Warner Bros. on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc. (commonly known as Warner Bros. or abbreviated as WB) is an American film and entertainment studio headquartered at the Warner Bros. Studios complex in Burbank,
 The three elder brothers began in the
The three elder brothers began in the 
 The first important deal was the acquisition of the rights to
The first important deal was the acquisition of the rights to
 In 1928, Warner Bros. released '' Lights of New York'', the first all-talking feature. Due to its success, the movie industry converted entirely to sound almost overnight. By the end of 1929, all the major studios were exclusively making sound films. In 1929, First National Pictures released their first film with Warner Bros., ''
In 1928, Warner Bros. released '' Lights of New York'', the first all-talking feature. Due to its success, the movie industry converted entirely to sound almost overnight. By the end of 1929, all the major studios were exclusively making sound films. In 1929, First National Pictures released their first film with Warner Bros., ''' s success, the studio produced profitable musicals. These starred Ruby Keeler and
 Another gangster film the studio produced was the critically acclaimed '' I Am a Fugitive from a Chain Gang'', based on a true story and starring
Another gangster film the studio produced was the critically acclaimed '' I Am a Fugitive from a Chain Gang'', based on a true story and starring  By 1936, contracts of musical and silent stars were not renewed, instead being replaced by tough-talking, working-class types who better fit these pictures. As a result, Dorothy Mackaill,
By 1936, contracts of musical and silent stars were not renewed, instead being replaced by tough-talking, working-class types who better fit these pictures. As a result, Dorothy Mackaill,
 In 1935, Cagney sued Jack Warner for breach of contract. Cagney claimed Warner had forced him to star in more films than his contract required. Cagney eventually dropped his lawsuit after a cash settlement. Nevertheless, Cagney left the studio to establish an independent film company with his brother Bill. The Cagneys released their films though
In 1935, Cagney sued Jack Warner for breach of contract. Cagney claimed Warner had forced him to star in more films than his contract required. Cagney eventually dropped his lawsuit after a cash settlement. Nevertheless, Cagney left the studio to establish an independent film company with his brother Bill. The Cagneys released their films though
 During the war era, the studio made ''
During the war era, the studio made ''' s Oscar for Best Picture, Wallis resigned. After ''Casablanca'' made Bogart a top star, Bogart's relationship with Jack deteriorated.
In 1943,
 In the early 1950s, the threat of television emerged. In 1953, Jack decided to copy
In the early 1950s, the threat of television emerged. In 1953, Jack decided to copy
 On March 21, 1955, the studio was finally able to engage in television through the successful Warner Bros. Television unit run by
On March 21, 1955, the studio was finally able to engage in television through the successful Warner Bros. Television unit run by  In 1958, the studio launched Warner Bros. Records. Initially, the label released recordings made by their television stars—whether they could sing or not—and records based on television soundtracks. Warner Bros. was already the owner of extensive music-publishing holdings, whose tunes had appeared in countless cartoons (arranged by
In 1958, the studio launched Warner Bros. Records. Initially, the label released recordings made by their television stars—whether they could sing or not—and records based on television soundtracks. Warner Bros. was already the owner of extensive music-publishing holdings, whose tunes had appeared in countless cartoons (arranged by
 In November 1966, Jack gave in to advancing age and changing times, selling control of the studio and music business to Seven Arts Productions, run by Canadian investors Eliot and Kenneth Hyman, for $32 million. The company, including the studio, was renamed Warner Bros.-Seven Arts. Warner remained president until the summer of 1967, when ''
In November 1966, Jack gave in to advancing age and changing times, selling control of the studio and music business to Seven Arts Productions, run by Canadian investors Eliot and Kenneth Hyman, for $32 million. The company, including the studio, was renamed Warner Bros.-Seven Arts. Warner remained president until the summer of 1967, when '' Although movie audiences had shrunk, Warner's new management believed in the drawing power of stars, signing co-production deals with several of the biggest names of the day, including
Although movie audiences had shrunk, Warner's new management believed in the drawing power of stars, signing co-production deals with several of the biggest names of the day, including
 Warner Communications merged in 1989 with white-shoe publishing company Time Inc. Time claimed a higher level of prestige, while Warner Bros. provided the profits. The
Warner Communications merged in 1989 with white-shoe publishing company Time Inc. Time claimed a higher level of prestige, while Warner Bros. provided the profits. The  In 1995, Warner and television station owner Tribune Company of Chicago launched
In 1995, Warner and television station owner Tribune Company of Chicago launched

California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
, and a subsidiary
A subsidiary, subsidiary company or daughter company is a company owned or controlled by another company, which is called the parent company or holding company. Two or more subsidiaries that either belong to the same parent company or having a ...
of Warner Bros. Discovery. Founded in 1923 by four brothers, Harry, Albert, Sam, and Jack Warner, the company established itself as a leader in the American film
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
industry before diversifying into animation
Animation is a method by which still figures are manipulated to appear as moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Today, most ani ...
, television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
, and video games
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedbac ...
and is one of the "Big Five" major American film studio
A film studio (also known as movie studio or simply studio) is a major entertainment company or motion picture company that has its own privately owned studio facility or facilities that are used to make films, which is handled by the productio ...
s, as well as a member of the Motion Picture Association
The Motion Picture Association (MPA) is an American trade association representing the five major film studios of the United States, as well as the video streaming service Netflix. Founded in 1922 as the Motion Picture Producers and Distribu ...
(MPA).
The company is known for its film studio
A film studio (also known as movie studio or simply studio) is a major entertainment company or motion picture company that has its own privately owned studio facility or facilities that are used to make films, which is handled by the productio ...
division the Warner Bros. Pictures Group, which includes Warner Bros. Pictures
Warner Bros. Pictures is an American film production and distribution company of the Warner Bros. Pictures Group division of Warner Bros. Entertainment (both ultimately owned by Warner Bros. Discovery). The studio is the flagship producer of li ...
, New Line Cinema
New Line Cinema is an American film production studio owned by Warner Bros. Discovery and is a film label of Warner Bros. It was founded in 1967 by Robert Shaye as an independent film distribution company; later becoming a film studio after ...
, the Warner Animation Group
The Warner Animation Group (WAG) is an American animation studio serving as the computer-animated feature film label of Warner Bros.' theatrical film production and distribution division, Warner Bros. Pictures. Established on January 7, 2013, ...
, Castle Rock Entertainment, and DC Studios
DC Studios is an American film and television studio that is a division of Warner Bros., which is a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. It is dedicated to the production of films, series, and animations based on characters from DC Comics, ...
. Among its other assets, stands the television production company Warner Bros. Television Studios
Warner Bros. Television Studios (operating under the name Warner Bros. Television; formerly known as Warner Bros. Television Division) is an American television production and distribution studio of the Warner Bros. Television Group division of ...
. Bugs Bunny
Bugs Bunny is an animated cartoon character created in the late 1930s by Leon Schlesinger Productions (later Warner Bros. Cartoons) and voiced originally by Mel Blanc. Bugs is best known for his starring roles in the ''Looney Tunes'' and ''Merr ...
, a cartoon character created by Tex Avery
Frederick Bean "Tex" Avery (February 26, 1908 – August 26, 1980) was an American animator, cartoonist, director, and voice actor. He was known for directing and producing animated cartoons during the golden age of American animation. His mo ...
, Ben Hardaway, Chuck Jones
Charles Martin Jones (September 21, 1912 – February 22, 2002) was an American animator, director, and painter, best known for his work with Warner Bros. Cartoons on the '' Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of shorts. He wrote, pro ...
, Bob Givens and Robert McKimson
Robert Porter McKimson Sr. (October 13, 1910 – September 29, 1977) was an American animator and illustrator, best known for his work on the ''Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of cartoons from Warner Bros. Cartoons and later DeP ...
as part of the ''Looney Tunes
''Looney Tunes'' is an American animated comedy short film series produced by Warner Bros. starting from 1930 to 1969, concurrently with its partner series '' Merrie Melodies'', during the golden age of American animation. ...
'' series, is the company's official mascot.
History
Founding
The company's name originated from the founding Warner brothers (born Wonsal, Woron and Wonskolaser before Anglicization): Harry, Albert, Sam, and Jack Warner. Harry, Albert and Sam emigrated as young children with theirPolish-Jewish
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the l ...
mother to the United States from Krasnosielc, Poland (then part of Congress Poland
Congress Poland, Congress Kingdom of Poland, or Russian Poland, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland, was a polity created in 1815 by the Congress of Vienna as a semi-autonomous Polish state, a successor to Napoleon's Duchy of Warsaw. I ...
within the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
), in October 1889, a year after their father emigrated to the U.S. and settled in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean t ...
. As in many other immigrant families, the elder Wonsal children gradually acquired anglicized versions of their Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
-sounding names: Szmuel Wonsal became Samuel Warner (nicknamed "Sam"), Hirsz Wonsal became Harry Warner, and Aaron Wonsal (although born with a given name common in the Americas) became Albert Warner. Jack, the youngest brother, was born in London, Ontario
London (pronounced ) is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, along the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor. The city had a population of 422,324 according to the 2021 Canadian census. London is at the confluence of the Thames River, approximat ...
, during the family's two-year residency in Canada.
 The three elder brothers began in the
The three elder brothers began in the movie theater
A movie theater (American English), cinema (British English), or cinema hall ( Indian English), also known as a movie house, picture house, the movies, the pictures, picture theater, the silver screen, the big screen, or simply theater is a ...
business, having acquired a movie projector
A movie projector is an opto-mechanical device for displaying motion picture film by projecting it onto a screen. Most of the optical and mechanical elements, except for the illumination and sound devices, are present in movie cameras. Mod ...
with which they showed films in the mining towns of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
. In the beginning, Sam and Albert Warner invested $150 to present '' Life of an American Fireman'' and '' The Great Train Robbery''. They opened their first theater, the Cascade
Cascade, Cascades or Cascading may refer to:
Science and technology Science
*Cascade waterfalls, or series of waterfalls
* Cascade, the CRISPR-associated complex for antiviral defense (a protein complex)
* Cascade (grape), a type of fruit
* Bioc ...
, in New Castle, Pennsylvania, in 1903. When the original building was in danger of being demolished, the modern Warner Bros. called the current building owners and arranged to save it. The owners noted people across the country had asked them to protect it for its historical significance.
In 1904, the Warners founded the Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County, Pennsylvania, Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Wester ...
-based Duquesne Amusement & Supply Company, to distribute films. In 1912, Harry Warner hired an auditor named Paul Ashley Chase
Paul Ashley Chase (February 5, 1878 – April 17, 1946) was one of the founding executives, first auditor, Assistant Secretary of the corporation, and comptroller for Warner Brothers Pictures. He was previously the traveling auditor for the Er ...
. By the time of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
they had begun producing films. In 1918 they opened the first Warner Brothers Studio on Sunset Boulevard in Hollywood. Sam and Jack produced the pictures, while Harry and Albert, along with their auditor and now controller Chase, handled finance and distribution in New York City. During World War I their first nationally syndicated film, ''My Four Years in Germany,'' based on a popular book by former ambassador James W. Gerard
James Watson Gerard III (August 25, 1867 – September 6, 1951) was a United States lawyer, diplomat, and justice of the New York Supreme Court.
Early life
Gerard was born in Geneseo, New York. His father, James Watson Gerard Jr., was a lawy ...
, was released. On April 4, 1923, with help from money loaned to Harry by his banker Motley Flint, they formally incorporated as Warner Bros. Pictures, Incorporated. (As late as the 1960s, Warner Bros. claimed 1905 as its founding date.)

 The first important deal was the acquisition of the rights to
The first important deal was the acquisition of the rights to Avery Hopwood
James Avery Hopwood (May 28, 1882 – July 1, 1928) was an American playwright of the Jazz Age. He had four plays running simultaneously on Broadway in 1920.
Early life
Hopwood was born to James and Jule Pendergast Hopwood on May 28, 1882 ...
's 1919 Broadway play, '' The Gold Diggers'', from theatrical impresario David Belasco. However, Rin Tin Tin, a dog brought from France after World War I by an American soldier, established their reputation. Rin Tin Tin's third film was the feature ''Where the North Begins
''Where the North Begins'' is a 1923 American silent drama film produced and distributed by Warner Bros. This was the third film for up-and-coming canine actor Rin Tin Tin. The film survives today and lapsed into the public domain on January 1 ...
'', which was so successful that Jack signed the dog to star in more films for $1,000 per week. Rin Tin Tin became the studio's top star. Jack nicknamed him "The Mortgage Lifter" and the success boosted Darryl F. Zanuck's career. Zanuck eventually became a top producer and between 1928 and 1933 served as Jack's right-hand man and executive producer
Executive producer (EP) is one of the top positions in the making of a commercial entertainment product. Depending on the medium, the executive producer may be concerned with management accounting or associated with legal issues (like copyrights ...
, with responsibilities including day-to-day film production.Behlmer (1985), p. xii More success came after Ernst Lubitsch
Ernst Lubitsch (; January 29, 1892November 30, 1947) was a German-born American film director, producer, writer, and actor. His urbane comedies of manners gave him the reputation of being Hollywood's most elegant and sophisticated director; as ...
was hired as head director; Harry Rapf left the studio to join Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc., also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures and abbreviated as MGM, is an American film, television production, distribution and media company owned by amazon (company), Amazon through MGM Holdings, founded o ...
.Thomas46, 47 Lubitsch's film '' The Marriage Circle'' was the studio's most successful film of 1924, and was on ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' best list for that year.
Despite the success of Rin Tin Tin and Lubitsch, Warner's remained a lesser studio. Sam and Jack decided to offer Broadway actor John Barrymore
John Barrymore (born John Sidney Blyth; February 14 or 15, 1882 – May 29, 1942) was an American actor on stage, screen and radio. A member of the Drew and Barrymore theatrical families, he initially tried to avoid the stage, and briefly att ...
the lead role in ''Beau Brummel
George Bryan "Beau" Brummell (7 June 1778 – 30 March 1840) was an important figure in Regency England and, for many years, the arbiter of men's fashion. At one time, he was a close friend of the Prince Regent, the future King George IV, but ...
''. The film was so successful that Harry signed Barrymore to a long-term contract; like '' The Marriage Circle'', ''Beau Brummel'' was named one of the ten best films of the year by the ''Times''. By the end of 1924, Warner Bros. was arguably Hollywood's most successful independent studio, where it competed with "The Big Three" Studios ( First National, Paramount Pictures
Paramount Pictures Corporation is an American film and television production company, production and Distribution (marketing), distribution company and the main namesake division of Paramount Global (formerly ViacomCBS). It is the fifth-oldes ...
, and Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc., also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures and abbreviated as MGM, is an American film, television production, distribution and media company owned by amazon (company), Amazon through MGM Holdings, founded o ...
). As a result, Harry Warner—while speaking at a convention of 1,500 independent exhibitors in Milwaukee, Wisconsin—was able to convince the filmmakers to spend $500,000 in newspaper advertising, and Harry saw this as an opportunity to establish theaters in places such as New York City and Los Angeles.
As the studio prospered, it gained backing from Wall Street, and in 1924 Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs () is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, Ho ...
arranged a major loan. With this new money, the Warners bought the pioneer Vitagraph Company which had a nationwide distribution system. In 1925, Warners' also experimented in radio, establishing a successful radio station, KFWB, in Los Angeles.
1925–1935: Sound, color, style
Warner Bros. was a pioneer of films with synchronized sound (then known as "talking pictures" or "talkies"). In 1925, at Sam's urging, Warner's agreed to add this feature to their productions. By February 1926, the studio reported a net loss of $333,413. After a long period denying Sam's request for sound, Harry agreed to change, as long as the studio's use of synchronized sound was for background music purposes only. The Warners signed a contract with the sound engineer company Western Electric and establishedVitaphone
Vitaphone was a sound film system used for feature films and nearly 1,000 short subjects made by Warner Bros. and its sister studio First National from 1926 to 1931. Vitaphone was the last major analog sound-on-disc system and the only one ...
. In 1926, Vitaphone began making films with music and effects tracks, most notably, in the feature '' Don Juan'' starring John Barrymore
John Barrymore (born John Sidney Blyth; February 14 or 15, 1882 – May 29, 1942) was an American actor on stage, screen and radio. A member of the Drew and Barrymore theatrical families, he initially tried to avoid the stage, and briefly att ...
. The film was silent, but it featured a large number of Vitaphone shorts at the beginning. To hype ''Don Juan''s release, Harry acquired the large Piccadilly Theater in Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
, New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
, and renamed it Warners' Theatre.
''Don Juan'' premiered at the Warners' Theatre in New York on August 6, 1926. Throughout the early history of film distribution, theater owners hired orchestras to attend film showings, where they provided soundtrack
A soundtrack is recorded music accompanying and synchronised to the images of a motion picture, drama, book, television program, radio program, or video game; a commercially released soundtrack album of music as featured in the soundtrac ...
s. Through Vitaphone, Warner Bros. produced eight shorts (which were played at the beginning of every showing of ''Don Juan'' across the country) in 1926. Many film production companies questioned the necessity. ''Don Juan'' did not recoup its production cost and Lubitsch left for MGM. By April 1927, the Big Five studios (First National, Paramount, MGM, Universal
Universal is the adjective for universe.
Universal may also refer to:
Companies
* NBCUniversal, a media and entertainment company
** Universal Animation Studios, an American Animation studio, and a subsidiary of NBCUniversal
** Universal TV, a t ...
, and Producers Distributing) had ruined Warner's, and Western Electric renewed Warner's Vitaphone contract with terms that allowed other film companies to test sound.
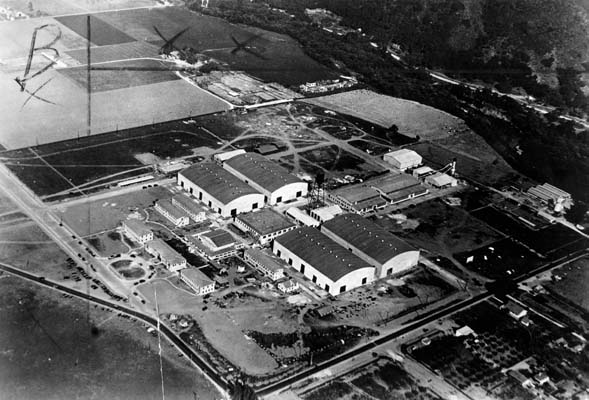
As a result of their financial problems, Warner Bros. took the next step and released '' The Jazz Singer'' starring Al Jolson. This movie, which includes little sound dialogue, but did feature sound segments of Jolson singing, was a sensation. It signaled the beginning of the era of "talking pictures" and the twilight of the silent era. However, Sam died the night before the opening, preventing the brothers from attending the premiere. Jack became sole head of production.Warner and Jennings (1964), pp.180–181 Sam's death also had a great effect on Jack's emotional state, as Sam was arguably Jack's inspiration and favorite brother. In the years to come, Jack kept the studio under tight control. Firing employees was common. Among those whom Jack fired were Rin Tin Tin (in 1929) and Douglas Fairbanks Jr. (in 1933), the latter having served as First National's top star since the brothers acquired the studio in 1928.
Thanks to the success of ''The Jazz Singer'', the studio was cash-rich. Jolson's next film for the company, '' The Singing Fool'' was also a success. With the success of these first talkies (''The Jazz Singer'', '' Lights of New York'', '' The Singing Fool'' and '' The Terror''), Warner Bros. became a top studio and the brothers were now able to move out from the Poverty Row section of Hollywood, and acquire a much larger studio lot in Burbank. They expanded by acquiring the Stanley Corporation, a major theater chain. This gave them a share in rival First National Pictures
First National Pictures was an American motion picture production and distribution company. It was founded in 1917 as First National Exhibitors' Circuit, Inc., an association of independent theatre owners in the United States, and became the count ...
, of which Stanley owned one-third. In a bidding war with William Fox, Warner Bros. bought more First National shares on September 13, 1928; Jack also appointed Zanuck as the manager of First National Pictures.
 In 1928, Warner Bros. released '' Lights of New York'', the first all-talking feature. Due to its success, the movie industry converted entirely to sound almost overnight. By the end of 1929, all the major studios were exclusively making sound films. In 1929, First National Pictures released their first film with Warner Bros., ''
In 1928, Warner Bros. released '' Lights of New York'', the first all-talking feature. Due to its success, the movie industry converted entirely to sound almost overnight. By the end of 1929, all the major studios were exclusively making sound films. In 1929, First National Pictures released their first film with Warner Bros., ''Noah's Ark
Noah's Ark ( he, תיבת נח; Biblical Hebrew: ''Tevat Noaḥ'')The word "ark" in modern English comes from Old English ''aerca'', meaning a chest or box. (See Cresswell 2010, p.22) The Hebrew word for the vessel, ''teva'', occurs twice in ...
''. Despite its expensive budget, ''Noah's Ark'' was profitable. In 1929, Warner Bros. released '' On with the Show!'', the first all-color all-talking feature. This was followed by ''Gold Diggers of Broadway
''Gold Diggers of Broadway'' is a 1929 American pre-Code musical comedy film directed by Roy Del Ruth and starring Winnie Lightner and Nick Lucas. Distributed by Warner Bros., the film is the second all-talking, all-Technicolor feature-lengt ...
'' which would play in theaters until 1939. The success of these pictures caused a color revolution. Warner Bros. color films from 1929 to 1931 included ''The Show of Shows
''The Show of Shows'' is a 1929 American pre-Code musical revue film directed by John G. Adolfi and distributed by Warner Bros. The all-talking Vitaphone production cost $850,000 and was shot almost entirely in Technicolor.
''The Show o ...
'' (1929), '' Sally'' (1929), '' Bright Lights'' (1930), ''Golden Dawn
Golden Dawn or The Golden Dawn may refer to:
Organizations
* Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, a nineteenth century magical order based in Britain
** The Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn, Inc., a modern revival founded in 1977
** Open Source ...
'' (1930), '' Hold Everything'' (1930), ''Song of the Flame
''Song of the Flame'' is a 1930 American pre-Code musical film photographed entirely in Technicolor. It was produced and distributed by First National Pictures. It was the first color film to feature a widescreen sequence, using a process called ...
'' (1930), '' Song of the West'' (1930), '' The Life of the Party'' (1930), '' Sweet Kitty Bellairs'' (1930), ''Under a Texas Moon
''Under A Texas Moon'' is a 1930 American pre-Code musical Western film photographed entirely in Technicolor. It was based on the novel ''Two-Gun Man'' (from 1929) which was written by Stewart Edward White. It was the second all-color, all-talk ...
'' (1930), ''Bride of the Regiment
''Bride of the Regiment'' is a 1930 American Pre-Code musical film directed by John Francis Dillon and filmed entirely in Technicolor. The screenplay by Ray Harris and Humphrey Pearson is based on the book of the 1922 stage musical ''The Lady ...
'' (1930), ''Viennese Nights
''Viennese Nights'' is a 1930 American all-talking pre-Code musical operetta film directed by Alan Crosland and starring Alexander Gray, Vivienne Segal, Walter Pidgeon, Jean Hersholt, Bela Lugosi and Louise Fazenda. It was photographed ...
'' (1931), '' Woman Hungry'' (1931), '' Kiss Me Again'' (1931), '' 50 Million Frenchmen'' (1931) and '' Manhattan Parade'' (1932). In addition to these, scores of features were released with Technicolor sequences, as well as numerous Technicolor Specials short subjects. The majority of these color films were musicals.
In 1929, Warner Bros. bought the St. Louis-based theater chain Skouras Brothers Enterprises. Following this takeover, Spyros Skouras
Spyros Panagiotis Skouras (; gr, Σπύρος Σκούρας; March 28, 1893 – August 16, 1971) was a Greek-American motion picture pioneer and film executive who was the president of 20th Century-Fox from 1942 to 1962. He resigned June 27, 19 ...
, the driving force of the chain, became general manager of the Warner Brothers Theater Circuit in America. He worked successfully in that post for two years and turned its losses into profits. Harry produced an adaptation of a Cole Porter
Cole Albert Porter (June 9, 1891 – October 15, 1964) was an American composer and songwriter. Many of his songs became standards noted for their witty, urbane lyrics, and many of his scores found success on Broadway and in film.
Born to ...
musical titled ''Fifty Million Frenchmen''. Through First National, the studio's profit increased substantially. After the success of the studio's 1929 First National film ''Noah's Ark
Noah's Ark ( he, תיבת נח; Biblical Hebrew: ''Tevat Noaḥ'')The word "ark" in modern English comes from Old English ''aerca'', meaning a chest or box. (See Cresswell 2010, p.22) The Hebrew word for the vessel, ''teva'', occurs twice in ...
'', Harry agreed to make Michael Curtiz a major director at the Burbank studio. Mort Blumenstock, a First National screenwriter, became a top writer at the brothers' New York headquarters. In the third quarter, Warner Bros. gained complete control of First National, when Harry purchased the company's remaining one-third share from Fox. The Justice Department
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
agreed to allow the purchase if First National was maintained as a separate company. When the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
hit, Warner asked for and got permission to merge the two studios. Soon afterward Warner Bros. moved to the First National lot in Burbank. Though the companies merged, the Justice Department required Warner to release a few films each year under the First National name until 1938. For thirty years, certain Warner productions were identified (mainly for tax purposes) as 'A Warner Bros.–First National Picture.'
In the latter part of 1929, Jack Warner hired George Arliss to star in '' Disraeli'', which was a success. Arliss won an Academy Award for Best Actor
The Academy Award for Best Actor is an award presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS). It is given to an actor who has delivered an outstanding performance in a leading role in a film released that year. The ...
and went on to star in nine more movies for the studio. In 1930, Harry acquired more theaters in Atlantic City
Atlantic City, often known by its initials A.C., is a coastal resort city in Atlantic County, New Jersey, United States. The city is known for its casinos, boardwalk, and beaches. In 2020, the city had a population of 38,497.
, despite the beginning of the Great Depression. In July 1930, the studio's banker, Motley Flint, was murdered by a disgruntled investor in another company.
Harry acquired a string of music publishers (including M. Witmark & Sons, Remick Music Corp., and T.B. Harms, Inc.) to form Warner Bros. Music. In April 1930, Warner Bros. acquired Brunswick Records. Harry obtained radio companies, foreign sound patents and a lithograph
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German a ...
company. After establishing Warner Bros. Music, Harry appointed his son, Lewis, to manage the company.
By 1931, the studio began to feel the effects of the Great Depression, reportedly losing $8 million, and an additional $14 million the following year. In 1931, Warner Bros. Music head Lewis Warner died from an infected wisdom tooth
A third molar, commonly called wisdom tooth, is one of the three molars per quadrant of the human dentition. It is the most posterior of the three. The age at which wisdom teeth come through ( erupt) is variable, but this generally occurs betw ...
. Around that time, Zanuck hired screenwriter Wilson Mizner, who had little respect for authority and found it difficult to work with Jack, but became an asset. As time passed, Warner became more tolerant of Mizner and helped invest in Mizner's Brown Derby
Brown Derby was a chain of restaurants in Los Angeles, California. The first and best known was shaped like a derby hat, an iconic image that became synonymous with the Golden Age of Hollywood. It was opened by Wilson Mizner in 1926. The chain ...
restaurant. Mizner died of a heart attack on April 3, 1933.
By 1932, musicals were declining in popularity, and the studio was forced to cut musical numbers from many productions and advertise them as straight comedies. The public had begun to associate musicals with color, and thus studios began to abandon its use. Warner Bros. had a contract with Technicolor to produce two more pictures in that process. As a result, the first horror films in color were produced and released by the studio: '' Doctor X'' (1932) and '' Mystery of the Wax Museum'' (1933). In the latter part of 1931, Harry Warner rented the Teddington Studios
Teddington Studios was a large British television studio in Teddington, London Borough of Richmond upon Thames, providing studio facilities for programmes airing on the BBC, ITV, Channel 4, Channel 5, Sky1 and others. The complex also prov ...
in London, England. The studio focused on making " quota quickies" for the domestic British market and Irving Asher was appointed as the studio's head producer. In 1934, Harry officially purchased the Teddington Studios.
In February 1933, Warner Bros. produced '' 42nd Street'', a very successful musical under the direction of Lloyd Bacon. Warner assigned Bacon to "more expensive productions including ''Footlight Parade
''Footlight Parade'' is a 1933 American pre-Code musical film starring James Cagney, Joan Blondell, Ruby Keeler and Dick Powell and featuring Frank McHugh, Guy Kibbee, Hugh Herbert and Ruth Donnelly. The film was written by Manuel Seff and Jam ...
,'' '' Wonder Bar,'' ''Broadway Gondolier
''Broadway Gondolier '' (1935) is a musical film directed by Lloyd Bacon. The film was released by Warner Bros., and featured Dick Powell, Joan Blondell and Adolphe Menjou.
Plot
Richard "Dick" Purcell (Dick Powell), a taxi driver, aspires to ach ...
''" (which he also starred in), and ''Gold Diggers'' that saved the company from bankruptcy. In the wake of ''42nd Street''Dick Powell
Richard Ewing Powell (November 14, 1904 – January 2, 1963) was an American actor, musician, producer, director, and studio head. Though he came to stardom as a musical comedy performer, he showed versatility, and successfully transformed into ...
and were mostly directed by Busby Berkeley. In 1935, the revival was affected by Berkeley's arrest for killing three people while driving drunk. By the end of the year, people again tired of Warner Bros. musicals, and the studio — after the huge profits made by 1935 film '' Captain Blood'' — shifted its focus to Errol Flynn
Errol Leslie Thomson Flynn (20 June 1909 – 14 October 1959) was an Australian-American actor who achieved worldwide fame during the Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood. He was known for his romantic swashbuckler roles, freque ...
swashbucklers.
1930–1935: Pre-code realistic period
With the collapse of the market for musicals, Warner Bros., under Zanuck, turned to more socially realistic storylines. Because of its many films about gangsters, Warner Bros. soon became known as a "gangster studio". The studio's first gangster film, '' Little Caesar'', was a great box office success andEdward G. Robinson
Edward G. Robinson (born Emanuel Goldenberg; December 12, 1893January 26, 1973) was a Romanian-American actor of stage and screen, who was popular during the Hollywood's Golden Age. He appeared in 30 Broadway plays and more than 100 films duri ...
starred in many of the subsequent Warner gangster films. The studio's next effort, '' The Public Enemy'', made James Cagney
James Francis Cagney Jr. (; July 17, 1899March 30, 1986) was an American actor, dancer and film director. On stage and in film, Cagney was known for his consistently energetic performances, distinctive vocal style, and deadpan comic timing. He ...
arguably the studio's new top star, and Warner Bros. made more gangster films.
 Another gangster film the studio produced was the critically acclaimed '' I Am a Fugitive from a Chain Gang'', based on a true story and starring
Another gangster film the studio produced was the critically acclaimed '' I Am a Fugitive from a Chain Gang'', based on a true story and starring Paul Muni
Paul Muni (born Frederich Meshilem Meier Weisenfreund; September 22, 1895– August 25, 1967) was an American stage and film actor who grew up in Chicago. Muni was a five-time Academy Award nominee, with one win. He started his acting career in ...
, joining Cagney and Robinson as one of the studio's top gangster stars after appearing in the successful film, which convinced audiences to question the American legal system. By January 1933, the film's protagonist Robert Elliot Burns—still imprisoned in New Jersey—and other chain gang
A chain gang or road gang is a group of prisoners chained together to perform menial or physically challenging work as a form of punishment. Such punishment might include repairing buildings, building roads, or clearing land. The system was not ...
prisoners nationwide appealed and were released. In January 1933, Georgia chain gang warden J. Harold Hardy—who was also made into a character in the film—sued the studio for displaying "vicious, untrue and false attacks" against him in the film. After appearing in the Warner's film '' The Man Who Played God'', Bette Davis
Ruth Elizabeth "Bette" Davis (; April 5, 1908 – October 6, 1989) was an American actress with a career spanning more than 50 years and 100 acting credits. She was noted for playing unsympathetic, sardonic characters, and was famous for her p ...
became a top star.
In 1933, relief for the studio came after Franklin D. Roosevelt became president and began the New Deal
The New Deal was a series of programs, public work projects, financial reforms, and regulations enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the United States between 1933 and 1939. Major federal programs agencies included the Civilian Con ...
. This economic rebound allowed Warner Bros. to again become profitable. The same year, Zanuck quit. Harry Warner's relationship with Zanuck had become strained after Harry strongly opposed allowing Zanuck's film '' Baby Face'' to step outside Hays Code boundaries. The studio reduced his salary as a result of losses from the Great Depression, and Harry refused to restore it as the company recovered. ZanuckBehlmer (1985), p.12 established his own company. Harry thereafter raised salaries for studio employees.
In 1933, Warner was able to link up with newspaper tycoon William Randolph Hearst
William Randolph Hearst Sr. (; April 29, 1863 – August 14, 1951) was an American businessman, newspaper publisher, and politician known for developing the nation's largest newspaper chain and media company, Hearst Communications. His flamboya ...
's Cosmopolitan Films. Hearst had previously worked with MGM, but ended the association after a dispute with head producer Irving Thalberg over the treatment of Hearst's longstanding mistress, actress Marion Davies, who was struggling for box office success. Through his partnership with Hearst, Warner signed Davies to a studio contract. Hearst's company and Davies' films, however, did not increase the studio's profits.
In 1934, the studio lost over $2.5 million, of which $500,000 was the result of a 1934 fire at the Burbank studio, destroying 20 years' worth of early Vitagraph, Warner Bros. and First National films. The following year, Hearst's film adaption of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
's ''A Midsummer Night's Dream
''A Midsummer Night's Dream'' is a comedy written by William Shakespeare 1595 or 1596. The play is set in Athens, and consists of several subplots that revolve around the marriage of Theseus and Hippolyta. One subplot involves a conflict a ...
'' (1935) failed at the box office
A box office or ticket office is a place where tickets are sold to the public for admission to an event. Patrons may perform the transaction at a countertop, through a hole in a wall or window, or at a wicket. By extension, the term is fre ...
and the studio's net loss increased. During this time, Harry and six other movie studio figures were indicted for conspiracy to violate the Sherman Antitrust Act
The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 (, ) is a United States antitrust law which prescribes the rule of free competition among those engaged in commerce. It was passed by Congress and is named for Senator John Sherman, its principal author.
...
, through an attempt to gain a monopoly over St Louis movie theaters. In 1935, Harry was put on trial; after a mistrial, Harry sold the company's movie theaters and the case was never reopened. 1935 also saw the studio make a net profit of $674,158.00.
 By 1936, contracts of musical and silent stars were not renewed, instead being replaced by tough-talking, working-class types who better fit these pictures. As a result, Dorothy Mackaill,
By 1936, contracts of musical and silent stars were not renewed, instead being replaced by tough-talking, working-class types who better fit these pictures. As a result, Dorothy Mackaill, Dolores del Río
María de los Dolores Asúnsolo y López Negrete (3 August 1904 – 11 April 1983), known professionally as Dolores del Río (), was a Mexican actress. With a career spanning more than 50 years, she is regarded as the first major female Latin Am ...
, Bebe Daniels, Frank Fay, Winnie Lightner, Bernice Claire
Bernice Claire (born Bernice Jahnigen; January 27, 1906 – January 17, 2003)Alice White
Alice White (born Alva White; August 25, 1904Katz, Ephraim (1979). ''The Film Encyclopedia: The Most Comprehensive Encyclopedia of World Cinema in a Single Volume''. Perigee Books. , pg. 1228. – February 19, 1983) was an American film ac ...
, and Jack Mulhall that had characterized the urban, modern, and sophisticated attitude of the 1920s gave way to James Cagney
James Francis Cagney Jr. (; July 17, 1899March 30, 1986) was an American actor, dancer and film director. On stage and in film, Cagney was known for his consistently energetic performances, distinctive vocal style, and deadpan comic timing. He ...
, Joan Blondell, Edward G. Robinson
Edward G. Robinson (born Emanuel Goldenberg; December 12, 1893January 26, 1973) was a Romanian-American actor of stage and screen, who was popular during the Hollywood's Golden Age. He appeared in 30 Broadway plays and more than 100 films duri ...
, Warren William and Barbara Stanwyck
Barbara Stanwyck (; born Ruby Catherine Stevens; July 16, 1907 – January 20, 1990) was an American actress, model and dancer. A stage, film, and television star, during her 60-year professional career she was known for her strong, realistic sc ...
, who would be more acceptable to the common man. The studio was one of the most prolific producers of Pre-Code pictures and had a lot of trouble with the censors once they started clamping down on what they considered indecency (around 1934). As a result, Warner Bros. turned to historical pictures from around 1935 to avoid confrontations with the Breen office. In 1936, following the success of ''The Petrified Forest
''The Petrified Forest'' is a 1936 American film directed by Archie Mayo and based on Robert E. Sherwood's 1935 Broadway drama of the same name. The motion picture stars Leslie Howard, Bette Davis and Humphrey Bogart. The screenplay was writ ...
'', Jack signed Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey DeForest Bogart (; December 25, 1899 – January 14, 1957), nicknamed Bogie, was an American film and stage actor. His performances in Classical Hollywood cinema films made him an American cultural icon. In 1999, the American Film In ...
to a studio contract. Warner, however, did not think Bogart was star material, and cast Bogart in infrequent roles as a villain opposite either James Cagney or Edward Robinson over the next five years.
After Hal B. Wallis succeeded Zanuck in 1933, and the Hays Code began to be enforced in 1935, the studio was forced to abandon this realistic approach in order to produce more moralistic, idealized pictures. The studio's historical dramas, melodrama
A modern melodrama is a dramatic work in which the plot, typically sensationalized and for a strong emotional appeal, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue that is often bombastic or exce ...
s (or "women's pictures"), swashbucklers, and adaptations of best-sellers, with stars like Bette Davis
Ruth Elizabeth "Bette" Davis (; April 5, 1908 – October 6, 1989) was an American actress with a career spanning more than 50 years and 100 acting credits. She was noted for playing unsympathetic, sardonic characters, and was famous for her p ...
, Olivia de Havilland
Dame Olivia Mary de Havilland (; July 1, 1916July 26, 2020) was a British-American actress. The major works of her cinematic career spanned from 1935 to 1988. She appeared in 49 feature films and was one of the leading actresses of her time. ...
, Paul Muni
Paul Muni (born Frederich Meshilem Meier Weisenfreund; September 22, 1895– August 25, 1967) was an American stage and film actor who grew up in Chicago. Muni was a five-time Academy Award nominee, with one win. He started his acting career in ...
, and Errol Flynn
Errol Leslie Thomson Flynn (20 June 1909 – 14 October 1959) was an Australian-American actor who achieved worldwide fame during the Classical Hollywood cinema, Golden Age of Hollywood. He was known for his romantic swashbuckler roles, freque ...
, avoided the censors. In 1936, Bette Davis, by now arguably the studio's top star, was unhappy with her roles. She traveled to England and tried to break her contract. Davis lost the lawsuit and returned to America. Although many of the studio's employees had problems with Jack Warner, they considered Albert and Harry fair.
Code era
In the 1930s many actors and actresses who had characterized the realistic pre-Code era, but who were not suited to the new trend into moral and idealized pictures, disappeared. Warner Bros. remained a top studio inHollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywoo ...
, but this changed after 1935 as other studios, notably MGM, quickly overshadowed the prestige and glamor that previously characterized Warner Bros. However, in the late 1930s, Bette Davis became the studio's top draw and was even dubbed as "The Fifth Warner Brother."
 In 1935, Cagney sued Jack Warner for breach of contract. Cagney claimed Warner had forced him to star in more films than his contract required. Cagney eventually dropped his lawsuit after a cash settlement. Nevertheless, Cagney left the studio to establish an independent film company with his brother Bill. The Cagneys released their films though
In 1935, Cagney sued Jack Warner for breach of contract. Cagney claimed Warner had forced him to star in more films than his contract required. Cagney eventually dropped his lawsuit after a cash settlement. Nevertheless, Cagney left the studio to establish an independent film company with his brother Bill. The Cagneys released their films though Grand National Films
Grand National Films, Inc (or Grand National Pictures, Grand National Productions and Grand National Film Distributing Co.) was an American Poverty Row motion picture production-distribution company in operation from 1936 to 1939. The company ha ...
, however they were not able to get good financing and ran out of money after their third film. Cagney then agreed to return to Warner Bros., after Jack agreed to a contract guaranteeing Cagney would be treated to his own terms. After the success of ''Yankee Doodle Dandy
''Yankee Doodle Dandy'' is a 1942 American biographical musical film about George M. Cohan, known as "The Man Who Owned Broadway". It stars James Cagney, Joan Leslie, Walter Huston, and Richard Whorf, and features Irene Manning, George To ...
'' at the box office, Cagney again questioned if the studio would meet his salary demand and again quit to form his own film production and distribution company with Bill.
Another employee with whom Warner had troubles was studio producer Bryan Foy. In 1936, Wallis hired Foy as a producer for the studio's low budget B movies leading to his nickname "the keeper of the B's". Foy was able to garnish arguably more profits than any other B-film producer at the time. During Foy's time at the studio, however, Warner fired him seven different times.
During 1936, '' The Story of Louis Pasteur'' proved a box office success and star Paul Muni won the Oscar for Best Actor in March 1937. The studio's 1937 film ''The Life of Emile Zola
''The Life of Emile Zola'' is a 1937 American biographical film about the 19th-century French author Émile Zola starring Paul Muni and directed by William Dieterle. It premiered at the Los Angeles Carthay Circle Theatre to great critical and ...
'' gave the studio the first of its seven Best Picture Oscar
The Academy Award for Best Picture is one of the Academy Awards presented annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) since the awards debuted in 1929. This award goes to the producers of the film and is the only category ...
s.
In 1937, the studio hired Midwestern radio announcer Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, who would eventually become the President of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States of America. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal gove ...
. Although Reagan was initially a B-film actor, Warner Bros. was impressed by his performance in the final scene of '' Knute Rockne, All American'', and agreed to pair him with Flynn in ''Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, ...
'' (1940). Reagan then returned to B-films. After his performance in the studio's 1942 '' Kings Row'', Warner decided to make Reagan a top star and signed him to a new contract, tripling his salary.
In 1936, Harry's daughter Doris read a copy of Margaret Mitchell's '' Gone with the Wind'' and was interested in making a film adaptation. Doris offered Mitchell $50,000 for screen rights. Jack vetoed the deal, realizing it would be an expensive production.
Major Paramount star George Raft
George Raft (born George Ranft; September 26, 1901 – November 24, 1980) was an American film actor and dancer identified with portrayals of gangsters in crime melodramas of the 1930s and 1940s. A stylish leading man in dozens of movies, Raft is ...
also eventually proved to be a problem for Jack. Warner had signed him in 1939, finally bringing the third top 1930s gangster actor into the Warners fold, knowing that he could carry any gangster picture when either Robinson or Cagney were on suspension. Raft had difficulty working with Bogart and refused to co-star with him. Eventually, Warner agreed to release Raft from his contract in 1943. After Raft had turned the role down, the studio gave Bogart the role of "Mad Dog" Roy Earle in the 1941 film '' High Sierra'', which helped establish him as a top star. Following ''High Sierra'' and after Raft had once again turned the part down, Bogart was given the leading role in John Huston
John Marcellus Huston ( ; August 5, 1906 – August 28, 1987) was an American film director, screenwriter, actor and visual artist. He wrote the screenplays for most of the 37 feature films he directed, many of which are today considered ...
's successful 1941 remake of the studio's 1931 pre-Code film, '' The Maltese Falcon'', based upon the Dashiell Hammett
Samuel Dashiell Hammett (; May 27, 1894 – January 10, 1961) was an American writer of hard-boiled detective novels and short stories. He was also a screenwriter and political activist. Among the enduring characters he created are Sam Spade ('' ...
novel.
Warner's cartoons
Warner'scartoon
A cartoon is a type of visual art that is typically drawn, frequently animated, in an unrealistic or semi-realistic style. The specific meaning has evolved over time, but the modern usage usually refers to either: an image or series of imag ...
unit had its roots in the independent Harman and Ising studio. From 1930 to 1933, Disney
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October ...
alumni Hugh Harman and Rudolf Ising produced musical cartoons for Leon Schlesinger
Leon Schlesinger (May 20, 1884 – December 25, 1949) was an American film producer who founded Leon Schlesinger Productions, which later became the Warner Bros. Cartoons studio, during the Golden Age of American animation. He was a distant rel ...
, who sold them to Warner. Harman and Ising introduced their character Bosko
Bosko is an animated cartoon character created by animators Hugh Harman and Rudolf Ising. Bosko was the first recurring character in Leon Schlesinger's cartoon series and was the star of 39 ''Looney Tunes'' shorts released by Warner Bros. He ...
in the first ''Looney Tunes
''Looney Tunes'' is an American animated comedy short film series produced by Warner Bros. starting from 1930 to 1969, concurrently with its partner series '' Merrie Melodies'', during the golden age of American animation. ...
'' cartoon, '' Sinkin' in the Bathtub'', and created a sister series, ''Merrie Melodies
''Merrie Melodies'' is an American animated series of comedy short films produced by Warner Bros. starting in 1931, during the golden age of American animation, and ending in 1969. Then some new cartoons were produced from the late 1970s to the ...
'', in 1931.
Harman and Ising broke away from Schlesinger in 1933 due to a contractual dispute, taking Bosko with them to MGM. As a result, Schlesinger started his own studio, Leon Schlesinger Productions, which continued with ''Merrie Melodies'' while starting production on ''Looney Tunes'' starring Buddy, a Bosko clone. By the end of World War II, a new Schlesinger production team, including directors Friz Freleng
Isadore "Friz" Freleng (August 21, 1905May 26, 1995), credited as I. Freleng early in his career, was an American animator, cartoonist, director, producer, and composer known for his work at Warner Bros. Cartoons on the ''Looney Tunes'' and ...
(started in 1934), Tex Avery
Frederick Bean "Tex" Avery (February 26, 1908 – August 26, 1980) was an American animator, cartoonist, director, and voice actor. He was known for directing and producing animated cartoons during the golden age of American animation. His mo ...
(started in 1935), Frank Tashlin
Frank Tashlin (born Francis Fredrick von Taschlein, February 19, 1913 – May 5, 1972), also known as Tish Tash and Frank Tash, was an American animator, cartoonist, children's writer, illustrator, screenwriter, and film director. He was best k ...
(started in 1936), Bob Clampett
Robert Emerson Clampett Sr. (May 8, 1913 – May 2, 1984) was an American animator, director, producer and puppeteer. He was best known for his work on the '' Looney Tunes'' animated series from Warner Bros. as well as the television shows '' ...
(started in 1937), Chuck Jones
Charles Martin Jones (September 21, 1912 – February 22, 2002) was an American animator, director, and painter, best known for his work with Warner Bros. Cartoons on the '' Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of shorts. He wrote, pro ...
(started in 1938), and Robert McKimson
Robert Porter McKimson Sr. (October 13, 1910 – September 29, 1977) was an American animator and illustrator, best known for his work on the ''Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of cartoons from Warner Bros. Cartoons and later DeP ...
(started in 1946), was formed. Schlesinger's staff developed a fast-paced, irreverent style that made their cartoons globally popular.
In 1935, Avery directed Porky Pig
Porky Pig is an animated character in the Warner Bros. ''Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of cartoons. He was the first character created by the studio to draw audiences based on his star power, and the animators created many criti ...
cartoons that established the character as the studio's first animated star.Barrier, Michael (1999). pp.329–333 In addition to Porky, Daffy Duck (who debuted in 1937's ''Porky's Duck Hunt
''Porky's Duck Hunt'' is a 1937 Warner Bros. ''Looney Tunes'' cartoon directed by Tex Avery. The cartoon was released on April 17, 1937, and stars Porky Pig and Daffy Duck, the latter making what is considered his first official appearance.
Plot ...
''), Elmer Fudd
Elmer J.'' Hare Brush'' (1956) Fudd is an animated cartoon character in the Warner Bros. ''Looney Tunes''/'' Merrie Melodies'' series and the archenemy of Bugs Bunny. He has one of the more disputed origins in the Warner Bros. cartoon panthe ...
(''Elmer's Candid Camera
''Elmer's Candid Camera'' is a 1940 Warner Bros. ''Merrie Melodies'' cartoon short directed by Chuck Jones. The short was released on March 2, 1940, and features Elmer Fudd and an early Bugs Bunny prototype.
This is the first appearance of a re ...
'', 1940), Bugs Bunny
Bugs Bunny is an animated cartoon character created in the late 1930s by Leon Schlesinger Productions (later Warner Bros. Cartoons) and voiced originally by Mel Blanc. Bugs is best known for his starring roles in the ''Looney Tunes'' and ''Merr ...
('' A Wild Hare'', 1940), and Tweety (''A Tale of Two Kitties
''A Tale of Two Kitties'' is a 1942 Warner Bros. ''Merrie Melodies'' cartoon directed by Bob Clampett, written by Warren Foster, and features music by Carl W. Stalling. The short was released on November 21, 1942, and features the debut of T ...
'', 1942) would achieve star power. By 1942, the Schlesinger studio had surpassed Walt Disney Studios as the most successful producer of animated shorts.
Warner Bros. bought Schlesinger's cartoon unit in 1944 and renamed it Warner Bros. Cartoons
Warner Bros. Cartoons, Inc. was an American animation studio, serving as the in-house animation division of Warner Bros. during the Golden Age of American animation. One of the most successful animation studios in American media history, it was ...
. However, senior management treated the unit with indifference, beginning with the installation as senior producer of Edward Selzer
Edward Selzer (January 12, 1893 – February 22, 1970) was an American film producer and publicist who served as head of Warner Bros. Cartoons from 1944 to 1958. He served in the US Navy and fought as a Golden Gloves boxer. He won a boxing exhibi ...
, whom the creative staff considered an interfering incompetent. Jack Warner had little regard for the company's short film product and reputedly was so ignorant about the animation division of the studio that he was mistakenly convinced that the unit produced cartoons of Mickey Mouse, the flagship character of Walt Disney Productions
The Walt Disney Company, commonly known as Disney (), is an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate headquartered at the Walt Disney Studios complex in Burbank, California. Disney was originally founded on October 1 ...
. He sold off the unit's pre-August 1948 library for $3,000 each, which proved a shortsighted transaction in light of its eventual value.
Warner Bros. Cartoons continued, with intermittent interruptions, until 1969 when it was dissolved as the parent company ceased film shorts entirely. Characters such as Bugs Bunny, Daffy Duck, Tweety, Sylvester
Sylvester or Silvester is a name derived from the Latin adjective ''silvestris'' meaning "wooded" or "wild", which derives from the noun ''silva'' meaning "woodland". Classical Latin spells this with ''i''. In Classical Latin, ''y'' represented ...
, and Porky Pig
Porky Pig is an animated character in the Warner Bros. ''Looney Tunes'' and '' Merrie Melodies'' series of cartoons. He was the first character created by the studio to draw audiences based on his star power, and the animators created many criti ...
became central to the company's image in subsequent decades. Bugs in particular remains a mascot to Warner Bros., its various divisions, and Six Flags (which Time Warner
Warner Media, LLC ( traded as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City, United States.
It was originally established in 1972 by ...
once owned). The success of the compilation film ''The Bugs Bunny/Road Runner Movie
''The Bugs Bunny/Road Runner Movie'' is a 1979 American animated comedy package film directed by Chuck Jones, consisting of a compilation of classic '' Looney Tunes/ Merrie Melodies'' shorts and newly animated bridging sequences hosted by Bugs ...
'' in 1979, featuring the archived film of these characters, prompted Warner Bros. to organize Warner Bros. Animation as a new production division to restart production of original material.
World War II
According to Warner's autobiography, prior to US entry inWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, Philip Kauffman, Warner Bros. German sales head, was murdered by the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
in Berlin in 1936. Harry produced the successful anti-German film ''The Life of Emile Zola
''The Life of Emile Zola'' is a 1937 American biographical film about the 19th-century French author Émile Zola starring Paul Muni and directed by William Dieterle. It premiered at the Los Angeles Carthay Circle Theatre to great critical and ...
'' (1937). After that, Harry supervised the production of more anti-German films, including '' Confessions of a Nazi Spy'' (1939), ''The Sea Hawk
''The Sea Hawk'' is a 1915 novel by Rafael Sabatini. The story is set over the years 1588–1593 and concerns a retired Cornish seafaring gentleman, Sir Oliver Tressilian, who is villainously betrayed by a jealous half-brother. After being ...
'' (1940), which made King Philip II an equivalent of Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
, ''Sergeant York
Alvin Cullum York (December 13, 1887 – September 2, 1964), also known as Sergeant York, was one of the most decorated United States Army soldiers of World War I. He received the Medal of Honor for leading an attack on a German machi ...
'', and ''You're In The Army Now'' (1941). Harry then decided to focus on producing war films. Warners' cut its film production in half during the war, eliminating its B Pictures unit in 1941. Bryan Foy joined Twentieth Century Fox.
 During the war era, the studio made ''
During the war era, the studio made ''Casablanca
Casablanca, also known in Arabic as Dar al-Bayda ( ar, الدَّار الْبَيْضَاء, al-Dār al-Bayḍāʾ, ; ber, ⴹⴹⴰⵕⵍⴱⵉⴹⴰ, ḍḍaṛlbiḍa, : "White House") is the largest city in Morocco and the country's econom ...
'', '' Now, Voyager'', ''Yankee Doodle Dandy
''Yankee Doodle Dandy'' is a 1942 American biographical musical film about George M. Cohan, known as "The Man Who Owned Broadway". It stars James Cagney, Joan Leslie, Walter Huston, and Richard Whorf, and features Irene Manning, George To ...
'' (all 1942), '' This Is the Army'', and '' Mission to Moscow'' (both 1943); the last of these films became controversial a few years afterwards. At the premieres of ''Yankee Doodle Dandy'' (in Los Angeles, New York, and London), audiences purchased $15.6 million in war bonds for the governments of England and the United States. By the middle of 1943, however, audiences had tired of war films, but Warner continued to produce them, losing money. In honor of the studio's contributions to the cause, the Navy named a Liberty ship after the brothers' father, Benjamin Warner. Harry christened the ship. By the time the war ended, $20 million in war bonds were purchased through the studio, the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
collected 5,200 pints of blood plasma
Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the int ...
from studio employees and 763 of the studio's employees served in the armed forces, including Harry Warner's son-in-law Milton Sperling and Jack's son Jack Warner Jr. Following a dispute over ownership of ''Casablanca''Olivia de Havilland
Dame Olivia Mary de Havilland (; July 1, 1916July 26, 2020) was a British-American actress. The major works of her cinematic career spanned from 1935 to 1988. She appeared in 49 feature films and was one of the leading actresses of her time. ...
(whom Warner frequently loaned to other studios) sued Warner for breach of contract. De Havilland had refused to portray famed abolitionist Elizabeth Blackwell in an upcoming film for Columbia Pictures. Warner responded by sending 150 telegrams to different film production companies, warning them not to hire her for any role. Afterwards, de Havilland discovered employment contracts in California could only last seven years; de Havilland had been under contract with the studio since 1935. The court ruled in de Havilland's favor and she left the studio in favor of RKO Radio Pictures, and, eventually, Paramount. Through de Havilland's victory, many of the studio's longtime actors were now freed from their contracts, and Harry decided to terminate the studio's suspension policy.
The same year, Jack signed newly released MGM actress Joan Crawford
Joan Crawford (born Lucille Fay LeSueur; March 23, ncertain year from 1904 to 1908was an American actress. She started her career as a dancer in traveling theatrical companies before debuting on Broadway. Crawford was signed to a motion pict ...
, a former top star who found her career fading. Crawford's first role with the studio was 1944's '' Hollywood Canteen''. Her first starring role at the studio, in the title role as '' Mildred Pierce'' (1945), revived her career and earned her an Oscar for Best Actress.
After World War II: changing hands
In the post-war years, Warner Bros. prospered greatly and continued to create new stars, includingLauren Bacall
Lauren Bacall (; born Betty Joan Perske; September 16, 1924 – August 12, 2014) was an American actress. She was named the 20th-greatest female star of classic Hollywood cinema by the American Film Institute and received an Academy Honorary ...
and Doris Day
Doris Day (born Doris Mary Kappelhoff; April 3, 1922 – May 13, 2019) was an American actress, singer, and activist. She began her career as a big band singer in 1939, achieving commercial success in 1945 with two No. 1 recordings, " Sent ...
. By 1946, company payroll reached $600,000 a week and net profit topped $19.4 million.
Jack Warner continued to refuse to meet Screen Actors Guild
The Screen Actors Guild (SAG) was an American labor union which represented over 100,000 film and television principal and background performers worldwide. On March 30, 2012, the union leadership announced that the SAG membership voted to me ...
salary demands. In September 1946, employees engaged in a month-long strike. In retaliation, Warner—during his 1947 testimony before Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
about ''Mission to Moscow''—accused multiple employees of ties to Communists. By the end of 1947, the studio reached a record net profit of $22 million.
Warner acquired Pathé News from RKO in 1947. On January 5, 1948, Warner offered the first color newsreel, covering the Tournament of Roses Parade and the Rose Bowl Game
The Rose Bowl Game is an annual American college football bowl game, usually played on January 1 (New Year's Day) at the Rose Bowl in Pasadena, California. When New Year's Day falls on a Sunday, the game is played on Monday, January 2. The Ro ...
. In 1948, Bette Davis, still their top actress and now hostile to Jack, was a big problem for Harry after she and others left the studio after completing the film ''Beyond the Forest
''Beyond the Forest'' is a 1949 American film noir directed by King Vidor, and featuring Bette Davis, Joseph Cotten, David Brian, and Ruth Roman. The screenplay is written by Lenore Coffee based on a novel by Stuart Engstrand.
The film marks Dav ...
''.
Warner was a party to the '' United States v. Paramount Pictures, Inc.'' antitrust case of the 1940s. This action, brought by the Justice Department and the Federal Trade Commission
The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is an independent agency of the United States government whose principal mission is the enforcement of civil (non-criminal) antitrust law and the promotion of consumer protection. The FTC shares jurisdiction o ...
, claimed the five integrated studio-theater chain combinations restrained competition. The Supreme Court
A supreme court is the highest court within the hierarchy of courts in most legal jurisdictions. Other descriptions for such courts include court of last resort, apex court, and high (or final) court of appeal. Broadly speaking, the decisions of ...
heard the case in 1948, and ruled for the government. As a result, Warner and four other major studios were forced to separate production from the exhibition. In 1949, the studio's net profit was only $10 million.
Warner Bros. had two semi-independent production companies that released films through the studio. One of these was Sperling's United States Pictures
United States Pictures (also known as United States Productions) was the name of the motion picture production company belonging to Milton Sperling who was Harry Warner's (of the Warner Bros. studio) son-in-law.
Sperling was a highly experience ...
.
 In the early 1950s, the threat of television emerged. In 1953, Jack decided to copy
In the early 1950s, the threat of television emerged. In 1953, Jack decided to copy United Artists
United Artists Corporation (UA), currently doing business as United Artists Digital Studios, is an American digital production company. Founded in 1919 by D. W. Griffith, Charlie Chaplin, Mary Pickford, and Douglas Fairbanks, the stu ...
successful 3D film ''Bwana Devil
''Bwana Devil'' is a 1952 American adventure B movie written, directed, and produced by Arch Oboler, and starring Robert Stack, Barbara Britton, and Nigel Bruce. ''Bwana Devil'' is based on the true story of the Tsavo maneaters and filmed with ...
'', releasing his own 3D films beginning with '' House of Wax''. However, 3D films soon lost their appeal among moviegoers.
3D almost caused the demise of the Warner Bros. cartoon studio. Having completed a 3D Bugs Bunny cartoon, ''Lumber Jack-Rabbit
''Lumber Jack-Rabbit'' is a 1953 3-D Warner Bros. ''Looney Tunes'' cartoon short directed by Chuck Jones and written by Michael Maltese The cartoon was released on September 25, 1953, and stars Bugs Bunny.
It was notable as the first Warner Bros. ...
'', Jack Warner ordered the animation unit to be closed, erroneously believing that all cartoons hence would be produced in the 3D process. Several months later, Warner relented and reopened the cartoon studio. Warner Bros. had enough of a backlog of cartoons and a healthy reissue program so that there was no noticeable interruption in the release schedule.
In 1952, Warner Bros. made their first film (''Carson City
Carson City is an independent city and the capital of the U.S. state of Nevada. As of the 2020 census, the population was 58,639, making it the sixth largest city in Nevada. The majority of the city's population lives in Eagle Valley, on th ...
'') in "Warnercolor", the studio's name for Eastmancolor.
After the downfall of 3D films, Harry Warner decided to use CinemaScope
CinemaScope is an anamorphic lens series used, from 1953 to 1967, and less often later, for shooting widescreen films that, crucially, could be screened in theatres using existing equipment, albeit with a lens adapter. Its creation in 1953 by ...
in future Warner Bros. films. One of the studio's first CinemaScope films, '' The High and the Mighty'' (owned by John Wayne
Marion Robert Morrison (May 26, 1907 – June 11, 1979), known professionally as John Wayne and nicknamed The Duke or Duke Wayne, was an American actor who became a popular icon through his starring roles in films made during Hollywood's Go ...
's company, Batjac Productions
Batjac Productions is an independent film production company co-founded by John Wayne in 1952 as a vehicle for Wayne to both produce and star in movies. The first Batjac production was '' Big Jim McLain'' released by Warner Bros. in 1952, and its ...
), enabled the studio to show a profit.
Early in 1953, Warner's theater holdings were spun off as Stanley Warner Theaters; Stanley Warner's non-theater holdings were sold to Simon Fabian Enterprises, and its theaters merged with RKO Theatres to become RKO-Stanley Warner Theatres.
By 1956, the studio was losing money, declining from 1953's net profit of $2.9 million and the next two years of between $2 and $4 million. On February 13, 1956, Jack Warner sold the rights to all of the studio's pre-1950 films to Associated Artists Productions
Associated Artists Productions, Inc. (a.a.p.) later known as United Artists Associated was an American distributor of theatrical feature films and subjects for television. Associated Artists Productions was the copyright owner of the ''Popey ...
(which merged with United Artists Television in 1958, and was subsequently acquired by Turner Broadcasting System
Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. (alternatively known as Turner Entertainment Networks from 2019 until 2022) was an American television and media conglomerate. Founded by Ted Turner and based in Atlanta, Georgia, it merged with Time Warner (lat ...
in early 1986 as part of a failed takeover of MGM/UA by Ted Turner
Robert Edward "Ted" Turner III (born November 19, 1938) is an American entrepreneur, television producer, media proprietor, and philanthropist. He founded the Cable News Network (CNN), the first 24-hour cable news channel. In addition, he ...
).WB retained a pair of features from 1949 that they merely distributed, and all short subjects released on or after September 1, 1948; in addition to all cartoons released in August 1948
In May 1956, the brothers announced they were putting Warner Bros. on the market. Jack secretly organized a syndicate—headed by Boston banker Serge Semenenko– to purchase 90% of the stock. After the three brothers sold, Jack—through his under-the-table deal—joined Semenenko's syndicate and bought back all his stock. Shortly after the deal was completed in July, Jack—now the company's largest stockholder—appointed himself its new president. Shortly after the deal closed, Jack announced the company and its subsidiaries would be "directed more vigorously to the acquisition of the most important story properties, talents, and to the production of the finest motion pictures possible."
Warner Bros. Television and Warner Bros. Records
By 1949, with the success of television threatening the film industry more and more, Harry Warner decided to emphasize television production. However, theFederal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) is an independent agency of the United States federal government that regulates communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable across the United States. The FCC maintains jurisdicti ...
(FCC) would not permit it. After an unsuccessful attempt to convince other movie studio bosses to switch, Harry abandoned his television efforts.
Jack had problems with Milton Berle's unsuccessful film '' Always Leave Them Laughing'' during the peak of Berle's television popularity. Warner felt that Berle was not strong enough to carry a film and that people would not pay to see the man they could see on television for free. However, Jack was pressured into using Berle, who replaced Danny Kaye
Danny Kaye (born David Daniel Kaminsky; yi, דוד־דניאל קאַמינסקי; January 18, 1911 – March 3, 1987) was an American actor, comedian, singer and dancer. His performances featured physical comedy, idiosyncratic pantomimes, and ...
. Berle's outrageous behavior on the set and the film's massive failure led to Jack banning television sets from film sets.
William T. Orr
William T. Orr (born William Ferdinand Quinn Jr.; September 27, 1917December 25, 2002) was an American actor and television producer associated with various Western and detective programs of the 1950s-1970s. In most of his Warner Bros. series, ...
, Jack Warner's son-in-law. Warner Bros. Television provided ABC with a weekly show, ''Warner Bros. Presents
''Warner Bros. Presents'' is the umbrella title for three series that were telecast as part of the 1955-56 season on ABC: ''Cheyenne'', a new Western series that originated on ''Presents'', and two based on classic Warner Bros motion picture prop ...
.'' The show featured rotating shows based on three film successes, '' Kings Row'', ''Casablanca
Casablanca, also known in Arabic as Dar al-Bayda ( ar, الدَّار الْبَيْضَاء, al-Dār al-Bayḍāʾ, ; ber, ⴹⴹⴰⵕⵍⴱⵉⴹⴰ, ḍḍaṛlbiḍa, : "White House") is the largest city in Morocco and the country's econom ...
'' and ''Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
'', followed by a promotion for a new film. It was not a success. The studio's next effort was to make a weekly series out of ''Cheyenne''. ''Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enr ...
'' was television's first hour-long Western. Two episodes were placed together for feature film release outside the United States. In the tradition of its B movies, the studio followed up with a series of rapidly produced popular Westerns, such as writer/producer Roy Huggins' critically lauded ''Maverick
Maverick, Maveric or Maverik may refer to:
History
* Maverick (animal), an unbranded range animal, derived from U.S. cattleman Samuel Maverick
Aviation
* AEA Maverick, an Australian single-seat sportsplane design
* General Aviation Design Bure ...
'' as well as '' Sugarfoot'', '' Bronco'', '' Lawman'', '' The Alaskans'' and '' Colt .45''. The success of these series helped to make up for losses in the film business. As a result, Jack Warner decided to emphasize television production. Warners produced a series of popular private detective shows beginning with '' 77 Sunset Strip'' (1958–1964) followed by ''Hawaiian Eye
''Hawaiian Eye'' is an American detective television series that ran from October 1959 to April 1963 on the ABC television network.
Premise
Private investigator Tracy Steele ( Anthony Eisley) and his half-Hawaiian partner, Tom Lopaka ( Robert ...
'' (1959–1963), ''Bourbon Street Beat
''Bourbon Street Beat'' is a private detective television series that aired on the ABC network from October 5, 1959, to July 4, 1960, starring Richard Long as Rex Randolph and Andrew Duggan as Cal Calhoun, with Arlene Howell as detective agen ...
'' (1960) and '' Surfside 6'' (1960–1962).
Within a few years, the studio provoked hostility among its TV stars such as Clint Walker and James Garner, who sued over a contract dispute and won. Edd Byrnes was not so lucky and bought himself out of his contract. Jack was angered by their perceived ingratitude. Television actors evidently showed more independence than film actors, deepening his contempt for the new medium. Many of Warner's television stars appeared in the casts of Warner's cinema releases. In 1963, a court decision forced Warner Bros. to end contracts with their television stars and to cease engaging them for specific series or film roles. That year, Jack Webb
John Randolph Webb (April 2, 1920 – December 23, 1982) was an American actor, television producer, director, and screenwriter, who is most famous for his role as Sgt. Joe Friday in the ''Dragnet'' franchise, which he created. He was a ...
, best known for originating the role of Sgt. Joe Friday in the ''Dragnet'' franchise, became the head of the studio's TV division.
Carl Stalling
Carl William Stalling (November 10, 1891 – November 29, 1972) was an American composer, voice actor and arranger for music in animated films. He is most closely associated with the ''Looney Tunes'' and ''Merrie Melodies'' shorts produced by War ...
) and television shows (arranged by Max Steiner). In 2004, Time Warner sold the Warner Music Group
Warner Music Group Corp. ( d.b.a. Warner Music Group, commonly abbreviated as WMG) is an American multinational entertainment and record label conglomerate headquartered in New York City. It is one of the " big three" recording companies and th ...
, along with Warner Bros. Records, to a private equity group led by Edgar Bronfman Jr. In 2019, the since-separated Warner Bros. record division was rechristened Warner Records, as WMG held a short-term license to use the Warner Bros. name and trademarks; as such, the label currently reissues the pre-2019 Warner Bros. back catalog.
In 1963, Warner agreed to a "rescue takeover" of Frank Sinatra
Francis Albert Sinatra (; December 12, 1915 – May 14, 1998) was an American singer and actor. Nicknamed the " Chairman of the Board" and later called "Ol' Blue Eyes", Sinatra was one of the most popular entertainers of the 1940s, 1950s, and ...
's Reprise Records
Reprise Records is an American record label founded in 1960 by Frank Sinatra. It is owned by Warner Music Group, and operates through Warner Records, one of its flagship labels.
Artists currently signed to Reprise Records include Enya, Michael ...
. The deal gave Sinatra US$1.5 million and part ownership of Warner Bros. Records, making Reprise a sub-label. Most significantly the deal brought Reprise manager Morris "Mo" Ostin into the company. In 1964, upon seeing the profits record companies made from Warner film music, Warner decided to claim ownership of the studio's film soundtracks. In its first eighteen months, Warner Bros. Records lost around $2 million.
New owners
Warner Bros. rebounded in the late 1950s, specializing in adaptations of popular plays like '' The Bad Seed'' (1956), '' No Time for Sergeants'' (1958), and '' Gypsy'' (1962). While he slowly recovered from a car crash that occurred while vacationing in France in 1958, Jack returned to the studio and made sure his name was featured in studio press releases. From 1961 to 1963, the studio's annual net profit was a little over $7 million. Warner paid an unprecedented $5.5 million for the film rights to the Broadway musical '' My Fair Lady'' in February 1962. The previous owner, CBS director William S. Paley, set terms including half the distributor's gross profits "plus ownership of the negative at the end of the contract." In 1963, the studio's net profit dropped to $3.7 million. By the mid-1960s, motion picture production was in decline, as the industry was in the midst of a painful transition from the Golden Age of Hollywood to the era now known as New Hollywood. Few studio films were made in favor of co-productions (for which Warner provided facilities, money and distribution), and pickups of independent pictures. With the success of the studio's 1964 film of Broadway play '' My Fair Lady'', as well as its soundtrack, Warner Bros. Records became a profitable subsidiary. The 1966 film '' Who's Afraid Of Virginia Woolf?'' was a huge success.Camelot
Camelot is a castle and court associated with the legendary King Arthur. Absent in the early Arthurian material, Camelot first appeared in 12th-century French romances and, since the Lancelot-Grail cycle, eventually came to be described as th ...
'' failed at the box office and Warner gave up his position to his longtime publicity director, Ben Kalmenson; Warner remained on board as an independent producer and vice-president. With the 1967 success of ''Bonnie and Clyde
Bonnie Elizabeth Parker (October 1, 1910May 23, 1934) and Clyde Chestnut (Champion) Barrow (March 24, 1909May 23, 1934) were an American criminal couple who traveled the Central United States with their gang during the Great Depression. The c ...
'', Warner Bros. was again profitable.
Two years later the Hymans were tired and fed-up with Jack Warner and his actions. They accepted a cash-and-stock offer from Kinney National Company for more than $64 million. In 1967, Kinney had previously acquired DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. ( doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery.
DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with the ...
(then officially known as National Periodical Publications), as well as a Hollywood talent agency, Ashley-Famous
Ashley-Famous was a talent agency started in 1955 by talent agent Ted Ashley. The agency had a successful 16-year run under that name and owner; it was responsible for many hit television shows and had several famous clients. It changed ownership a ...
, whose founder Ted Ashley led Kinney head Steve Ross to purchase Warner Bros. Ashley-Famous was soon spun off due to antitrust laws prohibiting the simultaneous ownership of a film studio and a talent agency. Ashley became the studio head and changed the name to Warner Bros. Inc. once again. Jack Warner was outraged by the Hymans' sale, and decided to move into independent production (most successfully with '' 1776'' at Columbia). He retired in 1973 and died from serious health complications of heart inflammation in September 1978.
Paul Newman
Paul Leonard Newman (January 26, 1925 – September 26, 2008) was an American actor, film director, race car driver, philanthropist, and entrepreneur. He was the recipient of numerous awards, including an Academy Award, a BAFTA Award, three ...
, Robert Redford
Charles Robert Redford Jr. (born August 18, 1936) is an American actor and filmmaker. He is the recipient of various accolades, including an Academy Award from four nominations, a British Academy Film Award, two Golden Globe Awards, the Cec ...
, Barbra Streisand
Barbara Joan "Barbra" Streisand (; born April 24, 1942) is an American singer, actress and director. With a career spanning over six decades, she has achieved success in multiple fields of entertainment, and is among the few performers awar ...
, and Clint Eastwood
Clinton Eastwood Jr. (born May 31, 1930) is an American actor and film director. After achieving success in the Western TV series '' Rawhide'', he rose to international fame with his role as the " Man with No Name" in Sergio Leone's "'' Do ...
, carrying the studio successfully through the 1970s and 1980s. Its hits in the early 1970s included those starring the aforementioned actors, along with comedian Mel Brooks
Mel Brooks (born Melvin James Kaminsky; June 28, 1926) is an American actor, comedian and filmmaker. With a career spanning over seven decades, he is known as a writer and director of a variety of successful broad farces and parodies. He began ...
' ''Blazing Saddles
''Blazing Saddles'' is a 1974 American satirical western black comedy film directed by Mel Brooks, who also wrote the screenplay with Andrew Bergman, Richard Pryor, Norman Steinberg, and Alan Uger. The film stars Cleavon Little and Gene Wilde ...
'', Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick (; July 26, 1928 – March 7, 1999) was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and photographer. Widely considered one of the greatest filmmakers of all time, his films, almost all of which are adaptations of nove ...
's ''A Clockwork Orange
''A Clockwork Orange'' may refer to:
* ''A Clockwork Orange'' (novel), a 1962 novel by Anthony Burgess
** ''A Clockwork Orange'' (film), a 1971 film directed by Stanley Kubrick based on the novel
*** ''A Clockwork Orange'' (soundtrack), the film ...
'', ''The Exorcist
''The Exorcist'' is a 1973 American supernatural horror film directed by William Friedkin and written for the screen by William Peter Blatty, based on his 1971 The Exorcist (novel), novel of the same name. It stars Ellen Burstyn, Max von Sydow, ...
'', John Boorman
Sir John Boorman (; born 18 January 1933) is a British film director, best known for feature films such as '' Point Blank'' (1967), ''Hell in the Pacific'' (1968), ''Deliverance'' (1972), '' Zardoz'' (1974), '' Exorcist II: The Heretic'' (1977 ...
's ''Deliverance
''Deliverance'' is a 1972 American survival thriller film produced and directed by John Boorman, and starring Jon Voight, Burt Reynolds, Ned Beatty, and Ronny Cox, with the latter two making their feature film debuts. The screenplay was adapt ...
'', and the Martin Scorsese
Martin Charles Scorsese ( , ; born November 17, 1942) is an American film director, producer, screenwriter and actor. Scorsese emerged as one of the major figures of the New Hollywood era. He is the recipient of many major accolades, incl ...
productions '' Mean Streets'' and ''Alice Doesn't Live Here Anymore
''Alice Doesn't Live Here Anymore'' is a 1974 American comedy drama film directed by Martin Scorsese and written by Robert Getchell. It stars Ellen Burstyn as a widow who travels with her preteen son across the Southwestern United States i ...
''. Warner Bros. also made major profits on films and television shows built around the characters of Superman
Superman is a superhero who appears in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by writer Jerry Siegel and artist Joe Shuster, and debuted in the comic book '' Action Comics'' #1 ( cover-dated June 1938 and pu ...
, Batman
Batman is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by DC Comics. The character was created by artist Bob Kane and writer Bill Finger, and debuted in the 27th issue of the comic book ''Detective Comics'' on March 30, 1939. I ...
and Wonder Woman
Wonder Woman is a superhero created by the American psychologist and writer William Moulton Marston (pen name: Charles Moulton), and artist Harry G. Peter. Marston's wife, Elizabeth, and their life partner, Olive Byrne, are credited as bein ...
owned by Warner Bros. subsidiary DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. ( doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery.
DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with the ...
. The 1970s also saw Warner Bros. Records become one of the major record labels worldwide, and that company gained sister labels in Elektra Records
Elektra Records (or Elektra Entertainment) is an American record label owned by Warner Music Group, founded in 1950 by Jac Holzman and Paul Rickolt. It played an important role in the development of contemporary folk and rock music between the ...
and Atlantic Records
Atlantic Recording Corporation (simply known as Atlantic Records) is an American record label founded in October 1947 by Ahmet Ertegun and Herb Abramson. Over its first 20 years of operation, Atlantic earned a reputation as one of the most im ...
. In 1971, Filmation
Filmation Associates was an American production company that produced animation and live-action programming for television from 1963 until 1989. Located in Reseda, California, the animation studio was founded in 1962. Filmation's founders and ...
and Warner Bros. entered into an agreement to produce and distribute cartoons for film and television, with its television subsidiary handling worldwide television rights.
In late 1973, Warner Bros. announced that it had partnered with 20th Century Fox to co-produce a single film: producer Irwin Allen's '' The Towering Inferno''. Both studios found themselves owning the rights to books about burning skyscrapers: Warner was attempting to adapt Thomas N. Scortia
Thomas Nicholas Scortia (August 29, 1926 – April 29, 1986) was an American science fiction author. He collaborated on several works with fellow author Frank M. Robinson. He sometimes used the pseudonyms "Scott Nichols", "Gerald MacDow ...
and Frank M. Robinson
Frank Malcolm Robinson (August 9, 1926 – June 30, 2014) was an American science fiction and techno-thriller writer. He was a speechwriter for gay politician Harvey Milk and Milk's designated successor in the event of his death but decline ...
's ''The Glass Inferno
''The Glass Inferno'' is a 1974 novel by American writer Thomas N. Scortia and Frank M. Robinson. It is one of the two books that was used to create the movie '' The Towering Inferno'', the other being the 1973 novel '' The Tower'' by Richard ...
'' and Fox was preparing an adaptation of Richard Martin Stern's '' The Tower''. Allen insisted on a meeting with the heads of both studios and announced that as Fox was already in the lead with their property it would be preferable to lump the two together as a single film, with Fox owning domestic rights and Warner Bros. handling the film's foreign distribution. The resulting partnership resulted in the second-highest-grossing film of 1974, turning profits for both studios, and influencing future co-productions between major studios. Although Allen would make further films for Warner Bros., he would not repeat the success he had with ''The Towering Inferno''.
Abandoning parking lots and funeral homes, the refocused Kinney renamed itself in honor of its best-known holding, Warner Communications
Warner Media, LLC ( traded as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City, United States.
It was originally established in 1972 by ...
. Throughout the 1970s and 1980s Warner Communications branched out into other business, such as video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This feedba ...
company Atari, Inc. in 1976, and later the Six Flags theme parks.
In 1972, in a cost-cutting move, Warner and Columbia formed a third company called The Burbank Studios (TBS). They would share the Warner lot in Burbank. Both studios technically became production entities, giving TBS day-to-day responsibility for studio grounds and upkeep. The Columbia Ranch (about a mile north of Warner's lot) was part of the deal. The Warner–Columbia relationship was acrimonious, but the reluctance of both studios to approve or spend money on capital upgrades that might only help the other did have the unintended consequence of preserving the Warner lot's primary function as a filmmaking facility while it produced relatively little during the 1970s and 1980s. (Most films produced after 1968 were filmed on location after the failure of ''Camelot'' was partially attributed to the fact it was set in England but obviously filmed in Burbank.) With control over its own lot tied up in TBS, Warner ultimately retained a significant portion of its backlot, while Fox sold its backlot to create Century City
Century City is a 176-acre (71.2 ha) neighborhood and business district in Los Angeles, California. Located on the Westside to the south of Santa Monica Boulevard around 10 miles (16 km) west of Downtown Los Angeles, Century City is one of ...
, Universal
Universal is the adjective for universe.
Universal may also refer to:
Companies
* NBCUniversal, a media and entertainment company
** Universal Animation Studios, an American Animation studio, and a subsidiary of NBCUniversal
** Universal TV, a t ...
turned part of its backlot into a theme park and shopping center
A shopping center (American English) or shopping centre (Commonwealth English), also called a shopping complex, shopping arcade, shopping plaza or galleria, is a group of shops built together, sometimes under one roof.
The first known collec ...
, and Disney replaced its backlot with office buildings and exiled its animation department to an industrial park in Glendale.
In 1989, a solution to the situation became evident when Warner Bros. acquired Lorimar-Telepictures
Lorimar-Telepictures Corporation was an entertainment company established in 1985 with the merger of Lorimar Productions, Inc. and Telepictures Corporation. Headquartered at the former Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios (now Sony Pictures Studios) ...
and gained control of the former MGM studio lot in Culver City
Culver City is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 40,779. Founded in 1917 as a "whites only" sundown town, it is now an ethnically diverse city with what was called the "third-most ...
, and that same year, Sony bought Columbia Pictures. Sony was flush with cash and Warner Bros. now had two studio lots. In 1990, TBS ended when Sony bought the MGM lot from Warner and moved Columbia to Culver City. However, Warner kept the Columbia Ranch, now known as the Warner Bros. Ranch.
Robert A. Daly
Robert Anthony Daly (born December 8, 1936) is an American business executive who has led organizations such as CBS Entertainment, Warner Bros., Warner Music Group, and the Los Angeles Dodgers.
Daly currently serves as a non-executive advisor to ...
joined Warner Bros. on December 1, 1980, taking over from Ted Ashley. His titles were chairman of the board and Co-Chief Executive Officer. One year later, he was named chairman of the board and chief executive officer and appointed Terry Semel
Terence Steven Semel (born February 24, 1943) is an American corporate executive who was the chairman and CEO of Yahoo! Incorporated from 2001 to 2007. He resigned as CEO due in part to pressure from shareholders' dissatisfaction over his compe ...
President and Chief Operating Officer.
Time Warner subsidiary
 Warner Communications merged in 1989 with white-shoe publishing company Time Inc. Time claimed a higher level of prestige, while Warner Bros. provided the profits. The
Warner Communications merged in 1989 with white-shoe publishing company Time Inc. Time claimed a higher level of prestige, while Warner Bros. provided the profits. The Time Warner
Warner Media, LLC ( traded as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City, United States.
It was originally established in 1972 by ...
merger was almost derailed when Paramount Communications (formerly Gulf+Western, later sold to the first incarnation of Viacom), launched a $12.2 billion hostile takeover bid for Time Inc., forcing Time to acquire Warner with a $14.9 billion cash/stock offer. Paramount responded with a lawsuit filed in Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent ...
court to break up the merger. Paramount lost and the merger proceeded.
In 1992, Warner Bros. Family Entertainment was established to produce various family-oriented films, plus animated films. The Family Entertainment label was dormant in 2009. In 1994, Jon Peters, whose Peters Entertainment company had a non-exclusive deal at Sony Pictures
Sony Pictures Entertainment Inc. (commonly known as Sony Pictures or SPE, and formerly known as Columbia Pictures Entertainment, Inc.) is an American diversified multinational mass media and entertainment studio conglomerate that produces, acq ...
, received another non-exclusive, financing deal at the studio, citing that then president Terry Samel and producer Jon Peters were friends.
The WB
The WB Television Network (for Warner Bros., or the "Frog Network", for its former mascot, Michigan J. Frog) was an American television network launched on broadcast television on January 11, 1995, as a joint venture between the Warner Bros. ...
Television Network, seeking a large share of the niche market of teenage viewers. The WB's early programming included an abundance of teenage fare, such as ''Buffy the Vampire Slayer
''Buffy the Vampire Slayer'' is an American supernatural drama television series created by writer and director Joss Whedon. It is based on the 1992 film of the same name, also written by Whedon, although the events of the film are not consid ...
'', ''Smallville
''Smallville'' is an American superhero television series developed by writer-producers Alfred Gough and Miles Millar, based on the DC Comics character Superman created by Jerry Siegel and Joe Shuster. The series was produced by Millar/G ...
'', '' Dawson's Creek'' and '' One Tree Hill''. Two dramas produced by Spelling Television, '' 7th Heaven'' and ''Charmed
''Charmed'' is an American fantasy drama television series created by Constance M. Burge and produced by Aaron Spelling and his production company Spelling Television, with Brad Kern serving as showrunner. The series was originally broadcas ...
'', helped bring The WB into the spotlight. ''Charmed'' lasted eight seasons, becoming the longest-running drama with female leads. ''7th Heaven'' ran for eleven seasons and was the longest-running family drama and longest-running show for the network. In 2006, Warner and CBS Corporation
The second incarnation of CBS Corporation (the first being a short-lived rename of the Westinghouse Electric Corporation) was an American multinational media conglomerate with interests primarily in commercial broadcasting, publishing, an ...
decided to close The WB and CBS's UPN and jointly launch The CW
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
Television Network.
In 1996, Turner Pictures was folded into Warner Bros. via the Turner-Time Warner merger and brought Turner projects into development like '' City of Angels'' and ''You've Got Mail
''You've Got Mail'' is a 1998 American romantic comedy film directed by Nora Ephron and starring Tom Hanks and Meg Ryan. Inspired by the 1937 Hungarian play '' Parfumerie'' by Miklós László (which had earlier been adapted in 1940 as ''The S ...
'' into the studio. Later that year, Warner Bros. partnered with PolyGram Filmed Entertainment
PolyGram Filmed Entertainment (formerly known as PolyGram Films and PolyGram Pictures or simply PFE) was a British film studio founded in 1979 which became a European competitor to Hollywood, but was eventually sold to Seagram Company Ltd. in 1 ...
to distribute various movies produced by Time Warner subsidiary Castle Rock Entertainment. Also that same year, Bruce Berman left Warner Bros. to begin Plan B Entertainment, then he subsequently headed Village Roadshow Pictures
Village Roadshow Pictures is the American subsidiary of the Australian co-producer and co-financier of major Hollywood motion pictures established in 1986. It is a division under Village Roadshow Entertainment Group (VREG), which in turn is o ...
with a deal at the studio.
In 1998, Time Warner sold Six Flags to Premier Parks. The takeover of Time Warner in 2000 by then-high-flying AOL
AOL (stylized as Aol., formerly a company known as AOL Inc. and originally known as America Online) is an American web portal and online service provider based in New York City. It is a brand marketed by the current incarnation of Yahoo! Inc. ...
did not prove a good match, and following the collapse in "dot-com" stocks, the AOL element was banished from the corporate name.
In 1998, Warner Bros. celebrated its 75th anniversary. In 1999, Terry Semel and Robert Daly resigned as studio heads after a career with 13 Oscar-nominated films. Daly and Semel were said to have popularized the modern model of partner financing and profit sharing for film production. In mid-1999, Alan F. Horn
Alan Frederick Horn (born February 28, 1943) is an American entertainment industry executive. Horn became President and COO of Warner Bros. from 1999 to 2012. Horn next served as the chairman of Walt Disney Studios from 2012 to 2020. During his ...
and Barry Meyer replaced Daly and Semel as new studio heads, in which the studio had continued success in movies, television shows, cartoons, that the previous studio heads had for the studio. In late 2003, Time Warner reorganized Warner Bros.' assets under Warner Bros. Entertainment Inc., in an effort to distinguish the film studio from its then-sister record label (which since became Warner Records in May 2019) and Warner Music Group.
In the late 1990s, Warner obtained rights to the ''Harry Potter
''Harry Potter'' is a series of seven fantasy novels written by British author J. K. Rowling. The novels chronicle the lives of a young wizard, Harry Potter, and his friends Hermione Granger and Ron Weasley, all of whom are students at ...
'' novels and released feature film adaptations of the first in 2001. Subsequently, they released the second film in 2002, the third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
in June 2004, the fourth in November 2005, the fifth in July 2007, and the sixth in July 2009. The seventh (and at that time, final) book was released as two movies; Deathly Hallows — Part 1 in November 2010 and Deathly Hallows — Part 2 in July 2011.
From 2006, Warner Bros. operated a joint venture with China Film Group Corporation and HG to form Warner China Film HG to produce films in Hong Kong and China, including '' Connected'', a remake of the 2004 thriller film
Thriller film, also known as suspense film or suspense thriller, is a broad film genre that evokes excitement and suspense in the audience. The suspense element found in most films' plots is particularly exploited by the filmmaker in this genre. ...
'' Cellular''.
Warner Bros. played a large part in the discontinuation of the HD DVD format. On January 4, 2008, Warner Bros. announced that they would drop support of HD DVD in favor of Blu-ray
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of st ...
Disc. HD DVDs continued to be released through May 2008, but only following Blu-ray and DVD releases.
Warner Bros.' ''Harry Potter'' film series was the worldwide highest-grossing film series of all time without adjusting for inflation. Its ''Batman'' film series was one of only two series to have two entries earn more than $1 billion worldwide. '' Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows – Part 2'' was Warner Bros.' highest-grossing movie ever (surpassing '' The Dark Knight''). However, the Harry Potter movies have produced a net loss due to Hollywood accounting. IMAX Corp. signed with Warner Bros. Pictures in April 2010 to release as many as 20 giant-format films through 2013.
On October 21, 2014, Warner Bros. created a short form digital unit, Blue Ribbon Content, under Warner Bros. Animation and Warner Digital Series president Sam Register. Warner Bros. Digital Networks announced its acquisition of online video company Machinima, Inc. on November 17, 2016.
As of 2015, Warner Bros. is one of only three studios to have released a pair of billion-dollar films in the same year (along with Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures
Walt Disney Studios Motion Pictures, formerly known as Buena Vista Pictures Distribution, Inc. until 2007, is an American film distribution studio within the Disney Media and Entertainment Distribution division of The Walt Disney Company. It h ...
and Universal Studios
Universal Pictures (legally Universal City Studios LLC, also known as Universal Studios, or simply Universal; common metonym: Uni, and formerly named Universal Film Manufacturing Company and Universal-International Pictures Inc.) is an Americ ...
); the distinction was achieved in 2012 with '' The Dark Knight Rises'' and '' The Hobbit: An Unexpected Journey''. As of 2016, it is the only studio to cross $1 billion at the domestic box office every year since 2000.
AT&T subsidiary
In June 2018, Warner Bros. parent company Time Warner was acquired by U.S. telecom companyAT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications holding company headquartered at Whitacre Tower in Downtown Dallas, Texas. It is the world's largest telecommunications company by revenue and the third largest provider of mobile ...
, and renamed WarnerMedia, the former Time Inc. properties having been sold off to new owners. On October 16, 2018, WarnerMedia shut down DramaFever
DramaFever was a video streaming website owned by Warner Bros. that offered on-demand streaming video of documentaries, movies, and TV shows with subtitles. DramaFever's content offering was both ad-supported for regular users and available in ...
, affecting 20 percent of Warner Bros.' digital networks staff.
On March 4, 2019, WarnerMedia announced a planned reorganization that would dissolve Turner Broadcasting System
Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. (alternatively known as Turner Entertainment Networks from 2019 until 2022) was an American television and media conglomerate. Founded by Ted Turner and based in Atlanta, Georgia, it merged with Time Warner (lat ...
by moving Cartoon Network
Cartoon Network (often abbreviated as CN) is an American cable television channel owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. It is a part of The Cartoon Network, Inc., a division that also has the broadcasting and production activities of Boomerang, ...
, Adult Swim
Adult Swim (AS; stylized as dult swim'' and often abbreviated as s'') is an American adult-oriented night-time cable television channel that shares channel space with the basic cable network Cartoon Network and is programmed by its in-house ...
, Boomerang, their respective production studios (Cartoon Network Studios
Cartoon Network Studios is an American animation studio owned by the Warner Bros. Television Studios division of Warner Bros., a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. The studio is the production arm of Cartoon Network, and started operating ...
and Williams Street), as well as Turner Classic Movies
Turner Classic Movies (TCM) is an American movie-oriented pay-TV network owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. Launched in 1994, Turner Classic Movies is headquartered at Turner's Techwood broadcasting campus in the Midtown business district of ...
and Otter Media, directly under Warner Bros. (Turner's remaining television services would be divided into WarnerMedia Entertainment and WarnerMedia News & Sports respectively). Aside from Otter Media, these assets operate under a newly formed Global Kids & Young Adults division, renamed on April 7, 2020, to Warner Bros. Global Kids, Young Adults and Classics. On May 31, 2019, Otter Media was transferred from Warner Bros. to WarnerMedia Entertainment to oversee the development of HBO Max
HBO Max is an American subscription video on-demand over-the-top streaming service owned by Warner Bros. Discovery. Launched in the United States on May 27, 2020, the service is built around the libraries of HBO, Warner Bros., Cartoon Ne ...
, a new streaming service that would feature content from HBO and WarnerMedia brands. Tom Ascheim
Tom Ascheim is an American television producer and executive. He most recently served president of Warner Bros. Global Kids, Young Adults and Classics from July 2020 until May 2022. From 1998 to 2003, Ascheim was the general manager of Noggin, whi ...
resigned as president of cable network Freeform to become the president of the Global Kids, Young Adults, and Classics division on July 1, 2020.
On November 13, 2019, Warner Bros. unveiled an updated iteration of its shield logo by Pentagram in anticipation of the company's upcoming centennial, which features a streamlined appearance designed to make it better-suited for multi-platform usage and iterations. The company also commissioned a new corporate typeface
A typeface (or font family) is the design of lettering that can include variations in size, weight (e.g. bold), slope (e.g. italic), width (e.g. condensed), and so on. Each of these variations of the typeface is a font.
There are thousands o ...
that is modeled upon the "WB" lettering.
Warner Bros. and HBO Max announced the Warner Max film label on February 5, 2020, which was to produce eight-to-ten mid-budget movies per year for the streaming service starting in 2020. However, the label was ultimately discontinued in October 2020 as part of a consolidation of the Warner Bros. Pictures group.
In February 2022, Village Roadshow, a co-financier of '' The Matrix Resurrections'', began a lawsuit against Warner Bros. over the hybrid release of the sci-fi sequel. Like all of Warner's 2021 films, the fourth ''Matrix'' film was given a simultaneous release on both HBO Max and in theaters due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
. According to a complaint filed by Village Roadshow, the decision ruined any December box office hopes. In May of that same year, Village Roadshow agreed to arbitration with Warner Bros. over the release of ''Resurrections''.
Warner Bros. Discovery
On March 23, 2022, Warner Bros. unveiled a logo and campaign for its upcoming centennial in 2023, "100 Years of Storytelling". It will begin in late 2022 and last throughout 2023, and include commemorative initiatives across all Warner Bros. divisions and properties. On April 8, 2022, AT&T divested WarnerMedia to its shareholders, and in turn merged with Discovery Inc. to form Warner Bros. Discovery. The new company is led by Discovery's CEO David Zaslav. In November 2022, James Gunn and Peter Safran became the co-chairpersons and CEOs ofDC Films
DC Studios is an American film and television studio that is a division of Warner Bros., which is a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. It is dedicated to the production of films, series, and animations based on characters from DC Comics, ...
, which was renamed to "DC Studios". The studio also become an independent division of Warner Bros.
Company units
Warner Bros. Entertainment operates three primary business segments they call "divisions": Motion Pictures, Television, and other entertainment assets (which includes Digital Networks, Technology,Live Theatre
Live Theatre, formerly Live Theatre Company, is a new writing theatre and company based in Newcastle upon Tyne, England. As well as producing and presenting new plays many of which go on to tour nationally and internationally, it seeks out an ...
, and Studio Facilities).
Motion Pictures includes the company's primary business units, such as Warner Bros. Pictures
Warner Bros. Pictures is an American film production and distribution company of the Warner Bros. Pictures Group division of Warner Bros. Entertainment (both ultimately owned by Warner Bros. Discovery). The studio is the flagship producer of li ...
, New Line Cinema
New Line Cinema is an American film production studio owned by Warner Bros. Discovery and is a film label of Warner Bros. It was founded in 1967 by Robert Shaye as an independent film distribution company; later becoming a film studio after ...
, DC Studios
DC Studios is an American film and television studio that is a division of Warner Bros., which is a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery. It is dedicated to the production of films, series, and animations based on characters from DC Comics, ...
and Castle Rock Entertainment.
Executive management
;Chairman of the board *Robert A. Daly
Robert Anthony Daly (born December 8, 1936) is an American business executive who has led organizations such as CBS Entertainment, Warner Bros., Warner Music Group, and the Los Angeles Dodgers.
Daly currently serves as a non-executive advisor to ...
(1980–1999)
* Barry Meyer (1999–2013)
* Kevin Tsujihara (2013–2019)
* Ann Sarnoff (2019–2022)
;Vice chairman
* Edward A. Romano (1994–2016)
;Presidents
*Terry Semel
Terence Steven Semel (born February 24, 1943) is an American corporate executive who was the chairman and CEO of Yahoo! Incorporated from 2001 to 2007. He resigned as CEO due in part to pressure from shareholders' dissatisfaction over his compe ...
(1994–1999)
;Chief executive officers
*Robert A. Daly
Robert Anthony Daly (born December 8, 1936) is an American business executive who has led organizations such as CBS Entertainment, Warner Bros., Warner Music Group, and the Los Angeles Dodgers.
Daly currently serves as a non-executive advisor to ...
(1980–1999)
* Barry Meyer (1999–2013)
* Kevin Tsujihara (2013–2019)
* Ann Sarnoff (2019–2022)
;Chief operating officers
*Terry Semel
Terence Steven Semel (born February 24, 1943) is an American corporate executive who was the chairman and CEO of Yahoo! Incorporated from 2001 to 2007. He resigned as CEO due in part to pressure from shareholders' dissatisfaction over his compe ...
(1982–1994)
* Barry Meyer (1994–1999)
International distribution arrangements
From 1971 until the end of 1987, Warner's international distribution operations were a joint venture withColumbia Pictures
Columbia Pictures Industries, Inc. is an American film production studio that is a member of the Sony Pictures Motion Picture Group, a division of Sony Pictures Entertainment, which is one of the Big Five studios and a subsidiary of the mu ...
. In some countries, this joint venture distributed films from other companies (such as EMI Films
EMI Films was a British film studio and distributor. A subsidiary of the EMI conglomerate, the corporate name was not used throughout the entire period of EMI's involvement in the film industry, from 1969 to 1986, but the company's brief conne ...
and Cannon Films in the UK). Warner ended the venture in 1988.
On May 4, 1987, Buena Vista Pictures Distribution signed a theatrical distribution agreement with Warner Bros. International for the release of Disney and Touchstone films in overseas markets, with Disney retaining full control of all distribution and marketing decisions on their product. In 1992, Disney opted to end their joint venture with Warner Bros. to start autonomously distributing their films in the aforementioned markets.
On February 6, 2014, Columbia TriStar Warner Filmes de Portugal Ltda., a joint venture with Sony Pictures
Sony Pictures Entertainment Inc. (commonly known as Sony Pictures or SPE, and formerly known as Columbia Pictures Entertainment, Inc.) is an American diversified multinational mass media and entertainment studio conglomerate that produces, acq ...
which distributed both companies' films in Portugal, announced that it would close its doors on March 31, 2014. NOS Audiovisuais handles distribution of Warner Bros. films in Portugal since then, while the distribution duties for Sony Pictures films in the country were taken over by Big Picture Films.
Warner Bros. still handles the distribution of Sony Pictures films in Italy.
Since January 1, 2021, Warner Bros. films are distributed through Universal Pictures
Universal Pictures (legally Universal City Studios LLC, also known as Universal Studios, or simply Universal; common metonym: Uni, and formerly named Universal Film Manufacturing Company and Universal-International Pictures Inc.) is an Americ ...
in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a List of cities in China, city and Special administrative regions of China, special ...
citing WarnerMedia's closure of its Hong Kong theatrical office. On January 12, 2021, Warner Bros. handles the theatrical distribution of Universal Pictures films in Brazil.
In August 2022, Warner Bros. Pictures entered into a multi-year deal for distributing MGM films outside the United States, including on home entertainment. The contract included joint participation of both companies for marketing, advertising, publicity, film distribution, and relationship with exhibitors for future MGM titles.
Film library

Acquired libraries
Mergers and acquisitions have helped Warner Bros. accumulate a diverse collection of films, cartoons and television programs. As of 2022, Warner Bros. owned more than 145,000 hours of programming, including 12,500 feature films and 2,400 television programs comprising more than tens of thousands of individual episodes. In the aftermath of the 1948 antitrust suit, uncertain times led Warner Bros. in 1956 to sell most of its pre-1950 films and cartoons toAssociated Artists Productions
Associated Artists Productions, Inc. (a.a.p.) later known as United Artists Associated was an American distributor of theatrical feature films and subjects for television. Associated Artists Productions was the copyright owner of the ''Popey ...
(a.a.p.). In addition, a.a.p. also obtained the Fleischer Studios
Fleischer Studios () is an American animation studio founded in 1929 by brothers Max and Dave Fleischer, who ran the pioneering company from its inception until its acquisition by Paramount Pictures, the parent company and the distributor of ...
and Famous Studios
Famous Studios (renamed Paramount Cartoon Studios in 1956) was the first animation division of the film studio Paramount Pictures from 1942 to 1967. Famous was founded as a successor company to Fleischer Studios, after Paramount seized control ...
'' Popeye'' cartoons, originally from Paramount Pictures
Paramount Pictures Corporation is an American film and television production company, production and Distribution (marketing), distribution company and the main namesake division of Paramount Global (formerly ViacomCBS). It is the fifth-oldes ...
. Two years later, a.a.p. was sold to United Artists
United Artists Corporation (UA), currently doing business as United Artists Digital Studios, is an American digital production company. Founded in 1919 by D. W. Griffith, Charlie Chaplin, Mary Pickford, and Douglas Fairbanks, the stu ...
, which owned the company until 1981, when Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc., also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures and abbreviated as MGM, is an American film, television production, distribution and media company owned by amazon (company), Amazon through MGM Holdings, founded o ...
acquired United Artists.
In 1982, during their independent years, Turner Broadcasting System
Turner Broadcasting System, Inc. (alternatively known as Turner Entertainment Networks from 2019 until 2022) was an American television and media conglomerate. Founded by Ted Turner and based in Atlanta, Georgia, it merged with Time Warner (lat ...
acquired Brut Productions, the film production arm of France-based then-struggling personal-care company Faberge Inc.
In 1986, Turner Broadcasting System acquired Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer
Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios Inc., also known as Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Pictures and abbreviated as MGM, is an American film, television production, distribution and media company owned by amazon (company), Amazon through MGM Holdings, founded o ...
. Finding itself in debt, Turner Entertainment kept the pre-May 1986 MGM film and television libraries and a small portion of the United Artists library (including the a.a.p. library and North American rights to the RKO Radio Pictures
RKO Radio Pictures Inc., commonly known as RKO Pictures or simply RKO, was an American film production and distribution company, one of the "Big Five" film studios of Hollywood's Golden Age. The business was formed after the Keith-Albee-Orph ...
library) while spinning off the rest of MGM.
In 1989, Warner Communications acquired Lorimar-Telepictures
Lorimar-Telepictures Corporation was an entertainment company established in 1985 with the merger of Lorimar Productions, Inc. and Telepictures Corporation. Headquartered at the former Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer Studios (now Sony Pictures Studios) ...
Corporation. Lorimar's catalogue included the post-1974 library of Rankin/Bass Productions
Rankin/Bass Animated Entertainment (founded and formerly known as Videocraft International, Ltd. and Rankin/Bass Productions, Inc.) was an American production company located in New York City, and known for its seasonal television specials, usua ...
, and the post-1947 library of Monogram Pictures
Monogram Pictures Corporation was an American film studio that produced mostly low-budget films between 1931 and 1953, when the firm completed a transition to the name Allied Artists Pictures Corporation. Monogram was among the smaller studios i ...
/Allied Artists Pictures Corporation.
In 1991, Turner Broadcasting System acquired animation studio Hanna-Barbera
Hanna-Barbera Cartoons, Inc. ( ) was an American animation studio and production company which was active from 1957 to 2001. It was founded on July 7, 1957, by William Hanna and Joseph Barbera following the decision of Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer to c ...
and the Ruby-Spears library from Great American Broadcasting, and years later, Turner Broadcasting System acquired Castle Rock Entertainment on December 22, 1993, and New Line Cinema
New Line Cinema is an American film production studio owned by Warner Bros. Discovery and is a film label of Warner Bros. It was founded in 1967 by Robert Shaye as an independent film distribution company; later becoming a film studio after ...
on January 28, 1994. On October 10, 1996, Time Warner
Warner Media, LLC ( traded as WarnerMedia) was an American multinational mass media and entertainment conglomerate. It was headquartered at the 30 Hudson Yards complex in New York City, United States.
It was originally established in 1972 by ...
acquired Turner Broadcasting System, thus bringing Warner Bros.' pre-1950 library back home. However, Warner Bros. only owns Castle Rock Entertainment's post-1994 library. In 2008, Time Warner integrated New Line into Warner Bros.
The Warner Bros. Archives
TheUniversity of Southern California
, mottoeng = "Let whoever earns the palm bear it"
, religious_affiliation = Nonsectarian—historically Methodist
, established =
, accreditation = WSCUC
, type = Private research university
, academic_affiliations =
, endowment = $8.1 ...
Warner Bros. Archives is the largest single studio collection in the world. Donated in 1977 to USC's School of Cinema-Television by Warner Communications, the WBA houses departmental records that detail Warner Bros. activities from the studio's first major feature, ''My Four Years in Germany'' (1918), to its sale to Seven Arts in 1968. It presents a complete view of the production process during the Golden Age of Hollywood. UA donated pre-1950 Warner Bros. nitrate negatives to the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The libra ...
and post-1951 negatives to the UCLA Film and Television Archive
The UCLA Film & Television Archive is a visual arts organization focused on the preservation, study, and appreciation of film and television, based at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA).
Also a nonprofit exhibition venue, the a ...
. Most of the company's legal files, scripts, and production materials were donated to the Wisconsin Center for Film and Theater Research.
See also
* Warner Bros. Studios, Burbank *Warner Bros. Studio Tour Hollywood
Warner Bros. Studio Tour Hollywood is a guided walk-through tour of Warner Bros. Studios, Burbank located in Los Angeles. It offers visitors the chance to glimpse behind the scenes of one of the oldest film studios in the world over a two-to-thr ...
* Warner Bros. Home Entertainment
Warner Bros. Home Entertainment Inc. (formerly known as Warner Home Video and WCI Home Video and sometimes credited as Warner Home Entertainment) is the home video distribution division of Warner Bros.
It was founded in 1978 as WCI Home Video ...
* Warner Bros. Family Entertainment
* Warner Bros. Television Studios
Warner Bros. Television Studios (operating under the name Warner Bros. Television; formerly known as Warner Bros. Television Division) is an American television production and distribution studio of the Warner Bros. Television Group division of ...
* Warner Bros. Discovery Enterprises
* Warner Records
Warner Records Inc. (formerly Warner Bros. Records Inc.) is an American record label. A subsidiary of the Warner Music Group, it is headquartered in Los Angeles, California. It was founded on March 19, 1958, as the recorded music division of the ...
* List of Warner Bros. short subjects
* Warner Bros. Animation
* Warner Bros. Studios, Leavesden
Warner Bros. Studios, Leavesden is an studio complex in Leavesden in Watford, Hertfordshire, in South East England. Formerly known as Leavesden Film Studios and still colloquially known as Leavesden Studios or simply Leavesden, it is a film an ...
Notes
References
Footnotes
Works cited
* * * * Sarris, Andrew. 1998. “You Ain’t Heard Nothin’ Yet.” The American Talking Film History & Memory, 1927–1949. Oxford University Press. * * * * * *Further reading
*External links
* * {{Authority control 1923 establishments in California American companies established in 1923 American corporate subsidiaries Film studios in Southern California Companies based in Burbank, California Entertainment companies based in California Entertainment companies established in 1923 Film distributors of the United States Film production companies of the United States Film studios Mass media companies established in 1923 Organizations awarded an Academy Honorary Award San Fernando Valley Sibling filmmakers Warner Bros. Discovery subsidiaries Major film studios