Martial arts on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as



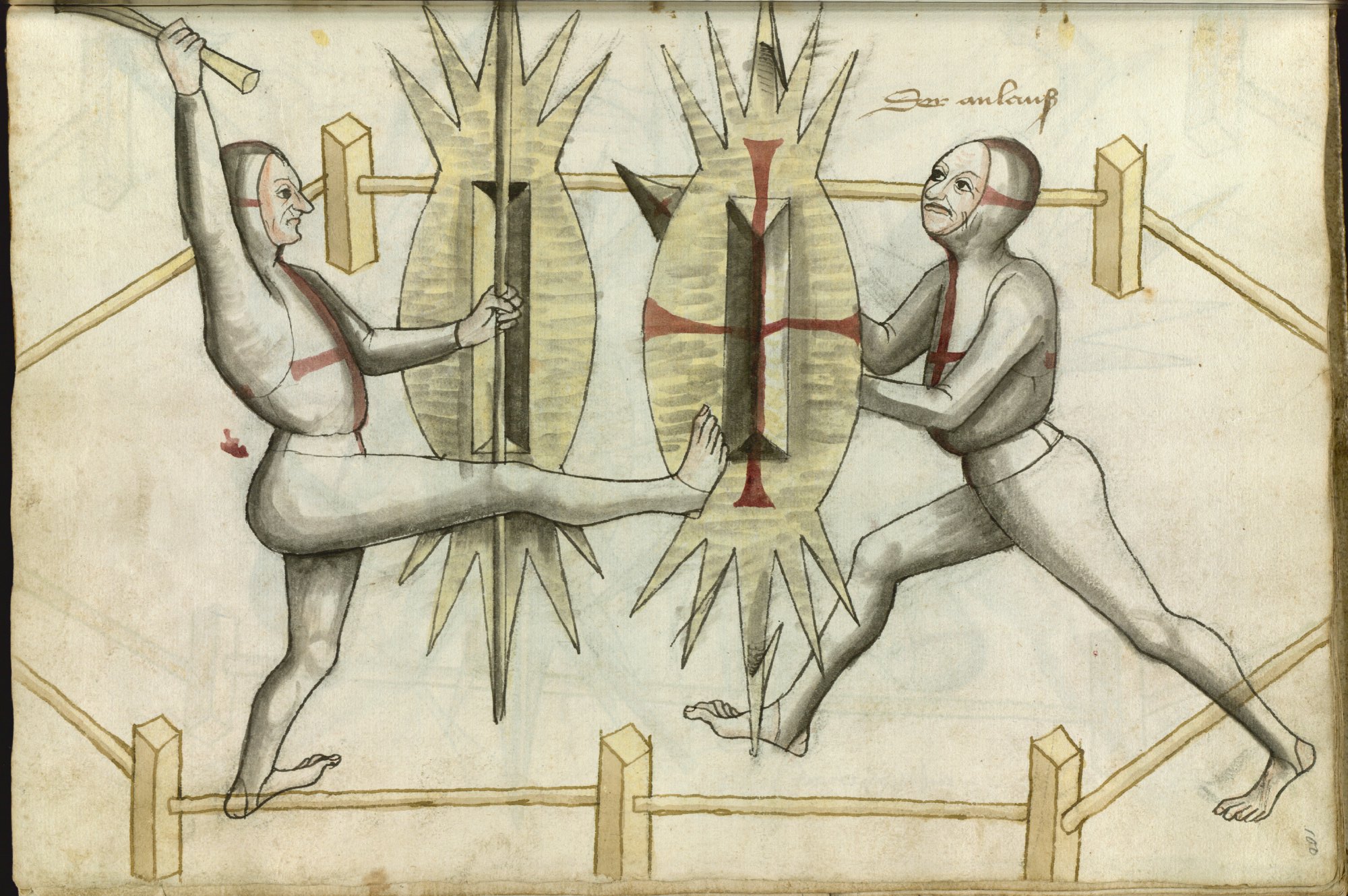 Human warfare dates back to the
Human warfare dates back to the  The foundation of modern East Asian martial arts and South Asian martial arts is likely facilitated by cultural exchanges of early Chinese and Indian martial arts. During the
The foundation of modern East Asian martial arts and South Asian martial arts is likely facilitated by cultural exchanges of early Chinese and Indian martial arts. During the  European swordsmanship always had a sportive component, but the duel was always a possibility until World War I. Modern fencing, sport fencing began developing during the 19th century as the French and Italian military academies began codifying instruction. The Olympic games led to standard international rules, with the Féderation Internationale d'Escrime founded in 1913. Modern boxing originates with Jack Broughton's rules in the 18th century, and reaches its present form with the Marquess of Queensberry Rules of 1867.
European swordsmanship always had a sportive component, but the duel was always a possibility until World War I. Modern fencing, sport fencing began developing during the 19th century as the French and Italian military academies began codifying instruction. The Olympic games led to standard international rules, with the Féderation Internationale d'Escrime founded in 1913. Modern boxing originates with Jack Broughton's rules in the 18th century, and reaches its present form with the Marquess of Queensberry Rules of 1867.
 Certain traditional combat sports and fighting styles exist all over the world, rooted in local culture and folklore. The most common of these are styles of
Certain traditional combat sports and fighting styles exist all over the world, rooted in local culture and folklore. The most common of these are styles of

 The International Boxing Association (amateur), International Boxing Association was established in 1920. World Fencing Championships have been held since 1921.
As Western influence grew in Asia a greater number of military personnel spent time in China, Japan and South Korea during World War II and the Korean War and were exposed to local fighting styles. Jujutsu, judo and karate first became popular among the mainstream from the 1950s–1960s. Due in part to Asian and Hollywood martial arts movies, most modern American martial arts are either Asian-derived or Asian influenced. The term kickboxing (キックボクシング) was created by the Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi for a variant of muay Thai and karate that he created in the 1950s. American kickboxing was developed in the 1970s, as a combination of boxing and karate. Taekwondo was developed in the context of the Korean War in the 1950s.
The later 1960s and 1970s witnessed an increased media interest in
The International Boxing Association (amateur), International Boxing Association was established in 1920. World Fencing Championships have been held since 1921.
As Western influence grew in Asia a greater number of military personnel spent time in China, Japan and South Korea during World War II and the Korean War and were exposed to local fighting styles. Jujutsu, judo and karate first became popular among the mainstream from the 1950s–1960s. Due in part to Asian and Hollywood martial arts movies, most modern American martial arts are either Asian-derived or Asian influenced. The term kickboxing (キックボクシング) was created by the Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi for a variant of muay Thai and karate that he created in the 1950s. American kickboxing was developed in the 1970s, as a combination of boxing and karate. Taekwondo was developed in the context of the Korean War in the 1950s.
The later 1960s and 1970s witnessed an increased media interest in
 Jackie Chan and Jet Li are prominent martial artists who have become major movie figures. Their popularity and media presence has been at the forefront for promoting Chinese martial arts since the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
With the continual discovery of more medieval and Renaissance fighting manuals, the practice of Historical European Martial Arts and other Western Martial Arts have been growing in popularity across the United States and Europe.
On 29 November 2011,
Jackie Chan and Jet Li are prominent martial artists who have become major movie figures. Their popularity and media presence has been at the forefront for promoting Chinese martial arts since the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
With the continual discovery of more medieval and Renaissance fighting manuals, the practice of Historical European Martial Arts and other Western Martial Arts have been growing in popularity across the United States and Europe.
On 29 November 2011,
 Various forms and sparring are commonly used in martial art exhibitions and tournaments. Some competitions pit practitioners of different disciplines against each other using a common set of rules, these are referred to as mixed martial arts competitions. Rules for sparring vary between art and organization but can generally be divided into ''light-contact'', ''medium-contact'', and ''full-contact'' variants, reflecting the amount of force that should be used on an opponent.
Various forms and sparring are commonly used in martial art exhibitions and tournaments. Some competitions pit practitioners of different disciplines against each other using a common set of rules, these are referred to as mixed martial arts competitions. Rules for sparring vary between art and organization but can generally be divided into ''light-contact'', ''medium-contact'', and ''full-contact'' variants, reflecting the amount of force that should be used on an opponent.
 Martial arts have crossed over into sports when forms of sparring become competitive, becoming a sport in its own right that is dissociated from the original combative origin, such as with western fencing. The Summer Olympic Games includes judo, taekwondo, western archery, boxing, javelin, wrestling and fencing as events, while Wushu (sport), Chinese wushu recently failed in its bid to be included, but is still actively performed in tournaments across the world. Practitioners in some arts such as kickboxing and Brazilian jiu-jitsu often train for sport matches, whereas those in other arts such as aikido generally spurn such competitions. Some schools believe that competition breeds better and more efficient practitioners, and gives a sense of good sportsmanship. Others believe that the rules under which competition takes place have diminished the combat effectiveness of martial arts or encourage a kind of practice which focuses on winning trophies rather than a focus such as cultivating a particular moral character.
The question of "which is the best martial art" has led to inter style competitions fought with very few rules allowing a variety of fighting styles to enter with few limitations. This was the origin of the first Ultimate Fighting Championship tournament (later renamed UFC 1, UFC 1: The Beginning) in the USA inspired by the Brazilian Vale tudo tradition and along with other minimal rule competitions, most notably those from Japan such as Shooto and Pancrase, have evolved into the
Martial arts have crossed over into sports when forms of sparring become competitive, becoming a sport in its own right that is dissociated from the original combative origin, such as with western fencing. The Summer Olympic Games includes judo, taekwondo, western archery, boxing, javelin, wrestling and fencing as events, while Wushu (sport), Chinese wushu recently failed in its bid to be included, but is still actively performed in tournaments across the world. Practitioners in some arts such as kickboxing and Brazilian jiu-jitsu often train for sport matches, whereas those in other arts such as aikido generally spurn such competitions. Some schools believe that competition breeds better and more efficient practitioners, and gives a sense of good sportsmanship. Others believe that the rules under which competition takes place have diminished the combat effectiveness of martial arts or encourage a kind of practice which focuses on winning trophies rather than a focus such as cultivating a particular moral character.
The question of "which is the best martial art" has led to inter style competitions fought with very few rules allowing a variety of fighting styles to enter with few limitations. This was the origin of the first Ultimate Fighting Championship tournament (later renamed UFC 1, UFC 1: The Beginning) in the USA inspired by the Brazilian Vale tudo tradition and along with other minimal rule competitions, most notably those from Japan such as Shooto and Pancrase, have evolved into the
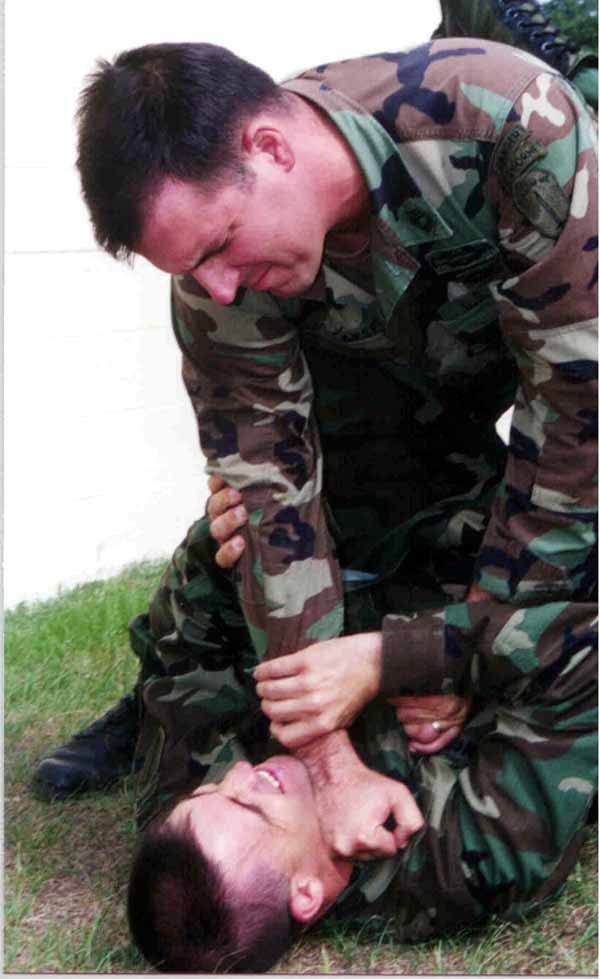 Some traditional martial concepts have seen new use within modern military training. Perhaps the most recent example of this is point shooting which relies on muscle memory to more effectively use a firearm in a variety of awkward situations, much the way an iaidoka would master movements with their sword.
Some traditional martial concepts have seen new use within modern military training. Perhaps the most recent example of this is point shooting which relies on muscle memory to more effectively use a firearm in a variety of awkward situations, much the way an iaidoka would master movements with their sword.
 During the World War II era William E. Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes were recruited by the Special Operations Executive (SOE) to teach their martial art of Defendu (itself drawing on Western boxing and Jujutsu) and pistol shooting to UK, US, and Canadian special forces. The book ''Kill or Get Killed'', written by Colonel Rex Applegate, was based on the Defendu taught by Sykes and Fairbairn. Both Fairbairn's ''Get Tough'' and Appelgate's ''Kill or Get Killed'' became classic works on hand-to-hand combat.
Traditional hand-to-hand, knife, and spear techniques continue to see use in the composite systems developed for today's wars. Examples of this include European Unifight, the US Army's Combatives system developed by Matt Larsen, the Israeli army's KAPAP and Krav Maga, and the US Marine Corps's ''Marine Corps Martial Arts Program'' (MCMAP). Unarmed dagger defenses identical to those found in the manual of Fiore dei Liberi and the Codex Wallerstein were integrated into the U.S. Army's training manuals in 1942
and continue to influence today's systems along with other traditional systems such as eskrima and silat.
The rifle-mounted bayonet which has its origin in the spear, has seen use by the United States Army, the United States Marine Corps, and the British Army as recently as the Iraq War.
Many martial arts are also seen and used in Law Enforcement hand-to-hand training. For example, the Tokyo Riot Police's use of aikido.Twigger, R. (1997). ''Angry White Pyjamas''. London: Phoenix.
During the World War II era William E. Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes were recruited by the Special Operations Executive (SOE) to teach their martial art of Defendu (itself drawing on Western boxing and Jujutsu) and pistol shooting to UK, US, and Canadian special forces. The book ''Kill or Get Killed'', written by Colonel Rex Applegate, was based on the Defendu taught by Sykes and Fairbairn. Both Fairbairn's ''Get Tough'' and Appelgate's ''Kill or Get Killed'' became classic works on hand-to-hand combat.
Traditional hand-to-hand, knife, and spear techniques continue to see use in the composite systems developed for today's wars. Examples of this include European Unifight, the US Army's Combatives system developed by Matt Larsen, the Israeli army's KAPAP and Krav Maga, and the US Marine Corps's ''Marine Corps Martial Arts Program'' (MCMAP). Unarmed dagger defenses identical to those found in the manual of Fiore dei Liberi and the Codex Wallerstein were integrated into the U.S. Army's training manuals in 1942
and continue to influence today's systems along with other traditional systems such as eskrima and silat.
The rifle-mounted bayonet which has its origin in the spear, has seen use by the United States Army, the United States Marine Corps, and the British Army as recently as the Iraq War.
Many martial arts are also seen and used in Law Enforcement hand-to-hand training. For example, the Tokyo Riot Police's use of aikido.Twigger, R. (1997). ''Angry White Pyjamas''. London: Phoenix.
Taekwondo: A new strategy for Brand Korea
(21 December 2009). Retrieved on 8 January 2010. The wholesale value of martial arts related sporting equipment shipped in the United States was estimated at US$314 million in 2007; participation in the same year was estimated at 6.9 million (ages 6 or older, 2% of US population). R. A. Court, CEO of Martial Arts Channel, stated the total revenue of the US martial arts industry at US$40 billion and the number of US practitioners at 30 million in 2003.
self-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force ...
; military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct ...
and law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act in an organized manner to enforce the law by discovering, deterring, rehabilitating, or punishing people who violate the rules and norms governing that society. The term ...
applications; competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, ind ...
; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment
Entertainment is a form of activity that holds the attention and interest of an audience or gives pleasure and delight. It can be an idea or a task, but is more likely to be one of the activities or events that have developed over thousa ...
; and the preservation of a nation's intangible cultural heritage.
Etymology
According to Paul Bowman, the term ''martial arts'' was popularized by mainstreampopular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
during the 1960s to 1970s, notably by Hong Kong martial arts films (most famously those of Bruce Lee) during the so-called " chopsocky" wave of the early 1970s.
According to John Clements, the term '' martial arts'' itself is derived from an older Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
term meaning "arts of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
", the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
god of war, and was used to refer to the combat systems of Europe ( European martial arts) as early as the 1550s.
The term martial science, or martial sciences, was commonly used to refer to the fighting arts of East Asia
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
( Asian martial arts) up until the 1970s, while the term ''Chinese boxing'' was also used to refer to Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to comm ...
up until then.
Some authors have argued that fighting arts or fighting systems would be more appropriate terms on the basis that many martial arts were never "martial" in the sense of being used or created by professional warrior
A warrior is a person specializing in combat or warfare, especially within the context of a tribal or clan-based warrior culture society that recognizes a separate warrior aristocracies, class, or caste.
History
Warriors seem to have be ...
s.
Variation and scope
Martial arts may be categorized using a variety of criteria, including: * Traditional/historical arts vs. contemporary styles: e.g.,folk wrestling
A folk wrestling style is any traditional style of wrestling, which may or may not be codified as a modern sport. Most cultures have developed regional forms of grappling.
Europe
Britain
Traditionally wrestling has two main centres in Great ...
compared to modern hybrid martial arts.
* Techniques taught: armed vs. unarmed, and within these categories
** armed: by type of weapon ( swordsmanship, stick fighting etc.)
** unarmed: by type of combat (grappling
Grappling, in hand-to-hand combat, describes sports that consist of gripping or seizing the opponent. Grappling is used at close range to gain a physical advantage over an opponent, either by imposing a position or causing injury. Grappling ...
vs. striking, stand-up fighting
In martial arts and combat sports, stand-up fighting is hand-to-hand combat between opponents in a standing position, as distinguished from ground fighting. Clinch fighting is stand-up grappling. Fighters employ striking, including striking ...
vs. ground fighting
Ground fighting (also called ground work or ground game) is hand-to-hand combat which takes place while the combatants are on the ground. The term is commonly used in mixed martial arts and other combat sports, as well as various forms of marti ...
)
* By application or intent: self-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force ...
, combat sport
A combat sport, or fighting sport, is a competitive contact sport that usually involves one-on-one combat. In many combat sports, a contestant wins by scoring more points than the opponent, submitting the opponent with a hold, disabling the oppo ...
, choreography or demonstration of forms, physical fitness, meditation
Meditation is a practice in which an individual uses a technique – such as mindfulness, or focusing the mind on a particular object, thought, or activity – to train attention and awareness, and achieve a mentally clear and emotionally calm ...
, etc.
* Within Chinese tradition: "external" vs. "internal" styles
By technical focus
Unarmed
Unarmed martial arts can be broadly grouped into those focusing on strikes, those focusing ongrappling
Grappling, in hand-to-hand combat, describes sports that consist of gripping or seizing the opponent. Grappling is used at close range to gain a physical advantage over an opponent, either by imposing a position or causing injury. Grappling ...
, and those that cover both fields, often described as hybrid martial arts.
Strikes
* Punching: Boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
, Wing Chun
* Kicking: Kickboxing, Taekwondo, Capoeira, Savate, Karate
* Others using strikes: Lethwei
Lethwei ( my, လက်ဝှေ့; IPA: ) or Burmese boxing, is a full contact combat sport from Myanmar that uses stand-up striking including headbutts. Lethwei is considered to be one of the most brutal martial arts in the world,
*
*
* a ...
, Muay Thai, Kung Fu, Pencak Silat, Kalaripayattu

Grappling
Grappling, in hand-to-hand combat, describes sports that consist of gripping or seizing the opponent. Grappling is used at close range to gain a physical advantage over an opponent, either by imposing a position or causing injury. Grappling ...
* Throwing: Hapkido, Judo
is an unarmed modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo") ...
, Sumo, Wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat s ...
, Aikido
* Joint lock/ Chokeholds/ Submission holds: Jujutsu
Jujutsu ( ; ja, link=no, 柔術 , ), also known as jiu-jitsu and ju-jitsu, is a family of Japanese martial arts and a system of close combat (unarmed or with a minor weapon) that can be used in a defensive or offensive manner to kill or subd ...
, Brazilian jiu-jitsu
Brazilian jiu-jitsu (BJJ; pt, jiu-jitsu brasileiro ) is a self-defence martial art and combat sport based on grappling, ground fighting (ne-waza) and submission holds. BJJ focuses on the skill of taking an opponent to the ground, control ...
, Sambo
, aka = Sombo (in English-speaking countries)
, focus = Hybrid
, country = Soviet Union
, pioneers = Viktor Spiridonov, Vasili Oshchepkov, Anatoly Kharlampiev
, famous_pract = List of Practitioners
, olymp ...
, Catch wrestling
Catch wrestling (originally catch-as-catch-can) is a classical hybrid grappling style and combat sport. It was developed by J. G. Chambers in Britain . It was popularised by wrestlers of travelling funfairs who developed their own submission ...
* Pinning Techniques: Judo, Wrestling, Aikido
Armed
The traditional martial arts that coverarmed combat
Combat (French for ''fight'') is a purposeful violent conflict meant to physically harm or kill the opposition. Combat may be armed (using weapons) or unarmed ( not using weapons). Combat is sometimes resorted to as a method of self-defense, or ...
often encompass a wide spectrum of melee weapons, including bladed weapons and polearms. Such traditions include eskrima, silat, kalaripayat, kobudo, and historical European martial arts, especially those of the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
. Many Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to comm ...
also feature weapons as part of their curriculum.
Sometimes, training with one specific weapon may be considered a style in its own right, especially in the case of Japanese martial arts, with disciplines such as kenjutsu and kendo (sword), bojutsu (staff), and kyūdō (archery). Similarly, modern martial arts and sports include modern fencing, stick-fighting systems like canne de combat, modern competitive archery and practical shooting
Practical shooting, also known as dynamic shooting or action shooting, is a set of shooting sports where the competitors try to unite the three principles of precision, power, and speed, by using a firearm of a certain minimum power factor to sc ...
.
By application or intent
Combat-oriented
Health-oriented
Many martial arts, especially those from Asia, also teach side disciplines which pertain to medicinal practices. This is particularly prevalent in traditional Asian martial arts which may teach bone-setting, herbalism, and other aspects of traditional medicine.Spirituality-oriented
Martial arts can also be linked with religion and spirituality. Numerous systems are reputed to have been founded, disseminated, or practiced by monks or nuns. Throughout the Asian arts, meditation may be incorporated as a part of training. In the arts influenced by a mix of Chan Buddhist, Taoist andConfucian
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
philosophy, the practice itself may be used as an aid to attaining mindfulness.
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
ese styles, when concerning non-physical qualities of the combat, are often strongly influenced by Mahayana
''Mahāyāna'' (; "Great Vehicle") is a term for a broad group of Buddhist traditions, texts, philosophies, and practices. Mahāyāna Buddhism developed in India (c. 1st century BCE onwards) and is considered one of the three main existing br ...
Buddhist philosophy. Concepts like " empty mind" and "beginner's mind" are recurrent. Aikido practitioners for instance, can have a strong philosophical belief of the flow of energy and peace fostering, as idealised by the art's founder Morihei Ueshiba.
Traditional Korean martial arts place emphasis on the development of the practitioner's spiritual and philosophical development. A common theme in most Korean styles, such as Taekkyon
Taekkyon, Taekgyeon, Taekkyeon, or Taekyun (Korean: 태껸/ 택견/ 托肩, ) is a traditional Korean martial art.
It is characterized by fluid, dynamic foot movement called "''pum balki''" or Stepping-on-Triangles. Taekkyon includes hands an ...
, taekwondo, and Hapkido is the value of "inner peace" in a practitioner, which is stressed to be only achievable through individual meditation and training. The Koreans believe that the use of physical force is only justifiable for self defense.
Systema draws upon breathing and relaxation techniques, as well as elements of Russian Orthodox thought, to foster self-conscience and calmness, and to benefit the practitioner in different levels: the physical, the psychological and the spiritual.
Some martial arts in various cultures can be performed in dance-like settings for various reasons, such as for evoking ferocity in preparation for battle or showing off skill in a more stylized manner, with capoeira being the most prominent example. Many such martial arts incorporate music, especially strong percussive rhythms (see also war dance).
Pahlevani and zourkhaneh rituals is the name of a Persian Martial arts inscribed by UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
for varzesh-e pahlavāni ( fa, آیین پهلوانی و زورخانهای, "heroic sport") or varzesh-e bāstāni (; ''varzeš-e bāstānī'', "ancient sport"), a traditional system of athletics originally used to train warriors in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
(Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
), and first appearing under this name and form in the Safavid era, with similarities to systems in adjacent lands under other names.
History
Historical martial arts


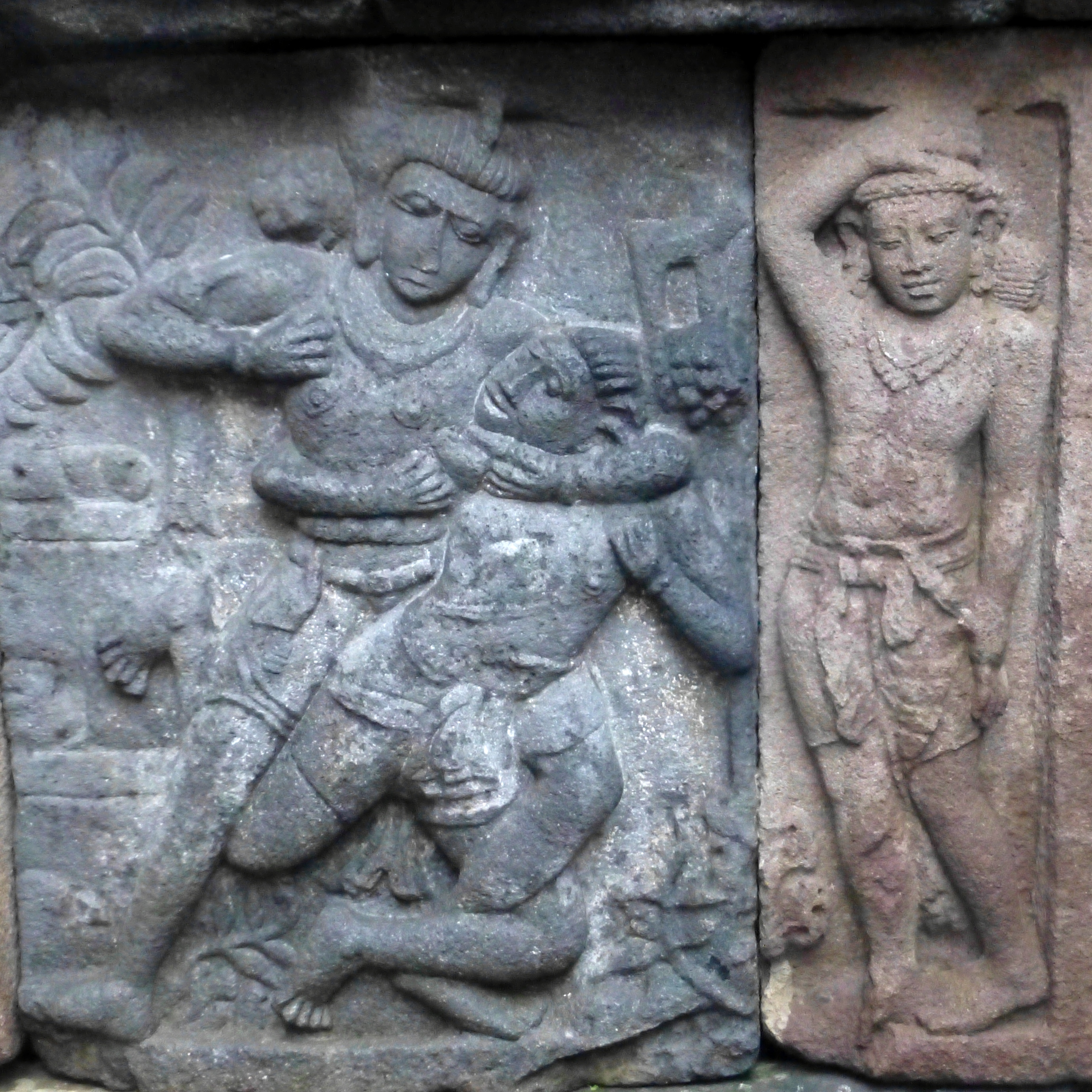
 Human warfare dates back to the
Human warfare dates back to the Epipalaeolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are som ...
to early Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
era. The oldest works of art depicting scenes of battle are cave paintings from eastern Spain ( Spanish Levante) dated between 10,000 and 6,000 BCE that show organized groups fighting with bows and arrows. Similar evidence of warfare has been found in Epipalaeolithic to early Neolithic era mass burials, excavated in Germany and at Jebel Sahaba in Northern Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
.
Wrestling
Wrestling is a series of combat sports involving grappling-type techniques such as clinch fighting, throws and takedowns, joint locks, pins and other grappling holds. Wrestling techniques have been incorporated into martial arts, combat s ...
is the oldest combat sport
A combat sport, or fighting sport, is a competitive contact sport that usually involves one-on-one combat. In many combat sports, a contestant wins by scoring more points than the opponent, submitting the opponent with a hold, disabling the oppo ...
, with origins in hand-to-hand combat
Hand-to-hand combat (sometimes abbreviated as HTH or H2H) is a physical confrontation between two or more persons at short range (grappling distance or within the physical reach of a handheld weapon) that does not involve the use of weapons.Hun ...
. Belt wrestling
Belt wrestling is a form of wrestling that is one of the oldest historically recorded sports. It involves two belted contestants aiming to take each other over by grappling with a belt. There are hundreds of national belt wrestling styles, but c ...
was depicted in works of art from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
and Ancient Egypt , and later in the Sumerian ''Epic of Gilgamesh
The ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' () is an epic poem from ancient Mesopotamia, and is regarded as the earliest surviving notable literature and the second oldest religious text, after the Pyramid Texts. The literary history of Gilgamesh begins with ...
''. The earliest known depiction of boxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
comes from a Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of ...
ian relief in Mesopotamia (modern Iraq) from the 3rd millennium BC.
 The foundation of modern East Asian martial arts and South Asian martial arts is likely facilitated by cultural exchanges of early Chinese and Indian martial arts. During the
The foundation of modern East Asian martial arts and South Asian martial arts is likely facilitated by cultural exchanges of early Chinese and Indian martial arts. During the Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in History of China#Ancient China, ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded ...
of Chinese history (480–221 BC) extensive development in martial philosophy and strategy emerged, as described by Sun Tzu in '' The Art of War'' (c. 350 BC). Legendary accounts link the origin of Shaolinquan
Shaolin Kung Fu (), also called Shaolin Wushu (), or Shaolin quan (), is one of the oldest, largest, and most famous styles of wushu, or kung fu of Chan Buddhism. It combines Ch'an philosophy and martial arts and originated and was developed i ...
to the spread of Buddhism
Buddhism entered Han China via the Silk Road, beginning in the 1st or 2nd century CE. The first documented translation efforts by Buddhist monks in China were in the 2nd century CE via the Kushan Empire into the Chinese territory bordering th ...
from ancient India
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by ...
during the early 5th century CE, with the figure of Bodhidharma, to China. Written evidence of martial arts in Southern India dates back to the Sangam literature of about the 2nd century BCE to the 2nd century AD. The combat techniques of the Sangam period were the earliest precursors to Kalaripayattu.
In Europe, the earliest sources of martial arts traditions date to Ancient Greece. Ancient Greek Boxing, Boxing (''pygme'', ''pyx''), Greek wrestling, wrestling (''pale'') and pankration were represented in the Ancient Olympic Games. The Roman Empire, Romans produced Gladiator, gladiatorial combat as a public spectacle.
A number of historical combat manuals have survived from the European Middle Ages. This includes such styles as Historical fencing, sword and shield, two-handed swordfighting and other types of melee weapons besides unarmed combat. Amongst these are transcriptions of Johannes Liechtenauer's mnemonic poem on the longsword dating back to the late fourteenth century. Likewise, Asian martial arts became well-documented during the medieval period, Japanese martial arts beginning with the establishment of the samurai nobility in the 12th century, Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to comm ...
with Ming dynasty, Ming era treatises such as Ji Xiao Xin Shu, Indian martial arts in medieval texts such as the Agni Purana and the Malla Purana, and Korean martial arts from the Joseon era and texts such as Muyejebo (1598).
 European swordsmanship always had a sportive component, but the duel was always a possibility until World War I. Modern fencing, sport fencing began developing during the 19th century as the French and Italian military academies began codifying instruction. The Olympic games led to standard international rules, with the Féderation Internationale d'Escrime founded in 1913. Modern boxing originates with Jack Broughton's rules in the 18th century, and reaches its present form with the Marquess of Queensberry Rules of 1867.
European swordsmanship always had a sportive component, but the duel was always a possibility until World War I. Modern fencing, sport fencing began developing during the 19th century as the French and Italian military academies began codifying instruction. The Olympic games led to standard international rules, with the Féderation Internationale d'Escrime founded in 1913. Modern boxing originates with Jack Broughton's rules in the 18th century, and reaches its present form with the Marquess of Queensberry Rules of 1867.
Folk styles
 Certain traditional combat sports and fighting styles exist all over the world, rooted in local culture and folklore. The most common of these are styles of
Certain traditional combat sports and fighting styles exist all over the world, rooted in local culture and folklore. The most common of these are styles of folk wrestling
A folk wrestling style is any traditional style of wrestling, which may or may not be codified as a modern sport. Most cultures have developed regional forms of grappling.
Europe
Britain
Traditionally wrestling has two main centres in Great ...
, some of which have been practiced since antiquity and are found in the most remote areas. Other examples include forms of stick fighting and boxing. While these arts are based on historical traditions of folklore, they are not "historical" in the sense that they reconstruct or preserve a historical system from a specific era. They are rather contemporary regional sports that coexist with the modern forms of martial arts sports as they have developed since the 19th century, often including cross-fertilization between sports and folk styles; thus, the traditional Thai art of muay boran developed into the modern national sport of muay Thai, which in turn came to be practiced worldwide and contributed significantly to modern hybrid styles like kickboxing and mixed martial arts. Singlestick, an English martial art can be seen often used in morris dancing. Many European dances share elements of martial arts with examples including Ukrainian Hopak, Polish Zbójnicki (use of ciupaga), the Czech dance odzemek, and the Norwegian Halling (dance), Halling.
Modern history
Late 19th to early 20th century
The mid to late 19th century marks the beginning of the history of martial arts as modern sports developed out of earlier traditional fighting systems. In Europe, this concerns the developments ofboxing
Boxing (also known as "Western boxing" or "pugilism") is a combat sport in which two people, usually wearing protective gloves and other protective equipment such as hand wraps and mouthguards, throw punches at each other for a predetermined ...
, wrestling and fencing as sports. In Japan, the same period marks the formation of the modern forms of judo, jujutsu, karate, and kendo (among others) based on revivals of koryu, old schools of Edo period martial arts which had been suppressed during the Meiji Restoration In 1882, Kano Jigoro established the Kodokan School of judo which began the sport of judo. Kano Jigoro had gathered the old knowledge of jujutsu before establishing his school of judo.
Modern muay Thai rules date to the 1920s. In China, the modern history of martial arts begins in the Nanjing decade (1930s) following the foundation of the Central Guoshu Institute in 1928 under the Kuomintang government.
Western interest in Asian martial arts arises towards the end of the 19th century, due to the increase in trade between the United States with China and Japan. Relatively few Westerners actually practiced the arts, considering it to be mere performance. Edward William Barton-Wright, a railway engineer who had studied jujutsu while working in Japan between 1894 and 1897, was the first man known to have taught Asian martial arts in Europe. He also founded an eclectic style named Bartitsu which combined jujutsu, judo, wrestling, boxing, savate and stick fighting.
Fencing and Greco-Roman wrestling was included in the 1896 Summer Olympics. FILA Wrestling World Championships and Boxing at the Summer Olympics were introduced in 1904. The tradition of awarding championship belts in wrestling and boxing can be traced to the Lonsdale Belt, introduced in 1909.

20th century (1914 to 1989)
 The International Boxing Association (amateur), International Boxing Association was established in 1920. World Fencing Championships have been held since 1921.
As Western influence grew in Asia a greater number of military personnel spent time in China, Japan and South Korea during World War II and the Korean War and were exposed to local fighting styles. Jujutsu, judo and karate first became popular among the mainstream from the 1950s–1960s. Due in part to Asian and Hollywood martial arts movies, most modern American martial arts are either Asian-derived or Asian influenced. The term kickboxing (キックボクシング) was created by the Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi for a variant of muay Thai and karate that he created in the 1950s. American kickboxing was developed in the 1970s, as a combination of boxing and karate. Taekwondo was developed in the context of the Korean War in the 1950s.
The later 1960s and 1970s witnessed an increased media interest in
The International Boxing Association (amateur), International Boxing Association was established in 1920. World Fencing Championships have been held since 1921.
As Western influence grew in Asia a greater number of military personnel spent time in China, Japan and South Korea during World War II and the Korean War and were exposed to local fighting styles. Jujutsu, judo and karate first became popular among the mainstream from the 1950s–1960s. Due in part to Asian and Hollywood martial arts movies, most modern American martial arts are either Asian-derived or Asian influenced. The term kickboxing (キックボクシング) was created by the Japanese boxing promoter Osamu Noguchi for a variant of muay Thai and karate that he created in the 1950s. American kickboxing was developed in the 1970s, as a combination of boxing and karate. Taekwondo was developed in the context of the Korean War in the 1950s.
The later 1960s and 1970s witnessed an increased media interest in Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, often called by the umbrella terms kung fu (; ), kuoshu () or wushu (), are multiple fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in Greater China. These fighting styles are often classified according to comm ...
, influenced by martial artist Bruce Lee. Bruce Lee is credited as one of the first instructors to openly teach Chinese martial arts to Westerners. World Judo Championships have been held since 1956, Judo at the Summer Olympics was introduced in 1964. Karate World Championships were introduced in 1970.
The "Chopsocky, kung fu wave" of Hong Kong action cinema in the 1970s, especially Bruce Lee films, popularized martial arts in global popular culture
Popular culture (also called mass culture or pop culture) is generally recognized by members of a society as a set of practices, beliefs, artistic output (also known as, popular art or mass art) and objects that are dominant or prevalent in a ...
. A number of mainstream films produced during the 1980s also contributed significantly to the perception of martial arts in Western popular culture. These include ''The Karate Kid (1984 film), The Karate Kid'' (1984) and ''Bloodsport (film), Bloodsport'' (1988). This era produced some Cinema of the United States, Hollywood action stars with martial arts background, such as Jean-Claude Van Damme and Chuck Norris.
Also during the 20th century, a number of martial arts were adapted for self-defense
Self-defense (self-defence primarily in Commonwealth English) is a countermeasure that involves defending the health and well-being of oneself from harm. The use of the right of self-defense as a legal justification for the use of force ...
purposes for military hand-to-hand combat
Hand-to-hand combat (sometimes abbreviated as HTH or H2H) is a physical confrontation between two or more persons at short range (grappling distance or within the physical reach of a handheld weapon) that does not involve the use of weapons.Hun ...
. World War II combatives, KAPAP (1930s) and Krav Maga (1950s) in Israel, Systema in Soviet-era Russia, and Sanshou in the People's Republic of China are examples of such systems. The US military de-emphasized hand-to-hand combat training during the Cold War period, but revived it with the introduction of LINE (combat system), LINE in 1989.
1990 to present
In 1993, the first Pancrase event was held in Japan. The K-1 rules of kickboxing were introduced, based on 1980s Seidokaikan karate. During the 1990s,Brazilian jiu-jitsu
Brazilian jiu-jitsu (BJJ; pt, jiu-jitsu brasileiro ) is a self-defence martial art and combat sport based on grappling, ground fighting (ne-waza) and submission holds. BJJ focuses on the skill of taking an opponent to the ground, control ...
became popular and proved to be effective in mixed martial arts (MMA) competitions such as the Ultimate Fighting Championship, UFC and Pride Fighting Championships, PRIDE.
 Jackie Chan and Jet Li are prominent martial artists who have become major movie figures. Their popularity and media presence has been at the forefront for promoting Chinese martial arts since the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
With the continual discovery of more medieval and Renaissance fighting manuals, the practice of Historical European Martial Arts and other Western Martial Arts have been growing in popularity across the United States and Europe.
On 29 November 2011,
Jackie Chan and Jet Li are prominent martial artists who have become major movie figures. Their popularity and media presence has been at the forefront for promoting Chinese martial arts since the late 20th and early 21st centuries.
With the continual discovery of more medieval and Renaissance fighting manuals, the practice of Historical European Martial Arts and other Western Martial Arts have been growing in popularity across the United States and Europe.
On 29 November 2011, UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
inscribed Taekkyon
Taekkyon, Taekgyeon, Taekkyeon, or Taekyun (Korean: 태껸/ 택견/ 托肩, ) is a traditional Korean martial art.
It is characterized by fluid, dynamic foot movement called "''pum balki''" or Stepping-on-Triangles. Taekkyon includes hands an ...
onto its Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity List.
Revival
Many styles of Indian martial arts were banned by the colonial authorities during the period of British Raj, British rule in India, which led to a decline in their popularity. Some, such as Kalaripayattu, did not undergo such declines since they were mostly practised in areas of the Indian subcontinent Princely states, outside direct British control. Other Indian martial art, such as Silambam, while not widely practiced in India, continue to be practiced in other countries in the Greater India, Indian cultural sphere such as Indonesia and Malaysia. Many other Indian martial arts such as Mardani khel, Mardhani Khel and Paika akhada, Paika Akhada survived by practitioners practicing the art in secret, or by telling the colonial authorities that it was a form of dance. While many regional Indian martial arts forms are fading into obscurity, martial arts such as Gatka and Kalaripayattu are experiencing a gradual resurgence.Testing and competition
Testing or evaluation is important to martial artists of many disciplines who wish to determine their progression or own level of skill in specific contexts. Students often undergo periodic testing and grading by their own teacher in order to advance to a higher level of recognized achievement, such as a different Belt (clothing), belt color or title. The type of testing used varies from system to system but may include forms or sparring. Various forms and sparring are commonly used in martial art exhibitions and tournaments. Some competitions pit practitioners of different disciplines against each other using a common set of rules, these are referred to as mixed martial arts competitions. Rules for sparring vary between art and organization but can generally be divided into ''light-contact'', ''medium-contact'', and ''full-contact'' variants, reflecting the amount of force that should be used on an opponent.
Various forms and sparring are commonly used in martial art exhibitions and tournaments. Some competitions pit practitioners of different disciplines against each other using a common set of rules, these are referred to as mixed martial arts competitions. Rules for sparring vary between art and organization but can generally be divided into ''light-contact'', ''medium-contact'', and ''full-contact'' variants, reflecting the amount of force that should be used on an opponent.
Light- and medium-contact
These types of sparring restrict the amount of force that may be used to hit an opponent, in the case of light sparring this is usually to 'touch' contact, e.g. a punch should be 'pulled' as soon as or before contact is made. In medium-contact (sometimes referred to as semi-contact) the punch would not be 'pulled' but not hit with full force. As the amount of force used is restricted, the aim of these types of sparring is not to knock out an opponent; a point system is used in competitions. A referee acts to monitor for fouls and to control the match, while judges mark down scores, as in boxing. Particular targets may be prohibited, certain techniques may be forbidden (such as headbutting or groin hits), and fighters may be required to wear Personal protective equipment, protective equipment on their head, hands, chest, groin, shins or feet. Some grappling arts, such as aikido, use a similar method of compliant training that is equivalent to light or medium contact. In some styles (such as fencing and some styles of taekwondo sparring), competitors score points based on the landing of a single technique or strike as judged by the referee, whereupon the referee will briefly stop the match, award a point, then restart the match. Alternatively, sparring may continue with the point noted by the judges. Some critics of point sparring feel that this method of training teaches habits that result in lower combat effectiveness. Lighter-contact sparring may be used exclusively, for children or in other situations when heavy contact would be inappropriate (such as beginners), medium-contact sparring is often used as training for full contact.Full-contact
Full-contact sparring or competition, where strikes or techniques are not pulled but used with full force as the name implies, has a number of tactical differences from light and medium-contact sparring. It is considered by some to be requisite in learning realistic unarmed combat. – An essay on contact levels in training In full-contact sparring, the aim of a competitive match is to knock out the opponent or to force the opponent to submission wrestling, submit. Where scoring takes place it may be a subsidiary measure, only used if no clear winner has been established by other means; in some competitions, such as the UFC 1, there was no scoring, though most now use some form of judging as a backup. Due to these factors, full-contact matches tend to be more aggressive in character, but rule sets may still mandate the use of protective equipment, or limit the techniques allowed. Nearly all mixed martial arts organizations such as Ultimate Fighting Championship, UFC, Pancrase, Shooto use a form of full-contact rules as do Professional Boxing, professional boxing organizations and K-1. Kyokushin karate requires advanced practitioners to engage in bare-knuckled, full-contact sparring allowing kicks, knees and punching although punching to the head is disallowed while wearing only a karate ''gi'' and groin protector. Brazilian jiu-jitsu and judo matches do not allow striking, but are full-contact in the sense that full force is applied in the permitted grappling and submission techniques. Competitions held by World Taekwondo Federation#Sparring, World Taekwondo requires the use of Headgear (martial arts), Headgear and padded vest, but are full contact in the sense that full force is applied to strikes to the head and body, and win by knockout is possible.Martial sport
 Martial arts have crossed over into sports when forms of sparring become competitive, becoming a sport in its own right that is dissociated from the original combative origin, such as with western fencing. The Summer Olympic Games includes judo, taekwondo, western archery, boxing, javelin, wrestling and fencing as events, while Wushu (sport), Chinese wushu recently failed in its bid to be included, but is still actively performed in tournaments across the world. Practitioners in some arts such as kickboxing and Brazilian jiu-jitsu often train for sport matches, whereas those in other arts such as aikido generally spurn such competitions. Some schools believe that competition breeds better and more efficient practitioners, and gives a sense of good sportsmanship. Others believe that the rules under which competition takes place have diminished the combat effectiveness of martial arts or encourage a kind of practice which focuses on winning trophies rather than a focus such as cultivating a particular moral character.
The question of "which is the best martial art" has led to inter style competitions fought with very few rules allowing a variety of fighting styles to enter with few limitations. This was the origin of the first Ultimate Fighting Championship tournament (later renamed UFC 1, UFC 1: The Beginning) in the USA inspired by the Brazilian Vale tudo tradition and along with other minimal rule competitions, most notably those from Japan such as Shooto and Pancrase, have evolved into the
Martial arts have crossed over into sports when forms of sparring become competitive, becoming a sport in its own right that is dissociated from the original combative origin, such as with western fencing. The Summer Olympic Games includes judo, taekwondo, western archery, boxing, javelin, wrestling and fencing as events, while Wushu (sport), Chinese wushu recently failed in its bid to be included, but is still actively performed in tournaments across the world. Practitioners in some arts such as kickboxing and Brazilian jiu-jitsu often train for sport matches, whereas those in other arts such as aikido generally spurn such competitions. Some schools believe that competition breeds better and more efficient practitioners, and gives a sense of good sportsmanship. Others believe that the rules under which competition takes place have diminished the combat effectiveness of martial arts or encourage a kind of practice which focuses on winning trophies rather than a focus such as cultivating a particular moral character.
The question of "which is the best martial art" has led to inter style competitions fought with very few rules allowing a variety of fighting styles to enter with few limitations. This was the origin of the first Ultimate Fighting Championship tournament (later renamed UFC 1, UFC 1: The Beginning) in the USA inspired by the Brazilian Vale tudo tradition and along with other minimal rule competitions, most notably those from Japan such as Shooto and Pancrase, have evolved into the combat sport
A combat sport, or fighting sport, is a competitive contact sport that usually involves one-on-one combat. In many combat sports, a contestant wins by scoring more points than the opponent, submitting the opponent with a hold, disabling the oppo ...
of Mixed Martial Arts (MMA).
Some martial artists compete in non-sparring competitions such as Breaking (martial arts), breaking or choreographed routines of techniques such as poomse, kata and aka (burmese), aka, or modern variations of the martial arts which include dance-influenced competitions such as tricking. Martial traditions have been influenced by governments to become more sport-like for political purposes; the central impetus for the attempt by the People's Republic of China in transforming Chinese martial arts into the committee-regulated sport of Wushu (sport), wushu was suppressing what they saw as the potentially subversion (politics), subversive aspects of martial training, especially under the traditional system of family lineages.
Health and fitness benefits
Martial arts training aims to result in several benefits to trainees, such as their physical, mental, emotional and spiritual health. Through systematic practice in the martial arts a person's physical fitness may be boosted (strength, stamina, speed, flexibility, movement coordination, etc.) as the whole body is exercised and the entire muscular system is activated. Beyond contributing to physical fitness, martial arts training also has benefits for mental health, contributing to self-esteem, self-control, emotional and spirituality, spiritual well-being. For this reason, a number of martial arts schools have focused purely on therapeutic aspects, de-emphasizing the historical aspect of self-defense or combat completely. According to Bruce Lee, martial arts also have the nature of an art, since there is emotional communication and complete emotional expression.Self-defense, military and law enforcement applications
 Some traditional martial concepts have seen new use within modern military training. Perhaps the most recent example of this is point shooting which relies on muscle memory to more effectively use a firearm in a variety of awkward situations, much the way an iaidoka would master movements with their sword.
Some traditional martial concepts have seen new use within modern military training. Perhaps the most recent example of this is point shooting which relies on muscle memory to more effectively use a firearm in a variety of awkward situations, much the way an iaidoka would master movements with their sword.
 During the World War II era William E. Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes were recruited by the Special Operations Executive (SOE) to teach their martial art of Defendu (itself drawing on Western boxing and Jujutsu) and pistol shooting to UK, US, and Canadian special forces. The book ''Kill or Get Killed'', written by Colonel Rex Applegate, was based on the Defendu taught by Sykes and Fairbairn. Both Fairbairn's ''Get Tough'' and Appelgate's ''Kill or Get Killed'' became classic works on hand-to-hand combat.
Traditional hand-to-hand, knife, and spear techniques continue to see use in the composite systems developed for today's wars. Examples of this include European Unifight, the US Army's Combatives system developed by Matt Larsen, the Israeli army's KAPAP and Krav Maga, and the US Marine Corps's ''Marine Corps Martial Arts Program'' (MCMAP). Unarmed dagger defenses identical to those found in the manual of Fiore dei Liberi and the Codex Wallerstein were integrated into the U.S. Army's training manuals in 1942
and continue to influence today's systems along with other traditional systems such as eskrima and silat.
The rifle-mounted bayonet which has its origin in the spear, has seen use by the United States Army, the United States Marine Corps, and the British Army as recently as the Iraq War.
Many martial arts are also seen and used in Law Enforcement hand-to-hand training. For example, the Tokyo Riot Police's use of aikido.Twigger, R. (1997). ''Angry White Pyjamas''. London: Phoenix.
During the World War II era William E. Fairbairn and Eric A. Sykes were recruited by the Special Operations Executive (SOE) to teach their martial art of Defendu (itself drawing on Western boxing and Jujutsu) and pistol shooting to UK, US, and Canadian special forces. The book ''Kill or Get Killed'', written by Colonel Rex Applegate, was based on the Defendu taught by Sykes and Fairbairn. Both Fairbairn's ''Get Tough'' and Appelgate's ''Kill or Get Killed'' became classic works on hand-to-hand combat.
Traditional hand-to-hand, knife, and spear techniques continue to see use in the composite systems developed for today's wars. Examples of this include European Unifight, the US Army's Combatives system developed by Matt Larsen, the Israeli army's KAPAP and Krav Maga, and the US Marine Corps's ''Marine Corps Martial Arts Program'' (MCMAP). Unarmed dagger defenses identical to those found in the manual of Fiore dei Liberi and the Codex Wallerstein were integrated into the U.S. Army's training manuals in 1942
and continue to influence today's systems along with other traditional systems such as eskrima and silat.
The rifle-mounted bayonet which has its origin in the spear, has seen use by the United States Army, the United States Marine Corps, and the British Army as recently as the Iraq War.
Many martial arts are also seen and used in Law Enforcement hand-to-hand training. For example, the Tokyo Riot Police's use of aikido.Twigger, R. (1997). ''Angry White Pyjamas''. London: Phoenix.
Martial arts industry
Martial arts since the 1970s has become a significant industry, a subset of the wider sport industry (including martial arts films, cinema and sports television). Hundreds of millions of people worldwide practice some form of martial art. Web Japan (sponsored by the Japanese Ministry of Foreign Affairs) claims there are 50 million karate practitioners worldwide. The South Korean government in 2009 published an estimate that taekwondo is practiced by 70 million people in 190 countries.Kim, H.-S. (2009)Taekwondo: A new strategy for Brand Korea
(21 December 2009). Retrieved on 8 January 2010. The wholesale value of martial arts related sporting equipment shipped in the United States was estimated at US$314 million in 2007; participation in the same year was estimated at 6.9 million (ages 6 or older, 2% of US population). R. A. Court, CEO of Martial Arts Channel, stated the total revenue of the US martial arts industry at US$40 billion and the number of US practitioners at 30 million in 2003.
Equipment
Martial arts equipment can include that which is used for conditioning, protection and List of martial arts weapons, weapons. Hojo undō, Specialized conditioning equipment can include breaking boards, dummy partners such as the Muk Yan Jong, wooden dummy, and targets such as punching bags and the makiwara. Personal protective equipment, Protective equipment for sparring and competition includes boxing gloves, Headgear (martial arts), headgear and mouthguards.Martial arts fraud
Asian martial arts experienced a surge of popularity in the West during the 1970s, and the rising demand resulted in numerous low quality or fraudulent schools. Fueled by fictional depictions in martial arts movies, this led to the ninja craze of the 1980s in the United States. There were also numerous fraudulent ads for martial arts training programs, inserted into comic books circa the 1960s and 1970s, which were read primarily by adolescent boys. In the seventies, lower ranks (kyu) began to be given colorful belts to show progress. This proved to be commercially viable and colored-belt systems were adopted in many martial arts degree mills (also known as ''McDojos'' and ''belt factories'') as a means to generate additional cash. This was covered in the ''Penn & Teller: Bullshit!'' List of Penn & Teller: Bullshit! episodes#Season 8: 2010, episode "Martial Arts" (June 2010).See also
* Martial arts timeline * History of martial arts * List of martial artsReferences
{{DEFAULTSORT:Martial arts Martial arts, Combat sports Individual sports Cognitive training Performing arts Self-defense