common cultural heritage".
Definition ...
. The linguistically isolated
Romansh culture in
Graubünden in eastern Switzerland constitutes an exception. It survives only in the upper valleys of the Rhine and the Inn and strives to maintain its rare linguistic tradition.
Switzerland is home to notable contributors to literature, art, architecture, music and sciences. In addition, the country attracted creatives during times of unrest or war. Some 1000 museums are found in the country; more than tripling since 1950.
Among the most important cultural performances held annually are the
Paléo Festival
The Paléo Festival de Nyon, usually just called Paléo, is an annual rock festival held in Nyon, Switzerland. It started in a small way in 1976 as the Nyon Folk Festival. The first one was held in the village hall in Nyon. From 1977 until 1989, ...
,
Lucerne Festival
Lucerne Festival is one of the leading international festivals in the world of classical music and presents a series of classical music festivals based in Lucerne, Switzerland. Founded in 1938 by Ernest Ansermet and Walter Schulthess, it curren ...
, the
Montreux Jazz Festival
The Montreux Jazz Festival (formerly Festival de Jazz Montreux and Festival International de Jazz Montreux) is a music festival in Switzerland, held annually in early July in Montreux on the Lake Geneva shoreline. It is the second-largest annual ...
, the
Locarno International Film Festival
The Locarno Film Festival is an annual film festival, held every August in Locarno, Switzerland. Founded in 1946, the festival screens films in various competitive and non-competitive sections, including feature-length narrative, documentary, ...
and
Art Basel
Art Basel is a for-profit, privately owned and managed, international art fair staged annually in Basel, Switzerland; Miami Beach; Hong Kong and from 2022, Paris. Art Basel works in collaboration with the host city's local institutions to help ...
.
Alpine symbolism played an essential role in shaping Swiss history and the Swiss national identity.
Many alpine areas and
ski resort
A ski resort is a resort developed for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter sports. In Europe, most ski resorts are towns or villages in or adjacent to a ski area – a mountainous area with pistes (ski trails) and a ski lift system. In Nort ...
s attract visitors for
winter sports
Winter sports or winter activities are competitive sports or non-competitive recreational activities which are played on snow or ice. Most are variations of skiing, ice skating and sledding. Traditionally, such games were only played in cold are ...
as well as
hiking
Hiking is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century.AMATO, JOSEPH A. "Mind over Foot: Romantic Walking and Rambling." In ''On Foot: A Histor ...
and
mountain biking in summer. The quieter seasons are spring and autumn. A traditional pastoral culture predominate in many areas, and small farms are omnipresent in rural areas. Folk art is nurtured in organisations across the country. Switzerland most directly in appears in music, dance, poetry, wood carving, and embroidery. The
alphorn
The alphorn or alpenhorn or alpine horn is a labrophone, consisting of a straight several-meter-long wooden natural horn of conical bore, with a wooden cup-shaped mouthpiece. Traditionally the Alphorn was made of one single piece, or two par ...
, a trumpet-like musical instrument made of wood has joined
yodeling and the accordion as epitomes of traditional
Swiss music
Switzerland has long had a distinct cultural identity, despite its diversity of German, French, Italian, Romansh and other ethnicities. Religious and folk music dominated the country until the 17th century, with growth in production of other kin ...
.
Religion
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
is the predominant religion according to national surveys of Swiss Federal Statistical Office (about 67% of resident population in 2016–2018
and 75% of Swiss citizens), divided between the Catholic Church (35.8% of the population), the Swiss Reformed Church (23.8%), further
Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
churches (2.2%),
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
(2.5%), and other Christian denominations (2.2%).
Switzerland has no official
state religion, though most of the
cantons (except
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
and
Neuchâtel) recognise official churches, either the
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
or the
Swiss Reformed Church. These churches, and in some cantons the
Old Catholic Church
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches or Old Catholic movement designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the undivide ...
and
Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
congregations, are financed by official taxation of members.
In 2020, the Roman Catholic Church had 3,048,475 registered and
church tax
A church tax is a tax collected by the state from members of some religious denominations to provide financial support of churches, such as the salaries of its clergy and to pay the operating cost of the church.
The constitution of a number o ...
paying members (corresponding to 35.2% of the total population), while the Swiss Reformed Church had 2,015,816 members (23.3% of the total population).
26.3% of Swiss permanent residents are not affiliated with a religious community.
As of 2020, according to a national survey conducted by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office, Christian minority communities included Neo-
Pietism
Pietism (), also known as Pietistic Lutheranism, is a movement within Lutheranism that combines its emphasis on biblical doctrine with an emphasis on individual piety and living a holy Christian life, including a social concern for the needy an ...
(0.5%),
Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a Protestant Charismatic Christian movement (0.4%, mostly incorporated in the
Schweizer Pfingstmission),
Apostolic communities (0.3%), other Protestant denominations (1.1%, including
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's br ...
), the
Old Catholic Church
The terms Old Catholic Church, Old Catholics, Old-Catholic churches or Old Catholic movement designate "any of the groups of Western Christians who believe themselves to maintain in complete loyalty the doctrine and traditions of the undivide ...
(0.1%), other Christian denominations (0.3%). Non-Christian religions are
Islam (5.3%),
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(0.6%),
Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
(0.5%),
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
(0.25%) and others (0.4%).
Historically, the country was about evenly balanced between Catholic and Protestant, in a complex patchwork. During the
Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
Switzerland became home to many
reformers.
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
converted to Protestantism in 1536, just before
John Calvin arrived. In 1541, he founded the ''
Republic of Geneva'' on his own ideals. It became known internationally as the ''Protestant Rome'' and housed such reformers as
Theodore Beza
Theodore Beza ( la, Theodorus Beza; french: Théodore de Bèze or ''de Besze''; June 24, 1519 – October 13, 1605) was a French Calvinist Protestant theologian, reformer and scholar who played an important role in the Protestant Reformation ...
,
William Farel or
Pierre Viret
Pierre Viret (1509/1510 – 4 April 1571) was a Swiss Reformed theologian, evangelist and Protestant reformer.
Early life
Pierre Viret was born in 1509 or 1510 in Orbe, then in the Barony of Vaud, now in the canton of Vaud, Switzerland. He wa ...
.
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
became another reform stronghold around the same time, with
Huldrych Zwingli
Huldrych or Ulrich Zwingli (1 January 1484 – 11 October 1531) was a leader of the Reformation in Switzerland, born during a time of emerging Swiss patriotism and increasing criticism of the Swiss mercenary system. He attended the Univ ...
and
Heinrich Bullinger
Heinrich Bullinger (18 July 1504 – 17 September 1575) was a Swiss Reformer and theologian, the successor of Huldrych Zwingli as head of the Church of Zürich and a pastor at the Grossmünster. One of the most important leaders of the Swiss R ...
taking the lead. Anabaptists
Felix Manz
Felix Manz (also Felix Mantz) (c. 1498 – 5 January 1527) was an Anabaptist, a co-founder of the original Swiss Brethren congregation in Zürich, Switzerland, and the first martyr of the Radical Reformation.
Birth and life
Manz was born an ...
and
Conrad Grebel
Conrad Grebel (c. 1498 – 1526), son of a prominent Swiss merchant and councilman, was a co-founder of the Swiss Brethren movement.
Early life
Conrad Grebel was born, probably in Grüningen in the Canton of Zurich, about 1498 to Junker Jak ...
also operated there. They were later joined by the fleeing
Peter Martyr Vermigli
Peter Martyr Vermigli (8 September 149912 November 1562) was an Italian-born Reformed theologian. His early work as a reformer in Catholic Italy and his decision to flee for Protestant northern Europe influenced many other Italians to convert a ...
and
Hans Denck
Hans Denck (c. 1495 – November 27, 1527) was a German theologian and Anabaptist leader during the Reformation.
Biography
Denck was born in 1495 in the Bavarian town of Habach. After a classical education, he became headmaster at the St. Sebal ...
. Other centres included
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
(
Andreas Karlstadt and
Johannes Oecolampadius),
Berne
Bern () or Berne; in other Swiss languages, gsw, Bärn ; frp, Bèrna ; it, Berna ; rm, Berna is the ''de facto'' Capital city, capital of Switzerland, referred to as the "federal city" (in german: Bundesstadt, link=no, french: ville fédérale ...
(
Berchtold Haller
Berchtold Haller (c. 149225 February 1536) was a German Protestant reformer. He was the reformer of the city of Bern, Switzerland, where the Reformation received little to none opposition.
Haller was born at Aldingen in Württemberg. After schoo ...
and
Niklaus Manuel
Niklaus Manuel Deutsch (''Niklaus Manuel'', c. 1484 – 28 April 1530), of Bern, was a Swiss artist, writer, mercenary and Reformed politician.
Biography
Niklaus was most likely the son of Emanuel Aleman (or Alleman), a pharmacist whose own fat ...
), and
St. Gallen
, neighboring_municipalities = Eggersriet, Gaiserwald, Gossau, Herisau (AR), Mörschwil, Speicher (AR), Stein (AR), Teufen (AR), Untereggen, Wittenbach
, twintowns = Liberec (Czech Republic)
, website = ...
(
Joachim Vadian
Joachim Vadian (29 November 1484 – 6 April 1551), born as Joachim von Watt, was a humanist, scholar, mayor and reformer in St. Gallen, Switzerland.
Biography
Vadian was born in St. Gallen into a family of wealthy and influential linen mer ...
). One canton, Appenzell, was officially divided into Catholic and Protestant sections in 1597. The larger cities and their cantons (Bern, Geneva, Lausanne, Zürich and Basel) used to be predominantly Protestant.
Central Switzerland
Central Switzerland is the region of the Alpine Foothills geographically the heart and historically the origin of Switzerland, with the cantons of Uri, Schwyz, Obwalden, Nidwalden, Lucerne and Zug.
Central Switzerland is one of the NUTS 2 Stat ...
, the
Valais
Valais ( , , ; frp, Valês; german: Wallis ), more formally the Canton of Valais,; german: Kanton Wallis; in other official Swiss languages outside Valais: it, (Canton) Vallese ; rm, (Chantun) Vallais. is one of the 26 cantons forming the S ...
, the
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . ...
,
Appenzell Innerrhodes, the
Jura, and
Fribourg
, neighboring_municipalities= Düdingen, Givisiez, Granges-Paccot, Marly, Pierrafortscha, Sankt Ursen, Tafers, Villars-sur-Glâne
, twintowns = Rueil-Malmaison (France)
, website = www.ville-fribourg.ch
, Location of , Location of ()
() ...
are traditionally Catholic.
The
Swiss Constitution
The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation (SR 10; german: Bundesverfassung der Schweizerischen Eidgenossenschaft (BV); french: Constitution fédérale de la Confédération suisse (Cst.); it, Costituzione federale della Confederaz ...
of 1848, under the recent impression of the clashes of Catholic vs Protestant cantons that culminated in the
Sonderbundskrieg, consciously defines a
consociational state, allowing the peaceful co-existence of Catholics and Protestants. A 1980 initiative calling for the complete
separation of church and state
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular sta ...
was rejected by 78.9% of the voters. Some traditionally Protestant cantons and cities nowadays have a slight Catholic majority, because since about 1970 a steadily growing minority were not affiliated with any religious body (21.4% in Switzerland, 2012) especially in traditionally Protestant regions, such as Basel-City (42%), canton of Neuchâtel (38%), canton of Geneva (35%), canton of Vaud (26%), or Zürich city (city: >25%; canton: 23%).
Literature

The earliest forms of literature were in German, reflecting the language's early predominance. In the 18th century, French became fashionable in Bern and elsewhere, while the influence of the French-speaking allies and subject lands increased.
Among the classic authors of Swiss literature are
Jeremias Gotthelf
Albert Bitzius (4 October 179722 October 1854) was a Swiss novelist; best known by his pen name of Jeremias Gotthelf.
Biography
Bitzius was born at Murten, where his father was pastor. The Bitzius family had once belonged to the Bernese patrici ...
(1797–1854) and
Gottfried Keller
Gottfried Keller (19 July 1819 – 15 July 1890) was a Swiss poet and writer of German literature. Best known for his novel '' Green Henry'' (German: ''Der grüne Heinrich'') and his cycle of novellas called ''The People from Seldwyla'' (''Die Leu ...
(1819–1890). The undisputed giants of 20th-century Swiss literature are
Max Frisch
Max Rudolf Frisch (; 15 May 1911 – 4 April 1991) was a Swiss playwright and novelist. Frisch's works focused on problems of identity, individuality, responsibility, morality, and political commitment. The use of irony is a significant featur ...
(1911–91) and
Friedrich Dürrenmatt
Friedrich Dürrenmatt (; 5 January 1921 – 14 December 1990) was a Swiss author and dramatist. He was a proponent of epic theatre whose plays reflected the recent experiences of World War II. The politically active author's work included avant-g ...
(1921–90), whose repertoire includes ''Die Physiker'' (
The Physicists
''The Physicists'' (german: Die Physiker) is a satiric drama/ tragic comedy written in 1961 by Swiss writer Friedrich Dürrenmatt. The play was mainly written as a result of the Second World War and many advances in science and nuclear technolo ...
) and ''Das Versprechen'' (
The Pledge), released in 2001 as a Hollywood film.
Famous French-speaking writers were
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
(1712–1778) and
Germaine de Staël
Anne Louise Germaine de Staël-Holstein (; ; 22 April 176614 July 1817), commonly known as Madame de Staël (), was a French woman of letters and political theorist, the daughter of banker and French finance minister Jacques Necker and Suzan ...
(1766–1817). More recent authors include
Charles Ferdinand Ramuz
Charles Ferdinand Ramuz (24 September 1878 – 23 May 1947) was a French-speaking Swiss writer.
Biography
He was born in Lausanne in the canton of Vaud and was educated at the University of Lausanne. He taught briefly in nearby Aubonne, and ...
(1878–1947), whose novels describe the lives of peasants and mountain dwellers, set in a harsh environment, and
Blaise Cendrars
Frédéric-Louis Sauser (1 September 1887 – 21 January 1961), better known as Blaise Cendrars, was a Swiss-born novelist and poet who became a naturalized French citizen in 1916. He was a writer of considerable influence in the European mo ...
(born Frédéric Sauser, 1887–1961).
Italian and Romansh-speaking authors also contributed to the Swiss literary landscape, generally in proportion to their number.
Probably the most famous Swiss literary creation, ''
Heidi
''Heidi'' (; ) is a work of children's fiction published in 1881 by Swiss author Johanna Spyri, originally published in two parts as ''Heidi: Her Years of Wandering and Learning'' (german: Heidis Lehr- und Wanderjahre) and ''Heidi: How She Use ...
'', the story of an orphan girl who lives with her grandfather in the Alps, is one of the most popular children's books and has come to be a symbol of Switzerland. Her creator,
Johanna Spyri
Louise Spyri (; ; 12 June 1827 – 7 July 1901) was a Swiss author of novels, notably children's stories, and is best known for her book '' Heidi''. Born in Hirzel, a rural area in the canton of Zurich, Switzerland, as a child she spent se ...
(1827–1901), wrote a number of books on similar themes.
Media
Freedom of the press and the right to
free expression
Freedom of speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction. The right to freedom of expression has been recog ...
is guaranteed in the constitution.
[Press and the media](_blank)
ch.ch. Retrieved on 25 June 2009 The
Swiss News Agency (SNA) broadcasts information in three of the four national languages—on politics, economics, society and culture. The SNA supplies almost all Swiss media and foreign media with its reporting.
Switzerland has historically boasted the world's greatest number of newspaper titles relative to its population and size.
The most influential newspapers are the German-language ''
Tages-Anzeiger
''Tages-Anzeiger'' (), also abbreviated ''Tagi'' or ''TA'', is a Swiss German-language national daily newspaper published in Zurich, Switzerland.
History and profile
The paper was first published under the name ''Tages-Anzeiger für Stadt und ...
'' and ''
Neue Zürcher Zeitung'' NZZ, and the French-language ''
Le Temps
''Le Temps'' ( literally "The Time") is a Swiss French-language daily newspaper published in Berliner format in Geneva by Le Temps SA. It is the sole nationwide French-language non-specialised daily newspaper of Switzerland. Since 2021, it has ...
'', but almost every city has at least one local newspaper, in the most common local language.
The government exerts greater control over broadcast media than print media, especially due to financing and licensing.
The Swiss Broadcasting Corporation, whose name was recently changed to
SRG SSR, is charged with the production and distribution of radio and television content. SRG SSR studios are distributed across the various language regions. Radio content is produced in six central and four regional studios while video media are produced in
Geneva
, neighboring_municipalities= Carouge, Chêne-Bougeries, Cologny, Lancy, Grand-Saconnex, Pregny-Chambésy, Vernier, Veyrier
, website = https://www.geneve.ch/
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevr ...
,
Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
,
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
, and
Lugano
Lugano (, , ; lmo, label=Ticinese dialect, Ticinese, Lugan ) is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Luga ...
. An extensive cable network allows most Swiss to access content from neighbouring countries.
Sports

Skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee ( ...
,
snowboarding and
mountaineering are among the most popular sports, reflecting the nature of the country Winter sports are practised by natives and visitors. The
bobsleigh
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Feder ...
was invented in
St. Moritz. The first
world ski championships were held in
Mürren
Mürren is a traditional Walser mountain village in the Bernese Highlands of Switzerland, at an elevation of above sea level and it cannot be reached by public road. It is also one of the popular tourist spots in Switzerland, and summer and w ...
(1931) and St. Moritz (1934). The latter town hosted the
second Winter Olympic Games in 1928 and the
fifth edition in 1948. Among its most successful skiers and world champions are
Pirmin Zurbriggen
Pirmin Zurbriggen (born 4 February 1963) is a former World Cup alpine ski racer from Switzerland. One of the most successful ski racers ever, he won the overall World Cup title four times, an Olympic gold medal in 1988 in Downhill, and nine W ...
and
Didier Cuche
Didier Cuche (born 16 August 1974) is a former World Cup alpine ski racer from Switzerland.
Career
Born in Le Pâquier, Neuchâtel, he competed in the downhill and super-G, along with the giant slalom. He won the World Cup downhill and super-G ...
.
The most prominently watched sports in Switzerland are
football,
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
,
Alpine skiing, "
Schwingen
(from German ' "to swing"), also known as Swiss wrestling (French ') and natively (and colloquially) as ' (Swiss German for "breeches-lifting"), is a style of folk wrestling native to Switzerland, more specifically the pre-alpine parts of Germ ...
", and
tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent ( singles) or between two teams of two players each ( doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball ...
.
The headquarters of the international football's and ice hockey's governing bodies, the
International Federation of Association Football
FIFA (; stands for ''Fédération Internationale de Football Association'' (French), meaning International Association Football Federation ) is the international governing body of association football, beach football and futsal. It was founded ...
(FIFA) and
International Ice Hockey Federation
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 ...
(IIHF) are located in Zürich. Many other headquarters of international sports federations are located in Switzerland. For example, the
International Olympic Committee
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
(IOC), IOC's
Olympic Museum
The Olympic Museum (french: Musée olympique) in Lausanne, Switzerland houses permanent and temporary exhibits relating to sport and the Olympic movement. With more than 10,000 artifacts, the museum is the largest archive of Olympic Games in the ...
and the
Court of Arbitration for Sport
The Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS; french: Tribunal arbitral du sport, ''TAS'') is an international body established in 1984 to settle disputes related to sport through arbitration. Its headquarters are in Lausanne, Switzerland and its c ...
(CAS) are located in
Lausanne
, neighboring_municipalities= Bottens, Bretigny-sur-Morrens, Chavannes-près-Renens, Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne, Crissier, Cugy, Écublens, Épalinges, Évian-les-Bains (FR-74), Froideville, Jouxtens-Mézery, Le Mont-sur-Lausanne, Lugrin (FR ...
.
Switzerland hosted the
1954 FIFA World Cup
The 1954 FIFA World Cup was the fifth edition of the FIFA World Cup, the quadrennial international football tournament for senior men's national teams of the nations affiliated to FIFA. It was held in Switzerland from 16 June to 4 July. Switzer ...
and was the joint host, with Austria, of the
UEFA Euro 2008
The 2008 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2008 or simply Euro 2008, was the 13th UEFA European Championship, a quadrennial football tournament contested by the member nations of UEFA (the Union of European ...
tournament. The
Swiss Super League is the nation's professional football club league. Europe's highest football pitch, at above sea level, is located in Switzerland, the ''Ottmar Hitzfeld Stadium''.
Many Swiss follow
ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice h ...
and support one of the 12 teams of the
National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team ...
, which is the most attended league in Europe. In 2009, Switzerland hosted the
IIHF World Championship
The International Ice Hockey Federation (IIHF; french: Fédération internationale de hockey sur glace; german: Internationale Eishockey-Föderation) is a worldwide governing body for ice hockey. It is based in Zurich, Switzerland, and has 83 m ...
for the tenth time. It also became
World Vice-Champion in 2013 and 2018. Its numerous lakes make Switzerland an attractive sailing destination. The largest,
Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial la ...
, is the home of the sailing team
Alinghi which was the first European team to win the
America's Cup in 2003 and which successfully defended the title in 2007.

Swiss tennis player
Roger Federer
Roger Federer (; born 8 August 1981) is a Swiss former professional tennis player. He was ranked world No. 1 by the Association of Tennis Professionals (ATP) for 310 weeks, including a record 237 consecutive weeks, and finished as the year-e ...
is widely regarded as among the sport's greatest players. He won 20
Grand Slam
Grand Slam most often refers to:
* Grand Slam (tennis), one player or pair winning all four major annual tournaments, or the tournaments themselves
Grand Slam or Grand slam may also refer to:
Games and sports
* Grand slam, winning category te ...
tournaments overall including a record 8
Wimbledon titles. He won a record 6
ATP Finals.
He was ranked no. 1 in the
ATP rankings
The Pepperstone ATP rankings are the merit-based method used by the Association of Tennis Professionals (ATP) for determining the qualification for entry as well as the seeding of players in all singles and doubles tournaments. The first rankings ...
for a record 237 consecutive weeks. He ended 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007 and
2009 ranked no. 1. Fellow Swiss players
Martina Hingis
Martina Hingis (, sk, Martina Hingisová; 30 September 1980) is a Swiss former professional tennis player. Hingis is the first Swiss player, male or female, to win a major title and attain a world No. 1 ranking. She spent a total of 209 weeks a ...
and
Stan Wawrinka also hold multiple Grand Slam titles. Switzerland won the
Davis Cup title in 2014.
Motorsport racecourses and events were banned in Switzerland following the
1955 Le Mans disaster
The 1955 Le Mans disaster was a major crash that occurred on 11 June 1955 during the 24 Hours of Le Mans motor race at Circuit de la Sarthe in Le Mans, Sarthe, France. Large pieces of debris flew into the crowd, killing 83 spectators and French ...
with exceptions for events such as
hillclimbing
Hillclimbing, also known as hill climbing, speed hillclimbing, or speed hill climbing, is a branch of motorsport in which drivers compete against the clock to complete an uphill course. It is one of the oldest forms of motorsport, since the firs ...
. The country continued to produce successful racing drivers such as
Clay Regazzoni
Gianclaudio Giuseppe "Clay" Regazzoni (5 September 1939 – 15 December 2006) was a Swiss racing driver. He competed in Formula One races from 1970 to 1980, winning five Grands Prix. His first win was the Italian Grand Prix at Monza in his debu ...
,
Sébastien Buemi
Sébastien Olivier Buemi (born 31 October 1988) is a Swiss professional racing driver, who competes in the FIA Formula E Championship for Envision Racing. He competed for Scuderia Toro Rosso in Formula One from 2009 to 2011. After leaving Formula ...
,
Jo Siffert
Joseph Siffert (; 7 July 1936 – 24 October 1971) was a Swiss racing driver.
Affectionately known as "Seppi" to his family and friends, Siffert was born in Fribourg, Switzerland, the son of a dairy owner. He initially made his name in racing ...
,
Dominique Aegerter, successful
World Touring Car Championship
The FIA World Touring Car Championship was an international touring car championship promoted by Eurosport Events and sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA). It has had several different incarnations, including a sin ...
driver
Alain Menu
Alain Menu (born 9 August 1963) is a Swiss racing driver who is currently working for Team BMR as a driving coach. He was one of the most successful touring car drivers of the 1990s, winning the prestigious British Touring Car Championship tw ...
,
2014 24 Hours of Le Mans winner
Marcel Fässler and 2015
24 Hours Nürburgring
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures.
In mathematics
Four is the smalle ...
winner
Nico Müller
Nico Müller (born 25 February 1992 in Thun) is a Swiss professional racing driver. He is currently competing in the FIA World Endurance Championship for Peugeot Sport.
Career
Karting
Müller began his karting career in 2004 and the following ...
.
Switzerland also won the
A1GP World Cup of Motorsport in
2007–08 with driver
Neel Jani
Neel Jani (born 8 December 1983) is a Swiss professional Porsche factory driver. His father is from India and his mother is German Swiss.
He achieved his greatest success winning the 24 Hours of Le Mans in 2016 after first joining Porsche's LMP ...
. Swiss
motorcycle racer
Motorcycle racing (also called moto racing and motorbike racing) is the motorcycle sport of racing motorcycles. Major varieties include motorcycle road racing and off-road racing, both either on circuits or open courses, and track racing. Oth ...
Thomas Lüthi won the 2005
MotoGP World Championship in the 125cc category. In June 2007 the
Swiss National Council
The National Council (german: Nationalrat; french: Conseil national; it, Consiglio nazionale; rm, Cussegl naziunal) is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, the upper house being the Council of States. With 200 seats, the ...
, one house of the
Federal Assembly of Switzerland
The Federal Assembly (german: Bundesversammlung, french: Assemblée fédérale, it, Assemblea federale, rm, Assamblea federala), also known as the Swiss parliament (''Parlament'', ''Parlement'', ''Parlamento''), is Switzerland's federal legi ...
, voted to overturn the ban, however the other house, the
Swiss Council of States
The Council of States (german: Ständerat, french: Conseil des États, it, Consiglio degli Stati, rm, Cussegl dals Stadis) is the upper house of the Federal Assembly of Switzerland, with the National Council being the lower house. It compri ...
rejected the change and the ban remains in place.
Traditional sports include Swiss wrestling or "
Schwingen
(from German ' "to swing"), also known as Swiss wrestling (French ') and natively (and colloquially) as ' (Swiss German for "breeches-lifting"), is a style of folk wrestling native to Switzerland, more specifically the pre-alpine parts of Germ ...
", a tradition from the rural central cantons and considered the national sport by some.
Hornussen
Hornussen is an indigenous Swiss sport. The sport gets its name from the puck which is known as a "Hornuss" (hornet) or "Nouss". When hit, it can whizz through the air at up to 300 km/h (186.4 mph) and create a buzzing sound.
Together with ...
is another indigenous Swiss sport, which is like a cross between baseball and golf.
Steinstossen
Steinstossen is the Swiss variant of stone put, a competition in throwing a heavy stone. Practiced among the alpine population since prehistoric times, it is recorded to have taken place in Basel in the 13th century. During the 15th century, it i ...
is the Swiss variant of
stone put
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's o ...
, a competition in throwing a heavy stone. Practised only among the alpine population since
prehistoric times, it is recorded to have taken place in
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese
, neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS ...
in the 13th century. It is central to the
Unspunnenfest
Unspunnenfest is a festival held in the town of Interlaken, Switzerland, near the old ruin of Unspunnen Castle, in the Bernese Alps, approximately once every twelve years, most recently in 2017. The festival highlights traditional Swiss culture ...
, first held in 1805, with its symbol the 83.5 stone named ''Unspunnenstein''.
Cuisine

The cuisine is multifaceted. While dishes such as
fondue,
raclette
Raclette (, ) is a Swiss dish, also popular in the other Alpine countries, based on heating cheese and scraping off the melted part, then typically served with boiled potatoes. Raclette cheese is historically a dish originating from the canton o ...
or
rösti
Rösti or rööschti () is a Swiss dish consisting mainly of potatoes, sautéed or shallow-fried in a pan. It was originally a breakfast dish, commonly eaten by farmers in the canton of Bern, but is now eaten all over Switzerland and around th ...
are omnipresent, each region developed its gastronomy according to the varieties of climate and language. Traditional Swiss cuisine uses ingredients similar to those in other European countries, as well as unique
dairy products and
cheeses such as
Gruyère or
Emmental
The Emmental ( en, Emme Valley) is a valley in west-central Switzerland, forming part of the canton of Bern. It is a hilly landscape comprising the basins of the rivers Emme (river), Emme and Ilfis (river), Ilfis. The region is mostly devoted to ...
, produced in the valleys of
Gruyères
Gruyères (; frp, Gruviéres ; german: Greyerz) is a town in the district of Gruyère in the canton of Fribourg in Switzerland.
The medieval town is an important tourist location in the upper valley of the Saane/Sarine river, and gives its nam ...
and
Emmental
The Emmental ( en, Emme Valley) is a valley in west-central Switzerland, forming part of the canton of Bern. It is a hilly landscape comprising the basins of the rivers Emme (river), Emme and Ilfis (river), Ilfis. The region is mostly devoted to ...
. The number of fine-dining establishments is high, particularly in western Switzerland.
Chocolate
Chocolate is a food made from roasted and ground cacao seed kernels that is available as a liquid, solid, or paste, either on its own or as a flavoring agent in other foods. Cacao has been consumed in some form since at least the Olmec civ ...
has been made in Switzerland since the 18th century. Its reputation grew at the end of the 19th century with the invention of modern techniques such as
conching and
tempering, which enabled higher quality. Another breakthrough was the invention of solid milk chocolate in 1875 by
Daniel Peter
Daniel Peter (9 March 1836 – 4 November 1919) was a Swiss chocolatier and entrepreneur who founded Peter's Chocolate. A neighbour of Henri Nestlé in Vevey, he was one of the first chocolatiers to make milk chocolate and is credited for inven ...
. The Swiss are the world's largest chocolate consumers.
Due to the popularisation of
processed foods at the end of the 19th century, Swiss
health food
A healthy diet is a diet that maintains or improves overall health. A healthy diet provides the body with essential nutrition: fluid, macronutrients such as protein, micronutrients such as vitamins, and adequate fibre and food energy.
A health ...
pioneer Maximilian Bircher-Benner created the first nutrition-based therapy in the form of the well-known rolled oats cereal dish, called Muesli, Birchermüesli.
The most popular alcoholic drink is wine. Switzerland is notable for its variety of grape varieties, reflecting the large variations in terroirs. Swiss wine is produced mainly in Valais (wine region), Valais, Vaud (Lavaux), Geneva (wine region), Geneva and Ticino, with a small majority of white wines. Vineyards have been cultivated in Switzerland since the Roman era, even though traces of a more ancient origin can be found. The most widespread varieties are the Chasselas (called Fendant in Valais) and Pinot noir, Pinot Noir. Merlot is the main variety produced in Ticino.
Table 38. Top wine consuming nations per capita, 2006
winebiz.com. Retrieved on 14 June 2010
See also
* Index of Switzerland-related articles
* Outline of Switzerland
Notes
References
Further reading
* Church, Clive H. (2004) ''The Politics and Government of Switzerland''. Palgrave Macmillan. .
* Fahrni, Dieter. (2003) ''An Outline History of Switzerland. From the Origins to the Present Day''. 8th enlarged edition. Pro Helvetia, Zürich.
* von Matt, Peter: ''Das Kalb vor der Gotthardpost. Zur Literatur und Politik in der Schweiz''. Carl Hanser Verlag, München, 2012, , S. 127–138.
* Historical Dictionary of Switzerland. Published electronically (1998–) and in print (2002–) simultaneously in three of the national languages of Switzerland
DHS/HLS/DSS
online edition in German, French and Italian
External links
The Federal Authorities of the Swiss Confederation
*
{{Authority control
Switzerland,
Central European countries
Federal republics
French-speaking countries and territories
German-speaking countries and territories
Italian-speaking countries and territories
Landlocked countries
States and territories established in 1848
Member states of the Council of Europe
Member states of the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie
Member states of the United Nations
Member states of the European Free Trade Association
Western European countries
Countries in Europe
Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
OECD members
 The earliest known tribes formed the
The earliest known tribes formed the  The Old Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of the central Alps. The Confederacy was governed by
The Old Swiss Confederacy was an alliance among the valley communities of the central Alps. The Confederacy was governed by  In 1798, the revolutionary French government invaded Switzerland and imposed a new unified constitution. This centralised the government of the country, effectively abolishing the cantons: moreover, Mülhausen left Switzerland and the
In 1798, the revolutionary French government invaded Switzerland and imposed a new unified constitution. This centralised the government of the country, effectively abolishing the cantons: moreover, Mülhausen left Switzerland and the  The restoration of power to the patriciate was only temporary. After a period of unrest with repeated violent clashes, such as the
The restoration of power to the patriciate was only temporary. After a period of unrest with repeated violent clashes, such as the  A single system of weights and measures was introduced, and in 1850 the Swiss franc became the Swiss
A single system of weights and measures was introduced, and in 1850 the Swiss franc became the Swiss  Switzerland was not invaded during either of the world wars. During
Switzerland was not invaded during either of the world wars. During  Switzerland was the last Western republic (the Principality of Liechtenstein followed in 1984) to grant women the
Switzerland was the last Western republic (the Principality of Liechtenstein followed in 1984) to grant women the  Extending across the north and south side of the
Extending across the north and south side of the  Between two-thirds and three-quarters of the population live in urban areas.Städte und Agglomerationen unter der Lupe
Between two-thirds and three-quarters of the population live in urban areas.Städte und Agglomerationen unter der Lupe The Federal Constitution adopted in 1848 is the legal foundation of Switzerland's federal state. A new Swiss Constitution was adopted in 1999 that did not introduce notable changes to the federal structure. It outlines rights of individuals and citizen participation in public affairs, divides the powers between the Confederation and the cantons and defines federal jurisdiction and authority. Three main bodies govern on the federal level: the bicameral parliament (legislative), the Federal Council (executive) and the Federal Court (judicial).
The Federal Constitution adopted in 1848 is the legal foundation of Switzerland's federal state. A new Swiss Constitution was adopted in 1999 that did not introduce notable changes to the federal structure. It outlines rights of individuals and citizen participation in public affairs, divides the powers between the Confederation and the cantons and defines federal jurisdiction and authority. Three main bodies govern on the federal level: the bicameral parliament (legislative), the Federal Council (executive) and the Federal Court (judicial).
 The Federal Council directs the federal government, the federal administration, and serves as a collective
The Federal Council directs the federal government, the federal administration, and serves as a collective  Direct democracy and federalism are hallmarks of the Swiss political system. Swiss citizens are subject to three legal jurisdictions: the municipality, canton and federal levels. The 1848 and 1999 Swiss Constitutions define a system of direct democracy (sometimes called half-direct or representative direct democracy because it includes institutions of a
Direct democracy and federalism are hallmarks of the Swiss political system. Swiss citizens are subject to three legal jurisdictions: the municipality, canton and federal levels. The 1848 and 1999 Swiss Constitutions define a system of direct democracy (sometimes called half-direct or representative direct democracy because it includes institutions of a  In 1848, the federal constitution provided that details concerning federal institutions, such as their locations, should be addressed by the Federal Assembly (BV 1848 Art. 108). Thus on 28 November 1848, the Federal Assembly voted in the majority to locate the seat of government in Bern and, as a prototypical federal compromise, to assign other federal institutions, such as the Federal Polytechnical School (1854, the later ETH) to Zürich, and other institutions to Lucerne, such as the later SUVA (1912) and the Federal Insurance Court (1917). Other federal institutions were subsequently attributed to
In 1848, the federal constitution provided that details concerning federal institutions, such as their locations, should be addressed by the Federal Assembly (BV 1848 Art. 108). Thus on 28 November 1848, the Federal Assembly voted in the majority to locate the seat of government in Bern and, as a prototypical federal compromise, to assign other federal institutions, such as the Federal Polytechnical School (1854, the later ETH) to Zürich, and other institutions to Lucerne, such as the later SUVA (1912) and the Federal Insurance Court (1917). Other federal institutions were subsequently attributed to  Traditionally, Switzerland avoids alliances that might entail military, political, or direct economic action and has been neutral since the end of its expansion in 1515. Its
Traditionally, Switzerland avoids alliances that might entail military, political, or direct economic action and has been neutral since the end of its expansion in 1515. Its  The
The  Overall, three general mobilisations have been declared to ensure the integrity and neutrality of Switzerland. The first one was held in response to the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71. The second was in response to the
Overall, three general mobilisations have been declared to ensure the integrity and neutrality of Switzerland. The first one was held in response to the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–71. The second was in response to the 

 Education in Switzerland is diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the operation for the school system to the cantons. Public and private schools are available, including many private international schools.
Education in Switzerland is diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the operation for the school system to the cantons. Public and private schools are available, including many private international schools.
 Geneva and the nearby French department of
Geneva and the nearby French department of 
 The densest rail network in Europe spans and carries over 596 million passengers annually as of 2015. In 2015, each Swiss resident travelled on average by rail, more than any other European country. Virtually 100% of the network is electrified. 60% of the network is operated by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS). Besides the second largest standard gauge railway company, BLS AG, two railways companies operate on
The densest rail network in Europe spans and carries over 596 million passengers annually as of 2015. In 2015, each Swiss resident travelled on average by rail, more than any other European country. Virtually 100% of the network is electrified. 60% of the network is operated by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS). Besides the second largest standard gauge railway company, BLS AG, two railways companies operate on 
 In common with other developed countries, the Swiss population increased rapidly during the industrial era, quadrupling between 1800 and 1990 and has continued to grow.
The population is about 8.7 million (2020 est.). Population growth was projected into 2035, due mostly to immigration. Like most of Europe, Switzerland faces an
In common with other developed countries, the Swiss population increased rapidly during the industrial era, quadrupling between 1800 and 1990 and has continued to grow.
The population is about 8.7 million (2020 est.). Population growth was projected into 2035, due mostly to immigration. Like most of Europe, Switzerland faces an  Switzerland has four
Switzerland has four  The earliest forms of literature were in German, reflecting the language's early predominance. In the 18th century, French became fashionable in Bern and elsewhere, while the influence of the French-speaking allies and subject lands increased.
Among the classic authors of Swiss literature are
The earliest forms of literature were in German, reflecting the language's early predominance. In the 18th century, French became fashionable in Bern and elsewhere, while the influence of the French-speaking allies and subject lands increased.
Among the classic authors of Swiss literature are  Swiss tennis player
Swiss tennis player