Cinerama on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Cinerama is a
Cinerama is a
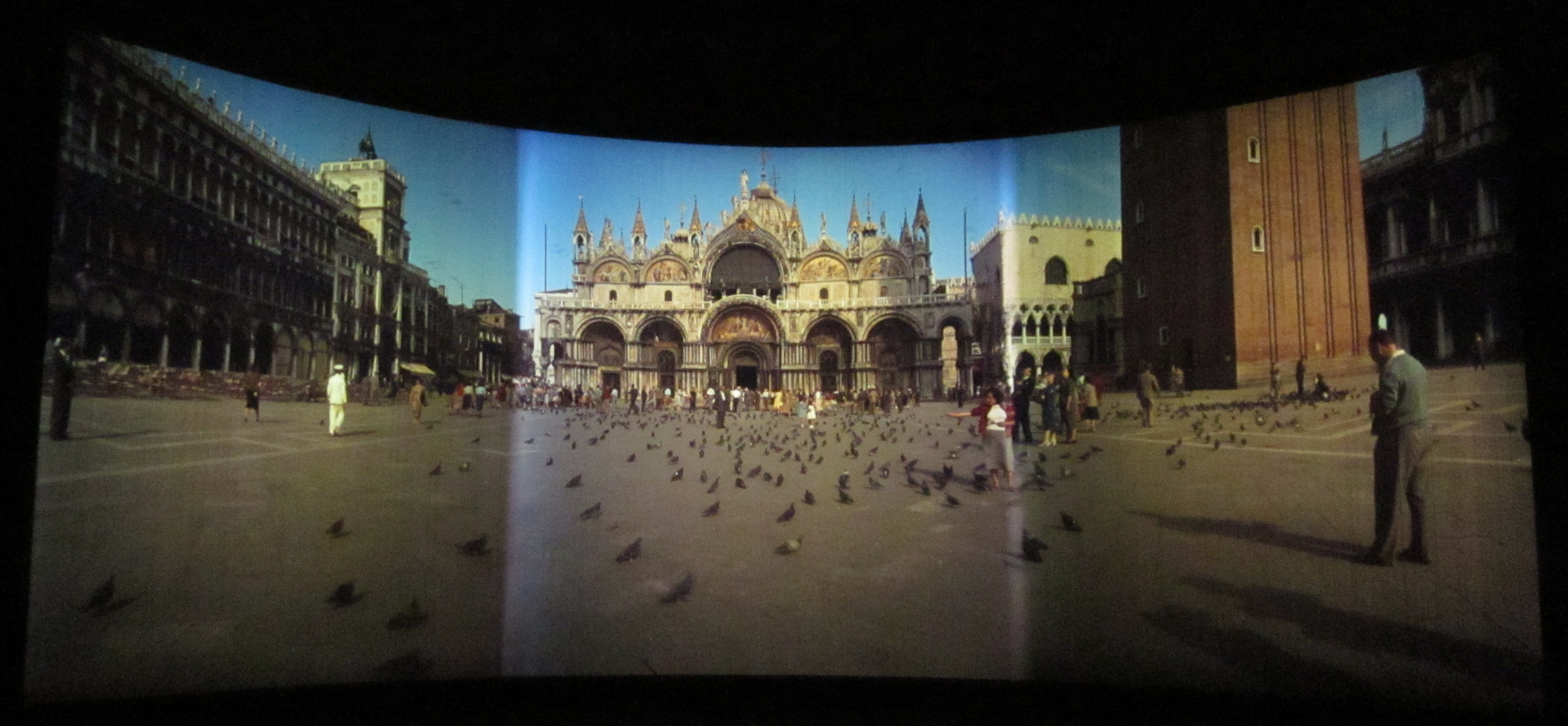
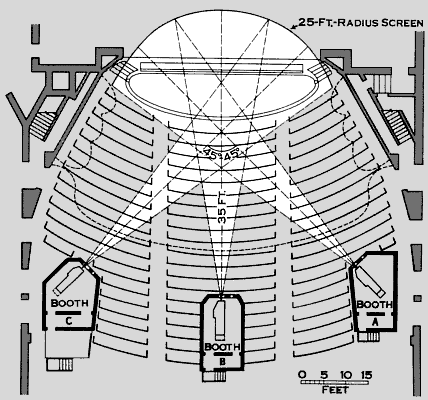 The photographic system used three interlocked 35 mm cameras equipped with 27 mm lenses, approximately the focal length of the human eye. Each camera photographed one third of the picture shooting in a crisscross pattern, the right camera shooting the left part of the image, the left camera shooting the right part of the image and the center camera shooting straight ahead. The three cameras were mounted as one unit, set at 48 degrees to each other. A single rotating shutter in front of the three lenses assured simultaneous exposure on each of the films. The three angled cameras photographed an image that was not only three times as wide as a standard film but covered 146 degrees of arc, close to the human field of vision, including peripheral vision. The image was photographed six sprocket holes high, rather than the usual four used in conventional 35 mm processes. The picture was photographed and projected at 26 frames per second rather than the usual 24.
According to film historian Martin Hart, in the original Cinerama system "the camera aspect ratio as2.59:1" with an "optimum screen image, with no architectural constraints, fabout 2.65:1, with the extreme top and bottom cropped slightly to hide anomalies". He further comments on the unreliability of "numerous websites and other resources that will tell you that Cinerama had an aspect ratio of up to 3:1."
In theaters, Cinerama film was projected from three projection booths arranged in the same crisscross pattern as the cameras. They projected onto a deeply curved screen, the outer thirds of which were made of over 1,100 strips of material mounted on "louvers" like a vertical venetian blind, to prevent light projected to each end of the screen from reflecting to the opposite end and washing out the image. This was a big-ticket, reserved-seats spectacle, and the Cinerama projectors were adjusted carefully and operated skillfully. To prevent adjacent images from creating an overilluminated vertical band where they overlapped on the screen, vibrating combs in the projectors, called "jiggolos," alternately blocked the image from one projector and then the other; the overlapping area thus received no more total illumination than the rest of the screen, and the rapidly alternating images within the overlap smoothed out the visual transition between adjacent image "panels." Great care was taken to match color and brightness when producing the prints. Nevertheless, the seams between panels were usually noticeable. Optical limitations with the design of the camera itself meant that if distant scenes joined perfectly, closer objects did not (
The photographic system used three interlocked 35 mm cameras equipped with 27 mm lenses, approximately the focal length of the human eye. Each camera photographed one third of the picture shooting in a crisscross pattern, the right camera shooting the left part of the image, the left camera shooting the right part of the image and the center camera shooting straight ahead. The three cameras were mounted as one unit, set at 48 degrees to each other. A single rotating shutter in front of the three lenses assured simultaneous exposure on each of the films. The three angled cameras photographed an image that was not only three times as wide as a standard film but covered 146 degrees of arc, close to the human field of vision, including peripheral vision. The image was photographed six sprocket holes high, rather than the usual four used in conventional 35 mm processes. The picture was photographed and projected at 26 frames per second rather than the usual 24.
According to film historian Martin Hart, in the original Cinerama system "the camera aspect ratio as2.59:1" with an "optimum screen image, with no architectural constraints, fabout 2.65:1, with the extreme top and bottom cropped slightly to hide anomalies". He further comments on the unreliability of "numerous websites and other resources that will tell you that Cinerama had an aspect ratio of up to 3:1."
In theaters, Cinerama film was projected from three projection booths arranged in the same crisscross pattern as the cameras. They projected onto a deeply curved screen, the outer thirds of which were made of over 1,100 strips of material mounted on "louvers" like a vertical venetian blind, to prevent light projected to each end of the screen from reflecting to the opposite end and washing out the image. This was a big-ticket, reserved-seats spectacle, and the Cinerama projectors were adjusted carefully and operated skillfully. To prevent adjacent images from creating an overilluminated vertical band where they overlapped on the screen, vibrating combs in the projectors, called "jiggolos," alternately blocked the image from one projector and then the other; the overlapping area thus received no more total illumination than the rest of the screen, and the rapidly alternating images within the overlap smoothed out the visual transition between adjacent image "panels." Great care was taken to match color and brightness when producing the prints. Nevertheless, the seams between panels were usually noticeable. Optical limitations with the design of the camera itself meant that if distant scenes joined perfectly, closer objects did not (
 The Cinerama system had some obvious drawbacks. If one of the films should break, it had to be repaired with a black slug exactly equal to the missing footage. Otherwise, the corresponding frames would have had to be cut from the other three films (the other two picture films plus the soundtrack film) in order to preserve synchronization. The use of
The Cinerama system had some obvious drawbacks. If one of the films should break, it had to be repaired with a black slug exactly equal to the missing footage. Otherwise, the corresponding frames would have had to be cut from the other three films (the other two picture films plus the soundtrack film) in order to preserve synchronization. The use of
 The first Cinerama film, ''
The first Cinerama film, ''
 ''
''
"Scenium" HD50LPW165
RCA receiver; full description of Cinerama mode in the instruction book says "The image of a 4:3 video signal is centered, expanding in the horizontal direction to fill the display with little distortion" whereas in "Stretch" mode "The image of a 4:3 video signal is stretched horizontally by approximately 33% while the vertical size stays the same."
The American WideScreen Museum
Rich, encyclopedic website on widescreen motion-picture processes
Cinerama
Detailed information on the history of Cinerama
Cinerama Corporation collection, 1950-1986
held by the Billy Rose Theatre Division,
Cinerama Adventure website
About the documentary on Cinerama
Transcript of a 1999 interview with two of the Denver Cooper Theater's original IATSE projectionists by Joel Genung
Widescreen Movies Corrections
Errata for the Carr & Hayes Book cited above. Periodically updated, the error list is now 60 pages long
Seattle Cinerama
Sometimes schedules special events showing original Cinerama features
Wide Screen Movies Magazine website – information on all widescreen formats, including Cinerama
{{Authority control Motion picture film formats Film and video technology 70 mm film


 Cinerama is a
Cinerama is a widescreen
Widescreen images are displayed within a set of aspect ratio (image), aspect ratios (relationship of image width to height) used in film, television and computer screens. In film, a widescreen film is any film image with a width-to-height aspect ...
process that originally projected images simultaneously from three synchronized 35mm 35 mm may refer to:
* 135 film, a type of still photography format commonly referred to as 35 mm film
* 35 mm movie film
35 mm film is a film gauge used in filmmaking, and the film standard. In motion pictures that record on fi ...
projectors onto a huge, deeply curved screen, subtending 146° of arc. The trademarked process was marketed by the Cinerama corporation. It was the first of a number of novel processes introduced during the 1950s, when the movie industry was reacting to competition from television. Cinerama was presented to the public as a theatrical event, with reserved seating and printed programs, and audience members often dressed in their best attire for the evening.
The Cinerama projection screen, rather than being a continuous surface like most screens, is made of hundreds of individual vertical strips of standard perforated screen material, each about inch (~22 mm) wide, with each strip angled to face the audience, so as to prevent light scattered from one end of the deeply curved screen from reflecting across the screen and washing out the image on the opposite end. The display is accompanied by a high-quality, seven-track discrete, directional, surround-sound system.
The original system involved shooting with three synchronized cameras sharing a single shutter. This process was later abandoned in favor of a system using a single camera and 70mm prints. The latter system lost the 146° field of view of the original three-strip system, and its resolution was markedly lower. Three-strip Cinerama did not use anamorphic lenses, although two of the systems used to produce the 70mm prints (Ultra Panavision 70
Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were, from 1957 to 1966, the marketing brands that identified motion pictures photographed with Panavision's anamorphic movie camera lenses on 65 mm film. Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were shot at 24 ...
and Super Technirama 70) ''did'' employ anamorphics. Later, 35mm anamorphic reduction prints were produced for exhibition in theatres with anamorphic CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by ...
-compatible projection lenses.
History
Process and production
Cinerama was invented byFred Waller
Frederic Waller (1886 – May 18, 1954) was an American inventor and film pioneer.
Career
Waller is most known for his contributions to film special effects while working at Paramount Pictures, for his creation of the Waller Flexible Gunnery Tr ...
(1886–1954) and languished in the laboratory for several years before Waller, joined by Hazard "Buzz" Reeves, brought it to the attention of Lowell Thomas
Lowell Jackson Thomas (April 6, 1892 – August 29, 1981) was an American writer, actor, broadcaster, and traveler, best remembered for publicising T. E. Lawrence (Lawrence of Arabia). He was also involved in promoting the Cinerama widescree ...
who, first with Mike Todd and later with Merian C. Cooper, produced a commercially viable demonstration of Cinerama that opened on Broadway on September 30, 1952. The film, titled ''This is Cinerama'', was received with enthusiasm. It was the outgrowth of many years of development. A forerunner was the triple-screen final sequence in the silent ''Napoléon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
'' (1927) directed by Abel Gance
Abel Gance (; born Abel Eugène Alexandre Péréthon; 25 October 188910 November 1981) was a French film director and producer, writer and actor. A pioneer in the theory and practice of montage, he is best known for three major silent films: ''J ...
; Gance's classic was considered lost in the 1950s, however, known of only by hearsay, and Waller could not have actually viewed it. Waller had earlier developed an 11-projector system called "Vitarama" at the Petroleum Industry exhibit in the 1939 New York World's Fair
The 1939–40 New York World's Fair was a world's fair held at Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in Queens, New York, United States. It was the second-most expensive American world's fair of all time, exceeded only by St. Louis's Louisiana Purc ...
. A five-camera version, the Waller Gunnery Trainer, was used during the Second World War.
The word "Cinerama" combines '' cinema'' with ''panorama
A panorama (formed from Greek πᾶν "all" + ὅραμα "view") is any wide-angle view or representation of a physical space, whether in painting, drawing, photography, film, seismic images, or 3D modeling. The word was originally coined i ...
'', the origin of all the "-orama" neologism
A neologism Ancient_Greek.html"_;"title="_from_Ancient_Greek">Greek_νέο-_''néo''(="new")_and_λόγος_/''lógos''_meaning_"speech,_utterance"is_a_relatively_recent_or_isolated_term,_word,_or_phrase_that_may_be_in_the_process_of_entering_com ...
s (the word "panorama" comes from the Greek words "pan", meaning ''all'', and "orama", which translates into ''that which is seen'', a ''sight'', or a ''spectacle''). It has been suggested that ''Cinerama'' could have been an intentional anagram of the word ''American;'' but an online posting by Dick Babish, describing the meeting at which it was named, says that this is "purely accidental, however delightful."
 The photographic system used three interlocked 35 mm cameras equipped with 27 mm lenses, approximately the focal length of the human eye. Each camera photographed one third of the picture shooting in a crisscross pattern, the right camera shooting the left part of the image, the left camera shooting the right part of the image and the center camera shooting straight ahead. The three cameras were mounted as one unit, set at 48 degrees to each other. A single rotating shutter in front of the three lenses assured simultaneous exposure on each of the films. The three angled cameras photographed an image that was not only three times as wide as a standard film but covered 146 degrees of arc, close to the human field of vision, including peripheral vision. The image was photographed six sprocket holes high, rather than the usual four used in conventional 35 mm processes. The picture was photographed and projected at 26 frames per second rather than the usual 24.
According to film historian Martin Hart, in the original Cinerama system "the camera aspect ratio as2.59:1" with an "optimum screen image, with no architectural constraints, fabout 2.65:1, with the extreme top and bottom cropped slightly to hide anomalies". He further comments on the unreliability of "numerous websites and other resources that will tell you that Cinerama had an aspect ratio of up to 3:1."
In theaters, Cinerama film was projected from three projection booths arranged in the same crisscross pattern as the cameras. They projected onto a deeply curved screen, the outer thirds of which were made of over 1,100 strips of material mounted on "louvers" like a vertical venetian blind, to prevent light projected to each end of the screen from reflecting to the opposite end and washing out the image. This was a big-ticket, reserved-seats spectacle, and the Cinerama projectors were adjusted carefully and operated skillfully. To prevent adjacent images from creating an overilluminated vertical band where they overlapped on the screen, vibrating combs in the projectors, called "jiggolos," alternately blocked the image from one projector and then the other; the overlapping area thus received no more total illumination than the rest of the screen, and the rapidly alternating images within the overlap smoothed out the visual transition between adjacent image "panels." Great care was taken to match color and brightness when producing the prints. Nevertheless, the seams between panels were usually noticeable. Optical limitations with the design of the camera itself meant that if distant scenes joined perfectly, closer objects did not (
The photographic system used three interlocked 35 mm cameras equipped with 27 mm lenses, approximately the focal length of the human eye. Each camera photographed one third of the picture shooting in a crisscross pattern, the right camera shooting the left part of the image, the left camera shooting the right part of the image and the center camera shooting straight ahead. The three cameras were mounted as one unit, set at 48 degrees to each other. A single rotating shutter in front of the three lenses assured simultaneous exposure on each of the films. The three angled cameras photographed an image that was not only three times as wide as a standard film but covered 146 degrees of arc, close to the human field of vision, including peripheral vision. The image was photographed six sprocket holes high, rather than the usual four used in conventional 35 mm processes. The picture was photographed and projected at 26 frames per second rather than the usual 24.
According to film historian Martin Hart, in the original Cinerama system "the camera aspect ratio as2.59:1" with an "optimum screen image, with no architectural constraints, fabout 2.65:1, with the extreme top and bottom cropped slightly to hide anomalies". He further comments on the unreliability of "numerous websites and other resources that will tell you that Cinerama had an aspect ratio of up to 3:1."
In theaters, Cinerama film was projected from three projection booths arranged in the same crisscross pattern as the cameras. They projected onto a deeply curved screen, the outer thirds of which were made of over 1,100 strips of material mounted on "louvers" like a vertical venetian blind, to prevent light projected to each end of the screen from reflecting to the opposite end and washing out the image. This was a big-ticket, reserved-seats spectacle, and the Cinerama projectors were adjusted carefully and operated skillfully. To prevent adjacent images from creating an overilluminated vertical band where they overlapped on the screen, vibrating combs in the projectors, called "jiggolos," alternately blocked the image from one projector and then the other; the overlapping area thus received no more total illumination than the rest of the screen, and the rapidly alternating images within the overlap smoothed out the visual transition between adjacent image "panels." Great care was taken to match color and brightness when producing the prints. Nevertheless, the seams between panels were usually noticeable. Optical limitations with the design of the camera itself meant that if distant scenes joined perfectly, closer objects did not (parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby object ...
error). A nearby object might split into two as it crossed the seams. To avoid calling attention to the seams, scenes were often composed with unimportant objects such as trees or posts at the seams, and action was blocked so as to center actors within panels. This gave a distinctly " triptych-like" appearance to the composition even when the seams themselves were not obvious. It was often necessary to have actors in different sections "cheat" where they looked in order to appear to be looking at each other in the final projected picture. Enthusiasts say the seams were not obtrusive; detractors disagree. Lowell Thomas
Lowell Jackson Thomas (April 6, 1892 – August 29, 1981) was an American writer, actor, broadcaster, and traveler, best remembered for publicising T. E. Lawrence (Lawrence of Arabia). He was also involved in promoting the Cinerama widescree ...
, an investor in the company with Mike Todd, was still raving about the process in his memoirs thirty years later.
Sound system
In addition to the visual impact of the image, Cinerama was one of the first processes to use multitrack magnetic sound. The system, developed by Hazard E. Reeves, one of the Cinerama investors, played back from a full coated 35 mm magnetic film with seven tracks of sound targeting a speaker layout similar to the more modernSDDS
is a cinema sound system developed by Sony, in which compressed digital sound information is recorded on both outer edges of the 35 mm film release print. The system supports up to eight independent channels of sound: five front chann ...
. There were five speakers behind the screen, two on the side and back of the auditorium with a sound engineer directing the sound between the surround speakers according to a script. The projectors and sound system were synchronized by a system using selsyn
A synchro (also known as selsyn and by other brand names) is, in effect, a transformer whose primary-to-secondary coupling may be varied by physically changing the relative orientation of the two windings. Synchros are often used for measuring ...
motors.
Drawbacks
 The Cinerama system had some obvious drawbacks. If one of the films should break, it had to be repaired with a black slug exactly equal to the missing footage. Otherwise, the corresponding frames would have had to be cut from the other three films (the other two picture films plus the soundtrack film) in order to preserve synchronization. The use of
The Cinerama system had some obvious drawbacks. If one of the films should break, it had to be repaired with a black slug exactly equal to the missing footage. Otherwise, the corresponding frames would have had to be cut from the other three films (the other two picture films plus the soundtrack film) in order to preserve synchronization. The use of zoom lens
A zoom lens is a mechanical assembly of lens elements for which the focal length (and thus angle of view) can be varied, as opposed to a fixed-focal-length (FFL) lens (see prime lens).
A true zoom lens, also called a parfocal lens, is one t ...
es was impossible since the three images would no longer match. Perhaps the greatest limitation of the process is that the picture looks natural only from within a rather limited "sweet spot." Viewed from outside the sweet spot, the picture can look distorted.
The system also required a bit of improvisation on the part of the film producers. It was not possible to film any scene where any part of the scene was close to the camera, as the fields of view no longer met exactly. Further, any close-up material had a noticeable bend in it at the joins. It was also difficult to film actors talking to each other where both were in shot, because when they looked at each other when filmed, the resultant image showed the actors appearing to look past each other, particularly if they appeared on different films. Early directors sidestepped this latter problem by only shooting one actor at a time and cutting between them. Later directors worked out where to have the actors looking to create a natural shot. Each actor was required not to look at their fellow actor, but at a predetermined cue place instead.
Finally, the three individual films would jitter and weave slightly as the films moved through the projectors. This normal frame-to-frame movement is typically imperceptible to cinema audiences where only a single projector is in use. However, in Cinerama, this resulted in the center picture constantly moving slightly relative to each of the side pictures. The shifting displacements were perceivable at the two points where the center picture met the side pictures, resulting in what appeared to many viewers to be jittering vertical lines at one-third and two-thirds of the way across the screen as the two touching images constantly moved around relative to each other. Cinerama projectors used a device to slightly blur the join lines to make the jitter less noticeable. Future systems such as Circle-Vision 360° would correct for this by having masked areas between the screens. The jitters continued, but viewers were less aware of them with the adjoining pictures no longer so close together.
The impact these films had on the big screen cannot be assessed from television or video, or even from 'scope prints, which marry the three images together with the seams clearly visible. Because they were designed to be seen on a curved screen, the geometry looks distorted on television; someone walking from left to right appears to approach the camera at an angle, move away at an angle, and then repeat the process on the other side of the screen.
Premiere
This Is Cinerama
''This Is Cinerama'' is a 1952 American documentary film directed by Mike Todd, Michael Todd, Jr., Walter A. Thompson and Fred Rickey and starring Lowell Thomas. It is designed to introduce the widescreen process Cinerama, which broadens the asp ...
'', premiered on September 30, 1952, at the Broadway Theatre
Broadway theatre,Although ''theater'' is generally the spelling for this common noun in the United States (see American and British English spelling differences), 130 of the 144 extant and extinct Broadway venues use (used) the spelling ''T ...
in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' judged it to be front-page news. Notables attending included: New York Governor Thomas E. Dewey
Thomas Edmund Dewey (March 24, 1902 – March 16, 1971) was an American lawyer, prosecutor, and politician who served as the 47th governor of New York from 1943 to 1954. He was the Republican candidate for president in 1944 and 1948: although ...
; violinist Fritz Kreisler
Friedrich "Fritz" Kreisler (February 2, 1875 – January 29, 1962) was an Austrian-born American violinist and composer. One of the most noted violin masters of his day, and regarded as one of the greatest violinists of all time, he was know ...
; James A. Farley
James Aloysius Farley (May 30, 1888 – June 9, 1976) was an American politician and Knight of Malta who simultaneously served as chairman of the New York State Democratic Committee, chairman of the Democratic National Committee, and Postmast ...
; Metropolitan Opera
The Metropolitan Opera (commonly known as the Met) is an American opera company based in New York City, resident at the Metropolitan Opera House at Lincoln Center, currently situated on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. The company is opera ...
manager Rudolf Bing; NBC chairman David Sarnoff
David Sarnoff (February 27, 1891 – December 12, 1971) was an American businessman and pioneer of American radio and television. Throughout most of his career, he led the Radio Corporation of America (RCA) in various capacities from shortly aft ...
; CBS chairman William S. Paley; Broadway composer Richard Rodgers
Richard Charles Rodgers (June 28, 1902 – December 30, 1979) was an American composer who worked primarily in musical theater. With 43 Broadway musicals and over 900 songs to his credit, Rodgers was one of the most well-known American ...
; and Hollywood mogul Louis B. Mayer.
Writing in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' a few days after the system premiered, film critic Bosley Crowther
Francis Bosley Crowther Jr. (July 13, 1905 – March 7, 1981) was an American journalist, writer, and film critic for ''The New York Times'' for 27 years. His work helped shape the careers of many actors, directors and screenwriters, though his ...
wrote:
:Somewhat the same sensations that the audience in Koster and Bial's Music Hall
Koster and Bial's Music Hall was an important vaudeville theatre in New York City, located at Broadway and Thirty-Fourth Street, where Macy's flagship store now stands. It had a seating capacity of 3,748, twice the size of many theaters. Ticket pr ...
must have felt on that night, years ago, when motion pictures were first publicly flashed on a large screen were probably felt by the people who witnessed the first public showing of Cinerama the other night... the shrill screams of the ladies and the pop-eyed amazement of the men when the huge screen was opened to its full size and a thrillingly realistic ride on a roller-coaster was pictured upon it, attested to the shock of the surprise. People sat back in spellbound wonder as the scenic program flowed across the screen. It was really as though most of them were seeing motion pictures for the first time.... the effect of Cinerama in this its initial display is frankly and exclusively "sensational," in the literal sense of that word.
While observing that the system "may be hailed as providing a new and valid entertainment thrill," Crowther expressed some skeptical reserve, saying "the very size and sweep of the Cinerama screen would seem to render it impractical for the story-telling techniques now employed in film.... It is hard to see how Cinerama can be employed for intimacy. But artists found ways to use the movie. They may well give us something brand-new here."
A technical review by Waldemar Kaempffert published in ''The New York Times'' on the same day hailed the system. He praised the stereophonic sound system and noted that "the fidelity of the sounds was irreproachable. Applause in La Scala
La Scala (, , ; abbreviation in Italian of the official name ) is a famous opera house in Milan, Italy. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778 and was originally known as the ' (New Royal-Ducal Theatre alla Scala). The premiere performan ...
sounded like the clapping of hands and not like pieces of wood slapped together". He noted, however that "There is nothing new about these stereophonic sound effects. The Bell Telephone Laboratories and Prof. Harold Burris-Meyer of Stevens Institute of Technology
Stevens Institute of Technology is a private research university in Hoboken, New Jersey. Founded in 1870, it is one of the oldest technological universities in the United States and was the first college in America solely dedicated to mechanical ...
demonstrated the underlying principles years ago." Kaempffert also noted:
:There is no question that Waller has made a notable advance in cinematography. But it must be said that at the sides of his gigantic screen there is some distortion more noticeable in some parts of the house than in others. The three projections were admirably blended, yet there were visible bands of demarcation on the screen.
Venues
Although existing theatres were adapted to show Cinerama films, in 1961 and 1962 the non-profit Cooper Foundation ofLincoln, Nebraska
Lincoln is the capital city of the U.S. state of Nebraska and the county seat of Lancaster County. The city covers with a population of 292,657 in 2021. It is the second-most populous city in Nebraska and the 73rd-largest in the United ...
, designed and built three near-identical circular "super-Cinerama" theaters in Denver, Colorado
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the Unit ...
; St. Louis Park, Minnesota (a Minneapolis
Minneapolis () is the largest city in Minnesota, United States, and the county seat of Hennepin County. The city is abundant in water, with thirteen lakes, wetlands, the Mississippi River, creeks and waterfalls. Minneapolis has its origin ...
suburb); and Omaha, Nebraska
Omaha ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Nebraska and the county seat of Douglas County. Omaha is in the Midwestern United States on the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's 39th-largest ...
. They were considered the finest venues in which to view Cinerama films. The theaters were designed by architect Richard L. Crowther of Denver, a Fellow
A fellow is a concept whose exact meaning depends on context.
In learned or professional societies, it refers to a privileged member who is specially elected in recognition of their work and achievements.
Within the context of higher education ...
of the American Institute of Architects
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) is a professional organization for architects in the United States. Headquartered in Washington, D.C., the AIA offers education, government advocacy, community redevelopment, and public outreach to s ...
.
The first such theater, the Cooper Theater, built in Denver, featured a 146-degree louvered screen (measuring ), 814 seats, courtesy lounges on the sides of the theatre for relaxation during intermission (including concessions and smoking facilities), and a ceiling which routed air and heating through small vent slots in order to inhibit noise from the building's ventilation equipment. It was demolished in 1994 to make way for a Barnes & Noble
Barnes & Noble Booksellers is an American bookseller. It is a Fortune 1000 company and the bookseller with the largest number of retail outlets in the United States. As of July 7, 2020, the company operates 614 retail stores across all 50 ...
bookstore.
The second, also called the Cooper Theater, was built in St. Louis Park at 5755 Wayzata Boulevard. The last film presented there was '' Dances with Wolves'' in January 1991, and at that time the Cooper was considered the "flagship" in the Plitt theatre chain. Efforts were made to preserve the theatre, but at the time it did not qualify for national or state historical landmark status (as it was not more than fifty years old) nor were there local preservation laws. It was torn down in 1992. An office complex with a TGI Friday's
TGI Fridays (operating in the UK as FRIDAYS) is an American restaurant chain focusing on primarily American cuisine and casual dining. The restaurant's founder said the name stood for "Thank God It's Friday", although some television commerc ...
on the west end of the property is there today.
The third super-Cinerama, the Indian Hills Theater, was built in Omaha, Nebraska
Omaha ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Nebraska and the county seat of Douglas County. Omaha is in the Midwestern United States on the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's 39th-largest ...
. It closed on September 28, 2000 as a result of the bankruptcy of Carmike Cinemas
Carmike Cinemas was a motion picture exhibitor headquartered in Columbus, Georgia. As of March 2016, the company had 276 theaters with 2,954 screens in 41 states, and was the fourth largest movie theater chain in the United States. The company ...
and the final film presented was the rap music-drama ''Turn It Up.'' The theater was demolished on August 20, 2001.
A fourth, the Kachina Cinerama Theater, was built in Scottsdale, Arizona by Harry L. Nace Theatres on Scottsdale Road and opened on November 10, 1960. It seated 600 people. It later became a Harkins theater, then closed in 1989 to make way for the Scottsdale Galleria.
Venues outside the U.S. included the Regent Plaza cinema in Melbourne
Melbourne ( ; Boonwurrung/ Woiwurrung: ''Narrm'' or ''Naarm'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian state of Victoria, and the second-most populous city in both Australia and Oceania. Its name generally refers to a metro ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands. With an area of , Australia is the largest country by ...
, which was adapted for Cinerama in 1960 to show ''This is Cinerama'' and ''Seven Wonders of the World''. The Imperial Theatre in Montreal and the Glendale in Toronto were the Canadian homes for Cinerama.
A Cinerama temporary venue was built on the location of the 1958 World Fair in Brussels, for the whole duration of the fair, from April till October 1958.
 ''
''This is Cinerama
''This Is Cinerama'' is a 1952 American documentary film directed by Mike Todd, Michael Todd, Jr., Walter A. Thompson and Fred Rickey and starring Lowell Thomas. It is designed to introduce the widescreen process Cinerama, which broadens the asp ...
'' received its London premiere on 30 September 1954 at the Casino Cinerama Theatre (now the Prince Edward Theatre), Old Compton Street, formerly a live theatre. The film ran for 16 months and was followed by the other three strip travelogues. '' How the West Was Won'' had its World Premiere at the Casino on 1 November 1962 and ran until April 1965 after which the Casino switched to 70mm single lens Cinerama. London had two other three strip venues, making it the only city in the world with three Cinerama theatres. These were the Coliseum Cinerama, from July 1963 and the Royalty Cinerama from November 1963, like the Casino both converted live venues. The Coliseum played only one film in three strip ('' The Wonderful World of the Brothers Grimm'') before switching to 70mm single lens from December 1963, and the Royalty had two runs of Brothers Grimm separated by a run of ''The Best of Cinerama'' before also switching to 70mm single lens in mid 1964. These London venues were directly operated by Cinerama themselves, elsewhere in the UK three strip Cinerama venues were operated by the two main UK circuits, ABC at ABC Bristol Road, Birmingham and Coliseum, Glasgow, Rank at Gaumont, Birmingham and Queens, Newcastle and by independents at the Park Hall, Cardiff, Theatre Royal, Manchester and Abbey, Liverpool. Most of these conversions of existing cinemas came just as Cinerama was switching to single lens and thus had short lives as three strip venues before switching to 70mm.
Roman Cinerama Theater (now Isetann Cinerama Recto) at Quezon Boulevard in Recto, Manila
Manila ( , ; fil, Maynila, ), officially the City of Manila ( fil, Lungsod ng Maynila, ), is the capital of the Philippines, and its second-most populous city. It is highly urbanized and, as of 2019, was the world's most densely populated ...
and Nation Cinerama Theater in Araneta Center
Araneta City (stylized in all lowercase), formerly and still commonly known as Araneta Center, is a transit oriented, commercial mixed-use development in Quezon City, Philippines. Situated in Barangay Socorro in Cubao, and at the intersectio ...
, Quezon City
Quezon City (, ; fil, Lungsod Quezon ), also known as the City of Quezon and Q.C. (read in Filipino as Kyusi), is the List of cities in the Philippines, most populous city in the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a populatio ...
were the only Cinerama theaters built in the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
in the 1960s. Both theaters are now defunct as Roman Super Cinerama burned down in the late 1970s and became Isetann Cinerama Recto in 1988 while Nation Cinerama closed down in the early 1970s it is now Manhattan Parkview Residences built by Megaworld Corporation.
The last Cinerama theater built was the Southcenter Theatre in 1970, opening near the Southcenter Mall of Tukwila, Washington
Tukwila ( ) is a suburban city in King County, Washington, United States, located immediately to the south of Seattle. The population was 21,798 at the 2020 census.
Tukwila is a community of communities, with residents of many diverse origin ...
. It closed in 2001.
Cinerama also purchased RKO-Stanley Warner (consisting of theaters formerly owned by Warner Bros. and RKO Pictures
RKO Radio Pictures Inc., commonly known as RKO Pictures or simply RKO, was an American film production and distribution company, one of the "Big Five" film studios of Hollywood's Golden Age. The business was formed after the Keith-Albee-Orph ...
) in 1970.
Stanley Warner
Stanley Warner Corporation acquired 35% of the company as well as the exhibition, production and distribution rights to Cinerama in 1953 during production of '' Seven Wonders of the World'' which was planned as the follow up feature.Single-film "Cinerama"
Rising costs of making three-camera widescreen films caused Cinerama to stop making such films in their original form shortly after the first release of '' How the West Was Won''. The use ofUltra Panavision 70
Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were, from 1957 to 1966, the marketing brands that identified motion pictures photographed with Panavision's anamorphic movie camera lenses on 65 mm film. Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were shot at 24 ...
for certain scenes (such as the river raft sequence) later printed onto the three Cinerama panels, proved that a more or less satisfactory wide screen image could be photographed without the three cameras. Consequently, Cinerama discontinued the three film process, with the exception of a single theater (McVickers' Cinerama Theatre in Chicago) showing ''Cinerama's Russian Adventure'', an American-Soviet co-production culled from footage of several Soviet films shot in the rival Soviet three-film format known as Kinopanorama Kinopanorama is a three-lens, three-film widescreen film format. Although Kinopanorama was initially known as ''Panorama'' (russian: панорамный фильм, ''panoramnyy film'') in the Soviet Union the name was later revised to include it ...
in 1966.
Cinerama continued through the rest of the 1960s as a brand name used initially with the Ultra Panavision 70 widescreen process (which yielded a similar 2.76 aspect ratio to the original Cinerama, although it did not simulate the 146 degree field of view.) Optically "rectified" prints and special lenses were used to project the 70 mm prints onto the curved screen. The films shot in Ultra Panavision for single lens Cinerama presentation were ''It's a Mad, Mad, Mad, Mad World
''It's a Mad, Mad, Mad, Mad World'' is a 1963 American comedy film produced and directed by Stanley Kramer with a story and screenplay by William Rose and Tania Rose. The film, starring Spencer Tracy with an all-star cast of comedians, is a ...
'' (1963), ''Battle of the Bulge
The Battle of the Bulge, also known as the Ardennes Offensive, was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II. The battle lasted from 16 December 1944 to 28 January 1945, towards the end of the war in ...
'' (1965), ''The Greatest Story Ever Told
''The Greatest Story Ever Told'' is a 1965 American epic film produced and directed by George Stevens. It is a retelling of the Biblical account about Jesus of Nazareth, from the Nativity through to the Ascension. Along with the ensemble cast ...
'' (1965), '' The Hallelujah Trail'' (1965) and ''Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
'' (1966).
The less wide but still spectacular Super Panavision 70 was used to film the Cinerama presentations ''Grand Prix
Grand Prix ( , meaning ''Grand Prize''; plural Grands Prix), is a name sometimes used for competitions or sport events, alluding to the winner receiving a prize, trophy or honour
Grand Prix or grand prix may refer to:
Arts and entertainment ...
'' (1966); '' 2001: A Space Odyssey'' (1968), which also featured scenes shot in Todd-AO
Todd-AO is an American post-production company founded in 1953 by Mike Todd and Robert Naify, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. For more than five decades, it was the worldwide leader in theater s ...
and MCS-70); '' Ice Station Zebra'' (1968); and ''Krakatoa, East of Java
''Krakatoa, East of Java'' is a 1968 American disaster film starring Maximilian Schell and Brian Keith. During the 1970s, the film was re-released under the title ''Volcano''. The story is loosely based on events surrounding the 1883 eruption o ...
'' (1969), which also featured scenes shot in Todd-AO.
The other 70mm systems used for single film Cinerama (Sovscope 70 and MCS-70) were similar to Super Panavision 70. Some films were shot in the somewhat lower resolution Super Technirama 70 process for Cinerama release, including '' Circus World'' (1964) and ''Custer of the West
''Custer of the West'' is a 1967 American Western film directed by Robert Siodmak that presents a highly fictionalised version of the life and death of George Armstrong Custer, starring Robert Shaw as Custer, Robert Ryan, Ty Hardin, Jeffrey Hun ...
'' (1967).
In the late 1960s and early 1970s, the Cinerama name was used as a film distribution company, ironically reissuing single strip 70 mm and 35 mm Cinemascope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by ...
reduction prints of ''This Is Cinerama
''This Is Cinerama'' is a 1952 American documentary film directed by Mike Todd, Michael Todd, Jr., Walter A. Thompson and Fred Rickey and starring Lowell Thomas. It is designed to introduce the widescreen process Cinerama, which broadens the asp ...
'' (1972).
Legacy
The Cinerama company exists today as an entity of the Pacific Theatres chain. In recent years, surviving and new Cinerama prints have been screened at the following venues: * the Pictureville Cinema at theNational Science and Media Museum
The National Science and Media Museum (formerly The National Museum of Photography, Film & Television, 1983–2006 and then the National Media Museum, 2006–2017), located in Bradford, West Yorkshire, is part of the national Science Museum G ...
in Bradford
Bradford is a city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 ...
, England, beginning in June 1993
* the New Neon Cinema in Dayton, Ohio
Dayton () is the List of cities in Ohio, sixth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Montgomery County, Ohio, Montgomery County. A small part of the city extends into Greene County, Ohio, Greene County. The 2020 United S ...
, from 1996 to 1999
* the refurbished Seattle Cinerama
The Seattle Cinerama Theatre is a landmark movie theater in Seattle, Washington, United States. Located in the city's Belltown neighborhood, it was one of only three movie theaters in the world capable of showing three-panel Cinerama films unti ...
in Seattle beginning in 1999
* Pacific Theatres’ Cinerama Dome in Hollywood beginning in 2002
In 1998, Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen
Paul Gardner Allen (January 21, 1953 – October 15, 2018) was an American business magnate, computer programmer, researcher, investor, and philanthropist. He co-founded Microsoft Corporation with childhood friend Bill Gates in 1975, whic ...
purchased Seattle's Martin Cinerama, which then underwent a major restoration/upgrade to become the Seattle Cinerama
The Seattle Cinerama Theatre is a landmark movie theater in Seattle, Washington, United States. Located in the city's Belltown neighborhood, it was one of only three movie theaters in the world capable of showing three-panel Cinerama films unti ...
.
As of 2015, the Pictureville Cinema, Seattle Cinerama, and Cinerama Dome continue to hold periodic screenings of three-projector Cinerama movies. The Cinerama Dome was designed for the three-projector system but never actually had it installed until recent years as it opened with the first of the single film 70 mm Cinerama films, ''It's a Mad, Mad, Mad, Mad World
''It's a Mad, Mad, Mad, Mad World'' is a 1963 American comedy film produced and directed by Stanley Kramer with a story and screenplay by William Rose and Tania Rose. The film, starring Spencer Tracy with an all-star cast of comedians, is a ...
'' (1963).
The documentary, ''Cinerama Adventure'' (2003) directed by David Strohmaier, looked at the history of the Cinerama process, as well as digitally recreating the Cinerama experience via clips of true Cinerama films (using transfers from original Cinerama prints). And Turner Entertainment
Turner Entertainment Company is an American multimedia company founded by Ted Turner in 1986. Purchased by Time Warner in 1996 as part of its acquisition of Turner Broadcasting System (TBS), the company was largely responsible for overseeing th ...
(via Warner Bros.) has struck new Cinerama prints of '' How the West Was Won'' (1962) for exhibition in true Cinerama theatres around the world.
Cinerama successors, Todd-AO
Todd-AO is an American post-production company founded in 1953 by Mike Todd and Robert Naify, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. For more than five decades, it was the worldwide leader in theater s ...
, CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by ...
, and the various 70 mm formats, all attempted to equal or surpass its grandeur while avoiding its problems to greater or lesser degrees of success. In movie theaters today the large format IMAX
IMAX is a proprietary system of high-resolution cameras, film formats, film projectors, and theaters known for having very large screens with a tall aspect ratio (approximately either 1.43:1 or 1.90:1) and steep stadium seating.
Graeme ...
system continues the tradition, although the screen is taller and often less wide.
In 2008, a Blu-ray
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of st ...
disc of ''How The West Was Won'' was released, offering a recreation of Cinerama for home viewing. The three Cinerama images were digitally stitched together so that the resulting image does not have the visible seams of older copies. Furthermore, as a second viewing option, 3D mapping technology was used to produce an image that approximates the curved screen, called "SmileBox".
On January 14, 2012, an original Cinerama camera was used to film a sequence at the Lasky-DeMille Barn, the original home to Famous Players-Lasky
Famous Players-Lasky Corporation was an American motion picture and distribution company formed on June 28, 1916, from the merger of Adolph Zukor's Famous Players Film Company—originally formed by Zukor as Famous Players in Famous Plays—and ...
, later to be renamed Paramount Pictures
Paramount Pictures Corporation is an American film and television production company, production and Distribution (marketing), distribution company and the main namesake division of Paramount Global (formerly ViacomCBS). It is the fifth-oldes ...
. This was the first film photographed in the Cinerama process in almost 50 years. This sequence is part of a new 12-minute production filmed entirely in the three panel process. The new film, ''In the Picture'', was presented at a Cinerama festival at the Cinerama Dome in Hollywood, California on September 30, 2012.
Features
All but two of the feature-length films produced using the original three-strip Cinerama process were travelogues or episodic documentaries such as ''This Is Cinerama
''This Is Cinerama'' is a 1952 American documentary film directed by Mike Todd, Michael Todd, Jr., Walter A. Thompson and Fred Rickey and starring Lowell Thomas. It is designed to introduce the widescreen process Cinerama, which broadens the asp ...
'' (1952), the first film shot in Cinerama. Other travelogues presented in Cinerama were ''Cinerama Holiday
''Cinerama Holiday'' is a 1955 film shot in Cinerama. Structured as a criss-cross travel documentary, it shows an American couple traveling in Europe and a European couple traveling in the United States. Like all of the original Cinerama produc ...
'' (1955), ''Seven Wonders of the World'' (1955), ''Search for Paradise'' (1957) and ''South Seas Adventure'' (1958). There was also one commercial short, ''Renault Dauphine'' (1960).
Even as the Cinerama travelogues were beginning to lose audiences in the late 50s, the spectacular travelogue ''Windjammer
A windjammer is a commercial sailing ship with multiple masts that may be square rigged, or fore-and-aft rigged, or a combination of the two. The informal term "windjammer" arose during the transition from the Age of Sail to the Age of Steam ...
'' (1958) was released in a competing process called Cinemiracle which claimed to have less noticeable dividing lines on the screen thanks to the reflection of the side images off of mirrors (this also allowed all three projectors to be in the same booth). Due to the small number of Cinemiracle theatres, specially converted prints of ''Windjammer'' were shown in Cinerama theaters in cities which did not have Cinemiracle theaters, and ultimately Cinerama bought up the process.
Only two films with traditional story lines were made, '' The Wonderful World of the Brothers Grimm'' and '' How the West Was Won''. In order to make these films compatible with single film systems for later standard releases, they were shot at 24 frames/s, not the 26 frames/s of traditional Cinerama.
The following feature films have been advertised as being presented "in Cinerama":
"Cinerama" video stretching mode
RCA uses the word "Cinerama" to refer to a display mode which fills a 16:9 video screen with 4:3 video with, in the words of the manufacturer, "little distortion." Manuals for products offering this mode give no detailed explanation. One online posting says it consists of "a slight cropping at the top & bottom combined with a slight stretch at only the sides," and praises it. The posting suggests that other vendors provide a similar function under different names. Mitsubishi calls it "stretch" mode. The RCA Scenium TV also has a "stretch mode" as well it is a 4:3 picture stretched straight across. There is no obvious connection between this video mode and any of the Cinerama motion picture processes. It is not clear why the name is used, unless the nonlinear stretch is vaguely evocative of a curved screen. (Ironically, some widescreen cinema processes—not Cinerama—displayed a fault known as "anamorphic mumps," which consisted of a lateral stretch of objects closer to the camera). In the U.S., RCA does not appear to have registered the word "Cinerama" as a trademark; conversely, a number of trademarks on "Cinerama," e.g. SN 74270575, are still "live" and held by Cinerama, Inc.See also
* Cinéorama * Curved screen *List of 70 mm films
The following movies were filmed using 65mm or 70mm negative stock. Titles are followed by the photographic process(es) employed.
Releases produced in Todd-AO, Todd-70, Super Panavision 70 (also known as Panavision 70), Panavision System 65 (als ...
*List of film formats
This list of motion picture film formats catalogues formats developed for shooting or viewing motion pictures, ranging from the Chronophotographe format from 1888, to mid-20th century formats such as the 1953 CinemaScope format, to more recent f ...
* Super Panavision 70
*Super Technirama 70 Super Technirama 70 was the marketing name for a special type of deluxe film exhibition that was most popular in the 1960s. It was the 70mm version of the Technirama exhibition format.
Unlike Super Panavision 70 and Ultra Panavision 70, Super Tec ...
*Todd-AO
Todd-AO is an American post-production company founded in 1953 by Mike Todd and Robert Naify, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. For more than five decades, it was the worldwide leader in theater s ...
*Ultra Panavision 70
Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were, from 1957 to 1966, the marketing brands that identified motion pictures photographed with Panavision's anamorphic movie camera lenses on 65 mm film. Ultra Panavision 70 and MGM Camera 65 were shot at 24 ...
*Kinopanorama Kinopanorama is a three-lens, three-film widescreen film format. Although Kinopanorama was initially known as ''Panorama'' (russian: панорамный фильм, ''panoramnyy film'') in the Soviet Union the name was later revised to include it ...
* Cinerama Dome
*Seattle Cinerama
The Seattle Cinerama Theatre is a landmark movie theater in Seattle, Washington, United States. Located in the city's Belltown neighborhood, it was one of only three movie theaters in the world capable of showing three-panel Cinerama films unti ...
* Cinerama Releasing Corporation
*IMAX
IMAX is a proprietary system of high-resolution cameras, film formats, film projectors, and theaters known for having very large screens with a tall aspect ratio (approximately either 1.43:1 or 1.90:1) and steep stadium seating.
Graeme ...
References
Bibliography
*"The Waller Flexible Gunnery Trainer." By Fred Waller. In: ''Journal of the SMPTE'', Vol. 47, July, 1946, pp. 73–87 *"New Movie Projection System Shown Here; Giant Wide Angle Screen Utilized." Bosley Crowther, ''The New York Times'', October 1, 1952, p. 1 *"Apparently Solid Motion Pictures Produced by Curved Screen and Peripheral Vision." Waldemar Kaempffert, ''The New York Times'', October 5, 1952, p. E9 *"Looking at Cinerama: An Awed and Quizzical Inspection of a New Film Projection System." Bosley Crowther, ''The New York Times'', October 5, 1952, p. X1 *Robert E. Carr and R. M. Hayes: ''Wide Screen Movies. A History and Filmography of Wide Gauge Filmmaking'', MC Farland & Company, Inc., 1988. Chapter II. "The Multiple-Film and Deep Curved Screen Processes" pp. 11–54 *Thomas, Lowell: ''So long until tomorrow: from Quaker Hill to Kathmandu'', G. K. Hall 1977, Chapter "The Wonderful Life and Premature Death of Cinerama""Scenium" HD50LPW165
RCA receiver; full description of Cinerama mode in the instruction book says "The image of a 4:3 video signal is centered, expanding in the horizontal direction to fill the display with little distortion" whereas in "Stretch" mode "The image of a 4:3 video signal is stretched horizontally by approximately 33% while the vertical size stays the same."
External links
The American WideScreen Museum
Rich, encyclopedic website on widescreen motion-picture processes
Cinerama
Detailed information on the history of Cinerama
Cinerama Corporation collection, 1950-1986
held by the Billy Rose Theatre Division,
New York Public Library for the Performing Arts
The New York Public Library for the Performing Arts, Dorothy and Lewis B. Cullman Center, at 40 Lincoln Center Plaza, is located in Manhattan, New York City, at the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts on the Upper West Side, between the Metro ...
Cinerama Adventure website
About the documentary on Cinerama
Transcript of a 1999 interview with two of the Denver Cooper Theater's original IATSE projectionists by Joel Genung
Widescreen Movies Corrections
Errata for the Carr & Hayes Book cited above. Periodically updated, the error list is now 60 pages long
Seattle Cinerama
Sometimes schedules special events showing original Cinerama features
Wide Screen Movies Magazine website – information on all widescreen formats, including Cinerama
{{Authority control Motion picture film formats Film and video technology 70 mm film