Neurotoxins on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Neurotoxins are
Neurotoxins are
 Exposure to neurotoxins in society is not new, as civilizations have been exposed to neurologically destructive compounds for thousands of years. One notable example is the possible significant lead exposure during the
Exposure to neurotoxins in society is not new, as civilizations have been exposed to neurologically destructive compounds for thousands of years. One notable example is the possible significant lead exposure during the  This barrier creates a tight hydrophobic layer around the capillary, capillaries in the brain, inhibiting the transport of large or hydrophilic compounds. In addition to the BBB, the choroid plexus provides a layer of protection against toxin absorption in the brain. The choroid plexuses are vascularized layers of tissue found in the third, fourth, and lateral ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, which through the function of their ependymal cells, are responsible for the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Martini 2009 Importantly, through selective passage of ions and nutrients and trapping heavy metals such as lead, the choroid plexuses maintain a strictly regulated environment which contains the brain and spinal cord.
This barrier creates a tight hydrophobic layer around the capillary, capillaries in the brain, inhibiting the transport of large or hydrophilic compounds. In addition to the BBB, the choroid plexus provides a layer of protection against toxin absorption in the brain. The choroid plexuses are vascularized layers of tissue found in the third, fourth, and lateral ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, which through the function of their ependymal cells, are responsible for the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Martini 2009 Importantly, through selective passage of ions and nutrients and trapping heavy metals such as lead, the choroid plexuses maintain a strictly regulated environment which contains the brain and spinal cord.
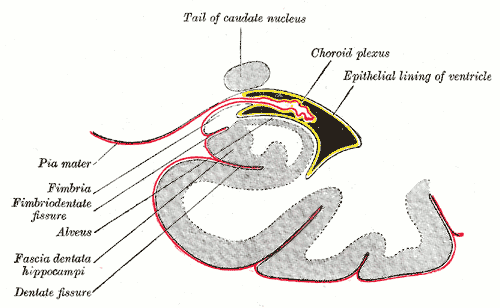 By being hydrophobic and small, or inhibiting astrocyte function, some compounds including certain neurotoxins are able to penetrate into the brain and induce significant damage. In modern times, scientists and physicians have been presented with the challenge of identifying and treating neurotoxins, which has resulted in a growing interest in both neurotoxicology research and clinical studies.Costa 2011 Though clinical neurotoxicology is largely a burgeoning field, extensive inroads have been made in the identification of many environmental neurotoxins leading to the classification of 750 to 1000 known potentially neurotoxic compounds. Due to the critical importance of finding neurotoxins in common environments, specific protocols have been developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for testing and determining neurotoxic effects of compounds (USEPA 1998). Additionally, in vitro systems have increased in use as they provide significant improvements over the more common in vivo systems of the past. Examples of improvements include tractable, uniform environments, and the elimination of contaminating effects of systemic metabolism. In vitro systems, however, have presented problems as it has been difficult to properly replicate the complexities of the nervous system, such as the interactions between supporting astrocytes and neurons in creating the BBB. To even further complicate the process of determining neurotoxins when testing in-vitro,
By being hydrophobic and small, or inhibiting astrocyte function, some compounds including certain neurotoxins are able to penetrate into the brain and induce significant damage. In modern times, scientists and physicians have been presented with the challenge of identifying and treating neurotoxins, which has resulted in a growing interest in both neurotoxicology research and clinical studies.Costa 2011 Though clinical neurotoxicology is largely a burgeoning field, extensive inroads have been made in the identification of many environmental neurotoxins leading to the classification of 750 to 1000 known potentially neurotoxic compounds. Due to the critical importance of finding neurotoxins in common environments, specific protocols have been developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for testing and determining neurotoxic effects of compounds (USEPA 1998). Additionally, in vitro systems have increased in use as they provide significant improvements over the more common in vivo systems of the past. Examples of improvements include tractable, uniform environments, and the elimination of contaminating effects of systemic metabolism. In vitro systems, however, have presented problems as it has been difficult to properly replicate the complexities of the nervous system, such as the interactions between supporting astrocytes and neurons in creating the BBB. To even further complicate the process of determining neurotoxins when testing in-vitro,
 Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a poison produced by organisms belonging to the Tetraodontiformes, Tetraodontiformes order, which includes the puffer fish, Molidae, ocean sunfish, and porcupine fish. Within the puffer fish, TTX is found in the liver, gonads, intestines, and skin. TTX can be fatal if consumed, and has become a common form of poisoning in many countries. Common symptoms of TTX consumption include paraesthesia (often restricted to the mouth and limb (anatomy), limbs), muscle weakness, nausea, and vomiting and often manifest within 30 minutes of ingestion. The primary mechanism by which TTX is toxic is through the inhibition of sodium channel function, which reduces the functional capacity of neuron communication. This inhibition largely affects a susceptible subset of sodium channels known as TTX-sensitive (TTX-s), which also happens to be largely responsible for the sodium current that drives the depolarization, depolarization phase of neuron action potentials. TTX-resistant (TTX-r) is another form of sodium channel which has limited sensitivity to TTX, and is largely found in axon, small diameter axons such as those found in nociceptor, nociception neurons. When a significant level of TTX is ingested, it will bind sodium channels on neurons and reduce their membrane permeability to sodium. This results in an increased effective threshold of required excitatory signals in order to induce an action potential in a postsynaptic neuron. The effect of this increased action potential, signaling threshold is a reduced excitability of chemical synapse, postsynaptic neurons, and subsequent loss of motor and sensory function which can result in paralysis and death. Though medical ventilator, assisted ventilation may increase the chance of survival after TTX exposure, there is currently no antitoxin. The use of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor Neostigmine or the muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist atropine (which will inhibit parasympathetic activity), however, can increase sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nerve activity enough to improve the chance of survival after TTX exposure.
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a poison produced by organisms belonging to the Tetraodontiformes, Tetraodontiformes order, which includes the puffer fish, Molidae, ocean sunfish, and porcupine fish. Within the puffer fish, TTX is found in the liver, gonads, intestines, and skin. TTX can be fatal if consumed, and has become a common form of poisoning in many countries. Common symptoms of TTX consumption include paraesthesia (often restricted to the mouth and limb (anatomy), limbs), muscle weakness, nausea, and vomiting and often manifest within 30 minutes of ingestion. The primary mechanism by which TTX is toxic is through the inhibition of sodium channel function, which reduces the functional capacity of neuron communication. This inhibition largely affects a susceptible subset of sodium channels known as TTX-sensitive (TTX-s), which also happens to be largely responsible for the sodium current that drives the depolarization, depolarization phase of neuron action potentials. TTX-resistant (TTX-r) is another form of sodium channel which has limited sensitivity to TTX, and is largely found in axon, small diameter axons such as those found in nociceptor, nociception neurons. When a significant level of TTX is ingested, it will bind sodium channels on neurons and reduce their membrane permeability to sodium. This results in an increased effective threshold of required excitatory signals in order to induce an action potential in a postsynaptic neuron. The effect of this increased action potential, signaling threshold is a reduced excitability of chemical synapse, postsynaptic neurons, and subsequent loss of motor and sensory function which can result in paralysis and death. Though medical ventilator, assisted ventilation may increase the chance of survival after TTX exposure, there is currently no antitoxin. The use of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor Neostigmine or the muscarinic acetylcholine antagonist atropine (which will inhibit parasympathetic activity), however, can increase sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic nerve activity enough to improve the chance of survival after TTX exposure.
 Botulinum toxin (BTX) is a group of neurotoxins consisting of eight distinct compounds, referred to as BTX-A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H, which are produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and lead to muscular paralysis.Brin, Mitchell F (1997) "Botulinum Toxin: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicity, and Immunology." ''Muscle & Nerve,'' 20 (S6): 146–68. A notably unique feature of BTX is its relatively common therapeutic use in treating dystonia and spasticity disorders, as well as in inducing muscular atrophy despite being the most poisonous substance known. BTX functions peripherally to inhibit acetylcholine (ACh) release at the neuromuscular junction through degradation of the SNARE proteins required for ACh vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle-membrane fusion. As the toxin is highly biologically active, an estimated dose of 1μg/kg body weight is sufficient to induce an insufficient tidal volume and resultant death by asphyxiation. Due to its high toxicity, BTX antitoxins have been an active area of research. It has been shown that capsaicin (active compound responsible for heat in chili peppers) can bind the TRPV1, TRPV1 receptor expressed on cholinergic, cholinergic neurons and inhibit the toxic effects of BTX.
Botulinum toxin (BTX) is a group of neurotoxins consisting of eight distinct compounds, referred to as BTX-A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H, which are produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and lead to muscular paralysis.Brin, Mitchell F (1997) "Botulinum Toxin: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicity, and Immunology." ''Muscle & Nerve,'' 20 (S6): 146–68. A notably unique feature of BTX is its relatively common therapeutic use in treating dystonia and spasticity disorders, as well as in inducing muscular atrophy despite being the most poisonous substance known. BTX functions peripherally to inhibit acetylcholine (ACh) release at the neuromuscular junction through degradation of the SNARE proteins required for ACh vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle-membrane fusion. As the toxin is highly biologically active, an estimated dose of 1μg/kg body weight is sufficient to induce an insufficient tidal volume and resultant death by asphyxiation. Due to its high toxicity, BTX antitoxins have been an active area of research. It has been shown that capsaicin (active compound responsible for heat in chili peppers) can bind the TRPV1, TRPV1 receptor expressed on cholinergic, cholinergic neurons and inhibit the toxic effects of BTX.
 Investigations into Anatoxin-a, anatoxin-''a'', also known as "Very Fast Death Factor", began in 1961 following the deaths of cows that drank from a lake containing an algal bloom in Saskatchewan, Canada.Carmichael 1978Carmichael 1975 It is a cyanotoxin produced by at least four different genera of cyanobacteria, and has been reported in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and New Zealand.
Toxic effects from anatoxin-''a'' progress very rapidly because it acts directly on the nerve cells (
Investigations into Anatoxin-a, anatoxin-''a'', also known as "Very Fast Death Factor", began in 1961 following the deaths of cows that drank from a lake containing an algal bloom in Saskatchewan, Canada.Carmichael 1978Carmichael 1975 It is a cyanotoxin produced by at least four different genera of cyanobacteria, and has been reported in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and New Zealand.
Toxic effects from anatoxin-''a'' progress very rapidly because it acts directly on the nerve cells (
 Caramboxin (CBX) is a
Caramboxin (CBX) is a
 Ammonia toxicity is often seen through two routes of administration, either through consumption or through endogenous ailments such as liver failure.Matsuoka 1991 One notable case in which ammonia toxicity is common is in response to cirrhosis of the liver which results in hepatic encephalopathy, and can result in cerebral edema (Haussinger 2006). This cerebral edema can be the result of nervous cell remodeling. As a consequence of increased concentrations, ammonia activity in-vivo has been shown to induce swelling of astrocytes in the brain through increased production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP (Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate) within the cells which leads to cGMP-dependent protein kinase, Protein Kinase G-mediated (PKG) cytoskeletal modifications. The resultant effect of this toxicity can be reduced brain energy metabolism and function. Importantly, the toxic effects of ammonia on astrocyte remodeling can be reduced through administration of carnitine, L-carnitine. This astrocyte remodeling appears to be mediated through ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. This mitochondrial transition is a direct result of glutamine activity a compound which forms from ammonia in-vivo.Norenberg 2004 Administration of antioxidants or glutaminase inhibitor can reduce this mitochondrial transition, and potentially also astrocyte remodeling.
Ammonia toxicity is often seen through two routes of administration, either through consumption or through endogenous ailments such as liver failure.Matsuoka 1991 One notable case in which ammonia toxicity is common is in response to cirrhosis of the liver which results in hepatic encephalopathy, and can result in cerebral edema (Haussinger 2006). This cerebral edema can be the result of nervous cell remodeling. As a consequence of increased concentrations, ammonia activity in-vivo has been shown to induce swelling of astrocytes in the brain through increased production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP (Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate) within the cells which leads to cGMP-dependent protein kinase, Protein Kinase G-mediated (PKG) cytoskeletal modifications. The resultant effect of this toxicity can be reduced brain energy metabolism and function. Importantly, the toxic effects of ammonia on astrocyte remodeling can be reduced through administration of carnitine, L-carnitine. This astrocyte remodeling appears to be mediated through ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. This mitochondrial transition is a direct result of glutamine activity a compound which forms from ammonia in-vivo.Norenberg 2004 Administration of antioxidants or glutaminase inhibitor can reduce this mitochondrial transition, and potentially also astrocyte remodeling.
 Lead is a potent neurotoxin whose toxicity has been recognized for at least thousands of years.Lidskey 2003 Though neurotoxic effects for lead are found in both adults and young children, the developing brain is particularly susceptible to lead-induced harm, effects which can include apoptosis and excitotoxicity. An underlying mechanism by which lead is able to cause harm is its ability to be transported by atpase, calcium ATPase pumps across the BBB, allowing for direct contact with the fragile cells within the central nervous system. Neurotoxicity results from lead's ability to act in a similar manner to calcium ions, as concentrated lead will lead to cellular uptake of calcium which disrupts cellular homeostasis and induces apoptosis. It is this intracellular calcium increase that activates protein kinase c, protein kinase C (PKC), which manifests as learning deficits in children as a result of early lead exposure. In addition to inducing apoptosis, lead inhibits interneuron signaling through the disruption of calcium-mediated neurotransmitter release.
Lead is a potent neurotoxin whose toxicity has been recognized for at least thousands of years.Lidskey 2003 Though neurotoxic effects for lead are found in both adults and young children, the developing brain is particularly susceptible to lead-induced harm, effects which can include apoptosis and excitotoxicity. An underlying mechanism by which lead is able to cause harm is its ability to be transported by atpase, calcium ATPase pumps across the BBB, allowing for direct contact with the fragile cells within the central nervous system. Neurotoxicity results from lead's ability to act in a similar manner to calcium ions, as concentrated lead will lead to cellular uptake of calcium which disrupts cellular homeostasis and induces apoptosis. It is this intracellular calcium increase that activates protein kinase c, protein kinase C (PKC), which manifests as learning deficits in children as a result of early lead exposure. In addition to inducing apoptosis, lead inhibits interneuron signaling through the disruption of calcium-mediated neurotransmitter release.
 As a neurotoxin,
As a neurotoxin,
, OSHA.gov
''Occurrence of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin, anatoxin-a, in New York State waters''
ProQuest. . *
Brain Facts Book
at The Society for Neuroscience
Neuroscience Texts
at University of Texas Medical School
In Vitro Neurotoxicology: An Introduction
at Springerlink
Biology of the NMDA Receptor
at NCBI
Advances in the Neuroscience of Addiction, 2nd edition
at NCBI
Environmental Protection Agency
at United States Environmental Protection Agency
Alcohol and Alcoholism
at Oxford Medical Journals
Neurotoxicology
at Elsevier Journals
Neurotoxin Institute
at Neurotoxin Institute
Neurotoxins] at Toxipedia {{Toxins Neurotoxins,
toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ...
s that are destructive to nerve tissue
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain ...
(causing neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specificall ...
). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous
In a variety of contexts, exogeny or exogeneity () is the fact of an action or object originating externally. It contrasts with endogeneity or endogeny, the fact of being influenced within a system.
Economics
In an economic model, an exogeno ...
chemical neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal c ...
insults
An insult is an expression or statement (or sometimes behavior) which is disrespectful or scornful. Insults may be intentional or accidental. An insult may be factual, but at the same time pejorative, such as the word " inbred".
Jocular exc ...
Spencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cu ...
, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
(drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin
Tetanus toxin (TeNT) is an extremely potent neurotoxin produced by the vegetative cell of ''Clostridium tetani'' in anaerobic conditions, causing tetanus. It has no known function for clostridia in the soil environment where they are normally ...
,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin. Its name derives from Tetraodontiformes, an order that includes pufferfish, porcupinefish, ocean sunfish, and triggerfish; several of these species carry the toxin. Although tetrodotoxin was discovere ...
. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.
Neurotoxins inhibit neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
control over ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
concentrations across the cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse.Arnon 2001 Local pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity
In excitotoxicity, nerve cells suffer damage or death when the levels of otherwise necessary and safe neurotransmitters such as glutamate become pathologically high, resulting in excessive stimulation of receptors. For example, when glutamate ...
or apoptosisDikranian 2001 but can also include glial cell
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form myel ...
damage.Deng 2003 Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
damage such as intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
, persistent memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
impairments, epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, and dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is one of two components that make up the nervous system of bilateral animals, with the other part being the central nervous system (CNS). The PNS consists of nerves and ganglia, which lie outside the brain ...
damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant and antitoxin
An antitoxin is an antibody with the ability to neutralize a specific toxin. Antitoxins are produced by certain animals, plants, and bacteria in response to toxin exposure. Although they are most effective in neutralizing toxins, they can also ...
Thyagarajan 2009 administration.
Background
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
resulting from the development of extensive plumbing networks and the habit of boiling vinegared wine in lead pans to sweeten it, the process generating lead acetate, known as "sugar of lead". In part, neurotoxins have been part of human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
history because of the fragile and susceptible nature of the nervous system, making it highly prone to disruption.
The nervous tissue found in the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a ve ...
, spinal cord, and periphery comprises an extraordinarily complex biological system that largely defines many of the unique traits of individuals. As with any highly complex system, however, even small perturbations to its environment can lead to significant functional disruptions. Properties leading to the susceptibility of nervous tissue include a high surface area of neurons, a high lipid content which retains lipophilic toxins, high blood flow to the brain inducing increased effective toxin exposure, and the persistence of neurons through an individual's lifetime, leading to compounding of damages.Dobbs 2009 As a result, the nervous system has a number of mechanisms designed to protect it from internal and external assaults, including the blood brain barrier.
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is one critical example of protection which prevents toxins and other adverse compounds from reaching the brain.Widmaier, Eric P., Hershel Raff, Kevin T. Strang, and Arthur J. Vander (2008) Vander's Human Physiology: the Mechanisms of Body Function.' Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. As the brain requires nutrient entry and waste removal, it is perfused by blood flow. Blood can carry a number of ingested toxins, however, which would induce significant neuron death if they reach nervous tissue. Thus, protective cells termed astrocytes surround the capillaries in the brain and absorb nutrients from the blood and subsequently transport them to the neurons, effectively isolating the brain from a number of potential chemical insults.
 This barrier creates a tight hydrophobic layer around the capillary, capillaries in the brain, inhibiting the transport of large or hydrophilic compounds. In addition to the BBB, the choroid plexus provides a layer of protection against toxin absorption in the brain. The choroid plexuses are vascularized layers of tissue found in the third, fourth, and lateral ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, which through the function of their ependymal cells, are responsible for the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Martini 2009 Importantly, through selective passage of ions and nutrients and trapping heavy metals such as lead, the choroid plexuses maintain a strictly regulated environment which contains the brain and spinal cord.
This barrier creates a tight hydrophobic layer around the capillary, capillaries in the brain, inhibiting the transport of large or hydrophilic compounds. In addition to the BBB, the choroid plexus provides a layer of protection against toxin absorption in the brain. The choroid plexuses are vascularized layers of tissue found in the third, fourth, and lateral ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, which through the function of their ependymal cells, are responsible for the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).Martini 2009 Importantly, through selective passage of ions and nutrients and trapping heavy metals such as lead, the choroid plexuses maintain a strictly regulated environment which contains the brain and spinal cord.
 By being hydrophobic and small, or inhibiting astrocyte function, some compounds including certain neurotoxins are able to penetrate into the brain and induce significant damage. In modern times, scientists and physicians have been presented with the challenge of identifying and treating neurotoxins, which has resulted in a growing interest in both neurotoxicology research and clinical studies.Costa 2011 Though clinical neurotoxicology is largely a burgeoning field, extensive inroads have been made in the identification of many environmental neurotoxins leading to the classification of 750 to 1000 known potentially neurotoxic compounds. Due to the critical importance of finding neurotoxins in common environments, specific protocols have been developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for testing and determining neurotoxic effects of compounds (USEPA 1998). Additionally, in vitro systems have increased in use as they provide significant improvements over the more common in vivo systems of the past. Examples of improvements include tractable, uniform environments, and the elimination of contaminating effects of systemic metabolism. In vitro systems, however, have presented problems as it has been difficult to properly replicate the complexities of the nervous system, such as the interactions between supporting astrocytes and neurons in creating the BBB. To even further complicate the process of determining neurotoxins when testing in-vitro,
By being hydrophobic and small, or inhibiting astrocyte function, some compounds including certain neurotoxins are able to penetrate into the brain and induce significant damage. In modern times, scientists and physicians have been presented with the challenge of identifying and treating neurotoxins, which has resulted in a growing interest in both neurotoxicology research and clinical studies.Costa 2011 Though clinical neurotoxicology is largely a burgeoning field, extensive inroads have been made in the identification of many environmental neurotoxins leading to the classification of 750 to 1000 known potentially neurotoxic compounds. Due to the critical importance of finding neurotoxins in common environments, specific protocols have been developed by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) for testing and determining neurotoxic effects of compounds (USEPA 1998). Additionally, in vitro systems have increased in use as they provide significant improvements over the more common in vivo systems of the past. Examples of improvements include tractable, uniform environments, and the elimination of contaminating effects of systemic metabolism. In vitro systems, however, have presented problems as it has been difficult to properly replicate the complexities of the nervous system, such as the interactions between supporting astrocytes and neurons in creating the BBB. To even further complicate the process of determining neurotoxins when testing in-vitro, neurotoxicity
Neurotoxicity is a form of toxicity in which a biological, chemical, or physical agent produces an adverse effect on the structure or function of the central and/or peripheral nervous system. It occurs when exposure to a substance – specificall ...
and cytotoxicity may be difficult to distinguish as exposing neurons directly to compounds may not be possible in-vivo, as it is in-vitro. Additionally, the response of cell (biology), cells to chemicals may not accurately convey a distinction between neurotoxins and cytotoxins, as symptoms like oxidative stress or human skeleton, skeletal modifications may occur in response to either.
In an effort to address this complication, neurite outgrowths (either axonal or dendritic) in response to applied compounds have recently been proposed as a more accurate distinction between true neurotoxins and cytotoxins in an in-vitro testing environment. Due to the significant inaccuracies associated with this process, however, it has been slow in gaining widespread support. Additionally, biochemical mechanisms have become more widely used in neurotoxin testing, such that compounds can be screened for sufficiency to induce cell mechanism interference, like the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase capacity of organophosphates (includes ddt, DDT and sarin gas). Though methods of determining neurotoxicity still require significant development, the identification of deleterious compounds and toxin exposure symptoms has undergone significant improvement.
Applications in neuroscience
Though diverse in chemical properties and functions, neurotoxins share the common property that they act by some mechanism leading to either the disruption or destruction of necessary components within the nervous system. Neurotoxins, however, by their very design can be very useful in the field of neuroscience. As the nervous system in most organisms is both highly complex and necessary for survival, it has naturally become a target for attack by both predators and prey. As venom, venomous organisms often use their neurotoxins to subdue a predator or prey very rapidly, toxins have evolved to become highly specific to their target channels such that the toxin does not readily bind other targetsAdams 2003 (see :Ion channel toxins, Ion Channel toxins). As such, neurotoxins provide an effective means by which certain elements of the nervous system may be accurately and efficiently targeted. An early example of neurotoxin based targeting used isotopic labeling, radiolabeled tetrodotoxin to assay sodium channels and obtain precise measurements about their concentration along nerve cell membrane, membranes. Likewise through isolation of certain channel activities, neurotoxins have provided the ability to improve the original Hodgkin–Huxley model, Hodgkin-Huxley model of the neuron in which it was theorized that single generic sodium and potassium channels could account for most nervous tissue function. From this basic understanding, the use of common compounds such as tetrodotoxin, tetraethylammonium, and bungarotoxins have led to a much deeper understanding of the distinct ways in which individual neurons may behave.Mechanisms of activity
As neurotoxins are compounds which adversely affect the nervous system, a number of mechanisms through which they function are through the inhibition of neuron cellular processes. These inhibited processes can range from membrane depolarization mechanisms to synapse, inter-neuron communication. By inhibiting the ability for neurons to perform their expected intracellular functions, or pass a signal to a neighboring cell, neurotoxins can induce systemic nervous system arrest as in the case of botulinum toxin, or even nervous tissue death.Brocardo 2011 The time required for the onset of symptoms upon neurotoxin exposure can vary between different toxins, being on the order of hours for botulinum toxin and years for lead.Inhibitors
Sodium channel
=Tetrodotoxin
=Potassium channel
=Tetraethylammonium
= Tetraethylammonium (TEA) is a compound that, like a number of neurotoxins, was first identified through its damaging effects to the nervous system and shown to have the capacity of inhibiting the function of motor nerves and thus the contraction of the muscular system, musculature in a manner similar to that of curare.Standfield 1983 Additionally, through chronic TEA administration, muscular atrophy would be induced. It was later determined that TEA functions in-vivo primarily through its ability to inhibit both the potassium channels responsible for the delayed rectifier outward potassium current, delayed rectifier seen in an action potential and some population of calcium-dependent potassium channels. It is this capability to inhibit potassium flux in neurons that has made TEA one of the most important tools in neuroscience. It has been hypothesized that the ability for TEA to inhibit potassium channels is derived from its similar space-filling structure to potassium ions. What makes TEA very useful for neuroscientists is its specific ability to eliminate potassium channel activity, thereby allowing the study of neuron response contributions of other ion channels such as voltage gated sodium channels. In addition to its many uses in neuroscience research, TEA has been shown to perform as an effective treatment of Parkinson's disease through its ability to limit the progression of the disease.Chloride channel
=Chlorotoxin
= Chlorotoxin (Cltx) is the active compound found in scorpion venom, and is primarily toxic because of its ability to inhibit the conductance of chloride channels. Ingestion of lethal volumes of Cltx results in paralysis through this ion channel disruption. Similar to botulinum toxin, Cltx has been shown to possess significant therapeutic value. Evidence has shown that Cltx can inhibit the ability for gliomas to infiltrate healthy nervous tissue in the brain, significantly reducing the potential invasive harm caused by tumors.Calcium channel
=Conotoxin
= Conotoxins represent a category of poisons produced by the marine cone snail, and are capable of inhibiting the activity of a number of ion channels such as calcium, sodium, or potassium channels.Jacob 2010 In many cases, the toxins released by the different types of Coninae, cone snails include a range of different types of conotoxins, which may be specific for different ion channels, thus creating a venom capable of widespread nerve function interruption. One of the unique forms of conotoxins, ω-conotoxin (conotoxin, ω-CgTx) is highly specific for Ca channels and has shown usefulness in isolating them from a system. As calcium flux is necessary for proper excitability of a cell, any significant inhibition could prevent a large amount of functionality. Significantly, ω-CgTx is capable of long term binding to and inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels located in the membranes of neurons but not those of muscle cells.Synaptic vesicle release
=Botulinum toxin
= Botulinum toxin (BTX) is a group of neurotoxins consisting of eight distinct compounds, referred to as BTX-A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H, which are produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and lead to muscular paralysis.Brin, Mitchell F (1997) "Botulinum Toxin: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicity, and Immunology." ''Muscle & Nerve,'' 20 (S6): 146–68. A notably unique feature of BTX is its relatively common therapeutic use in treating dystonia and spasticity disorders, as well as in inducing muscular atrophy despite being the most poisonous substance known. BTX functions peripherally to inhibit acetylcholine (ACh) release at the neuromuscular junction through degradation of the SNARE proteins required for ACh vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle-membrane fusion. As the toxin is highly biologically active, an estimated dose of 1μg/kg body weight is sufficient to induce an insufficient tidal volume and resultant death by asphyxiation. Due to its high toxicity, BTX antitoxins have been an active area of research. It has been shown that capsaicin (active compound responsible for heat in chili peppers) can bind the TRPV1, TRPV1 receptor expressed on cholinergic, cholinergic neurons and inhibit the toxic effects of BTX.
Botulinum toxin (BTX) is a group of neurotoxins consisting of eight distinct compounds, referred to as BTX-A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H, which are produced by the bacterium ''Clostridium botulinum'' and lead to muscular paralysis.Brin, Mitchell F (1997) "Botulinum Toxin: Chemistry, Pharmacology, Toxicity, and Immunology." ''Muscle & Nerve,'' 20 (S6): 146–68. A notably unique feature of BTX is its relatively common therapeutic use in treating dystonia and spasticity disorders, as well as in inducing muscular atrophy despite being the most poisonous substance known. BTX functions peripherally to inhibit acetylcholine (ACh) release at the neuromuscular junction through degradation of the SNARE proteins required for ACh vesicle (biology and chemistry), vesicle-membrane fusion. As the toxin is highly biologically active, an estimated dose of 1μg/kg body weight is sufficient to induce an insufficient tidal volume and resultant death by asphyxiation. Due to its high toxicity, BTX antitoxins have been an active area of research. It has been shown that capsaicin (active compound responsible for heat in chili peppers) can bind the TRPV1, TRPV1 receptor expressed on cholinergic, cholinergic neurons and inhibit the toxic effects of BTX.
=Tetanus toxin
= Tetanus, Tetanus neurotoxin (TeNT) is a compound that functionally reduces inhibitory transmissions in the nervous system resulting in muscular tetany. TeNT is similar to BTX, and is in fact highly similar in structure and origin; both belonging to the same category of clostridium tetani, clostridial neurotoxins. Like BTX, TeNT inhibits inter-neuron communication by means of vesicular neurotransmitter (NT) release. One notable difference between the two compounds is that while BTX inhibits muscle, muscular contractions, TeNT induces them. Though both toxins inhibit vesicle release at neuron synapses, the reason for this different manifestation is that BTX functions mainly in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) while TeNT is largely active in thecentral nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
(CNS). This is a result of TeNT migration through motor neurons to the inhibitory neurotransmitter, inhibitory neurons of the spinal cord after entering through endocytosis.Pirazzini 2011 This results in a loss of function in inhibitory neurons within the CNS resulting in systemic muscle contraction, muscular contractions. Similar to the prognosis of a lethal dose of BTX, TeNT leads to paralysis and subsequent suffocation.
Blood brain barrier
=Aluminium
= Neurotoxic behavior of aluminium (element), Aluminium is known to occur upon entry into the circulatory system, where it can migrate to the brain and inhibit some of the crucial functions of the blood brain barrier (BBB).Banks 1988 A loss of function in the BBB can produce significant damage to the neurons in the CNS, as the barrier protecting the brain from other toxins found in the blood will no longer be capable of such action. Though the metal is known to be neurotoxic, effects are usually restricted to patients incapable of removing excess ions from the blood, such as those experiencing renal failure. Patients experiencing aluminium toxicity can exhibit symptoms such as impaired learning and reduced motor coordination. Additionally, systemic aluminium levels are known to increase with age, and have been shown to correlate with Alzheimer's disease, Alzheimer's Disease, implicating it as a neurotoxic causative compound of the disease. Despite its known toxicity in its ionic form, studies are divided on the potential toxicity of using aluminium in packaging and cooking appliances.=Mercury
= Mercury (element), Mercury is capable of inducing CNS damage by migrating into the brain by crossing the BBB. Mercury exists in a number of different compounds, though methylmercury (MeHg), dimethylmercury and diethylmercury are the only significantly neurotoxic forms. Diethylmercury and dimethylmercury are considered some of the most potent neurotoxins ever discovered. MeHg is usually acquired through consumption of seafood, as it tends to concentrate in organisms high on the food chain. It is known that the mercuric ion inhibits amino acid (AA) and glutamate (Glu) transport, potentially leading to excitotoxic effects.Receptor agonists and antagonists
Anatoxin-a
neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
s). The progressive symptoms of anatoxin-''a'' exposure are loss of coordination, Fasciculation, twitching, convulsions and rapid death by respiratory paralysis. The nerve tissues which communicate with muscles contain a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor called the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Stimulation of these receptors causes a muscular contraction. The anatoxin-''a'' molecule is shaped so it fits this receptor, and in this way it mimics the natural neurotransmitter normally used by the receptor, acetylcholine. Once it has triggered a contraction, anatoxin-''a'' does not allow the neurons to return to their resting state, because it is not degraded by cholinesterase which normally performs this function. As a result, the muscle cells contract permanently, the communication between the brain and the muscles is disrupted and breathing stops.
When it was first discovered, the toxin was called the Very Fast Death Factor (VFDF) because when it was Intraperitoneal injection, injected into the body cavity of mice it induced tremors, paralysis and death within a few minutes. In 1977, the structure of VFDF was determined as a secondary, bicyclic amine alkaloid, and it was renamed anatoxin-''a''. Structurally, it is similar to cocaine.Metcalf 2009 There is continued interest in anatoxin-''a'' because of the dangers it presents to recreational and drinking waters, and because it is a particularly useful molecule for investigating acetylcholine receptors in the nervous system.Stewart 2008 The deadliness of the toxin means that it has a high military potential as a toxin weapon.Dixit 2005
Bungarotoxin
Bungarotoxin is a compound with known interaction with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), which constitute a family of ion channels whose activity is triggered by neurotransmitter binding.Tsetlin 2003 Bungarotoxin is produced in a number of different forms, though one of the commonly used forms is the long chain alpha form, α-bungarotoxin, which is isolated from the banded krait, banded krait snake. Though extremely toxic if ingested, α-bungarotoxin has shown extensive usefulness in neuroscience as it is particularly adept at isolating nAChRs due to its high affinity to the receptors. As there are multiple forms of bungarotoxin, there are different forms of nAChRs to which they will bind, and α-bungarotoxin is particularly specific for alpha-7 nicotinic receptor, α7-nAChR.Liu 2008 This α7-nAChR functions to allow calcium ion influx into cells, and thus when blocked by ingested bungarotoxin will produce damaging effects, as ACh signaling will be inhibited. Likewise, the use of α-bungarotoxin can be very useful in neuroscience if it is desirable to block calcium flux in order to isolate effects of other channels. Additionally, different forms of bungarotoxin may be useful for studying inhibited nAChRs and their resultant calcium ion flow in different systems of the body. For example, α-bungarotoxin is specific for nAChRs found in the musculature and κ-bungarotoxin is specific for nAChRs found in neurons.=Caramboxin
=toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ...
found in star fruit (''Averrhoa carambola)''. Individuals with some types of kidney disease are susceptible to adverse neurological effects including intoxication, seizures and even death after eating star fruit or drinking juice made of this fruit. Caramboxin is a new nonpeptide amino acid toxin that stimulate the glutamate receptors in neurons. Caramboxin is an agonist of both NMDA receptor, NMDA and AMPA receptor, AMPA glutamatergic ionotropic receptors with potent excitatory, convulsant, and neurodegenerative properties.
=Curare
= The term "curare" is ambiguous because it has been used to describe a number of poisons which at the time of naming were understood differently from present day understandings. In the past the characterization has meant poisons used by indigenous peoples of the americas, South American tribes on arrows or dart (missile), darts, though it has matured to specify a specific categorization of poisons which act on the neuromuscular junction to inhibit signaling and thus induce muscle relaxation.Bisset 1992 The neurotoxin category contains a number of distinct poisons, though all were originally purified from plants originating in South America. The effect with which injected curare poison is usually associated is muscle paralysis and resultant death.Schlesinger 1946 Curare notably functions to inhibit nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at the neuromuscular junction. Normally, these receptor channels allow sodium ions into muscle cells to initiate an action potential that leads to muscle contraction. By blocking the receptors, the neurotoxin is capable of significantly reducing neuromuscular junction signaling, an effect which has resulted in its use by anesthesiologists to produce muscular relaxation.Cytoskeleton interference
Ammonia
 Ammonia toxicity is often seen through two routes of administration, either through consumption or through endogenous ailments such as liver failure.Matsuoka 1991 One notable case in which ammonia toxicity is common is in response to cirrhosis of the liver which results in hepatic encephalopathy, and can result in cerebral edema (Haussinger 2006). This cerebral edema can be the result of nervous cell remodeling. As a consequence of increased concentrations, ammonia activity in-vivo has been shown to induce swelling of astrocytes in the brain through increased production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP (Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate) within the cells which leads to cGMP-dependent protein kinase, Protein Kinase G-mediated (PKG) cytoskeletal modifications. The resultant effect of this toxicity can be reduced brain energy metabolism and function. Importantly, the toxic effects of ammonia on astrocyte remodeling can be reduced through administration of carnitine, L-carnitine. This astrocyte remodeling appears to be mediated through ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. This mitochondrial transition is a direct result of glutamine activity a compound which forms from ammonia in-vivo.Norenberg 2004 Administration of antioxidants or glutaminase inhibitor can reduce this mitochondrial transition, and potentially also astrocyte remodeling.
Ammonia toxicity is often seen through two routes of administration, either through consumption or through endogenous ailments such as liver failure.Matsuoka 1991 One notable case in which ammonia toxicity is common is in response to cirrhosis of the liver which results in hepatic encephalopathy, and can result in cerebral edema (Haussinger 2006). This cerebral edema can be the result of nervous cell remodeling. As a consequence of increased concentrations, ammonia activity in-vivo has been shown to induce swelling of astrocytes in the brain through increased production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate, cGMP (Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate) within the cells which leads to cGMP-dependent protein kinase, Protein Kinase G-mediated (PKG) cytoskeletal modifications. The resultant effect of this toxicity can be reduced brain energy metabolism and function. Importantly, the toxic effects of ammonia on astrocyte remodeling can be reduced through administration of carnitine, L-carnitine. This astrocyte remodeling appears to be mediated through ammonia-induced mitochondrial permeability transition. This mitochondrial transition is a direct result of glutamine activity a compound which forms from ammonia in-vivo.Norenberg 2004 Administration of antioxidants or glutaminase inhibitor can reduce this mitochondrial transition, and potentially also astrocyte remodeling.
Arsenic
Arsenic is a neurotoxin commonly found concentrated in areas exposed to agricultural runoff, mining, and smelting sites (Martinez-Finley 2011). One of the effects of arsenic ingestion during the development of the nervous system is the inhibition of neurite growth which can occur both in PNS and the CNS. This neurite growth inhibition can often lead to defects in neuronal migration, neural migration, and significant morphological changes of neurons during developmental biology, development,Rocha 2011) often leading to neural tube defects in infant, neonates. As a metabolite of arsenic, arsenite is formed after ingestion of arsenic and has shown significant toxicity to neurons within about 24 hours of exposure. The mechanism of this cytotoxicity functions through arsenite-induced increases in intracellular calcium ion levels within neurons, which may subsequently reduce mitochondrial transmembrane potential which activates caspases, triggering cell death. Another known function of arsenite is its destructive nature towards the cytoskeleton through inhibition of neurofilament transport. This is particularly destructive as neurofilaments are used in basic cell structure and support. Lithium administration has shown promise, however, in restoring some of the lost neurofilament motility. Additionally, similar to other neurotoxin treatments, the administration of certain antioxidants has shown some promise in reducing neurotoxicity of ingested arsenic.Calcium-mediated cytotoxicity
Lead
 Lead is a potent neurotoxin whose toxicity has been recognized for at least thousands of years.Lidskey 2003 Though neurotoxic effects for lead are found in both adults and young children, the developing brain is particularly susceptible to lead-induced harm, effects which can include apoptosis and excitotoxicity. An underlying mechanism by which lead is able to cause harm is its ability to be transported by atpase, calcium ATPase pumps across the BBB, allowing for direct contact with the fragile cells within the central nervous system. Neurotoxicity results from lead's ability to act in a similar manner to calcium ions, as concentrated lead will lead to cellular uptake of calcium which disrupts cellular homeostasis and induces apoptosis. It is this intracellular calcium increase that activates protein kinase c, protein kinase C (PKC), which manifests as learning deficits in children as a result of early lead exposure. In addition to inducing apoptosis, lead inhibits interneuron signaling through the disruption of calcium-mediated neurotransmitter release.
Lead is a potent neurotoxin whose toxicity has been recognized for at least thousands of years.Lidskey 2003 Though neurotoxic effects for lead are found in both adults and young children, the developing brain is particularly susceptible to lead-induced harm, effects which can include apoptosis and excitotoxicity. An underlying mechanism by which lead is able to cause harm is its ability to be transported by atpase, calcium ATPase pumps across the BBB, allowing for direct contact with the fragile cells within the central nervous system. Neurotoxicity results from lead's ability to act in a similar manner to calcium ions, as concentrated lead will lead to cellular uptake of calcium which disrupts cellular homeostasis and induces apoptosis. It is this intracellular calcium increase that activates protein kinase c, protein kinase C (PKC), which manifests as learning deficits in children as a result of early lead exposure. In addition to inducing apoptosis, lead inhibits interneuron signaling through the disruption of calcium-mediated neurotransmitter release.
Neurotoxins with multiple effects
Ethanol
 As a neurotoxin,
As a neurotoxin, ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
has been shown to induce nervous system damage and affect the body in a variety of ways. Among the known effects of ethanol exposure are both transient and lasting consequences. Some of the lasting effects include long-term reduced neurogenesis in the hippocampus, widespread brain atrophy, and induced inflammation in the brain. Of note, chronic ethanol ingestion has additionally been shown to induce reorganization of cellular membrane constituents, leading to a lipid bilayer marked by increased membrane concentrations of cholesterol and saturated fat. This is important as neurotransmitter transport can be impaired through vesicular transport inhibition, resulting in diminished neural network function. One significant example of reduced inter-neuron communication is the ability for ethanol to inhibit nmda receptor, NMDA receptors in the hippocampus, resulting in reduced long-term potentiation (LTP) and memory acquisition. NMDA has been shown to play an important role in LTP and consequently memory formation. With chronic ethanol intake, however, the susceptibility of these NMDA receptors to induce LTP increases in the mesolimbic pathway, mesolimbic dopamine neurons in an inositol triphosphate, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) dependent manner. This reorganization may lead to neuronal cytotoxicity both through hyperactivation of postsynaptic neurons and through induced addiction to continuous ethanol consumption. It has, additionally, been shown that ethanol directly reduces intracellular calcium ion accumulation through inhibited NMDA receptor activity, and thus reduces the capacity for the occurrence of LTP.Takadera 1990
In addition to the neurotoxic effects of ethanol in mature organisms, chronic ingestion is capable of inducing severe developmental defects. Evidence was first shown in 1973 of a connection between chronic ethanol intake by mothers and defects in their offspring. This work was responsible for creating the classification of fetal alcohol syndrome, a disease characterized by common morphogenesis aberrations such as defects in craniofacial formation, limb development, and cardiovascular system, cardiovascular formation. The magnitude of ethanol neurotoxicity in fetuses leading to fetal alcohol syndrome has been shown to be dependent on antioxidant levels in the brain such as vitamin e, vitamin E. As the fetal brain is relatively fragile and susceptible to induced stresses, severe deleterious effects of alcohol exposure can be seen in important areas such as the hippocampus and cerebellum. The severity of these effects is directly dependent upon the amount and frequency of ethanol consumption by the mother, and the stage in development of the fetus. It is known that ethanol exposure results in reduced antioxidant levels, mitochondrial dysfunction (Chu 2007), and subsequent neuronal death, seemingly as a result of increased generation of reactive oxygen species, reactive oxidative species (ROS). This is a plausible mechanism, as there is a reduced presence in the fetal brain of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and peroxidase. In support of this mechanism, administration of high levels of diet (nutrition), dietary vitamin E results in reduced or eliminated ethanol-induced neurotoxic effects in fetuses.
n-Hexane
n-Hexane is a neurotoxin which has been responsible for the poisoning of several workers in Chinese electronics factories in recent years.Occupational Safety and Health Guideline for n-Hexane, OSHA.gov
Receptor-selective neurotoxins
MPP+
MPP+, MPP+, the toxic metabolite of MPTP is a selective neurotoxin which interferes with oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria by inhibiting complex I, leading to the depletion of Adenosine triphosphate, ATP and subsequent cell death. This occurs almost exclusively in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra, resulting in the presentation of permanent parkinsonism in exposed subjects 2–3 days after administration.Endogenous neurotoxin sources
Unlike most common sources of neurotoxins which are acquired by the body through ingestion, endogenous neurotoxins both originate from and exert their effects in vivo, in-vivo. Additionally, though most venoms and exogenous neurotoxins will rarely possess useful in-vivo capabilities, endogenous neurotoxins are commonly used by the body in useful and healthy ways, such as nitric oxide which is used in cell communication. It is often only when these endogenous compounds become highly concentrated that they lead to dangerous effects.Nitric oxide
Though nitric oxide (NO) is commonly used by the nervous system in inter-neuron communication and signaling, it can be active in mechanisms leading to ischemia in the cerebrum (Iadecola 1998). The neurotoxicity of NO is based on its importance in glutamate excitotoxicity, as NO is generated in a calcium-dependent manner in response to glutamate mediated NMDA activation, which occurs at an elevated rate in glutamate excitotoxicity. Though NO facilitates increased blood flow to potentially ischemic regions of the brain, it is also capable of increasing oxidative stress, inducing DNA damage and apoptosis.Bonfoco 1995 Thus an increased presence of NO in an ischemic area of the CNS can produce significantly toxic effects.Glutamate
Glutamate, like nitric oxide, is an endogenously produced compound used by neurons to perform normally, being present in small concentrations throughout the gray matter of the CNS. One of the most notable uses of endogenous glutamate is its functionality as an excitatory neurotransmitter. When concentrated, however, glutamate becomes toxic to surrounding neurons. This toxicity can be both a result of direct lethality of glutamate on neurons and a result of induced calcium flux into neurons leading to swelling and necrosis. Support has been shown for these mechanisms playing significant roles in diseases and complications such as Huntington's disease,epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrica ...
, and stroke.
See also
*Babycurus toxin 1 *CangitoxinNotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Chan, H. M. (2011) "Mercury in Fish: Human Health Risks." ''Encyclopedia of Environmental Health'': 697–704. * * * * * * * Costa, Lucio G., Gennaro Giordano, and Marina Guizzetti (2011) ''In Vitro Neurotoxicology: Methods and Protocols.'' New York: Humana. * * * * * Debin, John A., John E. Maggio, and Gary R. Strichartz (1993) "Purification and Characterization of Chlorotoxin, a Chloride Channel Ligand from the Venom of the Scorpion." ''The American Physiological Society'', pp. 361–69. * * Defuria, Jason (2006) "The Environmental Neurotoxin Arsenic Impairs Neurofilament Dynamics by Overactivation of C-JUN Terminal Kinase: Potential Role for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis." ''UMI'', pp. 1–16. * * * * * * Dobbs, Michael R (2009) ''Clinical Neurotoxicology.'' Philadelphia: Saunders-Elsevier. * * * * * * * * * * Herbert, M. R. (2006) "Autism and Environmental Genomics." ''NeuroToxicology'', pp. 671–84. Web. * Hodge, A. Trevor (2002) ''Roman Aqueducts and Water Supply''. London: Duckworth. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Lotti, Marcello, and Angelo Moretto (1989) "Organophosphate-Induced Delayed Polyneuropathy." ''Toxicological Reviews,'' 24 (1) (2005): 37–49. * * Martini, Frederic, Michael J. Timmons, and Robert B. Tallitsch (2009) ''Human Anatomy.'' San Francisco: Pearson/Benjamin Cummings. * * * * * * * * Morris, Stephanie A., David W. Eaves, Aleksander R. Smith, and Kimberly Nixon (2009) "Alcohol Inhibition of Neurogenesis: A Mechanism of Hippocampal Neurodegeneration in an Adolescent Alcohol Abuse Model." Hippocampus: NA. * * National Center for Environmental Assessment (2006) "Toxicological Reviews of Cyanobacterial Toxins: Anatoxin-a" NCEA-C-1743 * * * * Pirazzini, Marco, Ornella Rossetto, Paolo Bolognese, Clifford C. Shone, and Cesare Montecucco (2011) "Double Anchorage to the Membrane and Intact Inter-chain Disulfide Bond Are Required for the Low PH Induced Entry of Tetanus and Botulinum Neurotoxins into Neurons." Cellular Microbiology: No. Print. * * * * * * * * * Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH, Ludolph AC (Eds) (2000) Experimental and Clinical Neurotoxicology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp. 1310. * * * * * * * * USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1998) Health Effects Test Guidelines. OPPTS 870.6200. Neurotoxicity screening battery. Washington DC, USEPA. * Vahidnia, A., G.B. Van Der Voet, and F.A. De Wolff (2007) "Arsenic Neurotoxicity A Review." ''Human & Experimental Toxicology,'' 26 (10) : 823–32. * * Widmaier, Eric P., Hershel Raff, Kevin T. Strang, and Arthur J. Vander (2008) ''Vander's Human Physiology: the Mechanisms of Body Function.'' Boston: McGraw-Hill Higher Education. * * * * * Yang, X (2007''Occurrence of the cyanobacterial neurotoxin, anatoxin-a, in New York State waters''
ProQuest. . *
Further reading
Brain Facts Book
at The Society for Neuroscience
Neuroscience Texts
at University of Texas Medical School
In Vitro Neurotoxicology: An Introduction
at Springerlink
Biology of the NMDA Receptor
at NCBI
Advances in the Neuroscience of Addiction, 2nd edition
at NCBI
External links
Environmental Protection Agency
at United States Environmental Protection Agency
Alcohol and Alcoholism
at Oxford Medical Journals
Neurotoxicology
at Elsevier Journals
Neurotoxin Institute
at Neurotoxin Institute
Neurotoxins] at Toxipedia {{Toxins Neurotoxins,