Anarcho-capitalism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Anarcho-capitalism (or, colloquially, ancap) is an
Anarcho-capitalism (or, colloquially, ancap) is an
"Anarcho-Capitalism: An Annotated Bibliography"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 5 July 2020. but the first person to use the term ''anarcho-capitalism'' was Murray Rothbard, in the 1940s. Rothbard, a leading figure in the 20th-century
 Author J Michael Oliver says that during the 1960s, a philosophical movement arose in the United States that championed "reason, ethical egoism, and free-market capitalism". According to Oliver, anarcho-capitalism is a political theory which logically follows the philosophical conclusions of Objectivism, a philosophical system developed by Russian-American writer Ayn Rand. Professor
Author J Michael Oliver says that during the 1960s, a philosophical movement arose in the United States that championed "reason, ethical egoism, and free-market capitalism". According to Oliver, anarcho-capitalism is a political theory which logically follows the philosophical conclusions of Objectivism, a philosophical system developed by Russian-American writer Ayn Rand. Professor
''The Ethics of Liberty''
Atlantic Highlands: Humanities Press. p. 162. . In general, the non-aggression axiom is described by Rothbard as a prohibition against the initiation of force, or the threat of force, against persons (in which he includes direct violence, assault and murder) or property (in which he includes fraud, burglary, theft and taxation). The initiation of force is usually referred to as
"Exclusive Interview With Murray Rothbard"
''The New Banner: A Fortnightly Libertarian Journal''. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
"Review of Kosanke's Instead of Politics – Don Stacy"
''Libertarian Papers''. 3 (3).
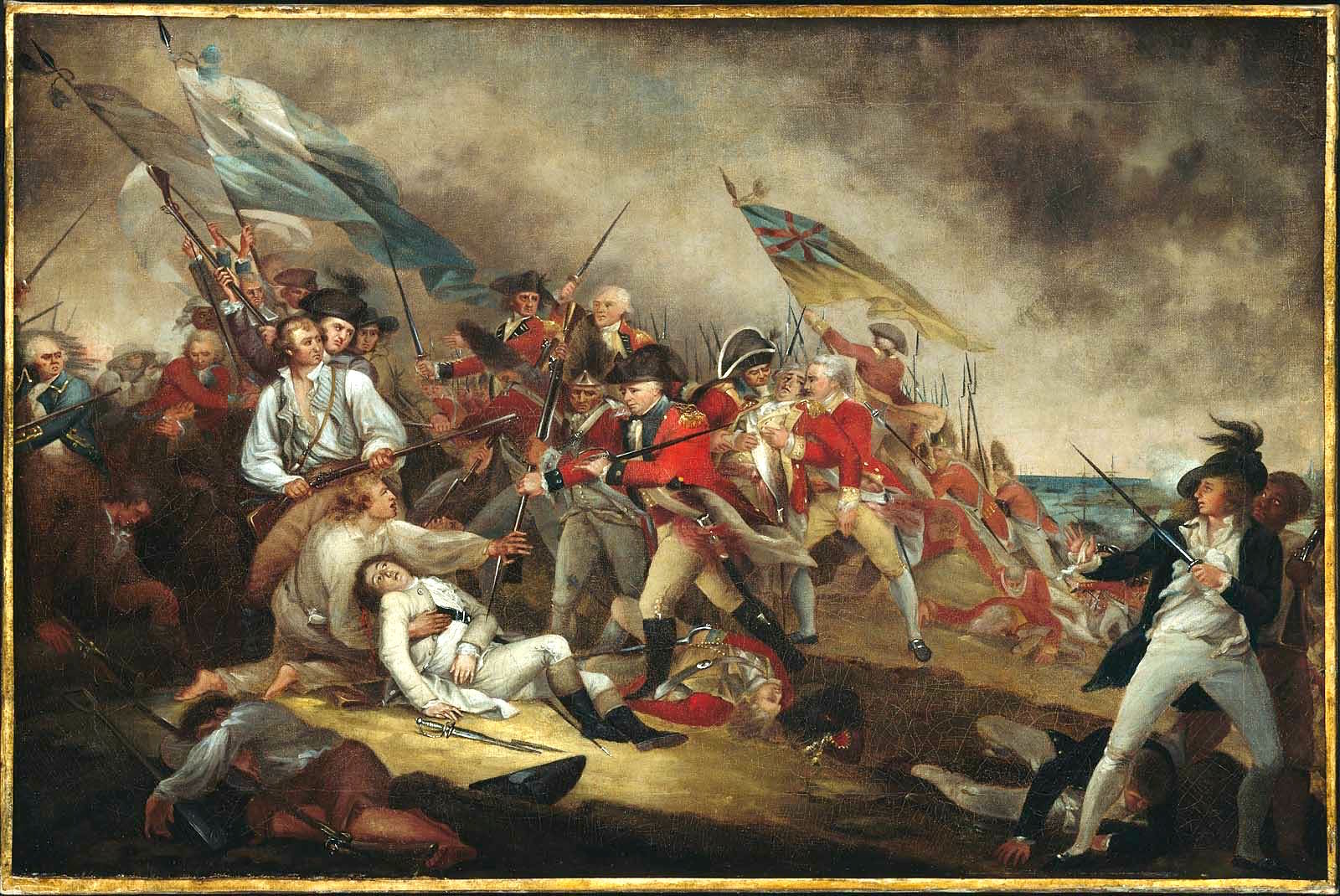 In the context of revolution, Rothbard stated that the American Revolutionary War was the only war involving the United States that could be justified. Some anarcho-capitalists such as Rothbard feel that violent revolution is counter-productive and prefer voluntary forms of
In the context of revolution, Rothbard stated that the American Revolutionary War was the only war involving the United States that could be justified. Some anarcho-capitalists such as Rothbard feel that violent revolution is counter-productive and prefer voluntary forms of
 Anarcho-capitalism as proposed by Murray Rothbard advocates the ownership of children and their sale. According to Rothbard: "the purely free society will have a flourishing free market in children. Superficially, this sounds monstrous and inhuman. But closer thought will reveal the superior humanism of such a market." Walter Block also supports the sale of children, stating that adoptive parents not being able to pay biological parents "is responsible for the trauma and heartbreak which attend adoption in the United States today".
Anarcho-capitalism as proposed by Murray Rothbard advocates the ownership of children and their sale. According to Rothbard: "the purely free society will have a flourishing free market in children. Superficially, this sounds monstrous and inhuman. But closer thought will reveal the superior humanism of such a market." Walter Block also supports the sale of children, stating that adoptive parents not being able to pay biological parents "is responsible for the trauma and heartbreak which attend adoption in the United States today".
"Exclusive Interview With Murray Rothbard"
''The New Banner: A Fortnightly Libertarian Journal''. Retrieved 13 September 2020. According to this argument, the capitalist
"Accounting and the Virtues of Anarchy"
''Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal''. 1 (1) 18–27. .Williams, Dana (2012). "From Top to Bottom, a Thoroughly Stratified World: An Anarchist View of Inequality and Domination". ''Race, Gender & Class''. 19 (3/4): 9–34. .White, Richard; Williams, Colin (2014)
"Anarchist Economic Practices in a 'Capitalist' Society: Some Implications for Organisation and the Future of Work"
''Ephermera: Theory and Politics in Organization''. 14 (4): 947–971. . Albert Meltzer argued that anarcho-capitalism simply cannot be anarchism because capitalism and the state are inextricably interlinked and because capitalism exhibits domineering hierarchical structures such as that between an employer and an employee. Anna Morgenstern approaches this topic from the opposite perspective, arguing that anarcho-capitalists are not really capitalists because "mass concentration of capital is impossible" without the state. According to Jeremy Jennings, " is hard not to conclude that these ideas", referring to anarcho-capitalism, argued to have "roots deep in classical liberalism" more so than in anarchism, "are described as anarchist only on the basis of a misunderstanding of what anarchism is". For Jennings, "anarchism does not stand for the untrammelled freedom of the individual (as the 'anarcho-capitalists' appear to believe) but, as we have already seen, for the extension of individuality and community". Similarly, Barbara Goodwin, Emeritus Professor of Politics at the University of East Anglia, Norwich, argues that anarcho-capitalism's "true place is in the group of right-wing libertarians", not in anarchism. Some right-libertarian scholars like Michael Huemer, who identify with the ideology, describe anarcho-capitalism as a "variety of anarchism". British author Andrew Heywood also believes that "individualist anarchism overlaps with libertarianism and is usually linked to a strong belief in the market as a self-regulating mechanism, most obviously manifest in the form of anarcho-capitalism". Frank H. Brooks, author of ''The Individualist Anarchists: An Anthology of Liberty (1881–1908)'', believes that "anarchism has always included a significant strain of radical individualism, from the hyperrationalism of Godwin, to the egoism of Stirner, to the libertarians and anarcho-capitalists of today".. While both anarchism and anarcho-capitalism are in opposition to the state, it is a necessary but not sufficient condition because anarchists and anarcho-capitalists interpret state-rejection differently. Austrian school economist David Prychitko, in the context of anarcho-capitalism says that "while society without a state is necessary for full-fledged anarchy, it is nevertheless insufficient". According to
''Authentic German Liberalism of the 19th century''
École Polytechnique, Centre de Recherche en Épistémologie Appliquée. Unité associée au CNRS. . Retrieved 10 June 2009. He also said that Gustave de Molinari was proposing a doctrine of the private production of security, a position which was later taken up by Murray Rothbard. Some anarcho-capitalists consider Molinari to be the first proponent of anarcho-capitalism. Raico, Ralph (29 March 2011
"Neither the Wars Nor the Leaders Were Great"
 Murray Rothbard, a student of
Murray Rothbard, a student of
''Journal of Libertarian Studies''. 20 (1): 5–15. However, Rothbard thought that they had a faulty understanding of economics as the 19th-century individualist anarchists had a labor theory of value as influenced by the classical economists, while Rothbard was a student of Without the labor theory of value, some argue that 19th-century individualist anarchists approximate the modern movement of anarcho-capitalism, although this has been contested or rejected.Peacott, Joe (18 April 1985)
Without the labor theory of value, some argue that 19th-century individualist anarchists approximate the modern movement of anarcho-capitalism, although this has been contested or rejected.Peacott, Joe (18 April 1985)
"Reply to Wendy Mc Elroy"
''New Libertarian'' (14, June 1985. . Retrieved 4 September 2020. "In her article on individualist anarchism in October 1984, ''New Libertarian'', Wendy McElroy mistakenly claims that modern-day individualist anarchism is identical with anarchist capitalism. She ignores the fact that there are still individualist anarchists who reject capitalism as well as communism, in the tradition of Warren, Spooner, Tucker, and others. ..Benjamin Tucker, when he spoke of his ideal 'society of contract,' was certainly not speaking of anything remotely resembling contemporary capitalist society. ..I do not quarrel with McElroy's definition of herself as an individualist anarchist. However, I dislike the fact that she tries to equate the term with anarchist capitalism. This is simply not true. I am an individualist anarchist and I am opposed to capitalist economic relations, voluntary or otherwise." As economic theory changed, the popularity of the labor theory of classical economics was superseded by the subjective theory of value of
"Are Libertarians 'Anarchists'?"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 4 September 2020. Joe Peacott, an American individualist anarchist in the mutualist tradition, criticizes anarcho-capitalists for trying to hegemonize the individualist anarchism label and make appear as if all individualist anarchists are in favor of
 According to the libertarian theorist David D. Friedman, " dieval Icelandic institutions have several peculiar and interesting characteristics; they might almost have been invented by a mad economist to test the lengths to which market systems could supplant government in its most fundamental functions".Friedman, David D. (1979).
According to the libertarian theorist David D. Friedman, " dieval Icelandic institutions have several peculiar and interesting characteristics; they might almost have been invented by a mad economist to test the lengths to which market systems could supplant government in its most fundamental functions".Friedman, David D. (1979).
Private Creation and Enforcement of Law: A Historical Case
. Retrieved 12 August 2005. While not directly labeling it anarcho-capitalist, Friedman argues that the legal system of the
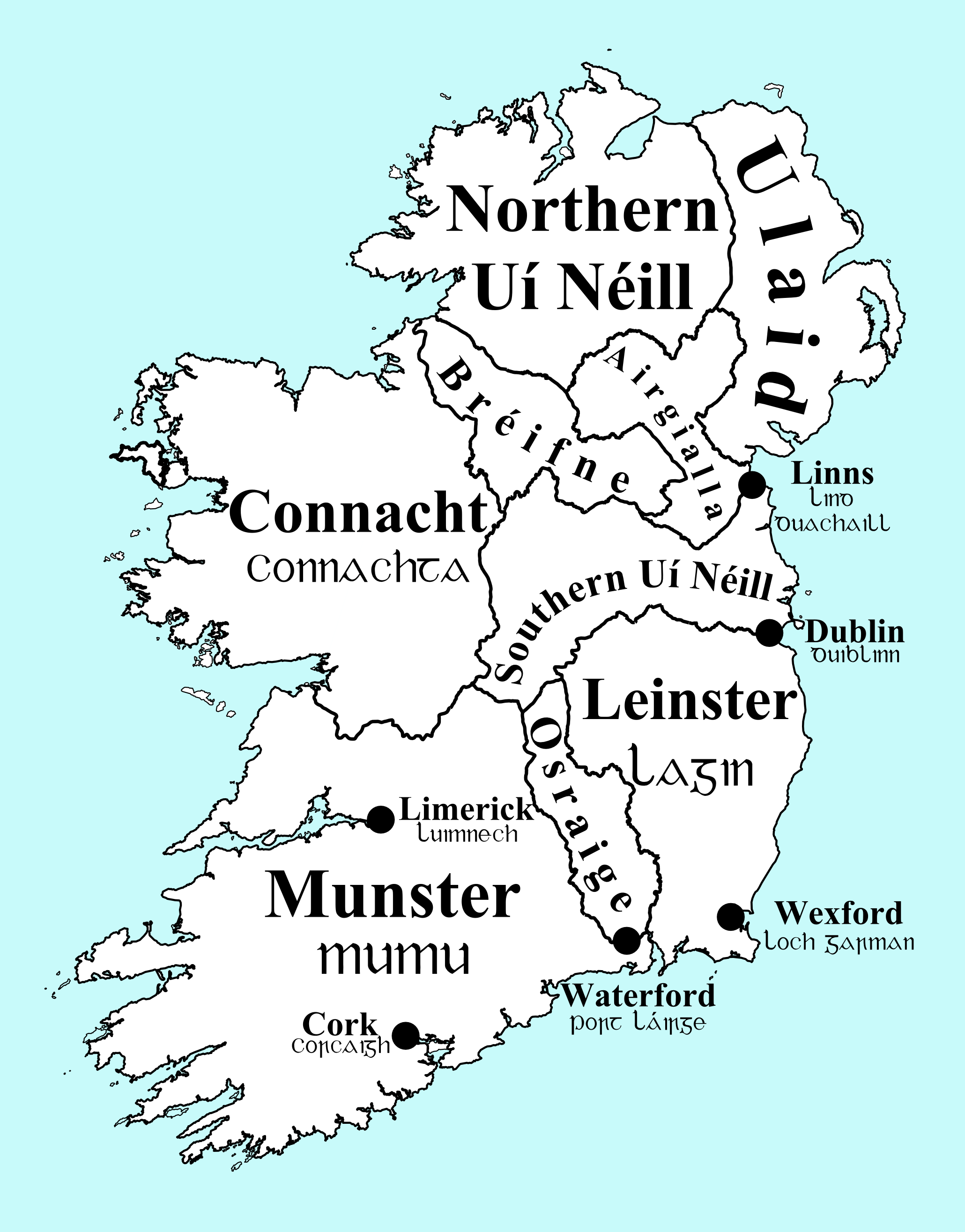 In his work '' For a New Liberty'', Murray Rothbard has claimed ancient Gaelic Ireland as an example of nearly anarcho-capitalist society. In his depiction, citing the work of Professor Joseph Peden, the basic political unit of ancient Ireland was the tuath, which is portrayed as "a body of persons voluntarily united for socially beneficial purposes" with its territorial claim being limited to "the sum total of the landed properties of its members". Civil disputes were settled by private arbiters called "brehons" and the compensation to be paid to the wronged party was insured through voluntary surety relationships. Commenting on the "kings" of tuaths, Rothbard stated:
In his work '' For a New Liberty'', Murray Rothbard has claimed ancient Gaelic Ireland as an example of nearly anarcho-capitalist society. In his depiction, citing the work of Professor Joseph Peden, the basic political unit of ancient Ireland was the tuath, which is portrayed as "a body of persons voluntarily united for socially beneficial purposes" with its territorial claim being limited to "the sum total of the landed properties of its members". Civil disputes were settled by private arbiters called "brehons" and the compensation to be paid to the wronged party was insured through voluntary surety relationships. Commenting on the "kings" of tuaths, Rothbard stated:
Intellectual Property: The Late Nineteenth Century Libertarian Debate
. ''Libertarian Heritage'' No. 14 . Retrieved 24 June 2005. Objectivist philosopher Harry Binswanger criticizes anarcho-capitalism by arguing that "capitalism requires government", questioning who or what would enforce treaties and contracts. Some right-libertarian critics of anarcho-capitalism who support the full privatization of capital such as
"The Free Market as Salvation from Government: The Anarcho-Capitalist View"
In Carrier, James G., ed. ''Meanings of the Market: The Free Market in Western Culture'' (illustrated ed.). Oxford: Berg Publishers. p. 99. . *
LewRockwell.com
– website run by
Mises Institute
– research and educational center of classical liberalism, including anarcho-capitalism, Austrian School of economics and American libertarian political theory
Property and Freedom Society
– international anarcho-capitalist society
Strike The Root
– an anarcho-capitalist website featuring essays, news, and a forum {{libertarianism Austrian School Capitalist systems Economic ideologies Anarcho-capitalism Ideologies of capitalism Classical liberalism Libertarianism by form Political ideologies Right-libertarianism Syncretic political movements Right-wing ideologies
anti-statist
Anti-statism is any approach to social, economic or political philosophy that rejects statism. An anti-statist is one who opposes intervention by the state into personal, social and economic affairs. In anarchism, this is characterized by a comp ...
, libertarian, and anti-political philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. ...
and economic theory
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyze ...
that seeks to abolish centralized states in favor of stateless societies with systems of private property enforced by private agencies, the non-aggression principle, free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
s and the right-libertarian
Right-libertarianism,Rothbard, Murray (1 March 1971)"The Left and Right Within Libertarianism" ''WIN: Peace and Freedom Through Nonviolent Action''. 7 (4): 6–10. Retrieved 14 January 2020.Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the ...
interpretation of self-ownership, which extends the concept to include control of private property as part of the self. In the absence of statute
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by ...
, anarcho-capitalists hold that society tends to contractually self-regulate and civilize through participation in the free market, which they describe as a voluntary society
A voluntary society, voluntary community or voluntary city is a term used in right-libertarianism to describe an entity in which all property (including streets, parks, etc.) and all services (including courts, police, etc.) are provided through w ...
involving the voluntary exchange of services and goods. In a theoretical anarcho-capitalist society, the system of private property would still exist and be enforced by private defense agencies and/or insurance companies selected by customers which would operate competitively in a market and fulfill the roles of courts and the police. According to many anti-capitalist modern anarchist schools of thought, the word "anarchy" is sometimes considered to be the antithesis of hierarchy, therefore, "anarcho-capitalism" is sometimes considered to be a term with differences philosophically to what they personally consider to be true anarchism, as an Anarcho-Capitalist society would inherently contain hierarchy – though said hierarchy is largely considered consensual. This point is typically responded to by Anarcho-Capitalists by pointing out that etymologically, " anarchy" simply means "the absence of government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government i ...
," and by arguing that the stark difference between "government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government i ...
" and "governance
Governance is the process of interactions through the laws, norms, power or language of an organized society over a social system ( family, tribe, formal or informal organization, a territory or across territories). It is done by the g ...
" be considered; thus, many believe the philosophy's common name is indeed consistent, as it promotes private governance, but is vehemently anti-government.
According to its proponents, various historical theorists have espoused philosophies similar to anarcho-capitalism, Hoppe, Hans-Hermann (31 December 2001)"Anarcho-Capitalism: An Annotated Bibliography"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 5 July 2020. but the first person to use the term ''anarcho-capitalism'' was Murray Rothbard, in the 1940s. Rothbard, a leading figure in the 20th-century
American libertarian
In the United States, libertarianism is a political philosophy promoting individual liberty. According to common meanings of conservatism and liberalism in the United States, libertarianism has been described as ''conservative'' on economic iss ...
movement, synthesized elements from the Austrian School
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
, classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics; civil liberties under the rule of law with especial emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, e ...
and 19th-century American individualist anarchists and mutualists Lysander Spooner and Benjamin Tucker while rejecting the labor theory of value. Rothbard's anarcho-capitalist society would operate under a mutually agreed-upon "legal code which would be generally accepted, and which the courts would pledge themselves to follow". This legal code would recognize contracts between individuals, private property, self-ownership and tort law in keeping with the non-aggression principle. Rothbard views the power of the state as unjustified, arguing that it restricts individual rights and prosperity, and creates social and economic problems.
Anarcho-capitalists and right-libertarians cite several historical precedents of what they believe to be examples of quasi-anarcho-capitalism, including the Republic of Cospaia, Acadia
Acadia (french: link=no, Acadie) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. During much of the 17th and earl ...
, Anglo‐Saxon England, Medieval Iceland, the American Old West
The American frontier, also known as the Old West or the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of American expansion in mainland North America that began with European colonial ...
, Gaelic Ireland, and law merchant, admiralty law, and early common law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
.
Anarcho-capitalism is distinguished from minarchism, which advocates a night-watchman state limited to protecting individuals from aggression and enforcing private property. Anarcho-capitalism is also distinguished from mainstream anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not neces ...
, an anti-capitalist movement that opposes unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, and social anarchism, a branch of anarchism that sees individual freedom as interrelated with mutual aid. Unlike most anarchists, anarcho-capitalists support private property and private institutions. Anarcho-capitalists also reject the libertarian socialist economic theories of anarchism, arguing that they are inherently authoritarian or require authoritarianism to achieve, while believing that there is no coercion under capitalism. Despite its name, anarcho-capitalism lies outside the tradition of the vast majority of anarchists school of thoughts and is more closely affiliated with capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
, right-libertarianism and classical liberalism
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics; civil liberties under the rule of law with especial emphasis on individual autonomy, limited government, e ...
. Traditional anarchist schools of thought oppose and reject capitalism, and consider "anarcho-capitalism" to be a contradiction in terms, although some, including anarcho-capitalists and right-libertarians, have argued that anarcho-capitalism is a form of anarchism. Anarcho-capitalism is usually seen as part of the New Right.
Philosophy
 Author J Michael Oliver says that during the 1960s, a philosophical movement arose in the United States that championed "reason, ethical egoism, and free-market capitalism". According to Oliver, anarcho-capitalism is a political theory which logically follows the philosophical conclusions of Objectivism, a philosophical system developed by Russian-American writer Ayn Rand. Professor
Author J Michael Oliver says that during the 1960s, a philosophical movement arose in the United States that championed "reason, ethical egoism, and free-market capitalism". According to Oliver, anarcho-capitalism is a political theory which logically follows the philosophical conclusions of Objectivism, a philosophical system developed by Russian-American writer Ayn Rand. Professor Lisa Duggan
Lisa Duggan () is Professor of Social and Cultural Analysis at New York University. Duggan was president of the American Studies Association from 2014 to 2015, presiding over the annual conference on the theme of "The Fun and the Fury: New Dial ...
also says that Rand's anti-statist, pro–"free market" stances went on to shape the politics of anarcho-capitalism.
According to Patrik Schumacher, the political ideology and programme of Anarcho-capitalism envisages the radicalization of the neoliberal
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent f ...
"rollback of the state", and calls for the extension of "entrepreneurial freedom" and "competitive market rationality" to the point where the scope for private enterprise is all-encompassing and "leaves no space for state action whatsoever".
On the state
Anarcho-capitalists opposition to the state is reflected in their goal of keeping butprivatizing
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
all functions of the state. They see capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
and the "free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
" as the basis for a free and prosperous society. Murray Rothbard, who is credited with coining the term ''anarcho-capitalism'', stated that the difference between free-market capitalism and state capitalism is the difference between "peaceful, voluntary exchange" and a "collusive partnership" between business and government that "uses coercion to subvert the free market".
Rothbard argued that all government services, including defense, are inefficient because they lack a market-based pricing mechanism regulated by "the voluntary decisions of consumers purchasing services that fulfill their highest-priority needs" and by investors seeking the most profitable enterprises to invest in. Furthermore, Linda and Morris Tannehill believe that no coercive monopoly of force can arise on a truly free market and that a government's citizenry can not desert them in favor of a competent protection and defense agency.
Maverick Edwards of the Liberty University
Liberty University (LU) is a private Baptist university in Lynchburg, Virginia. It is affiliated with the Southern Baptist Conservatives of Virginia ( Southern Baptist Convention). Founded in 1971 by Jerry Falwell Sr. and Elmer L. Towns, Lib ...
describes anarcho-capitalism as a political, social, and economic theory that places markets as the central "governing body" and where government no longer "grants" rights to its citizenry.
Non-aggression principle
Writer Stanisław Wójtowicz says that although anarcho-capitalists are against centralized states, they hold that all people would naturally share and agree to a specific moral theory based on the non-aggression principle. While the Friedmanian formulation of anarcho-capitalism is robust to the presence of violence and in fact, assumes some degree of violence will occur, anarcho-capitalism as formulated by Rothbard and others holds strongly to the central libertarian nonaggression axiom, sometimes non-aggression principle. Rothbard wrote: Rothbard's defense of the self-ownership principle stems from what he believed to be his falsification of all other alternatives, namely that either a group of people can own another group of people, or that no single person has full ownership over one's self. Rothbard dismisses these two cases on the basis that they cannot result in a universal ethic, i.e. a just natural law that can govern all people, independent of place and time. The only alternative that remains to Rothbard is self-ownership which he believes is both axiomatic and universal.Rothbard, Murray (1982)''The Ethics of Liberty''
Atlantic Highlands: Humanities Press. p. 162. . In general, the non-aggression axiom is described by Rothbard as a prohibition against the initiation of force, or the threat of force, against persons (in which he includes direct violence, assault and murder) or property (in which he includes fraud, burglary, theft and taxation). The initiation of force is usually referred to as
aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
or coercion. The difference between anarcho-capitalists and other libertarians is largely one of the degree to which they take this axiom. Minarchist libertarians such as libertarian political parties would retain the state in some smaller and less invasive form, retaining at the very least public police, courts, and military. However, others might give further allowance for other government programs. In contrast, Rothbard rejects any level of "state intervention
Economic interventionism, sometimes also called state interventionism, is an economic policy position favouring government intervention in the market process with the intention of correcting market failures and promoting the general welfare o ...
", defining the state as a coercive monopoly and as the only entity in human society, excluding acknowledged criminals, that derives its income entirely from coercion, in the form of taxation, which Rothbard describes as "compulsory seizure of the property of the State's inhabitants, or subjects."
Some anarcho-capitalists such as Rothbard accept the non-aggression axiom on an intrinsic moral or natural law basis. It is in terms of the non-aggression principle that Rothbard defined his interpretation of anarchism, "a system which provides no legal sanction for such aggression against person and property'; and wrote that "what anarchism proposes to do, then, is to abolish the State, i.e. to abolish the regularized institution of aggressive coercion". In an interview published in the American libertarian
In the United States, libertarianism is a political philosophy promoting individual liberty. According to common meanings of conservatism and liberalism in the United States, libertarianism has been described as ''conservative'' on economic iss ...
journal ''The New Banner'', Rothbard stated that "capitalism is the fullest expression of anarchism, and anarchism is the fullest expression of capitalism".Rothbard, Murray (25 February 1972)"Exclusive Interview With Murray Rothbard"
''The New Banner: A Fortnightly Libertarian Journal''. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
Property
Private property
Anarcho-capitalists postulate theprivatization
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
of everything, including cities with all their infrastructures, public spaces, streets and urban management systems.
Central to Rothbardian anarcho-capitalism are the concepts of self-ownership and original appropriation that combines personal and private property. Hans-Hermann Hoppe wrote:
Rothbard however rejected the Lockean proviso
The Lockean proviso is a feature of John Locke's labor theory of property which states that whilst individuals have a right to homestead private property from nature by working on it, they can do so only "at least where there is enough, and as g ...
, and followed the rule of "first come, first served", without any consideration of how much resources are left for other individuals, which opposed John Locke's beliefs.
Anarcho-capitalists advocate private ownership of the means of production and the allocation of the product of labor created by workers within the context of wage labour and the free market – that is through decisions made by property and capital owners, regardless of what an individual needs or does not need. Original appropriation allows an individual to claim any never-before-used resources, including land and by improving or otherwise using it, own it with the same "absolute right" as their own body, and retaining those rights forever, regardless of whether the resource is still being used by them. According to Rothbard, property can only come about through labor, therefore original appropriation of land is not legitimate by merely claiming it or building a fence around it—it is only by using land and by mixing one's labor with it that original appropriation is legitimized: "Any attempt to claim a new resource that someone does not use would have to be considered invasive of the property right of whoever the first user will turn out to be". Rothbard argued that the resource need not continue to be used in order for it to be the person's property as "for once his labor is mixed with the natural resource, it remains his owned land. His labor has been irretrievably mixed with the land, and the land is therefore his or his assigns' in perpetuity". published in
Rothbard also spoke about a theory of justice in property rights:
In ''Justice and Property Right'', Rothbard wrote that "any identifiable owner (the original victim of theft or his heir) must be accorded his property". In the case of slavery, Rothbard claimed that in many cases "the old plantations and the heirs and descendants of the former slaves can be identified, and the reparations can become highly specific indeed". Rothbard believed slaves rightfully own any land they were forced to work on under the homestead principle. If property is held by the state, Rothbard advocated its confiscation and "return to the private sector", writing that "any property in the hands of the State is in the hands of thieves, and should be liberated as quickly as possible".Gordon, David, ed.; Rothbard, Murray; Fuller, Edward W. (2019). ''Rothbard A to Z''. Auburn: Mises Institute. . Rothbard proposed that state universities be seized by the students and faculty under the homestead principle. Rothbard also supported the expropriation of nominally "private property" if it is the result of state-initiated force such as businesses that receive grants and subsidies. Rothbard further proposed that businesses who receive at least 50% of their funding from the state be confiscated by the workers, writing: "What we libertarians object to, then, is not government ''per se'' but crime, what we object to is unjust or criminal property titles; what we are for is not 'private' property ''per se'' but just, innocent, non-criminal private property".
Similarly, Karl Hess wrote that "libertarianism wants to advance principles of property but that it in no way wishes to defend, willy nilly, all property which now is called private ... Much of that property is stolen. Much is of dubious title. All of it is deeply intertwined with an immoral, coercive state system". published in
By accepting an axiomatic definition of private property and property rights, anarcho-capitalists deny the legitimacy of a state on principle. Hans-Hermann Hoppe argues:
Anarchists view capitalism as an inherently authoritarian and hierarchical system and seek the abolishment of private property. Proudhon, Pierre-Joseph (1840). '' What is Property?'' There is disagreement between anarchists and anarcho-capitalists as the former generally rejects anarcho-capitalism as a form of anarchism and considers ''anarcho-capitalism'' a contradiction in terms, while the latter holds that the abolishment of private property would require expropriation which is "counterproductive to order" and would require a state.Stacy, Don (2011)"Review of Kosanke's Instead of Politics – Don Stacy"
''Libertarian Papers''. 3 (3).
Common property
As opposed to anarchists, most anarcho-capitalists reject the commons. However, some of them propose that non-state public or community property can also exist in an anarcho-capitalist society. For anarcho-capitalists, what is important is that it is "acquired" and transferred without help or hindrance from what they call the "compulsory state". Deontological anarcho-capitalists believe that the only just and most economically beneficial way to acquire property is through voluntary trade, gift, or labor-based original appropriation, rather than through aggression or fraud. Anarcho-capitalists state that there could be cases wherecommon property
Common ownership refers to holding the assets of an organization, enterprise or community indivisibly rather than in the names of the individual members or groups of members as common property.
Forms of common ownership exist in every econo ...
may develop in a Lockean natural rights framework. Anarcho-capitalists make the example of a number of private businesses which may arise in an area, each owning the land and buildings that they use, but they argue that the paths between them become cleared and trodden incrementally through customer and commercial movement. These thoroughfares may become valuable to the community, but according to them ownership cannot be attributed to any single person and original appropriation does not apply because many contributed the labor necessary to create them. In order to prevent it from falling to the " tragedy of the commons", anarcho-capitalists suggest transitioning from common to private property, wherein an individual would make a homesteading claim based on disuse, acquire title by the assent of the community consensus, form a corporation with other involved parties, or other means.
Randall G. Holcombe see challenges stemming from the idea of common property under anarcho-capitalism, such as whether an individual might claim fishing rights in the area of a major shipping lane and thereby forbid passage through it. In contrast, Hoppe's work on anarcho-capitalist theory is based on the assumption that all property is privately held, "including all streets, rivers, airports, and harbors" which forms the foundation of his views on immigration.
Intellectual property
Some anarcho-capitalists strongly oppose intellectual property (i.e.,trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from ot ...
s, patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
s, copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educatio ...
s). Stephan N. Kinsella argues that ownership only relates to tangible assets.
Contractual society
The society envisioned by anarcho-capitalists has been labelled by them as a "contractual society" which Rothbard described as "a society based purely on voluntary action, entirely unhampered by violence or threats of violence" The system relies on contracts between individuals as the legal framework which would be enforced by private police and security forces as well as private arbitrations. Rothbard argues thatlimited liability
Limited liability is a legal status in which a person's financial liability is limited to a fixed sum, most commonly the value of a person's investment in a corporation, company or partnership. If a company that provides limited liability to it ...
for corporations could also exist through contract, arguing that " rporations are not at all monopolistic privileges; they are free associations of individuals pooling their capital. On the purely free market, those men would simply announce to their creditors that their liability is limited to the capital specifically invested in the corporation". However, corporations created in this way would not be able to replicate the limit on liabilities arising non-contractually such as liability in tort for environmental disasters or personal injury which corporations currently enjoy. Rothbard acknowledges that "limited liability for torts is the illegitimate conferring of a special privilege". published in
There are limits to the right to contract under some interpretations of anarcho-capitalism. Rothbard believes that the right to contract is based in inalienable rights and because of this any contract that implicitly violates those rights can be voided at will, preventing a person from permanently selling himself or herself into unindentured slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. However, Rothbard justifies the practice of child selling
Child-selling is the practice of selling children, usually by parents, legal guardians, or subsequent custodians, including adoption agencies, orphanages and Mother and Baby Homes. Where the subsequent relationship with the child is essentiall ...
. Other interpretations conclude that banning such contracts would in itself be an unacceptably invasive interference in the right to contract.
Included in the right of contract is "the right to contract oneself out for employment by others". While anarchists criticize wage labour describing it as wage slavery, anarcho-capitalists view it as a consensual contract. Some anarcho-capitalists prefer to see self-employment prevail over wage labor. David D. Friedman has expressed a preference for a society where "almost everyone is self-employed" and "instead of corporations there are large groups of entrepreneurs related by trade, not authority. Each sells not his time, but what his time produces".
Law and order and the use of violence
Different anarcho-capitalists propose different forms of anarcho-capitalism and one area of disagreement is in the area of law. In '' The Market for Liberty'', Morris and Linda Tannehill object to any statutory law whatsoever. They argue that all one has to do is ask if one is aggressing against another in order to decide if an act is right or wrong. However, while also supporting a on force and fraud, Rothbard supports the establishment of a mutually agreed-upon centralized libertarian legal code which private courts would pledge to follow, as he presumes a high degree of convergence amongst individuals about what constitutes natural justice. Unlike both the Tannehills and Rothbard who see an ideological commonality of ethics and morality as a requirement, David D. Friedman proposes that "the systems of law will be produced for profit on the open market, just as books and bras are produced today. There could be competition among different brands of law, just as there is competition among different brands of cars".Friedman, David. ''The Machinery of Freedom''. Second edition. La Salle, Ill, Open Court, pp. 116–17. Friedman says whether this would lead to a libertarian society "remains to be proven". He says it is a possibility that very un-libertarian laws may result, such as laws against drugs, but he thinks this would be rare. He reasons that "if the value of a law to its supporters is less than its cost to its victims, that law ... will not survive in an anarcho-capitalist society". Anarcho-capitalists only accept the collective defense of individual liberty (i.e. courts, military, or police forces) insofar as such groups are formed and paid for on an explicitly voluntary basis. However, their complaint is not just that the state's defensive services are funded by taxation, but that the state assumes it is the only legitimate practitioner of physical force—that is, they believe it forcibly prevents the private sector from providing comprehensive security, such as a police, judicial and prison systems to protect individuals from aggressors. Anarcho-capitalists believe that there is nothing morally superior about the state which would grant it, but not private individuals, a right to use physical force to restrain aggressors. If competition in security provision were allowed to exist, prices would also be lower and services would be better according to anarcho-capitalists. According to Molinari: "Under a regime of liberty, the natural organization of the security industry would not be different from that of other industries". Proponents believe that private systems of justice and defense already exist, naturally forming where the market is allowed to "compensate for the failure of the state", namely private arbitration, security guards, neighborhood watch groups and so on. These private courts and police are sometimes referred to generically as private defense agencies (PDAs). The defense of those unable to pay for such protection might be financed by charitable organizations relying on voluntary donation rather than by state institutions relying on taxation, or by cooperative self-help by groups of individuals. Edward Stringham argues that private adjudication of disputes could enable the market to internalize externalities and provide services that customers desire. In the context of revolution, Rothbard stated that the American Revolutionary War was the only war involving the United States that could be justified. Some anarcho-capitalists such as Rothbard feel that violent revolution is counter-productive and prefer voluntary forms of
In the context of revolution, Rothbard stated that the American Revolutionary War was the only war involving the United States that could be justified. Some anarcho-capitalists such as Rothbard feel that violent revolution is counter-productive and prefer voluntary forms of economic secession
Economic secession has been variously defined by sources. In its narrowest sense, it is abstention from the state's economic system, such as by replacing the use of government money with barter, Local Exchange Trading Systems, or commodity mon ...
to the extent possible. Retributive justice
Retributive justice is a theory of punishment that when an offender breaks the law, justice requires that they suffer in return, and that the response to a crime is proportional to the offence. As opposed to revenge, retribution—and thus ret ...
is often a component of the contracts imagined for an anarcho-capitalist society. According to Matthew O'Keefee, some anarcho-capitalists believe prisons or indentured servitude would be justifiable institutions to deal with those who violate anarcho-capitalist property relations while others believe exile or forced restitution are sufficient.
Bruce L. Benson argues that legal codes may impose punitive damages for intentional torts in the interest of deterring crime. Benson gives the example of a thief who breaks into a house by picking a lock. Even if caught before taking anything, Benson argues that the thief would still owe the victim for violating the sanctity of his property rights. Benson opines that despite the lack of objectively measurable losses in such cases, "standardized rules that are generally perceived to be fair by members of the community would, in all likelihood, be established through precedent, allowing judgments to specify payments that are reasonably appropriate for most criminal offenses".
Morris and Linda Tannehill raise a similar example, saying that a bank robber who had an attack of conscience and returned the money would still owe reparations for endangering the employees' and customers' lives and safety, in addition to the costs of the defense agency answering the teller's call for help. However, they believe that the robber's loss of reputation would be even more damaging. They suggest that specialized companies would list aggressors so that anyone wishing to do business with a man could first check his record, provided they trust the veracity of the companies' records. They further theorise that the bank robber would find insurance companies listing him as a very poor risk and other firms would be reluctant to enter into contracts with him.
Free market in children
 Anarcho-capitalism as proposed by Murray Rothbard advocates the ownership of children and their sale. According to Rothbard: "the purely free society will have a flourishing free market in children. Superficially, this sounds monstrous and inhuman. But closer thought will reveal the superior humanism of such a market." Walter Block also supports the sale of children, stating that adoptive parents not being able to pay biological parents "is responsible for the trauma and heartbreak which attend adoption in the United States today".
Anarcho-capitalism as proposed by Murray Rothbard advocates the ownership of children and their sale. According to Rothbard: "the purely free society will have a flourishing free market in children. Superficially, this sounds monstrous and inhuman. But closer thought will reveal the superior humanism of such a market." Walter Block also supports the sale of children, stating that adoptive parents not being able to pay biological parents "is responsible for the trauma and heartbreak which attend adoption in the United States today".
Influences
Murray Rothbard has listed different ideologies of which his interpretations, he said, have influenced anarcho-capitalism. This includes his interpretation of anarchism, and more precisely individualist anarchism; classical liberalism and theAustrian School
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
of economic thought. Scholars additionally associate anarcho-capitalism with neo-classical liberalism, radical neoliberalism
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent f ...
and right-libertarianism.
Anarchism
In both itssocial
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
and individualist forms, anarchism
Anarchism is a political philosophy and movement that is skeptical of all justifications for authority and seeks to abolish the institutions it claims maintain unnecessary coercion and hierarchy, typically including, though not neces ...
is usually considered an anti-capitalistWilliams, Dana M. (2018). "Contemporary Anarchist and Anarchistic Movements". ''Sociology Compass''. Wiley. 12 (6): 4. . . and radical left-wing or far-left movement that promotes libertarian socialist economic theories such as collectivism, communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
, individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-reli ...
, mutualism and syndicalism. Because anarchism is usually described alongside libertarian Marxism
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (2 ...
as the libertarian wing of the socialist movement and as having a historical association with anti-capitalism and socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes th ...
, anarchists believe that capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
is incompatible with social
Social organisms, including human(s), live collectively in interacting populations. This interaction is considered social whether they are aware of it or not, and whether the exchange is voluntary or not.
Etymology
The word "social" derives from ...
and economic equality
Equity, or economic equality, is the concept or idea of fairness in economics, particularly in regard to taxation or welfare economics. More specifically, it may refer to a movement that strives to provide equal life chances regardless of ident ...
and therefore do not recognize anarcho-capitalism as an anarchist school of thought
Anarchism is the political philosophy which holds ruling classes and the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful, The following sources cite anarchism as a political philosophy: Slevin, Carl. "Anarchism." ''The Concise Oxford Dict ...
.Marshall, Peter (1992). ''Demanding the Impossible: A History of Anarchism''. London: HarperCollins. pp. 564–565. . "Anarcho-capitalists are against the State simply because they are capitalists first and foremost. ..They are not concerned with the social consequences of capitalism for the weak, powerless and ignorant. ..As such, anarcho-capitalism overlooks the egalitarian implications of traditional individualist anarchists like Spooner and Tucker. In fact, few anarchists would accept the 'anarcho-capitalists' into the anarchist camp since they do not share a concern for economic equality and social justice. Their self-interested, calculating market men would be incapable of practising voluntary cooperation and mutual aid. Anarcho-capitalists, even if they do reject the state, might therefore best be called right-wing libertarians rather than anarchists."Goodway, David (2006). '' Anarchist Seeds Beneath the Snow: Left-Libertarian Thought and British Writers from William Morris to Colin Ward''. Liverpool: Liverpool University Press. p. 4. "'Libertarian' and 'libertarianism' are frequently employed by anarchists as synonyms for 'anarchist' and 'anarchism', largely as an attempt to distance themselves from the negative connotations of 'anarchy' and its derivatives. The situation has been vastly complicated in recent decades with the rise of anarcho-capitalism, 'minimal statism' and an extreme right-wing laissez-faire philosophy advocated by such theorists as Rothbard and Nozick and their adoption of the words 'libertarian' and 'libertarianism'. It has therefore now become necessary to distinguish between their right libertarianism and the left libertarianism of the anarchist tradition."Newman, Saul (2010). ''The Politics of Postanarchism''. Edinburgh University Press. p. 43. "It is important to distinguish between anarchism and certain strands of right-wing libertarianism which at times go by the same name (for example, Rothbard's anarcho-capitalism)." . In particular, anarchists argue that capitalist transactions are not voluntary and that maintaining the class structure of a capitalist society requires coercion which is incompatible with an anarchist society.Tame, Chris R. (October 1983). ''The Chicago School: Lessons from the Thirties for the Eighties''. Economic Affairs. p. 56.McKay, Iain (2008). ''An Anarchist FAQ''. 1. "What are the myths of capitalist economics?" "Is 'anarcho'-capitalism a type of anarchism?" Oakland/Edinburgh: AK Press. . The usage of ''libertarian'' is also in dispute. While both anarchists and anarcho-capitalists have used it, ''libertarian'' was synonymous with ''anarchist'' until the mid-20th century, when anarcho-capitalist theory developed.
Anarcho-capitalists are distinguished from the dominant anarchist tradition by their relation to property
Property is a system of rights that gives people legal control of valuable things, and also refers to the valuable things themselves. Depending on the nature of the property, an owner of property may have the right to consume, alter, share, r ...
and capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
. While both anarchism and anarcho-capitalism share general antipathy towards power by government authority, the latter exempts power wielded through free-market capitalism. Anarchists, including egoists such as Max Stirner, have supported the protection of an individual's freedom from powers of both government and private property owners. In contrast, while condemning governmental encroachment on personal liberties, anarcho-capitalists support freedoms based on private property rights. Anarcho-capitalist theorist Murray Rothbard argued that protesters should rent a street for protest from its owners. The abolition of public amenities is a common theme in some anarcho-capitalist writings.
As anarcho-capitalism puts ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
'' economics before economic equality, it is commonly viewed as incompatible with the anti-capitalist and egalitarian tradition of anarchism. Although anarcho-capitalist theory implies the abolition of the state in favour of a fully ''laissez-faire'' economy,Gay, Kathlyn; Gay, Martin (1999). ''Encyclopedia of Political Anarchy''. ABC-CLIO. . it lies outside the tradition of anarchism. While using the language of anarchism, anarcho-capitalism only shares anarchism's antipathy towards the state and not anarchism's antipathy towards hierarchy as theorists expect from anarcho-capitalist economic power relations.Davis, Laurence (2019). "Individual and Community". In Levy, Carl; Adams, Matthew S. (eds.). ''The Palgrave Handbook of Anarchism''. Cham: Springer. pp. 47–70. . . It follows a different paradigm from anarchism and has a fundamentally different approach and goals. In spite of the ''anarcho-'' in its title, anarcho-capitalism is more closely affiliated with capitalism, right-libertarianism, and liberalism than with anarchism. Some within this ''laissez-faire'' tradition reject the designation of ''anarcho-capitalism'', believing that ''capitalism'' may either refer to the ''laissez-faire'' market they support or the government-regulated system that they oppose.
Rothbard argued that anarcho-capitalism is the only true form of anarchism—the only form of anarchism that could possibly exist in reality as he maintained that any other form presupposes authoritarian enforcement of a political ideology such as "redistribution of private property", which he attributed to anarchism.Rothbard, Murray (25 February 1972)"Exclusive Interview With Murray Rothbard"
''The New Banner: A Fortnightly Libertarian Journal''. Retrieved 13 September 2020. According to this argument, the capitalist
free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
is "the natural situation" that would result from people being free from state authority and entails the establishment of all voluntary associations in society such as cooperatives, non-profit organizations, businesses and so on. Moreover, anarcho-capitalists, as well as classical liberal minarchists, argue that the application of anarchist ideals as advocated by what they term "left-wing anarchists" would require an authoritarian body of some sort to impose it. Based on their understanding and interpretation of anarchism, in order to forcefully prevent people from accumulating capital, which they believe is a goal of anarchists, there would necessarily be a redistributive organization of some sort which would have the authority to in essence exact a tax and re-allocate the resulting resources to a larger group of people. They conclude that this theoretical body would inherently have political power and would be nothing short of a state. The difference between such an arrangement and an anarcho-capitalist system is what anarcho-capitalists see as the voluntary nature of organization within anarcho-capitalism contrasted with a "centralized ideology" and a "paired enforcement mechanism" which they believe would be necessary under what they describe as a "coercively" egalitarian-anarchist system.
Rothbard also argued that the capitalist system of today is not properly anarchistic because it often colludes with the state. According to Rothbard, "what Marx and later writers have done is to lump together two extremely different and even contradictory concepts and actions under the same portmanteau term. These two contradictory concepts are what I would call 'free-market capitalism' on the one hand, and 'state capitalism' on the other". "The difference between free-market capitalism and state capitalism", writes Rothbard, "is precisely the difference between, on the one hand, peaceful, voluntary exchange, and on the other, violent expropriation". He continues: "State capitalism inevitably creates all sorts of problems which become insoluble".
Traditional anarchists reject the notion of capitalism, hierarchies and private property.Funnell, Warwick (2007)"Accounting and the Virtues of Anarchy"
''Australasian Accounting, Business and Finance Journal''. 1 (1) 18–27. .Williams, Dana (2012). "From Top to Bottom, a Thoroughly Stratified World: An Anarchist View of Inequality and Domination". ''Race, Gender & Class''. 19 (3/4): 9–34. .White, Richard; Williams, Colin (2014)
"Anarchist Economic Practices in a 'Capitalist' Society: Some Implications for Organisation and the Future of Work"
''Ephermera: Theory and Politics in Organization''. 14 (4): 947–971. . Albert Meltzer argued that anarcho-capitalism simply cannot be anarchism because capitalism and the state are inextricably interlinked and because capitalism exhibits domineering hierarchical structures such as that between an employer and an employee. Anna Morgenstern approaches this topic from the opposite perspective, arguing that anarcho-capitalists are not really capitalists because "mass concentration of capital is impossible" without the state. According to Jeremy Jennings, " is hard not to conclude that these ideas", referring to anarcho-capitalism, argued to have "roots deep in classical liberalism" more so than in anarchism, "are described as anarchist only on the basis of a misunderstanding of what anarchism is". For Jennings, "anarchism does not stand for the untrammelled freedom of the individual (as the 'anarcho-capitalists' appear to believe) but, as we have already seen, for the extension of individuality and community". Similarly, Barbara Goodwin, Emeritus Professor of Politics at the University of East Anglia, Norwich, argues that anarcho-capitalism's "true place is in the group of right-wing libertarians", not in anarchism. Some right-libertarian scholars like Michael Huemer, who identify with the ideology, describe anarcho-capitalism as a "variety of anarchism". British author Andrew Heywood also believes that "individualist anarchism overlaps with libertarianism and is usually linked to a strong belief in the market as a self-regulating mechanism, most obviously manifest in the form of anarcho-capitalism". Frank H. Brooks, author of ''The Individualist Anarchists: An Anthology of Liberty (1881–1908)'', believes that "anarchism has always included a significant strain of radical individualism, from the hyperrationalism of Godwin, to the egoism of Stirner, to the libertarians and anarcho-capitalists of today".. While both anarchism and anarcho-capitalism are in opposition to the state, it is a necessary but not sufficient condition because anarchists and anarcho-capitalists interpret state-rejection differently. Austrian school economist David Prychitko, in the context of anarcho-capitalism says that "while society without a state is necessary for full-fledged anarchy, it is nevertheless insufficient". According to
Ruth Kinna
Ruth Ellen Kinna (born March 1961) is a professor of political philosophy at Loughborough University, working in the Department of Politics, History and International Relations. Since 2007 she has been the editor of the journal '' Anarchist Stu ...
, anarcho-capitalists are anti-statists who draw more on right-wing liberal theory and the Austrian School
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
than anarchist traditions. Kinna writes that " order to highlight the clear distinction between the two positions", anarchists describe anarcho-capitalists as " propertarians".Kinna, Ruth, ed. (2012). ''The Bloomsbury Companion to Anarchism''. New York: Bloomsbury Publishing USA. pp. 330–331. . Anarcho-capitalism is usually seen as part of the New Right.
Classical liberalism
Historian and libertarian Ralph Raico argued that what liberal philosophers "had come up with was a form of individualist anarchism, or, as it would be called today, anarcho-capitalism or market anarchism".Raico, Ralph (2004)''Authentic German Liberalism of the 19th century''
École Polytechnique, Centre de Recherche en Épistémologie Appliquée. Unité associée au CNRS. . Retrieved 10 June 2009. He also said that Gustave de Molinari was proposing a doctrine of the private production of security, a position which was later taken up by Murray Rothbard. Some anarcho-capitalists consider Molinari to be the first proponent of anarcho-capitalism. Raico, Ralph (29 March 2011
"Neither the Wars Nor the Leaders Were Great"
Mises Institute
Ludwig von Mises Institute for Austrian Economics, or Mises Institute, is a libertarian nonprofit think tank headquartered in Auburn, Alabama, United States. It is named after the Austrian School economist Ludwig von Mises (1881–1973).
I ...
. In the preface to the 1977 English translation by Murray Rothbard called ''The Production of Security'' the "first presentation anywhere in human history of what is now called anarcho-capitalism", although admitting that "Molinari did not use the terminology, and probably would have balked at the name". Hans-Hermann Hoppe said that "the 1849 article 'The Production of Security' is probably the single most important contribution to the modern theory of anarcho-capitalism". According to Hans-Hermann Hoppe, one of the 19th century precursors of anarcho-capitalism were philosopher Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer (27 April 1820 – 8 December 1903) was an English philosopher, psychologist, biologist, anthropologist, and sociologist famous for his hypothesis of social Darwinism. Spencer originated the expression " survival of the f ...
, classical liberal Auberon Herbert and liberal socialist Franz Oppenheimer.
Ruth Kinna
Ruth Ellen Kinna (born March 1961) is a professor of political philosophy at Loughborough University, working in the Department of Politics, History and International Relations. Since 2007 she has been the editor of the journal '' Anarchist Stu ...
writes that ''anarcho-capitalism'' is a term coined by Murray Rothbard to describe "a commitment to unregulated private property and laissez-faire economics, prioritizing the liberty-rights of individuals, unfettered by government regulation, to accumulate, consume and determine the patterns of their lives as they see fit". According to Kinna, anarcho-capitalists "will sometimes label themselves market anarchists because they recognize the negative connotations of 'capitalism'. But the literature of anarcho-capitalism draws on classical liberal theory, particularly the Austrian School
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
– Friedrich von Hayek and Ludwig von Mises
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (; 29 September 1881 – 10 October 1973) was an Austrian School economist, historian, logician, and sociologist. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the societal contributions of classical liberalism. He is ...
– rather than recognizable anarchist traditions. Ayn Rand's laissez-faire, anti-government, corporate philosophy – Objectivism – is sometimes associated with anarcho-capitalism". Other scholars similarly associate anarcho-capitalism with anti-state classical liberalism, neo-classical liberalism, radical neoliberalism
Neoliberalism (also neo-liberalism) is a term used to signify the late 20th century political reappearance of 19th-century ideas associated with free-market capitalism after it fell into decline following the Second World War. A prominent f ...
and right-libertarianism.
Paul Dragos Aligica writes that there is a "foundational difference between the classical liberal and the anarcho-capitalist positions". Classical liberalism, while accepting critical arguments against collectivism, acknowledges a certain level of public ownership and collective governance as necessary to provide practical solutions to political problems. In contrast anarcho-capitalism, according to Aligica, denies any requirement for any form of public administration, and allows no meaningful role for the public sphere, which is seen as sub-optimal and illegitimate.
Individualist anarchism
 Murray Rothbard, a student of
Murray Rothbard, a student of Ludwig von Mises
Ludwig Heinrich Edler von Mises (; 29 September 1881 – 10 October 1973) was an Austrian School economist, historian, logician, and sociologist. Mises wrote and lectured extensively on the societal contributions of classical liberalism. He is ...
, stated that he was influenced by the work of the 19th-century American individualist anarchists
Anarchism in the United States began in the mid-19th century and started to grow in influence as it entered the American labor movements, growing an anarcho-communist current as well as gaining notoriety for violent propaganda of the deed and ca ...
. In the winter of 1949, Rothbard decided to reject minimal state ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
'' and embrace his interpretation of individualist anarchism. In 1965, Rothbard wrote that " Lysander Spooner and Benjamin R. Tucker
Benjamin Ricketson Tucker (; April 17, 1854 – June 22, 1939) was an American individualist anarchist and libertarian socialist.Martin, James J. (1953)''Men Against the State: The Expositers of Individualist Anarchism in America, 1827–1908''
were unsurpassed as political philosophers and nothing is more needed today than a revival and development of the largely forgotten legacy they left to political philosophy".Rothbard, Murray (2000) 965br>"The Spooner-Tucker Doctrine: An Economist's View"''Journal of Libertarian Studies''. 20 (1): 5–15. However, Rothbard thought that they had a faulty understanding of economics as the 19th-century individualist anarchists had a labor theory of value as influenced by the classical economists, while Rothbard was a student of
Austrian School
The Austrian School is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result exclusively from the motivations and actions of individuals. Austrian scho ...
economics which does not agree with the labor theory of value. Rothbard sought to meld 19th-century American individualist anarchists' advocacy of economic individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology and social outlook that emphasizes the intrinsic worth of the individual. Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and to value independence and self-relianc ...
and free market
In economics, a free market is an economic system in which the prices of goods and services are determined by supply and demand expressed by sellers and buyers. Such markets, as modeled, operate without the intervention of government or any ot ...
s with the principles of Austrian School economics, arguing that " ere is, in the body of thought known as 'Austrian economics', a scientific explanation of the workings of the free market (and of the consequences of government intervention in that market) which individualist anarchists could easily incorporate into their political and social Weltanschauung". Rothbard held that the economic consequences of the political system they advocate would not result in an economy with people being paid in proportion to labor amounts, nor would profit and interest disappear as they expected. Tucker thought that unregulated banking and money issuance would cause increases in the money supply so that interest rates would drop to zero or near to it. Peter Marshall Peter Marshall may refer to:
Entertainment
* Peter Marshall (entertainer) (born 1926), American game show host of ''The Hollywood Squares'', 1966–1981
* Peter Marshall (author, born 1939) (1939–1972), British novelist whose works include ''T ...
states that "anarcho-capitalism overlooks the egalitarian implications of traditional individualist anarchists like Spooner and Tucker". Stephanie Silberstein states that "While Spooner was no free-market capitalist, nor an anarcho-capitalist, he was not as opposed to capitalism as most socialists were."
In "The Spooner-Tucker Doctrine: An Economist's View", Rothbard explained his disagreements. Rothbard disagreed with Tucker that it would cause the money supply to increase because he believed that the money supply in a free market would be self-regulating. If it were not, then Rothbard argued inflation would occur so it is not necessarily desirable to increase the money supply in the first place. Rothbard claimed that Tucker was wrong to think that interest would disappear regardless because he believed people, in general, do not wish to lend their money to others without compensation, so there is no reason why this would change just because banking was unregulated. Tucker held a labor theory of value and thought that in a free market people would be paid in proportion to how much labor they exerted and that exploitation or usury was taking place if they were not. As Tucker explained in ''State Socialism and Anarchism'', his theory was that unregulated banking would cause more money to be available and that this would allow the proliferation of new businesses which would, in turn, raise demand for labor. This led Tucker to believe that the labor theory of value would be vindicated and equal amounts of labor would receive equal pay. As an Austrian School economist, Rothbard did not agree with the labor theory and believed that prices of goods and services are proportional to marginal utility rather than to labor amounts in the free market. As opposed to Tucker he did not think that there was anything exploitative about people receiving an income according to how much "buyers of their services value their labor" or what that labor produces.
 Without the labor theory of value, some argue that 19th-century individualist anarchists approximate the modern movement of anarcho-capitalism, although this has been contested or rejected.Peacott, Joe (18 April 1985)
Without the labor theory of value, some argue that 19th-century individualist anarchists approximate the modern movement of anarcho-capitalism, although this has been contested or rejected.Peacott, Joe (18 April 1985)"Reply to Wendy Mc Elroy"
''New Libertarian'' (14, June 1985. . Retrieved 4 September 2020. "In her article on individualist anarchism in October 1984, ''New Libertarian'', Wendy McElroy mistakenly claims that modern-day individualist anarchism is identical with anarchist capitalism. She ignores the fact that there are still individualist anarchists who reject capitalism as well as communism, in the tradition of Warren, Spooner, Tucker, and others. ..Benjamin Tucker, when he spoke of his ideal 'society of contract,' was certainly not speaking of anything remotely resembling contemporary capitalist society. ..I do not quarrel with McElroy's definition of herself as an individualist anarchist. However, I dislike the fact that she tries to equate the term with anarchist capitalism. This is simply not true. I am an individualist anarchist and I am opposed to capitalist economic relations, voluntary or otherwise." As economic theory changed, the popularity of the labor theory of classical economics was superseded by the subjective theory of value of
neoclassical economics
Neoclassical economics is an approach to economics in which the production, consumption and valuation (pricing) of goods and services are observed as driven by the supply and demand model. According to this line of thought, the value of a good ...
and Rothbard combined Mises' Austrian School of economics with the absolutist views of human rights and rejection of the state he had absorbed from studying the individualist American anarchists of the 19th century such as Tucker and Spooner. In the mid-1950s, Rothbard wrote an unpublished article named "Are Libertarians 'Anarchists'?" under the pseudonym "Aubrey Herbert", concerned with differentiating himself from communist and socialistic economic views of anarchists, including the individualist anarchists of the 19th century, concluding that "we are ''not'' anarchists and that those who call us anarchists are not on firm etymological ground and are being completely unhistorical. On the other hand, it is clear that we are not archists either: we do not believe in establishing a tyrannical central authority that will coerce the noninvasive as well as the invasive. Perhaps, then, we could call ourselves by a new name: ''non''archist."Rothbard, Murray (1950s)"Are Libertarians 'Anarchists'?"
Lew Rockwell.com. Retrieved 4 September 2020. Joe Peacott, an American individualist anarchist in the mutualist tradition, criticizes anarcho-capitalists for trying to hegemonize the individualist anarchism label and make appear as if all individualist anarchists are in favor of
capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, private ...
. Peacott states that "individualists, both past and present, agree with the communist anarchists that present-day capitalism is based on economic coercion, not on voluntary contract. Rent and interest are the mainstays of modern capitalism and are protected and enforced by the state. Without these two unjust institutions, capitalism could not exist".
Anarchist activists and scholars do not consider anarcho-capitalism as a part of the anarchist movement because anarchism has historically been an anti-capitalist movement and see it as incompatible with capitalist forms. Although some regard anarcho-capitalism as a form of individualist anarchism, many others disagree or contest the existence of an individualist–socialist divide because individualist anarchism is largely libertarian socialist. In coming to terms that anarchists mostly identified with socialism
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes th ...
, Rothbard wrote that individualist anarchism is different from anarcho-capitalism and other capitalist theories due to the individualist anarchists retaining the labor theory of value and socialist doctrines. Similarly, many writers deny that anarcho-capitalism is a form of anarchism or that capitalism is compatible with anarchism.
''The Palgrave Handbook of Anarchism'' writes that " Benjamin Franks rightly points out, individualisms that defend or reinforce hierarchical forms such as the economic-power relations of anarcho-capitalism are incompatible with practices of social anarchism based on developing immanent goods which contest such as inequalities". Laurence Davis cautiously asks " anarcho-capitalism really a form of anarchism or instead a wholly different ideological paradigm whose adherents have attempted to expropriate the language of anarchism for their own anti-anarchist ends?" Davis cites Iain McKay, "whom Franks cites as an authority to support his contention that 'academic analysis has followed activist currents in rejecting the view that anarcho-capitalism has anything to do with social anarchism'", as arguing "quite emphatically on the very pages cited by Franks that anarcho-capitalism is by no means a type of anarchism". McKay writes that " is important to stress that anarchist opposition to the so-called capitalist 'anarchists' does ''not'' reflect some kind of debate within anarchism, as many of these types like to pretend, but a debate between anarchism and its old enemy capitalism. ... Equally, given that anarchists and 'anarcho'-capitalists have fundamentally ''different'' analyses and goals it is hardly 'sectarian' to point this out".
Davis writes that "Franks asserts without supporting evidence that most major forms of individualist anarchism have been largely anarcho-capitalist in content, and concludes from this premise that most forms of individualism are incompatible with anarchism". Davis argues that "the conclusion is unsustainable because the premise is false, depending as it does for any validity it might have on the further assumption that anarcho-capitalism is indeed a form of anarchism. If we reject this view, then we must also reject the individual anarchist versus the communal anarchist 'chasm' style of argument that follows from it". Davis maintains that "the ideological core of anarchism is the belief that society can and should be organised without hierarchy and domination. Historically, anarchists have struggles against a wide range of regimes of domination, from capitalism, the state system, patriarchy, heterosexism, and the domination of nature to colonialism, the war system, slavery, fascism, white supremacy, and certain forms of organised religion". According to Davis, " ile these visions range from the predominantly individualistic to the predominantly communitarian, features common to virtually all include an emphasis on self-management and self-regulatory methods of organisation, voluntary association, decentralised society, based on the principle of free association, in which people will manage and govern themselves". Finally, Davis includes a footnote stating that " dividualist anarchism may plausibly be re regarded as a form of both socialism and anarchism. Whether the individualist anarchists were ''consistent'' anarchists (and socialists) is another question entirely. ... McKay comments as follows: 'any individualist anarchism which supports wage labour is ''inconsistent'' anarchism. It ''can'' easily be made ''consistent'' anarchism by applying its own principles . In contrast 'anarcho'-capitalism rejects so many of the basic, underlying, principles of anarchism ... that it cannot be made consistent with the ideals of anarchism'".
Historical precedents
Several anarcho-capitalists and right-libertarians have discussed historical precedents of what they believe were examples of anarcho-capitalism.Free cities of medieval Europe
Economist and libertarian scholarBryan Caplan
Bryan Douglas Caplan (born April 8, 1971) is an American economist and author. Caplan is a professor of economics at George Mason University, research fellow at the Mercatus Center, adjunct scholar at the Cato Institute, and former contributor ...
considers the free cities of medieval Europe as examples of "anarchist" or "nearly anarchistic" societies, further arguing:
Medieval Iceland
 According to the libertarian theorist David D. Friedman, " dieval Icelandic institutions have several peculiar and interesting characteristics; they might almost have been invented by a mad economist to test the lengths to which market systems could supplant government in its most fundamental functions".Friedman, David D. (1979).
According to the libertarian theorist David D. Friedman, " dieval Icelandic institutions have several peculiar and interesting characteristics; they might almost have been invented by a mad economist to test the lengths to which market systems could supplant government in its most fundamental functions".Friedman, David D. (1979).Private Creation and Enforcement of Law: A Historical Case
. Retrieved 12 August 2005. While not directly labeling it anarcho-capitalist, Friedman argues that the legal system of the
Icelandic Commonwealth
The Icelandic Commonwealth, also known as the Icelandic Free State, was the political unit existing in Iceland between the establishment of the Althing in 930 and the pledge of fealty to the Norwegian king with the Old Covenant in 1262. With ...
comes close to being a real-world anarcho-capitalist legal system. Although noting that there was a single legal system, Friedman argues that enforcement of the law was entirely private and highly capitalist, providing some evidence of how such a society would function. Friedman further wrote that " en where the Icelandic legal system recognized an essentially 'public' offense, it dealt with it by giving some individual (in some cases chosen by lot from those affected) the right to pursue the case and collect the resulting fine, thus fitting it into an essentially private system".
Friedman and Bruce L. Benson argued that the Icelandic Commonwealth saw significant economic and social progress in the absence of systems of criminal law, an executive, or bureaucracy. This commonwealth was led by chieftains, whose position could be bought and sold like that of private property. Being a member of the chieftainship was also completely voluntary.
American Old West
According to Terry L. Anderson and P. J. Hill, the Old West in the United States in the period of 1830 to 1900 was similar to anarcho-capitalism in that "private agencies provided the necessary basis for an orderly society in which property was protected and conflicts were resolved" and that the common popular perception that the Old West was chaotic with little respect for property rights is incorrect. Since squatters had no claim to western lands under federal law, extra-legal organizations formed to fill the void. Benson explains: According to Anderson, " fining anarcho-capitalist to mean minimal government with property rights developed from the bottom up, the western frontier was anarcho-capitalistic. People on the frontier invented institutions that fit the resource constraints they faced".Gaelic Ireland
 In his work '' For a New Liberty'', Murray Rothbard has claimed ancient Gaelic Ireland as an example of nearly anarcho-capitalist society. In his depiction, citing the work of Professor Joseph Peden, the basic political unit of ancient Ireland was the tuath, which is portrayed as "a body of persons voluntarily united for socially beneficial purposes" with its territorial claim being limited to "the sum total of the landed properties of its members". Civil disputes were settled by private arbiters called "brehons" and the compensation to be paid to the wronged party was insured through voluntary surety relationships. Commenting on the "kings" of tuaths, Rothbard stated:
In his work '' For a New Liberty'', Murray Rothbard has claimed ancient Gaelic Ireland as an example of nearly anarcho-capitalist society. In his depiction, citing the work of Professor Joseph Peden, the basic political unit of ancient Ireland was the tuath, which is portrayed as "a body of persons voluntarily united for socially beneficial purposes" with its territorial claim being limited to "the sum total of the landed properties of its members". Civil disputes were settled by private arbiters called "brehons" and the compensation to be paid to the wronged party was insured through voluntary surety relationships. Commenting on the "kings" of tuaths, Rothbard stated:
Law merchant, admiralty law, and early common law
Some libertarians have cited law merchant, admiralty law and earlycommon law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omniprese ...
as examples of anarcho-capitalism.
In his work ''Power and Market'', Rothbard stated:
Somalia from 1991 to 2006
Economist Alex Tabarrok argued that Somalia in its stateless period provided a "unique test of the theory of anarchy", in some aspects near of that espoused by anarcho-capitalists David D. Friedman and Murray Rothbard. Nonetheless, both anarchists and some anarcho-capitalists argue that Somalia was not an anarchist society.Analysis and criticism
State, justice and defense
Anarchists such as Brian Morris argue that anarcho-capitalism does not in fact get rid of the state. He says that anarcho-capitalists "simply replaced the state with private security firms, and can hardly be described as anarchists as the term is normally understood". In "Libertarianism: Bogus Anarchy", anarchist Peter Sabatini notes: Similarly,Bob Black
Robert Charles Black Jr. (born January 4, 1951) is an American anarchist and author. He is the author of the books '' The Abolition of Work and Other Essays'', ''Beneath the Underground'', ''Friendly Fire'', ''Anarchy After Leftism'', and ''Def ...
argues that an anarcho-capitalist wants to "abolish the state to his own satisfaction by calling it something else". He states that they do not denounce what the state does, they just "object to who's doing it".
Paul Birch argues that legal disputes involving several jurisdictions and different legal systems will be too complex and costly. He therefore argues that anarcho-capitalism is inherently unstable, and would evolve, entirely through the operation of free market forces, into either a single dominant private court with a natural monopoly of justice over the territory (a ''de facto'' state), a society of multiple city states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, each with a territorial monopoly, or a 'pure anarchy' that would rapidly descend into chaos.
Randall G. Holcombe argues that anarcho-capitalism turns justice
Justice, in its broadest sense, is the principle that people receive that which they deserve, with the interpretation of what then constitutes "deserving" being impacted upon by numerous fields, with many differing viewpoints and perspective ...
into a commodity as private defense and court firms would favour those who pay more for their services. He argues that defense agencies could form cartels and oppress people without fear of competition. Philosopher Albert Meltzer argued that since anarcho-capitalism promotes the idea of private armies, it actually supports a "limited State". He contends that it "is only possible to conceive of Anarchism which is free, communistic and offering no economic necessity for repression of countering it".
Robert Nozick argues that a competitive legal system would evolve toward a monopoly government—even without violating individuals' rights in the process. In '' Anarchy, State, and Utopia'', Nozick argues that an anarcho-capitalist society would inevitably transform into a minarchist state through the eventual emergence of a monopolistic private defense and judicial agency that no longer faces competition. He argues that anarcho-capitalism results in an unstable system that would not endure in the real world. While anarcho-capitalists such as Roy Childs and Murray Rothbard have rejected Nozick's arguments, with Rothbard arguing that the process described by Nozick, with the dominant protection agency outlawing its competitors, in fact violates its own clients' rights, John Jefferson actually advocates Nozick's argument and states that such events would best operate in ''laissez-faire
''Laissez-faire'' ( ; from french: laissez faire , ) is an economic system in which transactions between private groups of people are free from any form of economic interventionism (such as subsidies) deriving from special interest groups ...
''. Robert Ellickson presented a Hayekian case against anarcho-capitalism, calling it a "pipe-dream" and stating that anarcho-capitalists "by imagining a stable system of competing private associations, ignore both the inevitability of territorial monopolists in governance, and the importance of institutions to constrain those monopolists' abuses".
Some libertarians argue that anarcho-capitalism would result in different standards of justice and law due to relying too much on the market. Friedman responded to this criticism by arguing that it assumes the state is controlled by a majority group that has similar legal ideals. If the populace is diverse, different legal standards would therefore be appropriate.
Rights and freedom
Negative and positive rights are rights that oblige either action (positive rights) or inaction (negative rights). Anarcho-capitalists believe that negative rights should be recognized as legitimate, but positive rights should be rejected as an intrusion. Some critics reject the distinction between positive and negative rights.Peter Marshall Peter Marshall may refer to:
Entertainment
* Peter Marshall (entertainer) (born 1926), American game show host of ''The Hollywood Squares'', 1966–1981
* Peter Marshall (author, born 1939) (1939–1972), British novelist whose works include ''T ...
also states that the anarcho-capitalist definition of freedom is entirely negative and that it cannot guarantee the positive freedom
Positive liberty is the possession of the power and resources to act in the context of the structural limitations of the broader society which impacts a person's ability to act, as opposed to negative liberty, which is freedom from external restra ...
of individual autonomy and independence.
About anarcho-capitalism, anarcho-syndicalist and anti-capitalist intellectual Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky i ...
says:
Economics and property
Social anarchists argue that anarcho-capitalism allows individuals to accumulate significant power through free markets and private property. Friedman responded by arguing that the Icelandic Commonwealth was able to prevent the wealthy from abusing the poor by requiring individuals who engaged in acts of violence to compensate their victims financially. Anarchists argue that certain capitalist transactions are not voluntary and that maintaining the class structure of a capitalist society requires coercion which violates anarchist principles. AnthropologistDavid Graeber
David Rolfe Graeber (; February 12, 1961September 2, 2020) was an American anthropologist and anarchist activist. His influential work in economic anthropology, particularly his books '' Debt: The First 5,000 Years'' (2011) and ''Bullshit Job ...
noted his skepticism about anarcho-capitalism along the same lines, arguing:
Some critics argue that the anarcho-capitalist concept of voluntary choice ignores constraints due to both human and non-human factors such as the need for food and shelter as well as active restriction of both used and unused resources by those enforcing property claims. If a person requires employment in order to feed and house himself, the employer-employee relationship could be considered involuntary. Another criticism is that employment is involuntary because the economic system that makes it necessary for some individuals to serve others is supported by the enforcement of coercive private property relations. Some philosophies view any ownership claims on land and natural resources as immoral and illegitimate. McElroy, Wendy (1995).Intellectual Property: The Late Nineteenth Century Libertarian Debate
. ''Libertarian Heritage'' No. 14 . Retrieved 24 June 2005. Objectivist philosopher Harry Binswanger criticizes anarcho-capitalism by arguing that "capitalism requires government", questioning who or what would enforce treaties and contracts. Some right-libertarian critics of anarcho-capitalism who support the full privatization of capital such as
geolibertarians
Geolibertarianism is a political and economic ideology that integrates libertarianism with Georgism. It favors a taxation system based (as in Georgism) on income derived from land and natural resources instead of on labor, coupled with a minima ...
argue that land and the raw materials of nature remain a distinct factor of production and cannot be justly converted to private property because they are not products of human labor. Some socialists
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the econ ...
, including market anarchists and mutualists, adamantly oppose absentee ownership. Anarcho-capitalists have strong abandonment criteria, namely that one maintains ownership until one agrees to trade or gift it. Anti-state critics of this view posit comparatively weak abandonment criteria, arguing that one loses ownership when one stops personally occupying and using it as well as the idea of perpetually binding original appropriation is anathema to traditional schools of anarchism.
Literature
The following is a partial list of notable nonfiction works discussing anarcho-capitalism. * Bruce L. Benson, ''The Enterprise of Law: Justice Without The State'' ** ''To Serve and Protect: Privatization and Community in Criminal Justice'' * David D. Friedman, ''The Machinery of Freedom
''The Machinery of Freedom'' is a nonfiction book by David D. Friedman that advocates an anarcho-capitalist society from a consequentialist perspective.
The book was published in 1973, with a second edition in 1989 and a third edition in 2014.
...
''
* Edward P. Stringham, ''Anarchy and the Law: The Political Economy of Choice''
* George H. Smith, "Justice Entrepreneurship in a Free Market"
* Gerard Casey, ''Libertarian Anarchy: Against the State''
* Hans-Hermann Hoppe, ''Anarcho-Capitalism: An Annotated Bibliography''
** ''A Theory of Socialism and Capitalism''
** '' Democracy: The God That Failed''
** ''The Economics and Ethics of Private Property
Hans-Hermann Hoppe (; ; born 2 September 1949) is a German-American economist of the Austrian School, philosopher and political theorist. He is Professor Emeritus of Economics at the University of Nevada, Las Vegas (UNLV), Senior Fellow ...
''
* Linda and Morris Tannehill, '' The Market for Liberty''
* Michael Huemer, '' The Problem of Political Authority''
* Murray Rothbard, founder of anarcho-capitalism:
** '' For a New Liberty''
** ''Man, Economy, and State
''Man, Economy, and State: A treatise on economic principles'' is a 1962 book of Austrian School economics by Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian Schoo ...
''
** '' Power and Market''
** '' The Ethics of Liberty''
See also
*Agorism
Agorism is a social philosophy that advocates creating a society in which all relations between people are voluntary exchanges by means of counter-economics, engaging with aspects of nonviolent revolution. It was first proposed by American liber ...
* Anarcho-capitalism and minarchism
* Consequentialist libertarianism
* Counter-economics
Counter-economics is an economic theory and revolutionary method consisting of direct action carried out through the black market or the gray market. As a term, it was originally used by American libertarian activists and theorists Samuel Edward K ...
* Creative disruption
* Crypto-anarchism
* Definition of anarchism and libertarianism
* Issues in anarchism
Anarchism is generally defined as the political philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary and harmful
. The following sources cite anarchism as a political philosophy: Slevin, Carl (2003). McLean, Aiaun; McMillan, Allistai ...
* Left-wing market anarchism
* Natural-rights libertarianism
* Privatization in criminal justice
Privatization in criminal justice refers to a shift to private ownership and control of criminal justice services. The term is often used to refer simply to contracting out services, which takes place extensively in many countries today. For exam ...
* Propertarianism
* Stateless society
* ''The Libertarian Forum
''The Libertarian Forum'' was an anarcho-capitalist magazine published about twice a month from 1969 to 1984. Its editor and chief author was Murray Rothbard; initially, Karl Hess also served as Washington editor. Currently all the issues are ava ...
''
* Voluntaryism
References
Further reading
* Brown, Susan Love (1997)"The Free Market as Salvation from Government: The Anarcho-Capitalist View"
In Carrier, James G., ed. ''Meanings of the Market: The Free Market in Western Culture'' (illustrated ed.). Oxford: Berg Publishers. p. 99. . *
External links
LewRockwell.com
– website run by
Lew Rockwell
Llewellyn Harrison Rockwell Jr. (born July 1, 1944) is an American author, editor, and political consultant. A libertarian and a self-professed anarcho-capitalist, he founded and is the chairman of the Mises Institute, a non-profit dedicated t ...
Mises Institute
– research and educational center of classical liberalism, including anarcho-capitalism, Austrian School of economics and American libertarian political theory
Property and Freedom Society
– international anarcho-capitalist society
Strike The Root
– an anarcho-capitalist website featuring essays, news, and a forum {{libertarianism Austrian School Capitalist systems Economic ideologies Anarcho-capitalism Ideologies of capitalism Classical liberalism Libertarianism by form Political ideologies Right-libertarianism Syncretic political movements Right-wing ideologies